Session 1: Microbiota
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Microbiota
Community of microorganisms that live in a specific environment (living in and on our bodies)
Microorganisms can commonly be found in what anatomical locations of a human body?
Skin
Gut
Mouth
Lungs
The normal flora or microbiota are microorganisms that are regularly found at anatomical sites in humans and do not cause ___
Infection or disease
What is the microbiome?
Collective genomes of the micro-organisms in a particular environment (collection of all their genetic maternal - RNA/DNA)
What four important beneficial roles does the human microbiota have on health?
1) Digestion
Digesting carbohydrates
Producing vitamins/enzymes needed for digestion
2) Immunity
Microorganisms in gut help regulate immune function and protect against harmful pathogens
3) Mental health
Gut-brain axis = gut microbiota linked to anxiety and depression
4) Weight management
Some gut bacteria help prevent obesity via breaking down dietary fat and increasing energy expenditure

Name the four dominant phyla in the human gut (microbiota)?
FBAP = Firm Bacteria Active Protest
1) Firmicutes
2) Bacteroidetes
3) Actinobacteria
4) Proteobacteria
Most microbiota bacteria belong to which genera?
Fusobacterium
Eubacterium
Two main ways in which microbiota are acquired?
1) Vertical transmission from mother
2) Horizontal transmission from sources OTHER than parents e.g., diet/environment
In vertical transmission of microbiota to baby, what are the two main sources of microbiota for the baby?
1) Mother's vaginal bacteria
Onset of labor leads to rupturing of membranes
GBS bacteria travels up the vagina to amniotic fluid
GBS bacteria can also transfer as baby moves down birth canal during labour.
Aspiration of GBS bacteria into baby's lungs
2) Mother's gut bacteria
Baby exposed to GBS bacteria from contact with maternal fecal matter during birth process.
Would having a C-section rather than a vaginal delivery impact the microbiota of the baby?
Yes
As certain vaginal and gut bacteria from the mother are transferred to the baby via vertical transmission. This occurs during vaginal delivery.
Early-Onset GBS Disease
A common bacterium found in the vagina and rectum of healthy women.
However, an infant infected with this bacteria can develop sepsis, pneumonia, or meningitis in a condition known as...
What type of bacteria is GBS?
Gram positive
Beta-hemolytic bacterium

GBS is a common colonizer of the human ___ and ___ tracts
GBS is a common colonizer of the human gastrointestinal and genitourinary tract
GBS can cause severe disease in what demographics of people?
Young infants
Pregnant women
Older adults
Immunocompromised/immunosuppressed adults
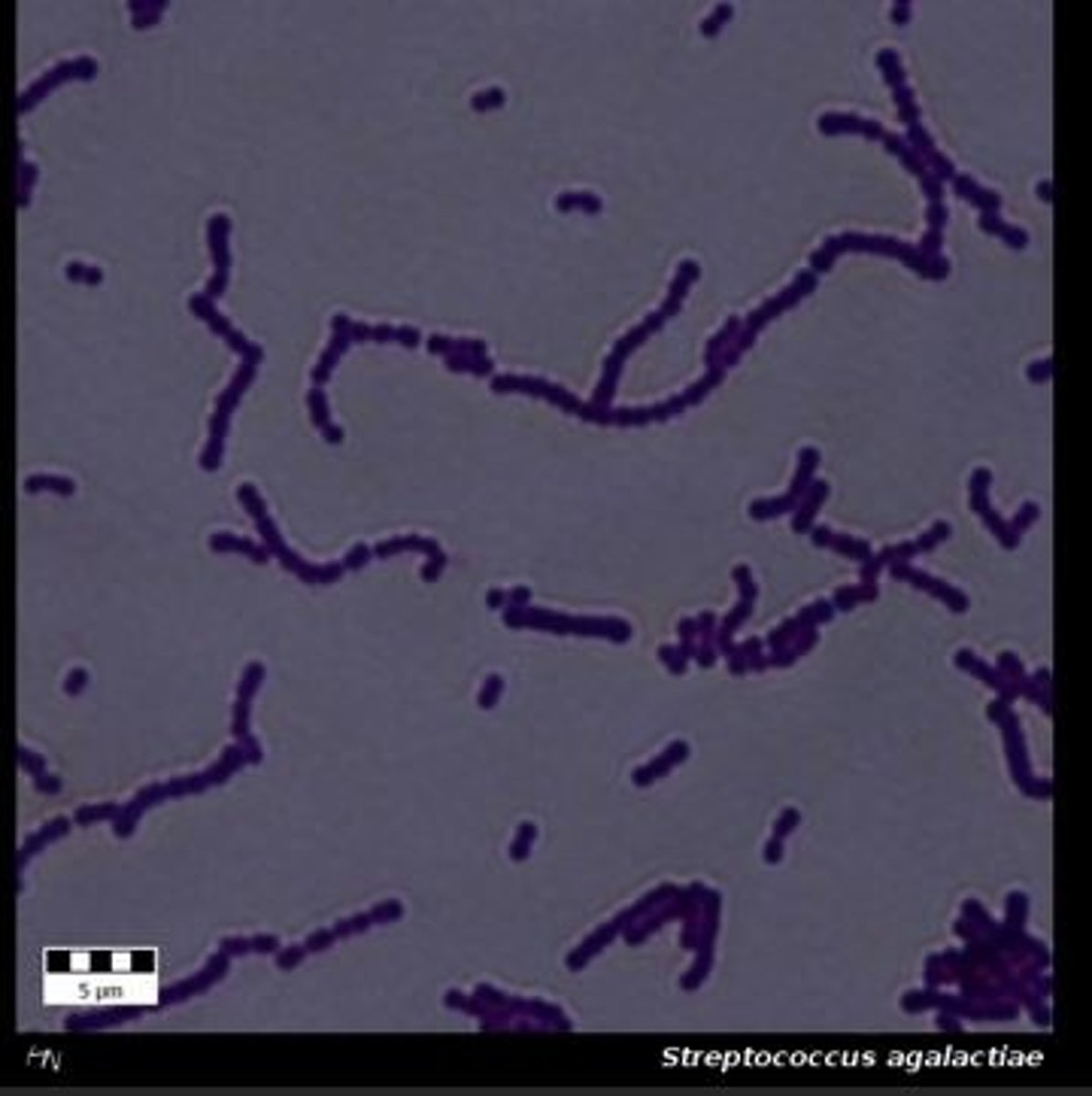
What bacteria is this image showing?
