industrial manufacturing techniques
- continues process
- batch process
production of aspirin
ethyl ethanoate and aspirin are produced by a batch process in industry
in a chemical plant large quantities of reactants are brought together in a reactor during which time the product is produced
after a certain time the reactor is emptied and the product is separated from the reaction mixture and purified
the product is then dried and packaged
esters and their manufacture
- these have the functional group -COO-
- they have the name -yl- anote eg methyl methoate
- both R groups form part of the same
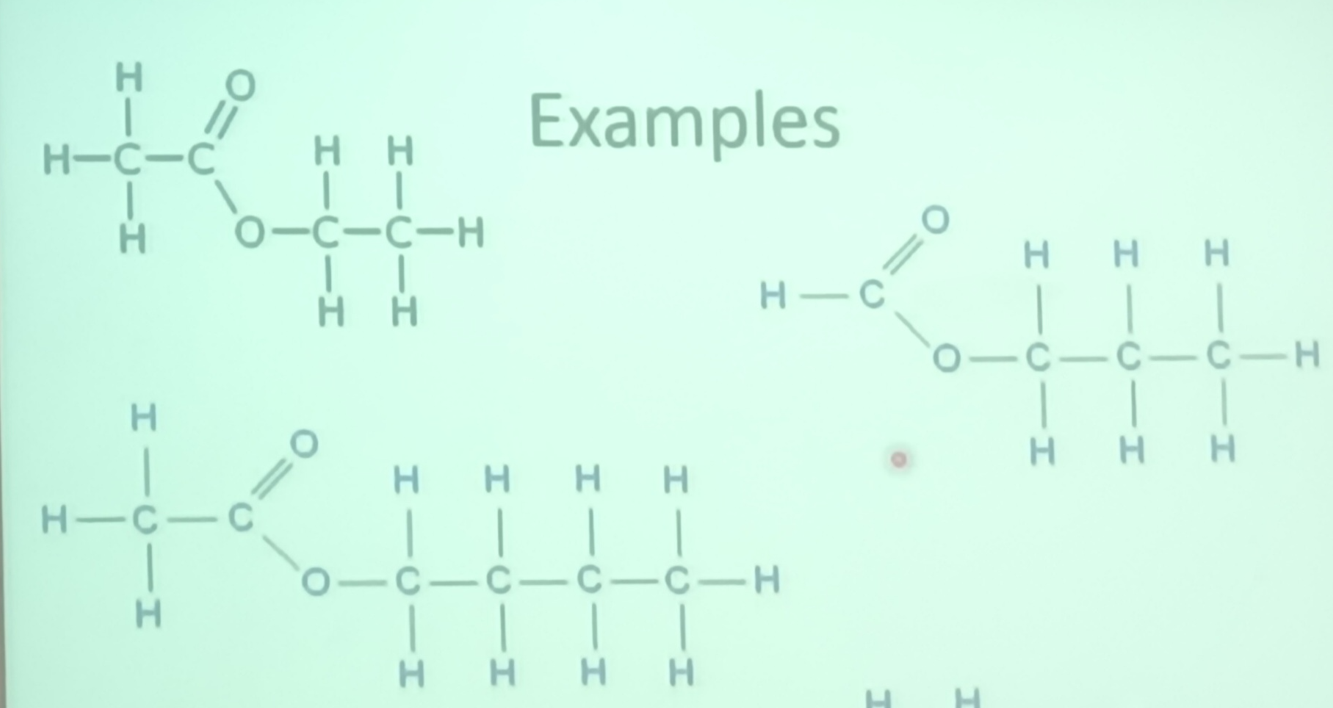
esters
- esters are useful products
- used as solvents
- making polyesters
- fruit smells are due to the presence of esters
- ethyl ethanoate is used in glue and nail polish removers
- ethyl ethanoate is used to remove caffeine from tea and coffee
manufacture
- made by reacting ethanol with ethanoic acid
- concentrated sulfuric acid is used as a catalyst
- the reaction is slow and reversable
- CH₃CH₂OH + CH₃COOH → CH₃COOCH₂CH₃ + H₂O
- in industry the ester is made in a batch process
- ethanol and ethanoic acid are added to a large reaction vessel together with the catalyst
- the reaction mixture is heated
- water produced during the rection is removed by distillation
- yields of up to 95% are possible
- other methods
- Tishchenko reaction
- liquid phase oxidation of butane
- alkylation ethanoic acid with ethene (Avada process)
testing methods and techniques
- boiling point determination
- boiling point of pure substances are known very accurately and are listed in databases and books
- the purity of a sample can be determined by comparing the boiling point of the sample to the actual value
- boiling point occurs when the intermolecular bonds are broken
- the greater the difference the more impurities are present
- distillation can be used to determine boiling point
- all values for boiling points are given as standard temperature and pressure