Kinesiology Vocab and Notes -- Unit 5 p.1
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Cardiovascular System
What system is the heart apart of?
Supplies muscles and organs with oxygen and nutrients
removes co2 and moves blood cells and hormones.
What Is the primary role of the CV system?
The mediastinum—an area in the thoracic cavity
Where is the heart located?
Diaphragm
What is the most important skeletal muscle in the body?
Heart
What is the most important muscle in the body?
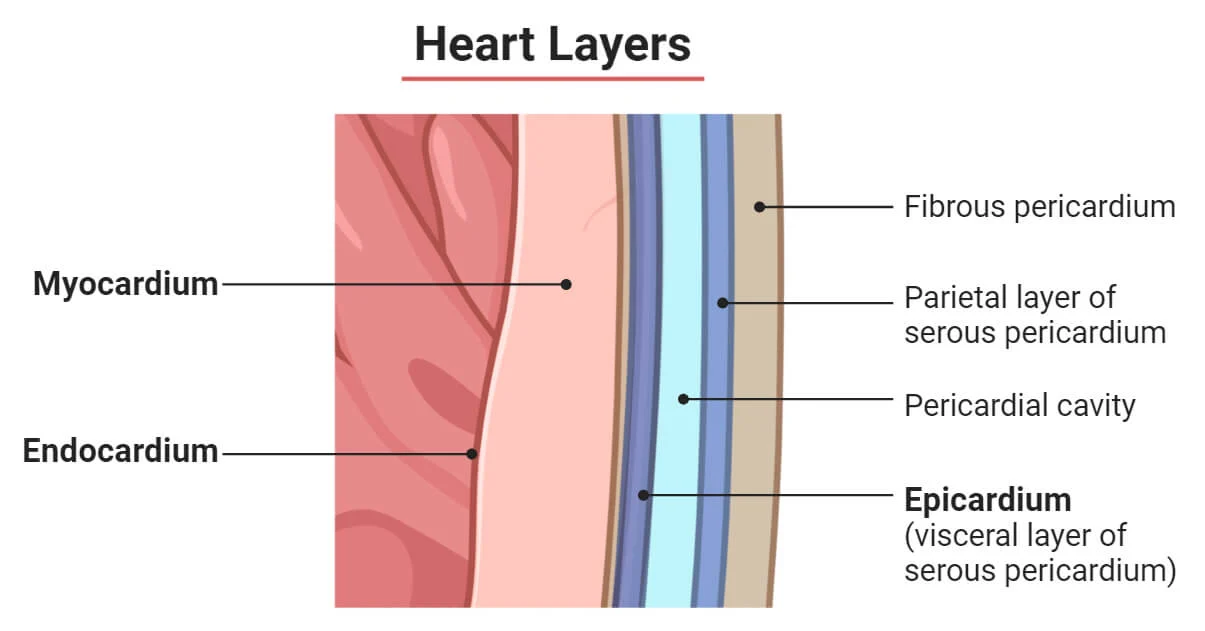
Pericardium
What layer of the heart is this?
A sac that surrounds the heart
Fibrous and serous pericardium
Endocardium
What layer of the heart is this?
