Chemistry Chapter 2 Study Guide: Sections 1,2
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Scientific method
logical approach to solving problems
Observing
the use of sense to obtain information
Qualitative
description
Quantitative
numerical
System
A specific portion of matter in a given region of space that has been selected for study during an experiment or observation
Hypothesis
testable statement
Hypothesis statements are often drafted as “______”
if-then
Controls
experimental conditions that remain constant
Variables
any condition that changes
Stages in the Scientific Method
Observing, Formulating Hypotheses, Testing, Theorizing, Publish Results
Model
A physical representation to explain something smaller or bigger
Theory
A broad generalization that explains a body of facts or phenomena
Quantity
Something that has magnitude, size, or amount
Length
meter
Mass
kilogram
Time
second
Temperature
kelvin
mega
10^6 | M
kilo
10³ | k
hecto
10² | h
deka
10^1 | da
deci
10^-1 | d
centi
10^-2 | c
milli
10^-3 | m
micro
10^-6 | µ
nano
10^-9 | n
Weight
measure of the gravitational pull on matter
To find density use:
D = m/v
To find mass use:
m = Dv
To find volume use:
v = m/D
cm³
mL
dm³
L
m³
kL
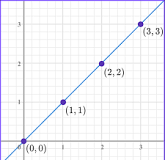
Directly Proportional
When one variable goes up, the other variable goes up.
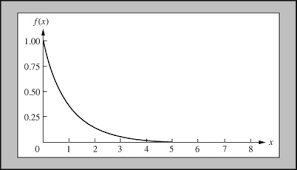
Inversely Proportional
When one variable goes up, the other goes down.
Pacific-Atlantic Rule
If there is no decimal point, start from right to left. If there is a decimal point, start from left to right,
Addition/Subtraction w/ Significant Figures
Round to the least precise decimal point
Multiplication/Division w/ Significant Figures
Round to the least number of significant figures
Scientific Notation
M ×10^n
65,000 in scientific notation is
6.5 ×10^4
The percentage error equation is…
a measurement of accuracy
When using scientific notation,
only the significant numbers are shown
Natural Law
Describes how nature behaves, but does not explain why nature behaves the way it does.