BIO 514 Unit 1 Content
1/253
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
254 Terms
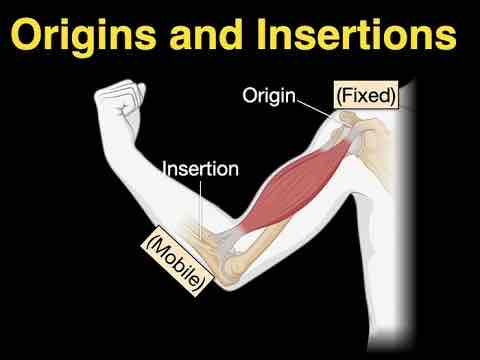
What is a muscle’s ORIGIN?
A fixed attachment point where a muscle starts and attaches to bone.
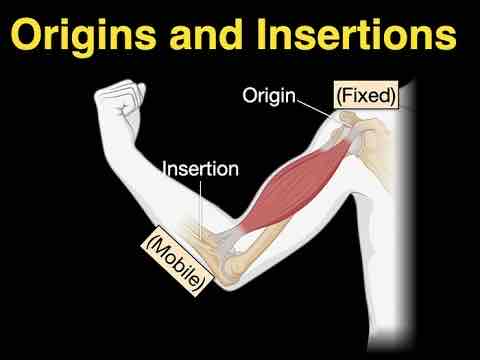
What is a muscle’s INSERTION?
A point where a muscle attaches and moves during contraction.
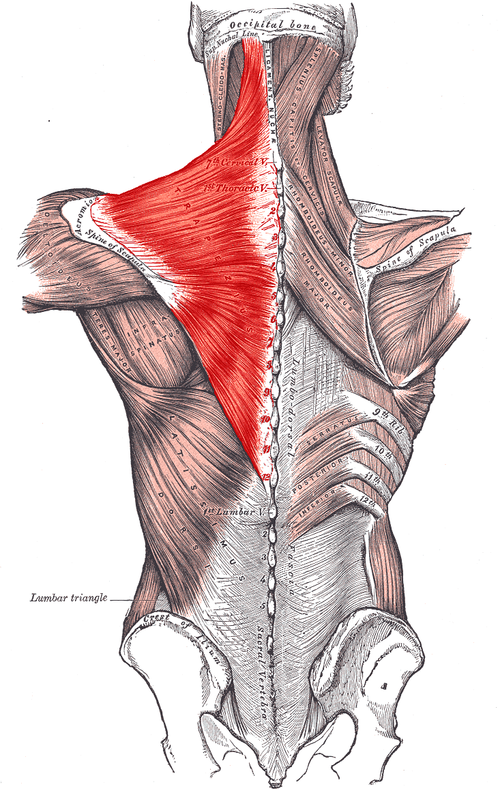
Trapezius ORIGIN
medial third of superior nuchal line
External occipital protuberance
Ligamentum nuchae
Spinous processes of C7 - T12
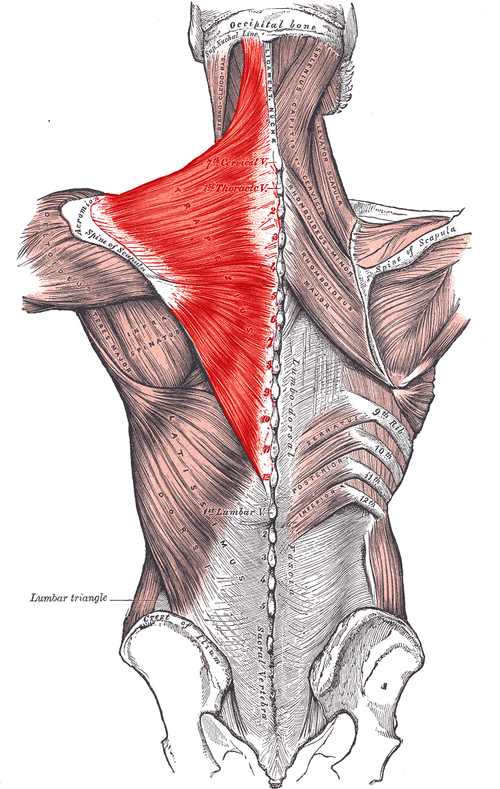
Trapezius INSERTION
lateral third of clavicle
Acromion process
spine of scapula
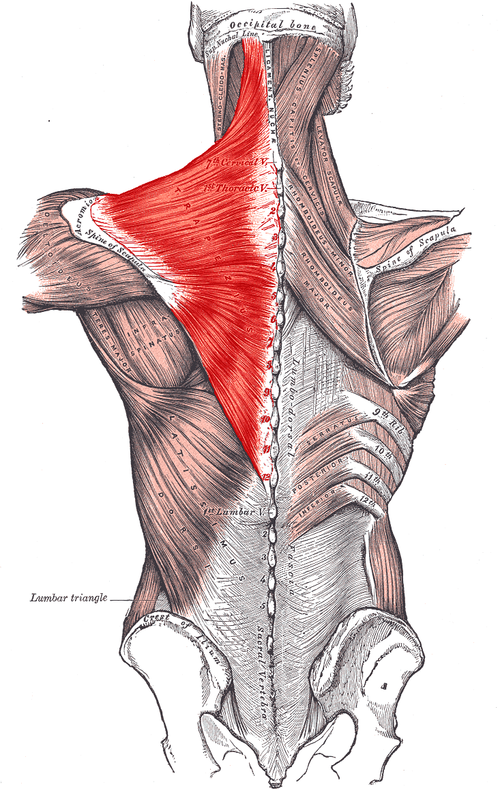
Trapezius ACTION
superior fibers - ELEVATE scapula
Middle fibers - RETRACT scapula
Inferior fibers - DEPRESS scapula
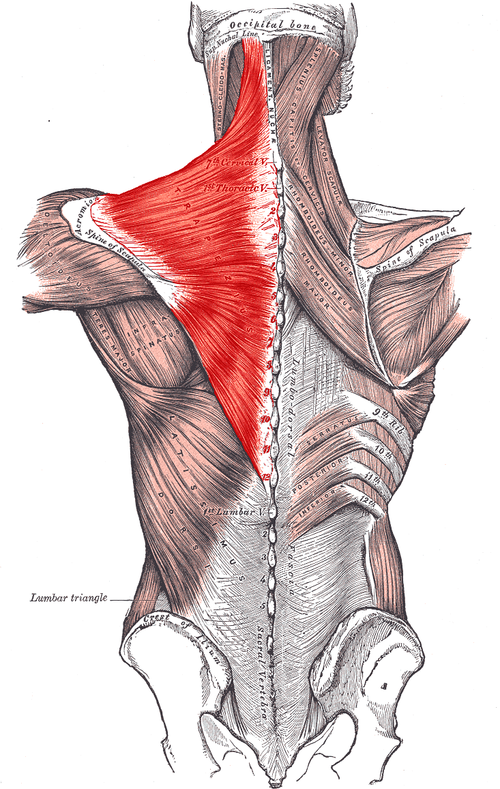
Trapezius INNERVATION
Spinal accessory nerve (cranial nerve 11)
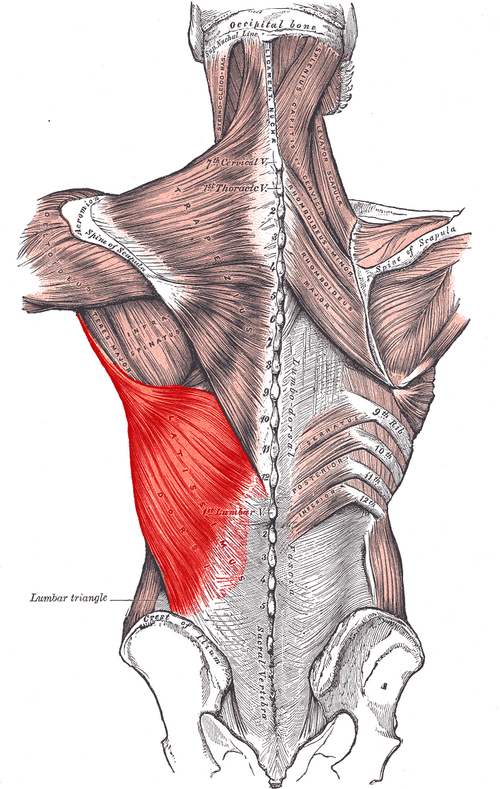
Latissimus dorsi ORIGIN
spinous processes from T7 - sacrum
Thoracolumbar fascia
Iliac crest
Lower ribs
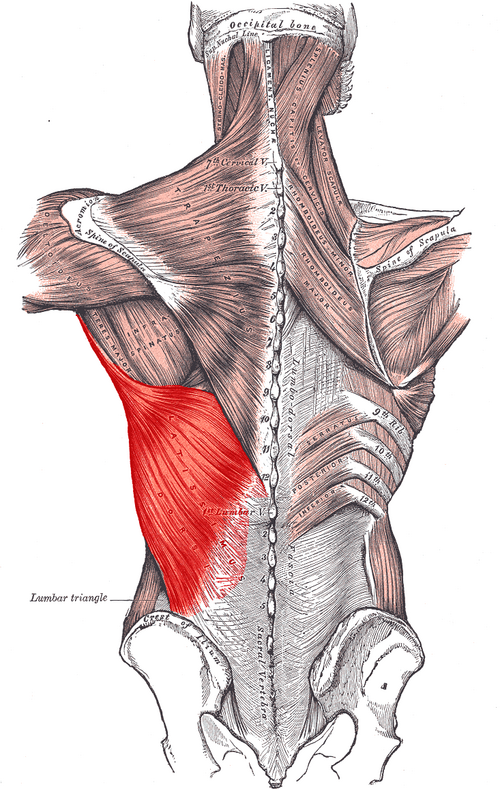
Latissimus dorsi INSERTION
Floor of intertubercular groove
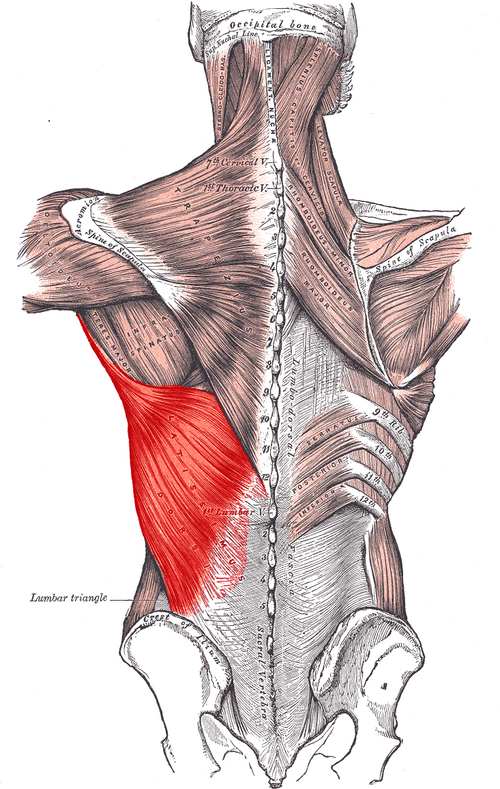
Latissimus dorsi ACTION
Extends, adducts, and medially rotates arm
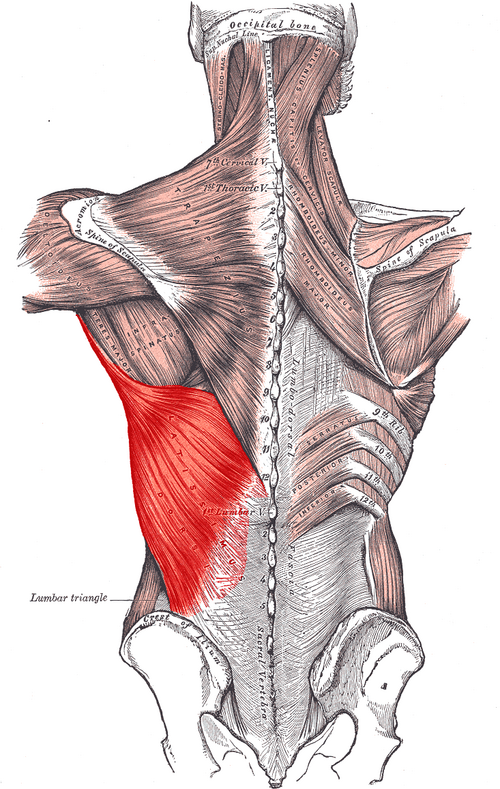
Latissimus dorsi INNERVATION
Thoracodorsal nerve (middle scapular n; off brachial plexus)
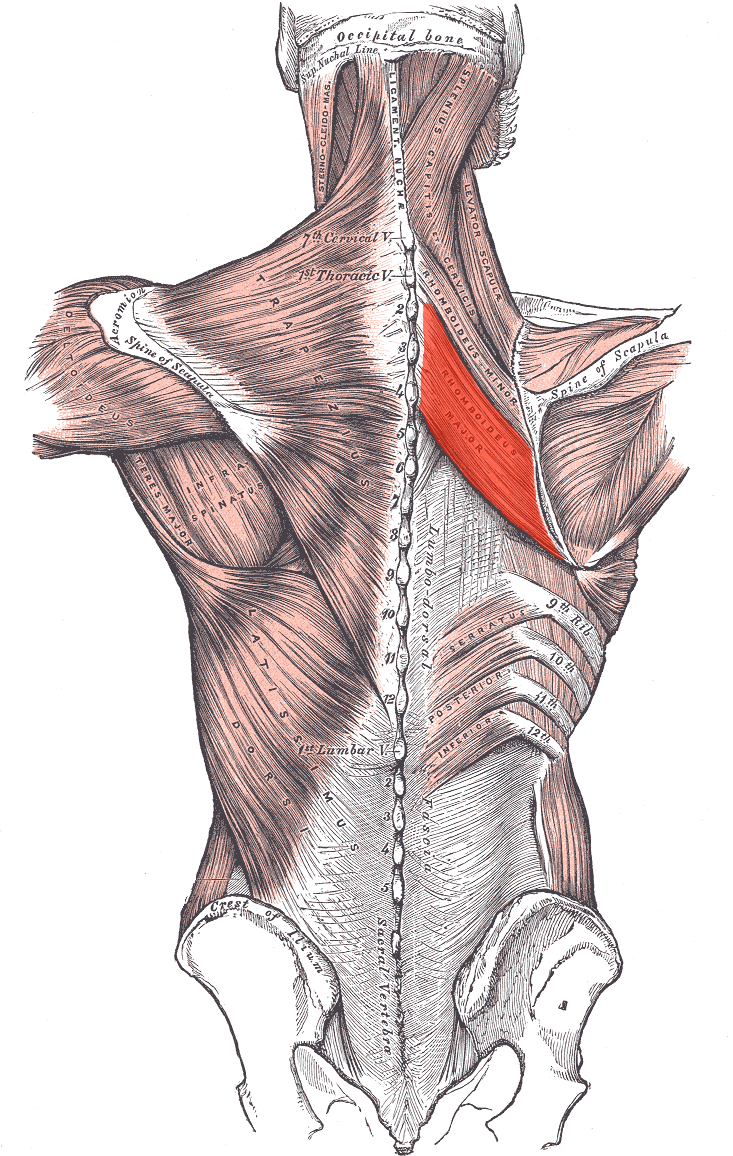
Rhomboideus major ORIGIN