Thin, smooth membrane
Deepest layer—Forms the surface of the valves
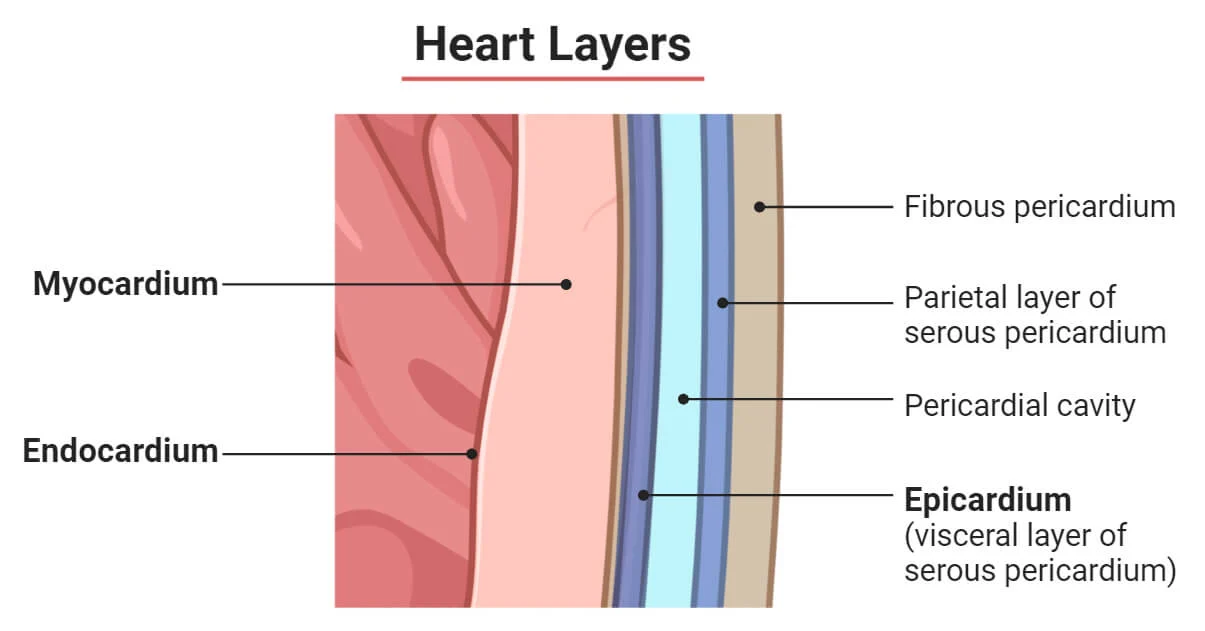
Epicardium
What layer of the heart is this?
Visceral layer of serous pericardium
Most artificial layer
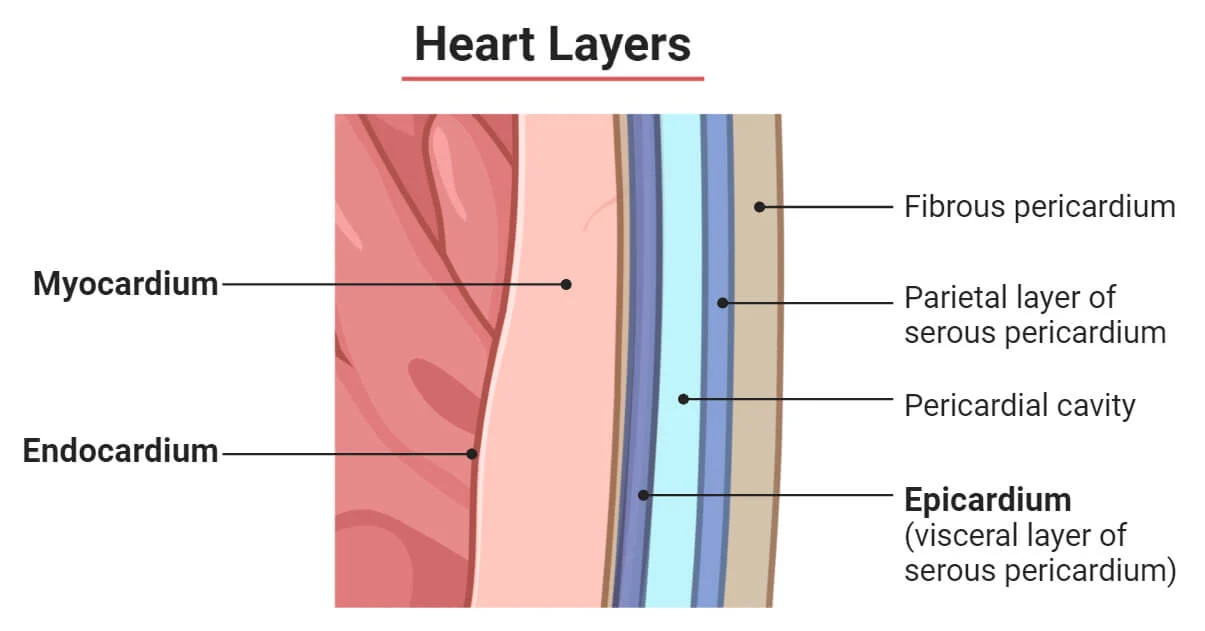
myocardium
What layer of the heart is this?
