Loanable funds market
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
loanable funds
money available for lending and borrowing
demand for loanable funds
The quantity of loanable funds wanted or needed
Real interest rate
The price of borrowing money adjusted for inflation
Changes in demand for loanable funds
foreign exchange, all borrowing, lending, credit; Deficit spending, expectations for the future
foreign exchange
other country converting to USD=Increase in demand
All Borrowing, Lending, and Credit
When there is an increase in loans, credit, and borrowing by consumers and firms, we will see the demand for loanable funds increase. When there is a decrease in loans, credit, and borrowing by consumers and firms, we will see the demand for loanable funds decrease.
deficit spending
situation in which a government spends more money than it takes in ( increase in spending=increase in demand, decrease in spending=decrease in demand)
Expectations for the future
Expect an increase in income, increase in current demand
Expect higher prices, increase in current demand
supply of loanable funds
the relationship between the quantity of loanable funds supplied and the real interest rate (have a positive relationship)
Changes in supply
Savings rate, expectations for the future, lending at the discount window, foreign purchases
Spending Multiplier
an initial change in spending causes a ripple effect through the total economy and leads to more total spending
Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC)
the increase in consumer spending when disposable income rises by $1
Marginal Propensity to Save (MPS)
the increase in household savings when disposable income rises by $1
Rule for the multiplier effect
Always = 1
spending multiplier equation
1/MPS
Tax Multiplier
MPC/MPS or always one less than the spending multiplier
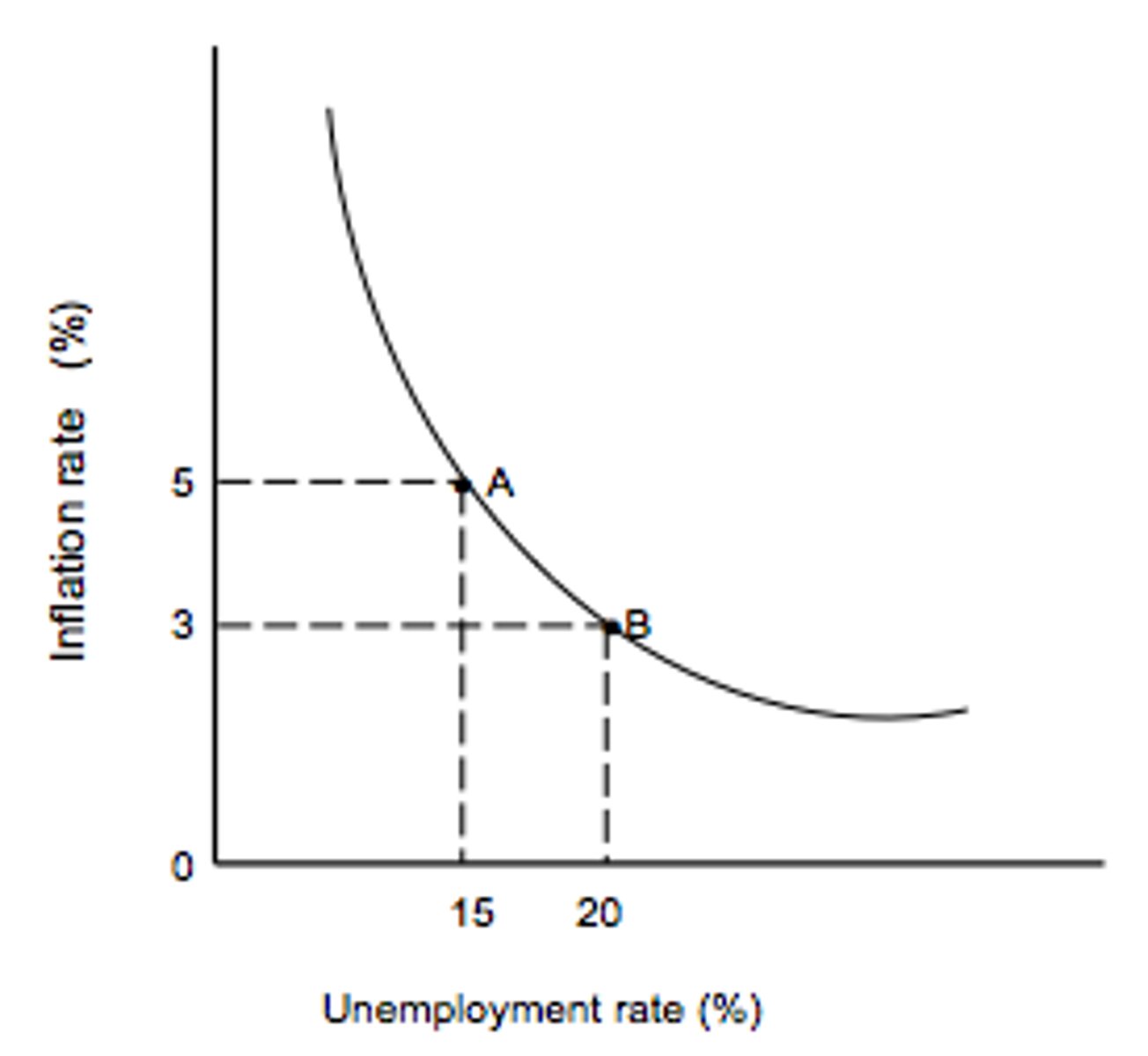
Phillips Curve
indicates a short-run inverse relationship between inflation and unemployment rates