Min Pet exam 2
1/48
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Enstatite is what on a ternary diagram?
Is the Mg end member for pyroxene
Enstatite chemical formula?
Mg2Si2O6
Diopside is what on a ternary diagram?
Calcium and Magnesium end members for pyroxene
Diopside chemical formula is?
CaMgSi2O6
Hedenbergite is what on a ternary diagram?
Calcium and iron end members for pyroxene
Hedenbergite chemical formula is?
CaFeSi2O6
Ferrosilite is what on a ternary diagram
Fe end member for pyroxene
Fayalite in a ternary diagram is?
The Fe end member for Olivines
Forsterite in a ternary diagram is?
The Mg end member for Olivines
Fayalite chemical formula?
Fe2SiO4
Forsterite chemical formula?
Mg2SiO4
Amphiboles need what in their environment to form?
H2O
How the silicate minerals are classified?
by how the Silicate Tettrhedens are bonded to make chains, islands, double —-chains, and sheets.
How are the following list of minerals are related: Olivine, Pyroxene, Amphibole, Mica, Feldspar, and Quartz
They are all silicate minerals classified based on their crystal structure and the arrangement of silicate tetrahedra.
How are the following list of silicates are related: Isolated vs Chain vs Double Chain vs Sheet vs Framework tetrahedra
Bridging oxygens! Where isolated tetrahedra do not share oxygens, chain tetrahedra share two oxygens, double chain tetrahedra share two and three oxygens, sheet tetrahedra share three oxygens, and framework tetrahedra share all four oxygens.
What is the importance of Bridging Oxygens in determining the identity, character, and behavior of all the silicate minerals.
Are crucial as they connect silicate tetrahedra, influencing the structure and properties of silicate minerals. Their arrangement affects mineral stability, reactivity, melting temperature, cleavage, and physical characteristics.
What does 'polymerization' mean in describing the structure of the silicate minerals.
Polymerization refers to the process by which silicate tetrahedra bond together to form larger structural units, such as chains, sheets, or frameworks, thereby influencing the mineral's overall structure and properties. (It does not have to be a silicate mineral)
The importance of the size and charge of ions in constructing mineral structures.
Determine how ions fit into the crystal lattice of minerals, affecting stability, coordination, and the overall geometry of mineral structures. must have the same charge but can be switched.
What is the meaning of coordination number in crystal lattices?
Refers to the number of nearest neighbor ions or atoms surrounding a central ion in a crystal lattice. shape of the cage
How and why can the size and charge of cations affect the topology phase diagrams?
The size and charge of cations can significantly influence the stability and determine how cations fit into the mineral structures, affecting coordination, bonding interactions, and phase transitions.
What 4 Fold site ions?
Si+4 and Al+3
What 6 fold site ions?
Fe+2, Mg+2, Al+3
What are the 8 fold site ions?
Ca+1
Fractionation is?
Bigger ions melting before smaller ions
What is the meaning and significance of solid solution
A homogeneous solid crystalline phase that contains two or more components, where the solute atoms can substitute for the solvent atoms in the crystal lattice. This affects mineral properties, stability, and the formation of new mineral phases.
What is the meaning of the solidus, the liquidus, and the melting interval in T-X phase diagrams
The solidus is the temperature below which a substance is entirely solid, the liquidus is the temperature above which a substance is entirely liquid, and the melting interval is the range of temperatures where both solid and liquid phases coexist. These concepts are crucial for understanding phase transitions in materials.
