Energy Systems
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
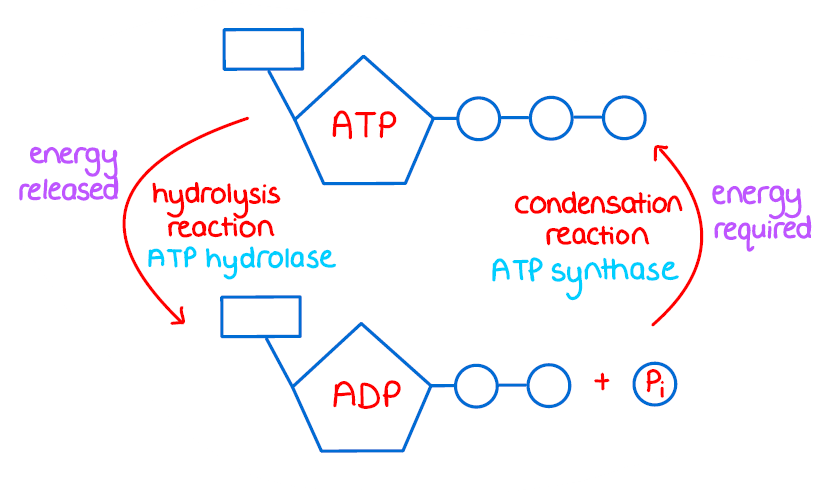
ATP Hydrolysis
the process of ATP breaking down into ADP+P+energy+heat, and the use of creatine for ADP to form ATP
Cellular respiration
process by which the chemical energy of “food” molecules is released and partially captured in the form ATP
ATP storage
The energy system that we use first. It powers the first few seconds of activity.
ATP/CP system
The energy system that takes over dominance after 2 seconds and provides energy until the creatine runs out after about 5 seconds.
Glycolytic Systems
In cytoplasm, glucose turns into pyruvate through glycolysis. If no O2 is present during the process, pyruvate will turn into lactic acid/ethanol+2ATP. If O2 is present, pyruvate will turn into Acetyl CoA and about 34 ATP in the mitochondrion.
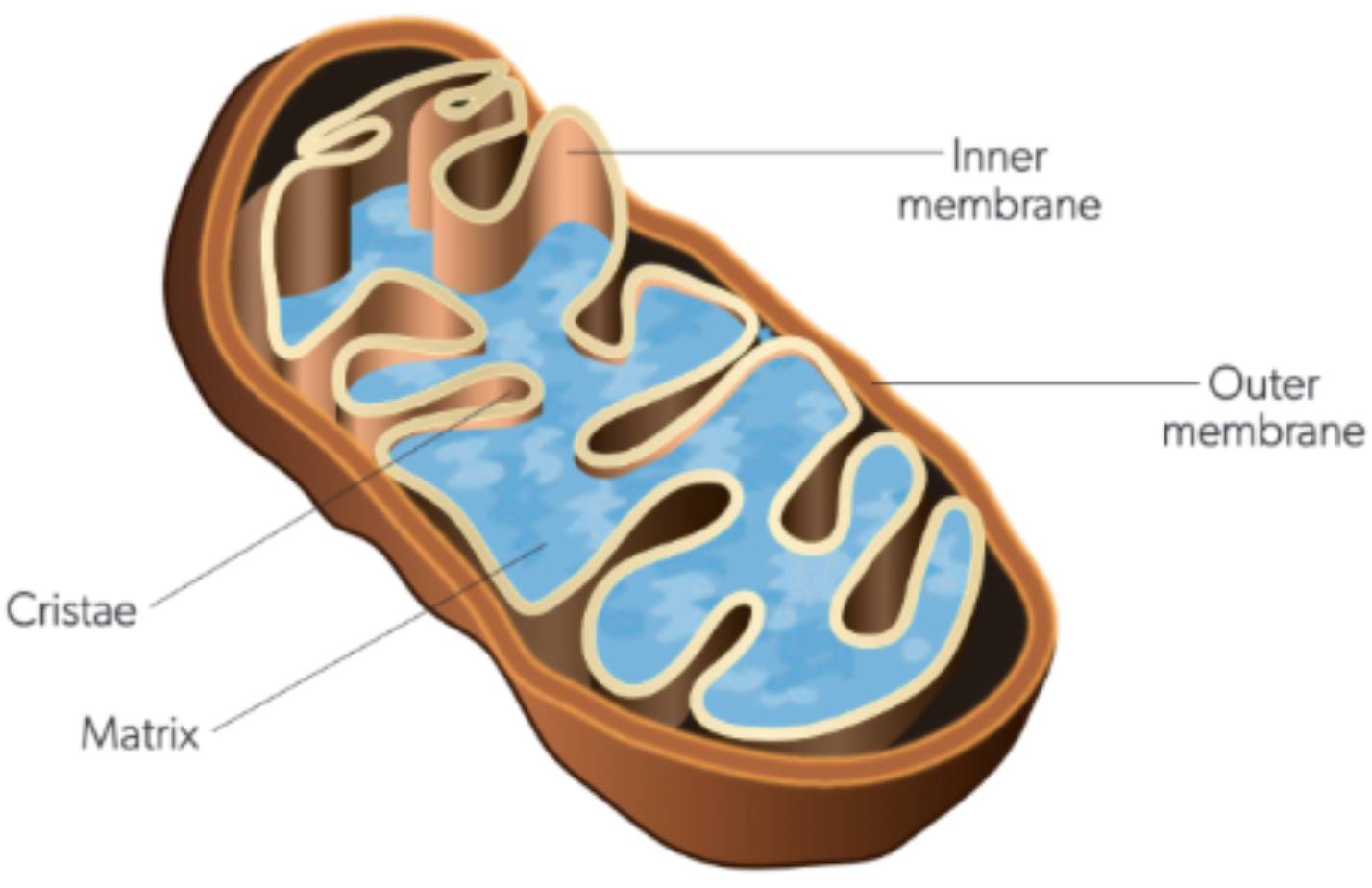
inner structure mitochondria
Anaerobic Glycolysis (lactic Acid System)
If no O2 present, the body produce 2 ATP and a build-up of lactate, this is fast but short.
Aerobic Glycolysis
If O2 is present, pyruvate enters matrix (in the mitochondria) where oxidative phosphorylation turns pyruvate into AcetylCoA. This enters the Krebs Cycle and 2 ATPs are formed plus NADH and FADH2 - high energy electrons. These then pass through the inner membrane to the cristae space where the Electron Transfer Chain produces 34 ATP.
Triglycerides
They are stored in the adipose tissue and skeletal muscles. When glucose stores run low lipolysis catabolises lipids to glycerol and 3 fatty acids to be used for energy
