ANAPHY MIDTERMS (SKELETAL SYSTEM)
1/194
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
195 Terms
rigid framework that supports the soft tissues
skeletal system
Greek word meaning dried
skeleton
2 Division of Skeleton (ax, ap)
axial and appendicular
bones that form longitudinal axis
axial
bones that forms the limbs and girdles
appendicular
structures of the skeletal system (b, j, c, l)
bones, joints, cartilages, ligaments
between at the end of the bone (c
cartilages
attached to the bone (l
ligaments
this matrix always contains collagen, ground substance, and other organic molecules, as well as minerals and water (starting phase of bone development) (em)
extracellular matrix
Categories of Bones (lb, sb, fb, ib)
long bones, short bones, flat bones, irregular bones
(upper and lower limbs) lb
long bones
wide as they are long sb
short bones
thin, flattened shape fb
flat bones
includes vertebrae and facial bones ib
irregular bones
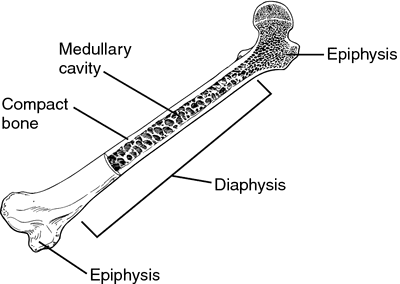
a tubular SHAFT, covered and protected by periostueum (dia)
Diaphysis
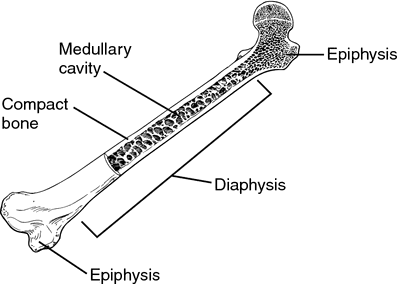
rounded end of a long bone, to connect adjacent bones (epi)
Epiphysis
a thin layer of specialized connective tissue with unique viscoelastric propertiets, to provide a smooth, lubricated surface (art c)
articular cartilage
the sheath outside your bones that supplies them with blood, nerves and the cell (peri)
periosteum
secures the periosteum to the underlying bone (shar f)
perforating or sharpey’s fibers
thin connective tissue membrane lined with the surface of the medullar cavity (endo)
endosteum
the bones’ growth plate, composed of cartilage that is responsible for bone growth (epi p)
epiphyseal plate
the bone’s growth has reached it’s limit, it converts into this line, indicating no longer growth can occur (epi l)
epiphyseal line
cavity in the bones, these spaces are filled with the soft tissue called marrow (mc)
medullar Cavity
consists mostly of adipose tissue (ym)
yellow marrow
consists of blood-forming cells and is the only site of blood formation in adults (rm)
red marrow
a cell that lies within the substance of fully formed bone. Function: to send signals of bone formation
osteocytes
repair and remodeling of bone (inserts calcium)
osteoblast
bone repair and remodeling by removing existing bone called bone reabsorption (bone destroying)
osteoclasts
thin sheets of extracellular matrix that forms the bone (lame)
lamellae
the spaces between the lamellae where osteocytes are loacated (lacu)
lacunae
cell processes extend from the osteocytes across the extracellular matrix of the lamellae within these tiny canals (canali)
canaliculi
also known as cortical bone, has more matrix and denser with few pores
compact bone
less bone matrix and more open space
spongy bone
spongy bone consists of delicate interconnecting rods or plates of bones (shaped as the beams or scaffolding of a building) (trab)
trabeculae
formation of bone by osteoblasts (bone os)
bone ossification
bone formation that occurs within the connective tissue membranes (intra os)
intramembranous ossification
bone formation that occurs inside the hyaline cartilage (endo os)
endochondral ossification
this occurs by the deposition of the new bone lamellae onto existing bone or other connective tissue (bg)
bone growth
the removal of existing bone by osteoclasts and the deposition of new bone by osteoblast (br)
bone remodeling
occurs when an open wound extends to the site of the fracture or when a fragment of bone protrudes through the skin
open fracture
the fracture did not protrudes through the skin
closed fracture
did not perforated through skin but damaged the soft tissues (compli)
complicated fracture
the fracture that did not extended completely across the bone structure
incomplete fracture
did extended completely across the bone
complete fracture
a complete fracture in which bone breaks into more than two pieces- usually two major fragments and a smaller fragment (commin)
comminuted fracture
one fragment is driven into the spongy portion of other fragment (imp)
`impacted fracture
a fracture that runs parallel to the length of the bone (line)
