Biology Exam #1
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Biology
study of life
The Properties of life
-composed of cells
-complex and ordered
-Respond to environment
-can grow and reproduce
-obtain and use energy
-main internal balance
-allow evolutionary adaptation
cell
Basic and smallest unit of life
Life
is complex and organized in hierarchical levels
Hierarchical levels
Population, Community, Ecosystem, Biosphere
Emergent Properties
New properties present at one level that are not seen in the pervious level.
the scientific method
Observation, Question, Hypothesis, Prediction, Design(expirnment), data collection, Analysis, Interpretation
Parts of a scientific paper
abstract, introduction, methods, results, discussion
abstract
provide complete summary of paper
Introduction
provides background information and lists hypothesis or predictions
methods
details of the experiment
Results
section provides the results of the study.
discussion
interprets the result/places then into the boarder context of the literature
Hypothesis
a possible explaination of an observation
3 things a hypothesis must have:
- must be tested to deretermine its vaildity
- often tested in many different ways
- allows for predictions to be made
A hypothesis can never be proven...
It can only be acccepted or regected
A scientific theory
-a body of interconnected concepts
-supported by much evidence and reasoning
-expresses ideas of which we are most certain
Primary Sources/ literature
report original findings and ideas
Secondary Sources/literature
put together from primary sources / literature (a review)
peer review process
