Biology - C5 cont.
1/78
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Photosynthesis, Respiration and ATP/Glucose
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Plants
What is the main organism that can carry out photosynthesis?
Light
Source of energy for photosynthesis to occur
Carbon dioxide and water
Two reactants taken in by a plant for photosynthesis
Oxygen and glucose
Two products of photosynthesis
C6H12O6
Formula for glucose
6 CO2 and 12 H+
What is combined to make glucose? (+ amounts)
Oxygen
What is the main waste product of making glucose?
Autotrophs
Organisms that only intake CO2 for energy/food - plants, algae and bacteria
Heterotrophs
Organisms that take in O2 and organic compounds for energy/food - animals and fungi
Cellular Respiration
The breakdown of glucose using oxygen to make usable energy (ATP)
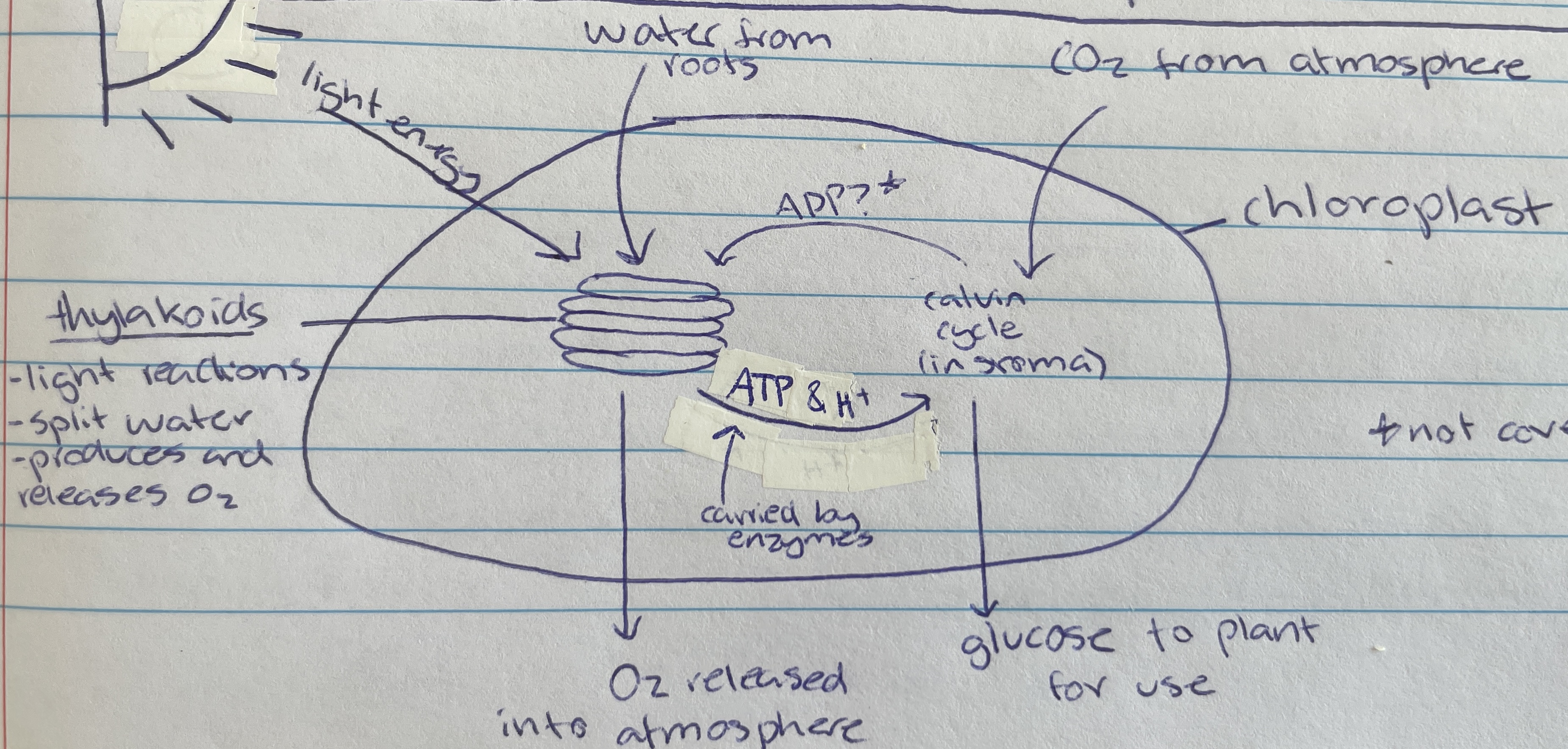
Photosynthesis
Process of using light energy to create organic compounds (glucose) and oxygen - glucose used as energy for organism
Chloroplast