linear fracture
these fracure are at the right angles to the length of the bone (transv)
transverse fracture
a fracture that takes a helical course around the bone (spi)
spiral fracture
a fracture that runs obliquely in relation to the length of the bone
oblique fracture
3 hormones that maintains calcium homeostasis (ph, d, c)
parathyroid hormone , vitamin D, and calcitonin
average adult skeleton
206 bones
are projections and depressions found on bones, which helps us to identify the location of other body structures, such as muscle (bm)
bone markings
2 categories of bone markings
projections and depressions
grows out from the bone surface (proj)
projection or processeses
indentations in the bone (dep)
depressions or cavities
a moderate prominence where muscles and connective tissues attach (tuber)
tuberosity
a raised or a prominent part of the edge of a bone. (cre)
crest
a large prominence on the side of the bone (tro)
trochanter
a small, rounded prominence where connective tissues attach (tubc)
tubercle
a prominence that sits atop of a condyle (epic)
epicondyle
a sharp, slender, often pointed projection (spin)
spine
a raised, sharp elevation of bone where muscle and connective tissue attach (sp)
spinous process
it is usually covered in hyaline cartilage inside a synovial capsule (he)
head
forms a joint with another flat bone (fac)
facet
a large prominence provides support to the hyaline cartilage (cond)
condyle
curved part of the bone that gives structural support to the rest of the bone (ram)
ramus
common projections (tube, cre, tro, tubc, epic, spin, sp, he, fac, cond, ram)
tuberosity, crest, trochanter, tubercle, epicondyle, spine, spinous process, head, facet, comdyle and ramus
common openings or depression (me, sin, fos, gro, fis, for)
meatus, sinus, fossa, groove, fissure, foramen
a tube-like channel that extends within the bone, which may provide passage and protecton to nervous system
meatus
a cavity within sny organ or tissues
sinus
a shallow depression in the bone surface
fossa
a furrow in the bone surface
groove
an open slit in a bone thatr usually houses nerves and blood vessels
fissure
a hole through wich nerves and blood vessels pass
foramen
how many bones ar there in the skull
22
how many facial bones does a person have
14
form a large portion of the side of the head
parietal bone and temporal bone
bone of your forehead
frontal
the bone at the back of your head
occipital
a single bone that extends completely across the skull. resembles a butterfly
sphenoid
anterior tot the sphenoid bone or cheekbone
zygomatic
consists of joined processes of the temporal and zygomatic
zygomatic arch
forms the upper jaw
maxilla
forms the upper jaw
mandible
sutures of the skull (spcssspol)
sagittal, parietal, coronal, sphenofrontal, sphenoparietal, squamous, parietomastoid, occipitomastoid, lamboid
skull anatomy on front view (o, s&i, nc, of, naso c, lb, ns, n con, ps, mac)
orbit, superior and inferior orbital fissures, nasal cavity, optic foramen, nasolacriminal canal, lacrimal bone, nasal septum, nasal conchae, paranasal sinuses, mastod air cells
paranasal sinuses (fesm)
frontal, ethmoid, sphenoid, maxillary
an auditory tube ‘connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx
mastoid air cells
anatomy of the inferior cranial cavity (for o& for rot, for mag, sel turc)
foramen ovale & foramen rotundum, foramen magnum, sella turcica
transmits nerve to the face
foramen ovale & foramen rotundum
enables the spinal cord to join with the brain
foramen magnum
resembles the saddle and also contains the pituitary gland
sella turcica
smooth points of articulation between the skull and the vertebral column
occipital condyles
the pharynx (throat) originates from this process
styloid process
mandible articulates with the temporal bone
mandibular fossa
roof of the mouth and the floor of nasal cavity
hard palate
the anterior two-thirds of the hard palate is formed by the maxillae
palatine bones
posteriorly located from the hard, or bony palate
soft palate
unpaired U-shaped bone
the only bone in the body that does not articulate with another bone
hyoid bone