Ch: 34 The Influence of Monetary and Fiscal Policy on Aggregate Demand
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
What’s the Aggregated Demand (AG) Curve?
A curve that shows the total quantity of goods demanded at any price level
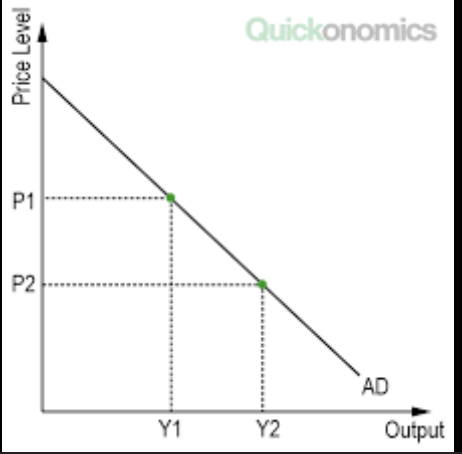
Why is the aggregated demand curve sloping downward?
The wealth effect
The interest rate effect
The exchange rate effect
What’s the wealth effect?
***price decrease = value of goods increase
a lower price (level) increases the real value of household money holdings.
This makes everyone wealthier, leading to consumers spending more, and demand increases for goods and services
What’s the interest rate effect?
The most important reason is that the AD curve is downward sloping!!
A lower price level leads to a decreased demand for money, because the value of holdings increases, so they don’t need to borrow as much.
People try to lend excess money, interest rate falls, this increases investment spending, leading to an increased demand in goods and services
What’s the exchange rate effect?
When a lower price → (household goods are valued higher → decrease money demand → shift in AD curve showing) reduces interest rates, some G&S are sold oversea → domestic currency falls, domestic goods become cheaper relative to foreign goods, increase the quantity of G & S demanded
Recall, what’s the formula for Y?
Y = C + I + G + NX
Y = GDP
C = Consumption
I = Investment
G = Government purchase
NX = Net exports
What’s the relationship between interest rate and investment spending?
inverse, as interest rates increase, investment spending decreases
What’s the theory of liquidity preference
factors that determine the interest rate
What does the interest rate adjust for?
to balance the S & D for money
What do you expect with the rate of inflation
it’s constant
What do you assume about the money supply?
It’s fixed, doesn’t depend on interest rate
What’s Money Demanded?
It shows ho much wealth people want to hold as cash/liquid form
What are the two ways households can hold wealth?
money - liquid & pays no interest
bonds - pays interest but not as liquid
What is interest rate?
It’s the opportunity cost of holding cash. When you hold cash, you lose the interest you could have earned had it been in invested.
What happens when you increase the interest rate, what happens to the money demanded?
it reduces quantity of money demanded.
If you increase the interest rate → the cost of holding money increases → and as a result, decreases quantity of money demanded
What are the 3 factors that influence money demanded?
Y, r, P
What happens when there’s an increase in Y (real income)?
households buy more goods, they need more money, money demanded increases
If income increases, resulting an increase in money demanded, how do they get this money?
By selling some of their bonds
What’s the relationship with Y and money demanded?
As Y increase, money demanded also increases (everything else held constant)
What’s the relationship between Y, r, and P with quantity of money demanded?
Y (real income) - positive relationship, as income increases, more money to spend, wants to sell bonds and get more money, quantity of money demanded increases
r (interest rate) - inverse relationship, as interest rates increase, the cost of holding money in cash increases, so they put it as bonds and don’t need as much liquid cash, quantity of money demanded decreases
P (price level) - positive relationship, as price level increases, value of money falls, people need more money to purchase goods, so quantity of money demanded increases

money demanded decreases
money demanded increases
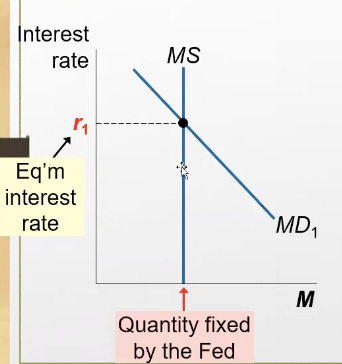
Based on this graph, what’s the relationship between R and MS & MD?