Membrane bound organelle that conducts photosynthesis - located in the plant cell, mostly in the palisade mesophyll in the leaves
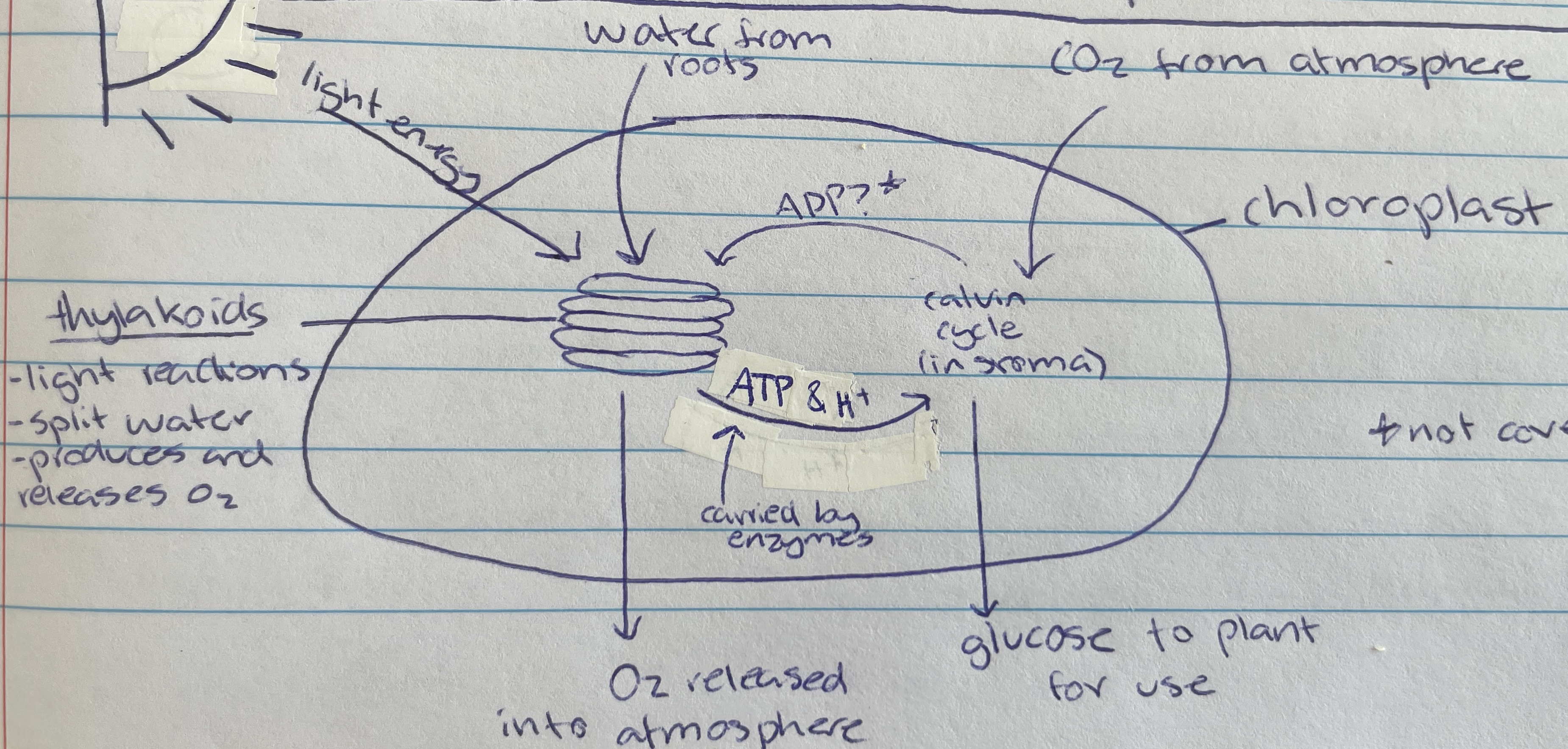
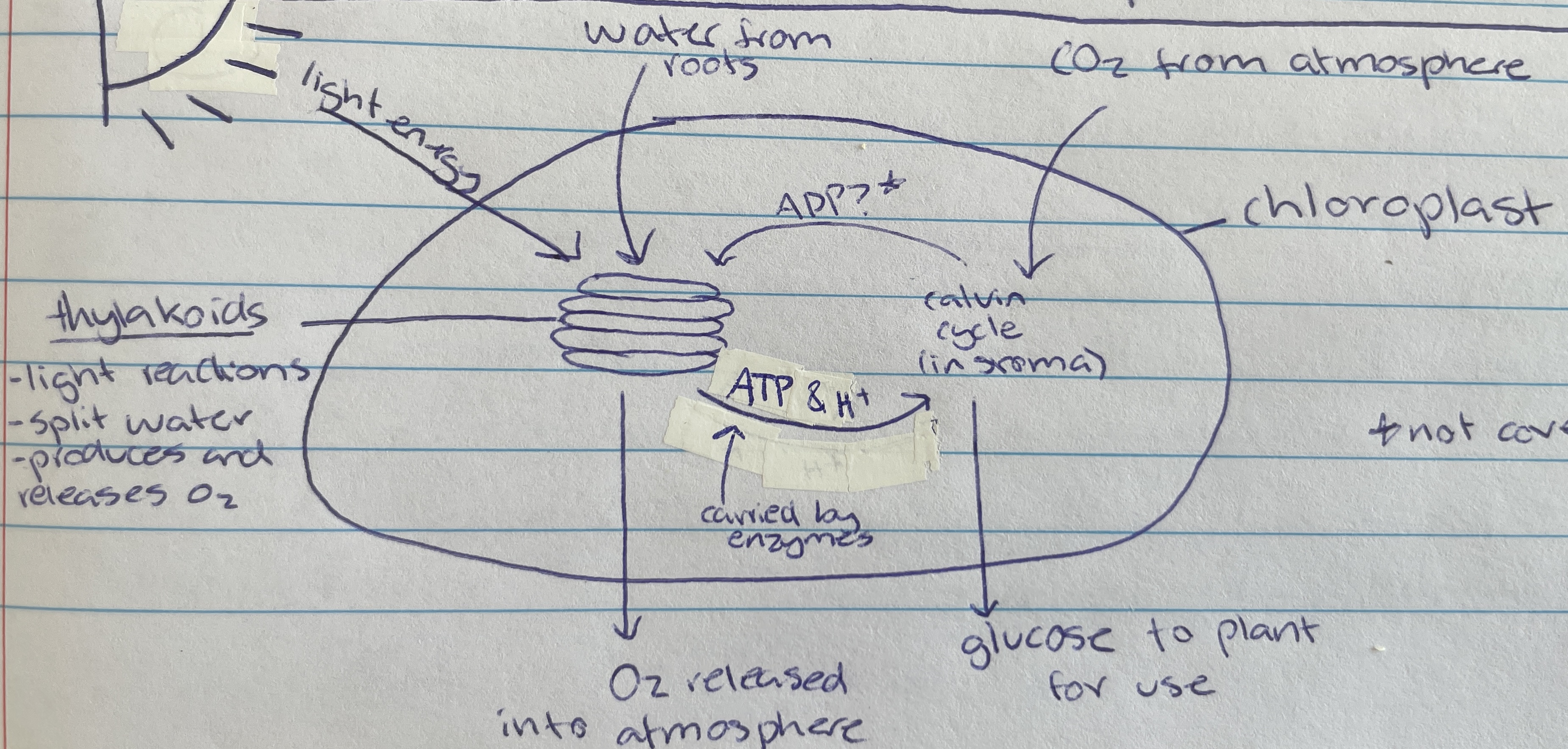
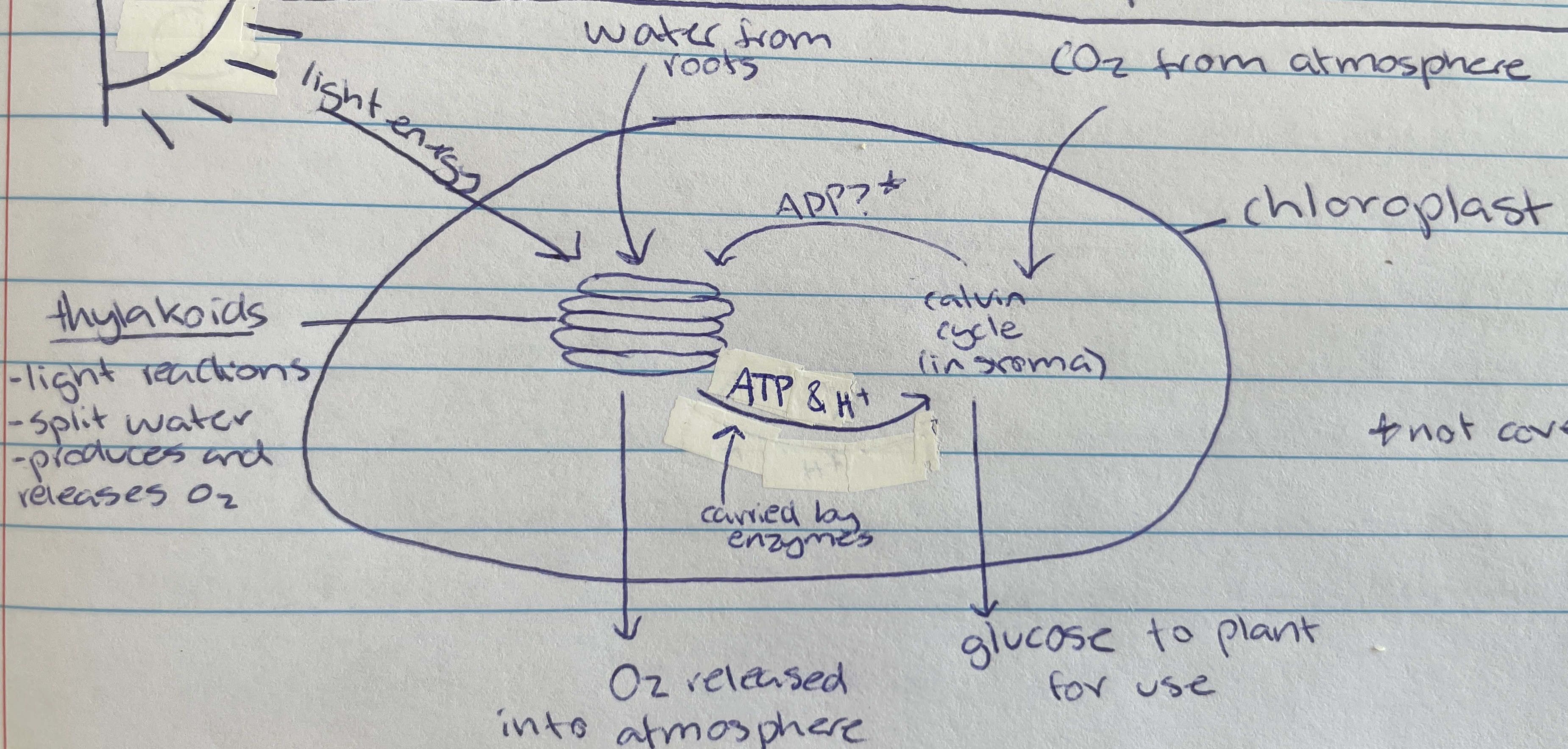
Thylakoid
Location of photolysis - stacks located in the chloroplast in pancake structure (LDS)
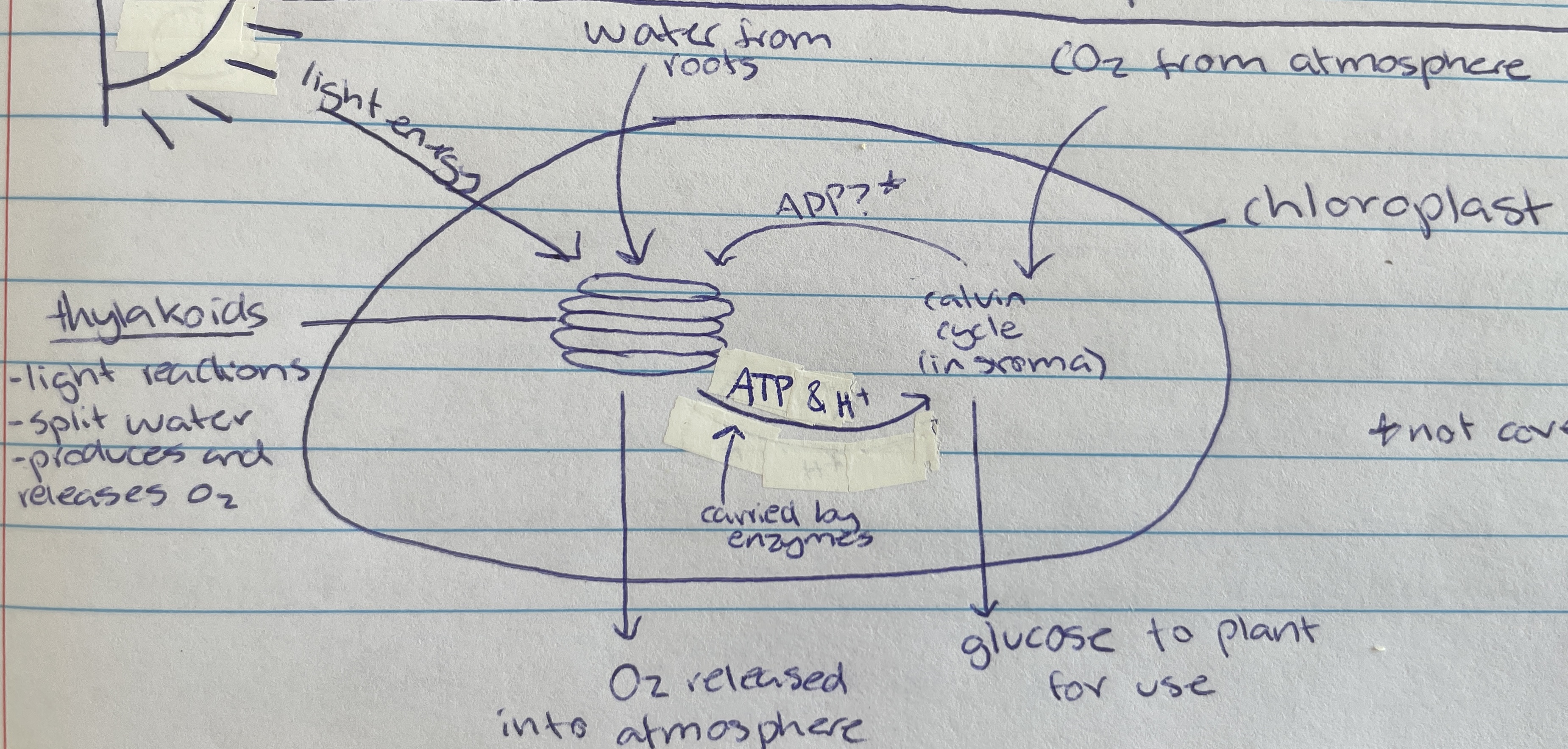
granum
The name of a stack of thylakoid (LDS)
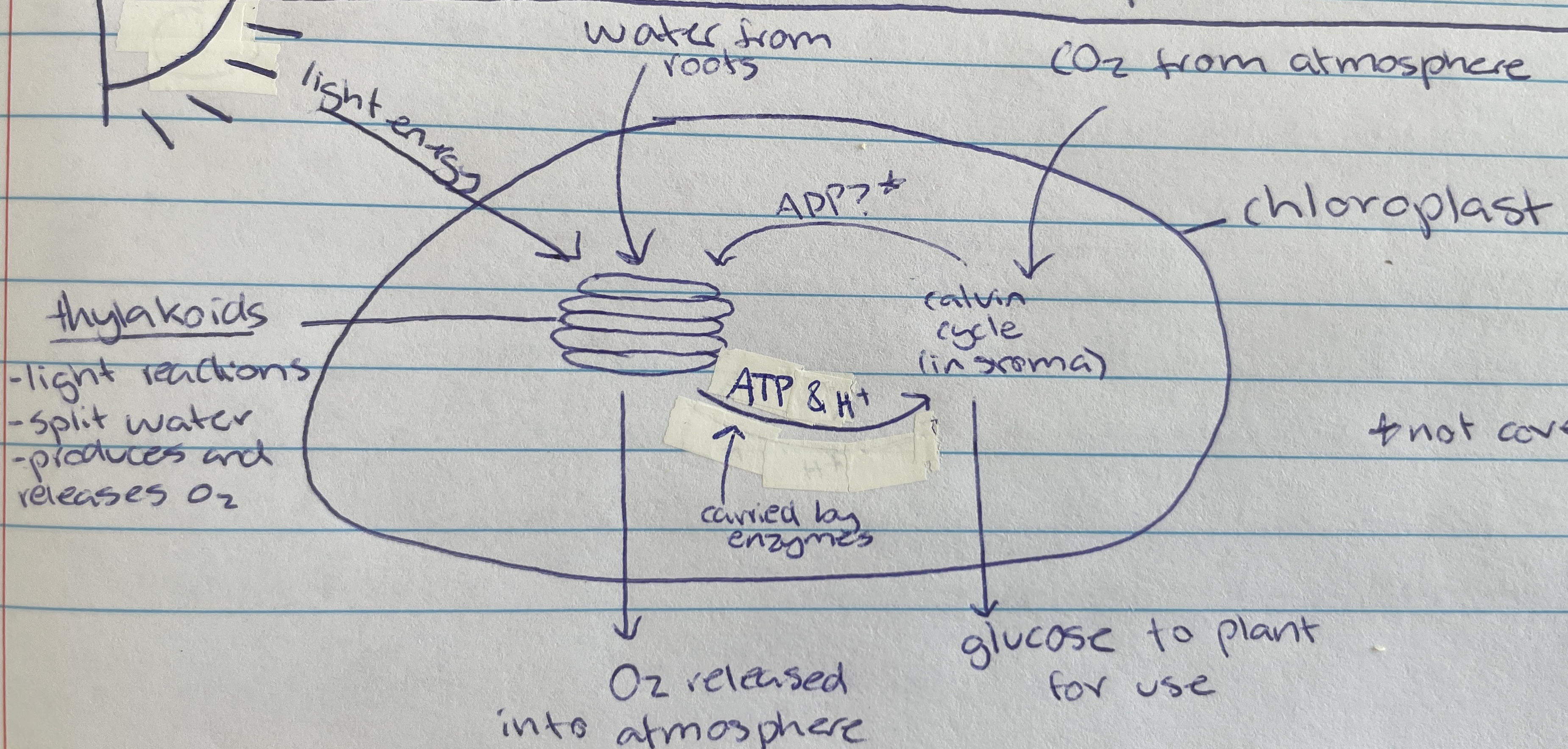
grana
The name of a stack of thylakoid, plural (LDS)
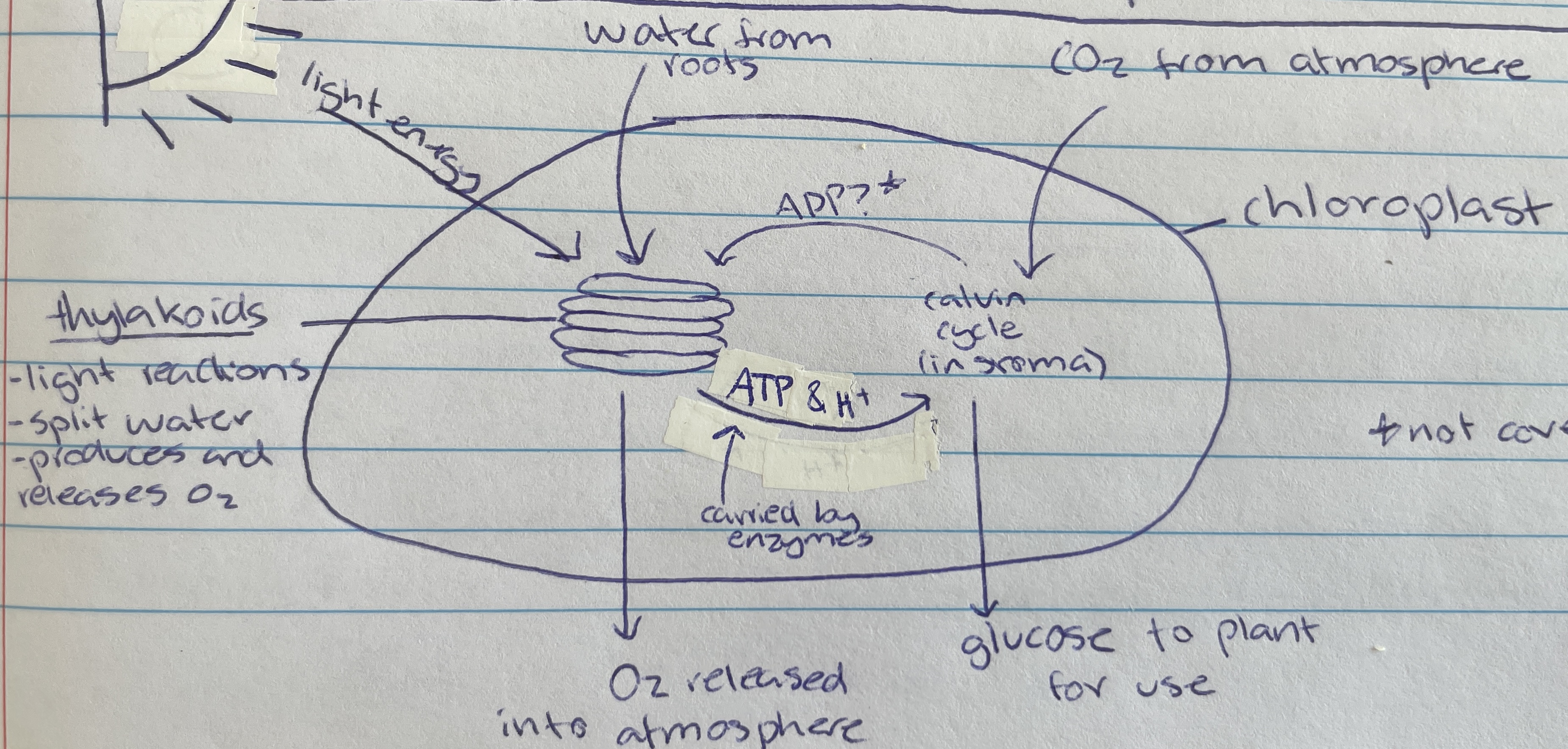