Spinous processes of T2 - T4
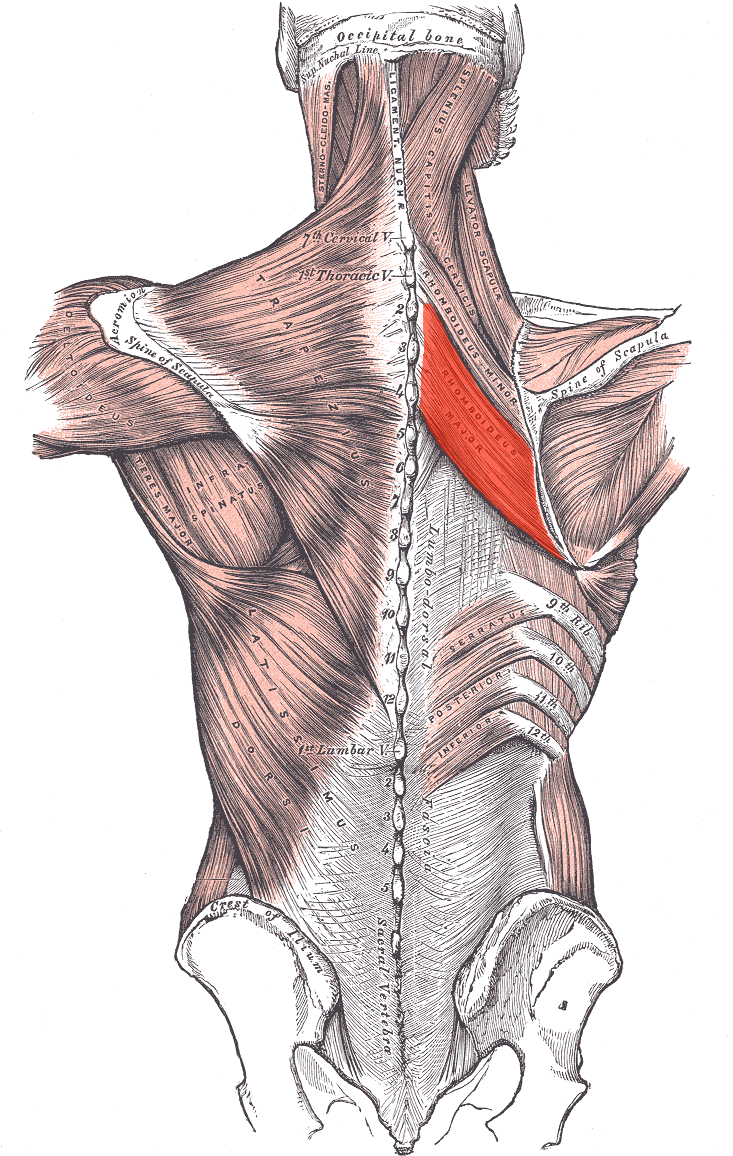
Rhomboideus major INSERTION
Medial border of the scapula
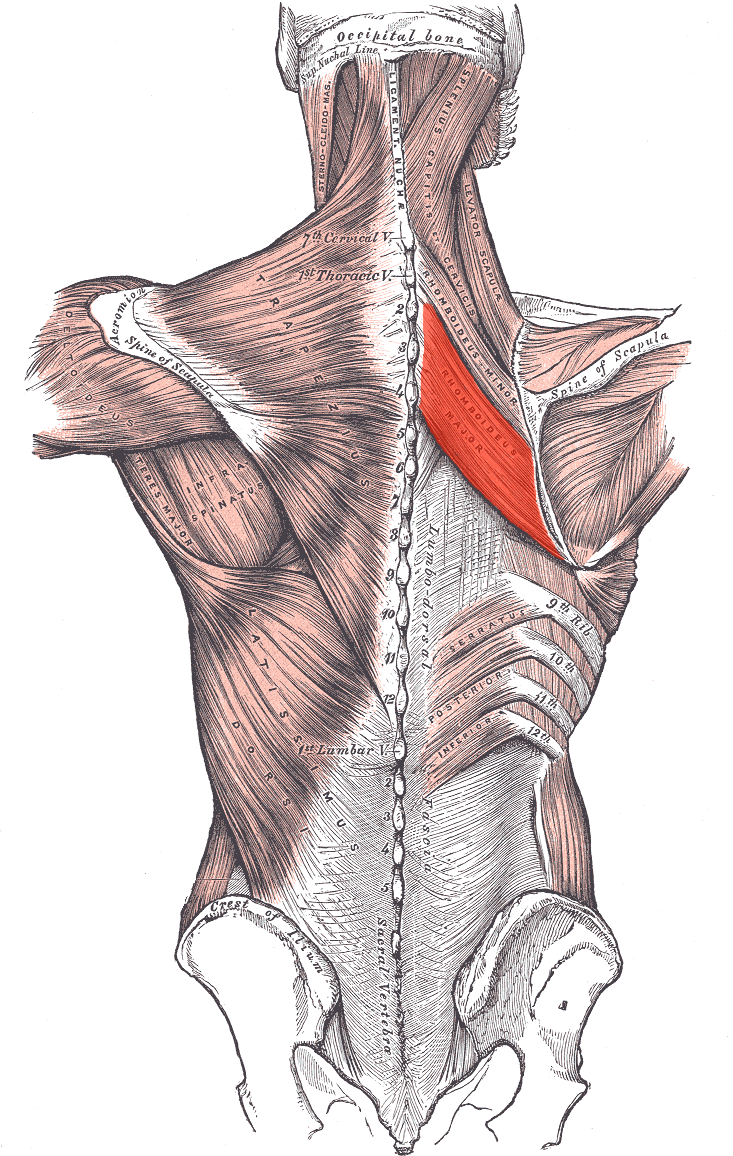
Rhomboideus major ACTION
Retracts and elevates scapula
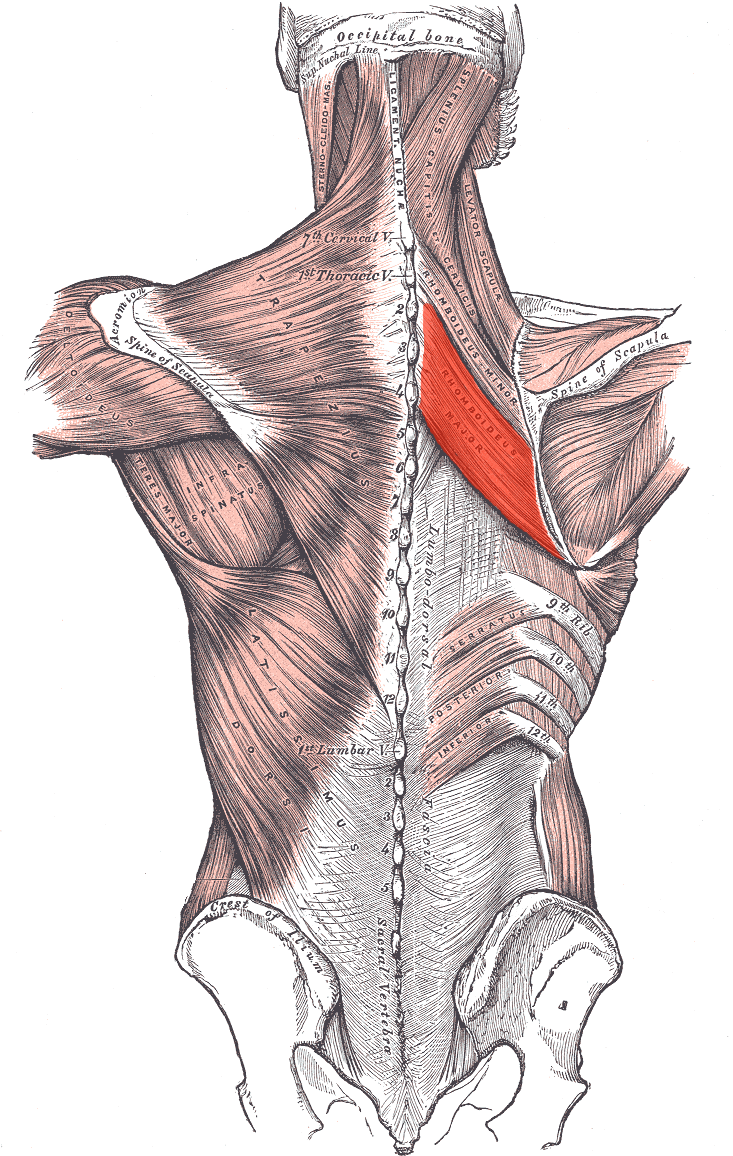
Rhomboideus major INNERVATION
Dorsal scapular nerve (off brachial plexus)
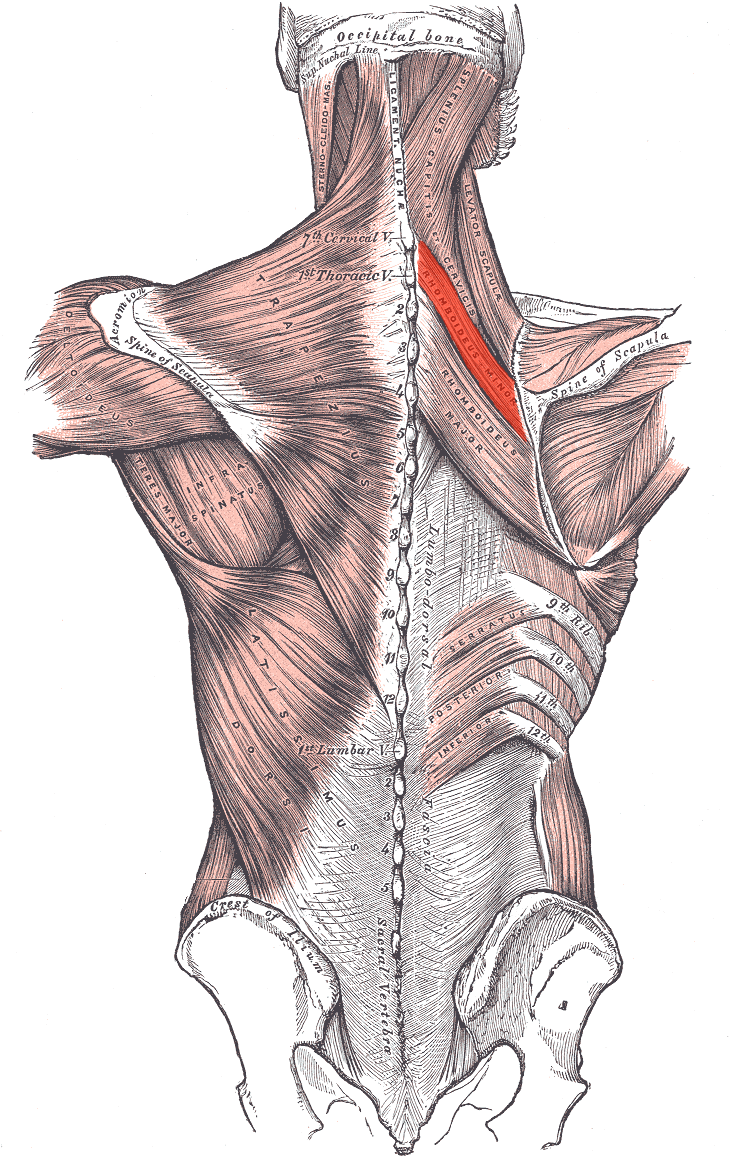
Rhomboideus minor ORIGIN
Spinous processes of C7 and T1
Lower end of ligamentum nuchae
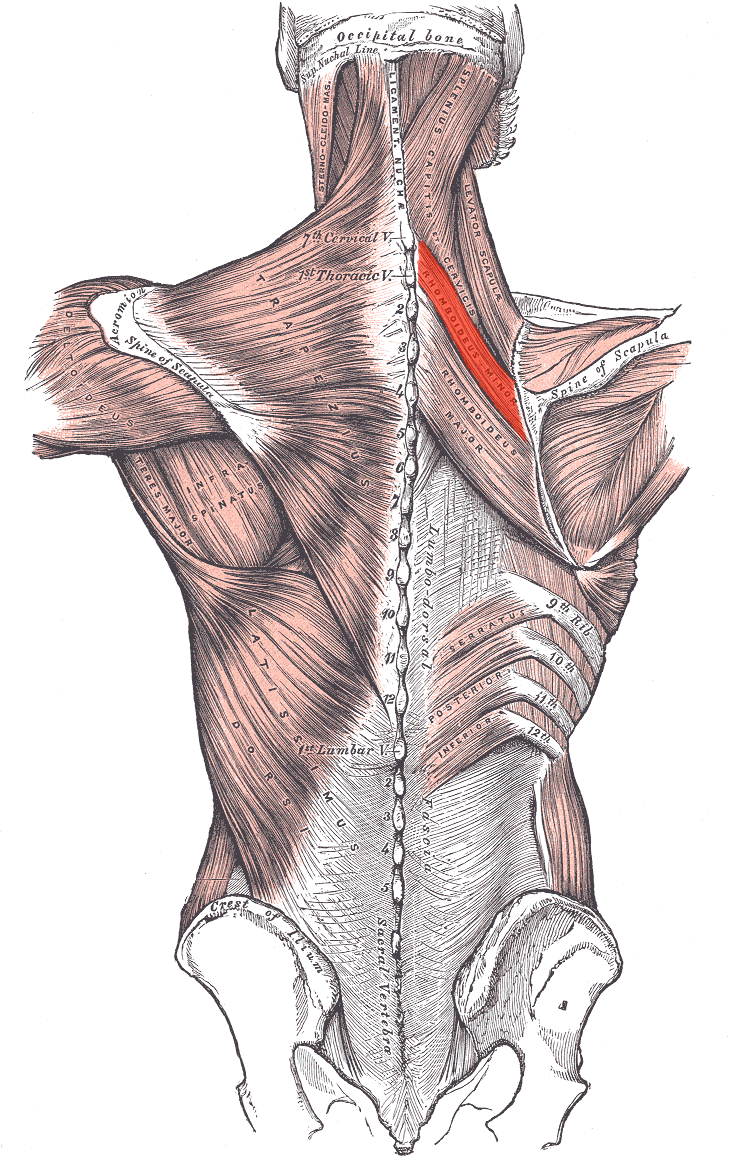
Rhomboideus minor INSERTION
Medial border of scapula
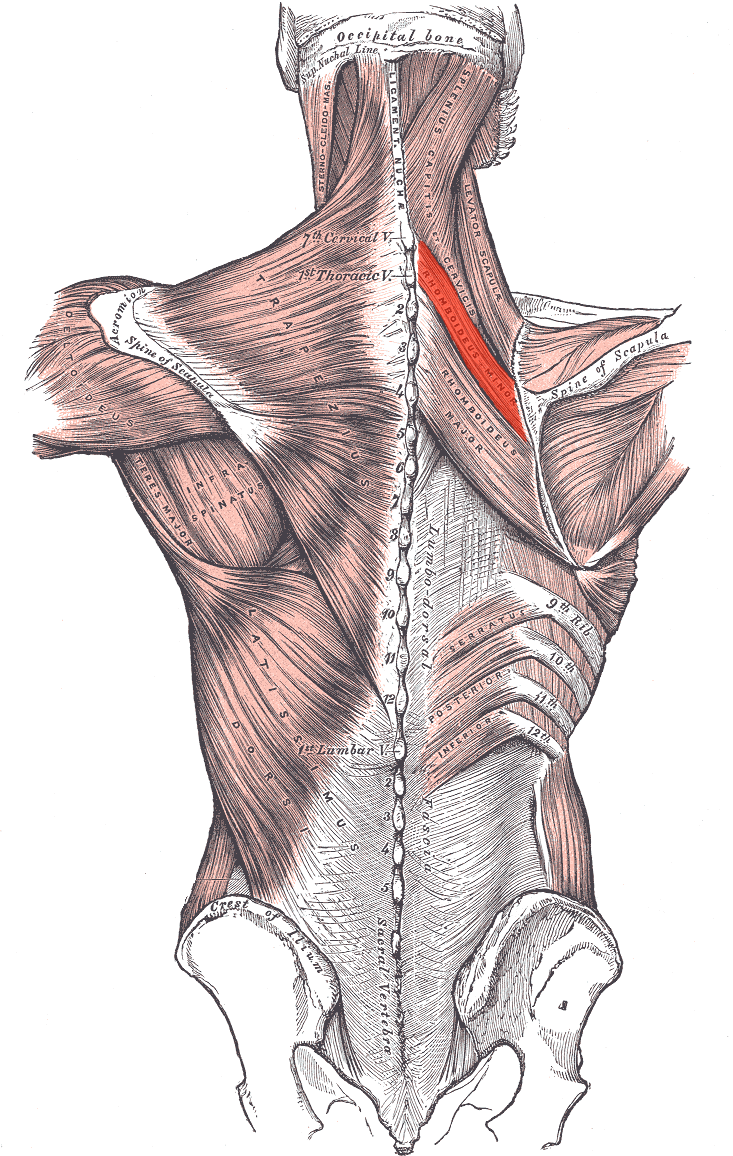
Rhomboideus minor ACTION
Retracts and elevates scapula
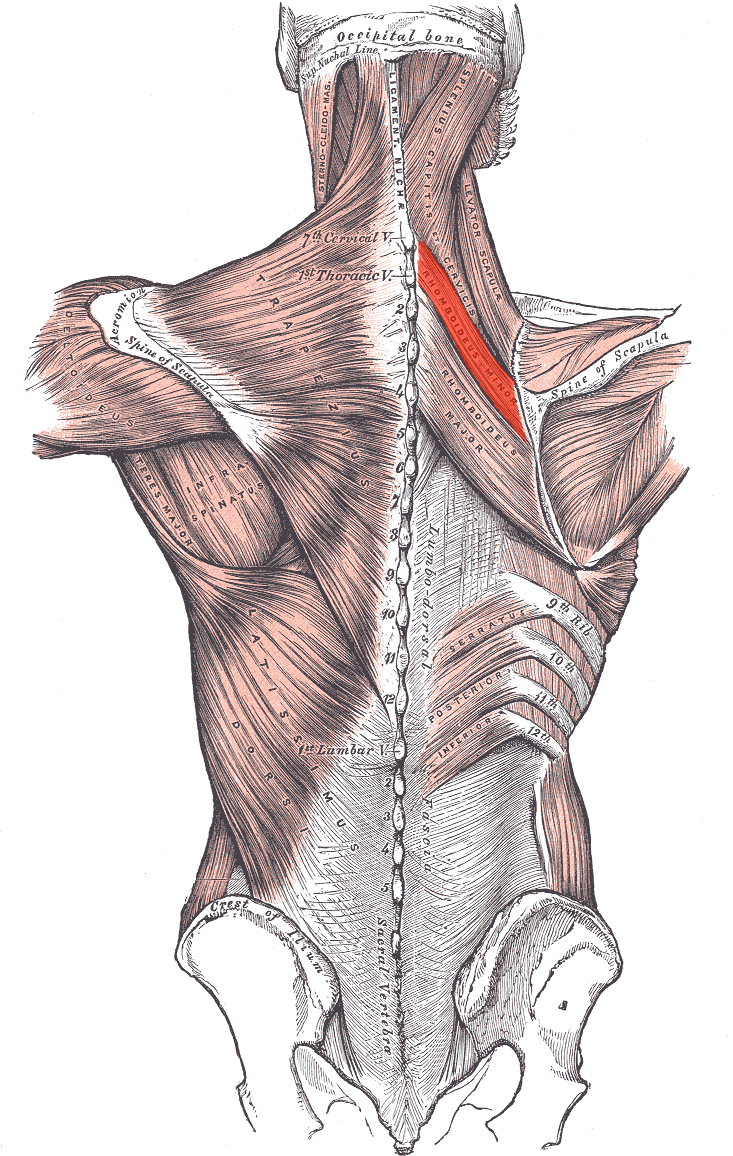
Rhomboideus minor INNERVATION
Dorsal scapular nerve (off brachial plexus)
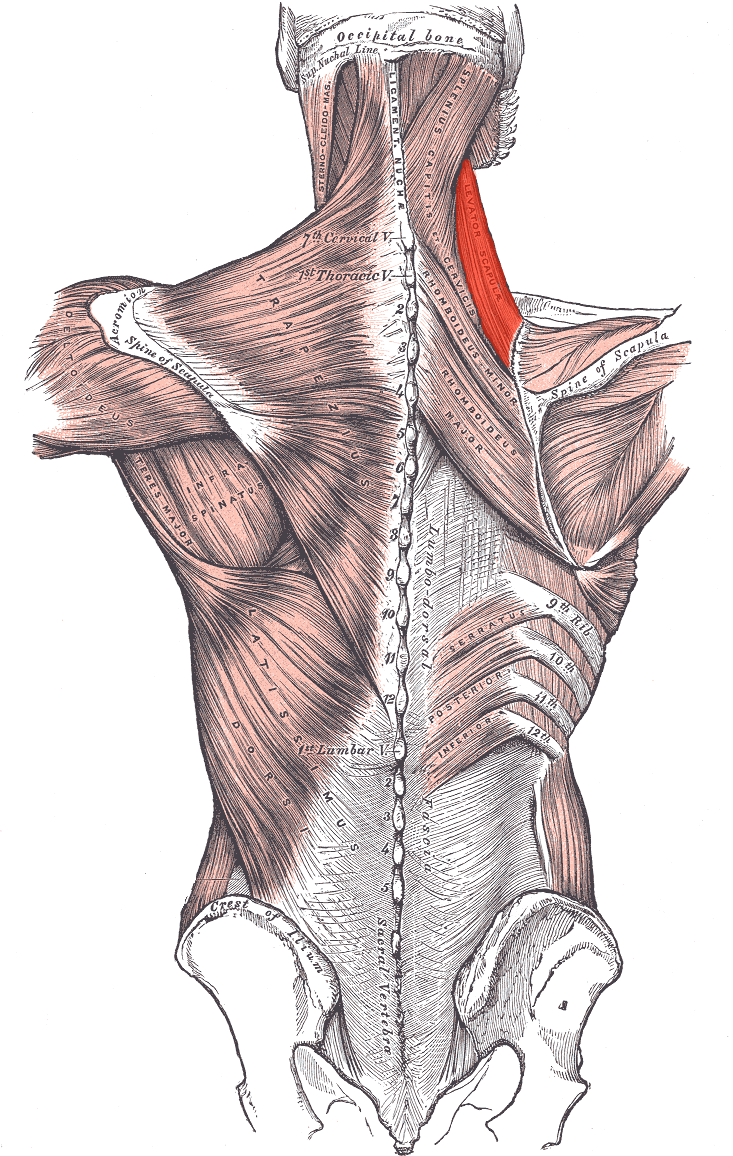
Levator scapulae ORIGIN
Transverse processes of C1 - C4
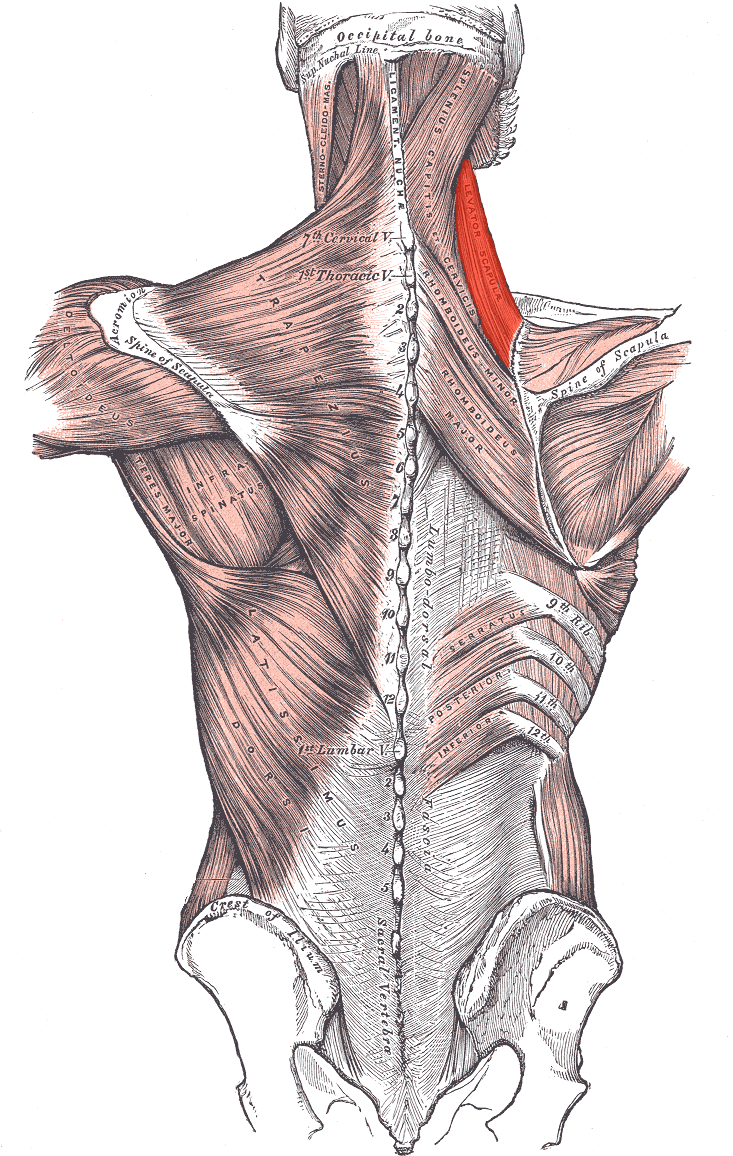
Levator scapulae INSERTION
Superior part of medial border of scapula
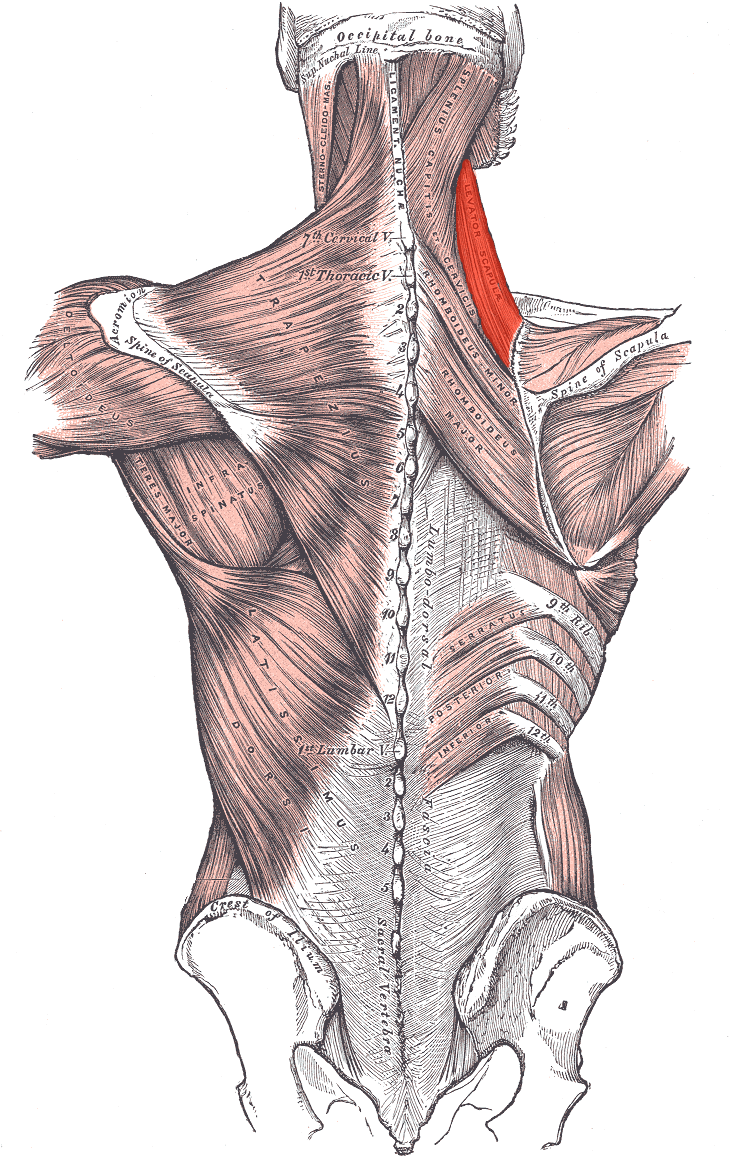
Levator scapulae ACTION
Elevates scapula
Levator scapulae INNERVATION
Dorsal scapular nerve (off brachial plexus)
Upper part receives branches of C3 and C4
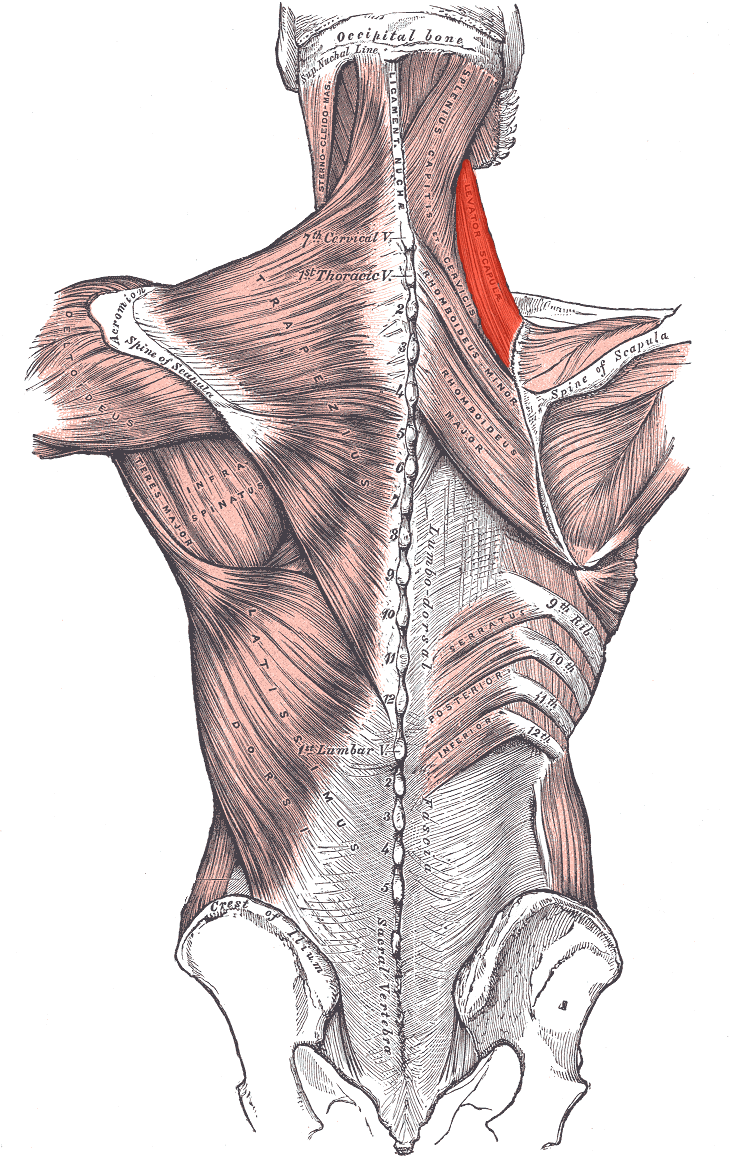
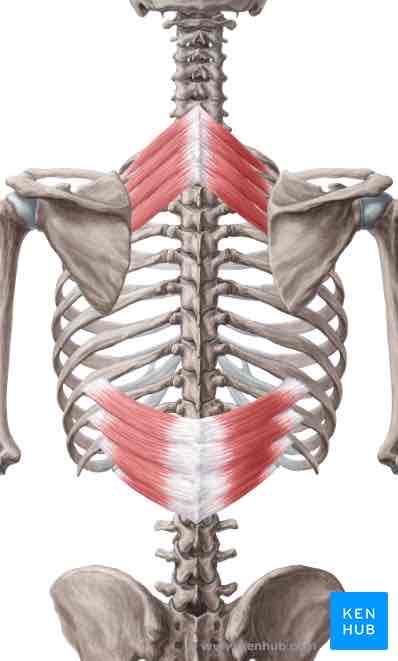
Serratus posterior superior ORIGIN
Nuchal ligament, spinous processes of C7-T3
Serratus posterior superior INSERTION
Ribs 2-5, lateral to angles
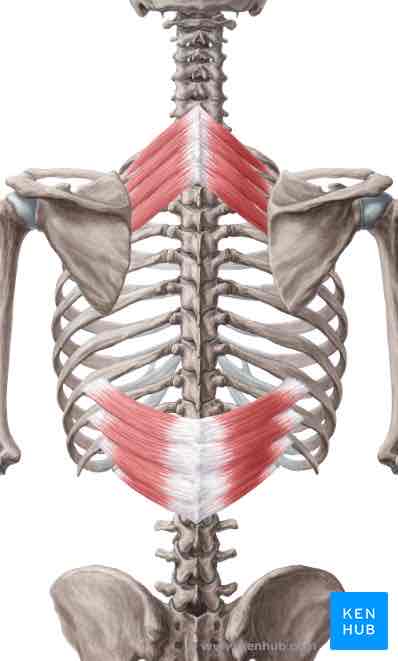