MS curve is vertical, changes in r don’t affect MS, bc it’s fixed
MD curve is downward sloping, decrease in r increases the demand for money
Recall, what’s the theory of liquidity preferences?
the interest rate adjusting to bring the quantity of money supplied and the quantity of money demanded into balance
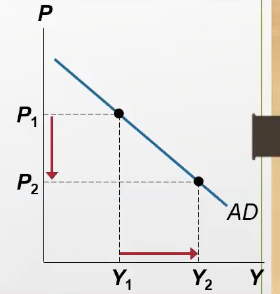
When the price level decreases, what happens to the money demand (MD) curve & interest rate?
The MD curve shifts left, interest rate falls
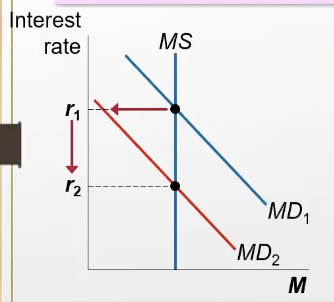
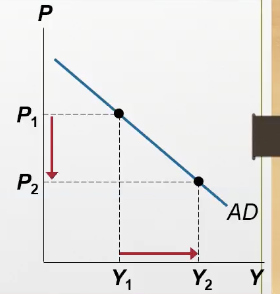
Recall, when the interest rate falls, what happens to the investment demand?
investment demanded (part of AD curve, bc it includes Y (which equals C + I + G + NX) as well as r and P) in the economy increases, leading to a movement down the AD curve
What does the Fed use to shift the AD curve? And how does it do it?
They use the Monetary Policies, which targets the interest rate (the federal fund rates) to alter the Money supply (MS)
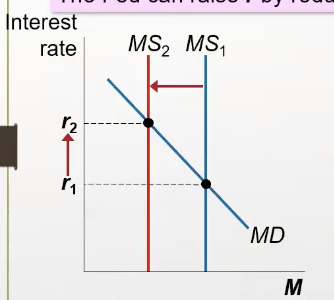
What happens when the FED reduces money in the MS, what happens to the interest rate, and the quantity of G’s & s’s demanded?
MS curve shifts left, interest rate increases, quantity of g & s demanded decreases
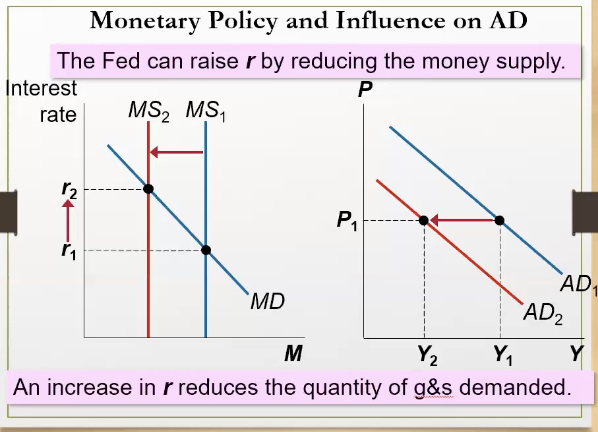
What happens to the AD curve when the fed reduces the money supply?
AD shifts to the left because of decreased demand for goods and services
What happens when the fed increases money supply?
MS curve shifts right, interest rate decreases, quantity of demanded goods & services increase, leading to a right shift of AD curve because quantity of aggravated goods increase
opposite of what the image is displaying

AD falls, shifts left, bc of lower gov spending
increase the money supply, MS shifts right, reducing the interest rate, so AD in the economy increases
Whats a liquidity traps?
when interest rates fall to 0
What happens to monetary policy when there’s a liquidity trap?
it isn’t effective anymore, because nominal interest rates cannot be reduced further
What are the two other tools central banks have to continue expanding the economy?
forward guidance
qualitative easing
What’s forward guidance?
keeping interest rates low for an extended period of time
Quantitative easing
buys short-term government bonds or mortgages, corporate debt, long-term gov bonds, which also lowers interest rates. Increases quantity of bank reserves
What’s the Fiscal Policy?
Setting the level of government spending (G) and taxation (T) by the government
What’s an expansionary fiscal policy?
when there’s an increase in G or a decrease in T, leading to AD shifting right
What’s a contractionary fiscal policy?
When G decreases, or T increases, AD curvey shifts left
What are the two affects the Fiscal policy has on AD?
