BIOL 319 Exam 1 Study Guide: Key Terms & Definitions
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
4 Types of tissues
Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nervous
Homeostasis
Balance in bodies internal environment
How does living organisms responding to stimuli relate to hemodynamics
hemodynamics is how your BLOOD reacts/move in your body, living organisms react to stimuli, and could alter hemodynamics
Which tissues have RMPs
ALL TISSUES (muscle, nervous, epithelial, connective)
-BUT ONLY Muscle and Nervous tissue are excitable = can use RMP to generate action potential
What is an RMP
resting membrane potential - difference in charge across membranes
Ultrasound vs radiograph
Ultrasound: sound waves pass into body and bounce back to receiver; visualized as a sonogram
Radiograph: Electromagnetic radiation moves through body and is exposed on photographic plate; creating radiograph
What is an ultrasound used for?
1. View the uterus and ovaries during pregnancy to monitor baby health
2. Diagnose gallbladder disease
3. evaluate blood flow
4. Guide a needle for biopsy or tumor treatment
5. Examine a breast Lump
6. Check for thyroid gland
7. Find genital and prostate problems
Lithotripsy
Extracorporeal shock-wave lithotripsy - ultrasound waves are used to break the kidney stone into smaller pieces
Basic function of lymphatic system
Capillaries leak fluid all the time, even when not injured, it is the duty of the lymphatic system to collect the leaked fluid from the capillary beds
Popliteal
behind the knee
Which tissues are capable of generating action potentials
Both nervous and muscle tissue can generate action potentials
5 physiologically relevant ions
sodium, potassium, magnesium, calcium, chloride
What is the definition of physiology
1. What it is made of
2. How it looks functioning properly
3. How it looks when functioning improperly
4. What type of pharmacology or procedures can we use to fix it
5. Overtime things tend to breakdown
4 physiologically relevant organic molecules (macromolecules)
1. Carbohydrates
2. Proteins
3. Lipids
4. Nucleic Acid
4 excretory organs
Skin, kidney, liver, colon
What protects the kidney
Ilium, abdominal fat, and the last three ribs
EPO (hormone) from the kidney. Function.
EPO from the kidney binds to receptors in red marrow cavities to increase red blood cells (hematopoiesis)
feedback inhibition
Homeostasis is regulated by feedback loops that allow for a process to be adjusted by the outcome
There are both positive and negative feedback loops
Feed forward stimulation loop example
