Cast irons
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Some cast iron properties
>2.1 wt% C but in reality 2.5 wt%C - 4 wt%C
1-3 wt% Si
Fe, C, Si main elements
brittle
excellent castability and good machinability
strong in compression but not tension
low shrinkage (reduction in size naturally)
cheaper than steel
Graphite in cast irons
Layered hexagonal structure with covalent bonding of atoms in each layer
Layers easily slide against each other
Solid lubricant
Soft and low strength
Promoted by presence of Si and slow cooling rates
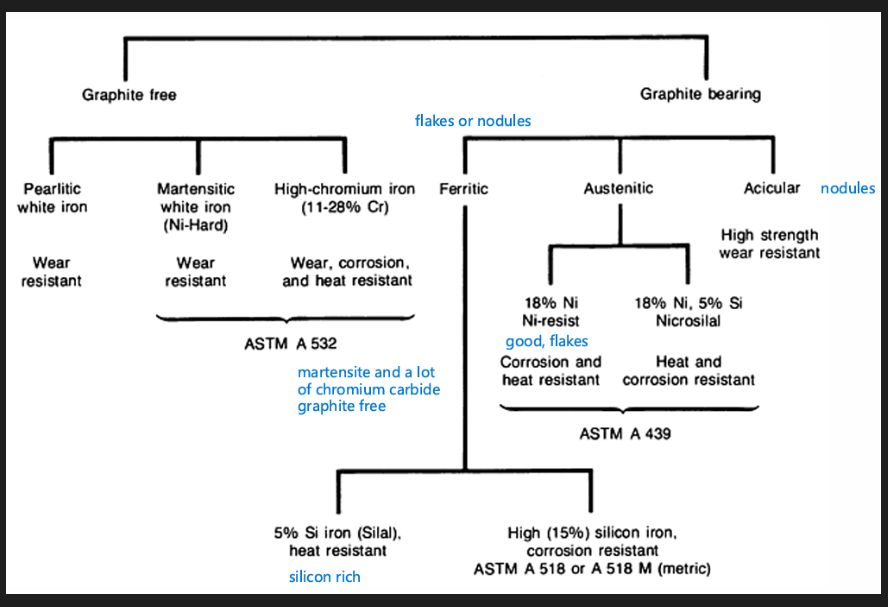
Types of cast irons
Grey cast iron
White cast iron
Malleable cast iron
Ductile/nodular/spheroidal cast iron
Alloy cast iron
Compacted graphite iron
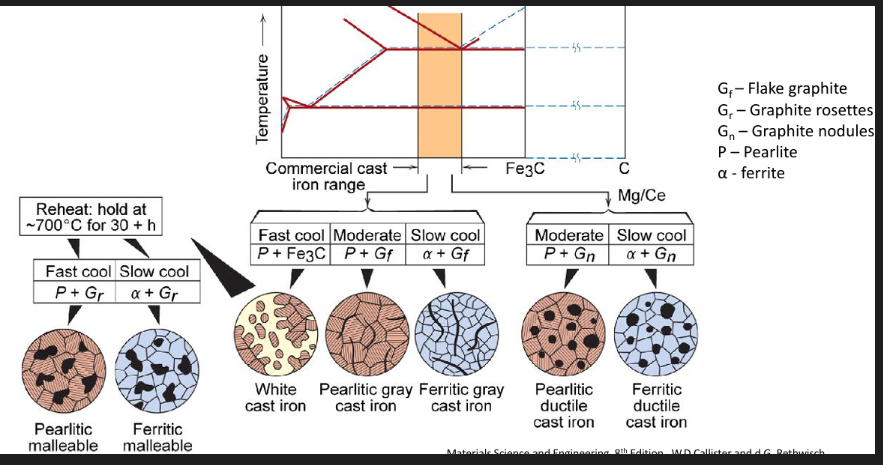
How to get the different cast irons:
Fast cool - white cast iron (pearlite + cementite)
Reheat and hold at 700 degrees Celsius for 30+ hours
Fast cool - pearlitic malleable cast iron (pearlite and rosette graphite)
Slow cool - ferritic malleable cast iron (ferrite and rosette graphite)
Moderate cool - Pearlitic grey cast iron (pearlite + flake graphite)
Adding Mg/Ce - pearlitic ductile cast iron (pearlite + nodule graphite)
Slow cool - Ferritic grey cast iron (ferrite + flake graphite)
Adding Mg/Ce - ferritic ductile cast iron (ferrite + nodule graphite)
Alloying elements and impurities
Sulfur:
Hardens CI by stabilising cementite
Promotes cementite formation with carbides
Embrittlement due to FeS formation
As high as 0.15 wt% for low quality CI
Impurity from fuel
Manganese:
Added in small quantities to combine with S to form MnS
Softens CI
If Mn increases, stabilises cementite
In excess, promotes pearlite
% amount varies by desired matrix (0.1% ferritic and 1.2% for pearlitic)
Phosphorus:
Impurity in the form of Fe3P
Increases embrittlement effect of CI (not good for shock loading)
Suitable for thin castings
Forms a eutectic at 950 degrees
Increases fluidity (liquid more fluid for more details in casting)
Si and Al:
Increases graphitisation potential by increasing number of graphite particles for both eutectic and eutectoid transformation
Increases the ferrite to pearlite ratio leading to low strength and hardness
Ni, Cu and Sn:
Increases graphitisation potential by increasing number of graphite particles for eutectic transformation but decreases it during eutectoid transformation
Increases the pearlite/ferrite ratio leading to high strength and hardness
Cr, Mo, W, V:
Decrease graphitisation potential for both eutectic and eutectoid transformation
Increase carbides and pearlite

Grey cast iron properties
Composition is selected to satisfy 3 structural requirements
graphite shape and distribution
chill free structure
required matrix
C and Si exist between 2.5% - 4% and 1% to 3% respectively.
