CHEM 205 in-class MCs
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Which topic is most directly concerned with whether a reaction can occur at all?
A. Kinetics
B. Thermodynamics
C. Spectroscopy
D. Analytical chemistry
B
A reaction is thermodynamically favourable but proceeds extremely slowly. Which statement is correct?
A. The reaction violates the second law
B. The reaction has a large activation energy
C. The reaction is impossible
D. The reaction is exothermic
B
Question-p4: Why are gases typically the first state of matter studied in thermodynamics?
A. Gases have the highest energies of all states of matter
B. Gas molecules do not move
C. Gases are simple to model because intermolecular interactions are weak
D. Gases never deviate from ideal behavior
C
Question-p5: Which of the following is not a state function?
A. Pressure
B. Temperature
C. Volume
D. Path taken between states
D
Question-p7: Why does the ideal gas constant R have different numerical
values?
A. It depends on the gas
B. It depends on temperature
C. It depends on the choice of units
D. It changes for real gases
C
Question-p10: At constant pressure, increasing the temperature of an ideal gas causes the volume to:
A. Decrease
B. Remain constant
C. Increase
D. Become zero
C
Question-p11: Which assumption of the kinetic molecular model fails first at
high pressure?
A. Random motion
B. Elastic collisions
C. Negligible molecular volume
D. Temperature proportional to kinetic energy
C
Question-p13: Why does the change in momentum upon collision equal 2mvₓ?
A. The molecule speeds up after collision
B. The molecule reverses direction elastically
C. The molecule loses kinetic energy
D. The molecule changes mass
B
A. Molecules prefer diagonal motion
B. The container is cubic
C. Space has no preferred direction
D. Collisions remove velocity components
C
Question-p14: For an ideal gas in CHEM 205, internal energy U depends on:
A. Pressure only
B. Volume only
C. Temperature only
D. Pressure and volume
C
Temperature of an ideal gas is proportional to:
A. Total kinetic energy
B. Average translational kinetic energy per molecule
C. Potential energy between molecules
D. Molecular mass
B
Why do vibrational modes often not contribute to internal energy at room temperature?
A. They do not exist
B. Vibrations require quantum excitation energies not thermally accessible
C. Vibrations reduce pressure
D. Vibrations violate equipartition
B
Two systems are in thermal equilibrium. Which must be equal?
A. Internal energy
B. Temperature
C. Enthalpy
D. Entropy
B
Which system(s) can exchange energy with its surroundings?
A. Isolated
B. Closed
C. Open
B, C
Which quantities depend on the path taken?
A. ΔU
B. T
C. q
D. w
E. U
C, D
Gas expands against external pressure. What is the sign of w?
A. Positive
B. Negative
C. Zero
D. Undefined
B
Joule’s experiments showed that:
A. Heat is conserved
B. Heat is matter
C. Work and heat are equivalent
D. Heat flows upward
C
Which process has q = 0?
A. Isothermal
B. Isochoric
C. Isobaric
D. Adiabatic
D
What pressure appears in expansion work?
A. Internal
B. External
C. Average
D. Atmospheric always
B
A gas expands into a vacuum. Which statement is correct?
A. w > 0
B. w < 0
C. w = 0
D. Depends on the gas
C
For expansion at constant external pressure, the work equals:
A. The slope of the p–V line
B. The height of the rectangle
C. The width of the rectangle
D. The area of the rectangle
D
In a constant-pressure process, the measured heat equals:
A) U
B) H
C) -w
D) qV
B
A system with a large heat capacity will show:
A) Large temperature changes
B) Small temperature changes
C) No temperature change
D) Negative temperature change
B
Heat capacity is best described as:
A) Stored heat
B) Energy per mole
C) Resistance to temperature change
D) Work capacity
C
In a rigid container, all supplied heat goes into:
A) Work
B) Enthalpy
C) Internal energy
D) Entropy only
C
For heating at constant pressure, the correct expression is:
A) U = nCPT
B) H = nCPT
C) H = nCVT
D) U = qP
B
For one mole of an ideal gas, CP - CV equals:
A) 0
B) R
C) 2R
D) depends on pressure
B
For an ideal gas, (U) depends on:
A) Path
B) Pressure
C) Volume
D) Temperature change
D
For an ideal gas, which condition guarantees ΔH = 0?
A) Constant pressure
B) No work done
C) No temperature change
D) Adiabatic process
C
If a balanced reaction equation is multiplied by 2, the reaction enthalpy:
A) Stays the same
B) Is halved
C) Doubles
D) Becomes zero
C
A reaction with ΔrH < 0 is:
A) Endothermic
B) Exothermic
C) Spontaneous
D) Reversible
B
Reaction enthalpy changes with temperature because:
A) Enthalpy is path-dependent
B) Heat capacities differ
C) Pressure changes
D) Entropy changes
B
Kirchhoff’s law allows calculation of ΔrH at a new temperature using:
A) Entropy data
B) Heat capacities
C) Volume changes
D) Work terms
B
Which statement about entropy change is always correct?