thylakoid
Light dependant stage (LDS) occurs within the…
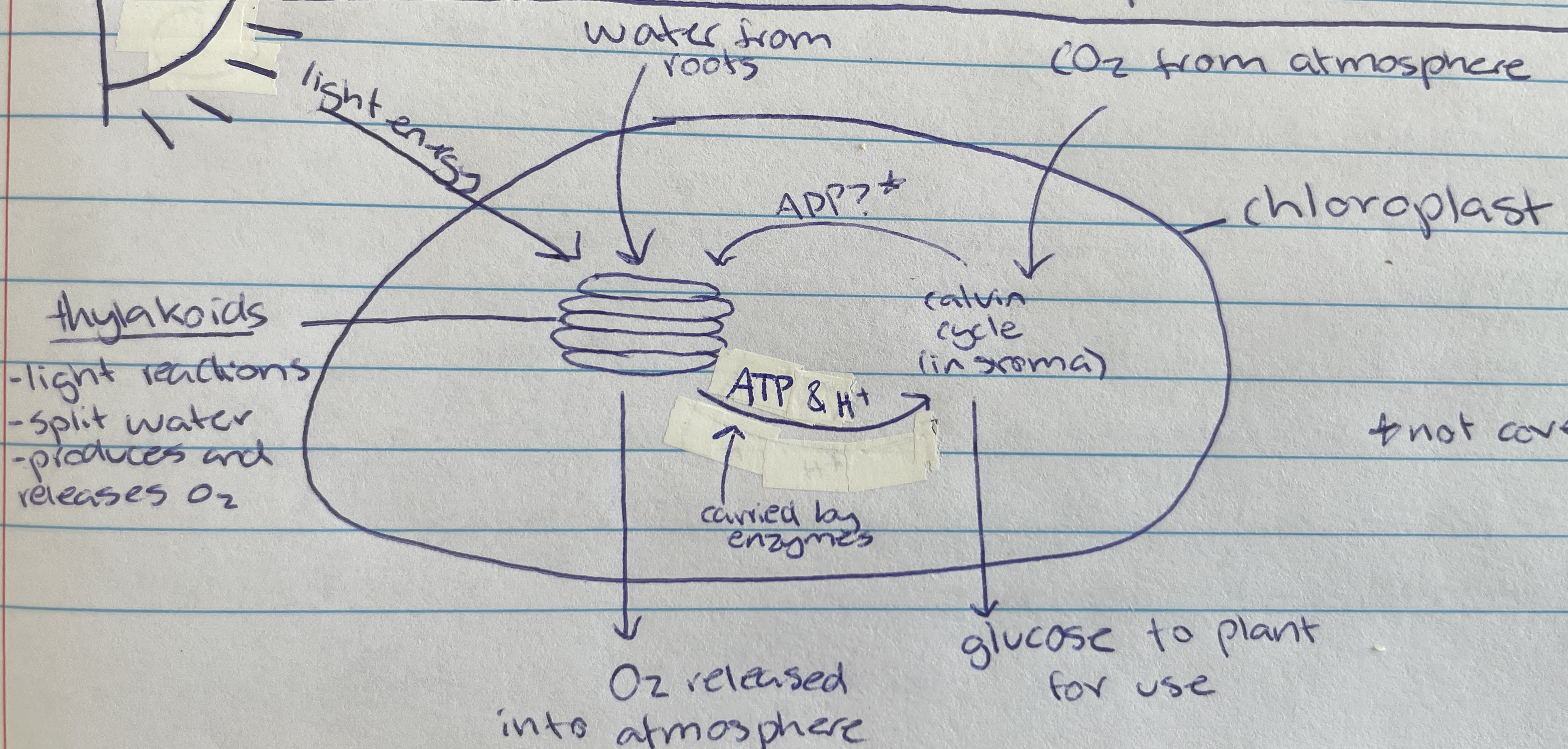
stroma
Light independent stage (LIS) occurs within the…
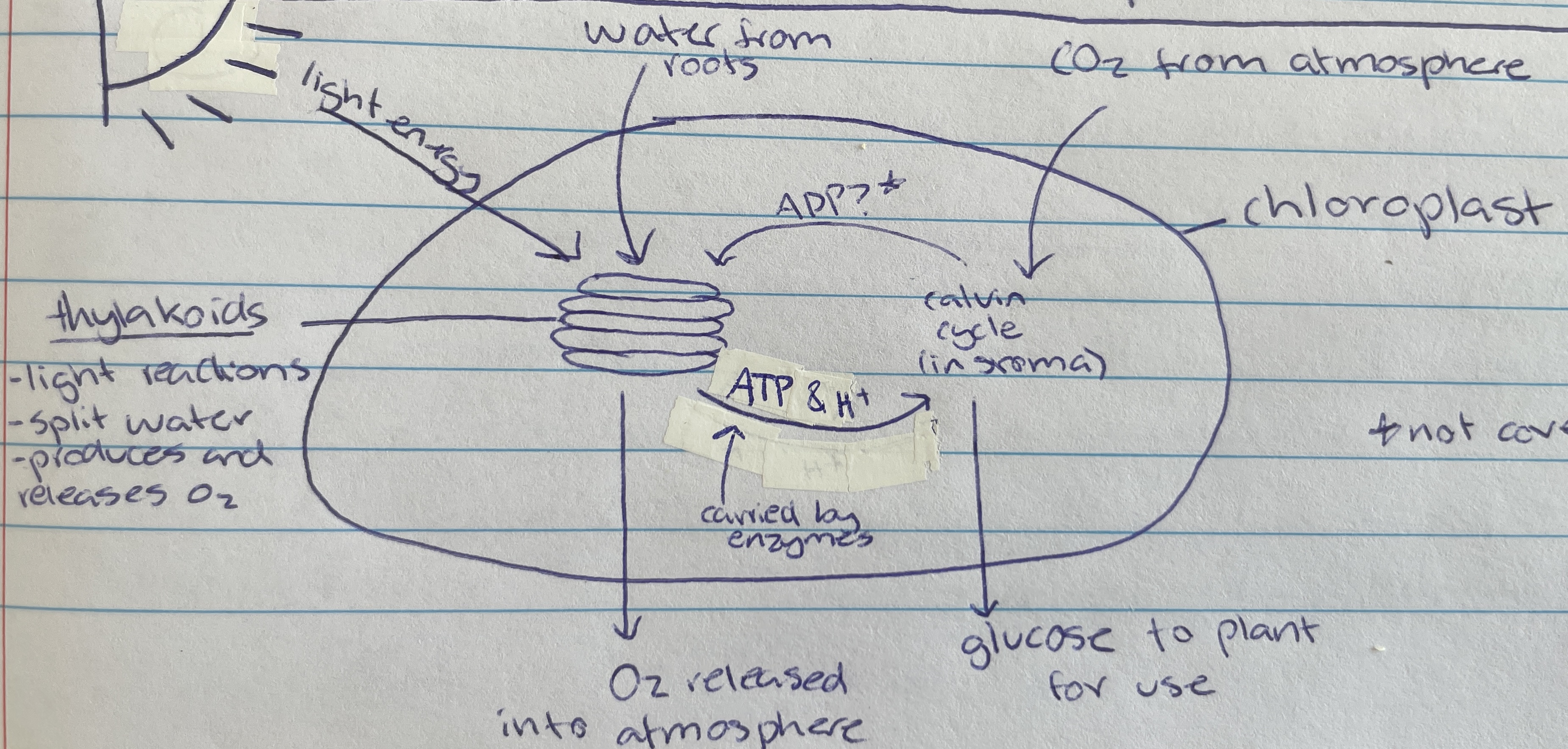
chlorophyll
In the thylakoid membrane and absorbs light energy - makes plants green (LDS)
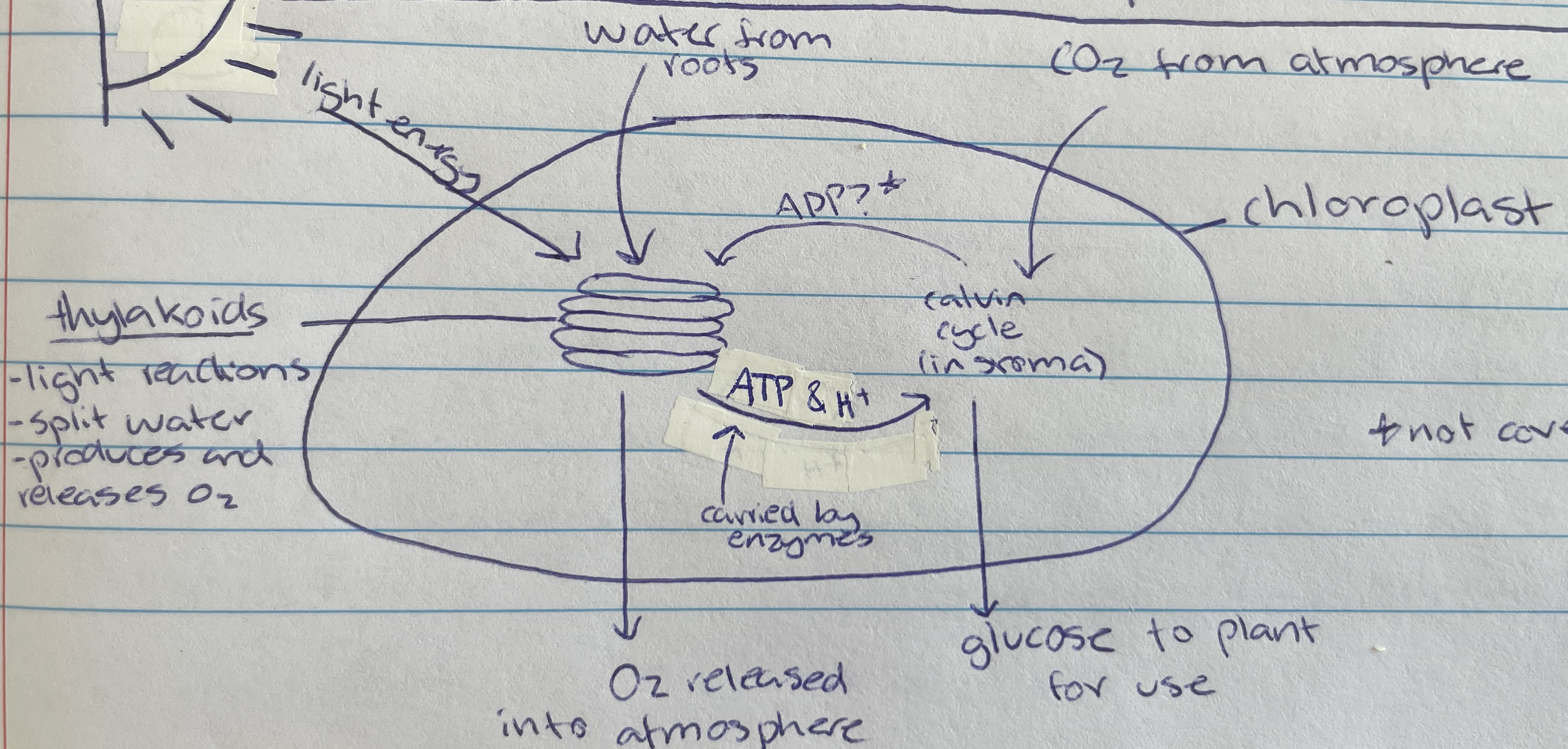
water
Taken in through the roots of the plant of the LDS of photosynthesis…
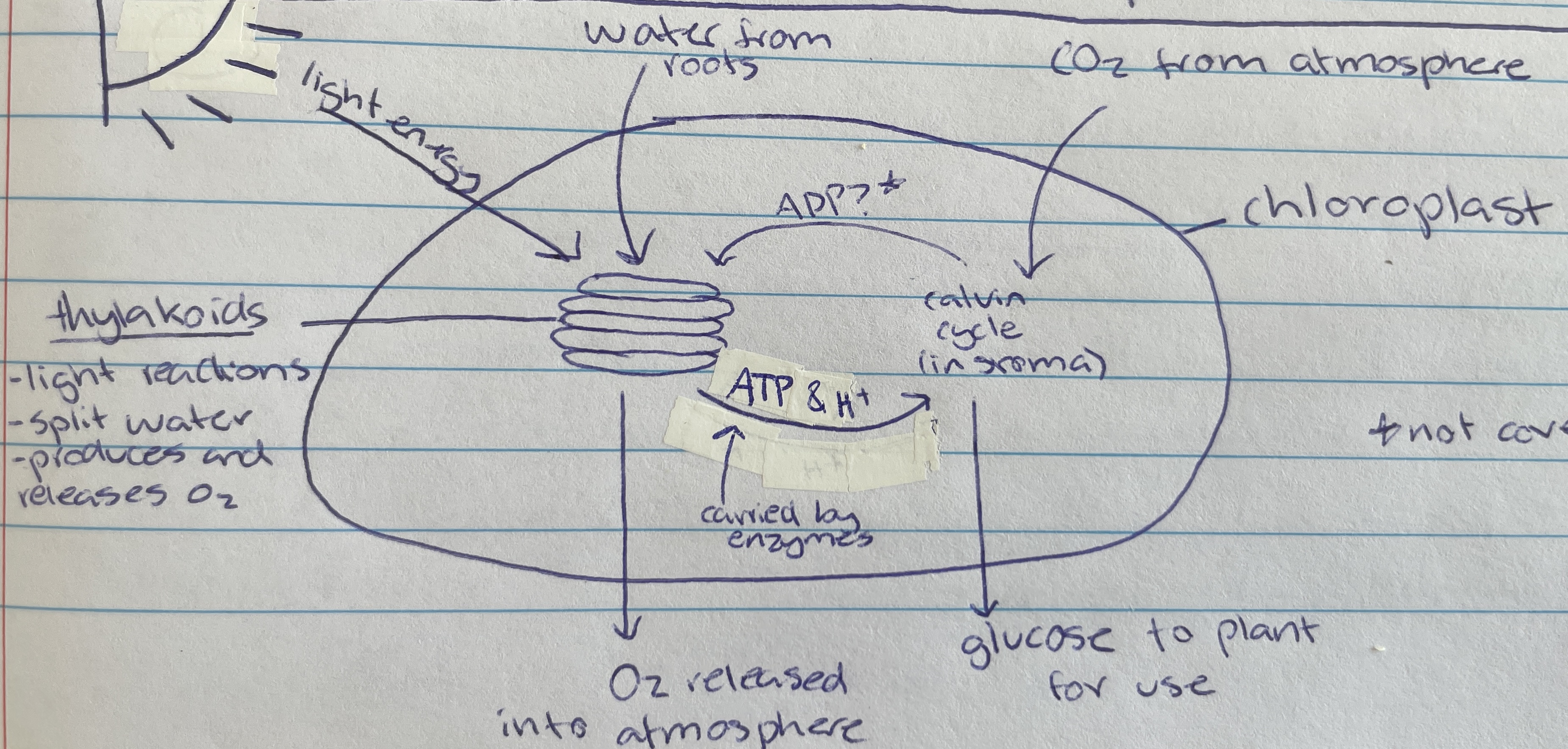
Photolysis
