Anatomy vs. Physiology: Body Parts and Functions; Homeostasis Mechanisms; Feedback Types; Body Organization Levels; Major Human Body Systems
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
124 Terms
how is studying anatomy different than studying physiology? what are some examples?
anatomy is the study of body parts while physiology is the study of the body part's functions EX: the heart; (anatomy) has four chambers, thick muscular walls, etc (physiology) pumps blood, maintains blood pressure
define homeostasis and state a homestatic mechanism in order (effectors, efferent pathway, afferent pathway, response, stimulus, receptor, control center)
homeostasis: the body's ability to maintain a stable, internal environment: stimulus, receptor, afferent pathway, control center, efferent pathway, effectors, response
what is the difference between positive and negative feedback?
P: effector responds by enhancing the stimulus
N: effector opposes or negates the stimulus
list the levels of organization starting with the cell
cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism
integumentary system
Consists of the skin, sweat and oil glands, hair, and nails, separates inside of body from outside, protects against physical and chemical damage
nervous system
processes info, controls movement, thoughts, memory, and automatic functions
skeletal system
provides support and levers on which the muscular system can act
muscular system
moves limbs; allows facial expressions
endocrine system
sends broad messages to entire body
cardiovascular system
delivers oxygen and nutrients to body tissues
lymphatic system
protects the body; destroys bacteria and tumor cells
digestive system
breaks down food into smaller particles that can be absorbed
