lecture 27: synthesis of Triacyl glycerols and major membrane lipids
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
what is phosphatidic acid?
A phosphorylated glycerol with 2 FA tails, intermediate to triglyceride production
what are the two sources of phosphatidic acid?
-glycerol from the liver
-glucose from adipose tissue and liiver
synthesis of phosphatidic acid from glycerol
-liver uses glycerol kinase
adipose tissue can only produce TGs IF
glycolysis is a ctiive
dephosphorylation of phosphatidic acid produces
DAG
-addition of another acetyl CoA produces triacylglycerol to be released to blood VLDL or adipose stores
Liver exports TAG as ________
VLDL
components of VLDL
-lots of TG
-mores phospholipids and cholesterol esters present
VLDL synthesis in the liver
-glycerol-3-phosphate + FACoA make TG
-PPP and TCA cycle must be active to generate precursors
-TGs are packaged into VLDL with the help of MTP and apoB-100 into the blood
describe the process of VLDL assembly
-proteins are made in the rough ER
-lipids are added in smooth ER and golgi
-secretory vesicles take particles to plasma membrane for release
role of lipoprotein lipase
-cleaves TG into FA and glycerol
-contributes to transformation of VLDL to IDL to LDL
what activates lipoprotein lipase?
ApoCII on VLDL or chylomicron
Muscle lipoprotein lipase
-low Km (high affinity)
-helps put TGs into work!
Adipose lipoprotein lipase
-high Km (low affinity)
-helps prevent overstorage
how are triglycerides degraded?
-glucagon activates protein kinase A
-PKA phosphorylates and activates HSL and ATGL
-ATGL cleaves first fatty acid, HSL the second
-other lipases complete the process and fatty acids and glycerol are released into circulation
ATGL (adipose triglyceride lipase)
what breaks a triglyceride into a diglyceride?
-rate limiting enzyme for triglyceride degradation
HSL (hormone sensitive lipase)
what breaks a Diglyceride into a Monoglyceride?
-activated by PKA
what regulates HSL?
-glucagon activates PKA
-PKA phosphhorylates and ACTIVATES HSL
relationship of insulin and LPL
-insulin stimulates synthesis and release of LPL
-leads to TG synthesis and storage
relationship of glucagon and HSL
-glucagon activates enzymes that break down TGs and cause release of fatty acids for metabolic use
if LPL and HSL were both active...
there would be a futile cycle of TG synthesis and degradation
structure of glycerophospholipids
1. Contains glycerol as a backbone
- Esterified to two fatty acids
- Third posistion of a phosphate which in turn in linked to a nitrogen containing base (polar/hydrophilic head group)
Ex: PIP2, phosphatidyl glycerol, cardiolipin
glycerophospholipid synthesis
-phosphorylated head group is degraded by CTP to form a diacyl glyceride, ultimately forming a glycerophospholipid
-different orders can be used, YOU ALWAYS USE CTP
can head groups of glycerophospholipids be interconverted?
yes!
ex: phasphatidylethanolamine
-externalizing the phosphatidylserine is associated with programmed cell death
benefit of lung surfactant
-lung surfactant reduces the surface tension of water lining the alveolar sac, preventing collapse
-low surfactant causes distress in premature infannts
which glycerophospholipid is surfactant?
dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine is a major component
-phosphatidylcholine which develops at 35 weeks utero
-cholesterol
-apolipoproteinis: Sp-A, Sp-B, Sp-C
Types of Sphingolipids
sphingophospholipids and glycolipids
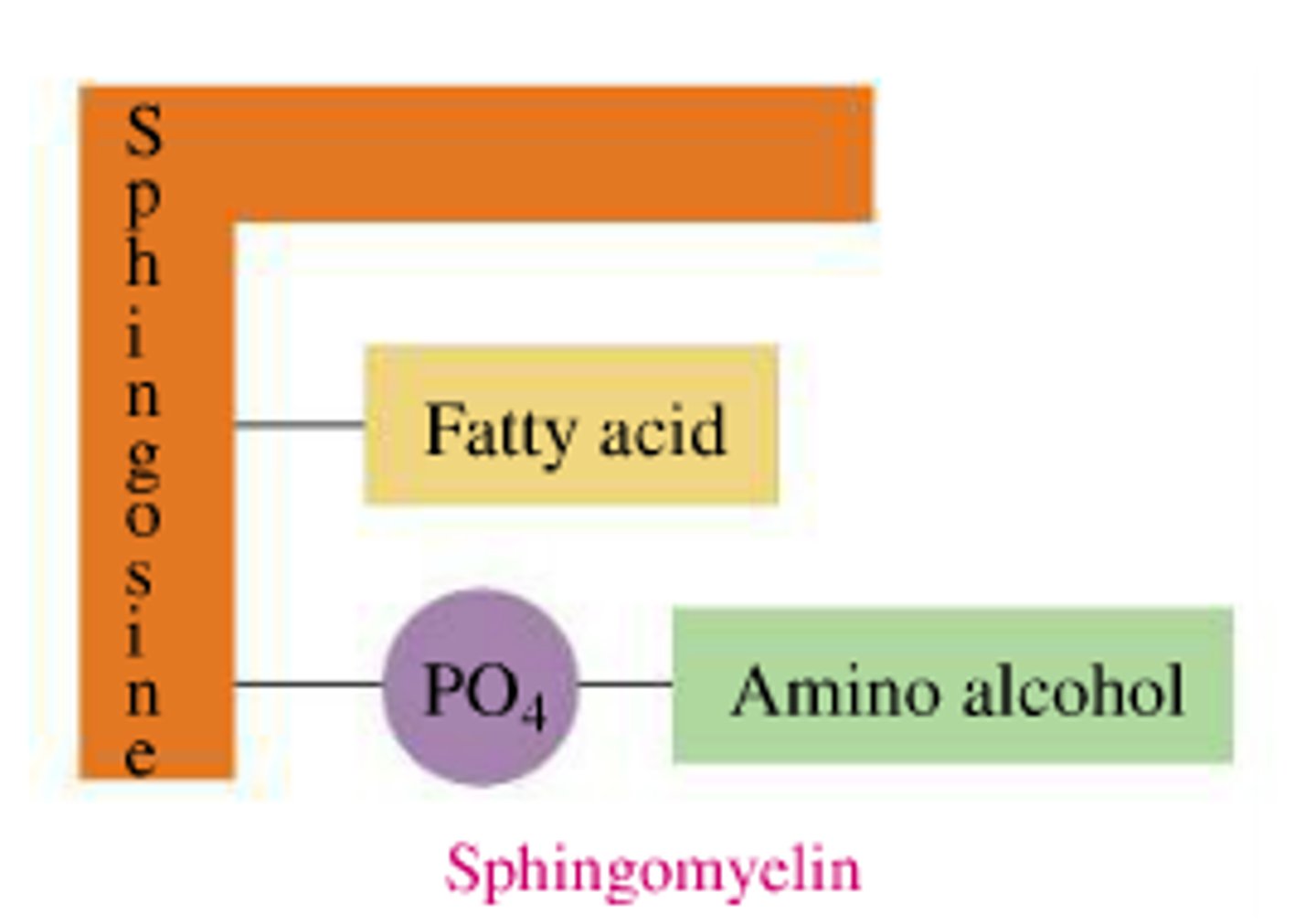
structure of sphingomyelin
-sphingosine back bone
-fatty acid
-phosphate with a head group