Group B Streptococcus (GBS)
or Streptococcus agalactiae
What is beta hemolysis?
Complete lysis of red blood cells.
Some bacteria produce hemolysin enzymes which break down hemoglobin in RBCs leading to lysis of RBCs.
E.g., GBS is a beta-hemolytic bacteria
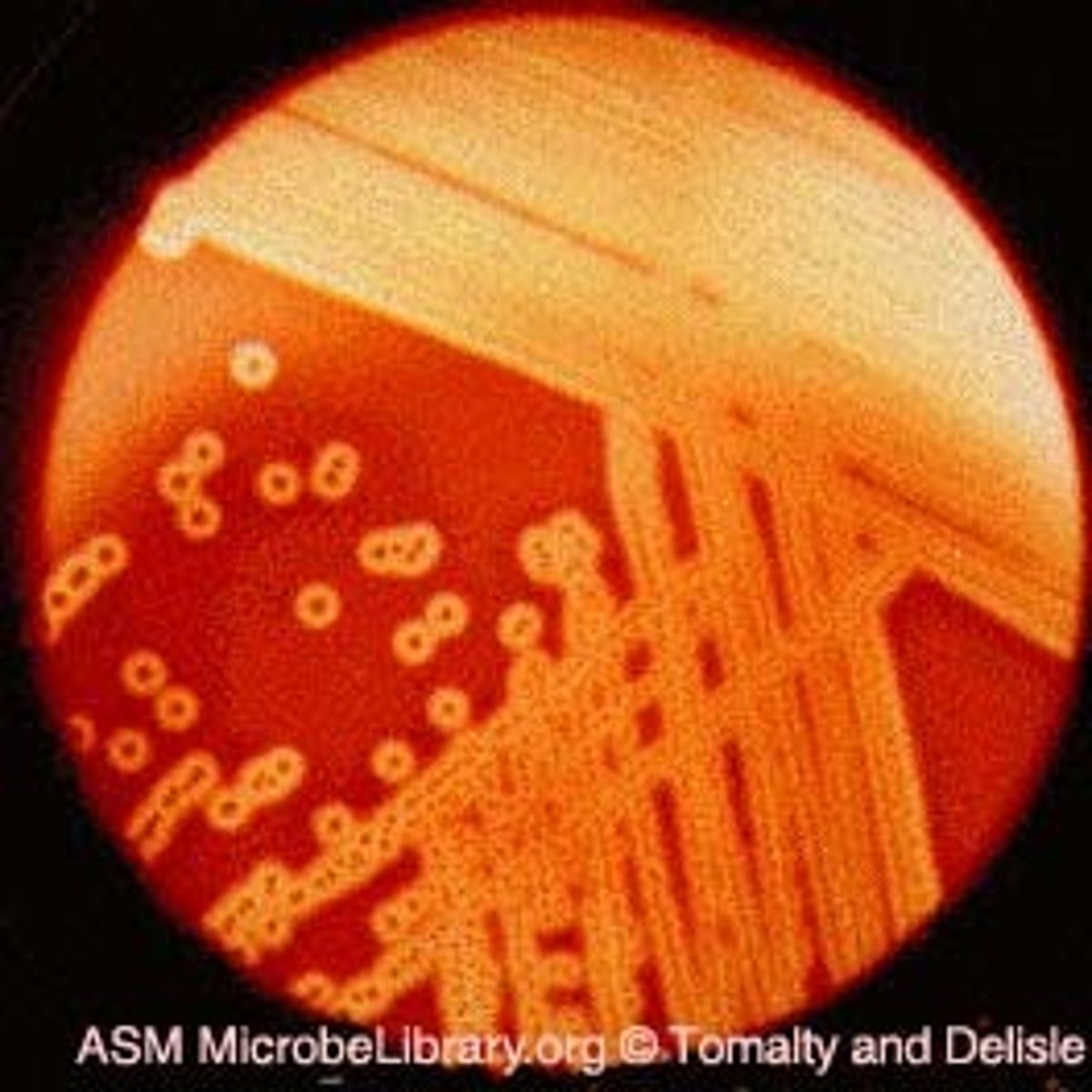
Why is beta hemolysis important in microbiology?
Diagnostic tool
Beta hemolytic bacteria (e.g., GBS) will produce clearing on blood agar mediums around the bacterial colonies on samples in the lab. This is due to production of hemolysin enzymes which break down the hemoglobin in RBCs leading to lysis (clearing).