Feed forward stimulation loops = positive feedback loops
- Effectors continue the response beyond the set point until the original stimulus is removed
Example: parturition (pregnancy)
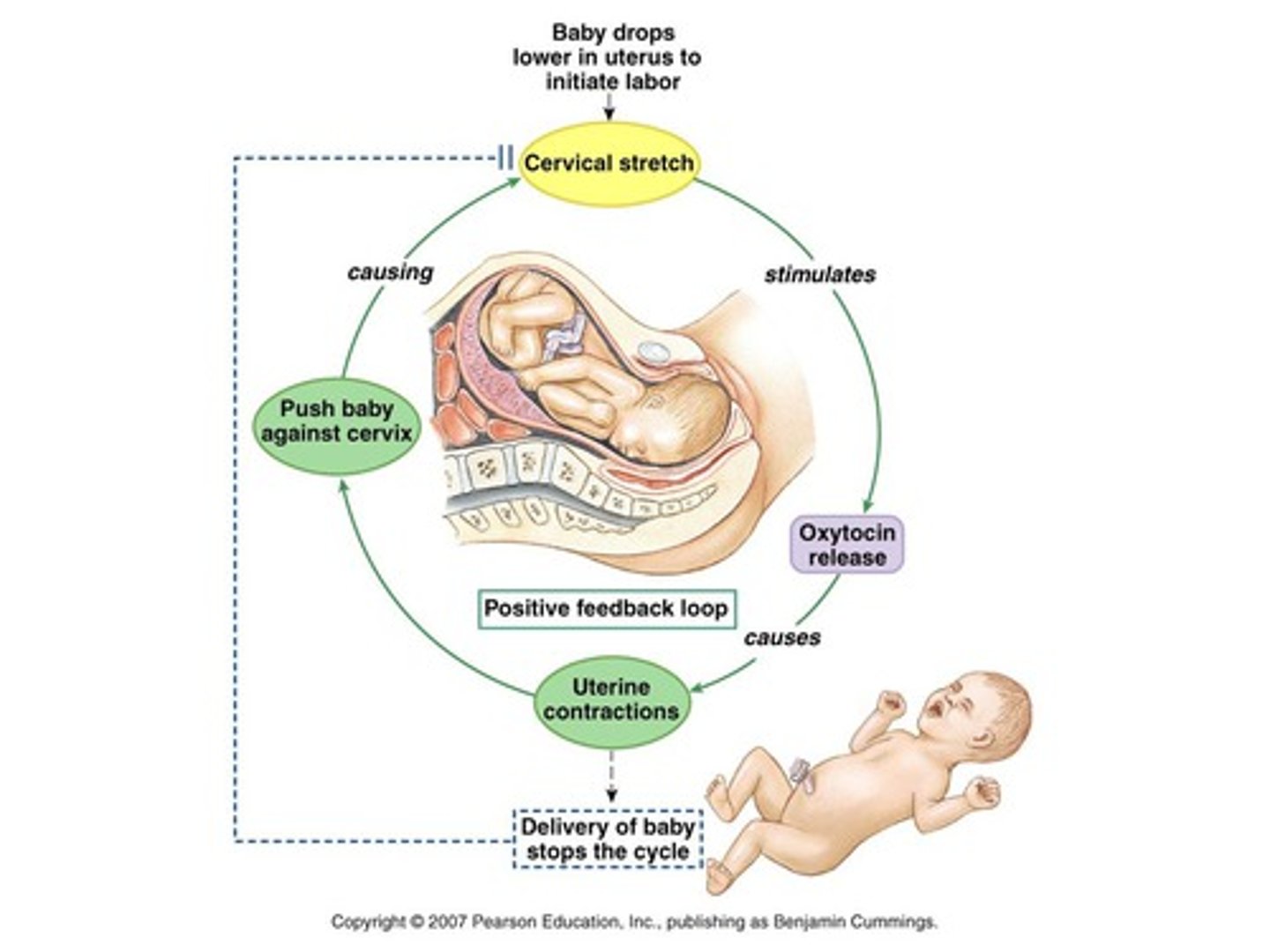
What and where are baroreceptors?
Baroreceptors detect pressure
Located in transitional epithelium: cervix, bladder
Temperature centers in the brain are located in the...
Hypothalamus
Hormones that are the major effectors of one's metabolism
Thyroxin, Growth hormone, and respective se hormones
Goblet cells
secrete mucus, which is a defense
Endocrine vs exocrine
Endocrine is secretion and exocrine is excretion (waste)
Endocrine: no open contact with exterior; no ducts; have an extensive network of blood vessels; produce hormones
Exocrine: open contact maintained with exterior by way of ducts that open onto the free surface of the epithelium
secretion vs excretion
Secretion: creation and transfer of something within the body; Positive
excretion: waste product
Ilium vs ileum
Ilium is a part of the coxal bone and protects the kidney
Ileum is the lower portion of the small intestine
Cognition
One of the four separating traits of humans
Our development of the prefrontal cortices allow us to engage in cognition (Personality, memory, think and reason & cause and effect)
endothelial vs epithelial cells
Endothelial: (type of epithelium) single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood and lymphatic vessels
Epithelial: thin and continuous layer of compactly packed cells with an intracellular matrix, lines the surfaces of organs and surfaces of blood vessels throughout the body. epithelial cells are AVASCULAR, but gases can DIFFUSE in and out
What is a collapsed lung called?
pneumothorax
If there is an increase in pressure in the interpleural (in between visceral and parietal pleural) space the lung may collapse
Serous membrane
Serous membranes covers and lines the body cavities of organs
Secretes serous fluid = sliding (LESS FRICTION)
peritoneum and mesentery
Peritoneum: lines the abdominopelvic cavity
Mesentery: regions of double-folded visceral peritoneum that is attached to certain points to the posterior abdominopelvic wall
Significance of being a deuterostome
Deuterostomes lead to body cavities
Apoptosis
programmed cell death
How many muscle types
Skeletal - voluntary
Cardiac and Smooth - involuntary
Actin in a non-muscle conjuncture means what to us at this juncture
Metastasize (cancer spread) & ameboid movement
Biopsies...sent to who? Why? 3 main questions answered regarding the biopsy.