Process where light energy splits 12 water molecules to make 6 oxygen molecules, hydrogen ions and electrons (LDS)
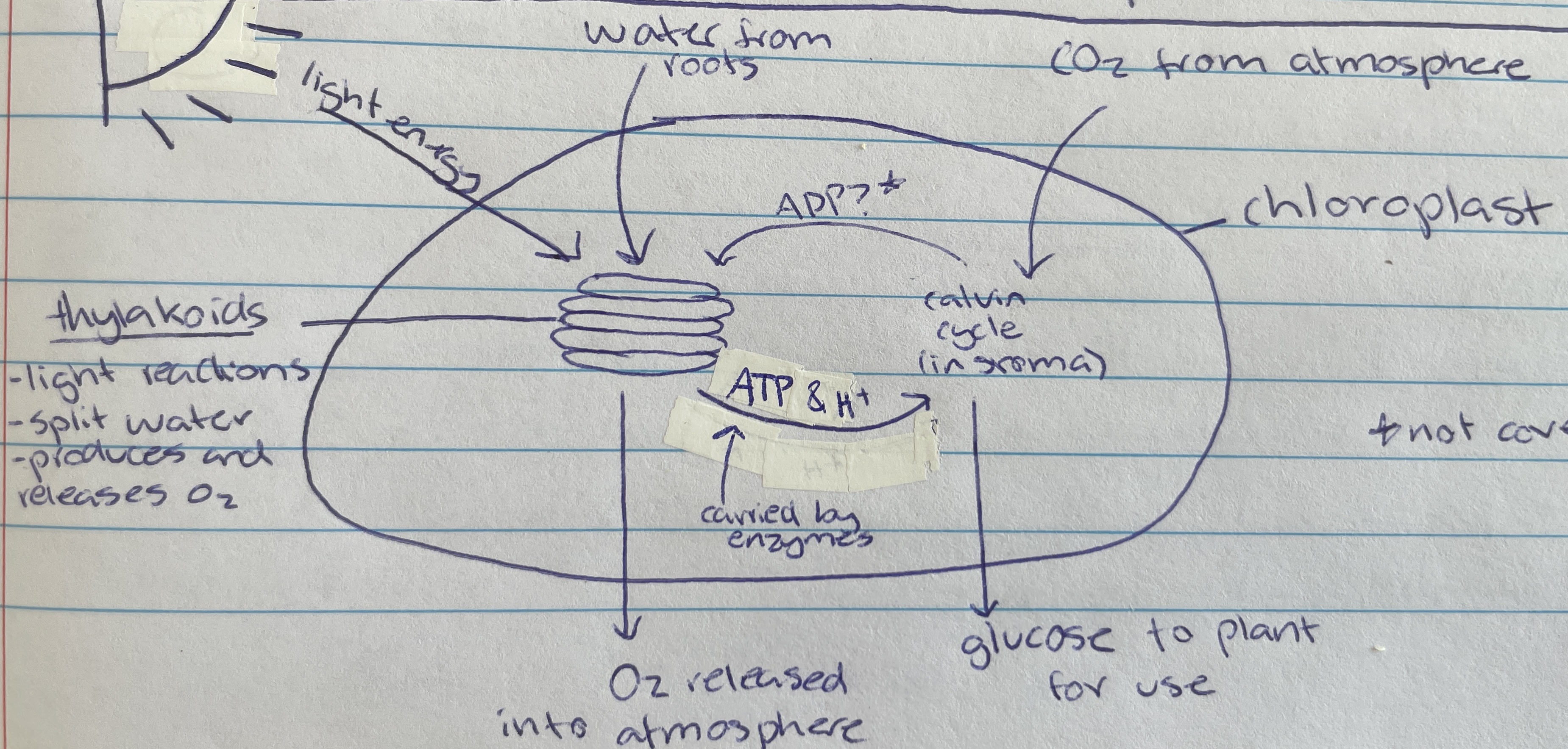
Oxygen
Waste product of photolysis (LDS)

ATP and H+
Useful product of photolysis (LIS) that enzymes carry to stroma for the light dependant stage
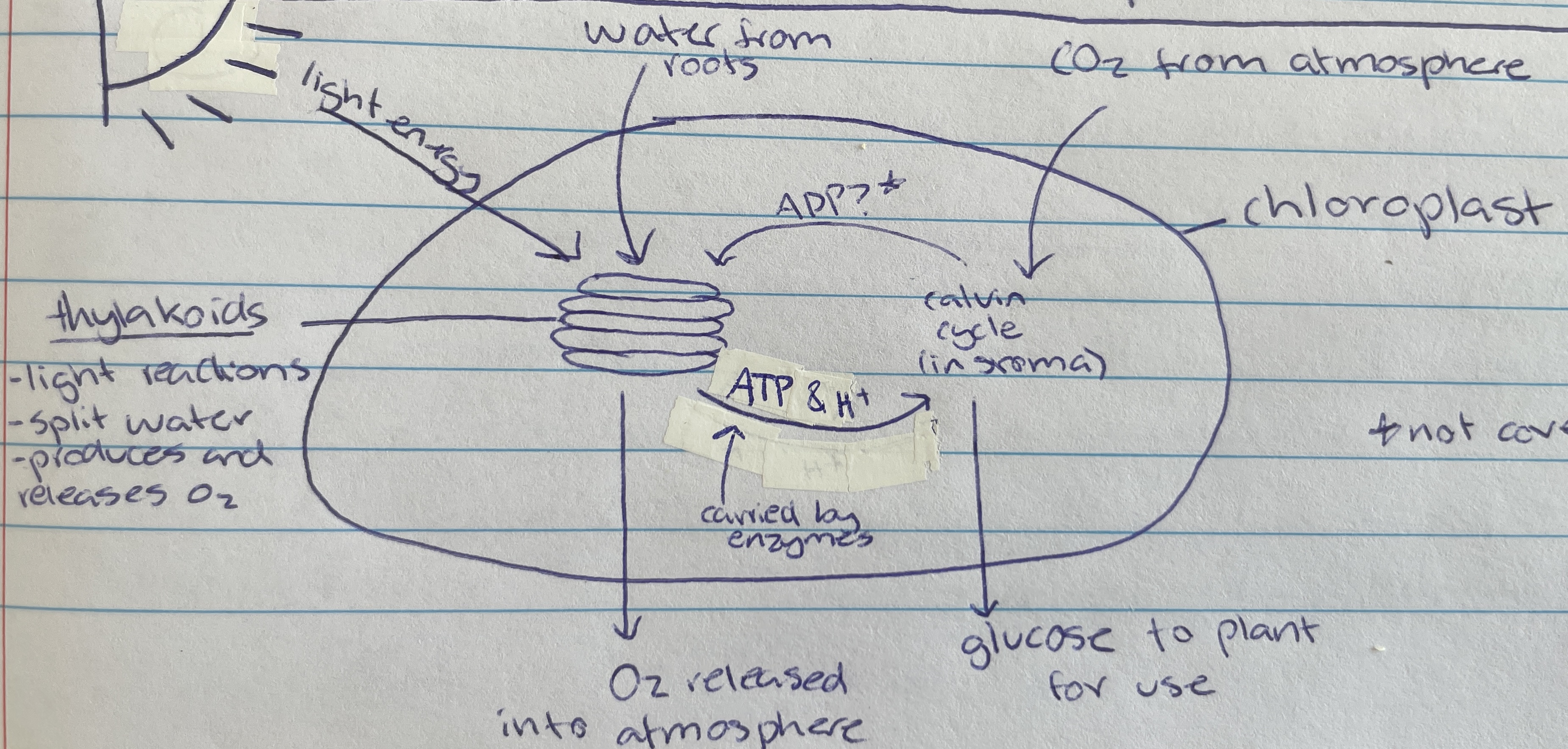
stroma
Most of the space of the chloroplast is filled with… (LIS)
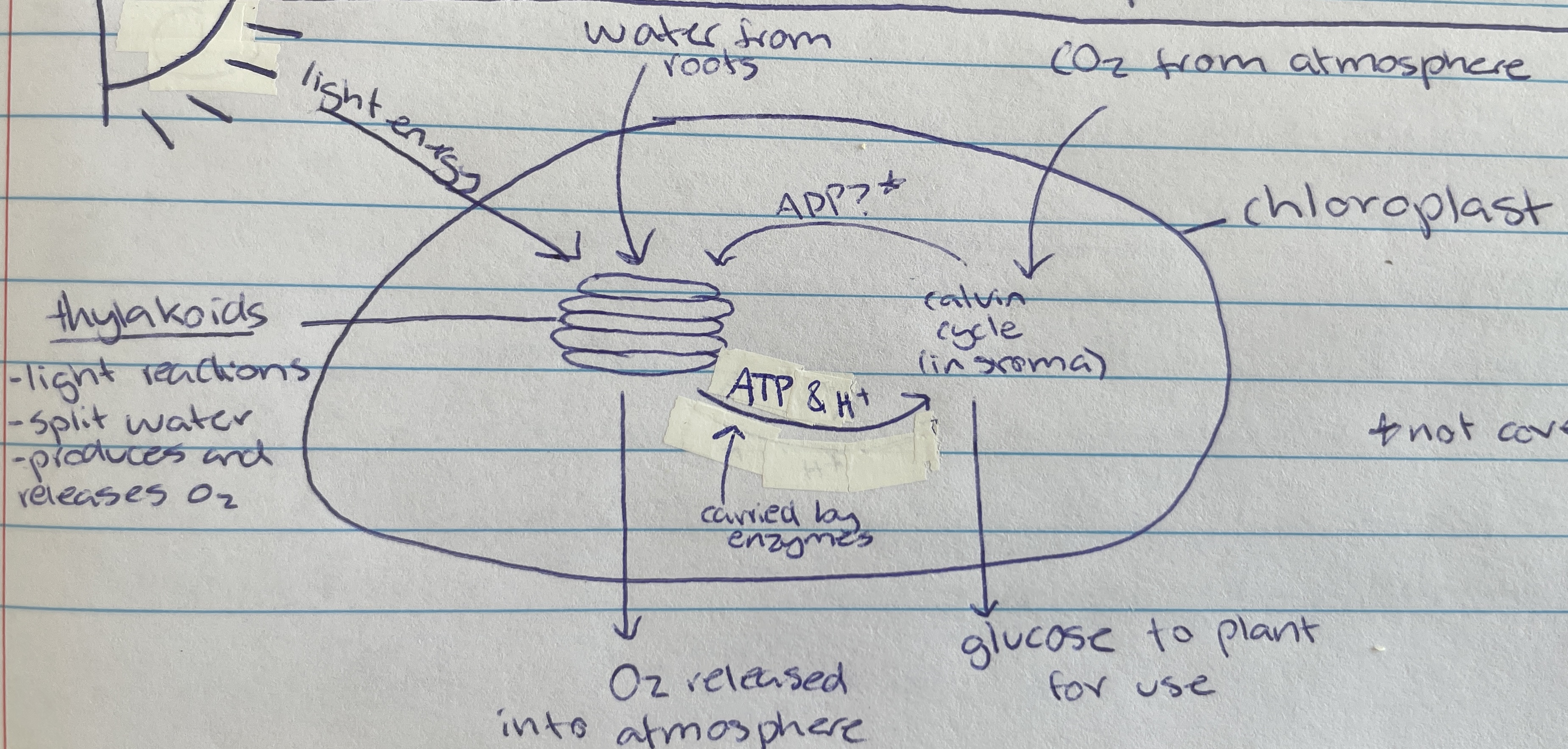
Carbon dioxide
Taken in through the stomata of the plant cell (from atmosphere) for the LIS of photosynthesis…
enzyme