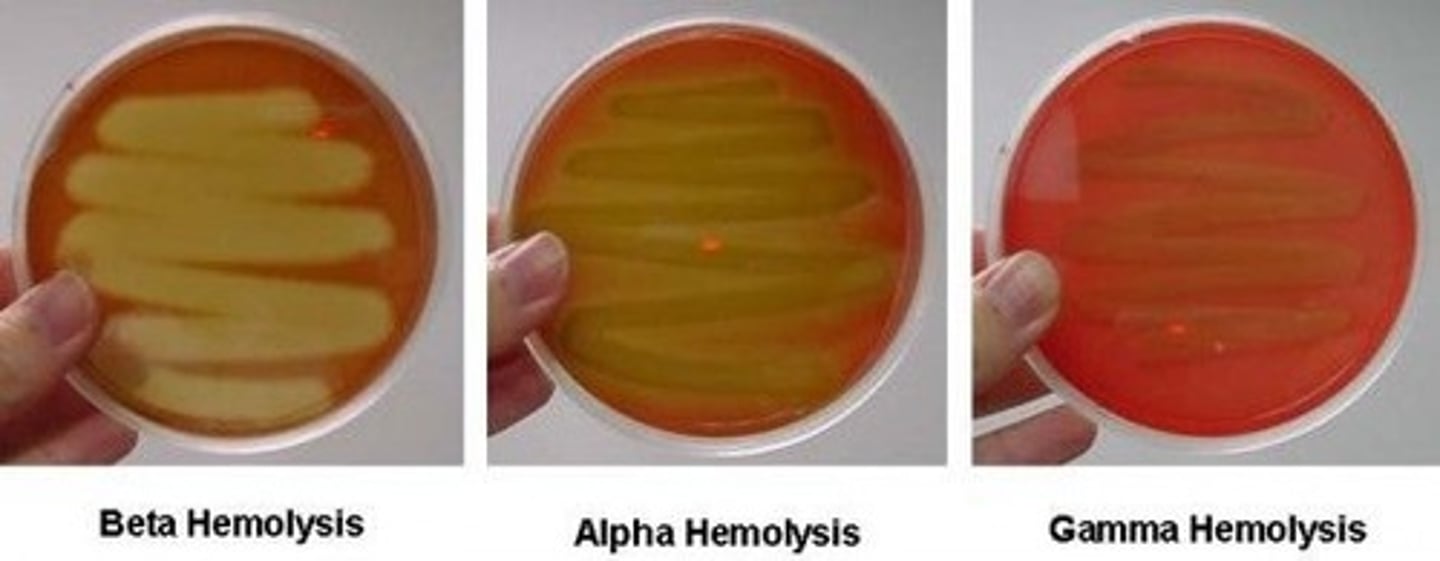
Beta hemolysis is the strongest
Alpha hemolysis is weaker
Gamma hemolysis is weakest
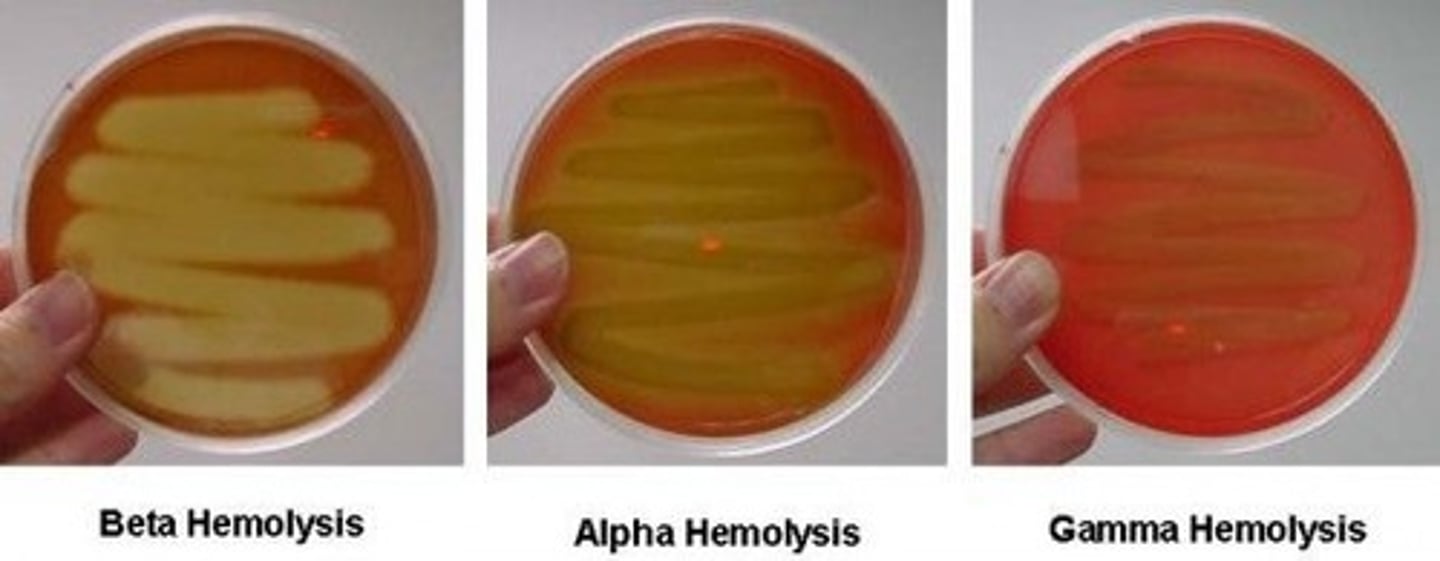
What condition can GBS lead to in minority of newborns?