Serratus posterior superior ACTION
Elevates upper ribs
Serratus posterior superior INNERVATION
Thoracic ventral rami
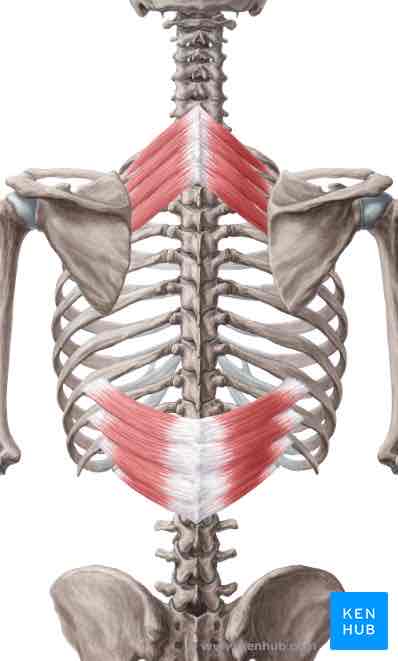
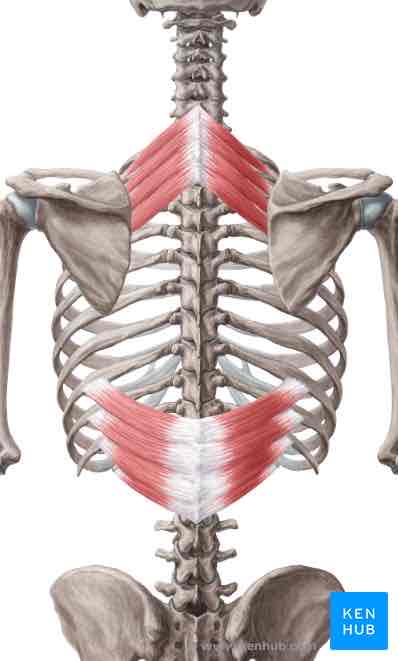
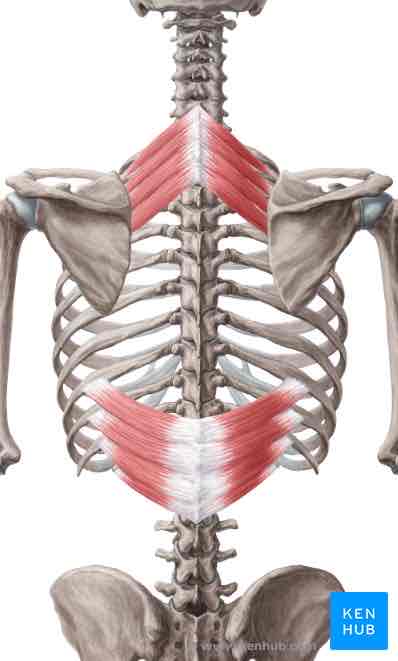
Serratus posterior inferior ORIGIN
Thoracolumbar fascia, spinous processes of T11-L2
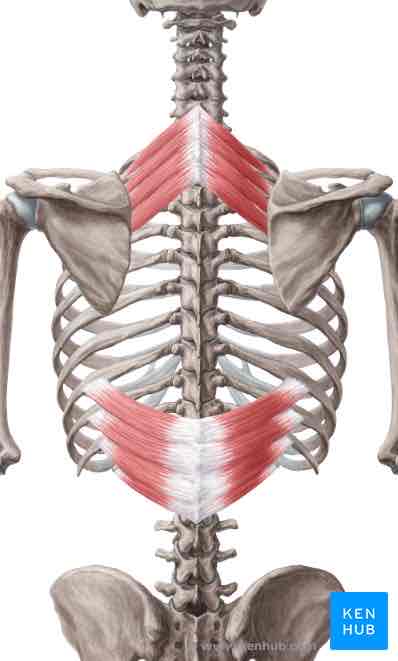
Serratus posterior inferior INSERTION
Ribs 9-12 lateral to angles
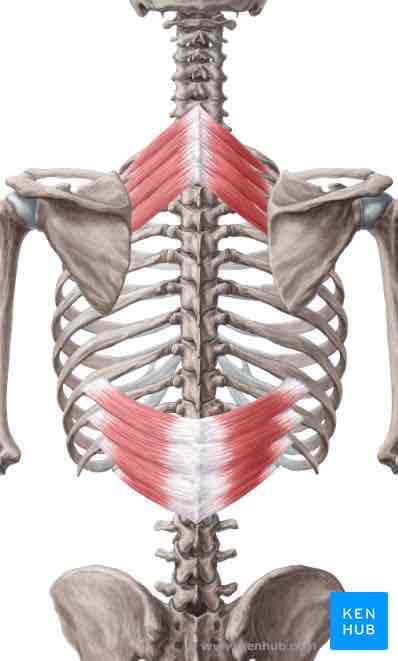
Serratus posterior inferior ACTION
Depresses lower ribs
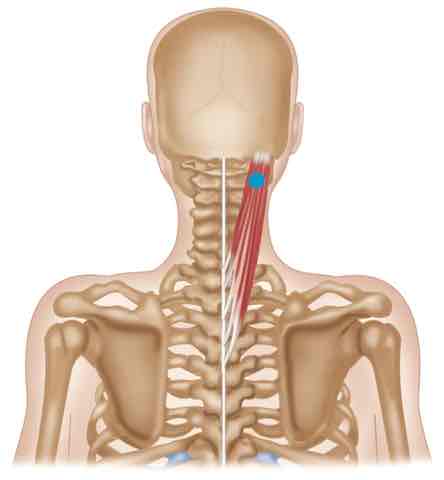
Splenius ORIGIN
Nuchal ligament, spinous processes C7-T6
Splenius INSERTION
Transverse processes C1-C4, superior nuchal line, and mastoid process
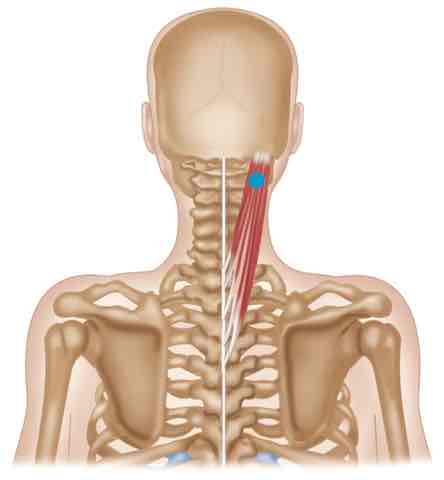
Splenius ACTION (BILATERALLY)
Extends head and neck
Splenius ACTION (UNILATERALLY)
Laterally flexes head and neck, rotates head ipsilaterally
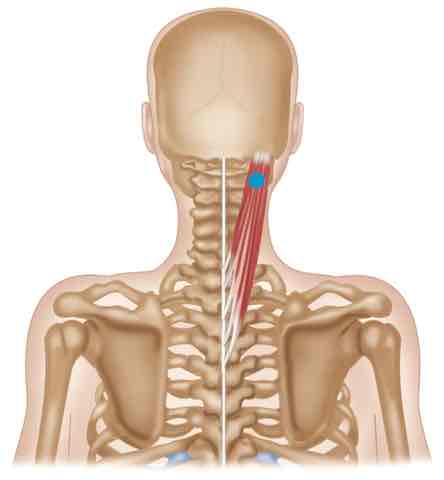
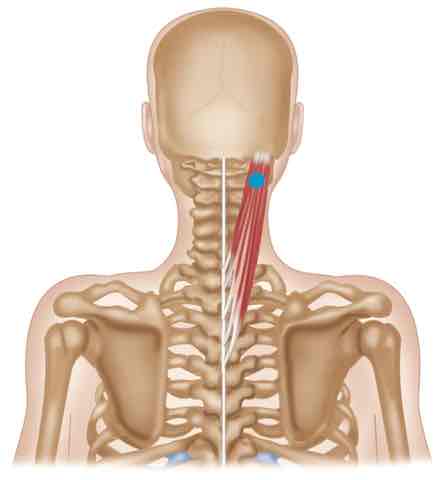
Splenius INNERVATION
Cervical ventral rami
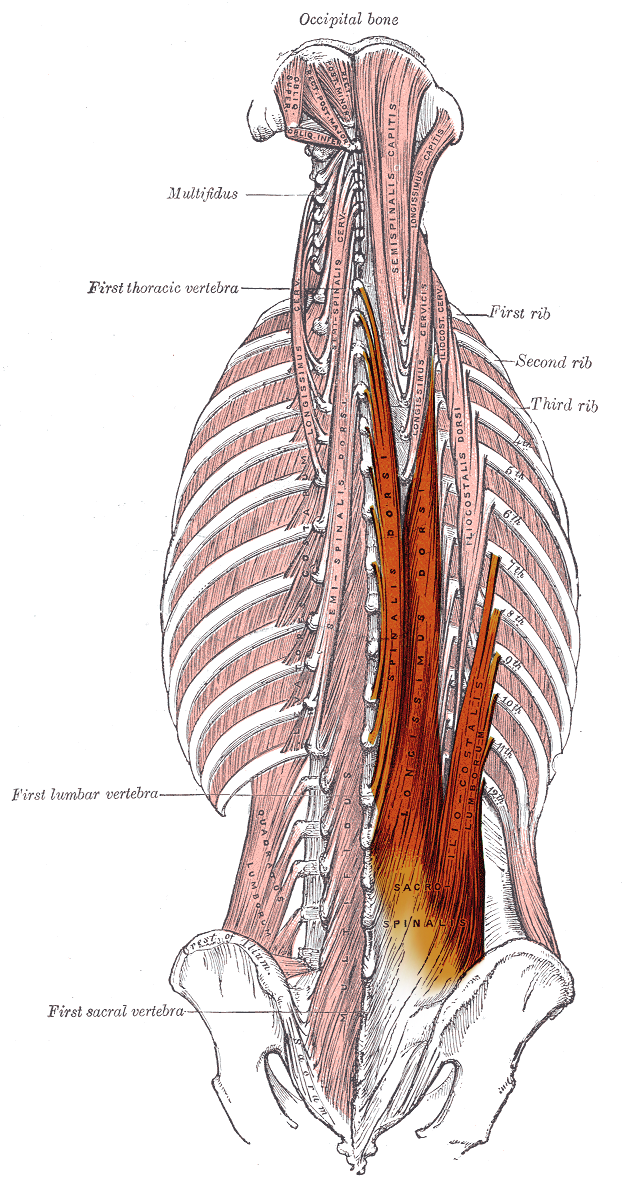
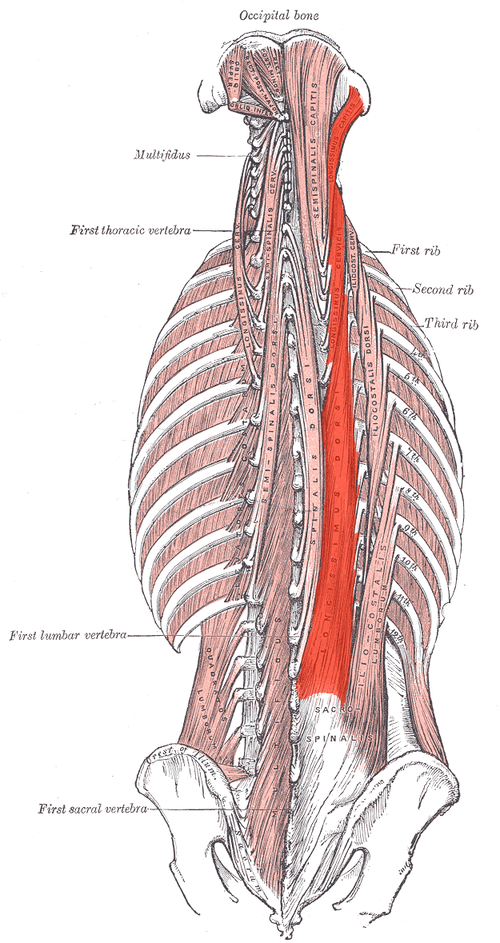
Name the three erector spinae muscles:
Iliocostalis, longissimus, spinalis
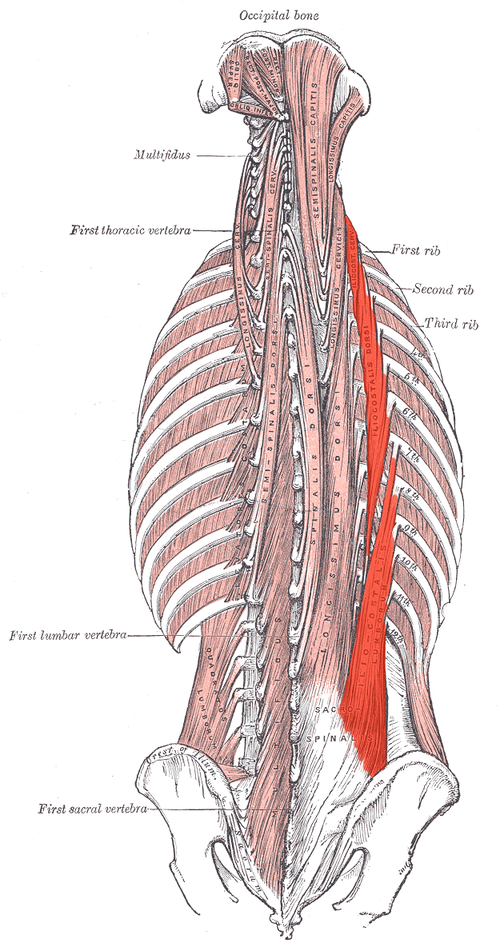
Iliocostalis ORIGIN
Posterior sacrum, iliac crest, spinous and transverse processes of lower lumbar and sacral vertebrae
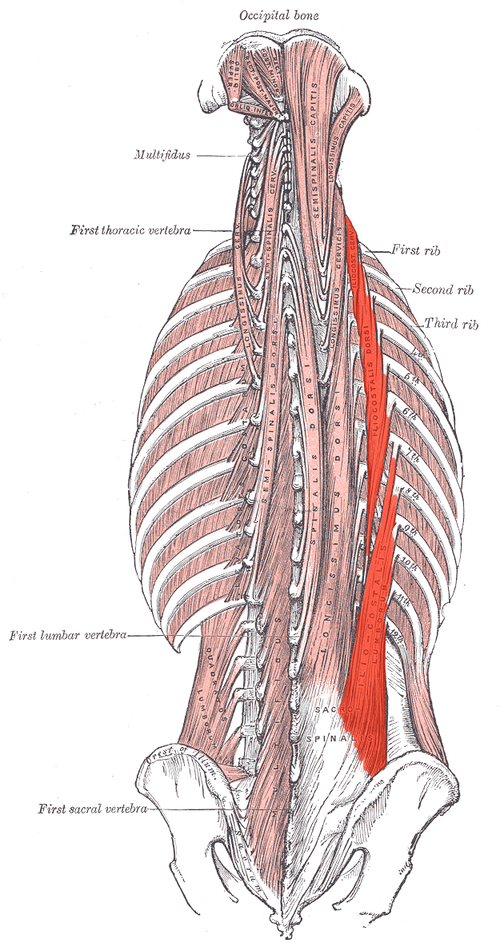
Iliocostalis INSERTION
Angles of ribs and transverse processes of C4-C6
