MLSP WEEK 13
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
1
New cards
MICROSCOPE
An optical instrument that is used to observe tiny objects, often objects that cannot be seen at all with the unaided human eye (the “naked eye”).
2
New cards
SIMPLE MICROSCOPE
Defined as a microscope containing only one magnifying lens.
3
New cards
COMPOUND MICROSCOPE
A microscope that contains more than one magnifying lens.
4
New cards
BRIGHTFIELD MICROSCOPE
Is used to observe morphology of microorganisms such as bacteria, protozoa, fungi, and algae in living (unstained) and non-living (stained) state
5
New cards
BRIGHTFIELD MICROSCOPE
Cannot observe microbes less than 0.2 um in diameter or thickness, such as spirochetes and viruses.
6
New cards
DARKFIELD MICROSCOPE
Unstained organisms are observed against a dark background.
7
New cards
DARKFIELD MICROSCOPE
Useful for examining thin spirochetes. Slightly more difficult to operate than bright field
8
New cards
PHASE-CONTRAST MICROSCOPE
Can be used to observe unstained living microorganisms.
9
New cards
FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPE
Fluorescent dye attached to organism (e.g., acridine orange and Auramine O).
10
New cards
FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPE
Primarily an immunodiagnostic technique (immunofluorescence).
11
New cards
FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPE
Used to detect presence of microbes in cells, tissues, and clinical specimens.
12
New cards
TRANSMISSION-ELECTRON MICROSCOPE (TEM)
Excellent resolution AND Allows examination of cellular and viral ultrastructure
13
New cards
TRANSMISSION-ELECTRON MICROSCOPE (TEM)
Specimen is non-living Reveals internal features of thin specimens
14
New cards
SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPE (SEM)
Gives the illusion of depth (three-dimensional). Useful for examining surface features of cells and viruses
15
New cards
SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPE (SEM)
Specimen is non-living. Resolution is less than that of TEM
16
New cards
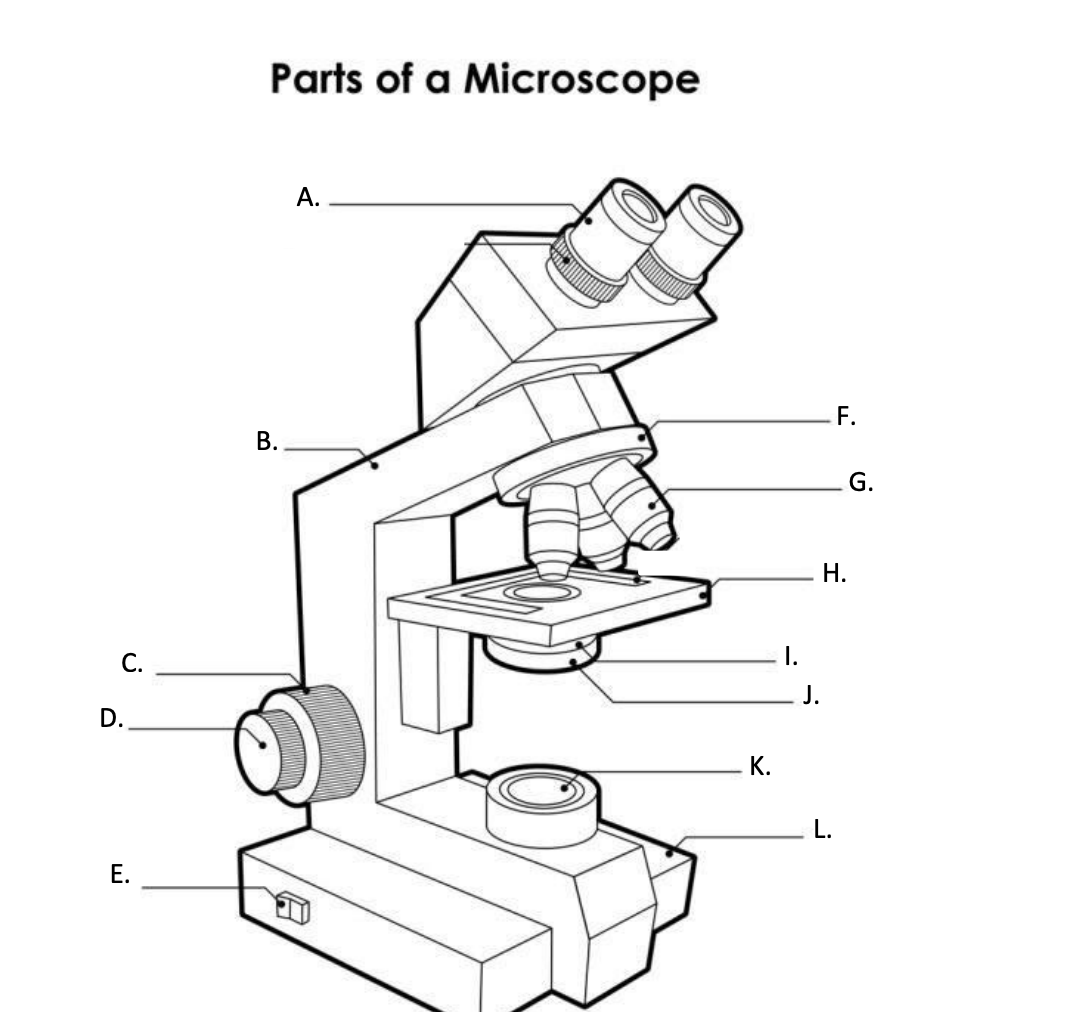
**A. Eyepiece Lens**
the lens at the top that you look through, usually 10x or 15x power.