Early-onset GBS disease
Leading to early-onset sepsis, pneumonia or meningitis

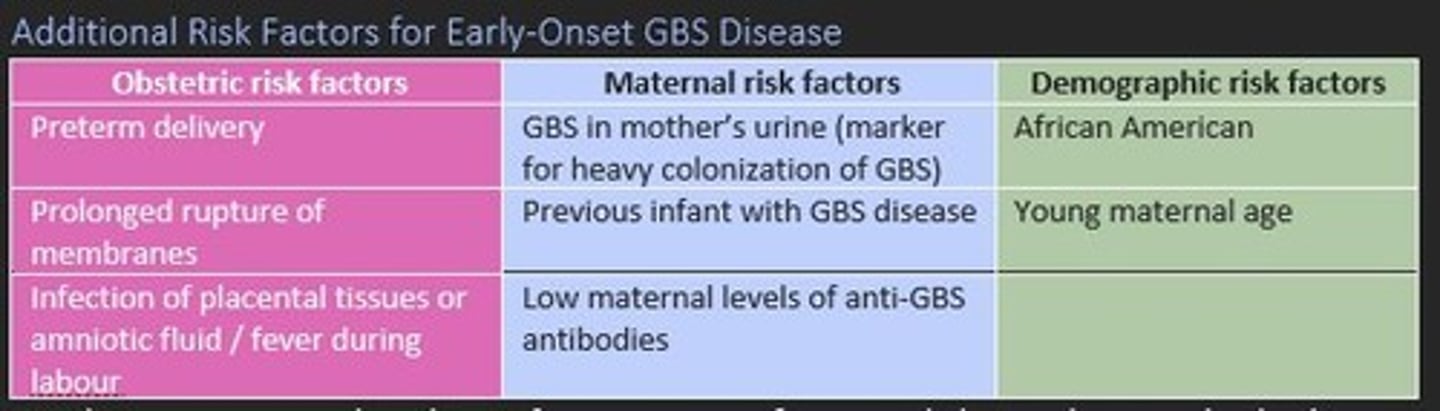
Risk factors for early-onset GBS disease
Obstetric
- Preterm delivery
- Prolonged rupture of membranes
- Infection of placental tissues/amniotic fluid
Maternal
- GBS in mother's urine
- Previous infant with GBS disease
- Low maternal levels of anti-GBS antibodies
Demographic
- African american
- Young maternal age
One of the major factors involved in horizontal transmission of microbiota is...
Diet
What types of microorganisms found in gut microbiome?
1) Symbiotic organisms
2) Opportunistic pathogens
3) Commensal organisms
The microbiota plays a major role in...
1) Digesting food
2) Absorbing/synthesizing some nutrients
3) Delivering variety of growth-promoting and growth-inhibiting factors that influence health
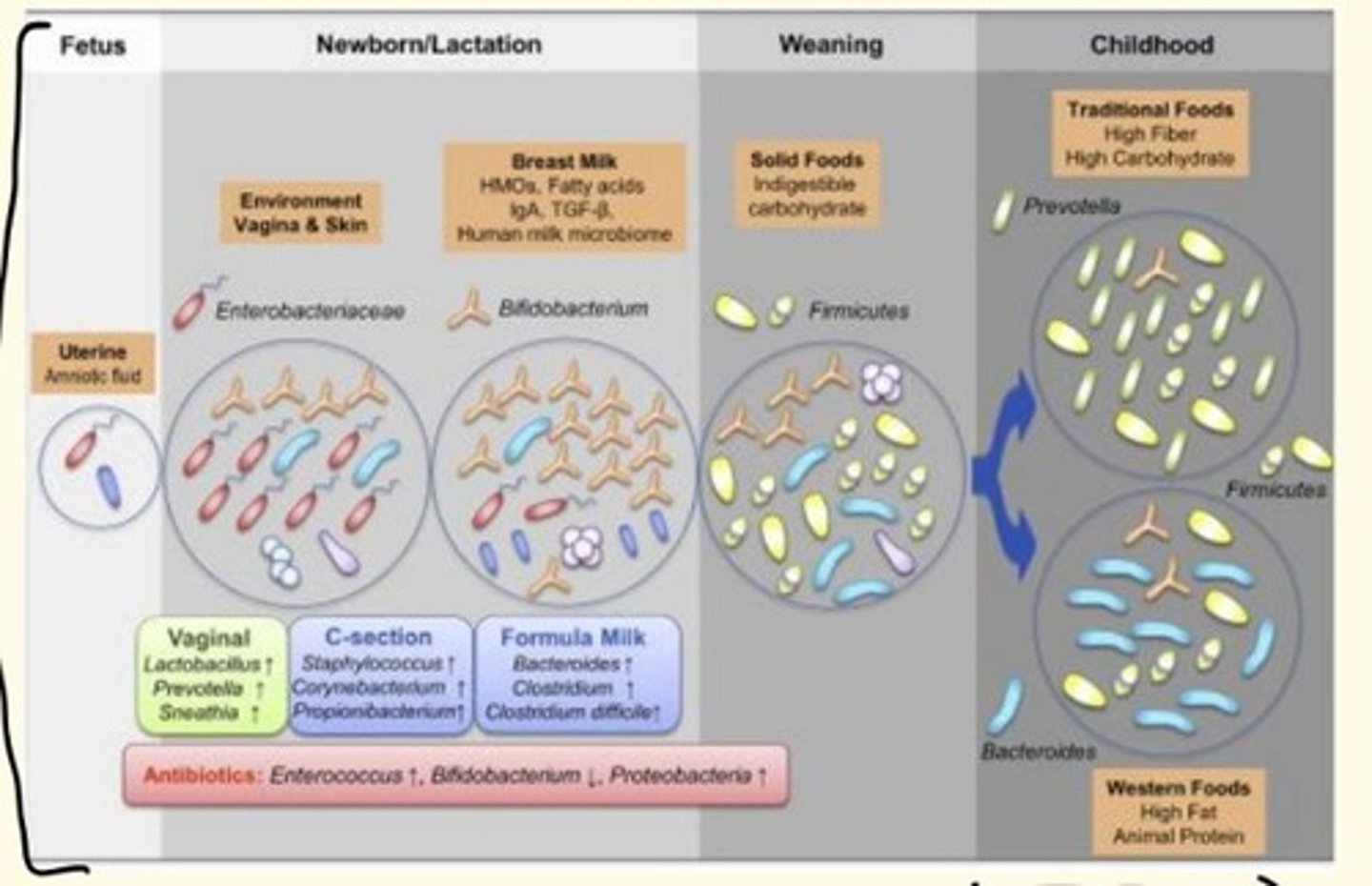
Babies that are breast-fed can have different microbiota than babies that are bottle-fed.