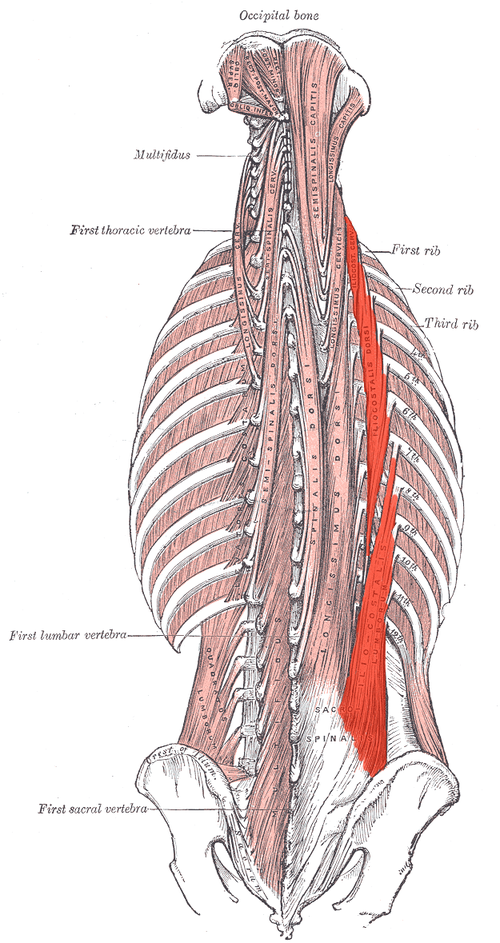
Iliocostalis ACTION (BILATERALLY)
Extends vertebral column
Iliocostalis ACTION (UNILATERALLY)
Laterally flexes vertebral column
Iliocostalis INNERVATION
Dorsal rami
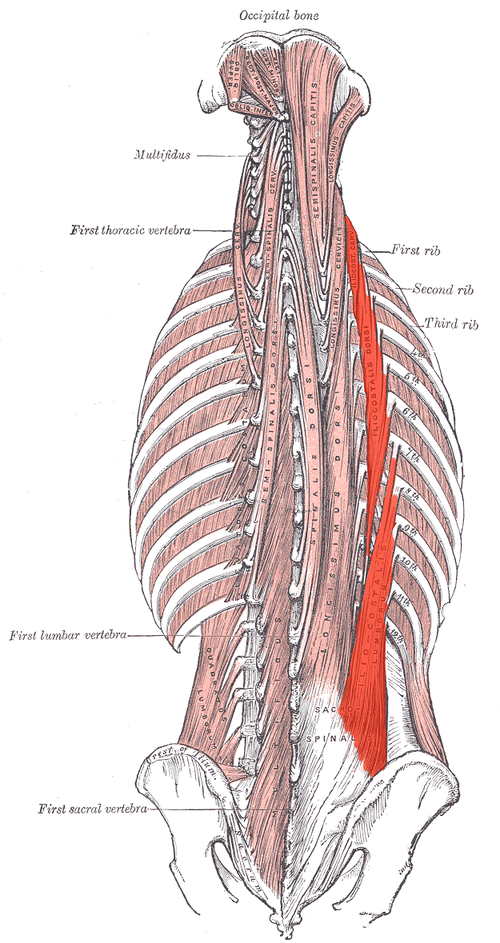
Longissimus ORIGIN
Posterior sacrum, iliac crest, spinous and transverse processes of lower lumbar and sacral vertebrae
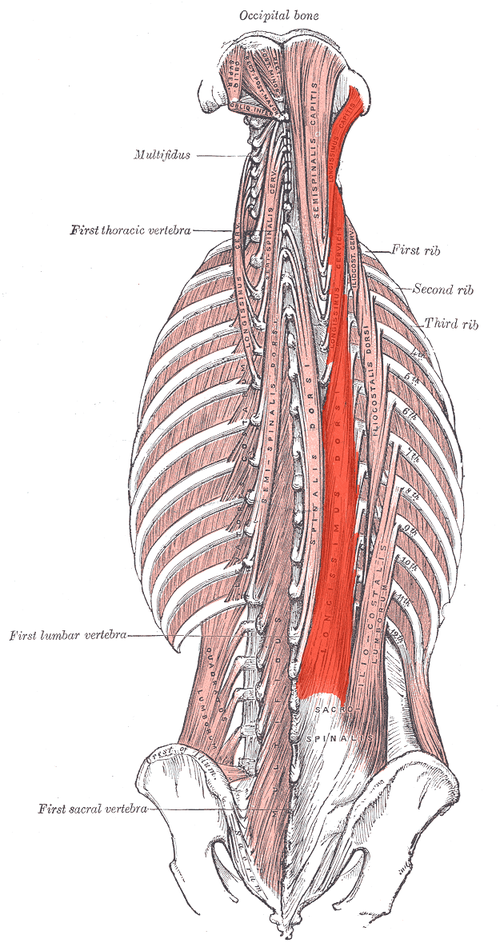
Longissimus INSERTION
Transverse processes at superior vertebral levels and mastoid process
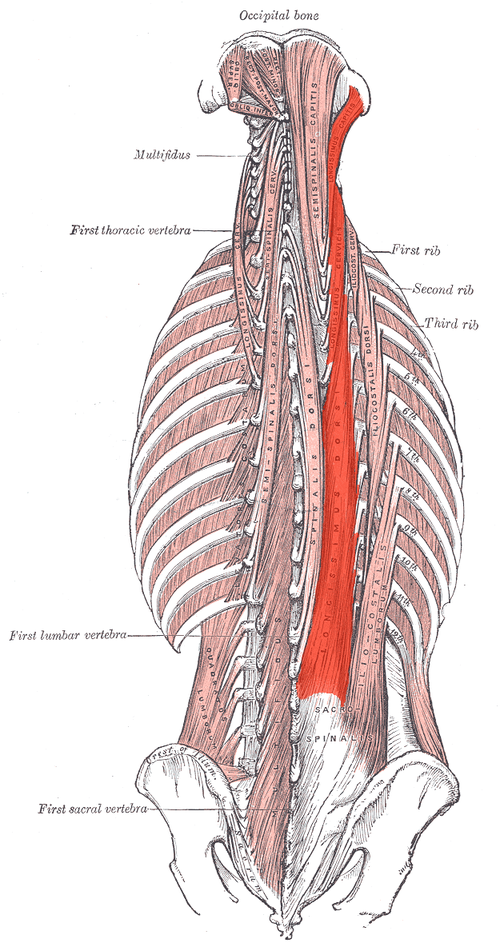
Longissimus ACTION (BILATERALLY)
Extends vertebral column and head
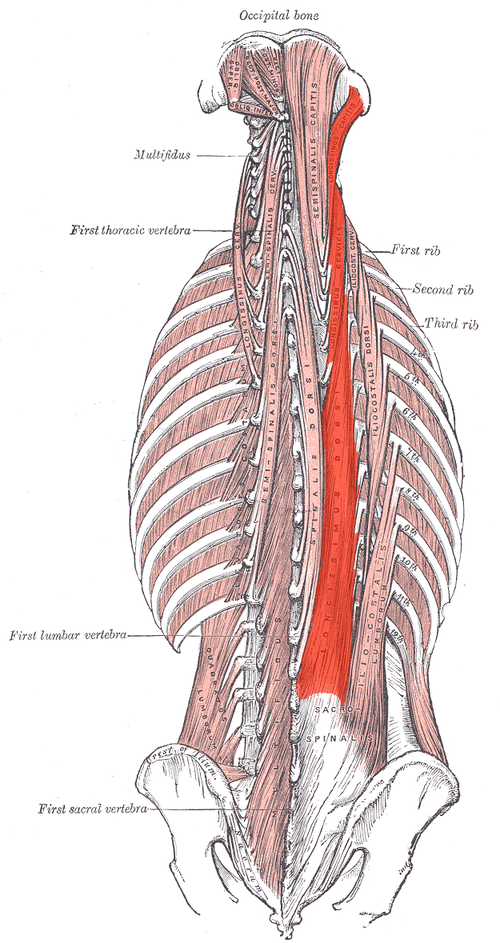
Longissimus ACTION (UNILATERALLY)
Laterally flexes vertebral column
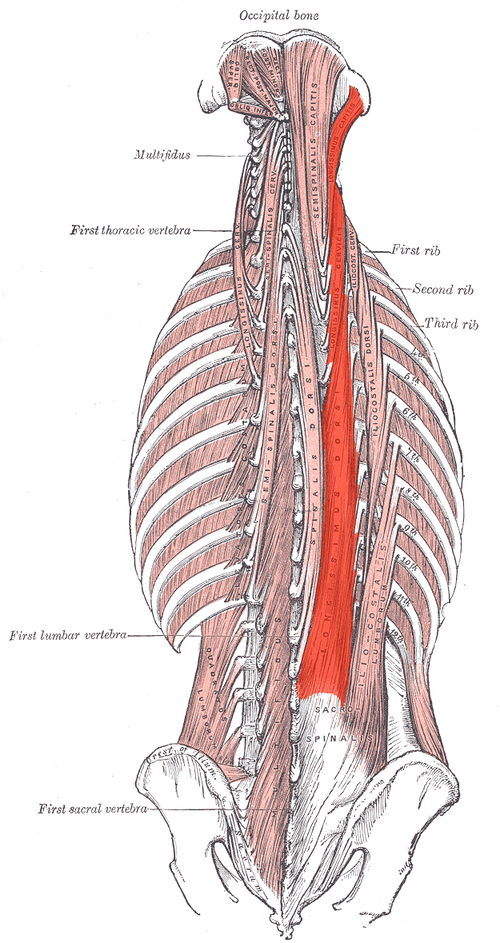
Longissimus INNERVATION
Dorsal rami
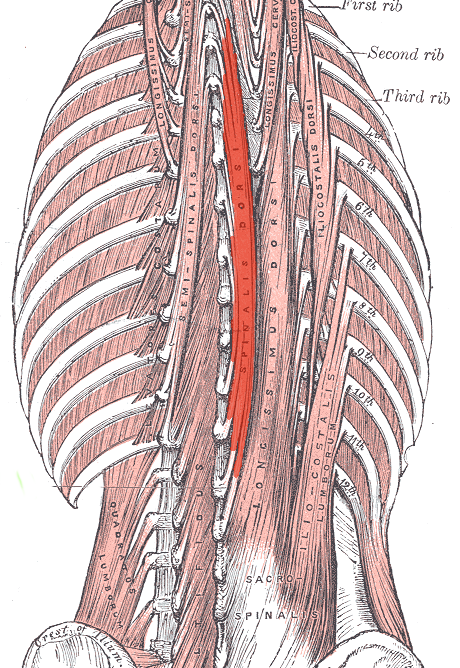
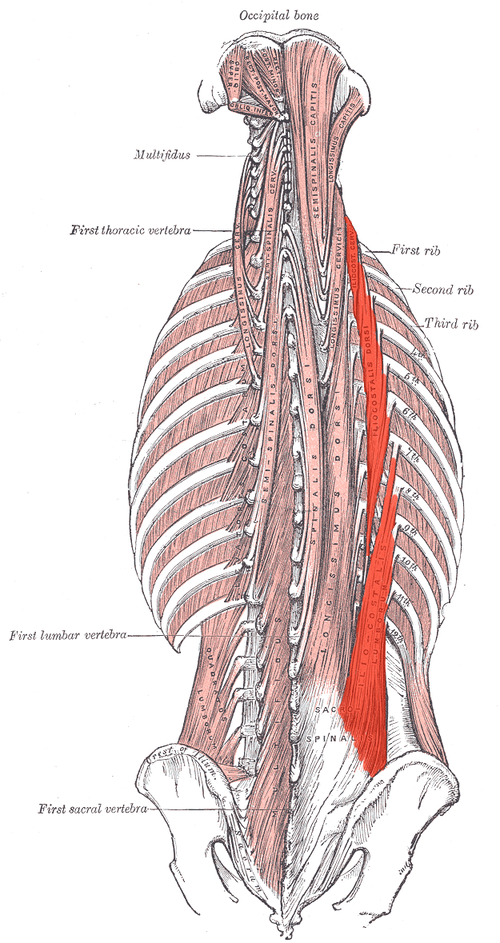
Spinalis ORIGIN
posterior sacrum
Iliac crest
Spinous and transverse processes of lower lumbar and sacral vertebrae
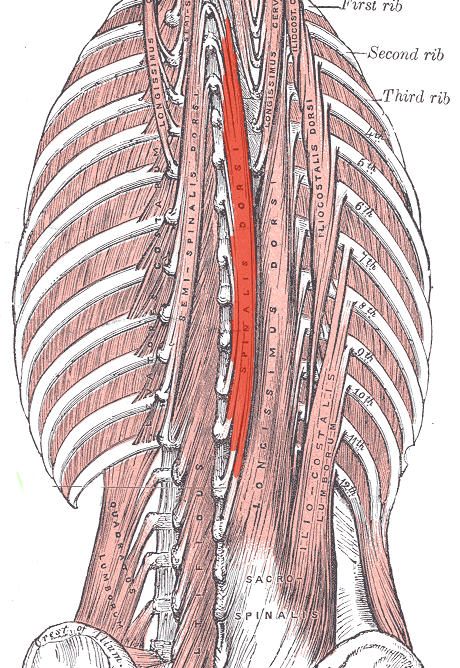
Spinalis INSERTION
spinous processes at superior vertebral levels
Base of skull
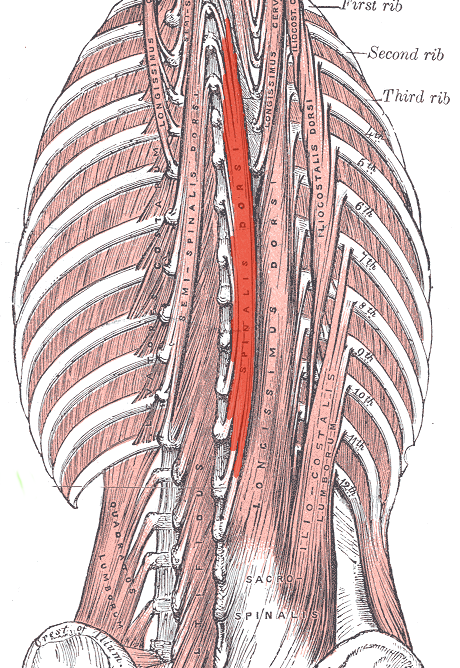
Spinalis ACTION (BILATERALLY)
Extends vertebral column and head
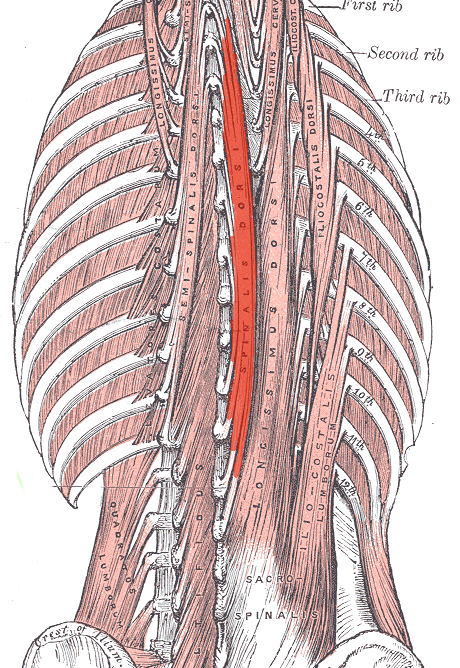
Spinalis ACTION (UNILATERALLY)
Laterally flexes vertebral column
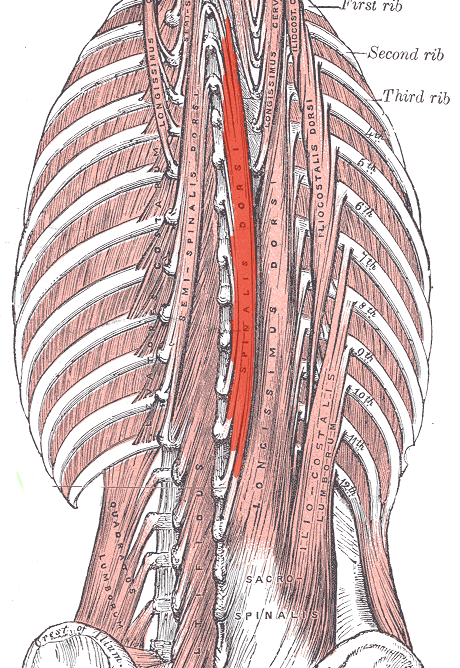
Spinalis INNERVATION
Dorsal rami
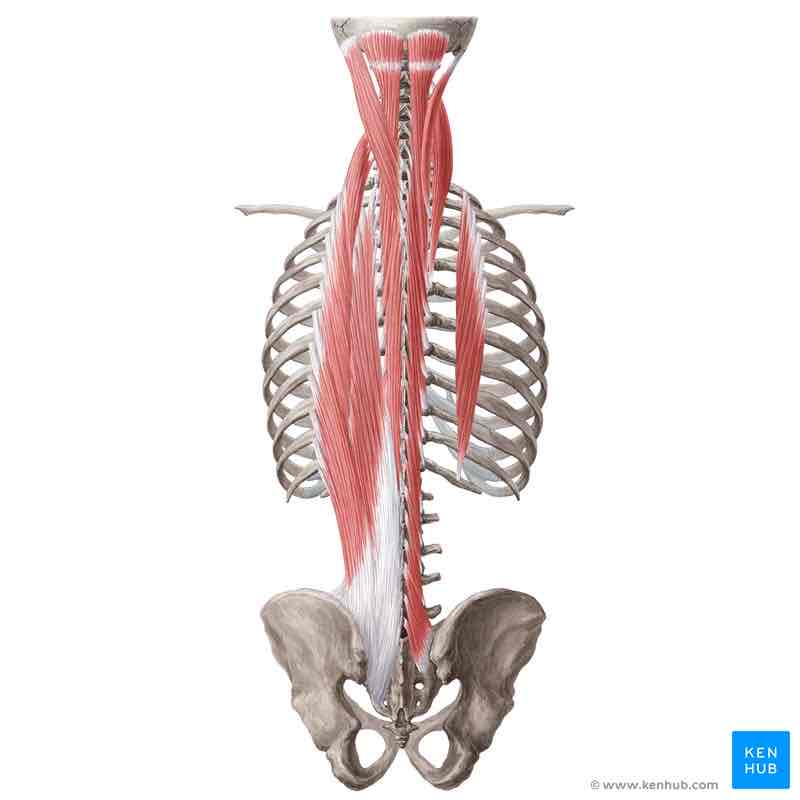
Name the three muscles that make up transversospinalis:
