analog electronics (all content)
1/200
Earn XP
Description and Tags
content from lectures 1 to 6
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
201 Terms
what are the 2 types of electronic signals
analog and digital
what is an analog signal
Continuous range of amplitude over time.
what is a digital signal
Discrete voltage over time
what is an Analog to Digital Converter (ADC)
Convert analog signal to digital signal
what is a Digital to Analog Converter (DAC)
Convert digital signal to analog signal.
what is the input of electronic systems
Measurement of physical quantities
what is an electronic system
Consists of electronic devices and components. Process electronic signals, interface between the sensors on the input side and actuators on the output side.
what is an electronic systems output
Vary other physical quantities
what are signal amplification types
voltage amplifier, current amplifier, power amplifier
what is a voltage amplifier
Increase the voltage level of the signal • High input impedance, low output impedance
what is a current amplifier
Increase the current level of the signal. • Low input impedance, high output impedance.
what is a power amplifier
Increase the power of a signal.
what are the functional types of amplifiers
operational amplifier, differential amplifier, instrumental amplifier, radio frequency
what is an operational amplifier
High-gain differential amplifier with feedback
what is a differential amplifier
Amplify the different between two signals
what is an instrumental amplifier
A precise differential amplifier with high CMRR.
what is a radio frequency amplifier
Amplify a signal for use over RF range
what are interstage coupling types of amplifier
RC-coupled, LC-coupled< Transformer-coupled, Direct-coupled
what is an RC-coupled amplifier
use a network of resistors and capacitors to connect stages of amplifiers
what is an LC-coupled amplifier
use a network of inductors and capacitors to connect stages of amplifiers.
what is a transformer-coupled amplifier
use transformers to match impedances to the load side and input side.
what is a direct coupled amplifier
use no interstage elements; each stage is connected directly to the following and preceding amplifier stages.
what are the frequency type amplifiers
DC amplifier, AF amplifiers, video amplifiers, ultra-high frequency
what is a DC amplifier
amplify signals from 0 frequency (DC) and above
what is an AC amplifier
amply audio signal from 20 Hz to 20 kHz
what is a video amplifier (frequency amplifier)
amplify signals up to a few hundred MHz.
what is an Ultra-high-frequency amplifier
amplify signal up to a few GHz.
what are the types of load amplifiers
audio amplifier video amplifier, tuned amplifier
what is an audio amplifier
audio type of load
what is a video amplifier (load type)
video type of load.
what is a tuned amplifier
amplify a single RF or band of frequencies
what is the system level design process purpose
Engineering systems are becoming increasingly complex. Transforms specifications into circuits.
what is the engineering design process
1. System designed using block functional block diagrams. 2. Circuit design 3. Device design
characteristic of conductors
Low resistivity, used in interconnects, electrodes
characteristics of semiconductors
Tuneable conductivity, core of transistors, diodes, ICs
characteristics of insulators
High resistivity, used in gates, capacitors, isolation
characteristic of semiconductor diodes
• Two-terminals: Anode and Cathode • Low resistance in the forwarded direction • High resistance in the reverse direction • Function as a controlled switch.
characteristics of Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT)
• Three-terminal: the emitter (E), the base (B), and the collector (C). • The arrowhead identifies the transistor as a npn or a pnp. • Operate as current-dependent devices. • Amplify of signals or switch.
Field-Effect Transistors (FET) characteristics
• Next generation of transistors • Three terminals: the drain (D), the gate (G), and the source (S). • Operate as a voltage-dependent device. →The drain (output) current depends on the input gate voltage
what are the other FETs technologies
• MESFET (Metal–Semiconductor FET): GaAs. • HFET: GaN or GaAs • IGFET, FinFET, DEFET,
characteristics of semi conductors
Conduct electricity more than insulators but less than conductors
what happens if semiconductors are faced with high temperature
becomes a conductors
what happens if semiconductors are faced with very low temperature
becomes an insulator
what material is the most common semiconductor material
silicon
what bonds dose silicon have
covalent
characteristics of covalent bonds
• Strong and stable • Hold two atoms together tightly. • Require high energy to break it down
what is the affect of higher temperature on covalent bonds
Higher temperature could break down the bonds free some electrons increase the conductivity.
what is the doping process
• Inject other elements to silicon structure
what dose the doping process result in
create more mobile charges in silicon.
what are the 2 types of doping
N-type, P-type
process of N-type doping
Inject small amount of another element whose atoms have one more valence electron,
result of N-type doping
Allow negative charged electrons moving around, conducts current
whats P-type doping
Inject small amount of another element whose atoms have one less valence electron
result of P-type doping
Allow positive charged “holes” moving around, conducts current
characterisitics of forward direction in a ideal diode
• Zero resistance • Zero voltage drop • Infinite forward current
characteristic of reverse bias in ideal diodes
infinite resistance, zero current
what are the types of methods to analyse practical diode circuits
• Graphical Method • Approximate Method • Interactive Method • Mathematical Method
benefits of graphical method
Help to understand the concept of Q-point and the mechanism of the diode circuit analysis.
