DSA24 - Medical Disorders of Pregnancy
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Molar Pregnancy
Define Condition:
Multisystem disorder unique to pregnancy; varying clinical presentations
-Hx: PRIOR to 20 WGA
-Sx/PE:
> CNS Sx
> Pulm Edema
-Dx:
> Thrombocytopenia
> DIC
> Elevated transaminases/other hepatic injury
> Elevated Cr
Preeclampsia/eclampsia
Define Condition:
Dx based on new-onset HTN in latter 1/2 of pregnancy + New-onset proteinuria and/or other evidence of organ dysfunction
-Hx:
> AFTER 20th Week of Pregnancy
> Affecting FIRST Pregnancy (determined by Father of Baby/FOB)
> Risk Factors
>> Maternal Vascular Dz (Chronic HTN, Advanced maternal age, Meth)
>> Primiparous (Immuno-mediated placental vascular damage)
>> Increased Metabolic Demand (Multiples. Macrosomia. Gestational Trophoblastic Dz = mole)
>> Genetic/Environmental
>> Familial Factors (risk of daughters of preeclamptic mothers)
-Path: Inadequate uteroplacental perfusion leading to placental ischemia, or hypoxia
> Failure of cytotrophoblasts to adequately invade the uterine spiral arteries and establish low-resistance uteroplacental circulation of a normal pregnancy --> endothelial dysfunction/disturbed PG production (more vasoconstrictors = PGF2a, TXA, endothelin; less vasodilators = PGE2, Prostacyclin, NO), vasoconstriction, activation of coagulation system
-Sx/PE:
> Rising Wt/Edema (leaky capillaries)
> Rising BPs
>> HTN > 160/110 mmHg on 2 occasions at least 4hrs apart
> Pulm/Generalized Edema
>> Renal Insufficiency (Cr > 1.1 or doubling baseline)
> CNS Sx
>> Severe HA (refractory to Tylenol)
>> Scotoma (spots in vision)
-Dx:
> Micro
>> Lack of decidualization of myometrial spiral arteries (MORE PLACENTAL INFARCTION)
>> Glom capillary endotheliosis
>> Ischemia, hemorrhage, necrosis in many organs (secondary to arteriolar constriction)
> New-onset Proteinuria:
>> 1+ dipstick
> Thrombocytopenia (< 100k)
> DIC
> Elevated transaminases/other hepatic injury
> Elevated Cr
-Tx:
> DELIVER PLACENTA + Expect Mgmt (Hospitalize if Severe)
> Seizure Prophylaxis (MgSO4) if severe
> HTN therapy (Prevent CNS Hemorrhage)
-Prog: A/w greater maternal/perinatal mortality
HELLP Syndrome
Define Condition:
Variant of Severe Pre-eclampsia w/ particularly high mortality
-Hx:
> MULTIPAROUS
> Age > 25 y/o
> <36 WGA
> 20% may not see HTN before
-Sx/PE:
> Rising Wt
> Rising BPs
>> HTN > 160/110 mmHg on 2 occasions at least 4hrs apart
> Pulm/Generalized Edema
>> Renal Insufficiency (Cr > 1.1 or doubling baseline)
> CNS Sx
>> Severe HA (refractory to Tylenol)
>> Scotoma (spots in vision)
-Dx:
> HEMOLYSIS
> New-onset Proteinuria:
>> > 0.3 g protein in 24 urine