Graphite exists in form of flakes surrounded by pearlite and ferrite
Graphite flakes results in a grey fractured surface appearance
Grey cast iron with eutectic composition (1150 degrees) may solidify into austenite and cementite (by rapid cooling) or austenite and graphite (by slow cooling)
Unless the cooling is very rapid for a given graphitisation potential, graphite will precipitate out from the austenite as a result of some of the elements present (particularly silicon). At eutectoid temperature, providing cooling is slow enough for the remaining austenite to change into ferrite and graphite
At room temp. the microstructure consists of ferrite + large flakes of graphite together with fine flakes of graphite formed by the decomposition of cementite after solidification, ferritic grey cast iron
For even faster cooling, the structure at RT will consist of flake graphite in a matrix which is entirely pearlite, pearlitic grey cast iron.
For ferritic see left, for pearlitic see right
Fast cooling rate, austenite transforms into pearlite and graphite flakes
Flake graphite shape
A - uniform distribution, random orientation
B - rosette groupings
C - Kish graphite (superimposed flake sizes, random orientation)
D - interdendritic segregation with random orientation
E - interdendritic segregation with preferred orientation.
Carbon equivalent
A parameter that accounts for the influence of composition and microstucture.
CE wt% = % C + 0.33(% Si) + 0.33(% P) - 0.027(% Mn) + 0.4(% S)
CE helps to distinguish grey cast irons (microstructure that contains graphite) and white irons (carbon mainly in the form of cementite). The carbon and silicon contents improves the graphitisation potential and therefore decreases the chilling tendency, the tensile strength is adversely affected because of ferrite formation and coarsening of the pearlite.
Cooling rate
The cooling rate can significantly influence the as-cast structure and therefore the mechanical properties of grey iron. The cooling rate of a casting is primarily a function of its section size. The dependence of structure and properties on section size is termed section sensitivity.
Increasing the cooling rate will:
- Refine both graphite size and matrix structure; this will result in increased strength and hardness
- Increase the chilling tendency; this may result in higher hardness, but will decrease the strength
Consequently, composition must be tailored in such a way as to provide the correct graphitization potential for a given cooling rate. For a given chemical composition and as the section thickness increases, the graphite becomes coarser, and the pearlite/ferrite ratio decreases, which results in lower strength and hardness.
Heat treatment of grey CI
Low proportion of grey cast iron are heat treatable. Most common are anneal and stress relief.