respiratory system
removes CO2 from blood
urinary system
rids the body of nitrogen containing waste
reproductive system
enables organisms to create offspring
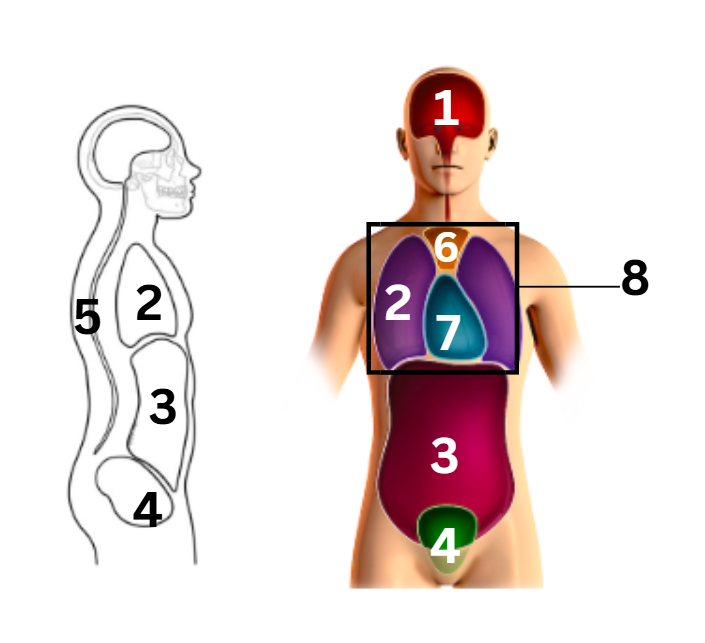
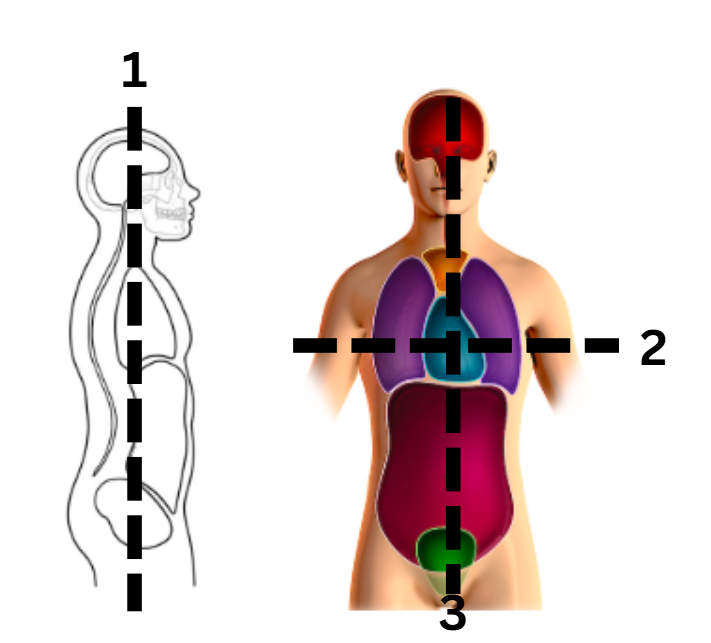
what number on the diagram represents the abdominal cavity
3
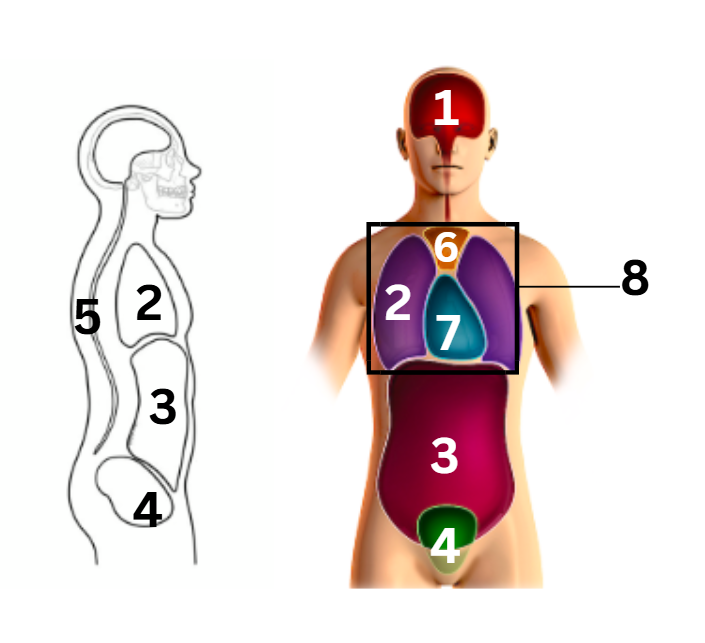
what number on the diagram represents the cranial cavity
1
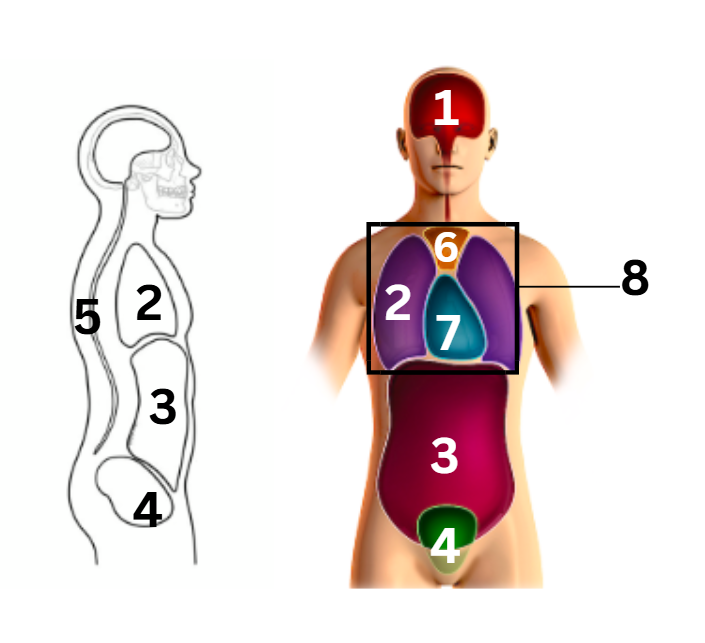
what number on the diagram represents the mediastinum cavity
6
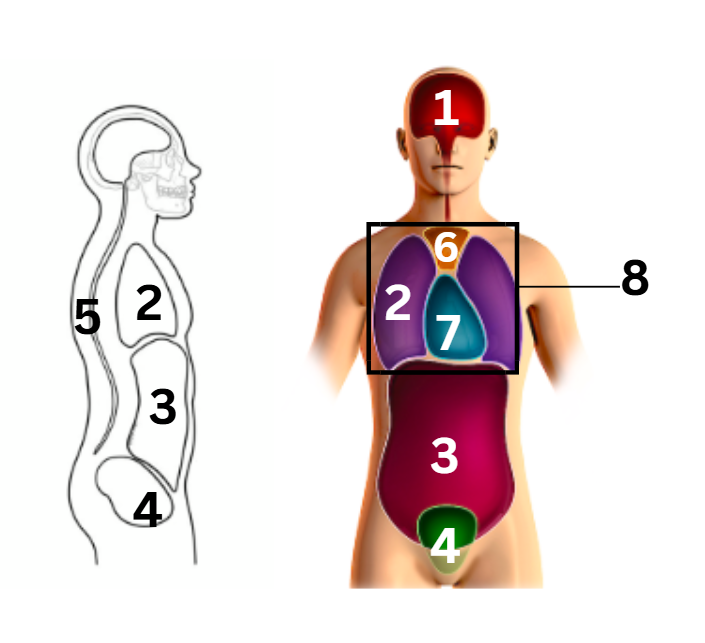
what number on the diagram represents the pelvic cavity
4
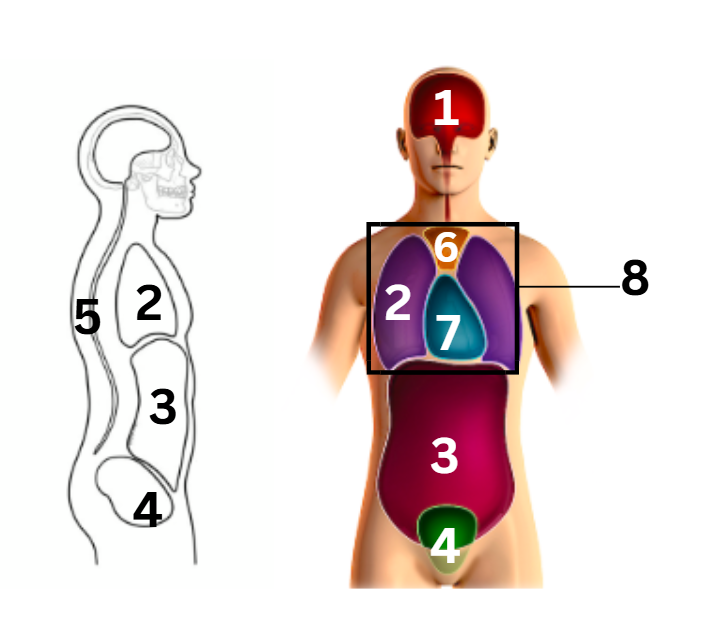
what number on the diagram represents the pericardial cavity
7
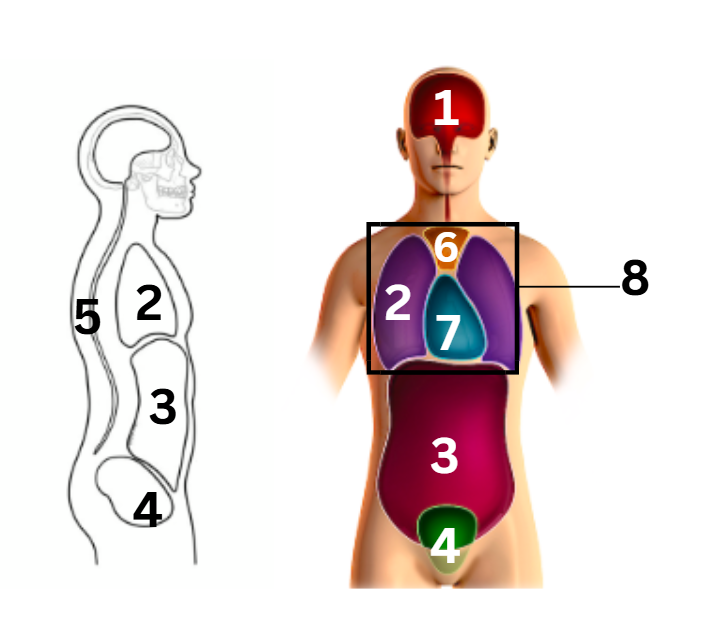
what number on the diagram represents the pleural cavity
2
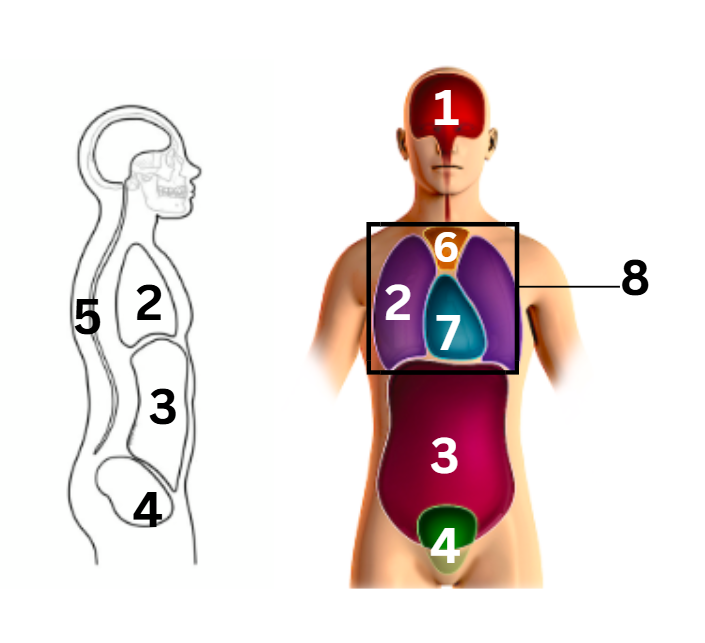