Biopsy (sample tissue) sent to pathologists
Sent to pathologists to aid in diagnosis and treatment
3 questions: can we biopsy it? Is it malignant? Can we treat it?
Defenses!!! Issues with defenses?? Vomiting and diarrhea get out of hand potentially means what physiologically?
Our defenses likes sneezing, coughing, fever, vomiting, etc. are there to aid us
Our defenses paradoxically can become overzealous leading to morbidity/medical issues
Medulla oblongata (what centers)
Has heart rate centers, blood rate centers, respiration centers and pressure centers
Compliant vs noncompliant organs
Compliant organs are those that give and stretch (think transitional epithelium i.e bladder, cervix)
Non-compliant organs are ones that do not give/stretch (i.e kidney)
Kidney stones.....ureter vs urethra. Where IS the stone? Why does location matter?
Urethra: expulsion of urine
ureter: take urine from kidney to bladder
The stone is in the ureters, if the stone reaches the bladder it can be passed out in urine.
If the stone is stuck in the ureter, it may cause severe pain
ECM
extracellular matrix
Can contain collagen, reticular fibers, elastin fibers and "ground substance" along with interstitial fluid
Hydroxyapatite
Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2
- typically 7-10% of our bones remodeled every year
- rigid and firm portion of bone
- Found in both bones and enamel
Hemodynamics
Study of flowing blood and through what it flows
Adipose tissues
Yellow adipose tissue: white at birth but turns yellow with age
Brown adipose tissue: color from cytochromes and is specialized to generate heat
Alveoli of lung and pulmonary capillary beds; one endothelial layer and one epithelial layer. Why so thin? Alveoli and capillary beds are SO THIN they appear CLEAR!! Why?
These cell layers need to be thin so that gas can come in and out (gas exchange)
Surfactant
Surfactant helps to keep alveoli open
produced in utero in weeks 24-28
Osteoblasts vs Osteoclasts vs Osteocytes
Osteoblasts = Build! Secrete collagen first the hydroxyapatite
Osteocytes = mature bones cells
Osteoclasts = Cleave bones
Tendon vs Ligament & Strain vs Sprain
Tendons: connect muscle to bone, strain
Ligaments: connect bone to bone, sprain
very slow to heal
Neuron vs Nerve
Neuron is one cell that has the ability to produce electrical signals called action potentials
Nerve is 1000s of neurons bundled together
multipolar neuron
Function in decision making, intraneuronal and control function of the nervous system
afferent vs efferent
afferent (sensory) - Going into something
efferent (motor) - Going away from something
Myelination! Which glial cells are involved AND which cell myelinates what specifically?
Glial cells create sheath around axon called myelin
Glial cells are support cells of the brain, spinal cord and nerves
- nourish, protect and insulate neurons
Oligodendrocytes = myelination (CNS)
Schwann cells = myelination (PNS)
Anatomy of neuron
One cell
Cell body: contains nucleus
Axon: cell process; conducts impulse away from cell body; usually only one per neuron
Dendrites: cell processes: receive impulse from other neurons; can be many per neuron
Number and types of vertebrae
cervical (7), thoracic (12), lumbar (5), sacral (5), caudal (coccyx) (4)
Marrow cavities; types; functionality
Red marrow: PRODUCES NEW BLOOD CELLS Hematopoietic tissue surrounded by a framework of reticular fibers. Produces red and white blood cells
Yellow marrow: STORES LIPIDS yellow adipose tissue; does not produce blood cells
- In children yellow marrow replaces much of red marrow
Osteon, Trabeculae, canaliculi
Osteon: Central canals are surrounded by lamellae
Trabeculae: Interconnecting rods of bone (SPONGY)
Canaliculi: small canals found in between lacuna, allow for "communication between central canal and osteocyte
Bone remodeling and hormones associated with it
Typically 7-10% if our bones remodel every year
4 hormones include:
- Calcitonin
- Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
- Calcitriol ( Vitamin D)
- Estrogen
Spongy vs Compact Bone
Spongy Bone
- Located in Epiphysis
- Has trabeculae
- strong but not very dense
- in living bones the space between trabeculae is filled with marrow.