Anneal:
- heated above Ac1 (700), soaked and slowly cooled
- excess cementite breaks down
- begins to form spheroidised lamellar carbide
- any residual stresses are removed
Stress relief:
- soaked at 550 degrees for several hours/days
- very slow cooling
Quenching:
- ferritic grey cast iron
- heated above Ac1 and quenched in water/oil
- pearlite/graphite forms
- stress relieved through tempering between 450 to 475 degrees
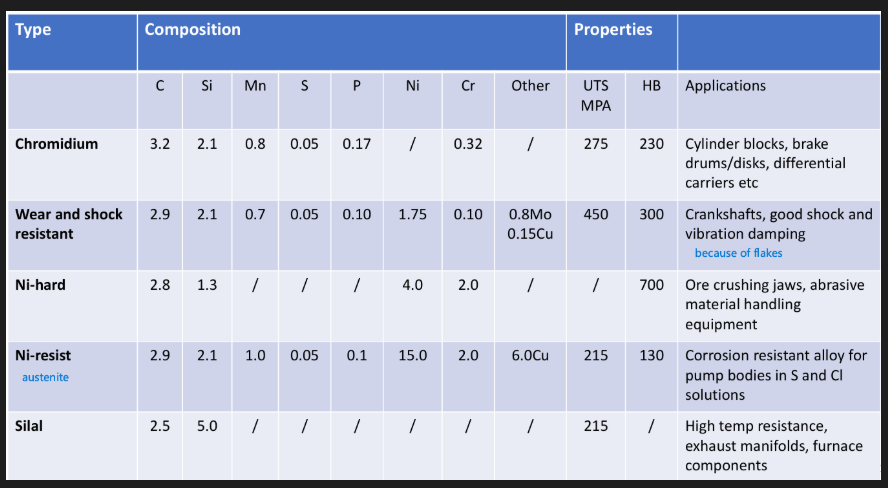
Applications
Motor vehicle brake drum 3.3%C, 1.9%Si, 0.65%Mn, 0.08%S, 0.15%P
Motor vehicle cylinder blocks 3.25%C, 2.25%Si, 0.65%Mn, 0.1%S, 0.15%P
Heavy machine castings 3.25%C, 1.25%Si, 0.50%Mn, 0.1%S, 0.35%P
Properties:
Excellent thermal conductivity and vibrational damping qualities (see notes for graph). Wear and abrasion resistance is comparable to non-heat treated medium carbon steel.
Grey irons typically have low ductility (0.5%) and moderate strength (150 - 300MPa, <250 MPa).
Grey cast iron maintain their mechanical properties up to approximately 500°C.
Typical applications of grey cast irons include brake drums, cylinder blocks and ornamental castings (depending on composition)
Cast irons with high Si (2.5 -3.5%) and P (1.5%) have high fluidity but poor mechanical strength
General purpose engineering irons should have reasonable strength – Ideally fine graphite flakes in a matrix of pearlite. This also gives good machinability. Here silicon content will depend on casting size. Large castings would contain ~ 1.5% Si and thin sections 2.5% Si. Phosphorus and sulphur need to be kept low.
Local hardening of these cast irons can be achieved by chilling – use chills or flame hardening
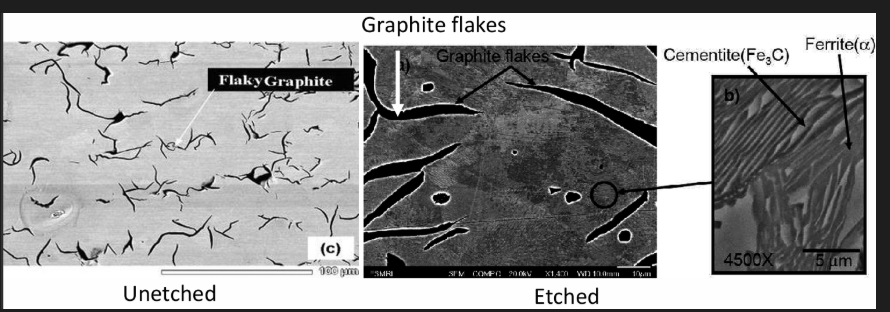

White cast iron
Low Si (<1wt%) content (Low C equivalence) and rapid cooling rates results in C exiting as cementite instead of graphite
Fractured surface will have a white appearance
Upon solidification, structure will consist of austenite and cementite. Further cooling will change the austenite into pearlite.
Final structure: pearlite + cementite
High amounts of cementite makes WCI hard but very brittle and virtually unmachinable. Limited to wear resistant/abrasive applications. Ex: slides, rollers, nozzles
WCI used as an intermediary for the production of malleable CI
Typical composition: 2.5% C, 0.8% Si, 0.4% Mn, 0.08% S, 0.1% P
The light cementite regions are surrounded by pearlite, which has the ferrite-cementite layered structure.