Aerobic Lipolysis
The process of releasing triglycerides from the body’s stores. Glycerol is glycolyzed to pyruvate in cytoplasm. Fatty acids are beta oxidised to AcetylCoA in the matrix. They produce more high energy electrons in the Krebs cycle which results in over 100 ATPs in the Electron Transport Chain.
System | Fuel | Duration | By-product | Activities when dominant | Intensity | Amount of ATP | Speed of production |
ATP-CP | |||||||
Lactic Acid | |||||||
Aerobic glycolysis | |||||||
Lipolysis |
System | Fuel | Duration | By-product | Activities when dominant | Intensity | Amount of ATP | Speed of production |
ATP-CP | ATP | 1-5s | N/A | Any early movement | Any | 1 ATP | Immediate |
Lactic Acid | Glucose | 2-15s | Lactate | HIIT | High | 2 ATP | Fast |
Aerobic glycolysis | Glucose | 1m- 2hrs | Co2+H2o | Endurance | Middle | 38 ATP | Medium |
Lipolysis | Lipids | 30m – 3hrs | Co2+H2o | Endurance | Low-middle | 100s ATP | Slow |
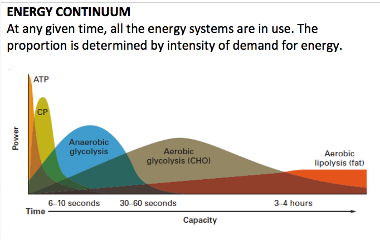
Energy Continuum
different energy systems dominate at different times and are dependent on different demands
glycogenesis
the process of storing glucose in liver and skeletal muscles
Glycogenolysis
It occurs when you are hungry or exercising and require more glucose. Glycogen is catabolised to become glucose
Gluconeogenesis
the production of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources like proteins, lactate and glycerol to create energy.
Metabolism
all biochemical reactions in body
Anabolism
energy requiring actions that build up
Catabolism
energy creating actions that break down