Semispinalis
Multifidus
Rotatores
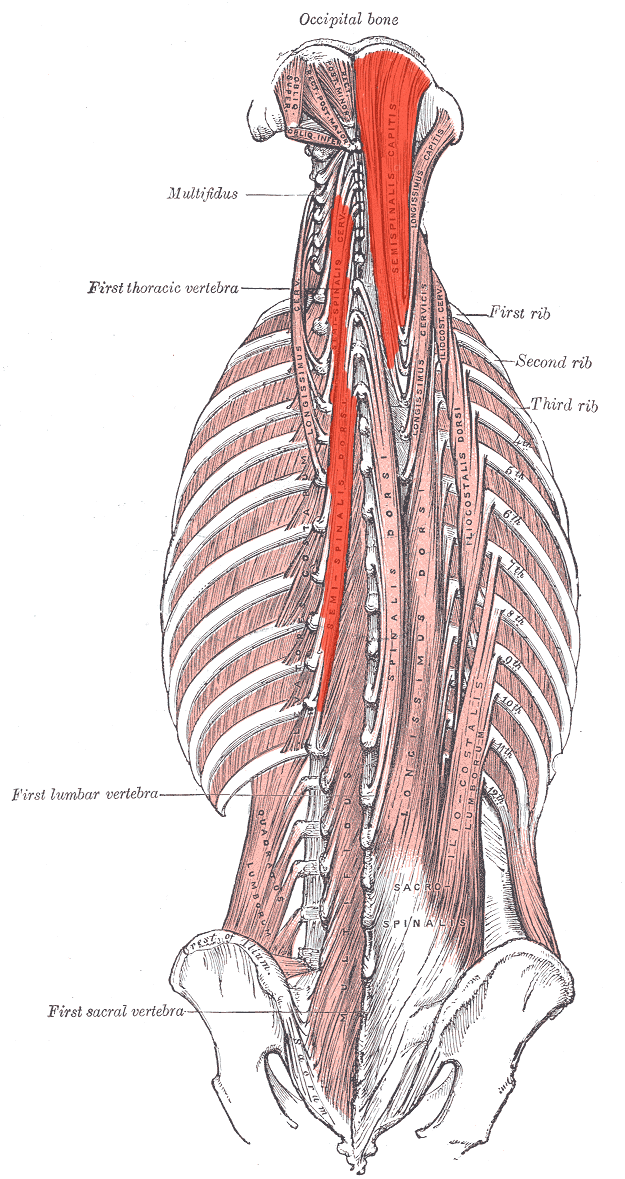
Semispinalis ORIGIN
Transverse processes of C7-T12
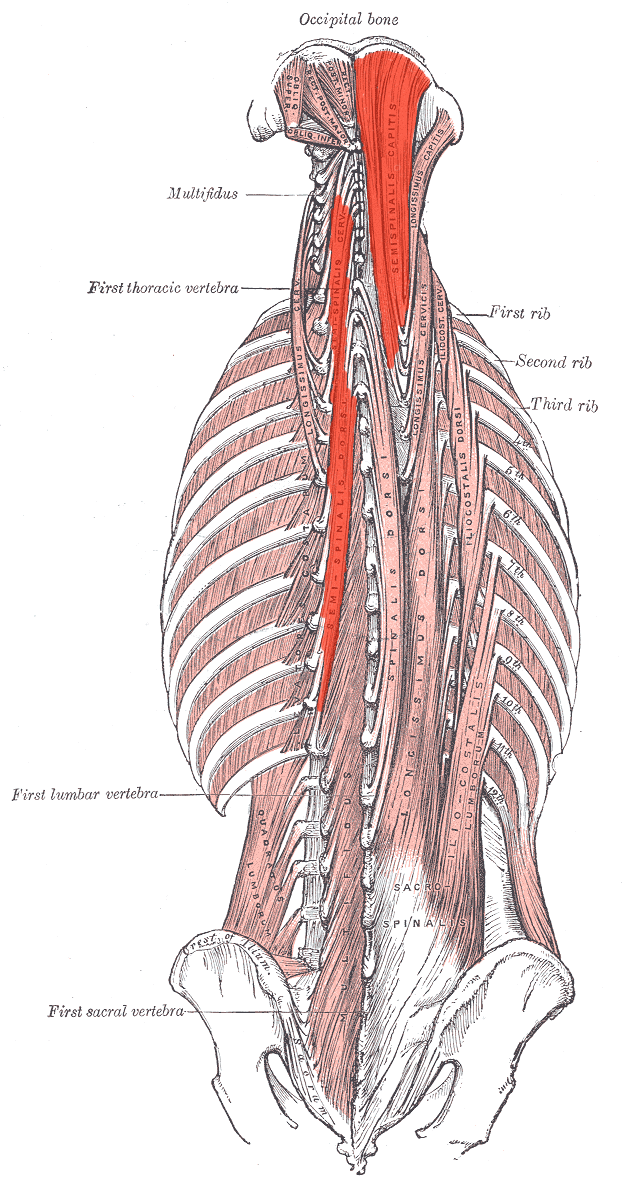
Semispinalis INSERTION
Spinous processes 4-6 vertebrae above origin
Occipital bone between nuchal lines
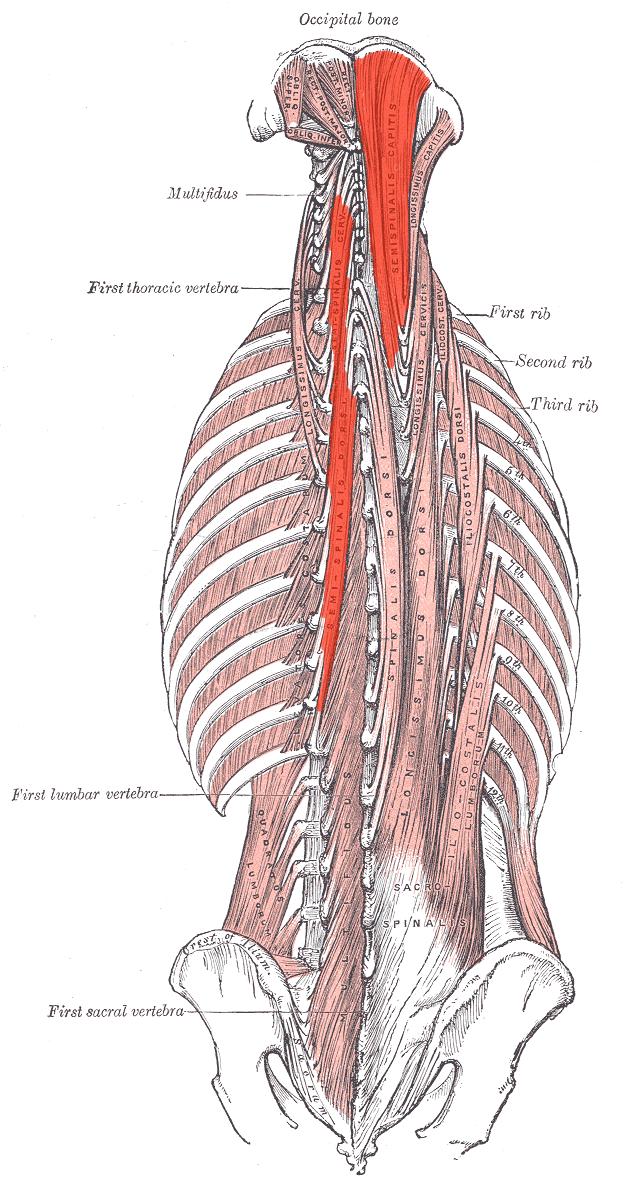
Semispinalis ACTION (BILATERALLY)
Extends head and neck
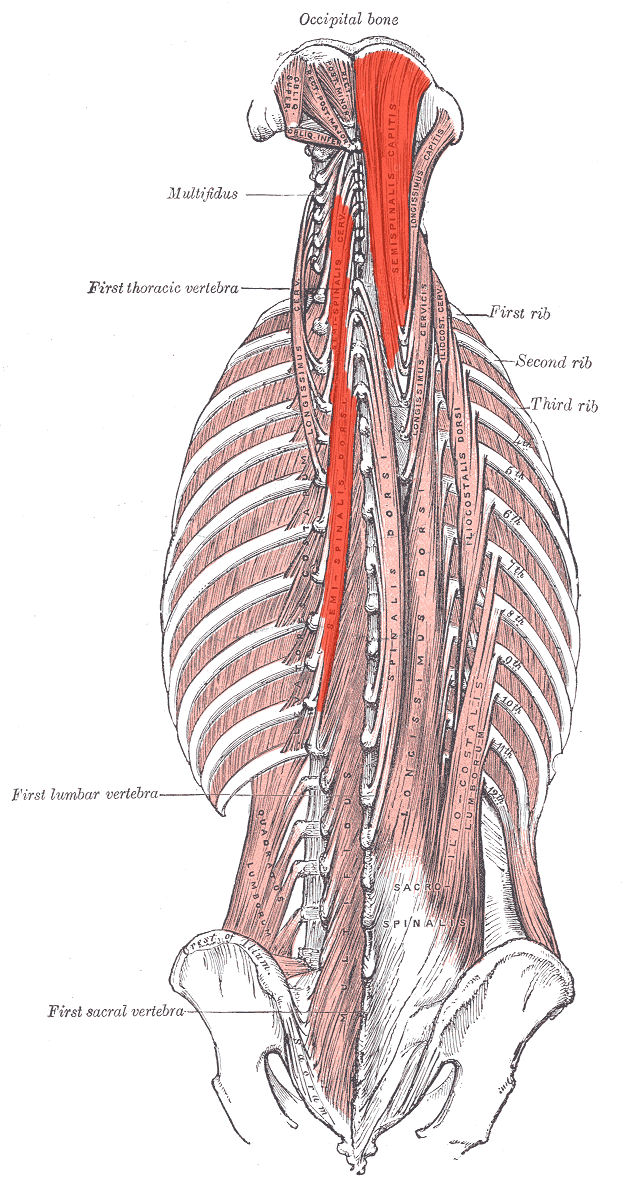
Semispinalis ACTION (UNILATERALLY)
laterally flexes neck and trunk
Rotates trunk contralaterally
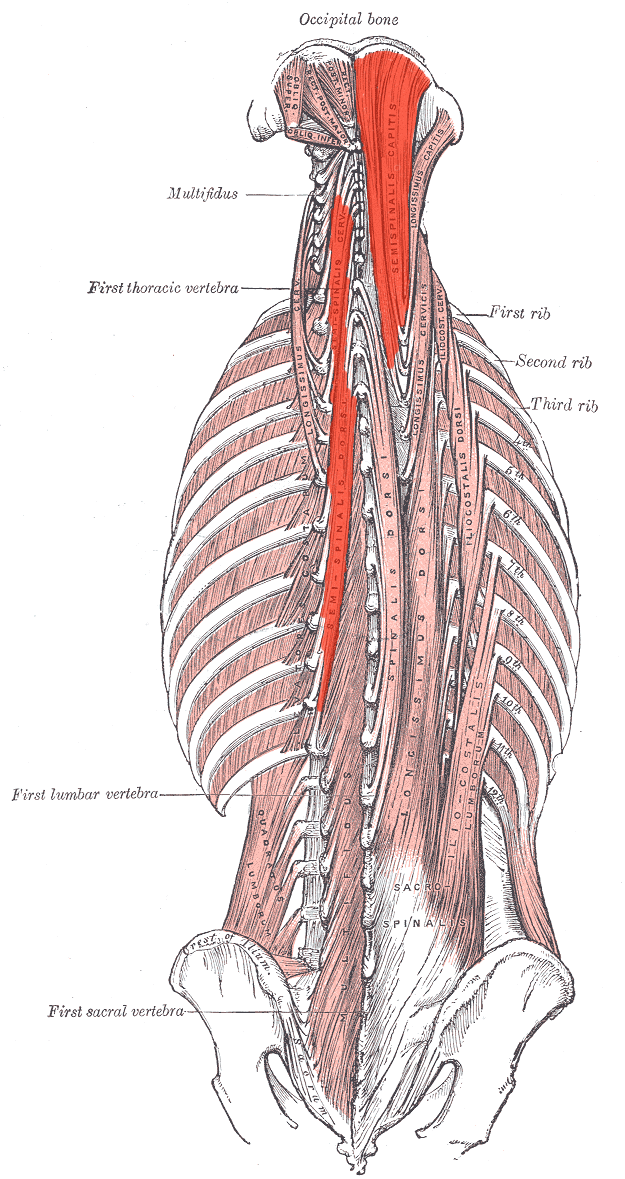
Semispinalis INNERVATION
Dorsal rami of cervical and thoracic regions
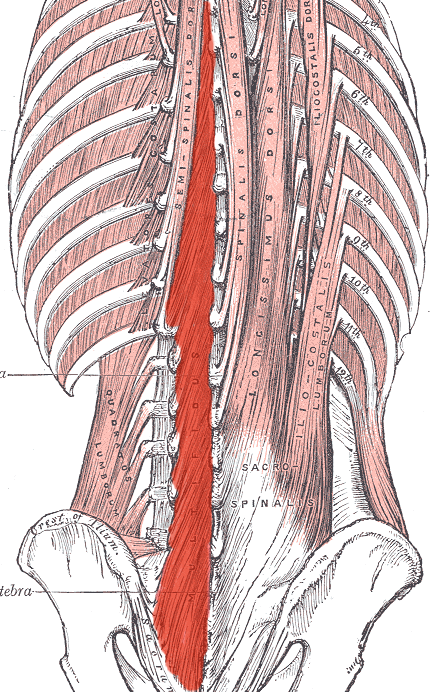
Multifidus ORIGIN
sacrum
Transverse processes of L5 to C3
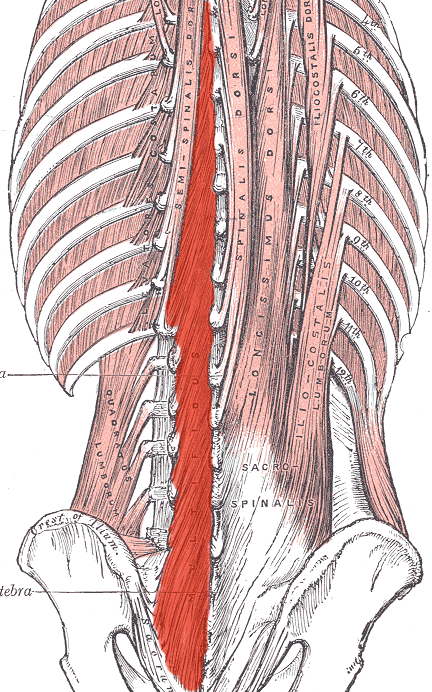
Multifidus INSERTION
Spinous processes 2-4 vertebrae superior to origin
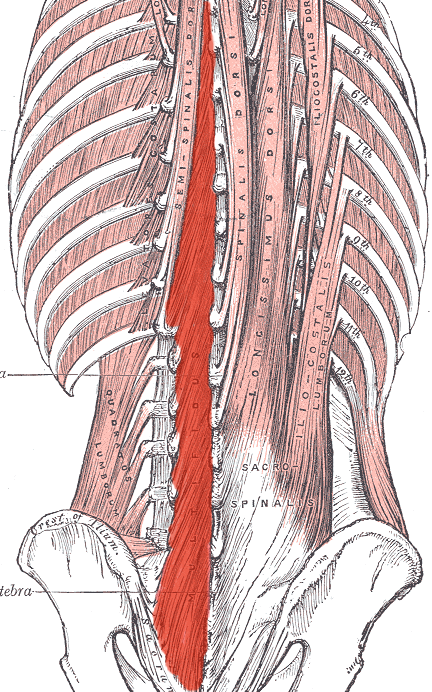
Multifidus ACTION (BILATERALLY)
Extends neck and trunk
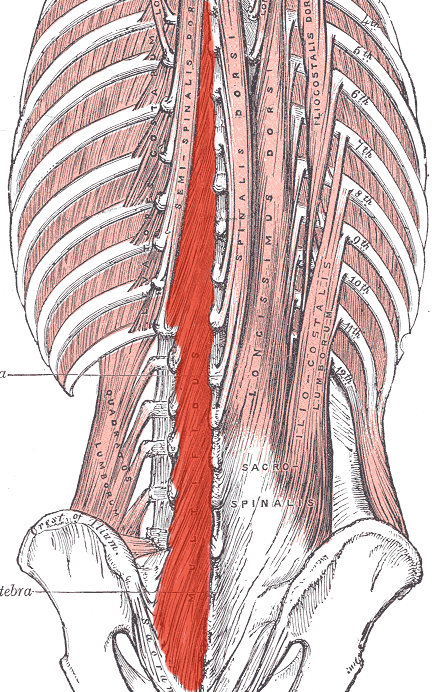
Multifidus ACTION (UNILATERALLY)
laterally flexes trunk
Rotates trunk contralaterally
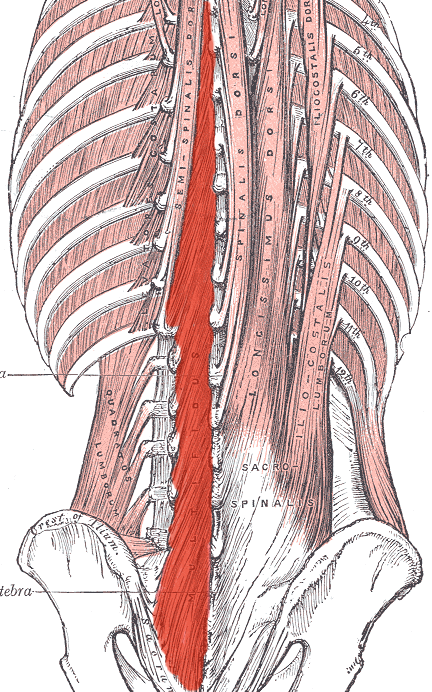
Multifidus INNERVATION
Dorsal rami
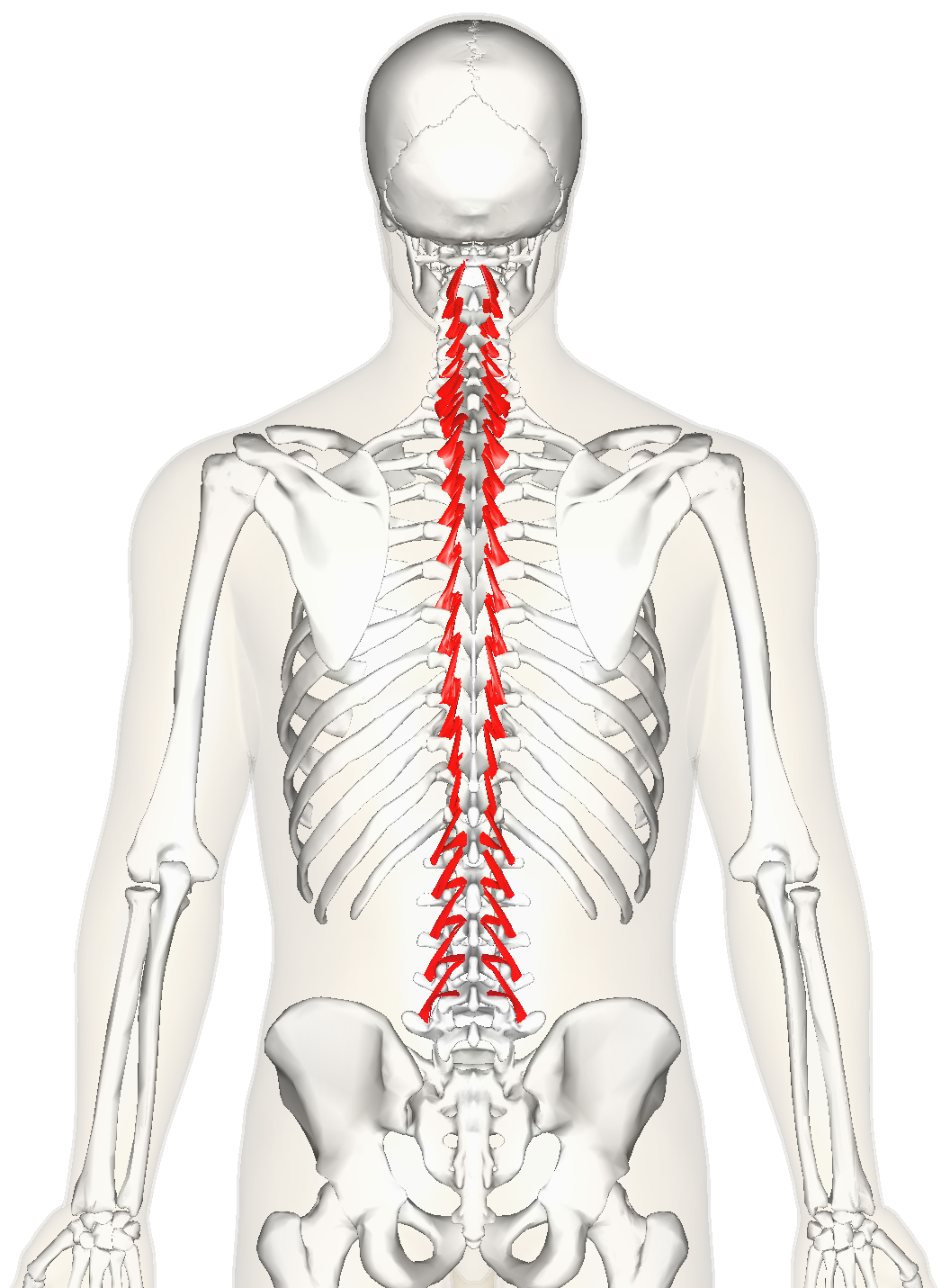
Rotatores ORIGIN
Transverse processes (most prominent in thoracic region)
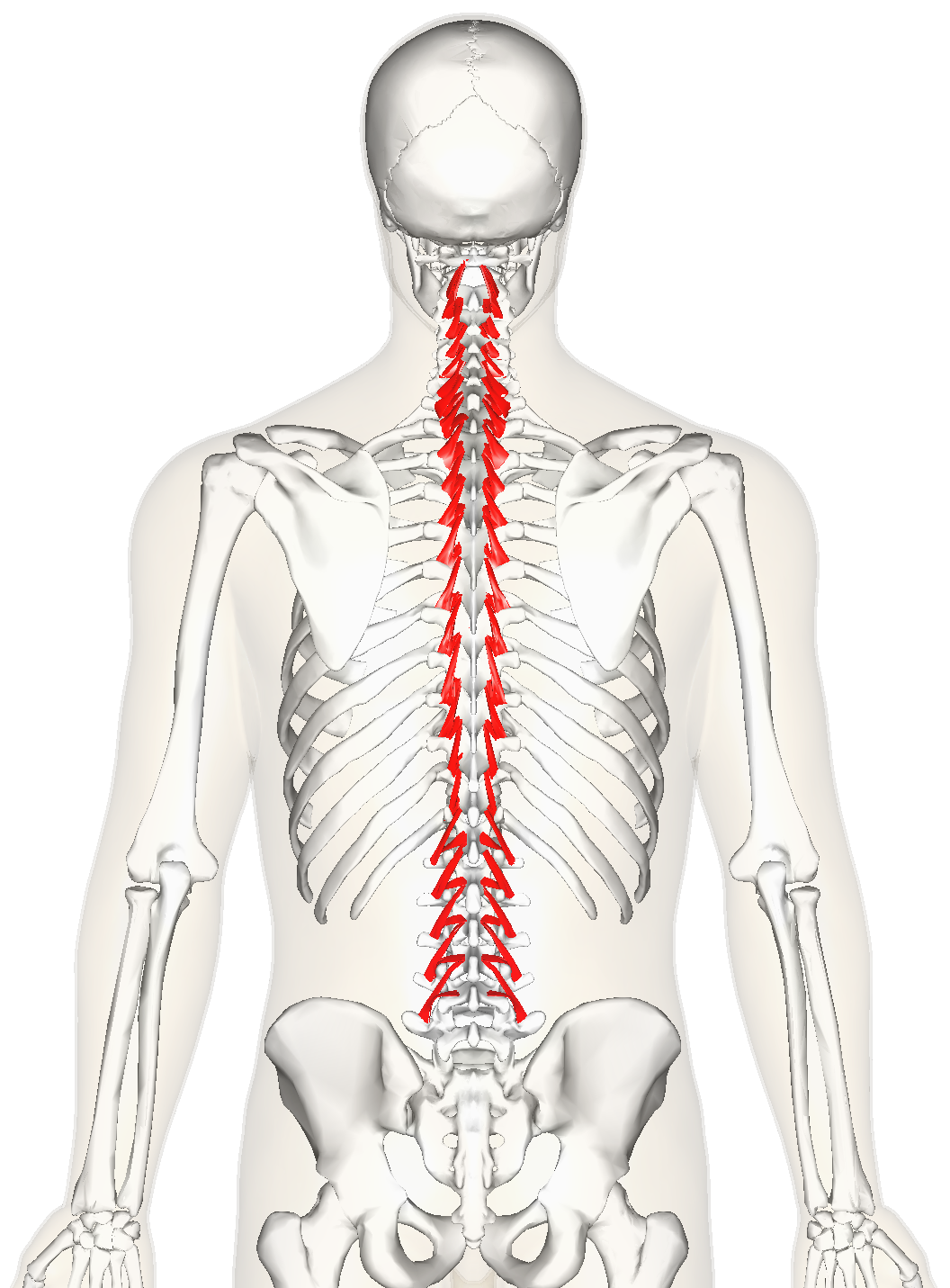
Rotatores INSERTION
Spinous processes 1-2 vertebrae superior to origin
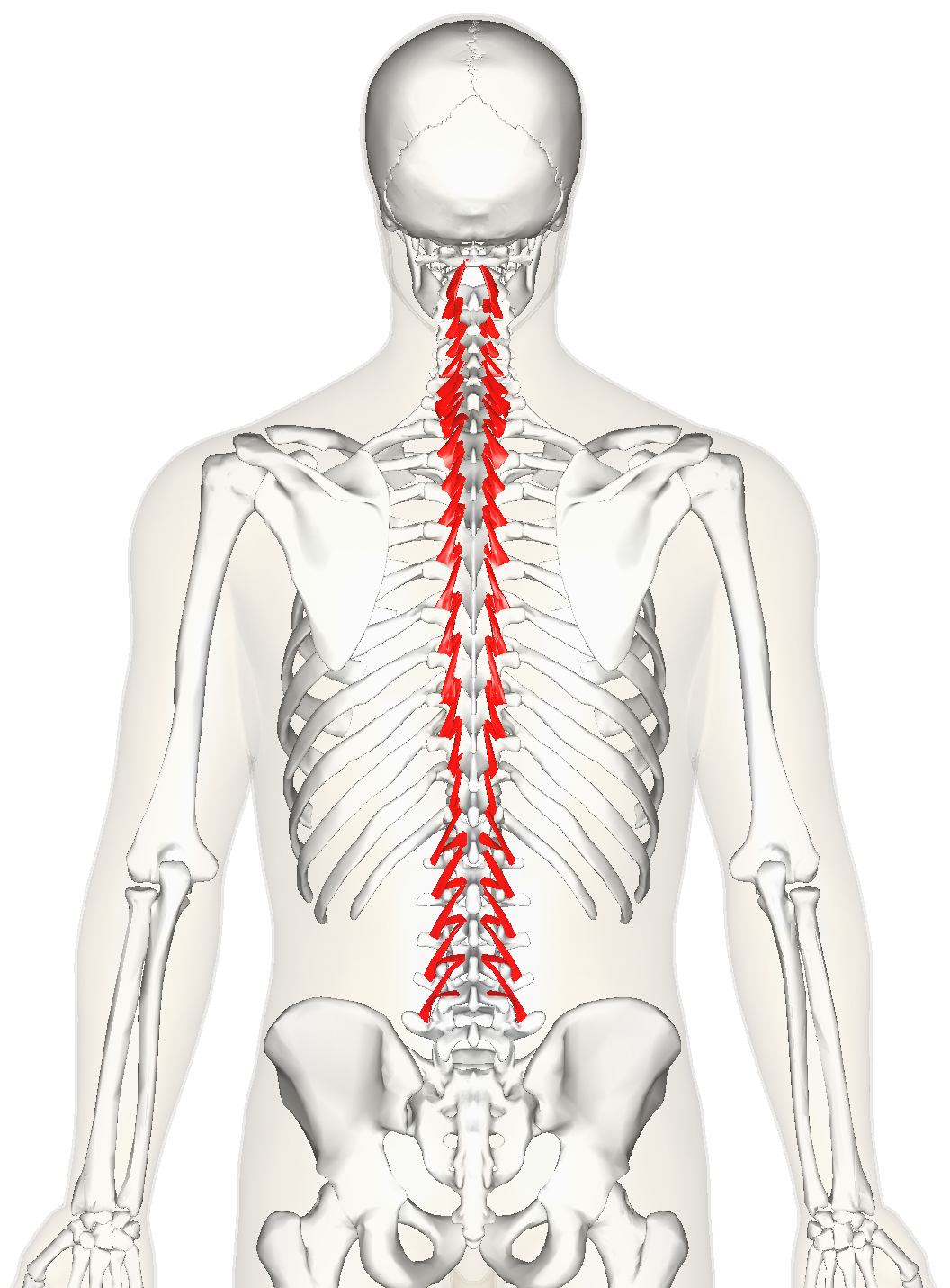
Rotatores ACTION
Rotates trunk contralaterally
