Cardiovascular 2
1/82
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
backman’s bundle
conducts action potentials from the SA pacemaker into the left atrium causing contraction
anterior, middle and posterior internodal pathways
conduct the action potential from the SA node to the AV node, depolarizing right atrial muscle along the way
speed of atrial conduction
relatively slow, 80-100ms
ventricular conduction
layer of connective tissue prevents conduction directly from atria to ventricle
conduction slows down through the AV node to allow blood from atria to empty into ventricles
bundle of HIS in ventricle conduction
depolarization proceeds through the septum to the apex
purkinje fibres in ventricular conduction
spreads up the walls to the ventricles from the apex to the base
direction of ventricular conduction
SA node → AV node → Bundle of His → bundle branches → purkinje fibres
ventricular muscles in contraction
have a spiral arrangement that ensures that blood is squeezed upward from the apex of the heart
complete conduction block
caused by damage in conduction pathway, block at the bundle of his results in a complete dissociation between the atria and the ventricles
blockage at the bundle of his
the SA node continues to be pacemaker for the atria but electrical activity does not make it to the ventricles so the purkinje fibres take over as the pacemaker for the ventricles
electrocardiograms
electrodes placed on the skin surface record the electrical activity of the heart. shows electrical activity summed from all the cells of the heart.
how does ECG work
salt solutions like our NaCl- based extracellular fluid are good conductors of electricity allowing the electrodes to pick up signals from the fluid
speed of ventricle conduction
occurs more rapidly, 60-100ms
Einthoven’s triangle
a hypothetical triangle created around the heart when electrodes are placed on both arms and the left leg to measure the heart's electrical activity.
leads
pairs of electrodes where one electrode acts as a positive electrode and one acts as a negative electrode
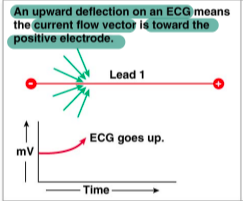
upward ECG deflection
if the electrical activity of the heart is moving towards the positive electrode
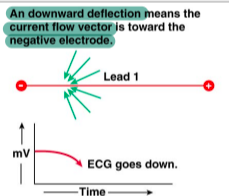
downward ECG deflection
electrical activity is moving away from the positive electrode
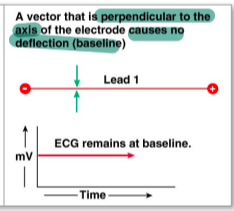
no deflection ECG
electrical activity is moving perpendicular to the axis of the electrodes
ECG waves
appear as deflections above of below the baseline
ECG segments
sections of the baseline between two waves with no detection of current flow
ECG intervals
the combination of waves and segments
P wave
atrial depolarization, contraction doesnt start until about halfway through the P wave
PQ or PR segement
conduction through the AV node and AV bundle
Q wave
depolarization of interventricular septum
R wave
contraction of outer walls of the septum
QRS complex
ventricular depolarization
ST segment
represents the plateau phase when the ventricle starts to contract upwards
T wave
ventricular repolarization, movement of K out of the cells
Tachyardia
faster than normal heart rate
bradycardia
slower than normal heart rate
changes in heart rate detection ECG
P wave to P wave or R to R
heart rhythm detection ECG
arrhythmia can be a result of many issues detectable on an ECG
QRS complex for every P wave ECG
there must be one QRS complex for every P wave, elongated segments indicative of damage
premature ventricular contractions
purkinje fibres randomly kick in as pacemaker, can be due to insufficent oxygen to myocardium, excessive Ca2+, hypokalemia, medications, exercise or high levels of adrenaline
shown as a skipped beat or palpitation
Long QT syndrome
inherited channelopathy
delayed repolarization of the ventricles, palpitations, fainting and sudden death due to ventricular fibrillation
cardiac cycle
one complete contraction and relaxation of the heart
diastole
the time durirng which cardiac muscle relaxes
systole
the time during which cardiac muscle contracts
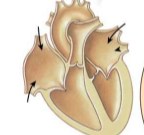
late diastole
both sets of chambers are relaxed and ventricles fill passively
atrial systole
atrial contraction forces a small amount of additional blood into ventricles
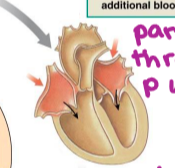
isovolumetric ventricular contraction
first phase of ventricular contraction pushes AV valves closed but does not create enough pressure to open semilunar valves
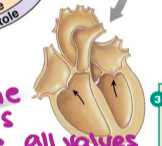
ventricular ejection
as ventricular pressure rises and exceeds pressure in the arteries, the semilunar valves open and blood is ejected
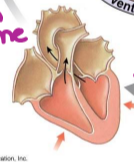
isovolumetric ventricular contraction
as ventricles relax, pressure in ventricles fall, blood flows back into cusps of semilunar valves and snaps them closed
A A’ segment
starts at end systolic volume, pressure in ventricles drops below the pressure in the atria and the AV valve opens causing the ventricle to fill with blood