17
New cards
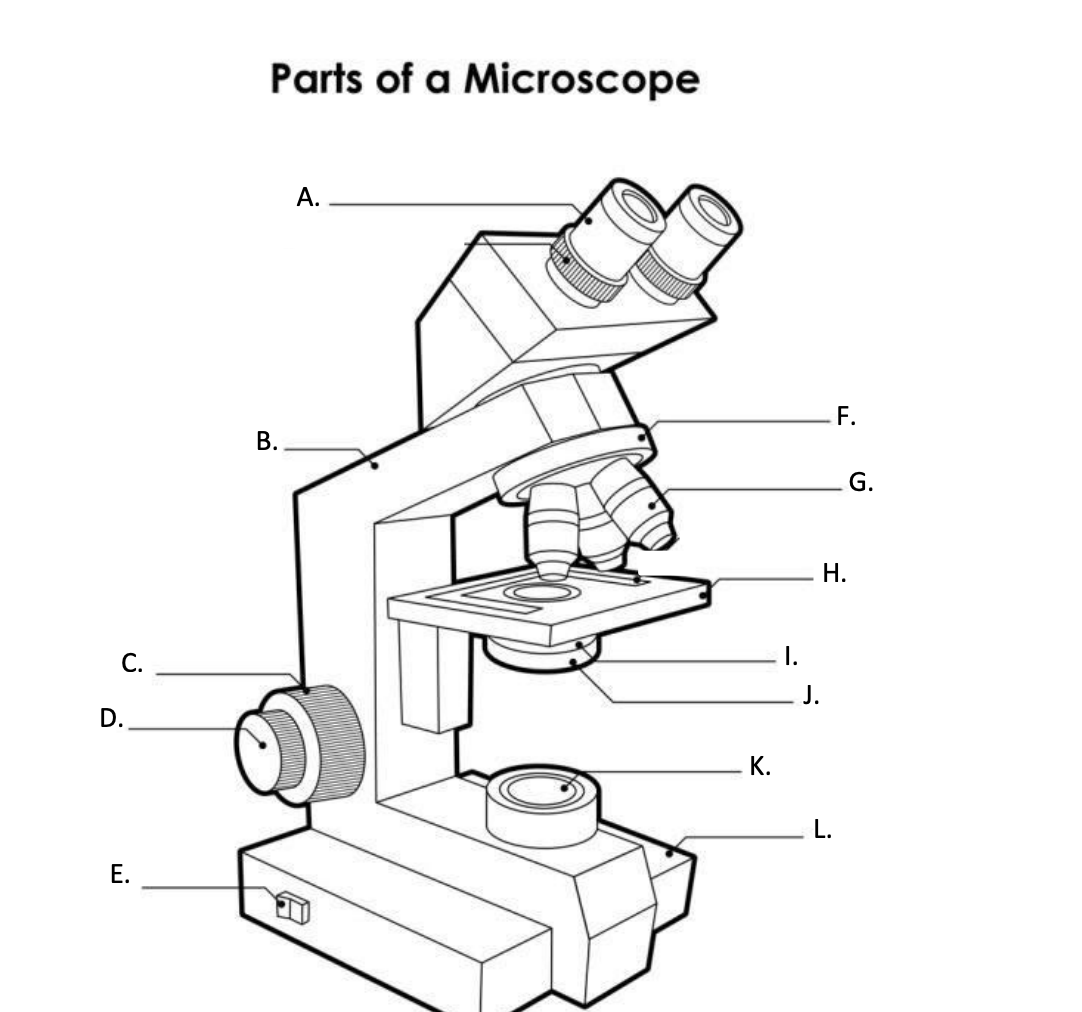
**B. Arm**
Supports the binocular body and the revolving nosepiece.
18
New cards
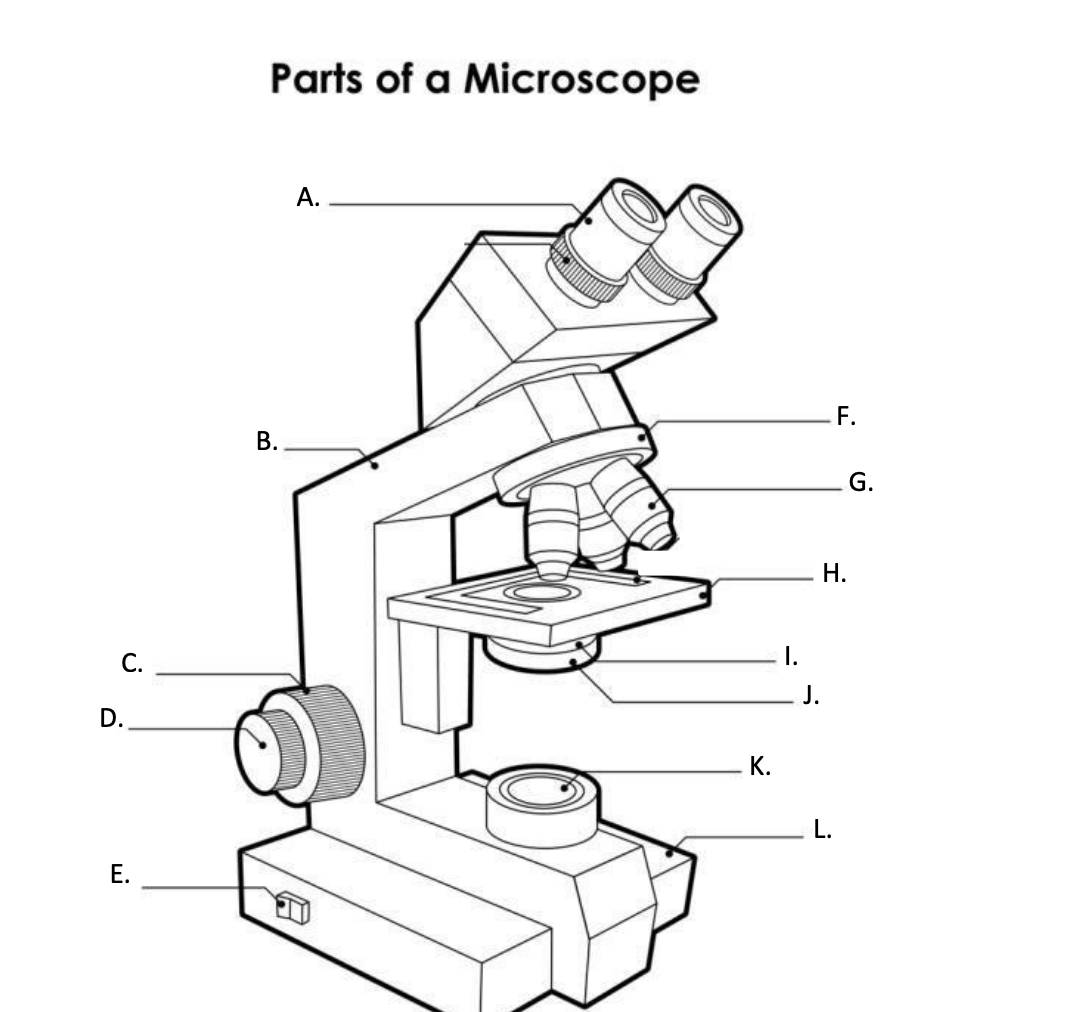
D. FINE ADJUSTMENT KNOB
— A slow but precise control used to fine focus the image when viewing at the higher magnifications.