True or false?
True
What is a biofilm
Small community of microbes (microbial community) enclosed by extracellular material such as mineral crystals, blood and other substances.
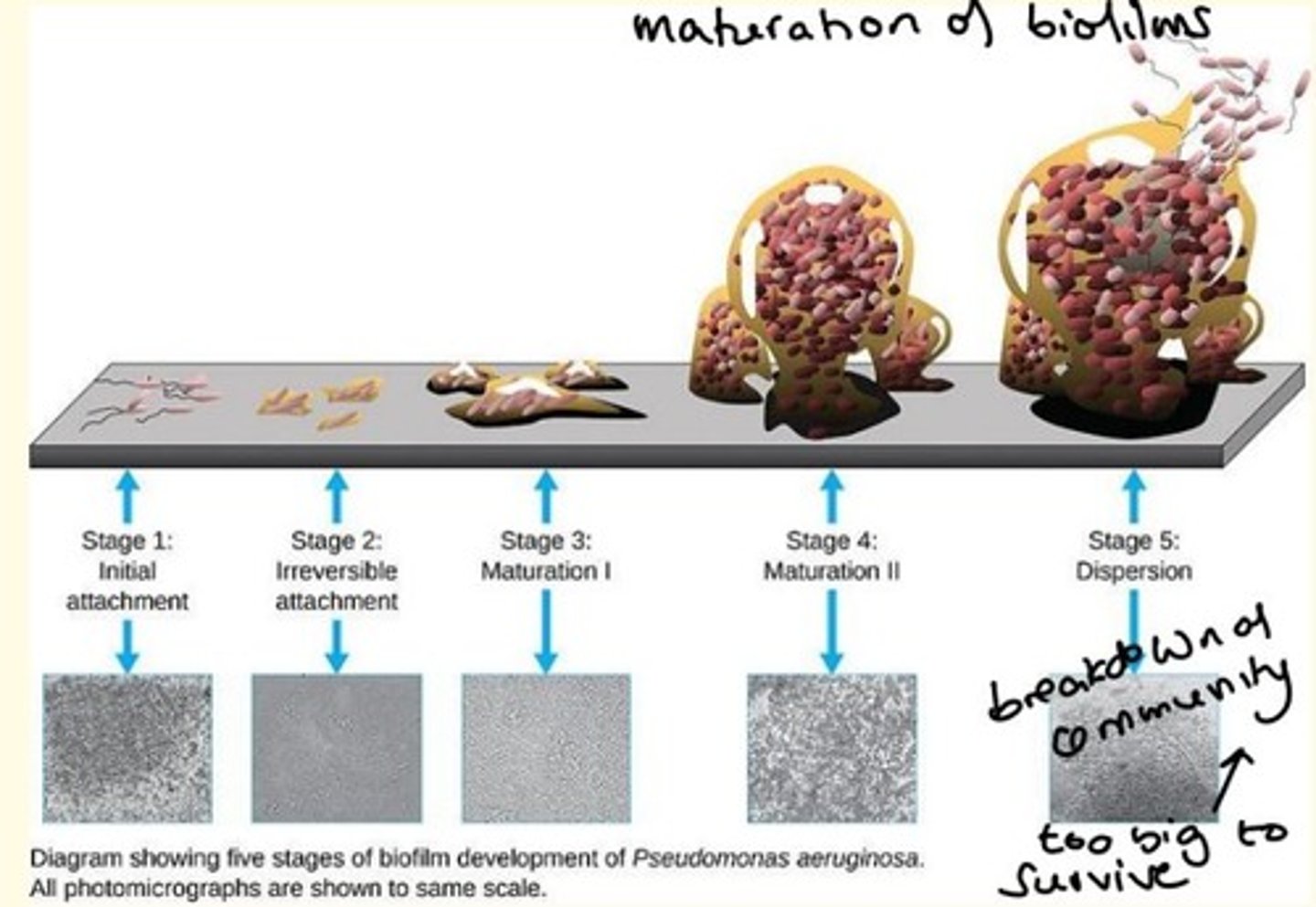
Where do biofilms typically form?
1) Medical devices
2) Surfaces
What do biofilms secrete?
Biofilms secrete slimy substance called extracellular polymeric substance (EPS)
This acts like a glue which allows them to irreversibly attach to a surface.