scientist-editor-reviewer (and back)
Science
process that involves hypothesis-prediction approach
Technology
tools, products, often derived from science.
Ecology
The study of how organisms relate to one another and to their environment
Biotic environment
other organisms (living)
Abiotic Environment
non-living (ex. light, water, temp.)
Homeostasis
a steady-state internal environment regardless of external environment
warm blooded animals - Endotherm
steady internal environment if outside changes.
cold blooded animals - Ectotherm
body temp depends on weather its cold or hot outside (they match)
Physiological Response
is quick, involuntary response of body, (ex. sweating, shivering)
morphological capabilities
slower, what they look like,(ex. thick coat during winter)
Behavioral Response
what they do, (ex. moving from one habitat to another)
Population
groups of individuals that belong to the same species and live in the same area
what are the two important questions about a species?
What Species
Where are they?
Demography
quantitative study of populations
- # of individuals in a population & how it changes
- how population size changes through time
demography questions
are they reproducing?
health of species?
How is system changing?
extinction?
two types of population growth
exponential and logistic
exponential growth
(no limits)
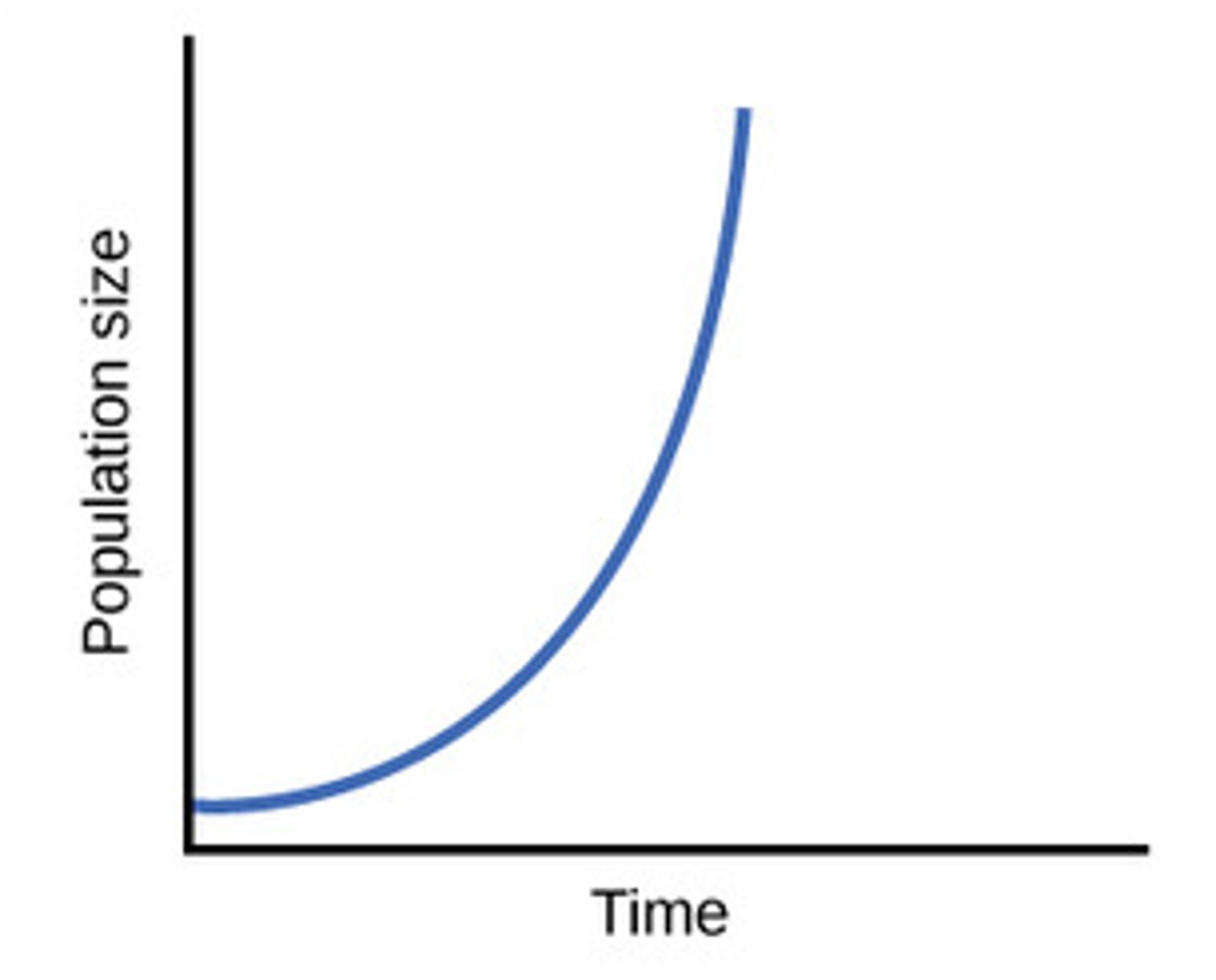
logistic growth
(limited)
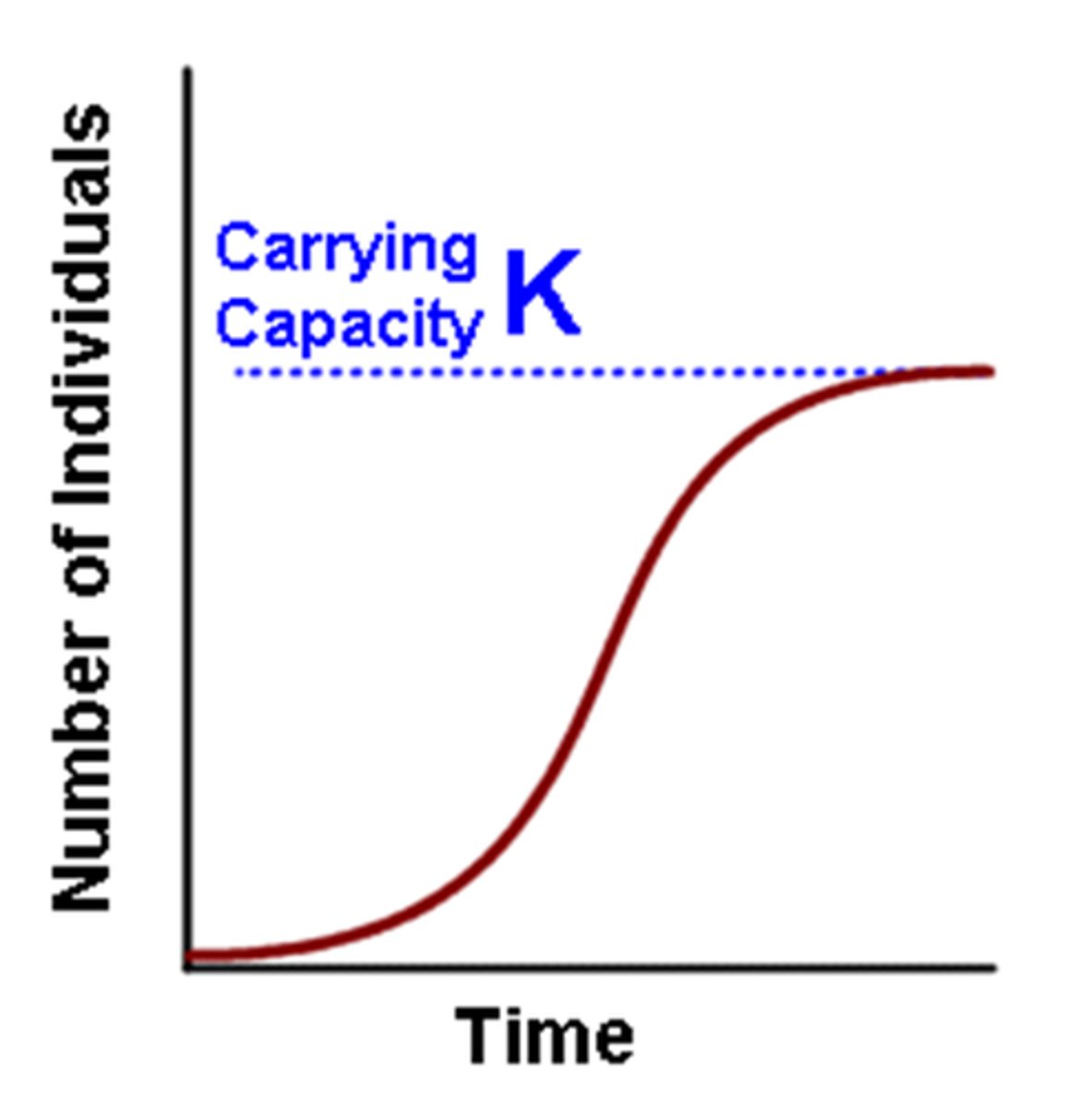
Increase
births
decrease
deaths
carrying capacity
The largest population that an area can support
r = ( b-d ) + ( i-e )
- R = growth rate
- b = birth rate
- d = death rate
- i = immigration
- e = emigration