19
New cards
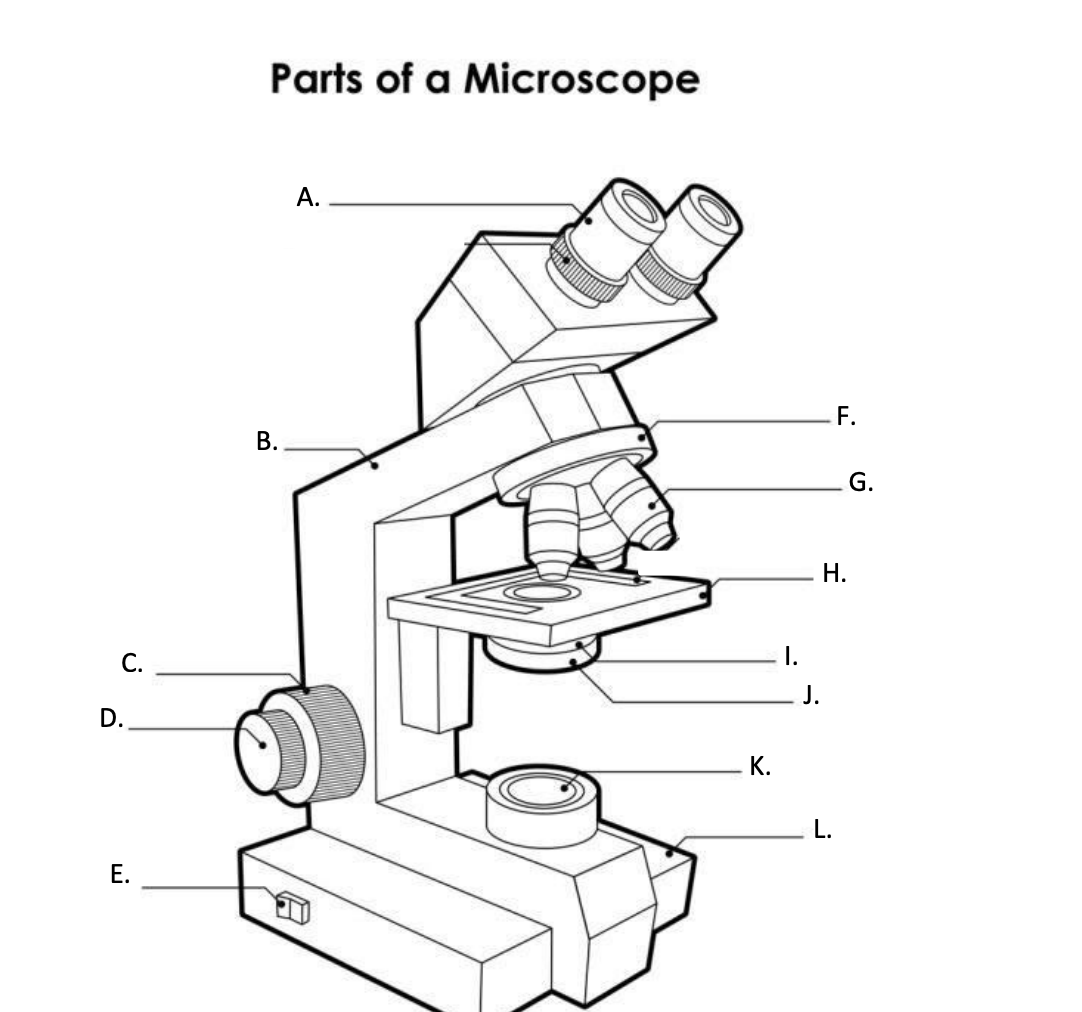
**E. Light Switch**
is an electrical control device. Light switches are used to on and off the illuminator.