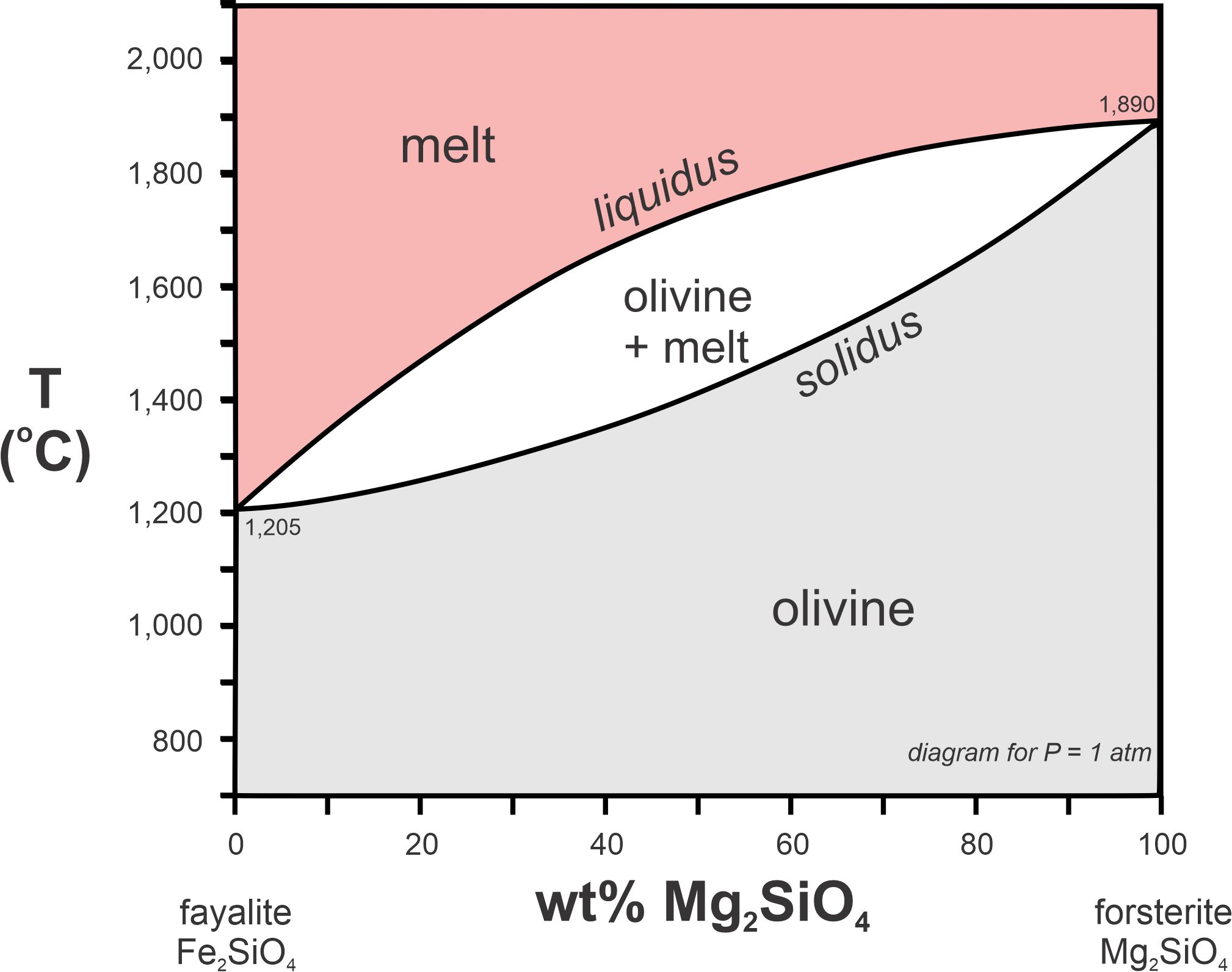
What does a tie line connect in a phase diagram?
It connects two(or three) phases at equilibrium and conveys the chemical composition of the two coexisting phases
What 'endmember composition' refers to in a ternary diagram?
The composition of a pure phase that corresponds to a corner of the ternary diagram, representing a specific mineral or component in the mixture.
Describe the compositional variations in all types of mafic minerals
Ca (top), Mg (bottom left), and Fe (bottom right) are used to describe the compositional variations
Strongest common bond?