- Covered with endosteum
Compact Bone
- Located in Diaphysis
- More mineralized
- Dense
Diaphysis vs Epiphysis
Diaphysis
- shaft of a long bone
Epiphysis
- Upon the end of a bone
Cartilage types - Where is articular cartilage?? how fast does cartilage heal and why?
Types (All AVASCULAR)
- Hyaline: allow for articulation
- Fibrocartilage: intervertebral discs
- elastic: Return to original shape after being stretched
Articular cartilage is located at the ends of bones and is a form of hyaline cartilage
Cartilage heals very slow because it is avascular
periosteum vs endosteum
Periosteum: covers outer layer of bone and consists of two layers
Endosteum: covers spongy bone, lines central canals (Haversian) and is a single layer
Defense...mucociliary escalator....stomach acid... Are these defenses always positive in terms of our physiological responses
Mucociliary escalator
- uses cilia to move mucus across the surface of cells
- up the trachea ad bronchi
Stomach acid
- helps maintain neutral pH
These defenses are not always positive, excess mucous can lead to cystic fibrosis
embryonic germ layers (3) can form what in the adult
1. Endoderm (inner skin)
- inner layer
- form linings of digestive tract
2. Mesoderm (middle skin)
- middle layer
- form tissues such as muscle, bone, blood vessels
3. Ectoderm (outer skin)
- outer layer
- form skin and neuroectoderm, which forms nervous system; neural crest cells give rise to peripheral nerves, skin pigment cells, medulla of the adrenal gland, and face tissue
What is living and nonliving tissue when looking at a person, what are the advantages of non-living tissue?
Skin, hair, nails are NOT living
Eyes, teeth are living
Non-living skin provides protection, helps regulates temperature, prevents water loss, helps produce vitamin D.
Ureters vs urethra; which gender typically incurs MORE UTIs? Why?
Ureters connect kidneys to bladder
Urethra is urine expulsion from bladder
Females typically experience more UTIs, because it is easier for bacteria to enter the urethra
Keratin - benefit....found where??
Keratin
- Keratin is found on the outer layer of the skin (epidermis)
- The benefit of keratin is that it helps protect against abrasions, forms a barrier against infection and reduces water loss
desmosomes and gap junctions
Desmosomes: disk shaped regions of cell membrane; often found in areas that are subjected to stress
Gap Junctions: protein channels that aid in intercellular communication
- allows ions and small molecules to pass through
- coordinate function of cardiac and smooth muscle
*Intercalated disks (between cardiac muscle cells) have gap junctions and desmosomes
Sebum?? Where?
group of oils and triglycerides
-lubricates and protects skin
Where: Sebaceous glands (holocrine)
Cerumen? Where?
Earwax
Where: ceruminous glands (apocrine)
merocrine vs apocrine vs holocrine
All modes of exocrine gland
Merocrine (sweat/salvary glands)
- exocytosis
Apocrine
- pinched off fragments of gland cells; mammary glands and ceruminous glands
Holocrine: (zits/pimple)
- shedding of entire cells, sebaceous glands
Local injury....histamine.....vasodilation. Why??
When injured capillaries get wider
Histamines: causes inflammation
Vasodilation: blood vessels get wider allowing for more blood to flow through
Histamine and vasodilation aid in the repair process
3 specific protein of the ECM
1. Collagen: Main structural protein, strong, flexible, inelastic
2. Reticular fiber: fill space between tissues and organs, forms branching networks
3. Elastic fiber: returns to original shape after distension or compression
"Pinched skin stay pinched as we get older..." Why?