what number on the diagram represents the spinal/vertebral cavity
5
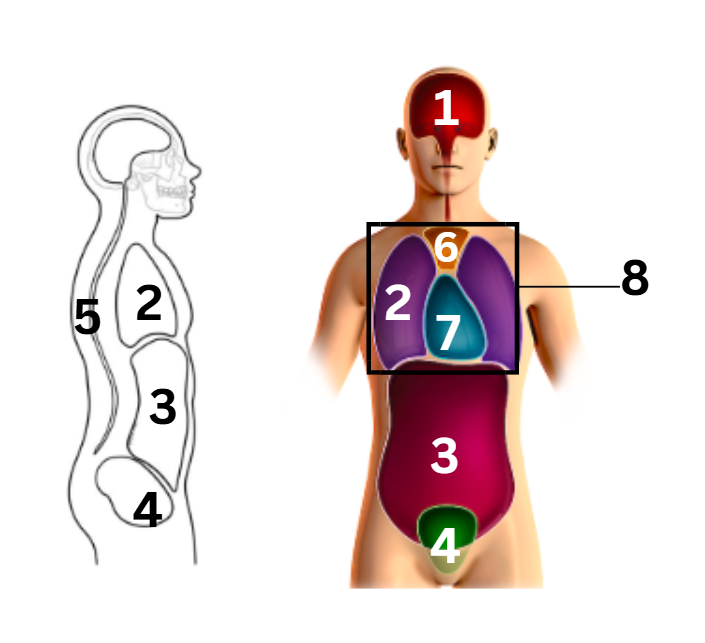
what number on the diagram represents the thoracic cavity
8
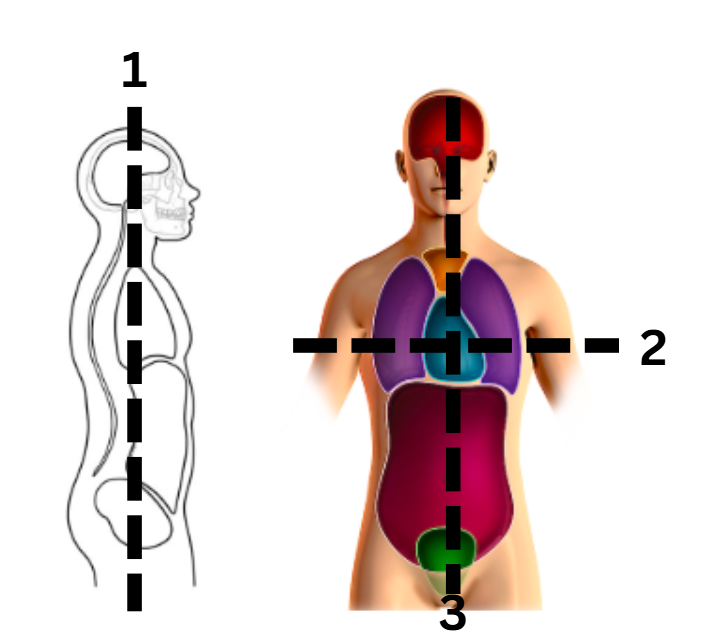
identify the sagittal cut
3
identify the frontal/coral cut
1
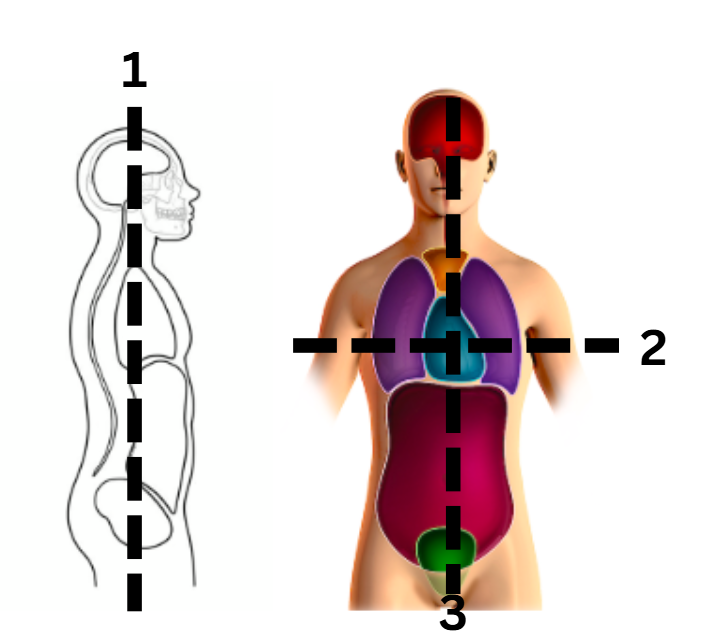
identify the transverse cut
2
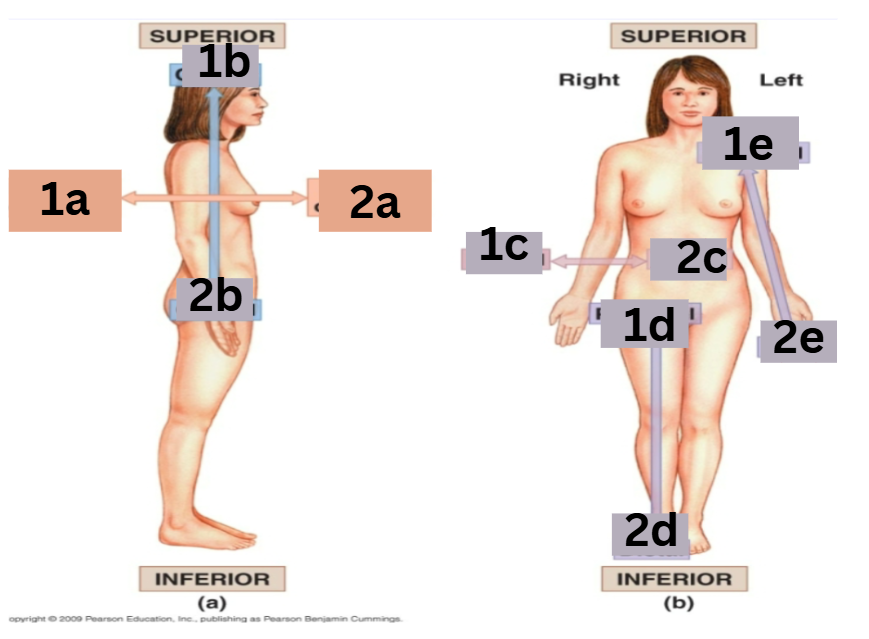
which arrows represent the medial and lateral directions
medial: 2c lateral: 1c
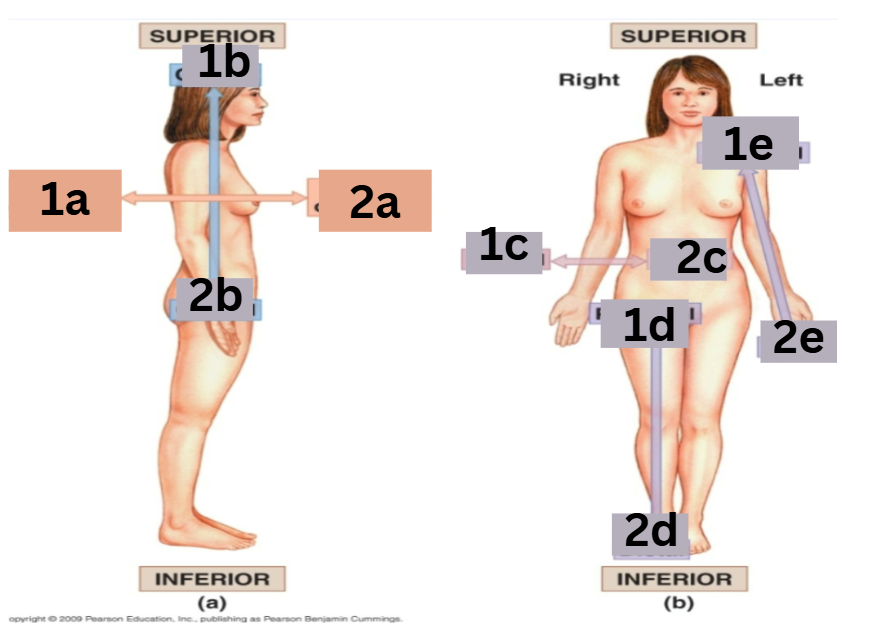
which arrows represent the proximal and distal directions
proximal: 1d distal: 2d
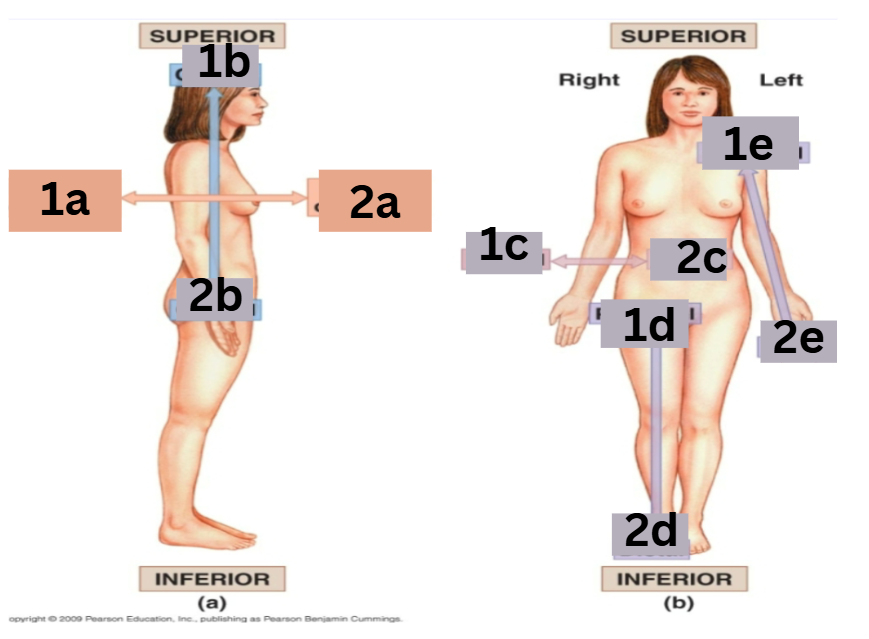
which arrows represent the cranial and caudal directions
cranial: 1b caudal: 2b
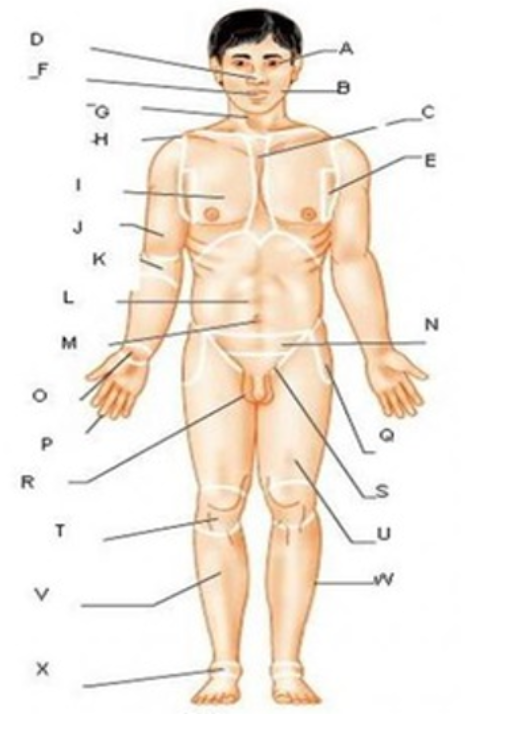
patellar
T
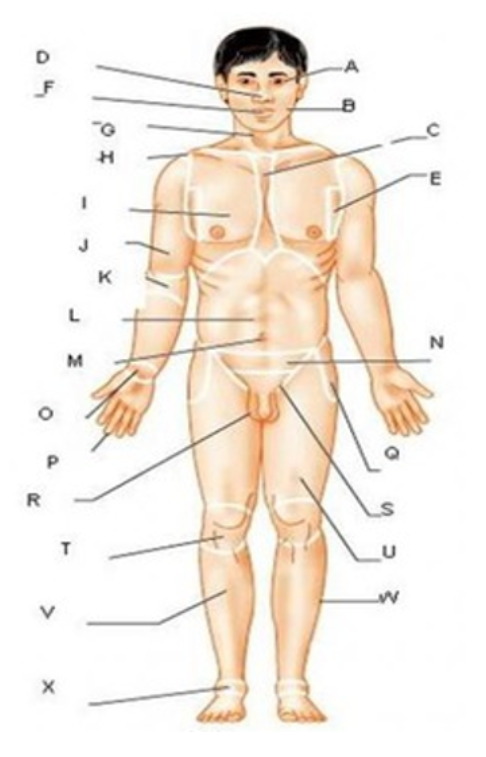
femoral
U
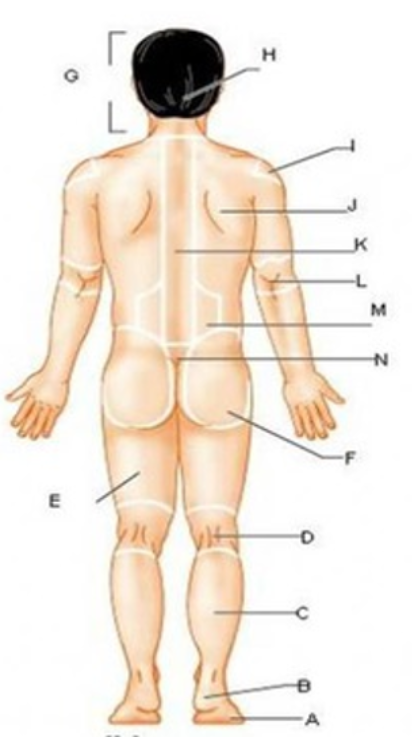
gluteal
F
thoracic