A) A spontaneous process must increase the entropy of the system
B) A reversible process must increase the entropy of the system
C) A spontaneous process must increase the entropy of the universe
D) Any process with ΔS = 0 is spontaneous
C
Why is entropy defined using δq_rev?
A) All real processes are reversible
B) Reversible paths maximize work
C) Entropy must be path independent
D) Irreversible heat cannot be measured
C
Two different paths connect the same initial and final states.
Which is correct?
A) ΔS depends on the path
B) ΔS is larger for the reversible path
C) ΔS is the same for both paths
D) ΔS cannot be calculated
C
What entropy is being calculated in p76?
A) Entropy change of the universe
B) Entropy change of the surroundings
C) Entropy change of the system
D) Entropy production due to irreversibility
C
Why can the formula ΔSsys=nR ln(V2/V1) be used even if the
expansion is irreversible?
A) Because irreversible processes always increase entropy
B) Because heat transfer is the same in reversible and irreversible processes
C) Because entropy is a state function
D) Because the gas is ideal
C
An ideal gas undergoes an irreversible free expansion at constant
temperature. Which statement is correct?
A) q=0 and ΔSsys=0
B) q=0 and ΔSsys>0
C) q≠0 and ΔSsys>0
D) Entropy cannot be calculated
B
At constant T and p, what condition guarantees spontaneity
A. ∆S_sys > 0
B. ∆H < 0
C. ∆G < 0
D. ∆S_univ = 0
C
Why does a perfect crystal have zero entropy at 0 K?
A. Atomic motion stops completely
B. Enthalpy is zero
C. Only one microstate exists
D. Heat capacity diverges
C
Which condition must hold for two phases to coexist?
A. Same density
B. Same temperature only
C. Same Gibbs energy
D. Same entropy
C
The normal boiling point is defined at:
A. Triple point
B. Critical point
C. 1 atm
D. Any pressure
C
At the triple point of a one-component system:
A. F = 2
B. F = 1
C. F = 0
D. F = 3
C
Above the critical temperature:
A. Gas can liquefy under pressure
B. Liquid and gas coexist
C. Only solid is possible
D. Only supercritical fluid exists
D
A key advantage of supercritical CO₂ is:
A. High toxicity
B. Fixed polarity
C. Tunable solvent properties
D. Low pressure operation
C
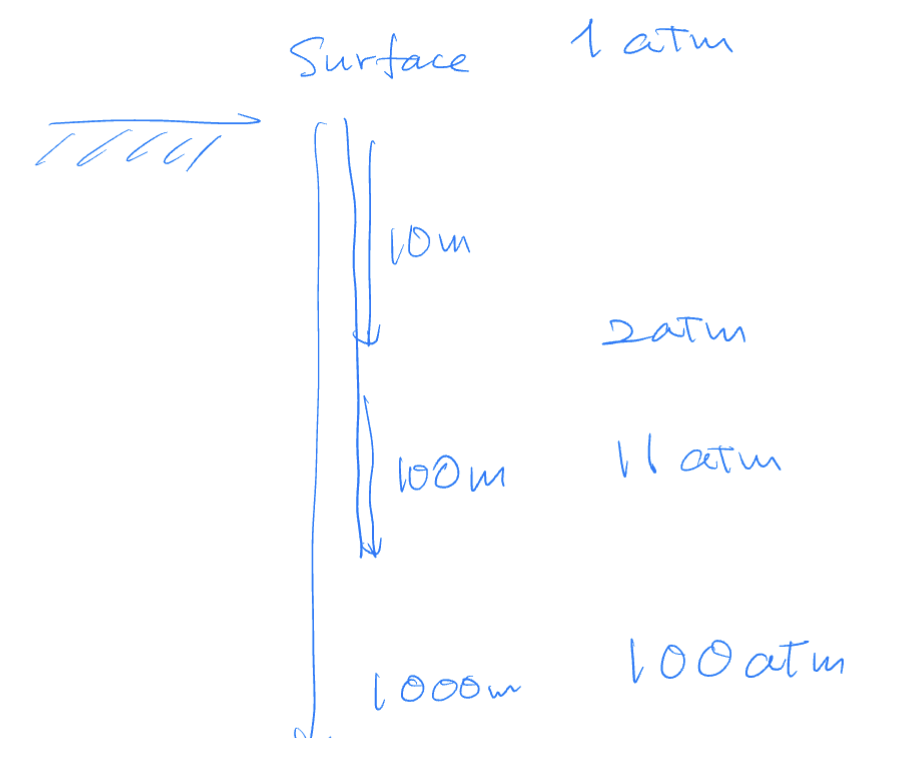
At approximately what ocean depth does the pressure reach the
critical pressure of water (~218 atm)?
A. 200 m
B. 2 km
C. 20 km
D. 200 km
B
For vaporization at the boiling point, which statement is correct?
A. ΔH < 0 and ΔS < 0
B. ΔH > 0 and ΔS < 0
C. ΔH > 0 and ΔS > 0
D. ΔH = 0 and ΔS > 0
C