-ex of sphingophospholipid
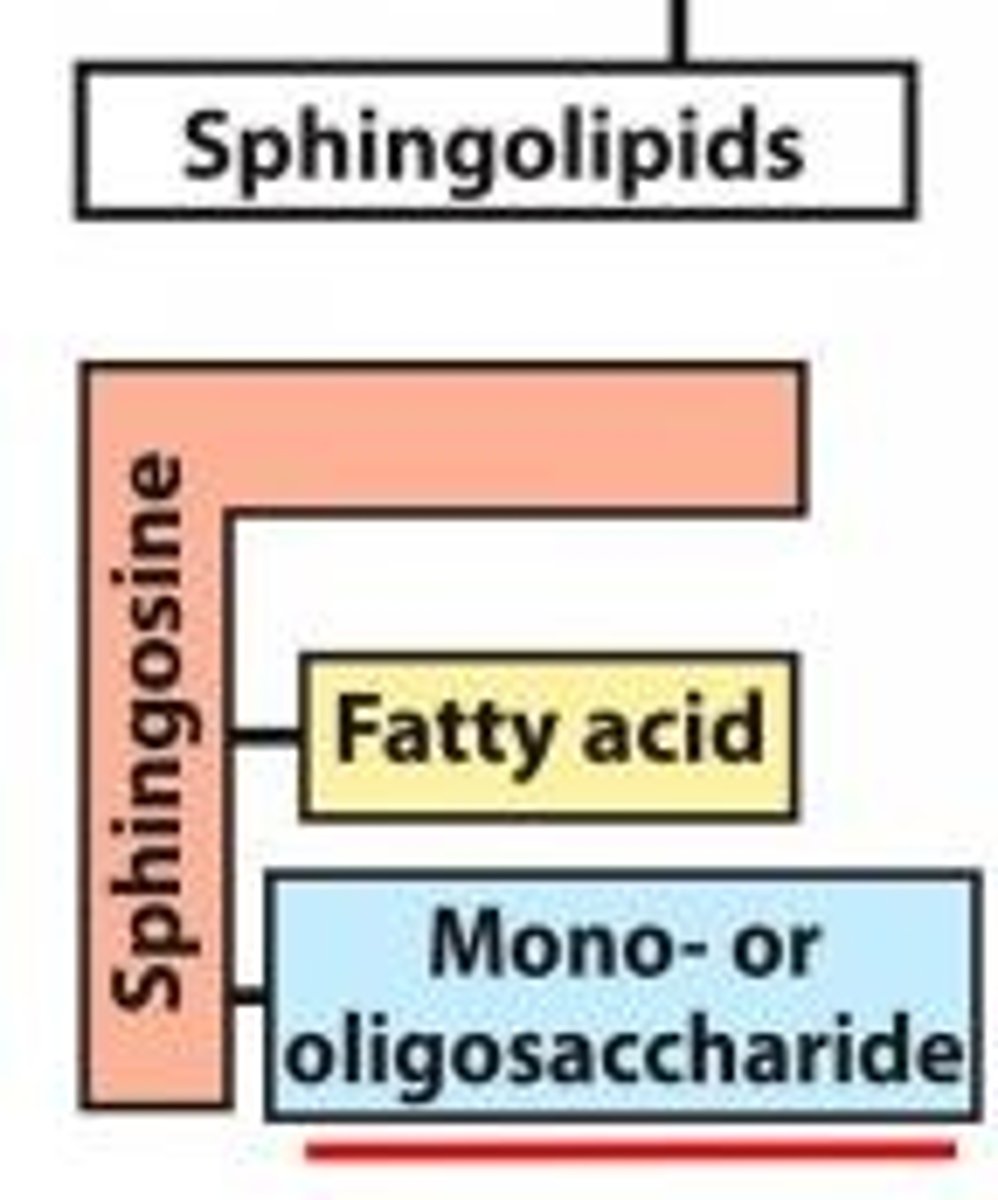
structure of glycolipids
-sphingosine backbone
-fatty acid
-carbohydrate
-ex: cerebrosides, sulfadidies
relevance of sphingolipids
-important in nervous system
-used in intercellular signaling, ABO blood groups
-binding sites for viruses and toxins
-based on ceramide backbone
how is the ceramide formed for sphingolipids?