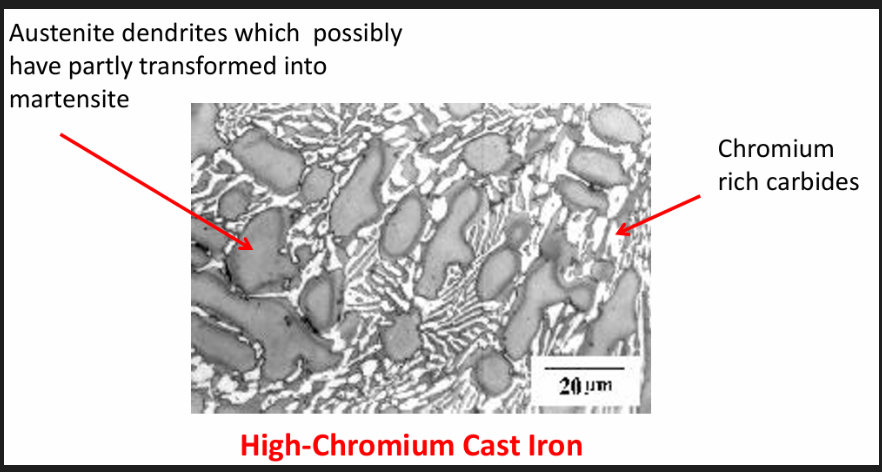
High Cr WCI
Typical composition: 3%C, 0.5%Mn, 0.7%Si, 15% Cr, possibly some Ni 2%
Properties: hard and erosion resistant
Uses: mining, milling, earth handling, manufacturing equipment industries (exceptional wear + corrosion resistance) exs: slurry pumps, brick dies, rock machining equipment

Malleable cast iron
Produced from white cast iron through a heat treatment process
Good castability of WCI but obtain a material with a good ductility and strength like mild steel
Number of varieties depending on microstructure needed (black heart, white heart, pearlitic processes)
Overall properties: increased malleability and ductility, increased TS and toughness.
As cast composition and the heat treatment itself will both influence the quantity, shape and distribution of the graphite nodules in the microstructure
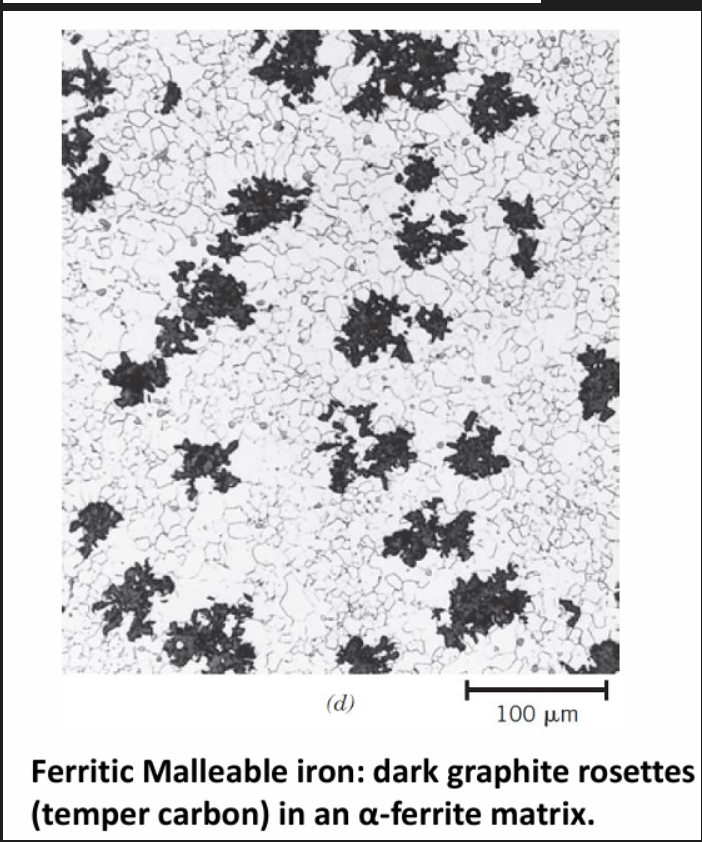
Black heart process:
White CI heated in air tight box (to prevent oxidation) between 850 to 950 degrees for 50 to 170 h. Cementite decomposes forming small irregular but equiaxed nodules of temper graphite called rosettes. Cooling rate and composition determines whether a pearlitic (fast cool) or ferritic (slow cool) matrix results.
See left.