>> Protein/Cr Ratio > 0.3 AFTER 20th Wk
>> 1+ dipstick
> Thrombocytopenia (< 100k)
> DIC
> Elevated transaminases/other hepatic injury
> Elevated Cr
-Tx: DELIVER PLACENTA
Eclampsia
Define Condition:
New-onset grand mal seizures in female w/ preeclampsia that cannot be attributed to other causes
-Hx: Preeclampsia +/- Neuro Sx
-Tx: DELIVER PLACENTA
Chronic Hypertension
Define Condition:
-Known HTN before pregnancy
-Development of HTN prior to 20 WGA
-Gestational HTN > 12 wks postpartum
-Hx:
> MCC = Essential HTN
> Secondary HTN (renal, vascular, endo, behavioral (cocaine, meth) causes)
> Need to r/o HypERthyroidism
-Tx: Control HTN + Detect Superimposed Preeclampsia in Pree mom/IUGR in fetus
> Early detect (r/o other causes + Labs/EKG)
> Review Meds
>> If > 160/105 --> Start Meds (Goal = 140/90; lower too much --> uteroplacental hypoperfusion --> IUGR) = Methyldopa, CCBs, Labetalol (may cause IUGR)
Gestational HTN
Define Condition:
HTN w/o proteinuria/other signs of organ dysfunction after 20 WGA, or within 24-48hrs of delivery and resolves by 12wks postpartum
-Hx: Dx made RETROSPECTIVELY (pregnancy completed w/o proteinuria or other evidence of preeclampsia and normotensive by 12wks PP)
-Prog: May progress to preeclampsia or chronic HTN that was previously undiagnosed
Chronic hypertension w/superimposed preeclampsia
Define Condition:
Chronic HTN + New-Onset Proteinuria AFTER 20 WGA
-Hx:
> Preexisting HTN w/ Proteinura
-Sx/PE/Dx:
> SUDDEN BP CHANGES
> Worsening Proteinuria
> Severe Features (Thrombocytopenia, LFT, etc)
Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM)
Define Condition:
Glucose intolerance with onset/first recognition during pregnancy
-Hx:
> Previous Occurence
> PCOS
> Obesity
-Path: Rising levels of HPL (stimulates insulin production AND increases insulin resistance), progesterone, prolactin, and cortisol in pregnancy --> progressive insulin resistance during pregnancy + maternal pancreatic function CANNOT overcome resistance
-Tx:
> OB + MFM + Nutrition
> Diet
> Exercise (walking after dinner)
> Pharm
>> Glyburide if diet/exercise doesn't help
>> Insulin
> Stages
>> Antepartum = achieve euglycemia
>> Intrapartum = maternal euglycemia + monitor fetus
>> Postpartum = Insulin requirements drop (monitor BS) + OGTT Test (AVOID Estrogen OCP if DM w/ vascular Dz)
-Prog: D/t Maternal HYPERglycemia or Vascular Dz + Placenta allows for fetal hyperglycemia (glucose passes via facilitated diffusion) --> fetal hyperinsulinemia
> T2DM later in life
> NTDs
> Polyhydraminos
> Fetal hyperinsulinemia = Teratogenic during embryogenesis OR Macrosomia/Shoulder dystocia during 3rd Tri
Rhesus Alloimmunization
