sustaining ecosystems and distinctive landscapes
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
118 Terms
Define term “ecosystem”
An ecosystem is an interdependence of a community of plants and animals and the environment in which they live
What is the difference between biotic and abiotic factors? Give some examples for each
Biotic factors are living things whereas abiotic factors are non-living things. Abiotic factors are most times environmental such as the climate, landscape, altitude and location in relation to equator. Meanwhile examples of biotic factors include plants, animals and diseases.
What is interdependence
Interdependence is the reliance of every form of life on other living things and on the natural resources in its environment such as air, soil and water
What is a biome
A biome is a large-scale ecosystem that is spread across continents and have plants and animals that are unique to them
What are the different biomes?
Polar, Hot deserts, Grasslands (Savannah grasslands and Temperate grasslands), Coral reefs, Temperate Forests (Decidous forests and Coniferous forests), Tropical rainforests
Why do different biomes have such different climates?
This is to do with the Global Atmospheric Circulation (GAC) which shows the circular air movements in “cells”. The GAC is made up of three main “cells”: Hadley cells (at equator, below 30° north latitude and above 30° south latitude) , Ferrel cell (above 30° north/south latitude and below 60° north/south latitude respectively) and Polar cell ( at the poles, between both north and south 60° and 90° latitude). At equator, Hadley cells are hit by the sun vertically and strongly heated. The hot moist air rises at equator (rising air = low pressure) and as it cools it forms clouds and creates a hot humid weather with high rainfall (this is where we find tropical rainforests) . The air in the Hadley cells then start to move away from equator towards 30° latitudes where it starts to sink (= high pressure) and begins to warm and dry meaning there is low rainfall in these areas but still warm (e.g deserts) . The air then flows back to equator called trade winds and process repeats. At polar cells, there isnt much sun so the cold air sinks(= high pressure) giving little rainfall (polar biome). Then the cold air flows to lower latitudes (60° north and south) where it meets with Ferrel cells. The dense cold air from polar cells meet with light warm air from Hadley cells (that are coming from 30° north/south and pick up moisture as it travels over oceans). The two contrasting airs meet at 60° north/south and the mixture of the two air types creates unstable weather conditions in a low pressure system. (Temperate Forests - e.g the UK)
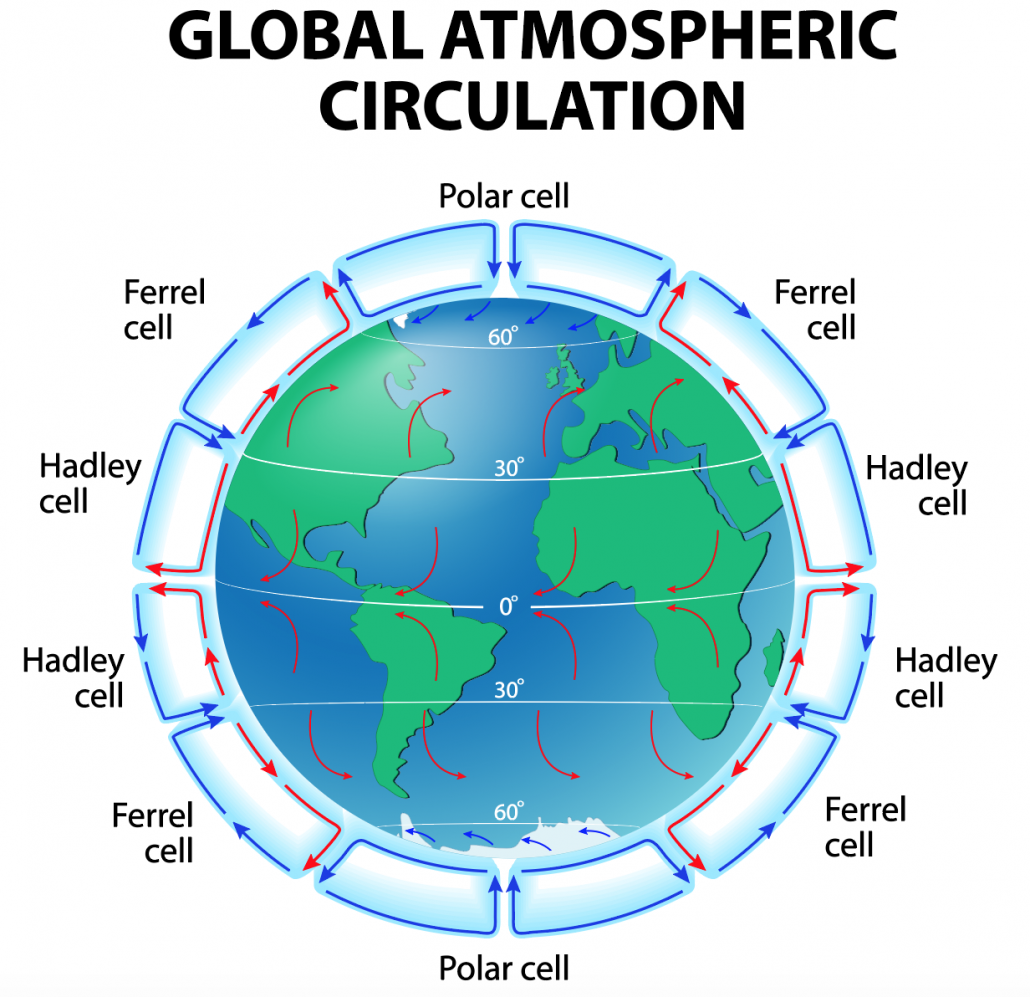
Compare the climates of the different biomes
Polar - cold all year round but summer is usually less than 10°C and winters normally below - 40° so distinct seasons (cold summer and even colder winters). Low rainfall, below 500mm a year which is mainly in summer.