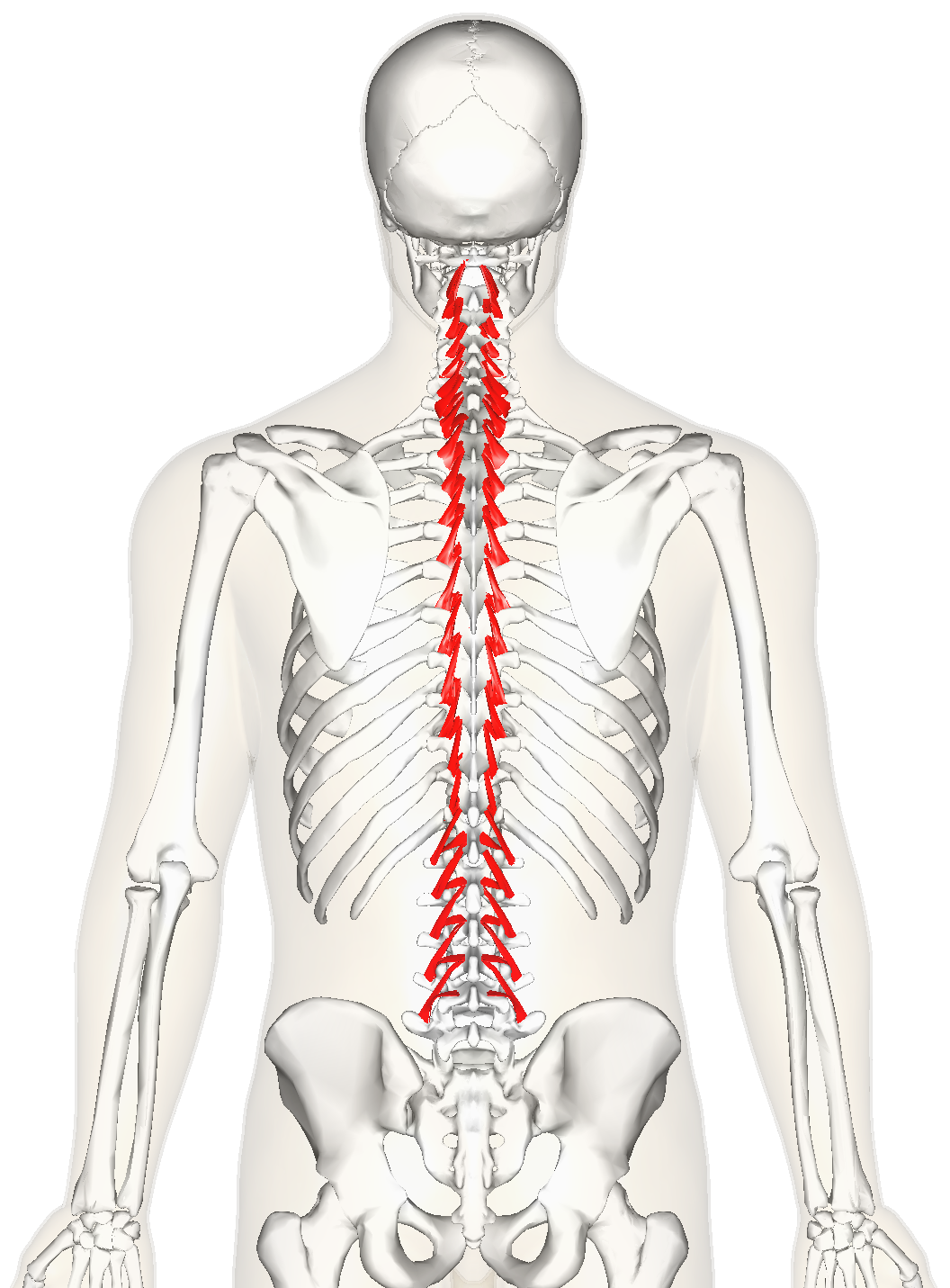
Rotatores INNERVATION
Dorsal rami
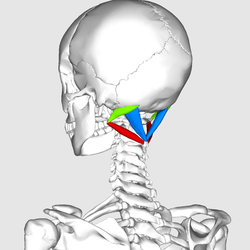
Name the muscles that make up the suboccipital triangle:
rectus capitis posterior major
Rectus capitis posterior minor
Obliquus capitis superior
Obliquus capitis inferior
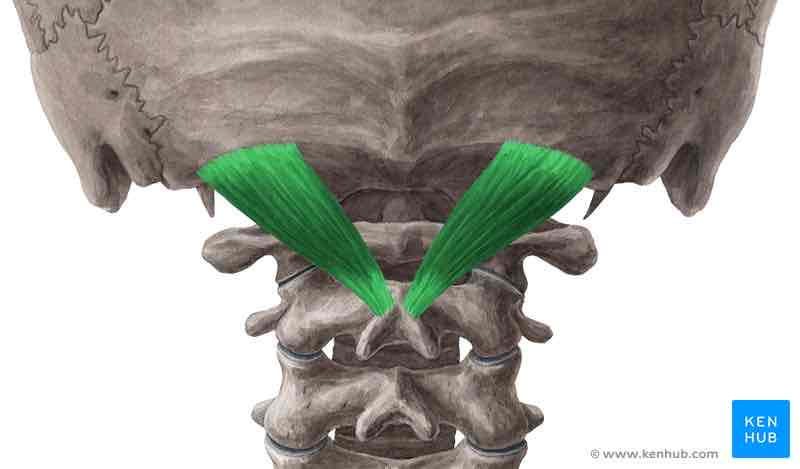
Rectus capitis posterior major ORIGIN
Spinous process of C 2 (axis)
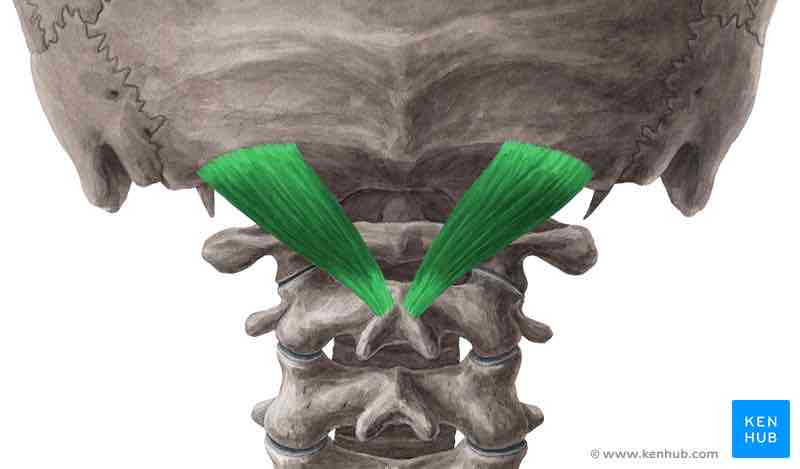
Rectus capitis posterior major INSERTION
Inferior nuchal line
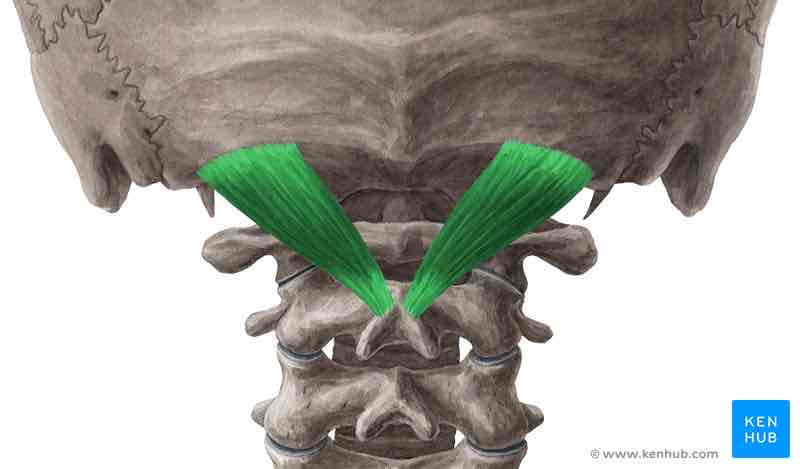
Rectus capitis posterior major ACTION
Extends and rotates head ipsilaterally
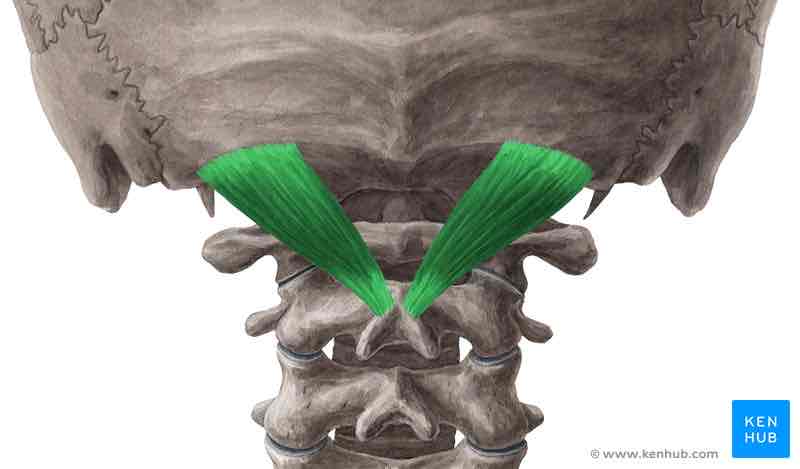
Rectus capitis posterior major INNERVATION
Dorsal ramus of C1 (suboccipital nerve)
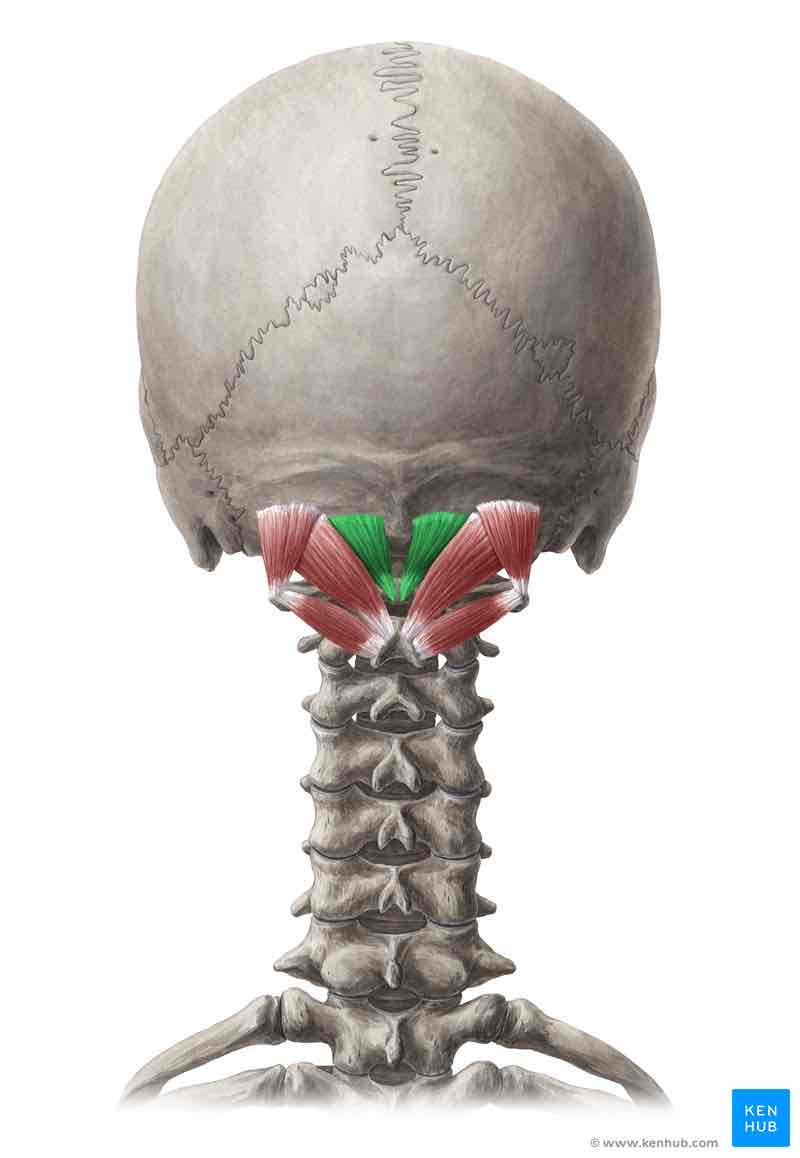
Rectus capitis posterior minor ORIGIN
Posterior tubercle of C1 (atlas)
Rectus capitis posterior minor INSERTION
Medial portion of inferior nuchal line
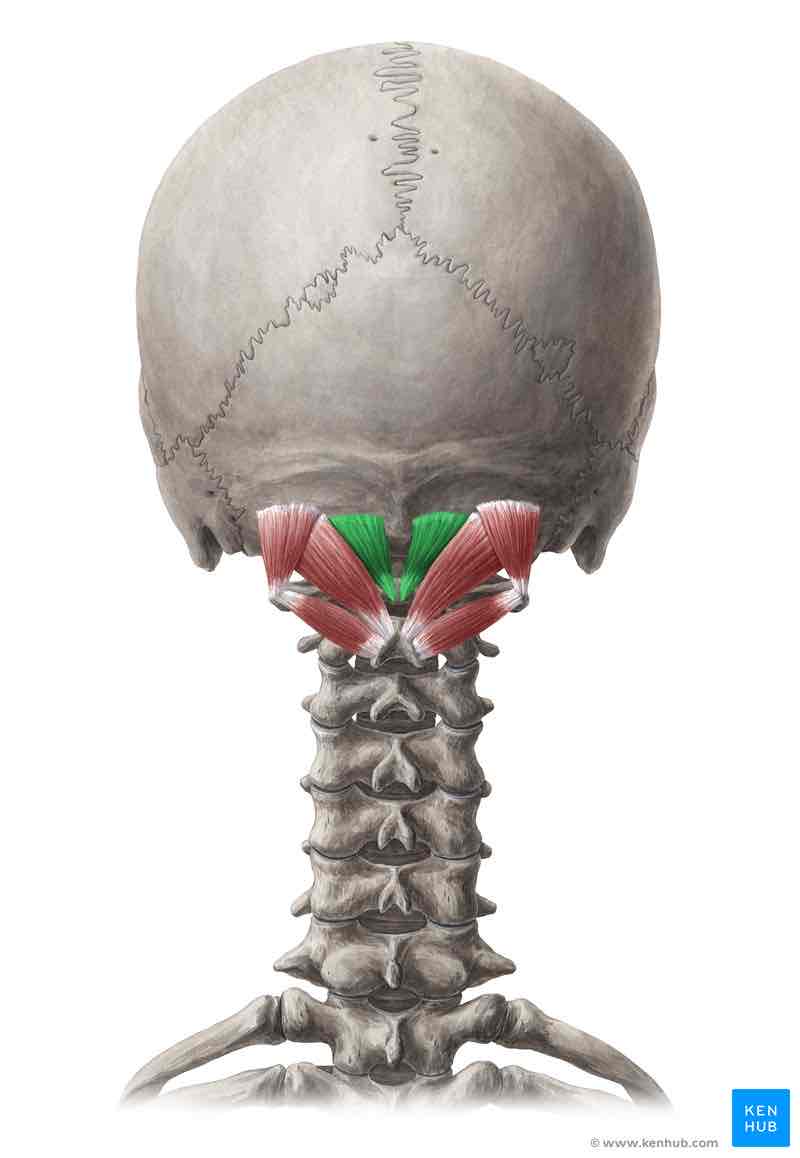
Rectus capitis posterior minor ACTION
Extends the head
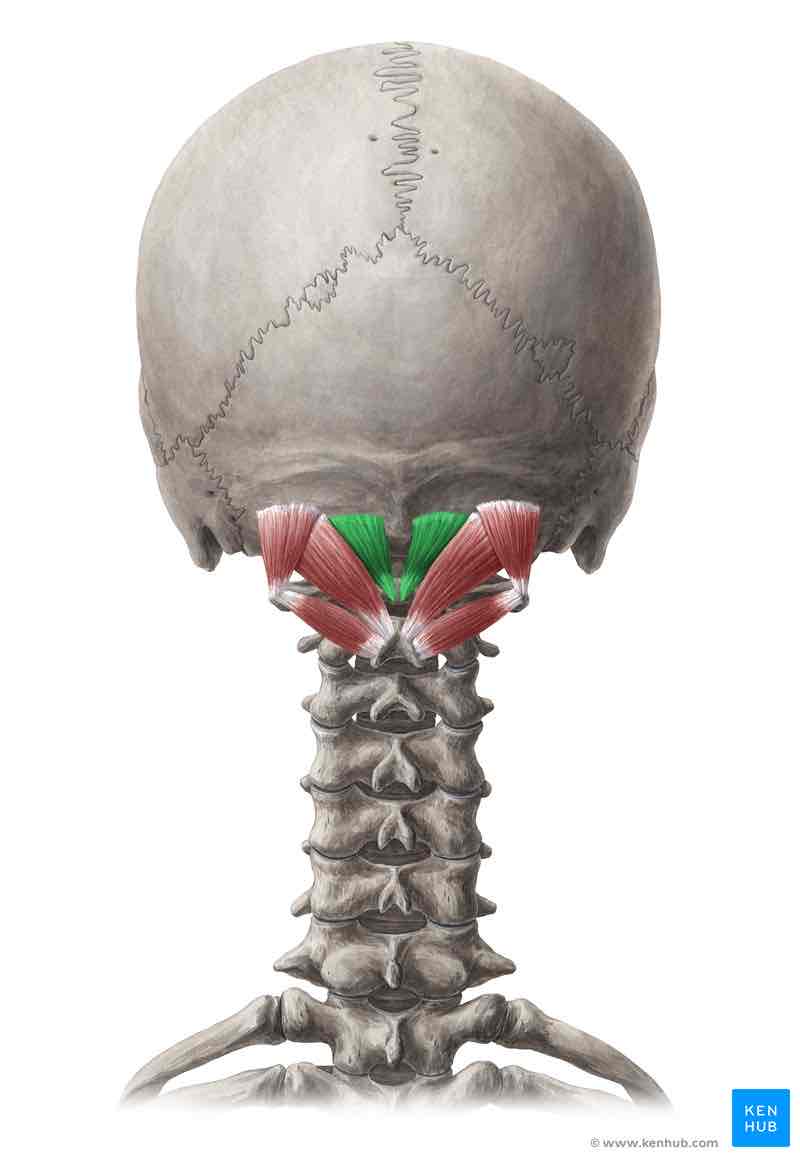
Rectus capitis posterior minor INNERVATION
Dorsal ramus of C1 (suboccipital nerve)
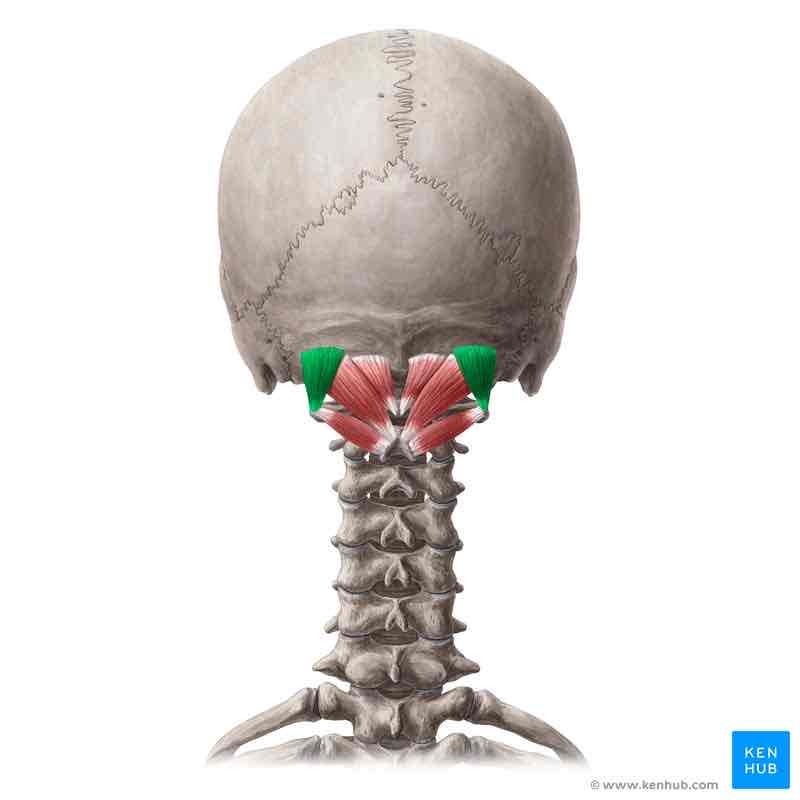
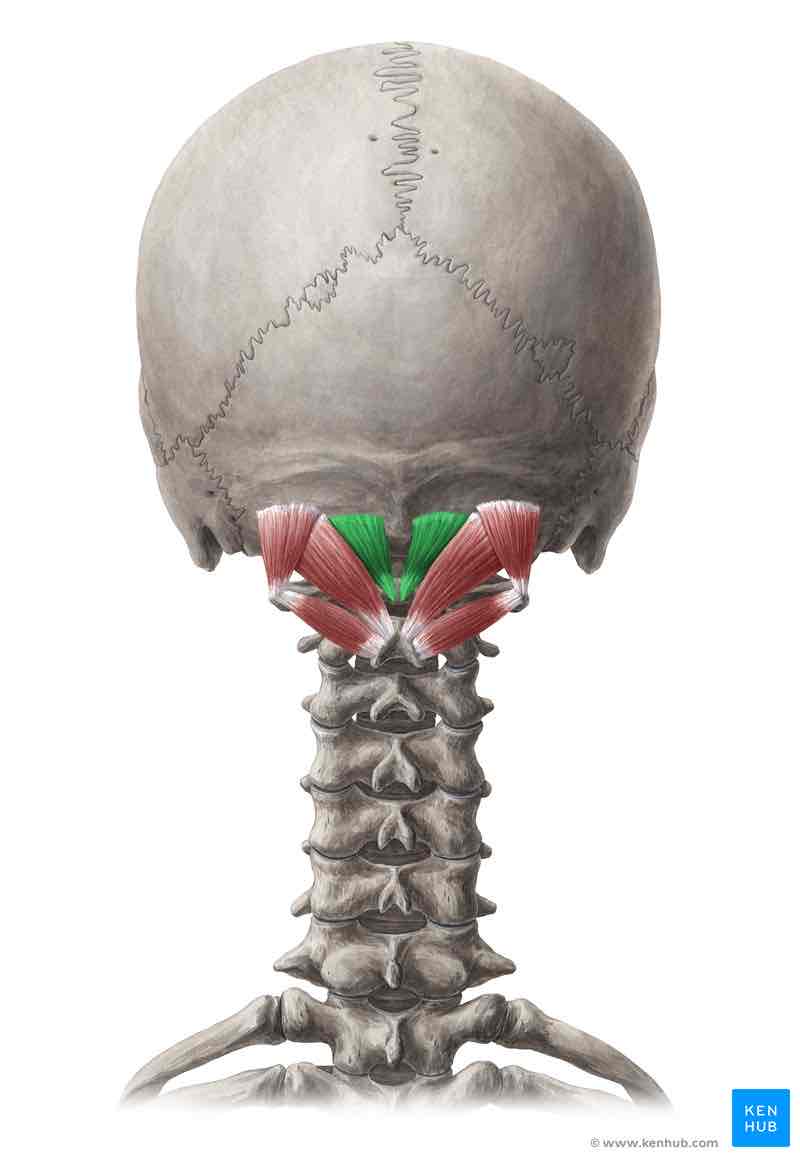
Obliquus capitis superior ORIGIN
Transverse process of C2 (atlas)
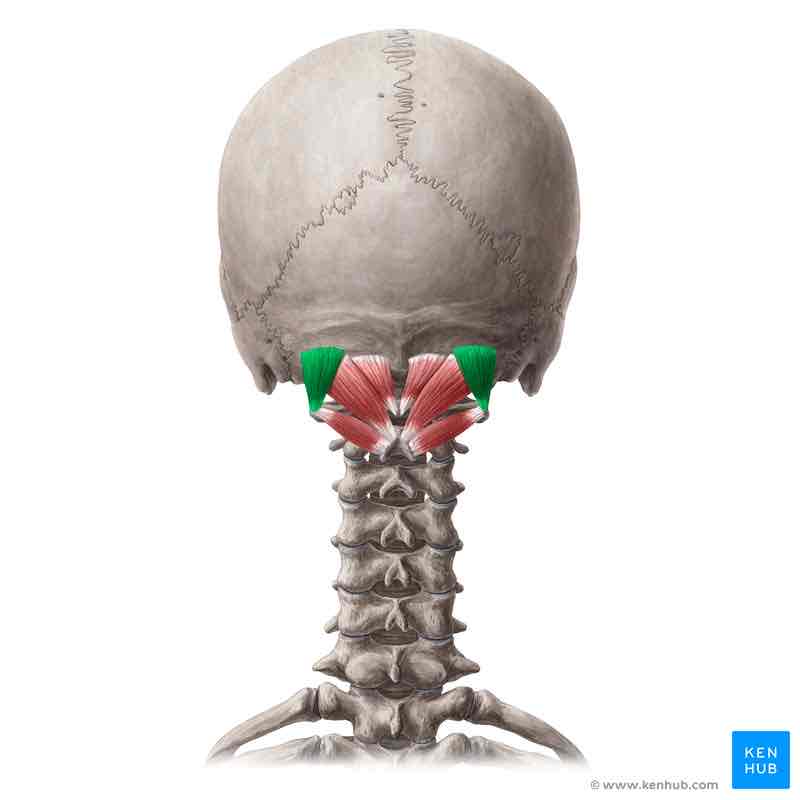
Obliquus capitis superior INSERTION
Occipital bone superior to inferior nuchal line
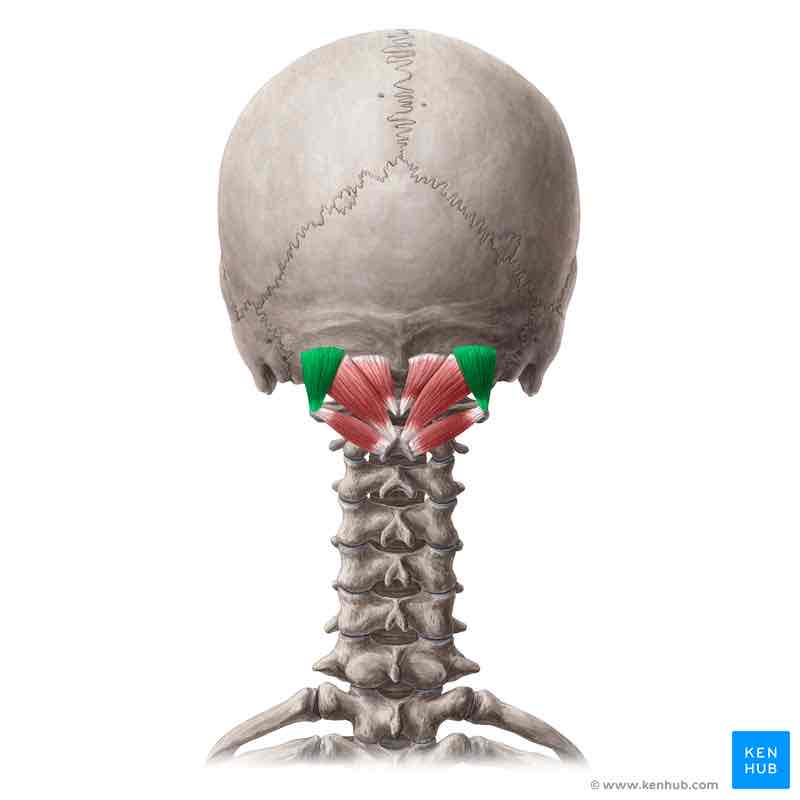