Define Condition:
Immunologic disorder in pregnant Rh-negative woman carrying Rh- positive fetus
-Hx:
> Most occur AT Delivery
> Sensitization may also occur if Rh-neg is exposed to to Rh-pos blood via Transfusion
-Path:
1. Fetal cells enter maternal circulation at placental barrier during 1st pregnancy
2. Anti-D IgM Abs made (can't cross placenta) for short time --> Maternal immune system produces Abs (anti-D IgG) to the Rh antigen
3. Post-partum/Subsequent pregnancy: Maternal anti-D IgG crosses placenta into fetal circulation and opsonizes/attacks fetal Rh-positive RBCs (TYPE II HYPERSENSITIVITY RXN), if Fetus has RhD antigen --> resulting in their destruction in fetal spleen (hemolytic disease in fetus/newborn)
-Sx/PE: HDF/N
> Mild = Fetal compensation by increased rate of erythropoiesis
> Severe = PROFOUND FETAL ANEMIA
>> Extramedullary hematopoiesis
>> Portal HTN
>> Hypoalbuminemia
>> Hyperbilirubinemia
>> Heart Failure (Hydrops fetalis)
>> Intrauterine fetal demise (IUFD)
>> Neonatal encephalopathy + Kernicterus (High bilirubin --> CNS damage)
-Dx: Genetics
> Rh-D neg + Sensitized --> RhD of FOB determined
> Rh-D (-) FOB --> Fetus Rh-D neg
> Rh-D (+) FOB --> Rh genotype using PCR
>> HOMO for D Ag = Rh-D+ Fetus
>> HETERO for D Ag = 50% Rh-D+ chance --> Genotype via cell-free fetal DNA in maternal plasma
-Tx: PROPHYLACTIC Rh IMMUNE GLOBULIN at 28 WGA/RHOGAM (if RhD-negative) Or if experiencing bleeds
> Prevents maternal anti-D IgG production
> Used Postpartum, Antepartum event w/ risk of fetomaternal hemorrhage
-Prog:
> 1st Tri Bleed = MCC of Fetomaternal Hemorrhage (SABs, EABs)
> 2nd/3rd Tri Bleed = After Amnio/CVS, trauma, external cephalic
Hydrops fetalis (fka Erythroblastosis fetalis)
Define Condition:
Form of in-utero heart failure d/t Rhesus Alloimmunization
-Path: Most are d/t Abs to the D antigen of Rh
-Sx/PE:
> Fetal Ascites
> Pericardial effusion
> Pleural effusion
> Subcuticular edema (scalp)
> Polyhydramnios
Polyhydramnios
Define Condition:
Too much amniotic fluid
-Hx:
> MCC = IDIOPATHIC
> A/w fetal malformations that increase difficulty of swallowing fluid (ex: Esophageal/Duodenal Atresia, Anencephaly)
> Maternal Diabetes
> Fetal Anemia
> Multiple Gestations
Oligohydramnios
Define Condition:
Too little amniotic fluid
-Hx: A/w...
> Placental insufficiency
> Bilateral renal agenesis
> Posterior urethral valves (males)
> Potter Sequence
>> Pulm Hypoplasia
>> Twisted face
>> Twisted skin
>> Extremity defects
>> Renal Failure
Endometritis
Define Condition:
Inflammation of the endometrium associated with retained products of conception following delivery, miscarriage, abortion, or foreign body (IUD)