Annealing at ~ 900 degrees results in decomposition of eutectic cementite into graphite and austenite
The composition of malleable irons must be selected in such a way as to produce a white as-cast structure and to allow for fast annealing times.
A higher carbon and silicon reduce the heat treatment time, but must be limited to ensure a graphite-free structure upon solidification.
Annealing time also depends on no. of graphite nuclei available for graphitisation
Phosphorous is limited to <0.1 to prevent embrittlement
Sulphur is balanced with Manganese. Low Mn content favours ferrite. Increasing Mn to 1% will favour formation of pearlite
Nitride forming elements ex: 0.001 – 0.003% B and up to 0.005% Al maybe added before pouring to encourage nucleation of graphite aggregated during annealing
Bismuth (0.01%) may be added to increase undercooling resulting in a finer structure with more nucleation sites for graphite. Higher undercooling also prevents graphite formation during solidification.
Ferritic malleable
UTS: 300 to 350 MPa
YS: 225 MPa
Ductility: 6 to 12%
Hardness: 150 HB max
Applications: wheel hubs, brake drums, pedals
Pearlitic malleable
UTS: 450 to 700 MPa
YS: >300 MPa
Ductility: 3 to 6%
Hardness: 150 to 290 HB
Applications: Chain links, cam shaft, gears, differential housing.
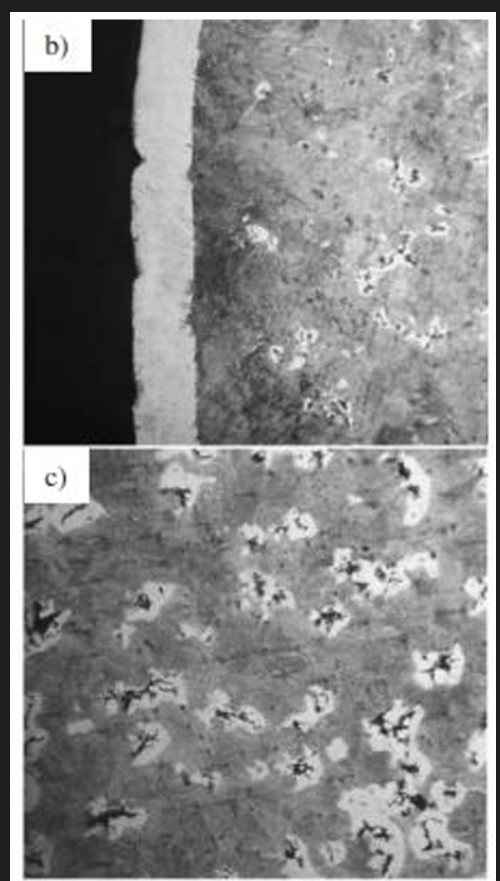
White heart process:
Heated to 1000 degrees
Casting is packed in iron oxide ore (decarburising atmosphere) in air tight container. The ore draws out the carbon leaving a ferritic structure near the surface and a pearlitic structure near the centre of the casting. Some fine graphite rosettes will be present.
Behaviour similar to mild steel but could be easily cast.
UTS: 340 to 480 MPa
Ductility: 3 to 15%
Hardness HB: 230 max
Applications: Wheel hubs, motor cycle frame fittings, water fittings
What about cross sectional area?
Thin sections are completely decarburised (close to mild steel).
- Lower strength higher ductility
Thick sections have a carbon concentration gradient.
- Higher strength, lower ductility
Pearlite in the central region will cause white fracture
see right
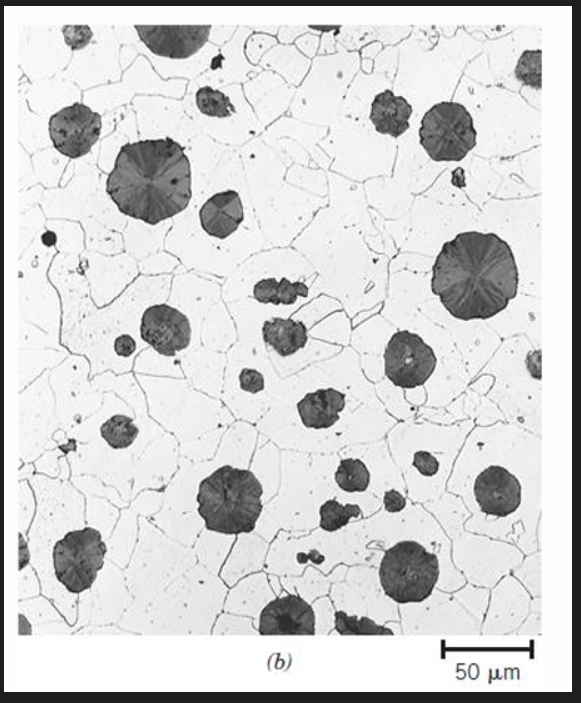
Spheroidal/ductile cast iron
Uses minor alloying elements to change the graphite shape from flake to spheroidal.