20
New cards
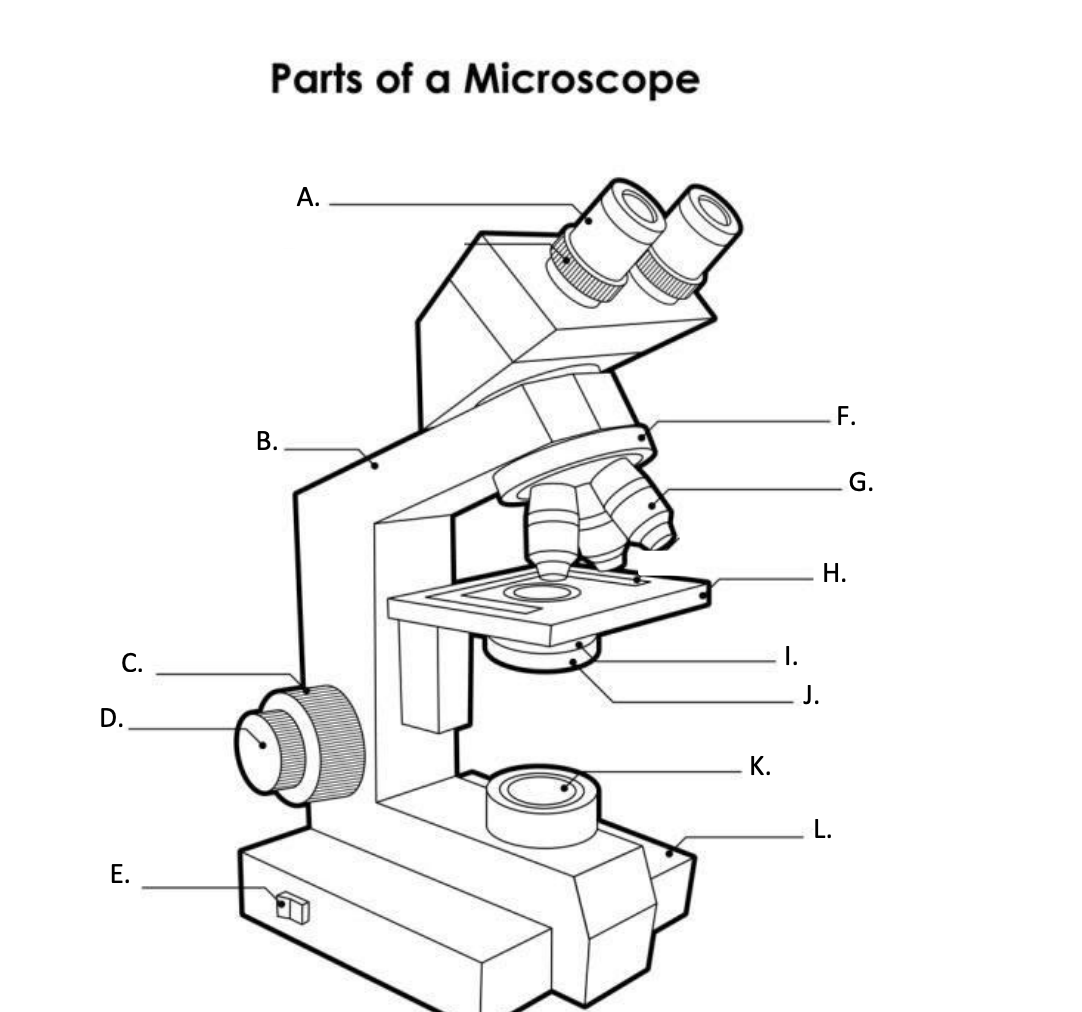
F. Revolving Nosepiece or Turret
is the part that holds two or more objective lenses and can be rotated to easily change power.
21
New cards
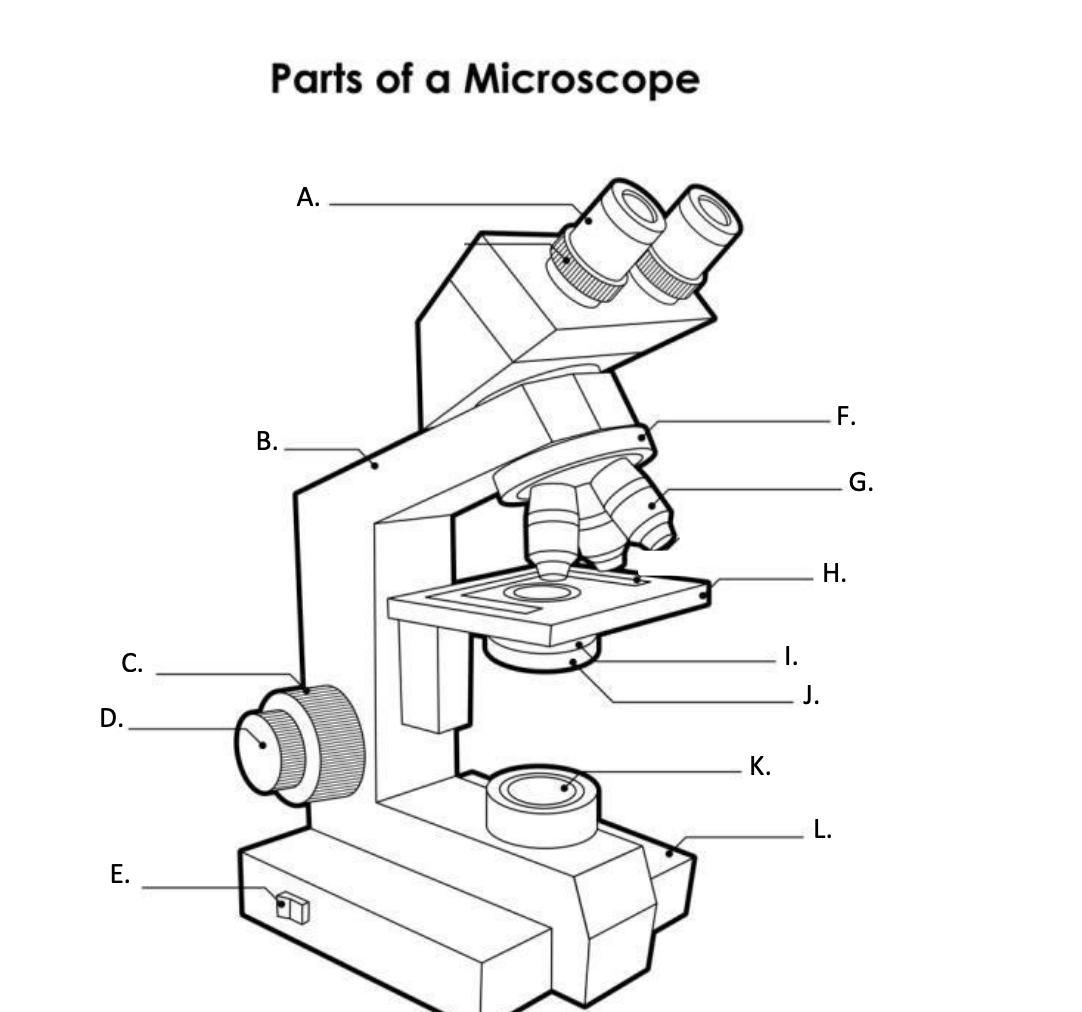
**G. Objective Lens**
Used to magnify objects placed on the stage.