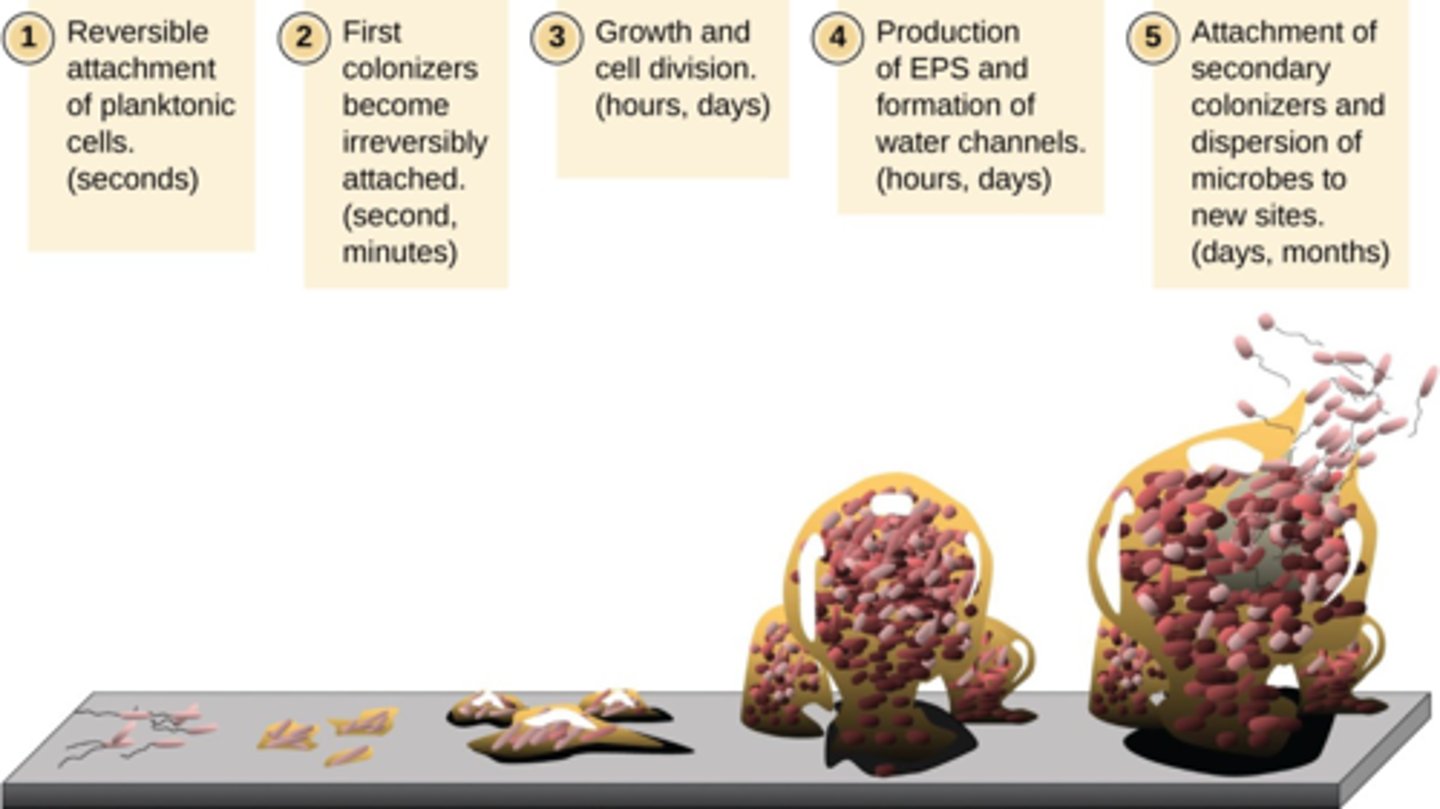
Why are biofilms important in infectious disease?
Bacteria in biofilms are often protected from antibiotics
Bacteria within biofilms have increased resistance to antimicrobial drugs (antibiotic resistance)
Biofilms encompass over ___% of microbial infections
>80%
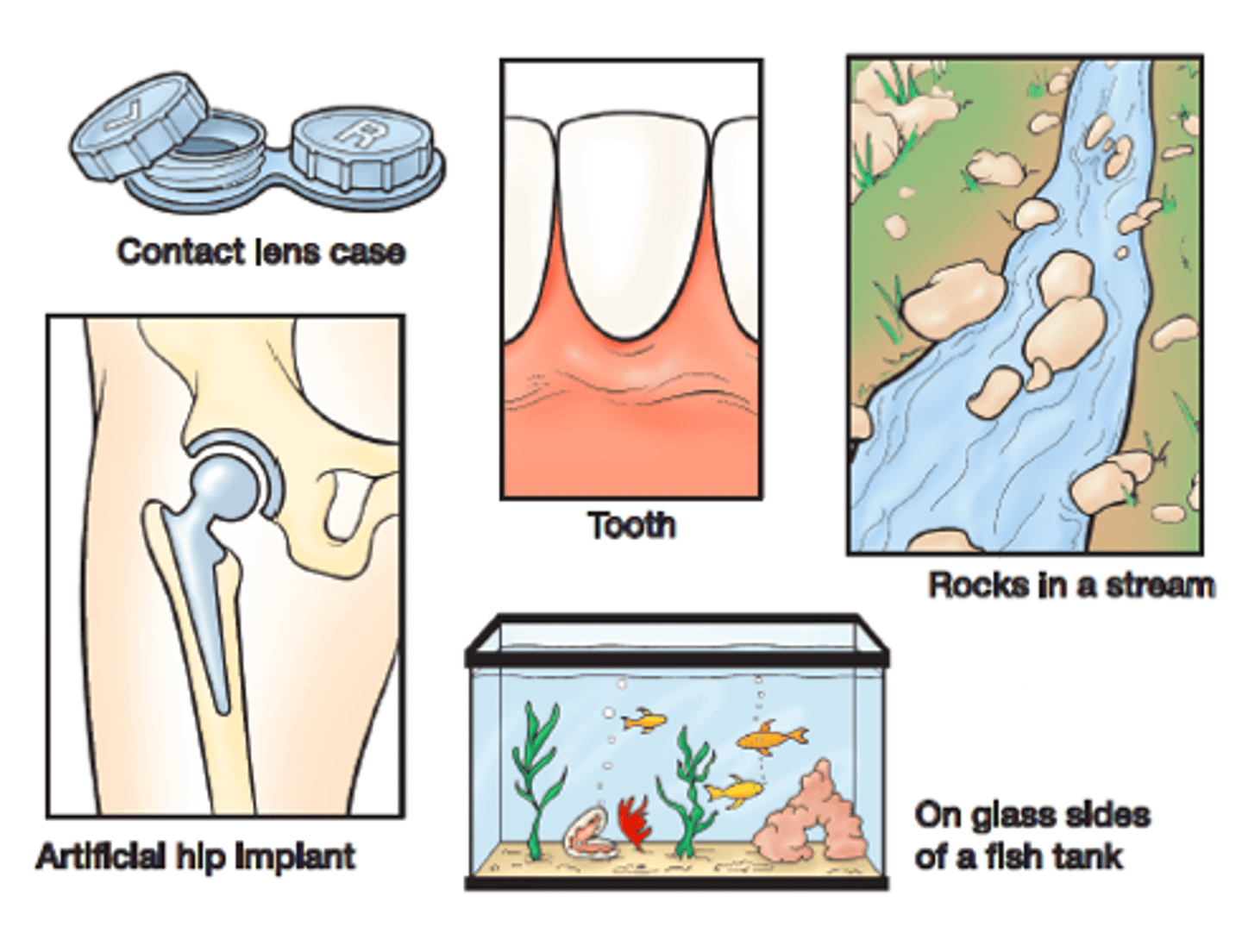
Where are biofilms found in body?