Obliquus capitis superior ACTION
Extends and rotates head ipsilaterally
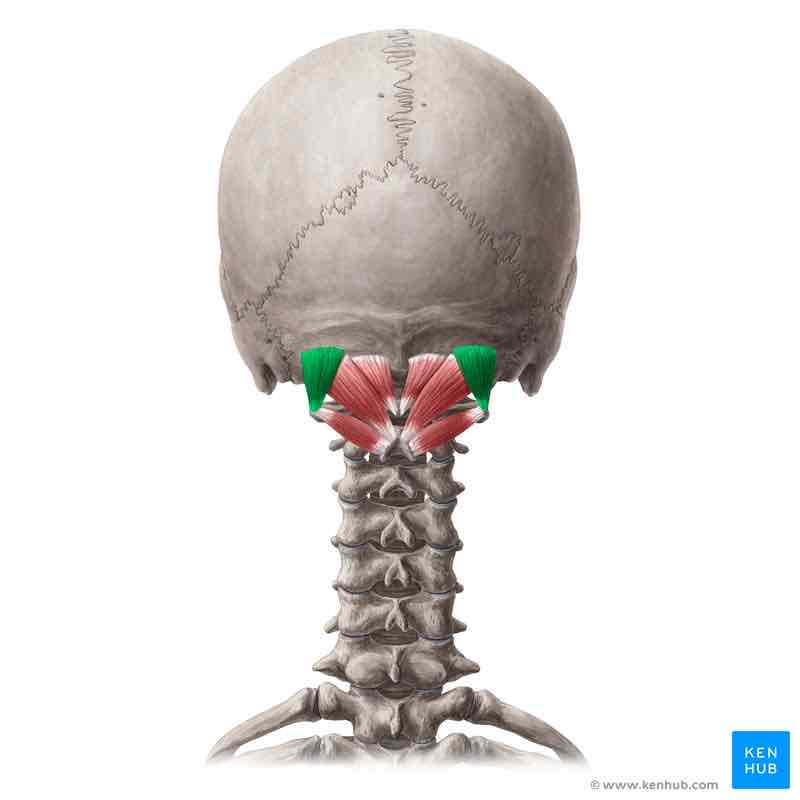
Obliquus capitis superior INNERVATION
Dorsal ramus of C1 (suboccipital nerve)
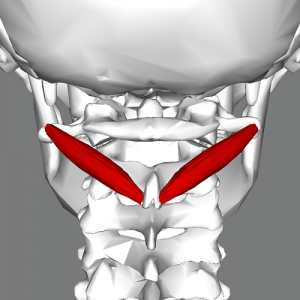
Obliquus capitis inferior ORIGIN
Spinous process of C2 (axis)
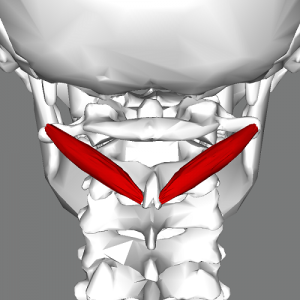
Obliquus capitis inferior INSERTION
Transverse process of C1 (atlas)
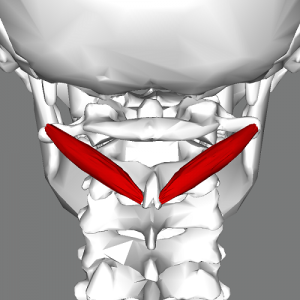
Obliquus capitis inferior ACTION
Rotates head ipsilaterally
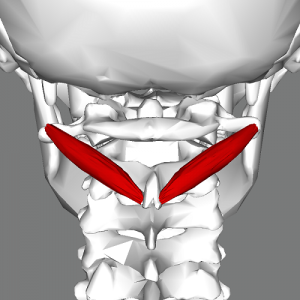
Obliquus capitis inferior INNERVATION
Dorsal ramus of C1 (suboccipital nerve)
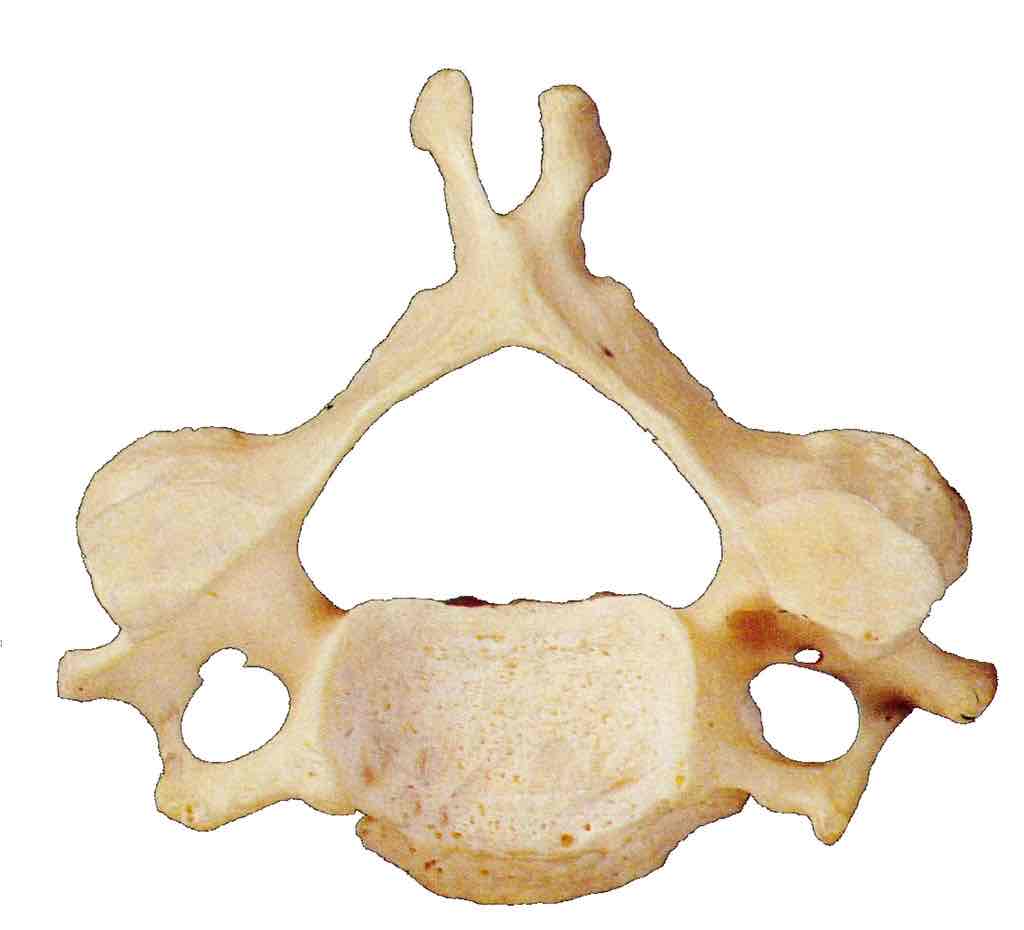
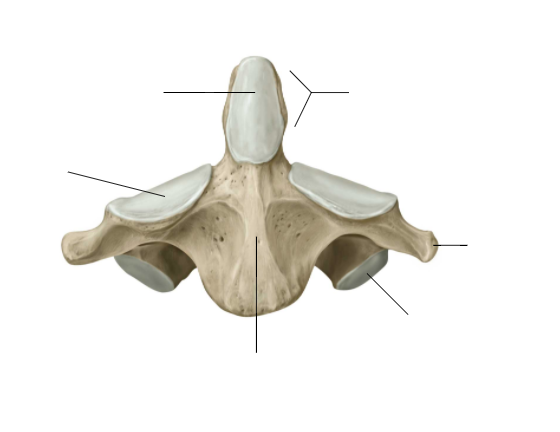
Name this vertebrae
Cervical
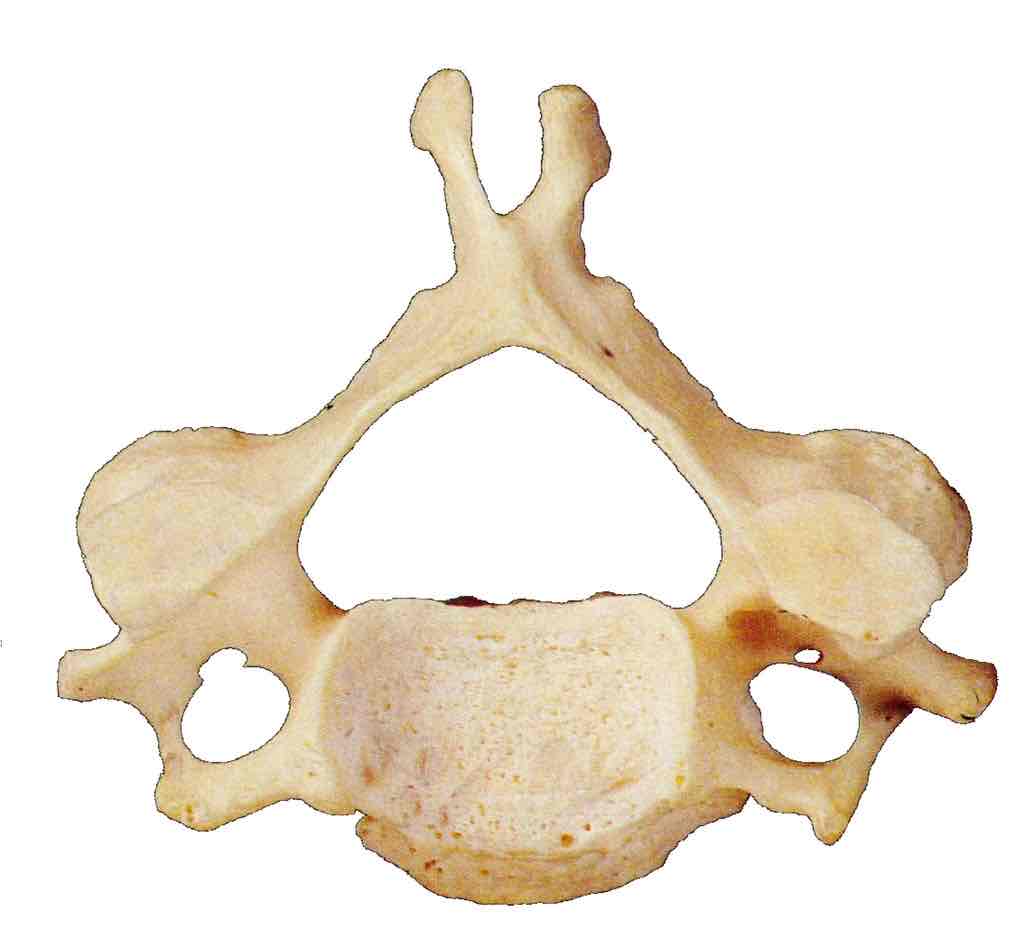
Defining factor of cervical vertebrae
Foramina in transverse processes
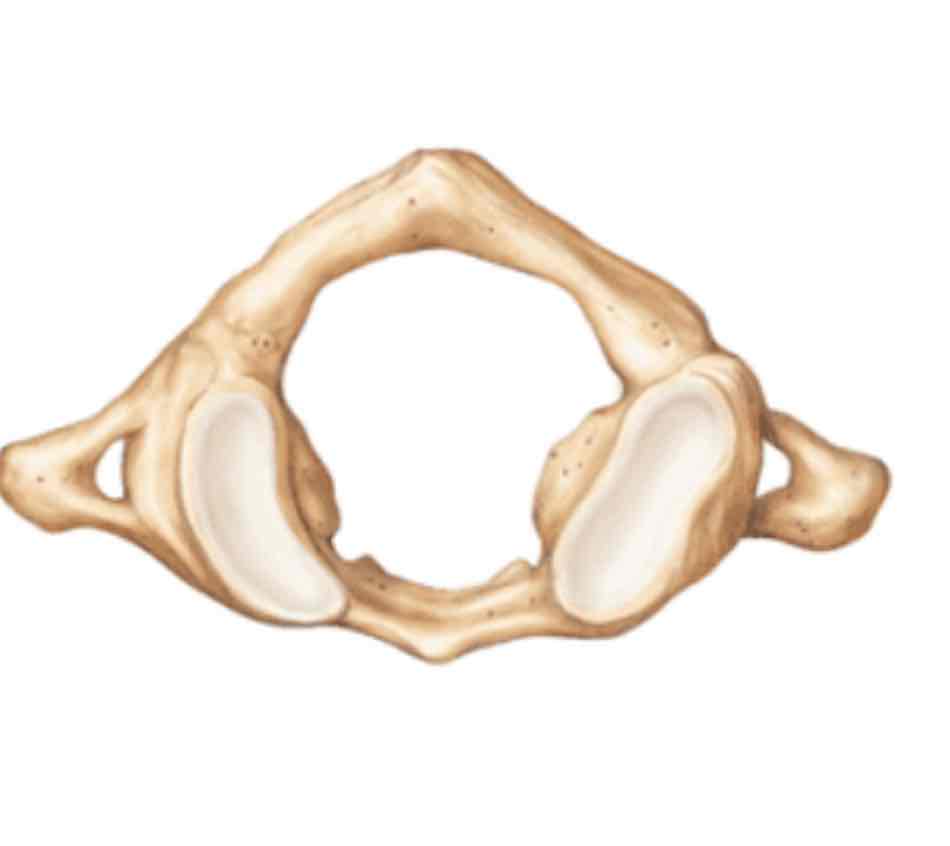
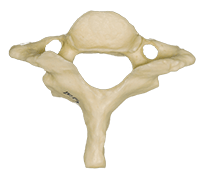
Name this special cervical vertebrae and its defining factor
C1
Atlas
No vertebral body
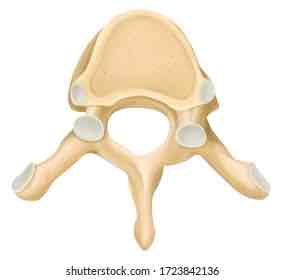
Name this special cervical vertebrae and its defining factor
C2
Axis
Dens (adotoid process)
Name this cervical vertebrae and its defining factor
C7
Vertebra prominens
Large spinous process
Name this vertebrae and its defining characteristic
thoracic
Costal facets on transverse processes
Name this vertebrae and its defining characteristic
lumbar
Large vertebral body
“Stubby” processes