22
New cards
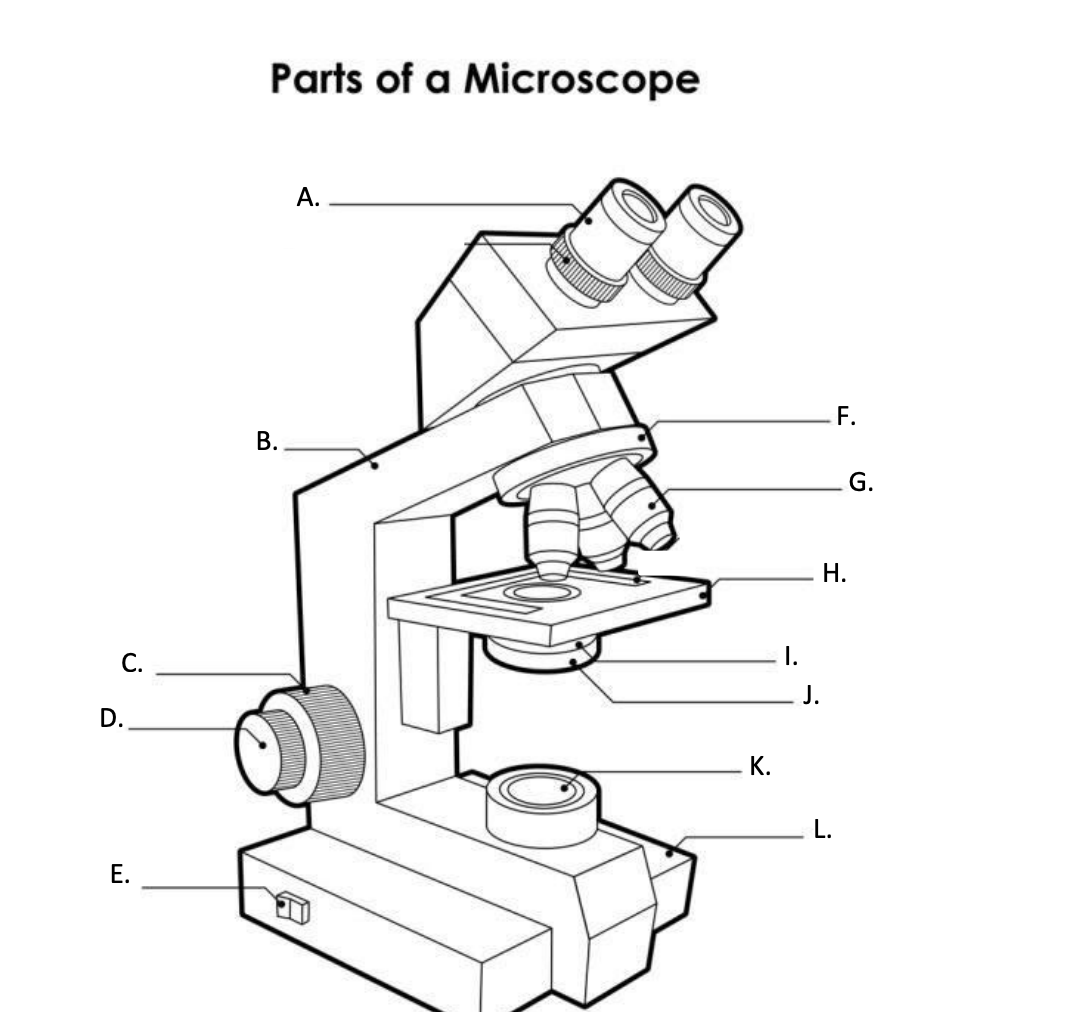
**H. s**tage
is a flat platform where a slide with a specimen is placed for viewing. The stage has a central aperture through which the focused light from the condenser strikes the specimen. It contains two-stage clips for holding the slide in a fixed position.