-serine and palmitoyl coA condense
what is attached to the ceramide inn sphingomyelin
choline
Phospholipase A1 and A2
-remove fatty acids at 1 and 2 for glycerophospholipid degradation
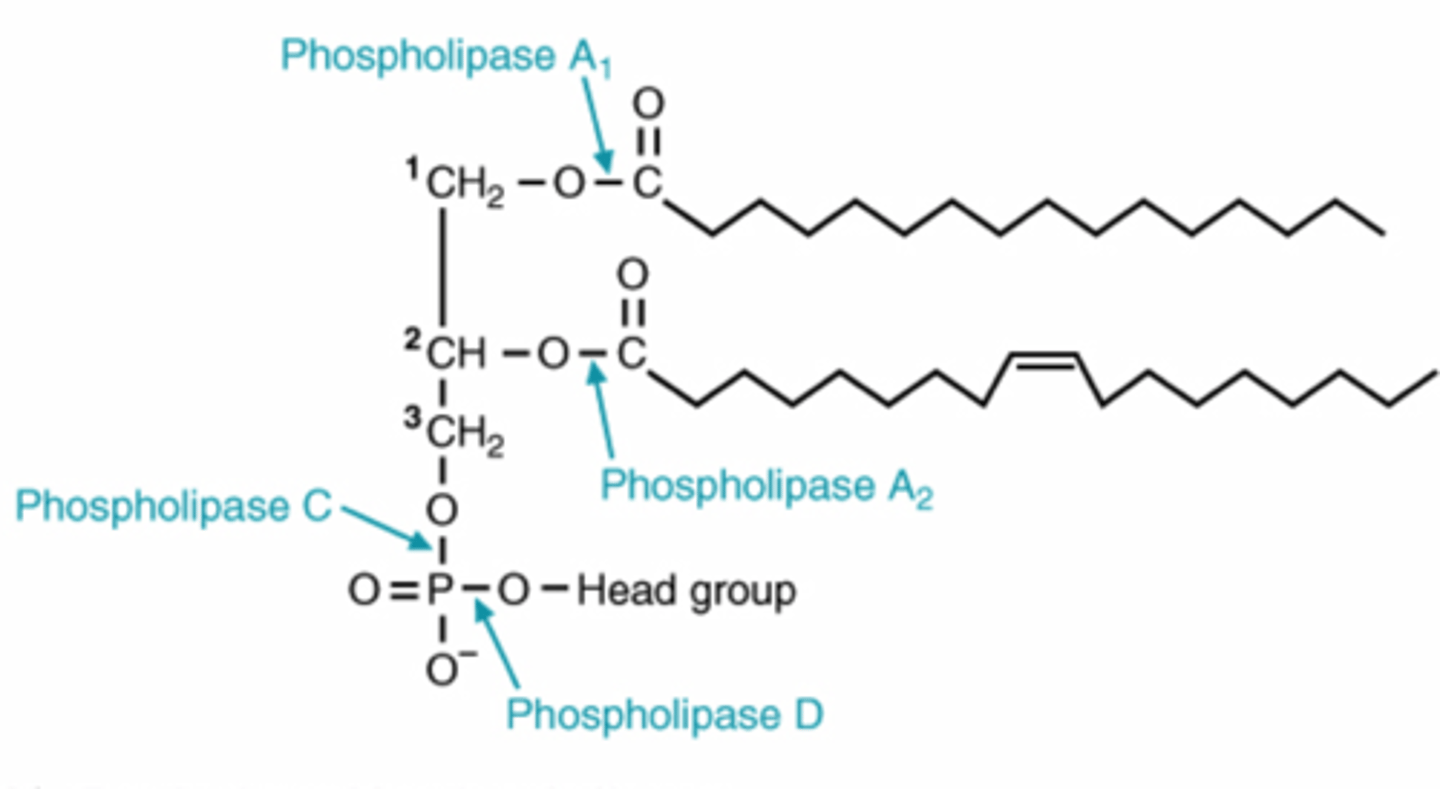