Most widely used is Mg(0.03 to 0.05%) and others that can be used are Ca or rare earths ex Ce.
Presence of minor elements ex S, Al, Bi, Ti, Pb may result in graphite shape deterioration
Rounded nodules reduce stress concentration compared to flake graphite resulting in better mechanical properties (strength, fatigue. impact when compared to steel)
The dark graphite nodules are surrounded by an alpha ferrite matrix
Heat treatment of ductile iron
Used extensively in the processing of ductile iron (compared to grey iron) because great advantage can be taken from the matrix structure. Heat treatments applied are:
stress relieving
annealing to produce a ferrite matrix
normalising to produce a pearlitic matrix
hardening to produce tempering structure
austempering to produce acicular (needle) ferrite and stabilised austenite matrix (ausferrite). Advantages of austempering is that it results in ductile irons with twice the TS for the same toughness. It work hardens and provides good wear resistance. Used for gears, axles, crankshafts
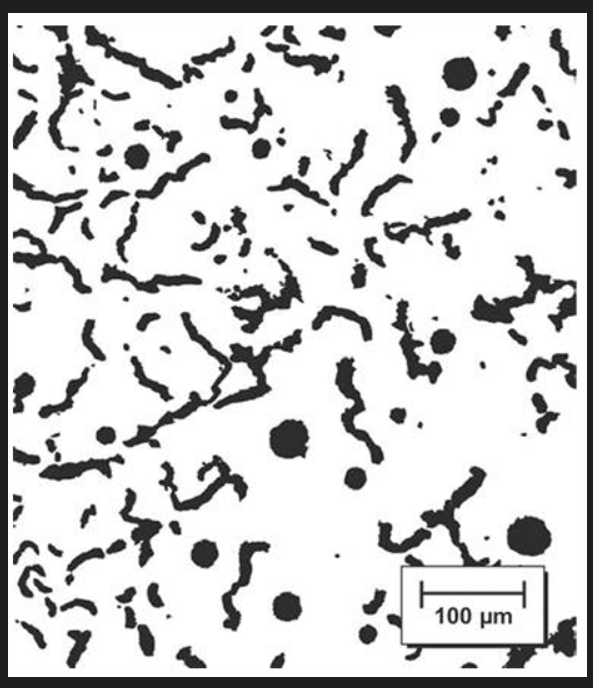
Compacted graphite iron
C exists as graphite
C 3.1 to 4wt% and Si 1.7 to 3wt%
graphite has wormlike (vermicular) shape
microstructure is intermediate between grey and nodular iron
Mg and/or Ce are added at concentrations lower than ductile iron
Very careful control of composition to obtain wormlike graphite morphology
Mechanical properties depend on graphite shape and matrix phase/microconstituents
TS and YS comparable to ductile irons and ductility intermediate between grey nodular iron
Desirable characteristics:
Higher thermal conductivity
Better resistance to thermal shock
Lower oxidation at elevated temps.
Typical composition:
3.1% - 4% C
1.7%-3% Si
0.015% - 0.035% Mg
0.06% - 0.13% Ti
Uses:
diesel engine blocks
exhaust manifolds
flywheels
brake discs for high speed trains
Dark graphite wormlike particles embedded within an alpha ferrite matrix

Alloy cast iron
Alloying elements in CI are similar to those in alloy steels
Ni (grain refinement, adds strength, promotes free graphite)
Cr (stabilises C, increases strength, improves corrosion resistance)
Cu (reduce atmospheric corrosion)
V (stabilises carbides and reduces tendency to decompose at high T)
Mo (improves impact strength, prevents decay at high T)
Welding of cast iron
CI are difficult to weld.
Large castings may need repair because of casting defects.
Preheating and slow cooling are required to avoid cracking and martensite formation
Filler material needs to contain a high Ni content to stabilise austenite phase and reduce C pick up from the bulk material
Advantages:
Vibration damping
Machinability
Castability
Disadvantages:
Strength