23
New cards
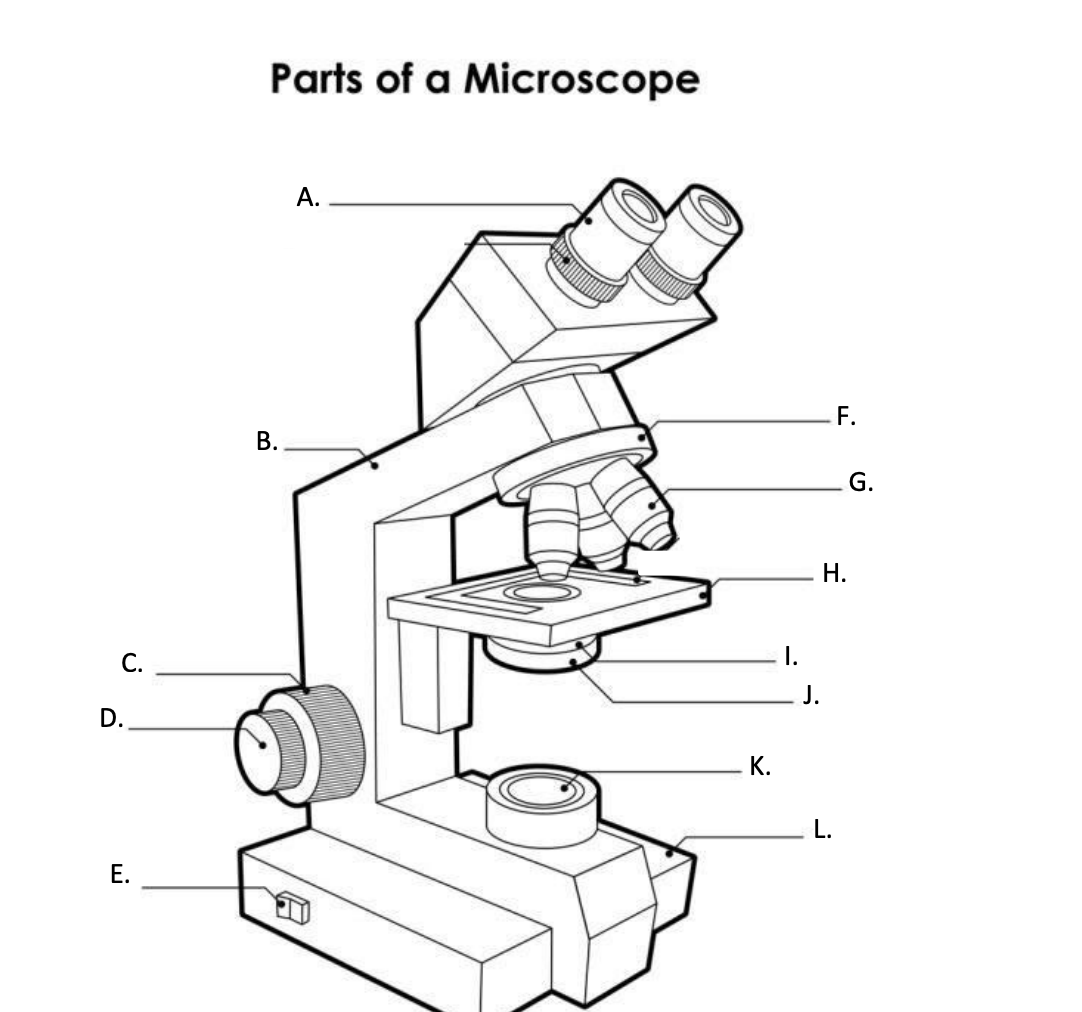
I. Aperture
The hole in the middle of the stage that allows light from the illuminator to reach the specimen
24
New cards
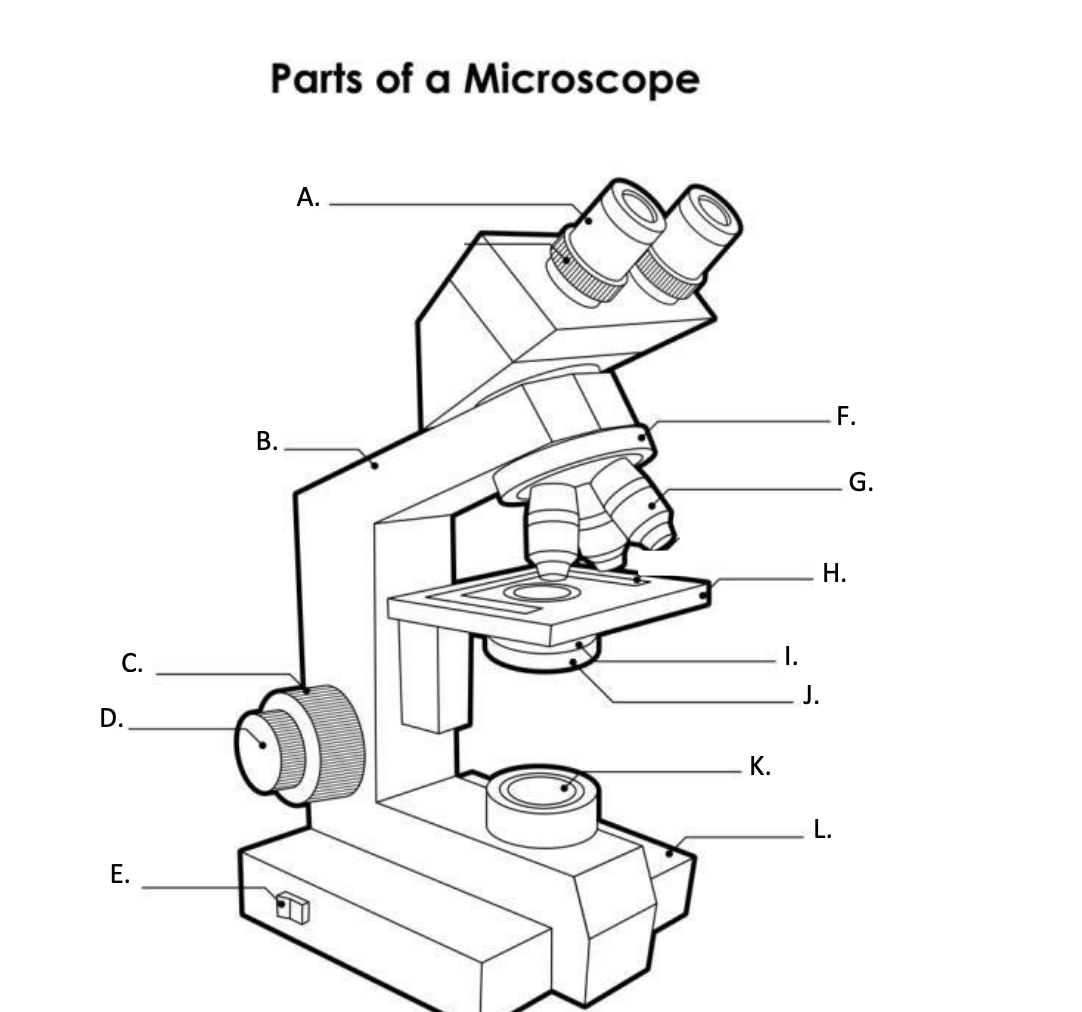
**J. condenser**
is a lens system that collects and focuses the light rays coming from the illuminator on the specimen being viewed.