Cardiac muscle—responsible for contracting the heart for cardiac pump
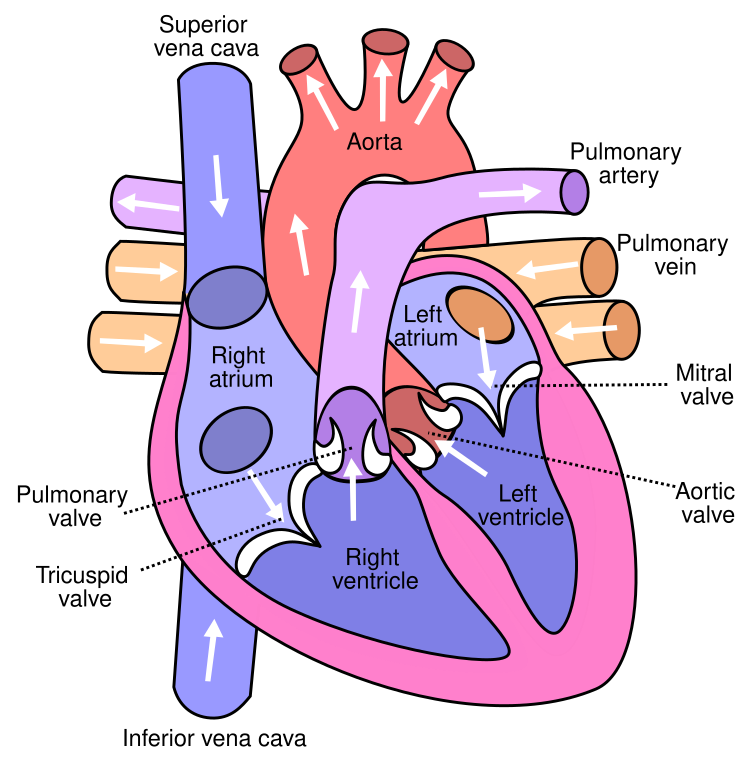
4 chambers
How many chambers of the heart are there?
Right Atrium
Pumps blood to the right ventricle
Slightly larger than the left atrium
Left Atrium
Smaller atrium
More muscular than right atrium
Right Ventricle
Slightly smaller than left ventricle
Pumps blood to the lungs for oxygenation
Left Ventricle
Larger than right ventricle
More muscular as it pumps oxygenated blood to the entire body
4 valves
How many valves do we have?
Tricupid Valve
Located between the heart’s two right chambers
3 flaps (cusps/leaflets) open to let blood move to the lower right ventricle
Bicuspid Valve (mitral valve)
regulates blood flow from the left atrium into the left ventricle
Left side
Pulmonic Valve
Structure and function
Enables deoxygenated blood to be pumped from the right ventricle to the pulmonary circulation
Aortic Valve
lets blood flow from your left ventricle to your aorta by opening and closing
Superior Vena Cava
Blood from above the neck enters through this entry
Inferior Vena Cava
Blood below the heart enters from this entry
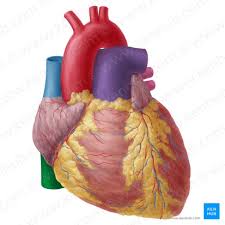
Pulmonary Artery (Pulmonary Trunk)
Takes deoxygenated blood away from the heart
only time arteries carry deoxygenated blood
Pulmonary Vein
Brings oxygenated blood back to the heart
Only time veins carry oxygenated blood
Septum
The wall separating the right and left side of the heart
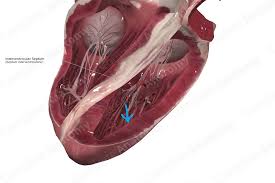
Auricles
Act as reservoirs to help hold more blood
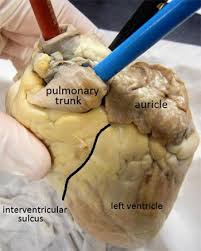
Apex
The tip of the heart where we take the apical pulse
point of strongest contraction/maximal impulse
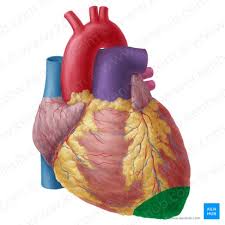
Base
Superior to the apex
major blood vessels are attached (superior vena cava and pulmonary trunk)
Pumps blood to the lungs
Holds deoxygenated blood
What does the RIGHT SIDE of the heart do?