SiO4
Olivine’s and pyroxenes have endmember compositions ___?__the way toward the pure Ca-endmember?
½ the way to Ca-endmember
Amphiboles have endmember compositions ___?__ the way toward the pure Ca-endmember.
2/7 the way toward the pure Ca-endmember.
What are the mineral names and chemical formulas for quadrilateral endmember olivines?
forsterite (Mg2SiO4), fayalite (Fe2SiO4), and (Ca2SiO4).
What are the mineral names and chemical formulas for quadrilateral endmember pyroxenes?
enstatite (MgSiO3), ferrosilite (FeSiO3), and diopside (CaMgSi2O6).
What are the mineral names and chemical formulas for quadrilateral endmember Amphiboles ?
tremolite (Ca2Mg5Si8O22(OH)2), actinolite (Ca2(Mg,Fe)5Si8O22(OH)2), and hornblende (a complex mixture of several endmembers).
what 'coupled substitution' means in mineral sites
That cations other than with a charge of 2+ can readily fit within the M-sites of pyroxenes and amphiboles (but not olivines), as long as they are accompanied by another cation that keeps the formula charge balanced (e.g., Na+1 & Sl+3 for two Mg2+).
What defines the difference between tri- and di-octahedral phyllosilicates.
The difference lies in the arrangement of cations in the octahedral sites; tri-octahedral phyllosilicates have three cations per octahedral site, while di-octahedral phyllosilicates have two.
What makes biotite different from muscovite both compositionally and structurally?
Biotite contains iron and magnesium, giving it a darker color, while muscovite is composed mainly of potassium and aluminum, making it lighter. Structurally, biotite has a more complex layer arrangement due to heavier cations.
What is the ternary diagram for feldspars (K, Na, Ca) and the chemical range within which natural feldspars are found
The three end-member feldspar minerals: potassium (K), sodium (Na), and calcium (Ca). Natural feldspars are found within this diagram, typically ranging from K-feldspar (orthoclase) to Na-feldspar (albite) to Ca-feldspar (anorthite), illustrating their solid solution series.
Why hydrothermal fluids are responsible for (and necessary) to increase polymerization (and water content) of minerals during weathering (via meteoric waters) AND decrease polymerization (and water content) of minerals during metamorphism.
Facilitate the transport of ions and enhance chemical reactions during weathering, increasing the polymerization of minerals through the addition of water. Conversely, during metamorphism, these fluids can lead to a decrease in polymerization and water content as minerals undergo recrystallization under heat and pressure, promoting denser structures.
What are meteoric waters?
Meteoric waters are fresh waters derived from precipitation, such as rain or snow, that infiltrate the ground and contribute to weathering processes.
What exsolution is, and WHY it happens.
is the process by which a homogeneous solid solution separates into two distinct phases, typically due to changes in temperature or pressure. This phenomenon occurs when conditions favor the stability of different mineral compositions, leading to the formation of distinct mineral phases from the original solid solution.
What is the meaning of polymorph?
A polymorph is a mineral that can crystallize in more than one distinct crystal structure, depending on temperature and pressure conditions.
Know where the minerals alpha quartz, beta quartz, stishovite, and cristobalite plot on a P-T phase diagram of pure silica.
These minerals represent different polymorphic forms of silica that occur at varying temperatures and pressures on the phase diagram.
Coordination number refers to what?
the number of nearest neighboring atoms or ions surrounding a central atom in a crystal structure. It plays a crucial role in determining the geometry and stability of the crystal.
Tectosilicates are?
Three-dimensional framework of silicate tetrahedra. They include minerals like quartz and feldspar.
Double chain silicates have how many bridging oxygens?
Two bridging oxygens between tetrahedra, forming a structure that allows for complex arrangements and various mineral types.
Single chain silicates have how many bridging oxygens?
Feldspar is classified under what silicate type?
Tectosilicates