25
New cards
Condenser Control Knob
Used to adjust the height of the condenser
26
New cards
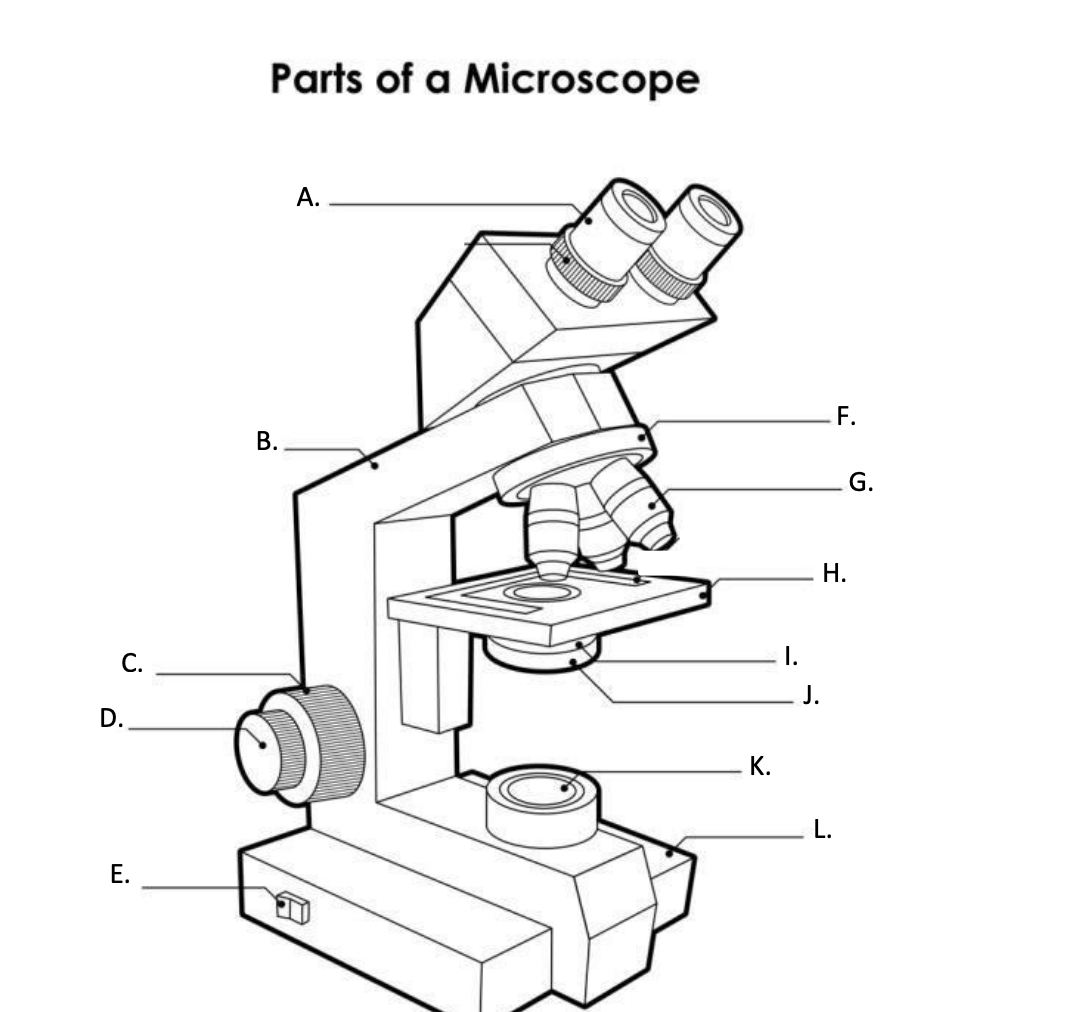
K. Collector Lens with field diaphgram
controls the amount of light entering the condenser
27
New cards
Rheostat Control Knob
Controls the amount of light emitted from the light source
28
New cards
Field Diaphgram Lever
Used to adjust the amount of light passing through the collector lens
29
New cards
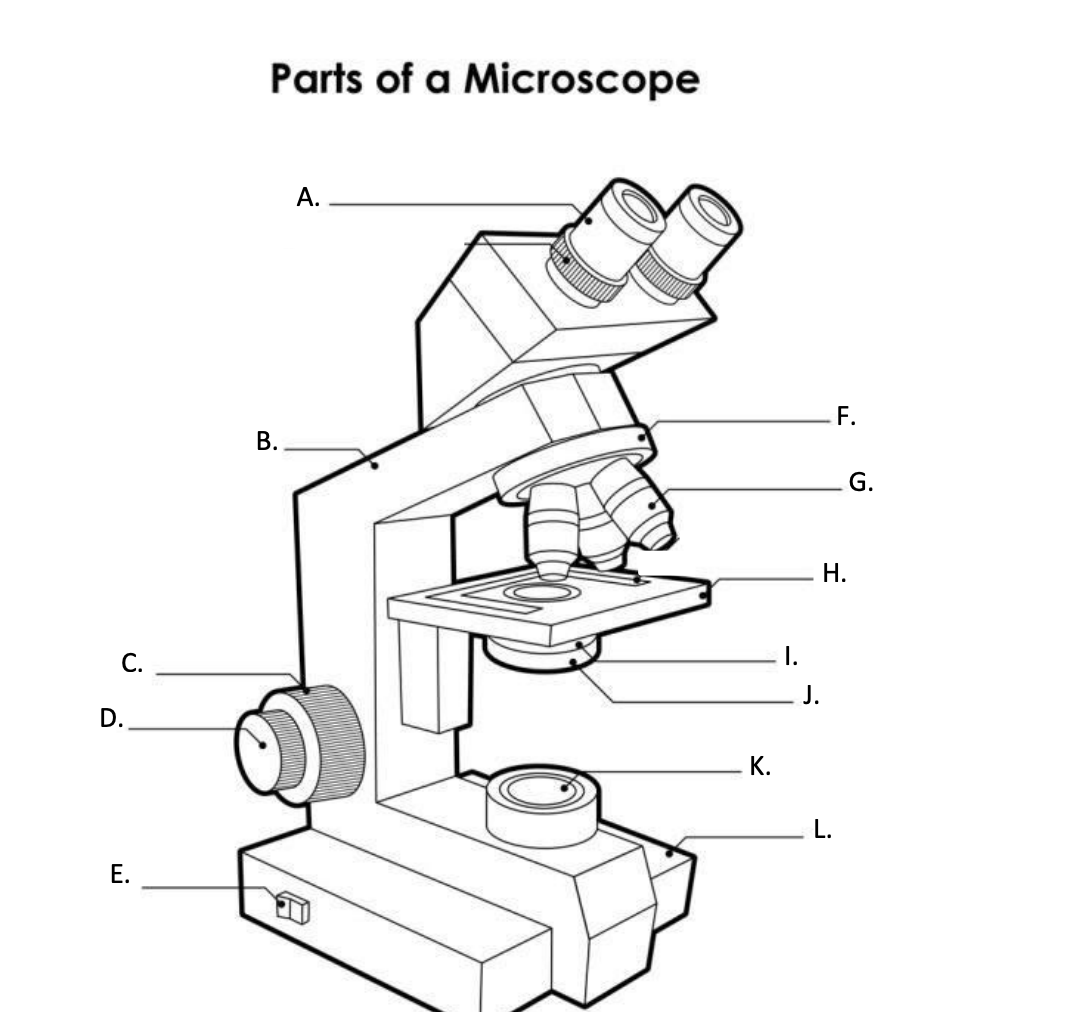
**F. Base**
is the lowermost part of the microscope that supports the entire microscope structure. It provides stability for the microscope. Illuminator, light switches, and electrical wiring system are fitted in the base.
30
New cards
Stage adjustment Knob
Used to move the stage and microscope slide
31
New cards
Binocular Body
Holds the ocular lenses in their proper locations
32
New cards
Magnification
The ratio of the apparent size of an object as seen through the microscope & the actual size of the object
33
New cards
Resolution/Resolving Power
The ability of the lens to clearly separate or distinguish two points of two lines individually in the image.
34
New cards
Resolution/Resolving Power
It is determined by the shortest wavelength of visible light & maximum numerical aperture
35
New cards
Numerical Aperture
A measurement of the ability of the condenser and the objective lens to gather light. (magnification α numerical aperture)
36
New cards
Scanner
4x and 0.10
37
New cards
LPO
10x and 0.25
38
New cards
HPO
40x and 0.65
39
New cards
OIO (oil immersion objectives)
100x and 1.25
40
New cards
Focal length
Thickness of the object that maybe seen at one time under focus. (focal length 1/α numerical aperture)
41
New cards
Working distance