phospholipase A2 activity leads to release of
arachidonic acid
phospholipase C
removes phosphorylated head group for glycerophospholipid degradation
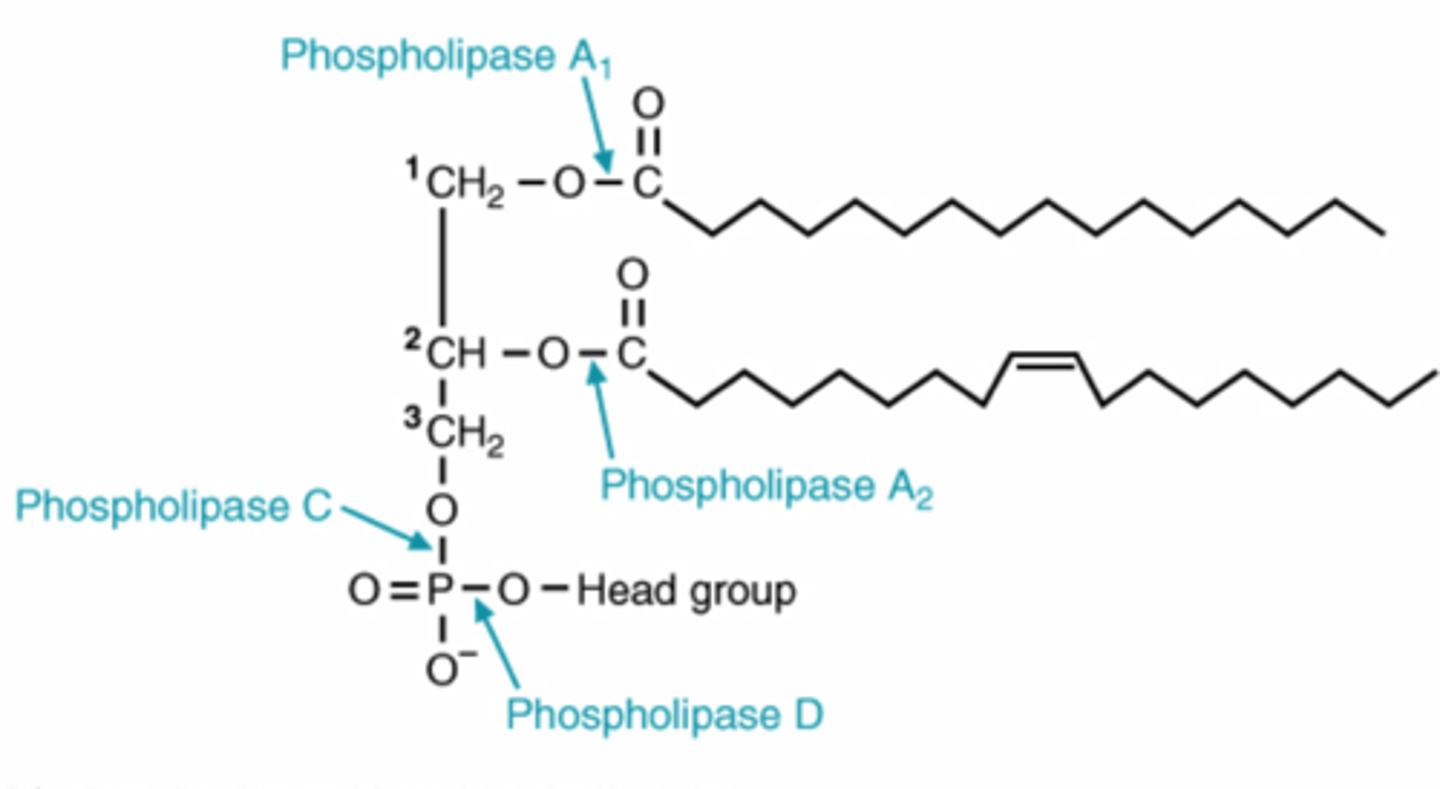
phospholipase C activity can triigger