As we age elastin fibers lose their "elasticity" cause our skin to remain as it is.
hyaluronic acid
Polysaccharide, good lubricant, helps retain water in the skin
- Hydrophilic
Synovial membranes produce fluid rich in hyaluronic acid
Mammary glands vs breast tissue
Mammary glands are in all mammals whereas breast tissue is found on primates
What is the cell distance that oxygen can diffuse to tissues? And if a tissue is beyond this distance??
Oxygen can diffuse 6-8 cells, cells that are not receiving oxygen are dead.
Elastic cartilage location
external ear, epiglottis
Blood cell types
Red blood cells (erythrocytes) - NO nuclei and NO mitochondria, only way to make ATP via glycolysis
White blood cells (leukocyte) - respond to injury or infection
Platelets (thrombocytes) - involved with clotting
Lipid....fat....triglyceride....categorization
Lipid is a macromolecule, fat is a type of lipid and triglycerides are the most abundant fat in humans
Membranes that decrease friction
Mucous membranes
- line cavities open to outside of body
- secrete mucus
- contains epithelium with goblet cells
Serous Membranes
- simple squamous epithelium called mesothelioma, basement membrane, thin layer of loose C.T.
- lines cavities not open to exterior]
- Pericardial, pleural, peritoneal
Synovial Membrane
- line freely moveable joints
- Produce fluid rich in hyaluronic acid
edema
Swelling
What is EGF?
Epidermal Growth Factor Protein that stimulates cell growth and differentiation by bind to its receptor
differentiation: cell knows what to become
Functions of bone
support, protection, movement, storage, blood cell formation, Energy source
Types of bone
Long bone, short bone, irregular bone, flat bone and sesamoid bone
compact bone: strong, dense, mineralized
Spongy bone: not very dense, but strong, and has trabeculae
What is the nexus between skeletal muscle and blood pressure
Every time skeletal muscle is flexed it causes a jolt of pressure
Fontanelle? Significance?
Fontanelles are soft spots in a newborns cranium
- 2-6 depending on age and how they are counted
- allow for contortion
Bone remodeling and hormones
Typically 7-10% of our bones are remodeled every year
Osteoblasts will secrete collagen then hydroxyapatite
Calcitonin
- decrease blood Ca
- inhibit osteoclasts and renal/GI re/absorption
PTH
- Increase blood Ca
- stimulate osteoclasts & renal/GI re/absorption
Calcitriol
- increase blood Ca
- stimulate osteoclasts & renal/GI re/absorption
Estrogen
- inhibits apoptosis of osteocytes -> bone cells numbers go up -> stronger bones
- Post-menopausal (female)
Osteoporosis
Condition of holes in the body
- Diagnosis: bone scan -> help tell you level of bone density
- Treatment (4 methods)
1. Increase Ca
2. E.R.T
3. Low impact, low weight exercise
4. "Pulsatile PTH" (negative feedback)
- trick brain into thinking PTH levels are high -> PTH levels go down
-> osteoclasts activity goes down
Apical vs Basolateral Surface of cells
Apical surface is typically the surface closest to the lumen of a vessel
Basolateral surface are basal surfaces and lateral surfaces
TMJ
temporomandibular joint = Jaw = a hinge and ball and socket joint ALL at the same time
- jaw moves out of socket during normal function
Gomphosis
Tooth joint
Effect of aging on tissue
Cells divide more slowly (ironically more cancers are in elderly)
Collage fibers become more irregular in structure
Tendons and ligaments become less flexible and more fragile
interstitium
Space between cells
Ischemia
Low blood flow
Hypoglycemia
low blood sugar
"Angio" means?
vessel
CO2 vs pH, relationship between the two
CO2 and pH are inverse
visceral vs parietal
Parietal layer lines wall of body cavity
Visceral layer covers organs
Collagen
Collagen fibers are the must abundant connective tissue in the body
MAIN structural protein in the ECM found in the bodies various connective tissues
ALL 3 are AVASCULAR (therefore takes a long time to repair)