MCAT Physics/Chemistry Tests
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
In extraction purification, which compound will remain in the organic layer and which will remain in the non organic layer?
Nonpolar molecules will move to the organic layer and polar molecules will move to the nonorganic layer
Are ionic compounds polar?
yes
Avogadro’s number
6.02 × 1023
Normality
is the number of equivalents of reactive species per liter of solution, for which we must define the reactive species. Often used to express the concentration of H+ or OH− ions produced in acid-base reactions
Ex. HCl generates one equivalent of H+ ions and one equivalent of Cl− ions per mole
H2SO4 generates two equivalents of H+ ions and one equivalent of SO42− ions per mole.
Do cations and anions have smaller atomic radii?
cations
Atomic radius trend on the periodic table
Down and Left
Electronegativity trend on the periodic table
Right and Up
Ionization energy trend on periodic table
Right and Up
Ionization energy
the energy required to remove an electron from a isolated atom
Electronegativity
an atom’s tendency to attract electrons when it is already in a bond
Fatty acid chain structure
carboxyl group with a hydrocarbon chain and a methyl group at the end
Radioactive decay
The process by which an unstable atomic nucleus spontaneously loses energy by emitting radiation. The loss of energy results in the nucleus becoming more stable, often transforming the atom into a different element
What are the four kinds of radioactive decay?
Alpha decay, beta (+ and -) decay, gamma decay, and electron capture
alpha decay
In this mechanism of decay, an alpha particle containing two protons, two neutrons, and two electrons
beta minus decay
In this mechanism of decay, a neutron is converted into a proton in the nucleus, and a β− particle (an electron) is ejected to maintain charge balance
beta plus decay
In this mechanism of decay, a proton is converted into a neutron and a β+ (positron) molecule is emitted to preserve charge
gamma decay
This mechanism of decay involved the emission of a high energy photon (gamma ray) from an excited nucleus
electron capture
In this mechanism of decay, a proton in the nucleus grabs an electron, converting a proton into a neutron.
Why can ions not cross the cell membrane?
Ions are charged particles, making them hydrophilic
Magnetic field strength equation
B = µoI/2r
B is the field strength
µo is the permeability of space (a constant)
I is the electrical current through the circuit
R is the radius of the loop.
Work equation
W = Fdcos(ø)
Work-Energy Theorum
this theory states that work is equal to the change in kinetic energy of a system
W=∆KE
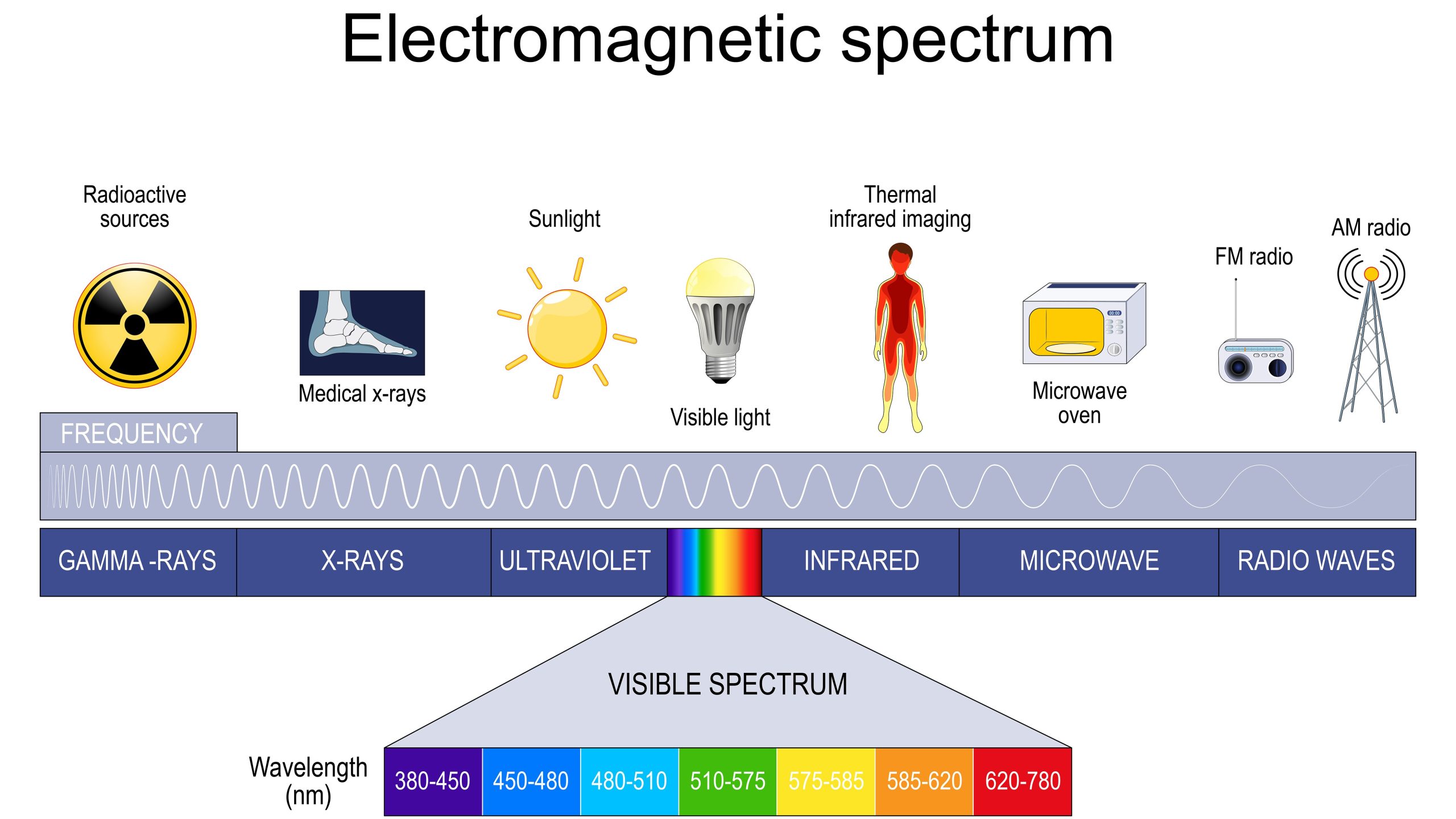
Electromagnetic spectrum
Kinetic energy formula
KE = 1/2mv2
Formulas for power
P = W/t
P = F v
surface tension
a force that should be understood as the property of the surface of a liquid that allows it to resist an external force
what makes a good nucleophile?
an electron-rich species that is effective at donating a lone pair of electrons to an electron-poor atom.
Nucleophilicity is governed by four main factors: charge, electronegativity, steric hindrance, and solvent
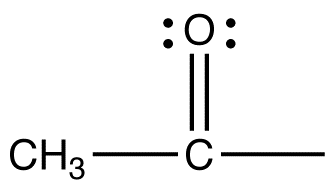
acetyl group
Relative reactivity
alcohols and ethers< aldehydes and ketones < amides < esters and carboxylic acids < acid halides
imine

specific gravity
a dimensionless constant referring to how dense a substance is compared to water, defined as ρ/ρwater
sulfonyl

urea

How to calculate pH
[H+] = 0.1 M = 1 x 10-1 M
pH = -log[1 x 10-1] = 1
pOH = 14-pH
viscosity
resistance to flow
Poiseuille’s law
used to describe laminar flow of incompressible fluids through a long cylindrical tube.
Contains 5 variables:
the flow rate (Q), the pressure drop between both ends of the tube (ΔP), the radius of the tube (r), the length of the tube (L), and the viscosity (η)