6 CO2, ATP and H+ are used to create glucose through what type of reactions during the calvin cycle(LIS)
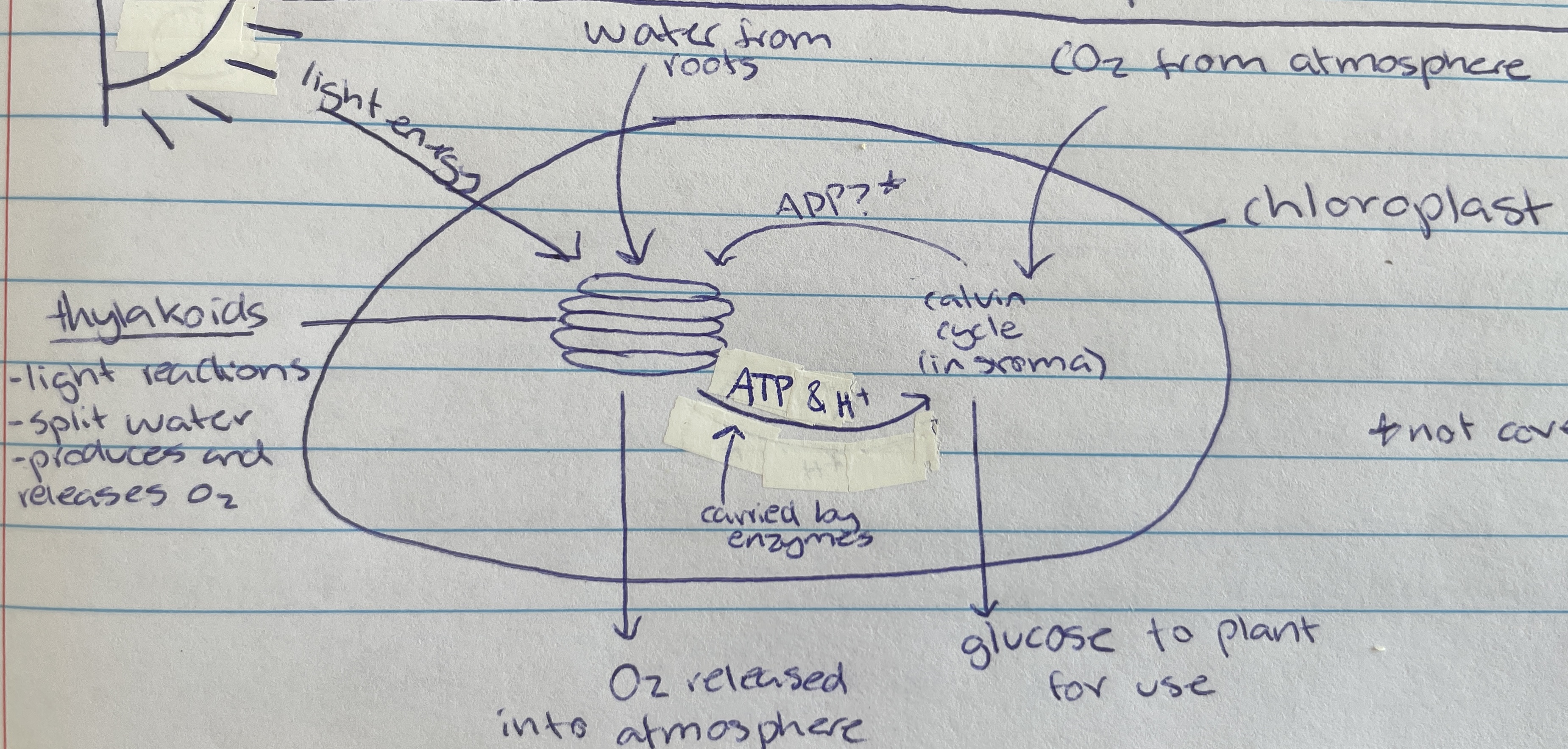
calvin cycle
Name of process in the LIS that creates glucose
Water
Formed as a waste product during the calvin cycle when making glucose (LIS)
Rate
In photosynthesis: measured through uptake of CO2 or production of O2 or glucose
Limiting factors
In photosynthesis: A reactant/substance that slows the rate - CO2 concentration, H2O, chlorophyll, light and temperature
wavelength and intensity