The multiplier effect
What’s the multiplier effect?
The additional shifts in AD that result when fiscal policy increases income and increases consumer spending
1st shift: government spending: 2nd shift: higher income leads to increase consumer spending
When does the multiplier effect happen?
When the government makes Government purchases, they distribute the wealth through wages, profits and stock dividend. Consumers will spend this extra income and FURTHER increases consumption in aggregated demand
What’s Marginal Propensity to consume? (MPC) as well as its formula
MPC = Change in C / Change in Y (income)
the fraction of extra income that households consume rather than save
If MPC is If income rises 100 and consumption rises 80, how much is MPC?
0.8
What’s the formula for the multiplier?
Change in income = 1/(1-MPC) x Change in G
When MPC is bigger, what ‘s the relationship between Y and C?
When MPC is bigger… changes in Y cause bigger changes in C, which in turn cause a bigger change in Y.
What’s the deviation of the multiplier?
Y = C + I + G + NX
∆Y = ∆C + ∆G (I & NX are constant)
∆Y =(MPC) X ∆Y + ∆G (Marginal Propensity Consume, MPC = ∆C/∆Y
Simplify to ∆Y = (1/1-MPC) ∆G
What is another application of the multiplier effect (when it comes to a reduced government money?
The fall in income, leads to a fall in consumption, which further reduces AD, so it can happen both in an increasing and decreasing fashion
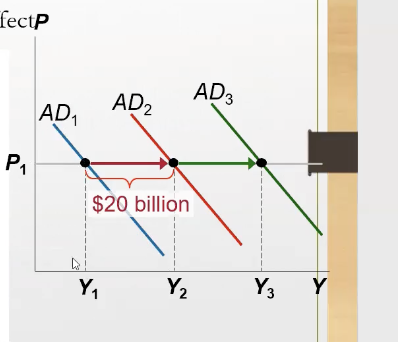
What’s the crowding out effect?
increased government spending leads to a decrease in spending, investment, and overall economic activity
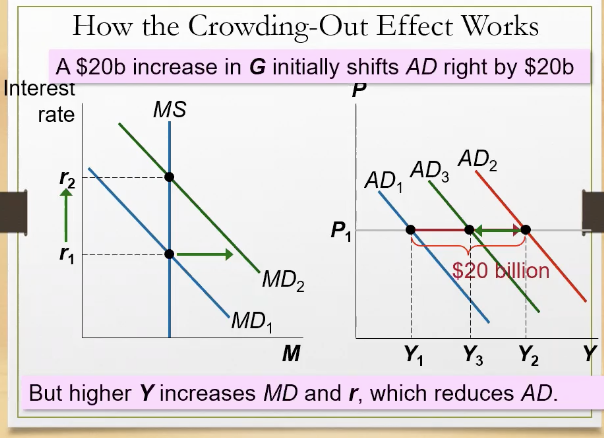
When does the crowding out effect occur?
When there’s an expansionary fiscal policy that raises the interest rate
What happens when there’s an increase in income, because of the fiscal expansion?
the demand for money increases, shifts right, interest rate increases (making borrowing more expensive), leading to investment falling
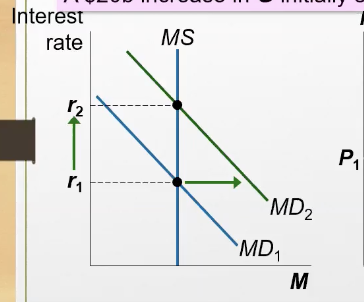
Why does investment fall?
When gov purchases more , it increases demand for good but crowds out investments.
How does the crowding affect impact the AD?
It slightly “undo’s” the government purchases’s impacts on AD, making it go backward
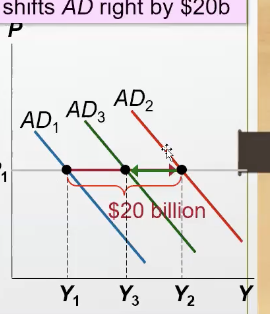
When the gov increases purchases by 20 billion dollars, the AD for goods and services could rise more or less than 20, because it depends on…
the multiplier and crowing out effect
What happens when there’s a tax cut? What happens to income and AD?
Increase in household take home pay, spend more, shifting AD to the right
What happens to the AD when there’s a permanent tax cut?