c
abdominal
L
brachial
J
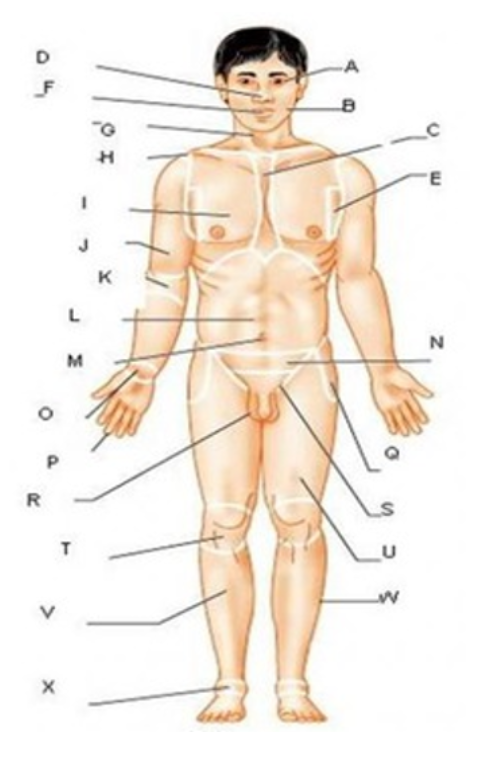
cervical
G
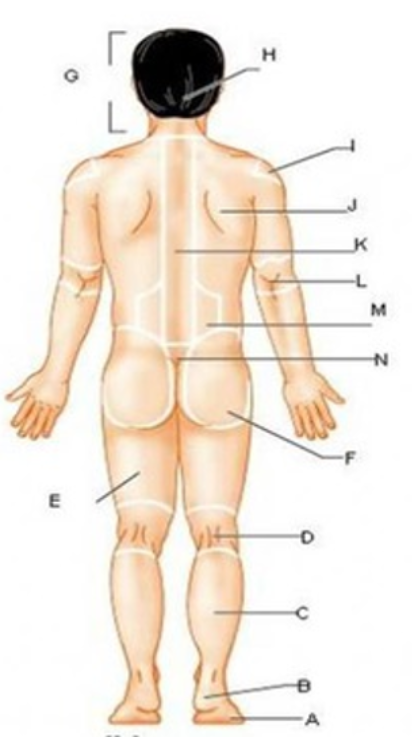
lumbar
M
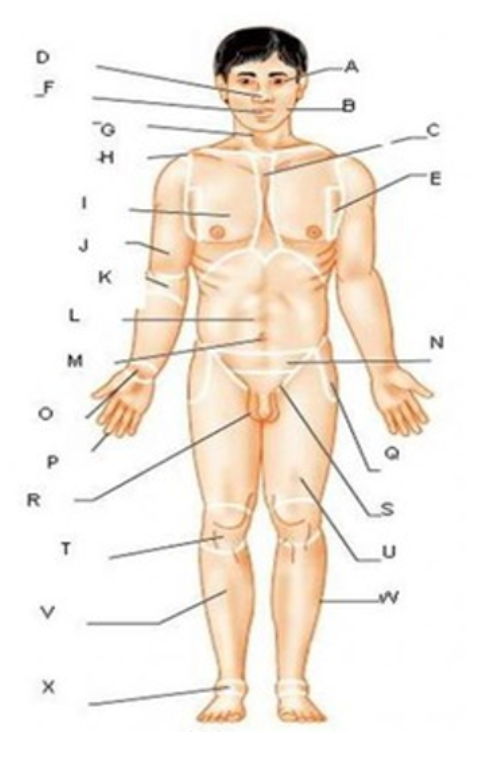
tarsal
x
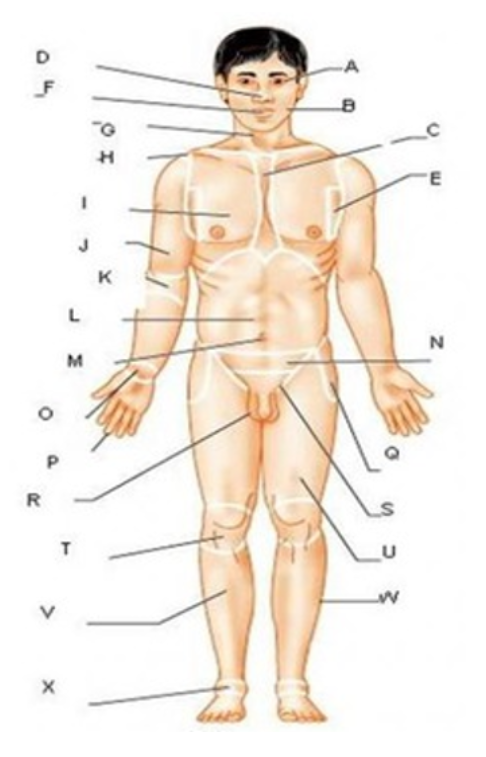
digital
P
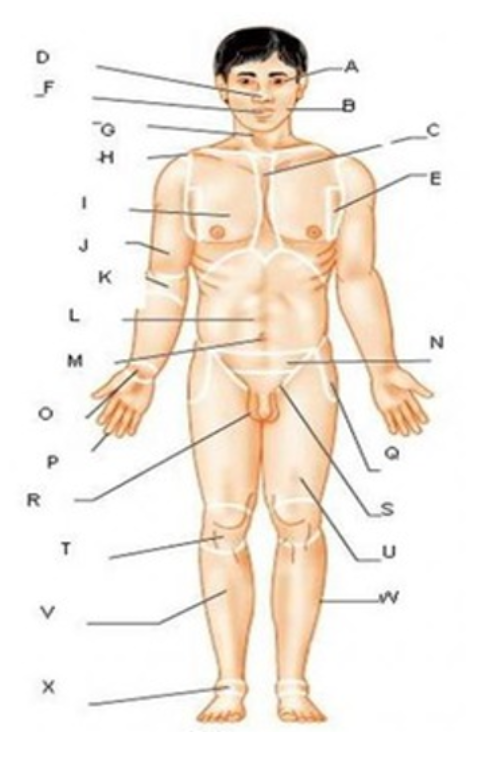
carpal
O
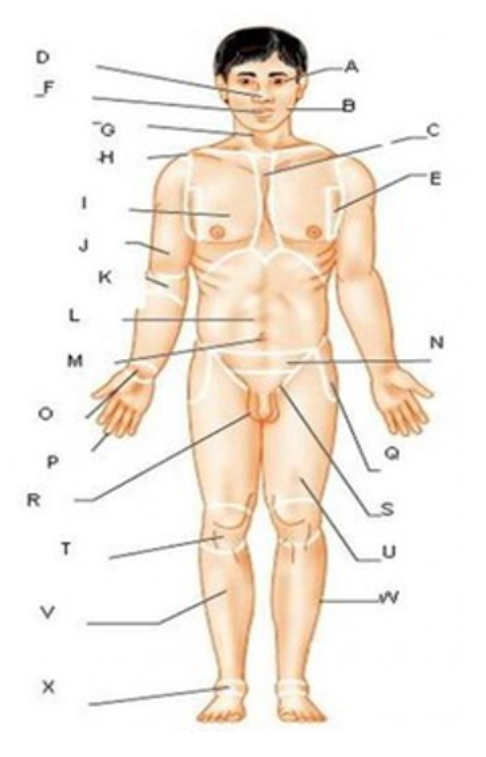
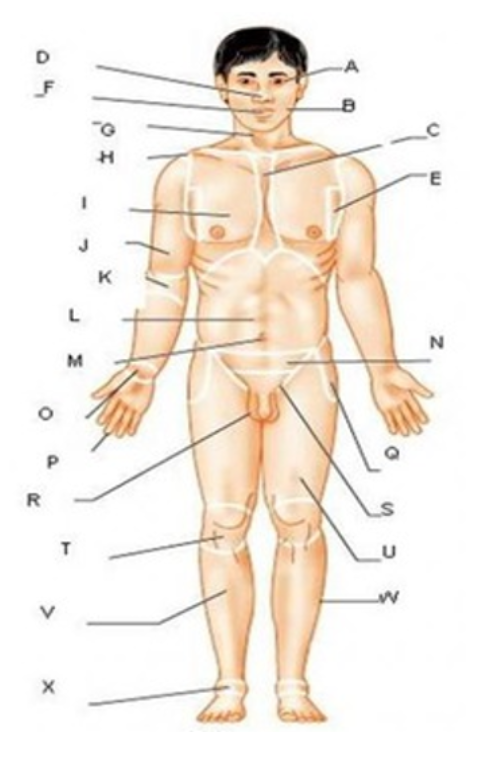
ocular
A
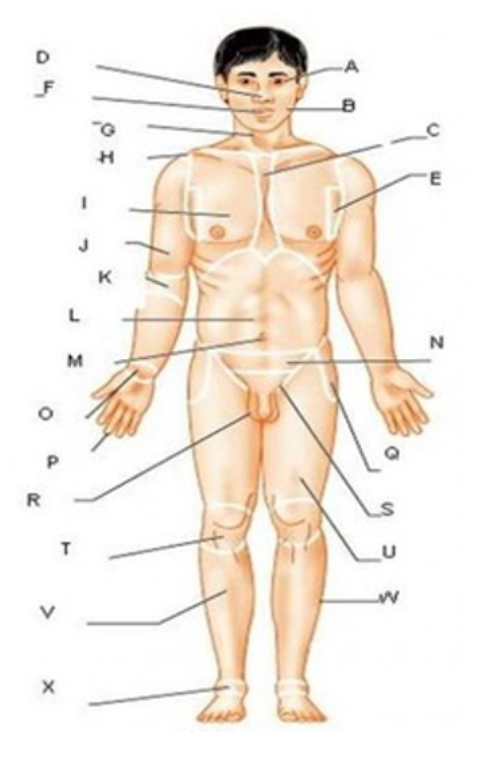
buccal
B
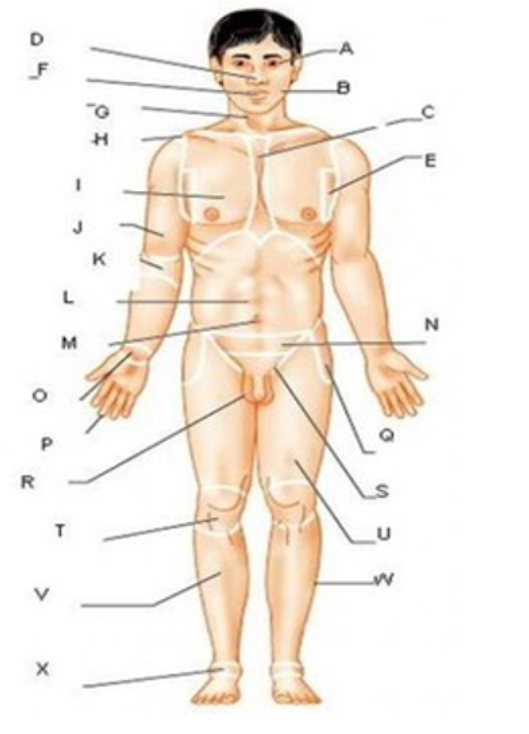
oral
F
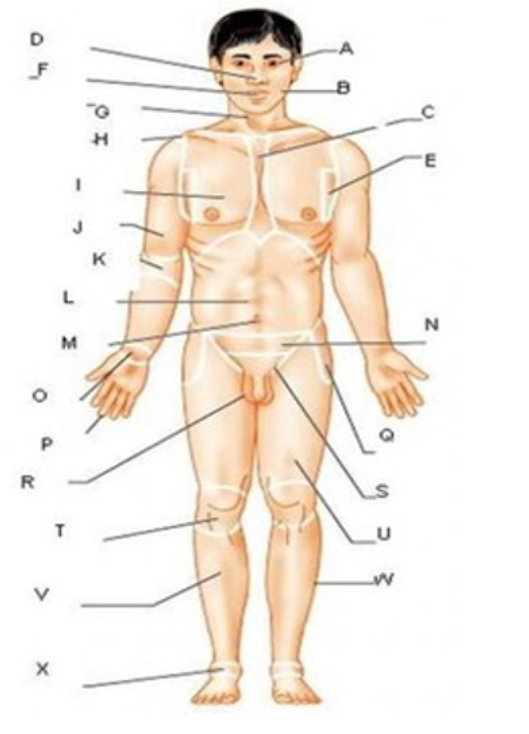
nasal
D
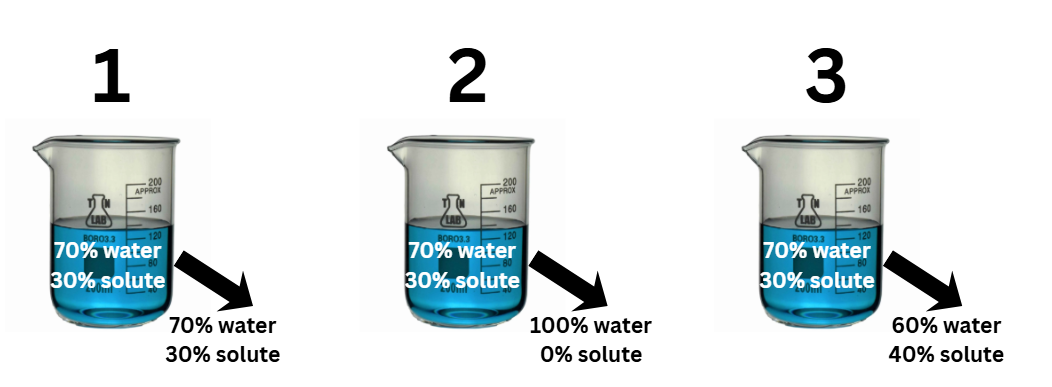
which solution represents a hypertonic solution
3
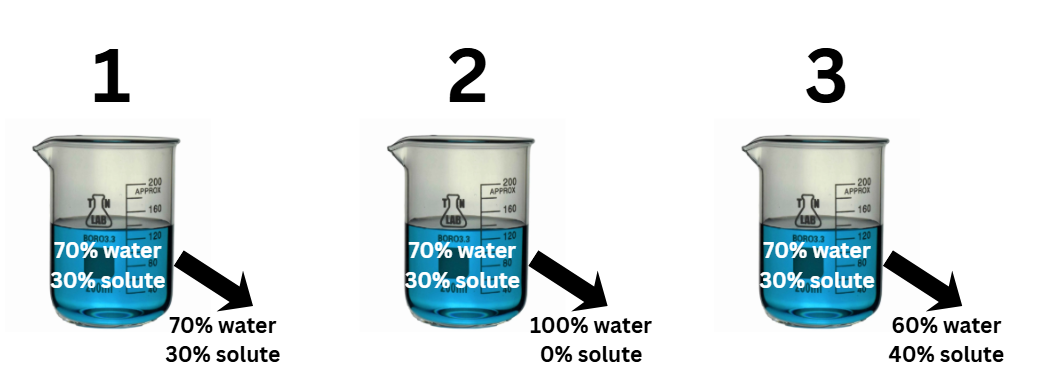
which solutions represents an isotonic solution
1
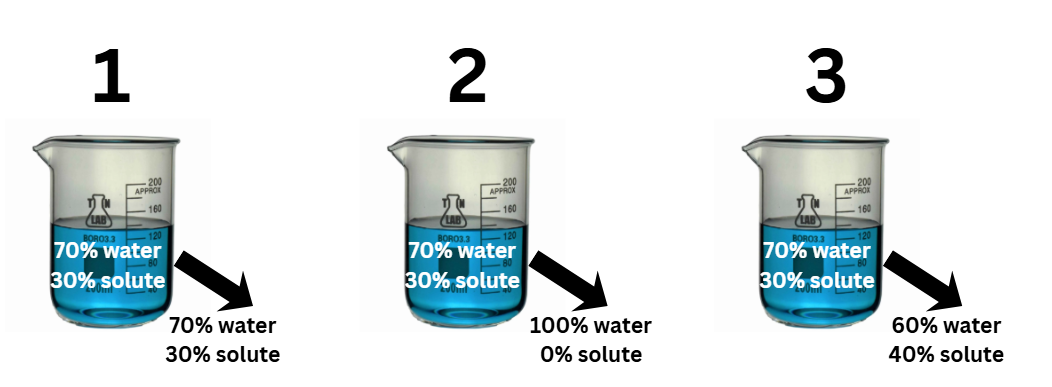
which one represents a hypotonic solution
2
list the four types of tissue and how they are unique or different from one another.