- Dental plaques
- Gastrointestinal tract
- Airways (CF)
- Medical implants e.g., on pacemaker in heart
What is dysbiosis?
Disturbance to microbiota homeostasis
Causes of dysbiosis
Imbalance in flora
Change in functional composition of flora
Change in metabolic activities of flora
Change in local distribution of flora
Dysbiosis leads to three harmful effects. What are they?
1) Loss of beneficial organisms
2) Excess growth of potentially harmful organisms
3) Loss of overall microbial diversity
Dysbiosis has been linked to some diseases...
Give some examples of these diseases
- IBD
- Obesity
- Allergy disorders
- Type 1 diabetes
- Autism
- Colorectal cancer
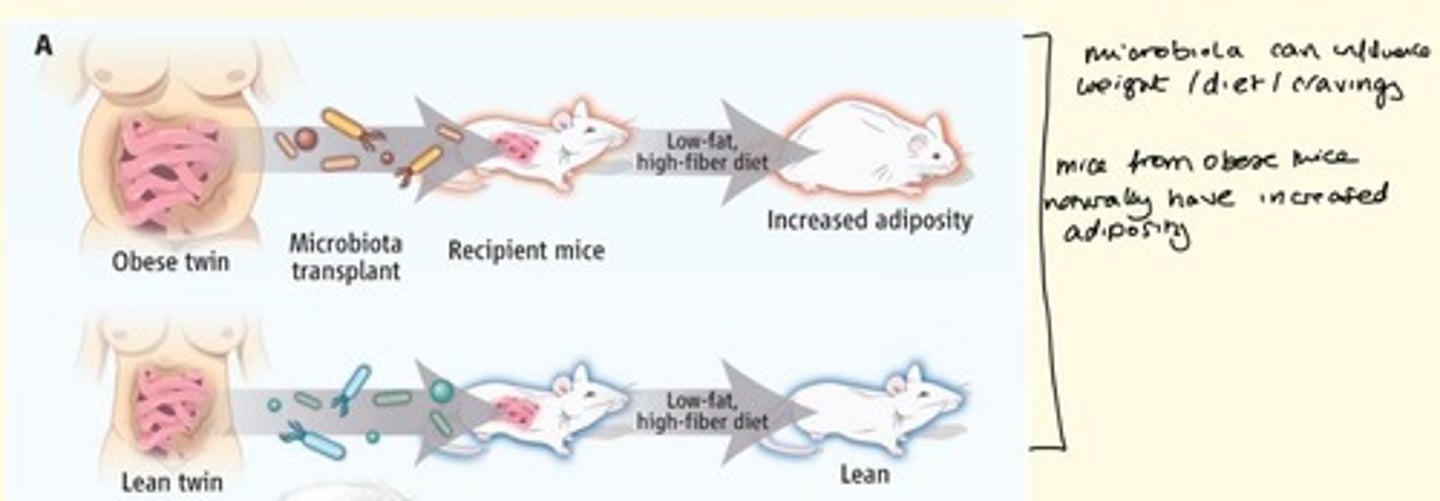
What is the effect of the microbiota on adiposity?
The microbiota can influence weight, diet, cravings and metabolism.
Microbiota can help prevent obesity via...
1) Breaking down dietary fat
2) Increasing energy expenditure
Healthy mice with microbiota transplant from obese mice have ___ adiposity
Increased
List three types of symbiotic interventions
1) Probiotics
2) Fecal transplantation
3) Environmental change
Describe probiotics and prebiotics and how they are useful symbiotic interventions
Probiotics are live microorganisms that intend to have health benefits when consumed.
Prebiotics are nondigestible food components which selectively stimulate activity or growth of certain desirable microorganisms.
Synbiotics are products that combine both probiotics and prebiotics.
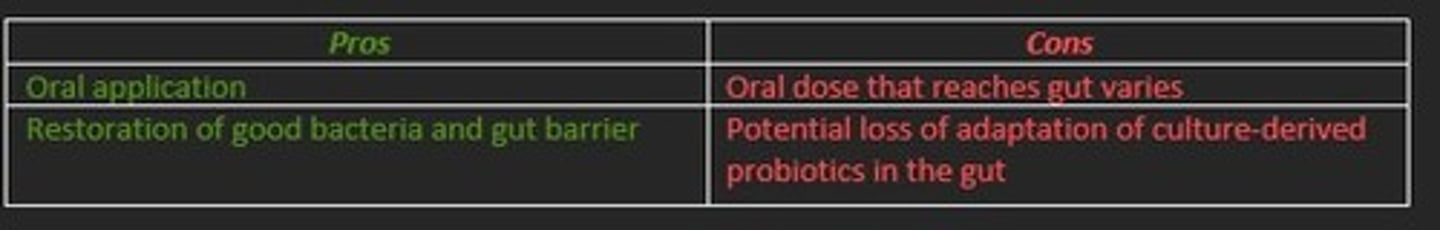
Pros and cons of probiotic and prebiotic symbiotic interventions
PROS
- Oral application
- Restoration of good bacteria and gut barrier
CONS
- Oral dose that reaches gut varies
- Potential loss of adaptation of culture-derived probiotics in the gut
Describe fecal transplants and how they are useful symbiotic interventions
Fecal microbiota transplants (FMT) or bacteriotherapy is the transfer of stool from healthy donors into the gastrointestinal tract of a patient for the purpose of treating.