LARGE impact on AD
What happens to the AD when there’s a temporary tax cut?
SMALL impact on AD

A.
find multiplier = 1/(1-MPC) = 1/(1-.8) = 5
Solve for change in G, 200b = 5 x (?), where ? = 40 (theres no crowding out)
B. increase G even more if there’s crowding out
When feds buy bonds in an open market, what happens to money supply curve?
shifts right
When households hold money, what happens to money demand curve
shifts right, they demand more physical cash
when fed reduces banks reserve requirements, what happens to money supply curve?
shifts right
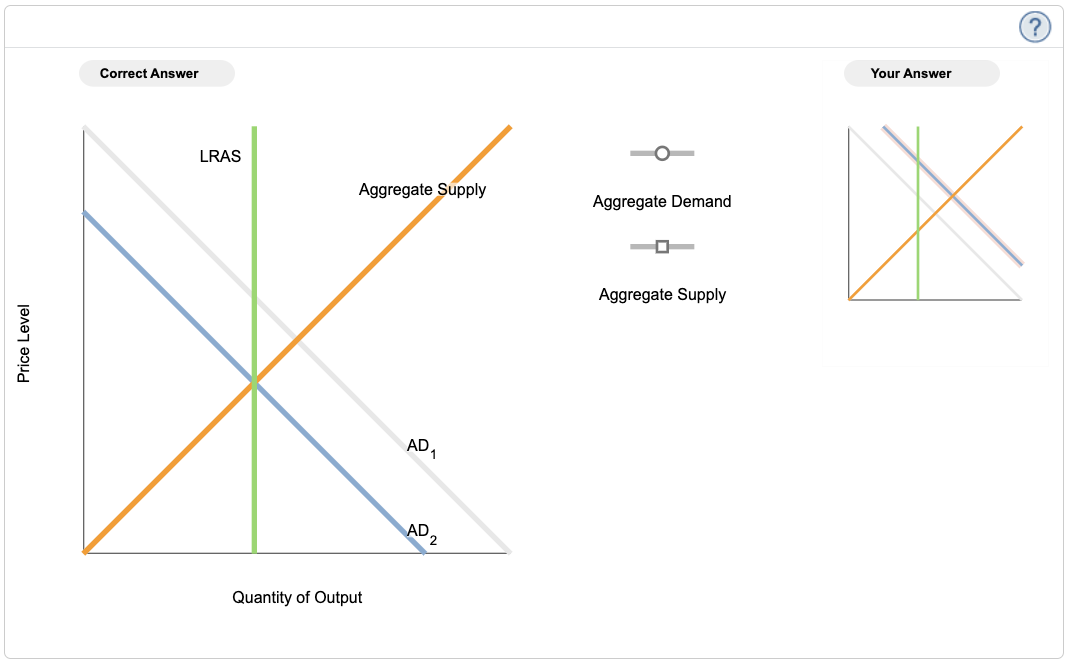
Is this recession or expansion?
expansion bc equilibrium of AS and AD are infront of the LRAS
If there’s crowding out, then would the MPC be larger or smaller than what it originally was without MPC?
larger
If the gov increases its spending, would the effect on aggregate demand be larger if
a. the Fed held the MS constant
b. fed committed to maintaining a fixed interest rate
b. commiteed to maintaining a fixed interest rate
The increase in money demand leads to a rise in the interest rate and, thus, a decline in aggregate demand if the Fed keeps the money supply constant. But if the Fed maintains a fixed interest rate, it will increase the money supply, so aggregate demand will not decline. Thus, the effect on aggregate demand from an increase in government spending will be larger if the Fed maintains a fixed interest rate.
Will the expansionary fiscal policy lead to a short run increase if the investment accelerator is large or small
large
A large investment accelerator means that the increase in demand caused by expansionary fiscal policy will induce a large increase in investment. Without a large accelerator, investment might even decline because expansionary fiscal policy raises the interest rate.
Will the expansionary fiscal policy lead to a short run increase in investment when the interest rate sensistivity is large or small?
small
An expansionary fiscal policy increases aggregate demand, thus increasing money demand and the interest rate, so the greater the sensitivity of investment to the interest rate, the greater the decline in investment will be, offsetting the positive accelerator effect.