release of DAG and IP3 from PIP2
phospholipase D
removes head group in for glycerophospholipid degradation
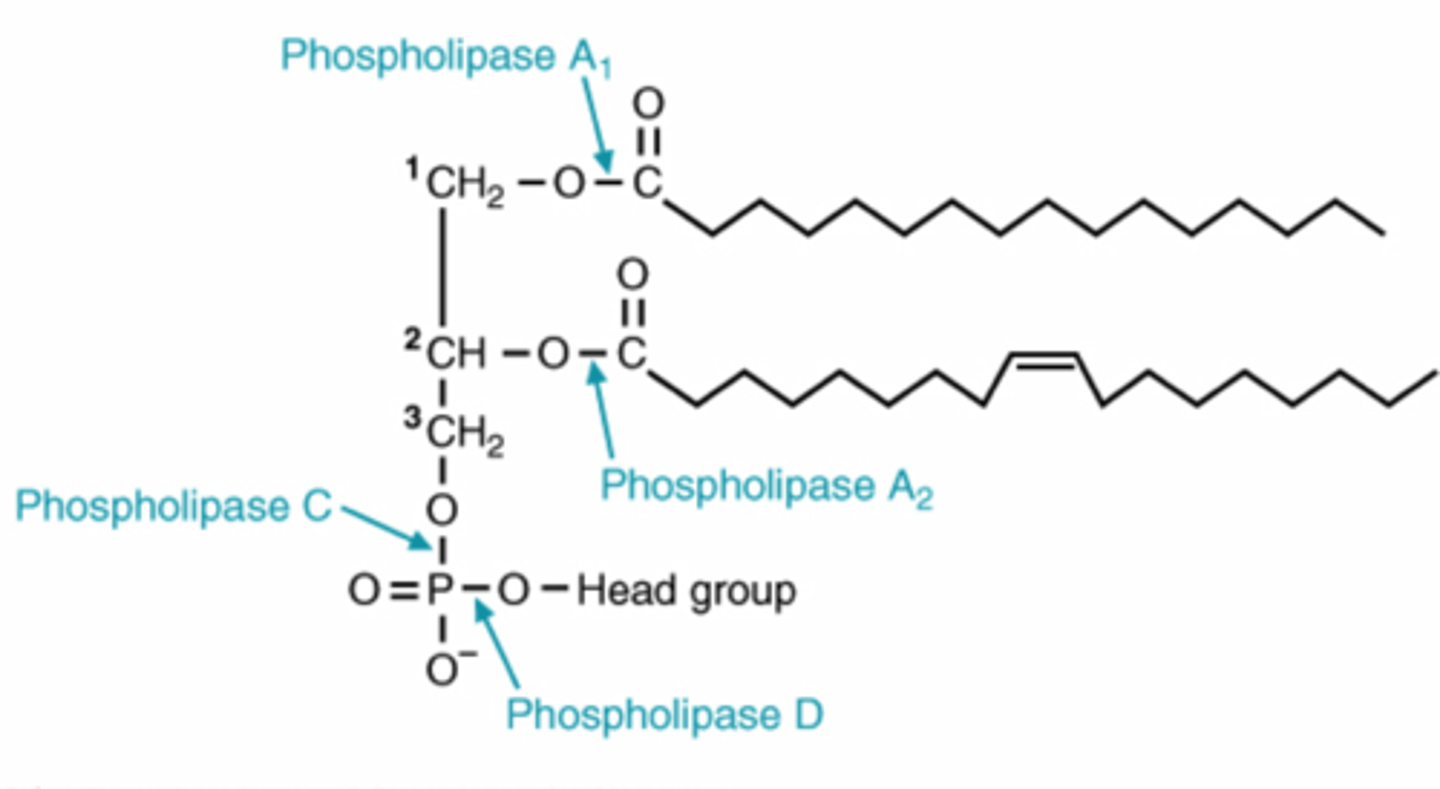
phospholipase D activity produces
phosphatidic acid
sphingolipids are degraded by
lysosomal enzymes