disadvantages of graphical method
• Not convenient for analysis. • Rarely used
benefits of approximate method
• Adequate for many applications • Useful as a starting point for a circuit design.
disadvantages of approximate method
• Does not take the nonlinear characteristic into account. • Result in approximate solution.
what are the types of models for diode circuits
• constant-drop DC model, • piecewise linear DC model, • low-frequency AC model, • high-frequency AC model, or • SPICE diode model.
why do we model practical diodes
In practice, multiple diodes are used in a circuit therefore diode circuits become complex• Analysis by the graphical or iterative method becomes time-consuming and laborious. • To simplify the analysis and design, diodes can be modeled
what is the constant-drop DC model
The constant-drop DC model assumes that a conducting diode has a voltage drop 𝒗𝑫 that remains almost constant and is independent of the diode current,
what is the piecewise linear DC model
The diode characteristic can be represented approximately by a fixed voltage drop 𝑽𝑻𝑫 and a straight line. This model represents the diode characteristic approximately by two piecewise parts: a fixed part and a current-dependent part. A piecewise linear.
what is the Low-Frequency Small-Signal Model
The operating point, which consists of both a DC component and an AC signal, will vary with the magnitude of the AC signal.
What happens if the reverse voltage of a diode exceeds the breakdown voltage?
The diode operates in the breakdown region, where reverse current increases rapidly and diode voltage remains nearly constant.
How does a Zener diode behave in the forward direction?
Like a normal diode.
How does a Zener diode behave in reverse if vd<Vz
It offers very high resistance, acting like a normal reverse-biased diode.
How is the reversed Zener characteristic approximated?
As a fixed voltage VZ0 and an ideal diode in series with Zener resistance RZ, with vD=VZ0+RZiZ
What is a Zener regulator?
A circuit where the Zener diode maintains constant voltage across terminals, used as a voltage reference diode (shunt regulator).
Is Zener voltage dependent on current?
No, VZ is independent of reverse current iD=−iZ
What is line regulation?
The ability of the Zener regulator to maintain constant output despite changes in supply voltage.
What is load regulation?
The ability of the Zener regulator to maintain constant output despite changes in load current
What is the rule of thumb for selecting iZ(min)
Choose iZ(min) as 10% of the maximum current.
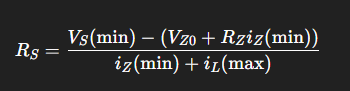
what is this formula used for
finding the Zener current lower bound
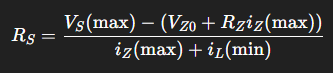
what is this formula used for
to find the zener current upper bound
how is the Zener diode modeled in limiters?
As a piecewise linear characteristic: forward direction VD0+RD, reverse direction VZ0+RZ
What are typical values of RZ and RD?
Very small, typically ~20 Ω, often neglected in analysis.
How is a symmetrical limiter made?
By connecting two Zener diodes in series opposing each other.
How does an unsymmetrical limiter with a Zener diode work?
when Vs is greater than VD0 the output is limited to VD0. when VS is less than -VZ0 the output is limited to -VZ0
How does junction temperature affect VZ?
Zener voltage changes with temperature, ~2 mV/°C, opposite to forward-biased diode.
How can temperature effects be minimized?
Connect Zener diode in series with a forward-biased diode—their temperature coefficients cancel out.
What happens to small-signal Zener diodes under power?
Power is low (milliwatts), junction temperature stays safe.
how is temperature reduced in power diodes?
They are mounted on heat sinks to keep junction temperature below limits.
When must a diode be derated?
If ambient temperature is above specified value.
Can a diode handle more power if ambient temperature is lower?
Yes, it can handle higher power.
What does a diode rectifier do?
Converts AC voltage to unidirectional DC voltage (AC–DC converter).
What are the most common diode applications?
Rectifiers.
What are the two main classifications of rectifiers?
Single-phase rectifiers and three-phase rectifiers.
Why is a transformer used in rectifiers?
To step AC input voltage up/down to required DC output.
How many diodes are required for single phase full wave bridge rectifier
4 diodes
for Single-Phase Full-Wave Bridge Rectifier what is the power factor assuming no loss
PF=1.0
dose Single-Phase Full-Wave Bridge Rectifier provide electrical isolation
no
What do rectifier outputs consist of?
A DC component and harmonics (cosine terms).
What is the role of filters?
Smooth the output by reducing ripple, producing nearly pure DC.
What are the three types of filters?
L filters, C filters, LC filters.
What do L filters oppose?
Changes in output current.
Which applications are L-filters generally used for?
High-power DC supplies.
What do C filters oppose?
Changes in output voltage.