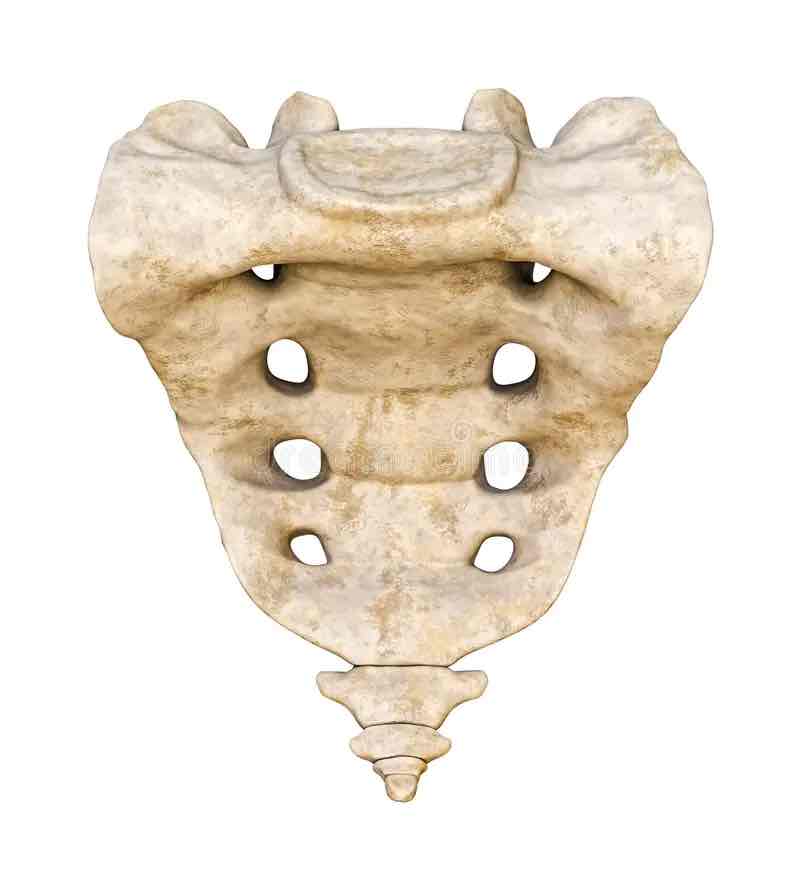
Name this part of the vertebral column that is FUSED
Sacrum
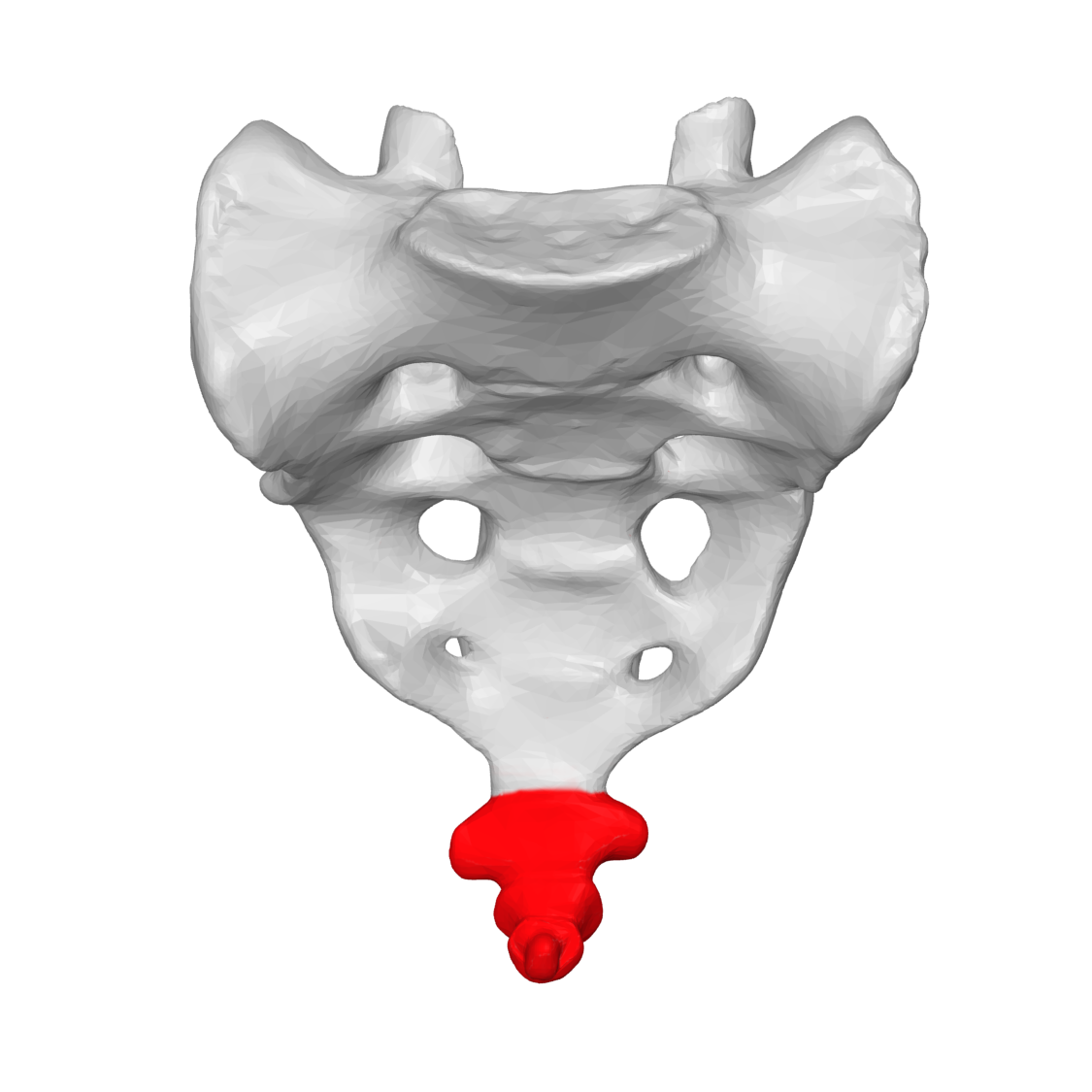
Name this part of the vertebral column that is FUSED
Coccyx
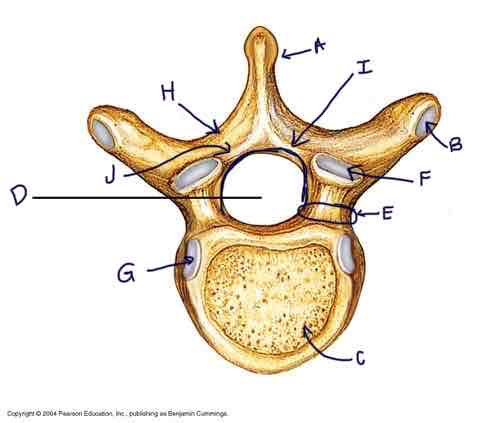
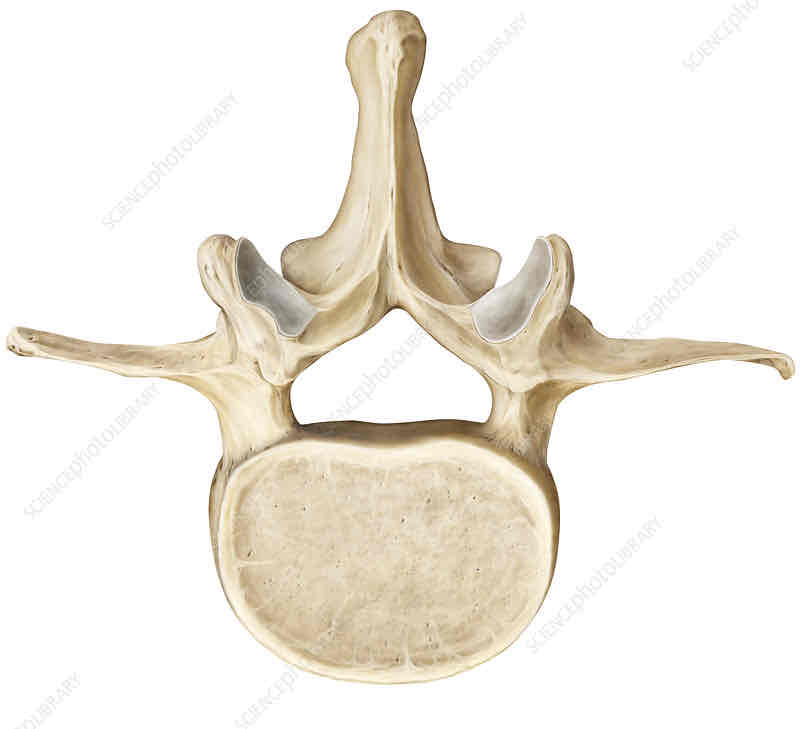
Identify the parts of the vertebrae (label from A to J)
A. Spinous process
B. Costal facet
C. Vertebral Body
D. Vertebral foremen
E. Pedicle
F. Superior Articular Facet
G. Inferior Articular Facet
H. Transverse Process
I. Vertebral Arch
J. Lamina
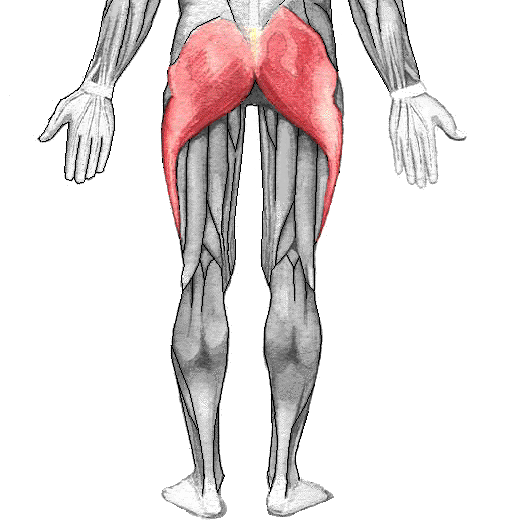
Gluteus maximus ORIGIN
posterior ilium
Sacrum
Coccyx
Sacrotuberous ligament
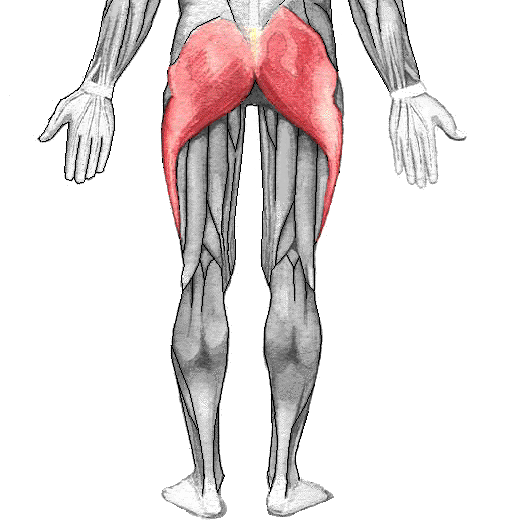
Gluteus maximus INSERTION
superior fibers - iliotibial tract (IT band)
Inferior fibers - gluteal tuberosity of femur
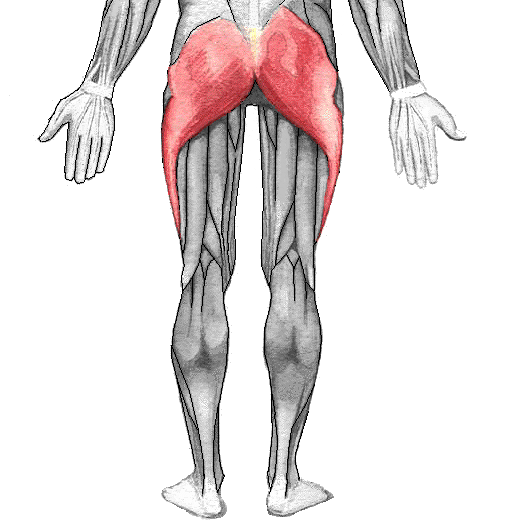
Gluteus maximus ACTION
Extends and laterally rotates thigh at hip
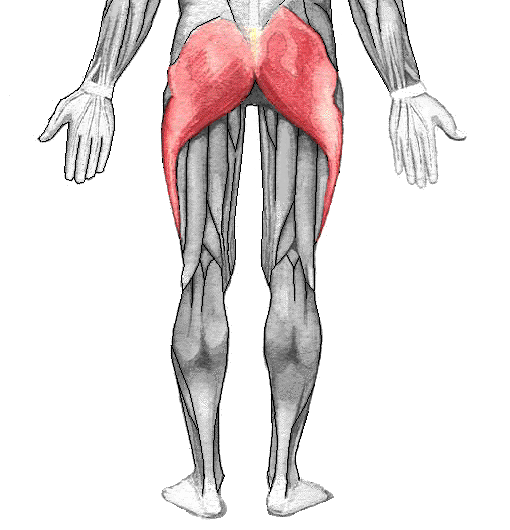
Gluteus maximus INNERVATION
Inferior gluteal nerve
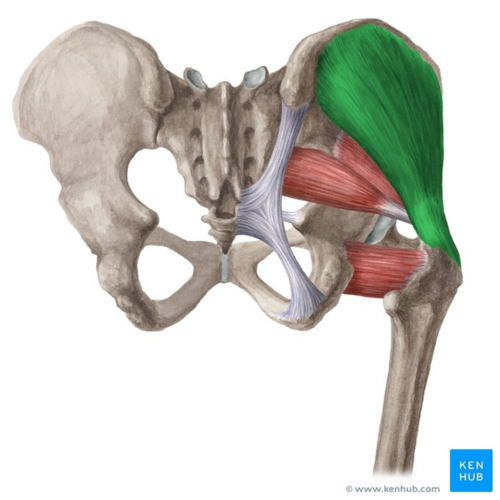
Gluteus medius ORIGIN
Lateral surface of ilium between gluteal lines
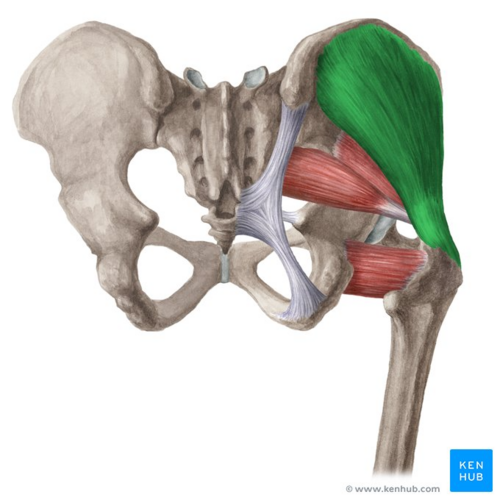
Gluteus medius INSERTION
Lateral surface of greater trochanter of femur
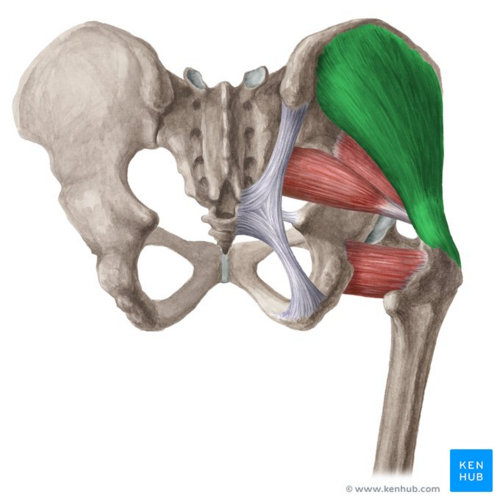
Gluteus medius ACTION
Abducts and medially rotates thigh at hip
Stabilizes pelvis when opposite leg is lifted
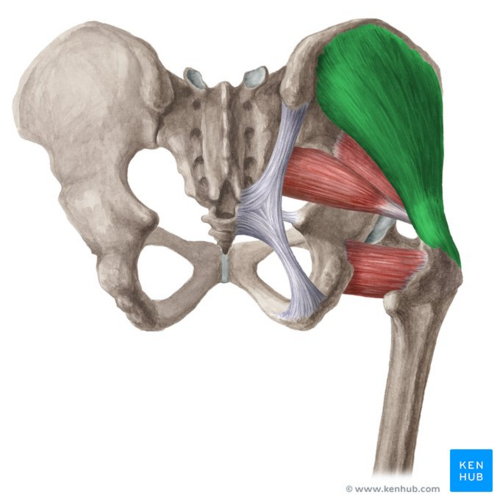
Gluteus medius INNERVATION
Superior gluteal nerve