What aspects of light affect the rate of photosynthesis
Temperature
This graph indicates which limiting factor
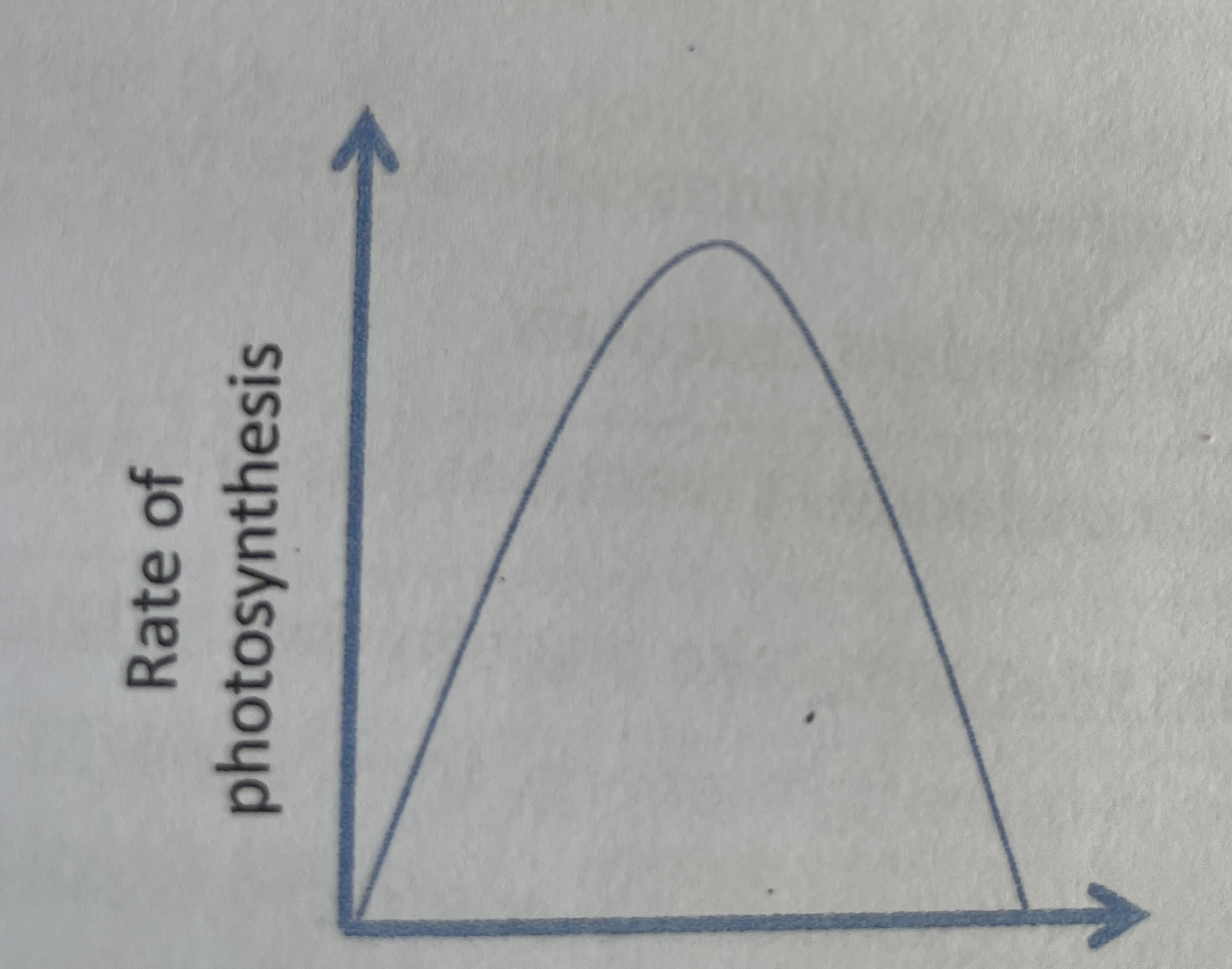
CO2 concentration and light intensity
This graph indicates which limiting factors (2)
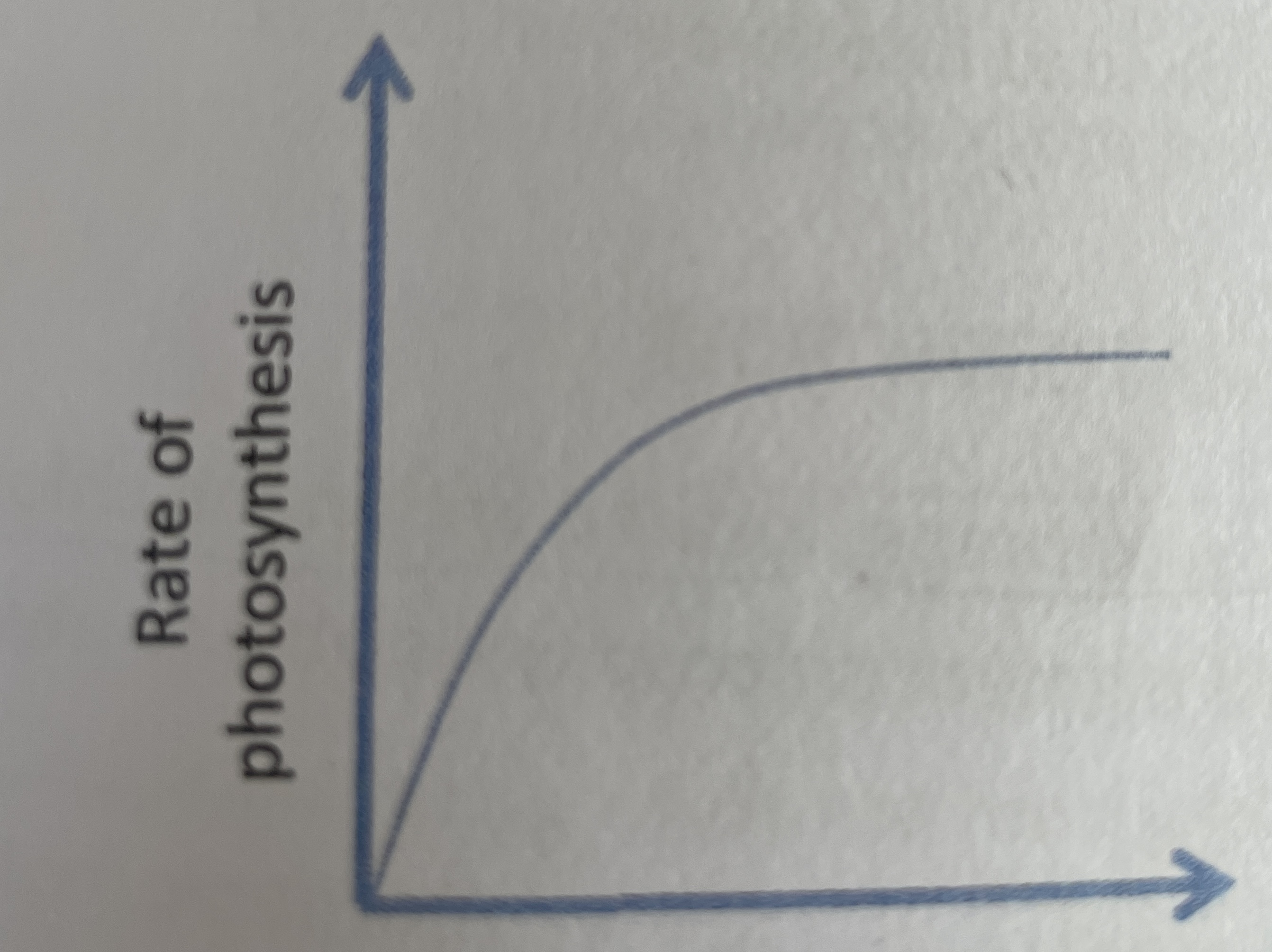
45
What is the optimum temperature for photosynthesis (degrees celsius)
Glycolysis
The break down of glucose into two pyruvate, 2 ATP and two NADH
Glycolysis
First stage of cellular respiration
Cytosol
Where does glycolysis occur in the cell?