Pumps blood to the body
Holds oxygenated blood
What does the LEFT SIDE of the heart do?
heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure, and swallowing
What does the Medulla oblongata control?
Involuntary actions
SA Node
AV Node
Bundle of His
Purkinje Fibers
What is the order of the cardiac conduction system?
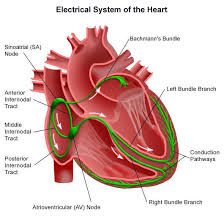
Sinus Atrial Node (SA)
Pace-maker for the heart, collects beat signal from brain
Controls the RATE of the heartbeat (60-100 is average)
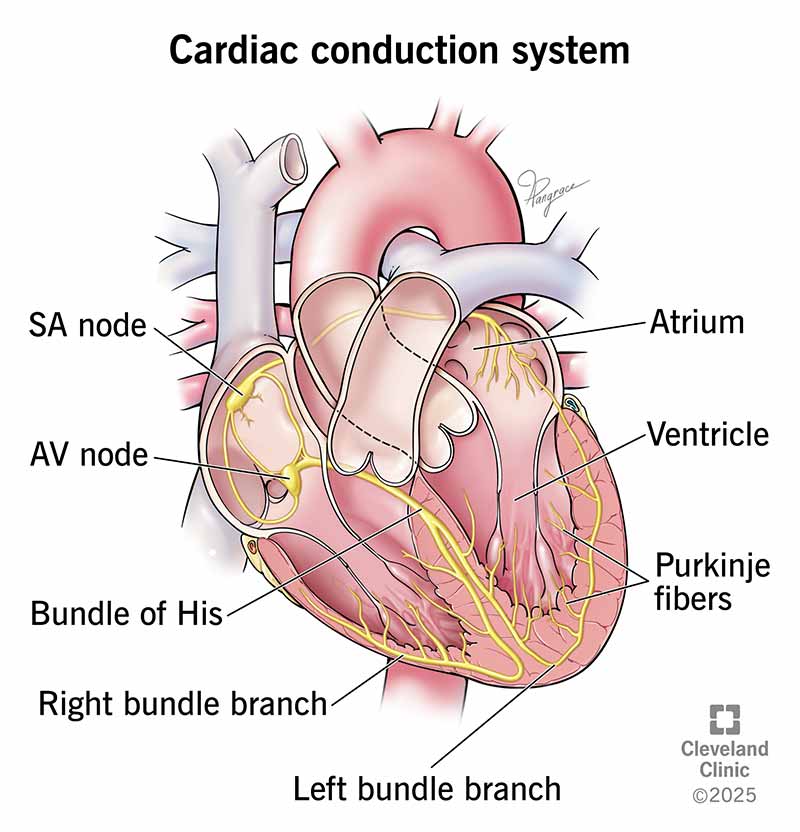
Atrioventricular Node
Conducts impulses from the atria to the ventricles
Doesn't fire until the atria are EMPTY
Bundle of His
Carries electrical signals from AV Node to the Right and Left purkinje fibers