-Path: Retained material is the nidus for bacteria from vagina/GI tract
-Sx/PE:
> Uterine TTP
> Foul-smelling uterine bleeding
> +/- Fever
-Dx: Histo (Chronic) = Plasma Cells
-Tx: Gentamicin + Clindamycin +/- Ampicillin
Primary Infertility
Define Condition:
Unsuccessful conception after attempting to achieve pregnancy x 1yr
-Hx:
> Stress
> Increased age (reduced embryo quality/reduced coital frequency)
> Male vs Female Coital Factors
-Path: NO PRIOR PREGNANCIES
> Recurrent Spontaneous Abortions (SABs) = Even when fertilization occurs, >70% embryos are abnormal and fail to develop/become nonviable shortly after implantation
> Major deficiency (tubal occlusion) or Multiple minor deficiencies
-Dx: First 6-8 mo
> Noninvasive = Hysterosalpinogram (may be therapeutic)
> Operative Laparoscopy (only if needed)
Secondary Infertility
Define Condition:
Unsuccessful conception after attempting to achieve pregnancy x 1yr
-Hx:
> Stress
> Increased age (reduced embryo quality/reduced coital frequency)
> Male vs Female Coital Factors
-Path: Follows previous conception
> Recurrent Spontaneous Abortions (SABs) = Even when fertilization occurs, >70% embryos are abnormal and fail to develop/become nonviable shortly after implantation
> Major deficiency (tubal occlusion) or Multiple minor deficiencies
-Dx: First 6-8 mo
> Noninvasive = Hysterosalpinogram (may be therapeutic)
> Operative Laparoscopy (only if needed)
Male Coital Factors
Define Cause of Infertility:
FIRST to be evaluated (cheaper & easier/less invasive)
-Hx:
> Previous pregnancies
> Genital Tract Infex (Prostatitis, Mumps, Orchitis)
> Surgery/Trauma to inguinal or genital region
> Exposure to lead/cadmium/radiation/chemo
> Excessive EtOH
> Tobacco
> Environmental heat
> Varicocele (d/t increased temperature)
> Use of Furantoins + CCBs (reduce sperm quality/function)
-Dx:
> Accurate appraisal of abnormal semen requires at least 3 samples
> Endocrine eval: hypothyroidism, hypothalamic-pituitary failure, prolactinoma, elevated FSH (parenchymal damage to testes)
-Tx: Scheduled intercourse w/nontoxic lubricant (Pre-Seed)
> Limit tobacco, EtOH (or stop all together)
> Avoid sauna, hot tub, tight undergarments
> Sperm abnormalities --> sperm washing and Intrauterine Insemination (IUI)
> Meds for H-P failure (FSH, LH) or hyperprolactinemia (bromocriptine, cabergoline – dopamine agonists)
> Ligation of venous plexus if varicocele causing low semen quality
> IVF: Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI)--> only 1 motile sperm required for each egg
Refractory cases: donor sperm
Primary Ovarian Insufficiency (fka Premature Ovarian Failure)