Distance between the front lens of the objective lens & the top of the cover glass when the specimen is in focus. (working distance 1/α magnification)
42
New cards
Parfocal
Refers to quality of the objectives & eyepiece where practically no change in focus has to be made when objective is substituted for another
43
New cards
Refractive Index
Bending of light rays away from the objective lens when light passes from the glass of the microscope slide to the air.
44
New cards
CARE OF MICROSCOPE
The microscope should be cleaned with lens paper before and after use.
45
New cards
CARE OF MICROSCOPE
Other materials such as laboratory tissue may scratch the lenses.
46
New cards
CARE OF MICROSCOPE
It is especially important that lenses never be left with oil on them.
47
New cards
TRANSPORTING THE MICROSCOPE
A microscope should be left in a permanent position on a study laboratory table in an area where it will not get jammed.
48
New cards
TRANSPORTING THE MICROSCOPE
If the microscope must be moved, it should be held securely with one hand supporting the base and the other had holding the arm.
49
New cards
TRANSPORTING THE MICROSCOPE
The microscope should be places gently on tabletops, to avoid jarring
50
New cards
PRECAUTIONS
Use the coarse adjustment only with the low power objective
51
New cards
PRECAUTIONS
Use oil immersion oil with the oil immersion objective only
52
New cards
PRECAUTIONS
Clean all oculars and objectives with lens paper after each use
53
New cards
PRECAUTIONS
Move or transport the microscope with one hand under the base and the other hand gripping the arm.
54
New cards
PRECAUTIONS
Avoid jarring or bumping the microscope.
55
New cards
PRECAUTIONS
Store the microscope covered in a protected area