Glycolisis
What stage is in both aerobic and anaerobic respiration? - does not need oxygen
Aerobic
Type of respiration that includes oxygen
Anaerobic
Type of respiration that does not include oxygen
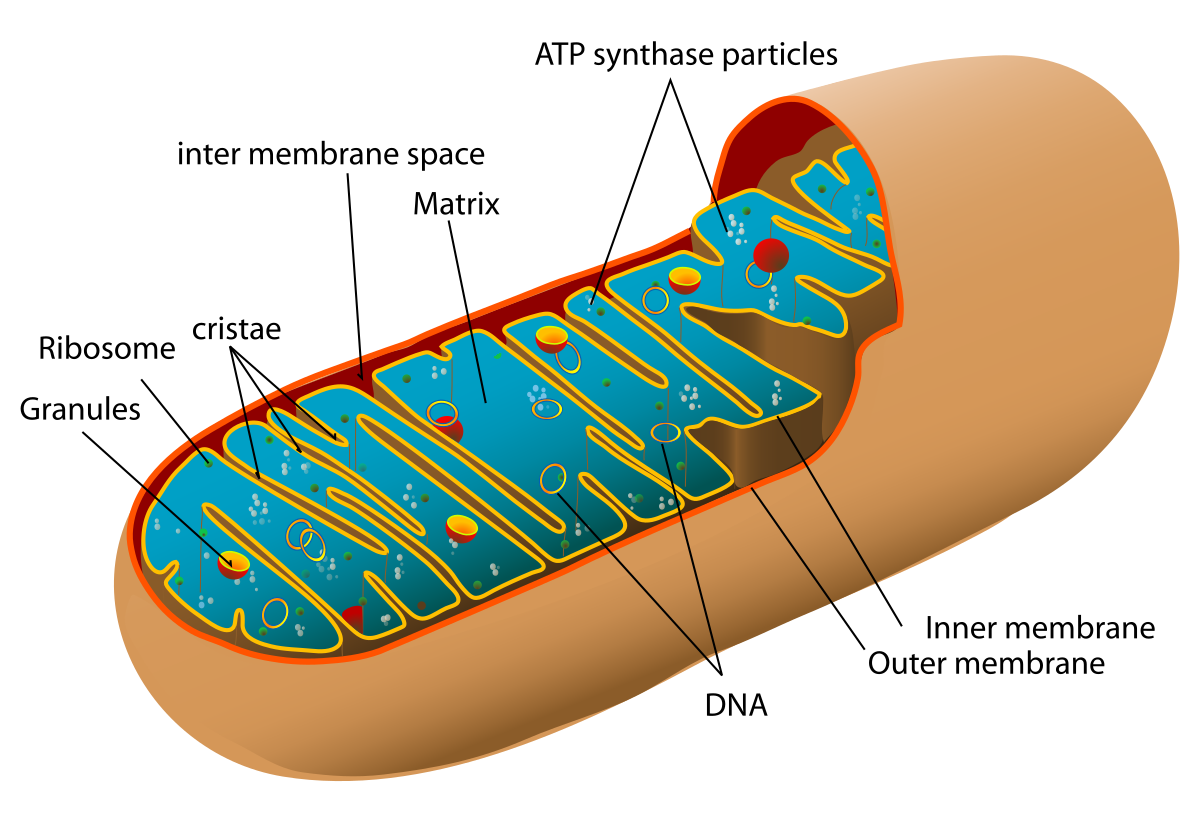
The mitochondria
Where is the krebs cycle and electron transport chain?
The matrix
What part of the mitochondria does the krebs cycle occur in?
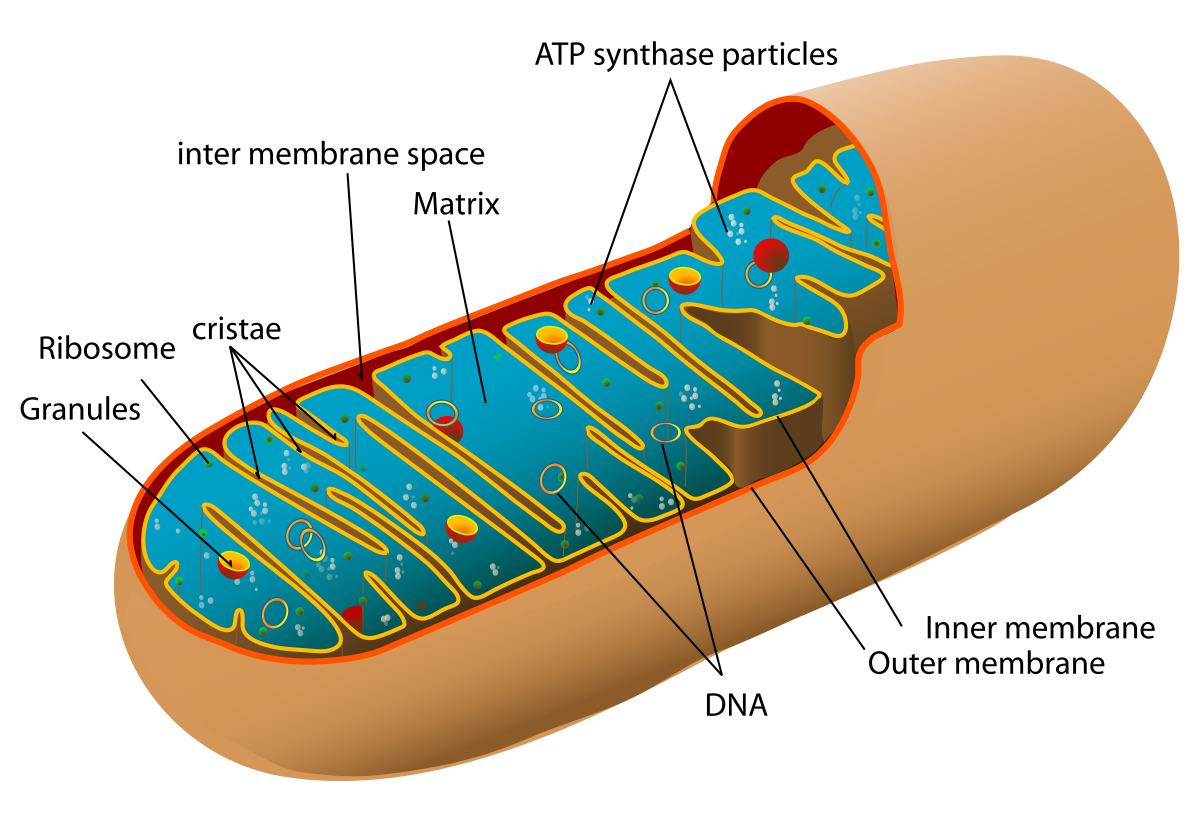
Cristae
What part of the mitochondria is the electron transport chain in?
acetyl coenzyme A
What is used in the krebs cycle after glycolysis (transformed from pyruvate)?
Two pyruvate
What molecules where converted into acetyl coenzyme A when transported from the cytosol to the matrix?
Krebs cycle
What stage uses an eight step enzyme controlled reaction series?
The Krebs cycle
The conversion of acetyl coenzyme A into 2 ATP, 8 H+ carrying coenzymes and CO2
Carbon dioxide
What product of the krebs cycle is waste?
NADH and FADH
Both types of H+ carrying coenzymes created during glycolysis and the krebs cycle
protein pumps
What the electrons released by the H+ carrying coenzymes power
cristae membrane
What are the protein pumps in? (location)
Electron transport chain
Stage of aerobic respiration that creates the most ATP
ATP synthase
Enzyme in the cristae membrane that is spun by the H+ ions to force a bond between ADP and Pi (smashed together) - electron transport chain
ADP and Pi
What is combined to create ATP in the ATP synthase molecule?
Water
What is created in the ATP synthase as a waste product? (oxygen is needed for the electron transport chain).
High hydrogen ion gradient
Why do the H+ ions move through the ATP synthase (from the inner membrane of the cristae to the matrix)?
32-34
Amount of ATP created by the electron transport chain
Anerobic
Type of respiration that takes place if there is no oxygen or not enough to meet demands
Anaerobic
Is anaerobic or aerobic respiration more inefficient (ATP production)?
Two
How many ATP does anaerobic respiration produce?
36-38
How many ATP does aerobic respiration produce?
NADH
The joining of H+ with NAD+ to makes what? (H+ carrying co-enzyme)
Ethanol and CO2
In fungi/plants the NADH give the H+ (electron) to the pyruvate to make what?
Lactic acid
In animals the NADH give the H+ (electron) to the pyruvate to make what?
no
Is the process for anaerobic respiration in fungi/plants reversible? (no/yes)
yes
Is the process for anaerobic respiration in animals reversible? no/yes
Oxygen increase
What causes the lactic acid to become pyruvate again?
toxic
Is the product of anaerobic respiration toxic or non-toxic?
non-toxic
Is the product of aerobic respiration toxic or non-toxic?
Limiting factors
In cellular respiration: Substrate/glucose, pH, temperature, mitochondrial density and O2 concentration are all what?
Cellular respiration
What produces ATP in a cell?
adenine
The base in ATP
phosphate
Three groups of what are attached to the ribose in ATP?
ribose
Another name for the pentose sugar in ATP
Adenosine
What do adenine and ribose make together?
electrons
The bonds between the phosphate in ATP contain a large amount of what?
adenosine triphosphate
ATP full name
hydrolysis
The process name in ATP where the end phosphate breaks off (bond breaks) releasing energy
ADP
What does ATP become after undergoing hydrolysis?
glucose
What provides the energy to reform ATP from ADP during reactions of cellular respiration?