Define Cause of Infertility:
Premature atresia of ovarian follicles in women of reproductive age
-Hx:
> MCC = IDIOPATHIC
> Injury during surgery
> Radiation/chemo
> Fragile X carrier status
> Autoimmune disorders (Screen for Diabetes, Hypothyroidism, Hypocortisolism)
-Path: Before the age of 40 (if occurs before age 30, likely caused by chromosomal disorder à karyotype; If Y-chromosome is present, gonadectomy needed to prevent malignancy)
-Dx: Labs
> Low Estrogen
> Increased LH & FSH
-Tx: Replacement of hormone therapy to prevent effects of early menopause (i.e. osteoporosis)
Ovulation Issues
Define Cause of Infertility:
Irregular cycles and/or Advanced age --> reduced egg quality/number + less fecundity
-Tx: Fertility Rxs
> Clomiphene citrate or gonadotropins: will correct any luteal insufficiency
> If oligomenorrhea, induce more frequent ovulation
>> Following workup for thyroid disease, hyperprolactinemia, PCOS
> Pituitary insuffiency/hypothalamic amenorrhea: FSH/LH injections
> Hyperprolactinemia: bromocriptine or cabergoline (dopamine agonists)
> PCOS: clomiphene- inhibits neg feedback of endogenous estrogen --> rise in FSH and stimulates follicular maturation
> Metformin
> Ovarian "drilling" - old, rare, laparoscopic procedure
-Prog:
> Ovarian HyperStimulation Syndrome (OHSS) = marked ovarian enlargement + exudation of fluid and protein into peritoneal cavity --> Need to monitor to prevent
> Multiple fetal gestation
>> 8-10% clomiphene conceptions
>> 20-30% FSH/LH
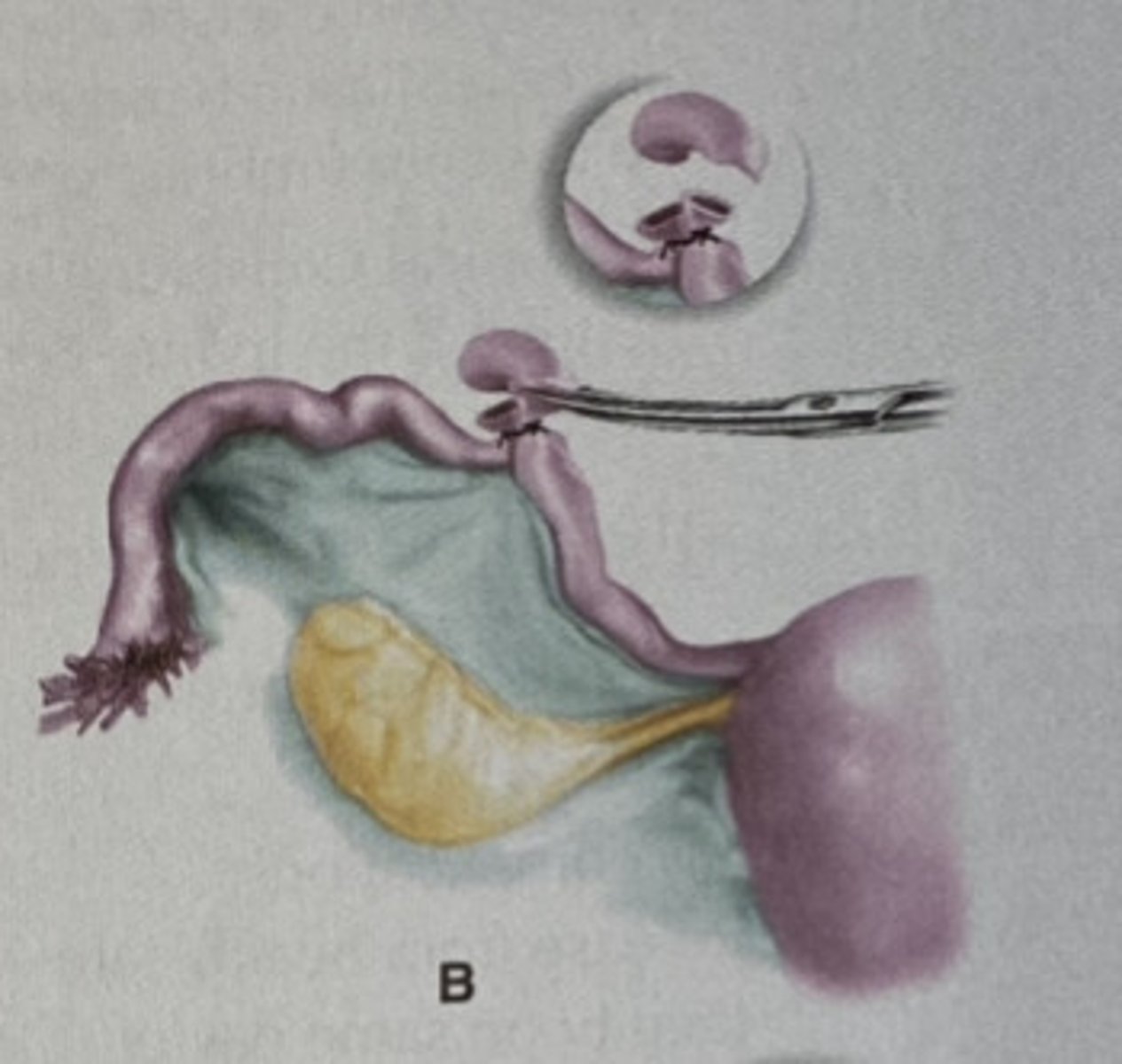
Tubal Occlusion
Define Cause of Infertility:
-Hx:
> Salpingitis (Untreated/Undertreated GC/CT/PID --> Tubal scarring & infertility ==> Risk of Ectopic Pregnancy)
> Endometriosis
> Tubal Adenomyosis
> Tubal Surgery
> TB
-Path: Locations of Occlusion
> 1st MC = Fimbrial end
> 2nd MC = Mid-Segment
> 3rd MC = Isthmus-cornu
-Dx: HSG or Laparoscopy w/ chromotubation
-Tx: Microsurgical tuboplasty
> 60-80% pregnancy thereafter
>> 10% are ectopic
> Hydrosalpinx reduces IVF success by 50% -- repair or remove
Unexplained Infertility
Define Cause of Infertility:
No cause found in 10-15% patients with normal ovulation, Semen analysis, & HSG
-Hx/Path:
> Problem w/sperm transport?
>> IUI with washed sperm increases rate of conception
> Defect in ability of sperm to fertilize egg?
>> Lower fertilization rates during IVF
> Presence of antisperm antibodies?
> Minimal endometriosis?
> Mildly reduced ovarian reserve?
>> Reduced # of normal oocytes w/o hormonal abnormalities
-Tx: IUI Controlled w/ Ovarian Stimulation (Clomiphene or Letrozole and/or FSH/LH) --> IVF/IVF w/ embryo transfer (coception in about 80-85% infertile couples)