Pros and cons of fecal microbiota transplants (FMT) symbiotic interventions
PROS
- Safe application
- Simple procedure
- 90% success rate to treat Clostridium difficile
CONS
- Variable impact
- Not very effective in IBD
- Quality of donor stool is important in efficacy of treatment
Success rate of 90% for fecal microbiota transplants (FMT) in what infection?
Clostridium difficile
Describe environmental change as a symbiotic intervention
This is an extreme symbiotic intervention.
Changing the environment microbial status can either promote disease or confer protection.
Pros and cons of environmental change as a symbiotic intervention
PROS
- Early-life exposure to microbes is important for improving later life immunity
CONS
- Not qualitative/quantitative
- Mechanisms of effect unknown
Antibiotics alter the population structure of the ___
Microbiome
While the overall structure of the gut microbiome is recovered after some time (when using antibiotics), the genomic structure of the microbiome is...
Not fully recovered
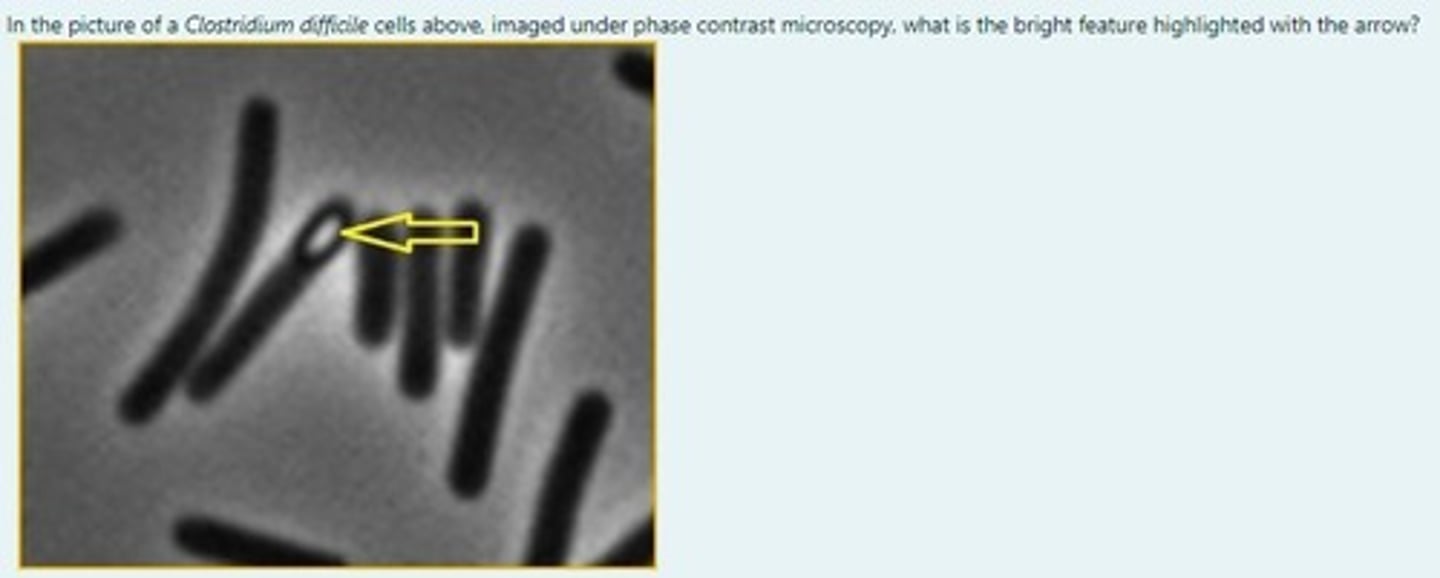
In the picture of a Clostridium difficile cells here, imaged under phase contrast microscopy, what is the bright feature highlighted with the arrow?
A spore
3 multiple choice options
Upon studying bacteria under the light microscope, you will observe that cells will be arranged in a particular way. This can be useful in identification. Which genus of bacteria will be arranged in a cluster, which could be describe as a bunch of grapes?
Staphylococcus
3 multiple choice options
If you observe a chain of coccus shaped bacteria under the light microscope, which Genera would you be looking at?
Streptococcus
3 multiple choice options
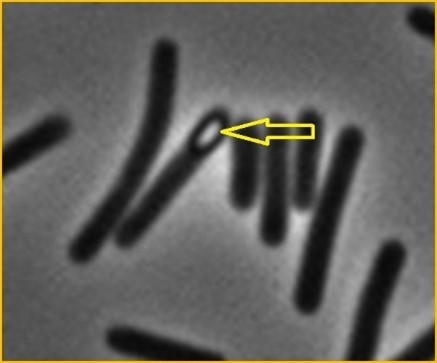
In the picture of a Clostridium difficile cells above, imaged under phase contrast microscopy, what is the bright feature
A spore
Infectious agents can be classified as cellular or acellular. An example of a acellular
infectious agent may include:
fungi
prion
bacteria
algae
protozoa
prion
The majority of microbes which can cause human infection are found to have a cellular structure including organelles, however some infectious agents do not have organelles. Which organism might this be?
bacteria
algae
protozoa
virus
fungi
virus
If you observe a chain of coccus shaped bacteria under the light microscope, which Genera would you be looking at?
Streptococcus
Diplococcus
Staphylococcus
Micrococcus
Tetracoccus
Streptococcus