epithelial: covers exposed surfaces, lines internal cavities and forms glands
connective: connects the epithelium to the rest of the body
muscle: responsible for movement
neural: conducts electrical impulses across body
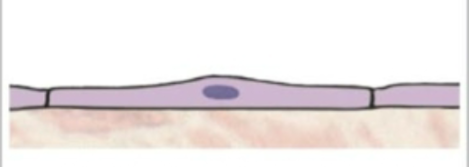
what is this tissue type
simple squamous (epithelium)
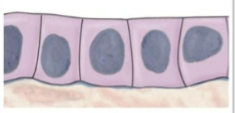
what is this tissue type
simple cuboidal (epithelial)
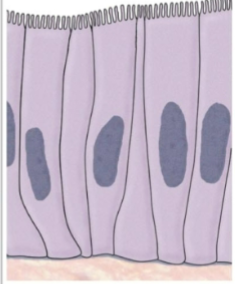
what is this tissue type
simple columnar (epithelial)
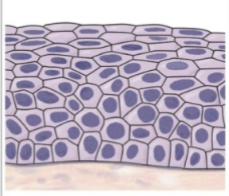
what is this tissue
stratified squamous (epithelium)
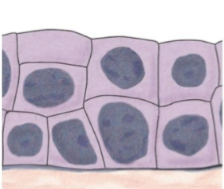
what is this tissue
stratified cuboidal (epithelium)
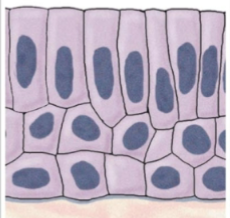
what is this tissue
stratified columnar (epithelium)
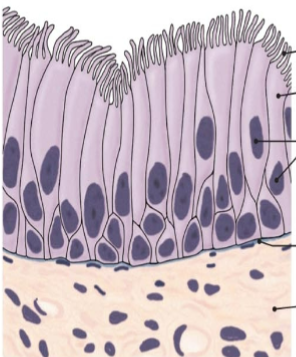
what is this tissue
pseudostratified columnar (epithelium)
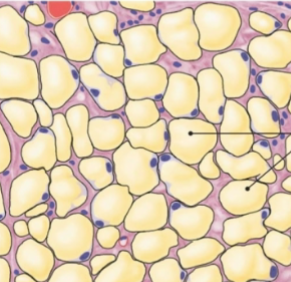
what is this tissue
adipose (connective)
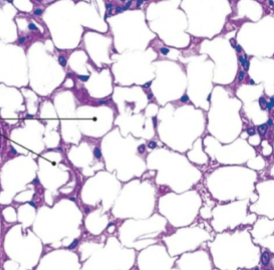
what is this tissue
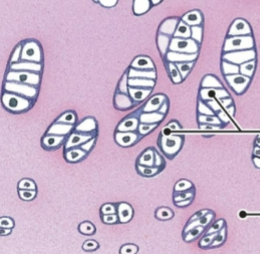
cartilage (connective)
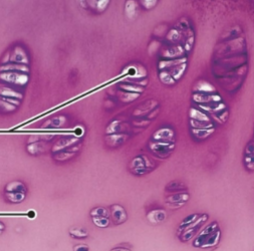
what is this tissue
skeletal (muscle)
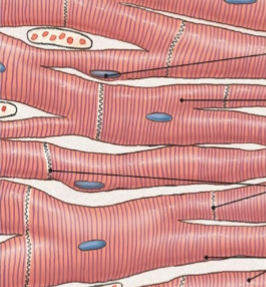
what is this tissue
cardiac (muscle)
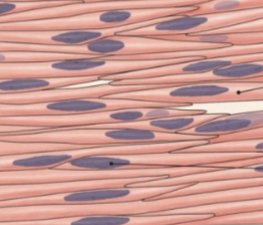
what is this tissue
smooth (muscle)
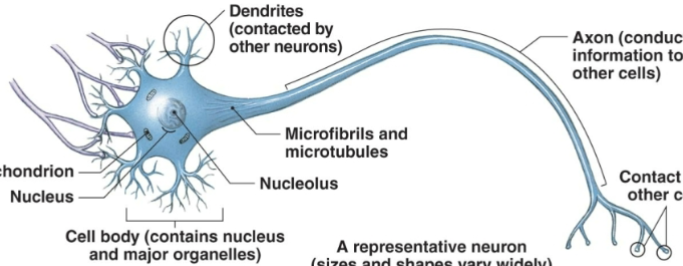
what tissue is this
neuron
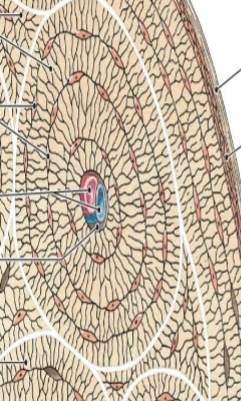
what is this tissue
bone (osseous) [connective]
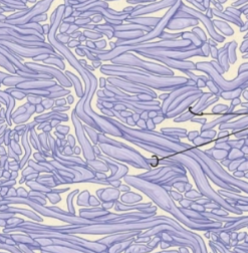
what is this tissue
dense irregular (connective)
list the three layers of the skin and their functions
epidermis: outermost, thinnest layer, waterproof barrier
dermis: middle layer, has connective tissue, hair follicles, blood vessels, sweat glands
hypodermis: deepest layer of skin, made of fat and connective tissue
what kind of specialized cells are in the epidermis and what do they do
keratinocytes: tough layer | melanocytes: pigment | dendritic: immune defense | merkel: sensory receptor
what kind of specialized cells are in the dermis and what do they do