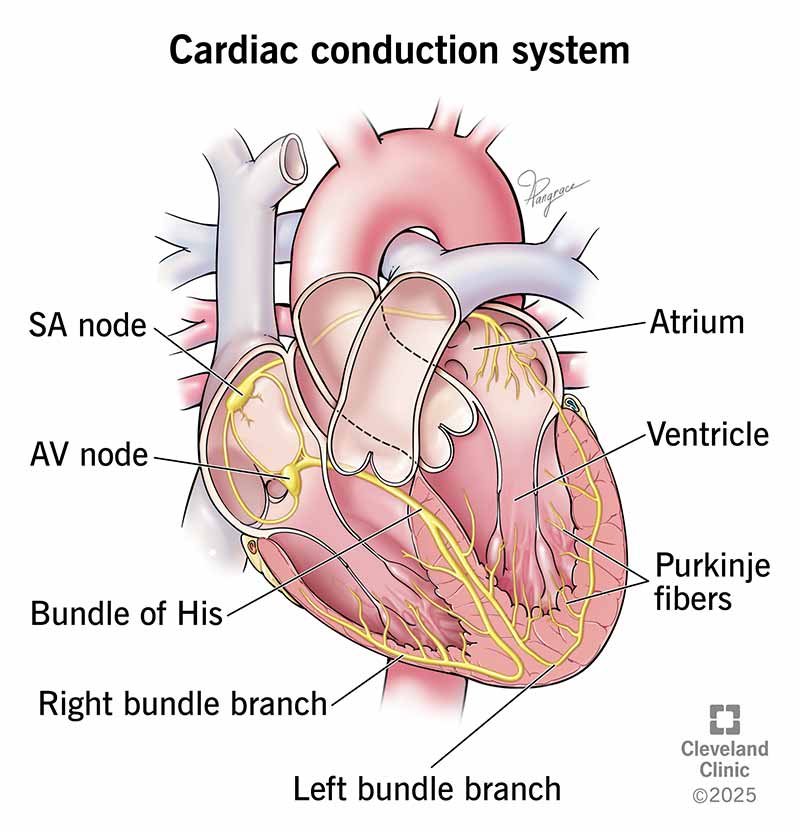
Purkinje Fibers
Allows for synchronized contractions of its ventricles by carrying the electrical signal to them
Essential for consistent heart rhythm
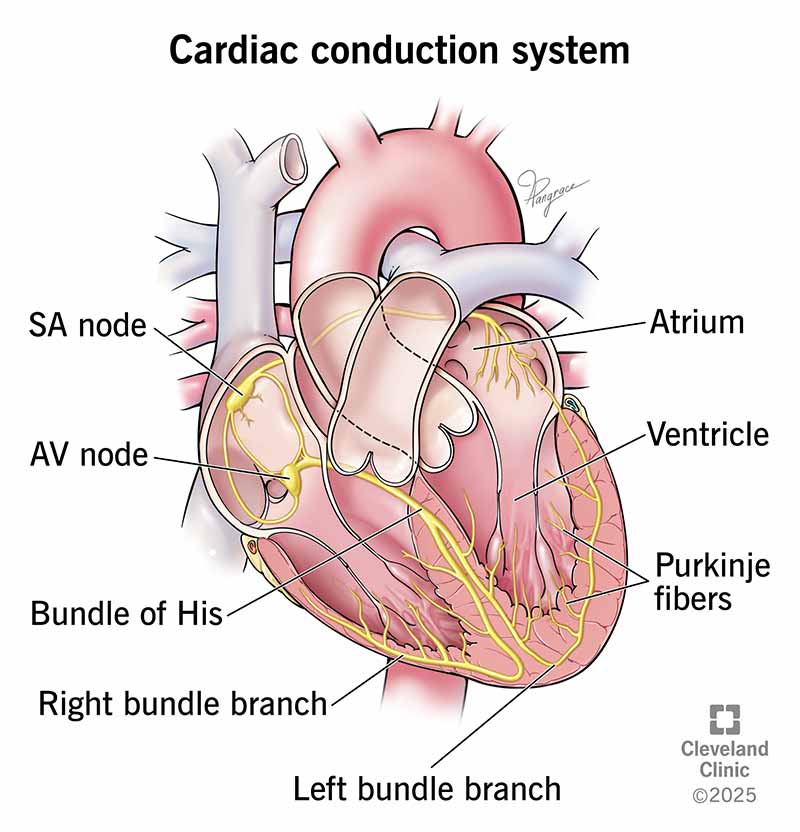
Blood enters RIGHT ATRIUM from superior/inferior Vena cava (deoxygenated)
Blood is passed to RIGHT VENTRICLE through TRISCUPID VALVE
Blood exits right ventricle through PULMONARY ARTERY and enters the lungs
Blood (oxygenated) renters through PULMONARY VEIN into LEFT ATRIUM
Blood enters LEFT VENTRICLE through BISCUPID VALVE
Left Ventricle pumps blood to the entire body through the AORTIC VALVE
What is the sequence of a drop of blood in the heart?