A’ B segment
atria contracts forcing more blood into the ventricle and slightly increasing volume and pressure. at the end, the max amount of blood is in the ventricles
B-C segment
the ventricle begins contracting closing AV valve, continued contraction causes a large increase in pressure within the ventricle
C-D segment
Once pressure in the ventricle rises above 80 mmHg it exceeds the aorta and the aortic valve opens causing a rapid ejection of blood
the ventricle begins to relax and pressure begins to drop but blood still flows due to inertia
DA segment
pressure in aorta begins to exceed ventricle causing semi-lunar valve to close, ventricle continues to relax
End of wiggers diagram
ventricle relaxes, pressure in atria begins to exceed ventricle
AV valve opens and you get the passive filling of the ventricle
Start of wiggers diagram
ventricle begins to contract, increasing pressure within ventricle causing the AV valves to snap shut
end diastolic volume
the maximum volume in the ventricle after ventricular filling
end systolic volume
the minimal amount of blood in the ventricles, blood left after ventricular contraction
stroke volume
amount of blood ejected during a single ventricular contraction
stroke volume equation
stroke volume = end diastolic volume - end systolic volume
End systolic volume purpose
leaves a small amount of blood in the ventricle, providing a safety margin
increase of stroke volume
can be caused by the autonmic nervous system, venous return and by certain medications
ejection fraction equation
ejection fraction = stroke volume/ end diastolic volume
cardiac output
the flow of blood delivered from one ventricle in a given time period str
cardiac output equation
cardiac output = heart rate x stroke volume
unbalanced cardiac outputs of circuits
if balance of cardiac outputs is offset, blood tends to pool in the healthy circuit feeding the weaker side of the heart
how can cardiac output be changed
through adjusting heart rate in pacemaker cells. slowing down depolarization, starting at a more negative value
contractility of the heart factor
the intrinsic ability of a cardiac muscle fibre to contract at any given fibre length and is a function of Ca2+ entering and interacting with the contractile filaments
the length of fibres factor
determined by the volume of blood in the ventricle at the beginning of contraction, creates more force when stretched
inotropic agent
any chemical that affects contractility
positive inotropic effect
chemicals increasing contractility
negative ionotropic effect
chemicals decreasing contractility
norepinephrine ionotropic effect
released from the sympathetic neurons or adrenal medulla cause a positive iontotropic effect regardless of EDV
sympathetic modulation of stroke volume step 1
phosphorylation of Ca2+ channels increases calcium conductance during action potentials causing greater calcium entry
sympathetic modulation of stroke volume step two
phosphorylation of ryanodine receptors enhances sensitivity to Ca2+ increasing release of Ca2+ from sarcoplasmic reticulum
sympathetic modulation of stroke volume step 3
increases rate of myosin ATPase which speeds up myosin head binding
sympathetic modulation of stroke volume step 4
phosphorylation of serca increases the speed of Ca2+ reuptake which increases Ca2+ storage creating a bigger calcium pool in SR
frank starling law of the heart
the amount of force developed by the cardiac muscle of a ventricle depends on the initial stretch of the ventricle walls by ventricle filling
preload
the degree of myocardial stretch prior to contraction on the heart
heart stretch
indicated by ventricular end diastolic volume
skeletal muscle pump
skeletal muscle activity compresses veins in the extremeties pushing blood back to the heart increasing venous return
respiratory pump in venous return
during breathing in the chest expands and the diaphragm moves down creating a subatmospheric pressure in the thoracic cavity, this draws blood into the vena cava increasing venous return
sympathetic constriction of veins
decreases their volume squeezing blood back towards the heart
afterload
the end load against which the heart contracts to eject blood
primarily determined by the combination of the EDV and the pressure in the outflow artery prior to contraction
afterload increase
can be increased in pathological situations like hypertrophy where the heart decreases the cavity size decreasing the EDV
inadequate lymph drainage
cause of edema
can occur from obstructions in the lymphatic system and lymph nodes
disruption in normal capillary filtration and absorption
cause of edema
increased capillary hydrostatic pressure, decrease in plasma protein concentration or increase in interstitial protiens
Cross sectional area of vessels
with each branching of a vessel, the two new branches always have a higher total cross sectional area than the parent vessel
velocity of blood formula
velocity of blood = flow rate/ cross sectional area