fibroblast; collagen | mast cells; immune response | macrophages; engulf debris | sensory neurons; detect pain
what kind of specialized cells are in the hypodermis and what do they do
adipocytes: fat storage | fibroblasts: structural support
what are three ways the integumentary system regulates temperature
sweat (cools), blood flow (releases and conserves heat), hair and fat insulation (traps warmth)
list and describe the three types of burns
1st degree: effects only epidermis (sunburns)
2nd degree: effects epidermis and upper epidermis (no permanent scarring)
3rd degree: effects all layers of skin, has permanent scarring
define acne, athletes foot, boils and carbuncles, cold sores, psoriasis, impetigo, and basal cell carcinoma
acne: infection of the sebaceous glands
athletes foot: fungal infection between toes
boils and carbuncles: inflammation of hair follicles and sebaceous glands
cold sores: blisters caused by herpes
psoriasis: chronic autoimmune disease where the body overproduces skin causing itching and burning
impetigo: bacterial staph infection around mouth and nose
basal cell carcinoma: malignancy in the lowest epidermal layer
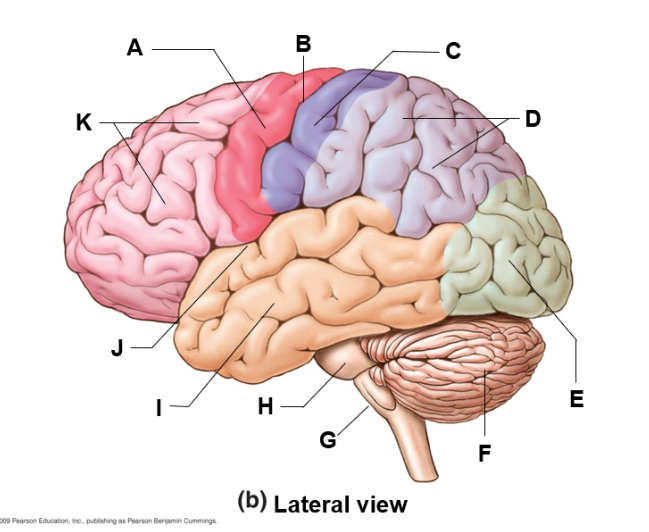
where is the cerebellum and what does it do
f | motor patterns, balance and equilibrium
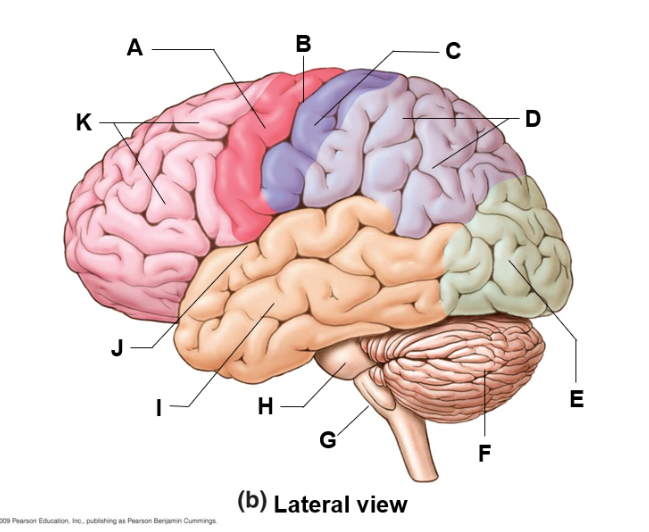
where is the frontal lobe and what does it do
k | reasoning and problem solving
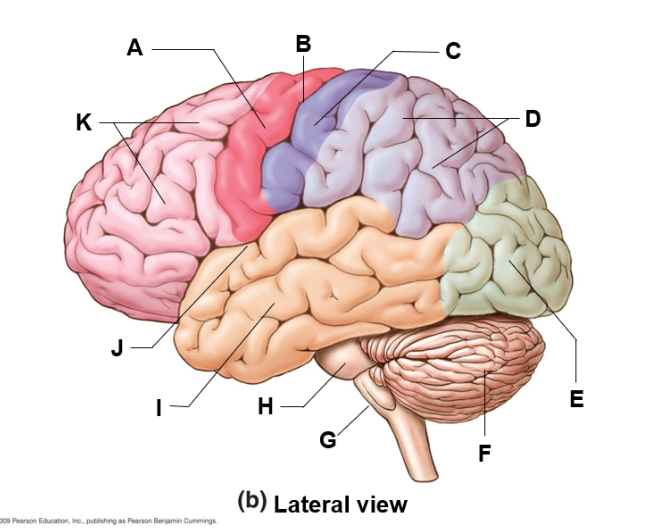
where are the pons
H
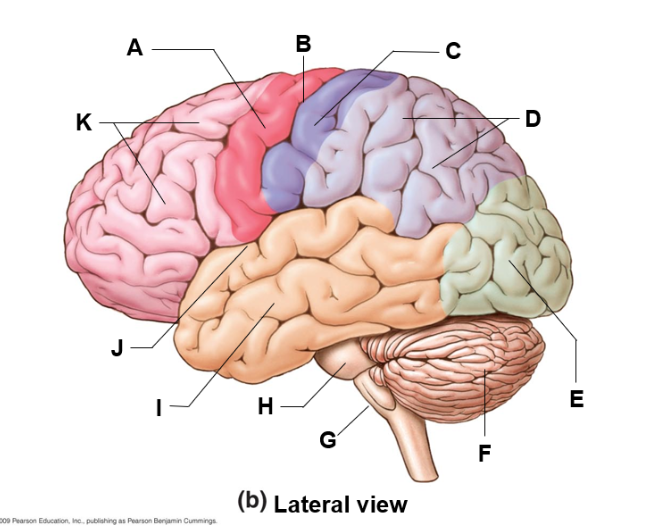
where is the medulla oblongata and what does it do
G | regulates cardiovascular, respiratory, and digestive center
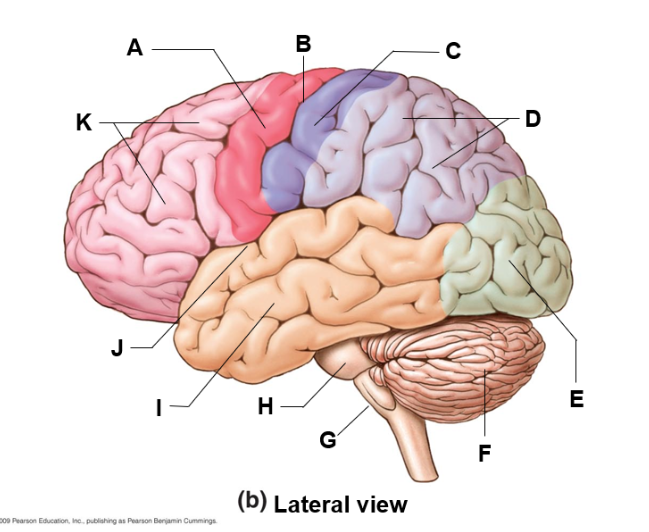
where is the occipital lobe and what does do
E | in charge of visual interpretations
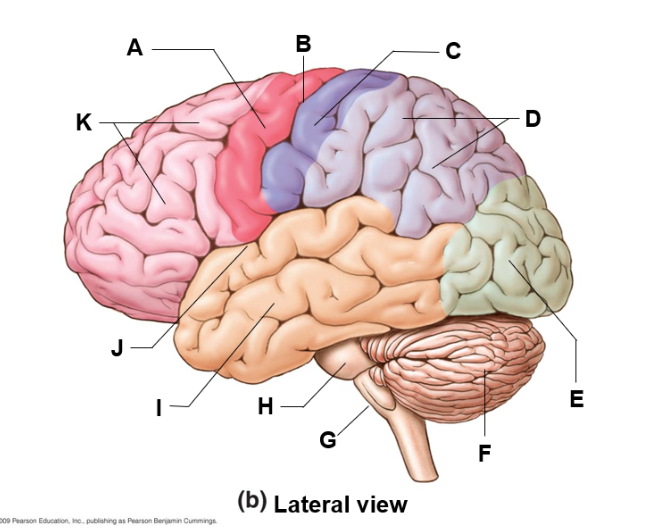
where is the parietal lobe and what does it do
D | sensory relay
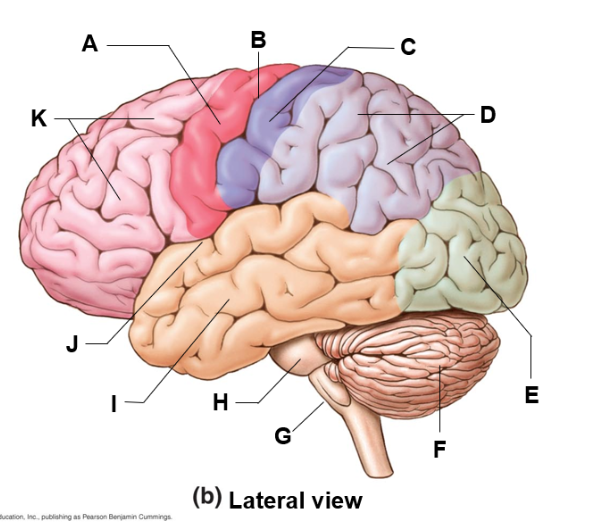
where is the temporal lobe and what does it do
i | hearing, memory, language comprehension, emotional processing, and object recognition
what does the hypothalamus do
links basic functions with emotions
what does the hippocampus do
retrieves long term memories
what does the wernickes area
it is the general interpretive area
what is the brochas area in charge of
speech
what is the raised area of the brain referred as
gyri
what are the grooves of the brain referred as
sulci
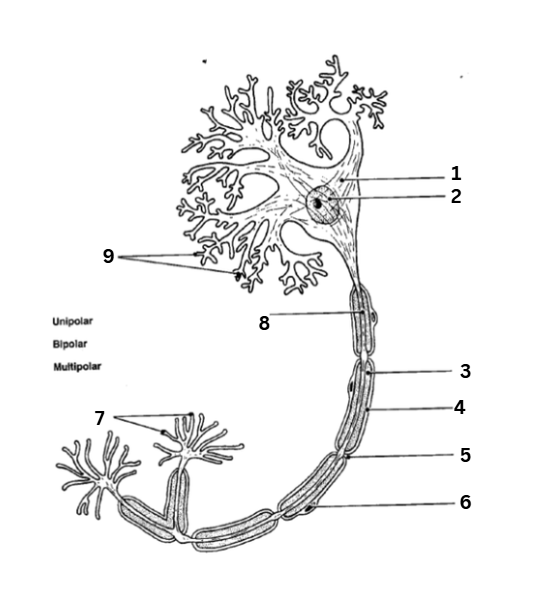
where is the axon
8
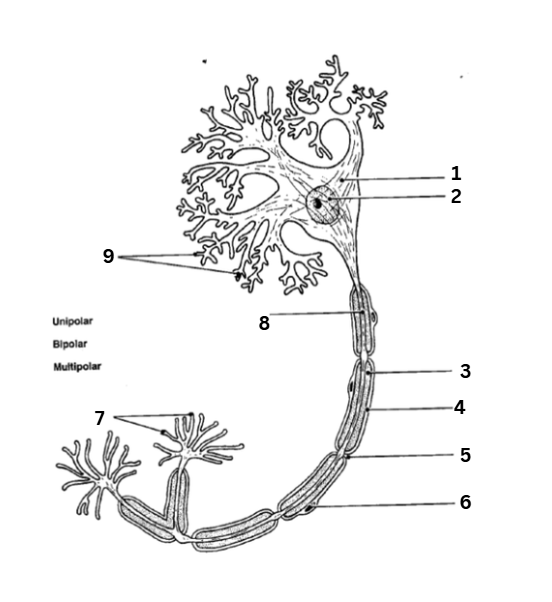
where are the dendrites
9
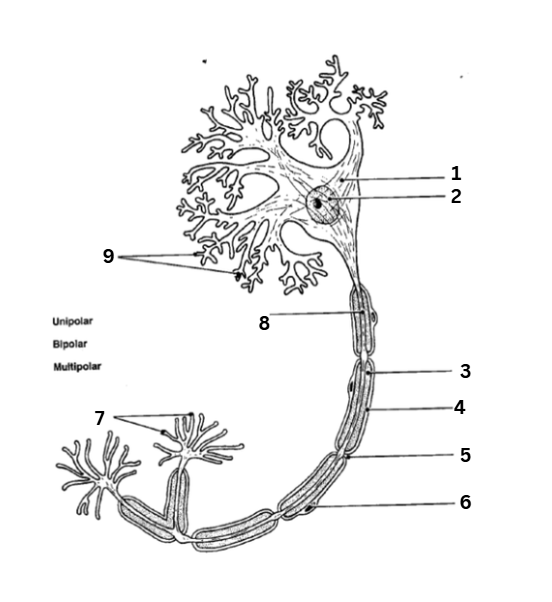
where is the myelin sheath
3
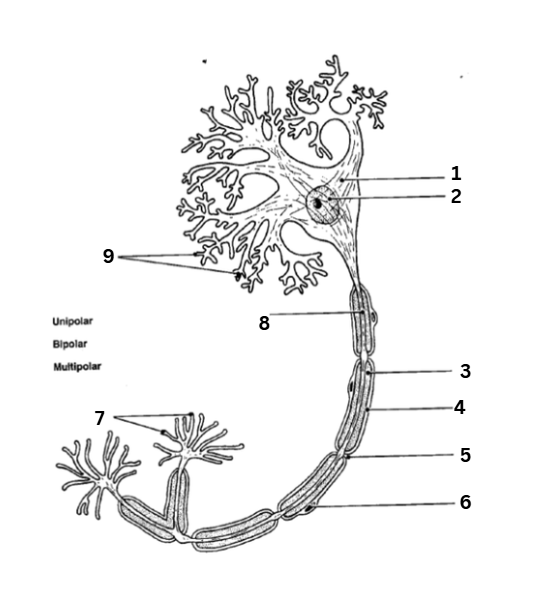
where are the synaptic terminals
7
what is the cns (central nervous system)
consists of the brain and spinal cord; acts as the body’s control center
what is the pns
consists of all other nerves; communication highway
what is the difference between neurons and neuroglia (which one can divide)
nerouns signal cells while neuroglia provides support and can divide
list the kinds of neurotransmitters discussed in unit 4 and their general functions
excitatory: causes depolarization and promotion olfaction potential
inhibitory: causes hyperpolarization and inhibits action potential
list and describe the homeostatic imbalances discussed w/ the nervous system
parkinsons: death of dopamine receptors
multiple sclerosis: degration of the myelin sheath
huntingtons disease: genetic disorder that breaks down brain
alzheimers: gradual cell death in brain
epilepsy: neurons send abnormal signals causing seizures
list the 6 primary taste sensations and describe the benefit of being able to taste certain flavors
sweet: can identify energy rich food for survival
sour: a safeguard; can identify spoiled foods
umami: can identify protein rich foods for nutrtition
water: guides hyrdration; can identify safe/pure water
salty: can detect and regulate sodium intake for health
bitter: a survival mechanism; identify poisonous foods
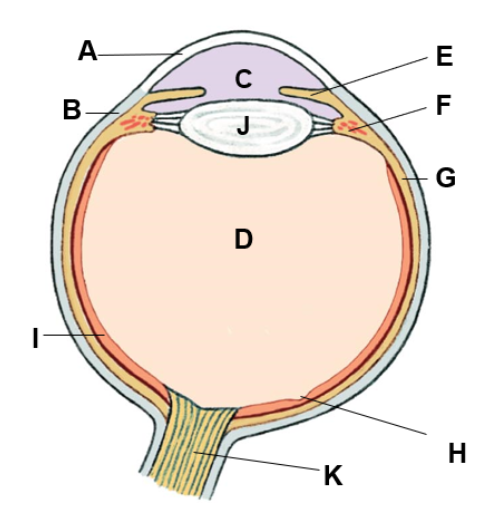
where is the aqueous humor
C (fluid in cavity)
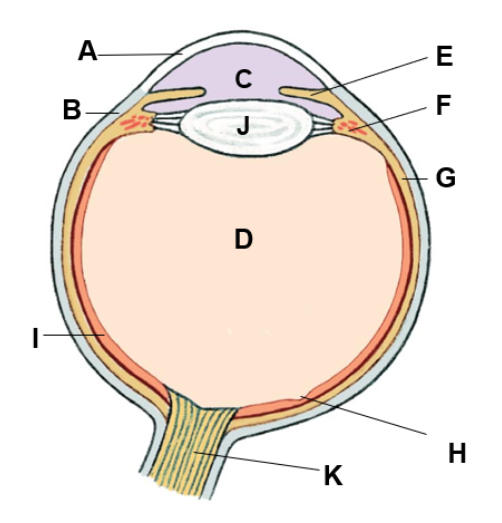
where is the choroid
G
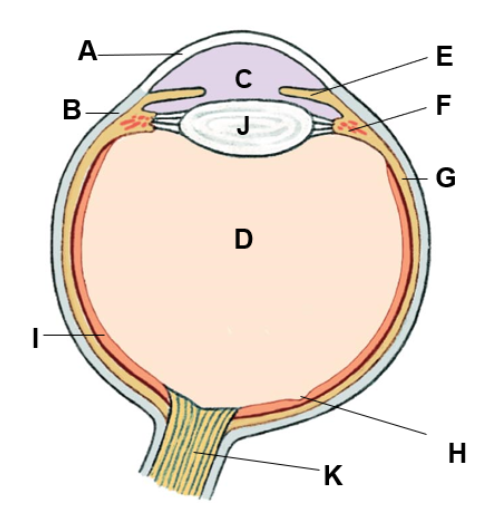
where is the ciliary body
F
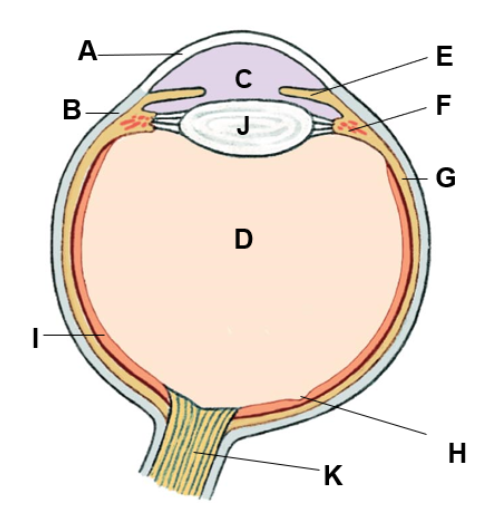
where is the cornea
A
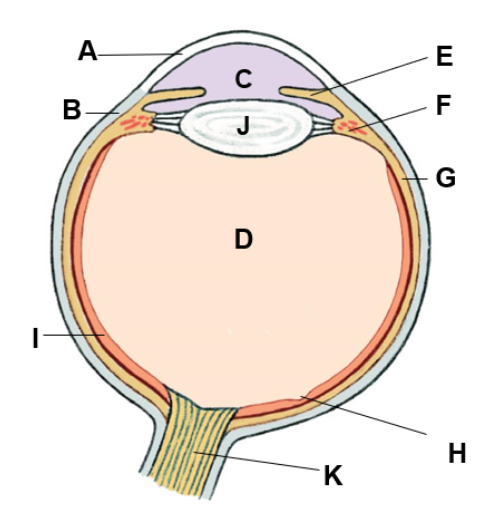
where is the fovea
H
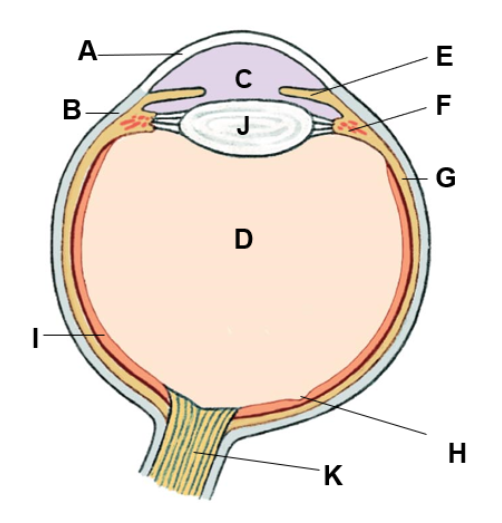
where is the iris
E