Hot desserts - Diurnal temperature range is extreme, ranging from 45°C in the te to below 0° at night. Very little varied rainfall, below 250mm a year and might only rain once or twice every three years
Grasslands (Savannah) - Distinct wet and dry seasons. Highest temps of 35°C before wet season and lowest temps of 15°C just after wet season. Quite low rainfall of 850mm per year.G
Grasslands (Temperate) - Hot summers of 40°C and cold winters of 40°C. Little rainfall mostly in late spring/early summer (350mm per year)
Coral reefs - Warm areas that receive lots of sunlight. Grow best in shallow, clear, salty water.
Temperate forests (decidous and coniferous both have similar climates) - Four distinct seasons with warm summers (20°C) and mild winters (5°C). High rainfall all year round of up to 1500mm per year
Tropical Rainforest - NO distinct seasons. Hot, usually between 20°C and 28°C. High rainfall around 2000mm per year. And it rains everyday usually in afternoon
Flora and Fauna in hot deserts
Flora - Plant growth is a sparse due to lack of rainfall. Long plant roots to reach deep water supply or plant roots are spread out wide to catch as much water when it rains. Some plants have fleshy stems and thick waxy skin to cope with the dry conditions.
Fauna - Many animals are nocturnal so they can stay in shade during hot day. Bigger animals adapted to lose very little water and tolerate dehydration (e.g camels). Many birds leave during the hottest times. Small mammals have large surface area to volume ratio so can lose heat easier and don't overheat
Where are tropical rainforests found
Between the tropics, around the equator
Where are hot deserts found
Between 15° and 35° north and south of the equator
Where are polar biomes found
North and South pole. 90° north and south latitude.
Where are Coral reefs found
Mostly between 30° north and south of equator. A few miles off the coast
Where are savannah grasslands found
Between the tropics
Where are temperate grasslands found
Mid- latitudes
Where are Temperate Forests found
Mainly in mid latitudes. Between tropics (23.5° north and south of equator) and Polar regions
Flora and Fauna of Grasslands (Savannah and Temperate)
Savannah - mainly grass with a few scattered trees. Plants have long roots and small waxy leaves to cope with low rainfall. Home to insects and larger animals. Both have grazing animals that can travel long distances in search or water. Non - grazing animals can dig burrows to escape harsh climate.
Temperate - mainly grass with very little trees. Grass have wide roots to absorb as much water as possible. Home to fewer animals. Both have grazing animals that can travel long distances in search or water. Non - grazing animals can dig burrows to escape harsh climate.
Flora and Fauna of coral reefs
Few plants since it is underwater. Tiny aglae live inside tissue of corals and they (corals and algae) depend on each for nutrients. Fauna-wise : Coral itself is an animal and around 25% of all marine species live in coral reefs. Many fish have flat bodies so they can easily swim on hide in small gaps in coral
Flora and Fauna in Temperate Forests (Decidous and Coniferous)
Deciduous - Broad trees that drop their leaves in autumn. Forest floor plants often in spring before trees grows it’s leaves and blocks light out.
Coniferous forests - Evergreen trees to make use of available sunlight all year round. Low growing plants and grasses on forest floor
Both (Fauna) - Lots of different species of mammals, birds and insects.
What is the nutrient cycle and how does it work
A system where energy and matter are transferred between abiotic and biotic parts of the environment.
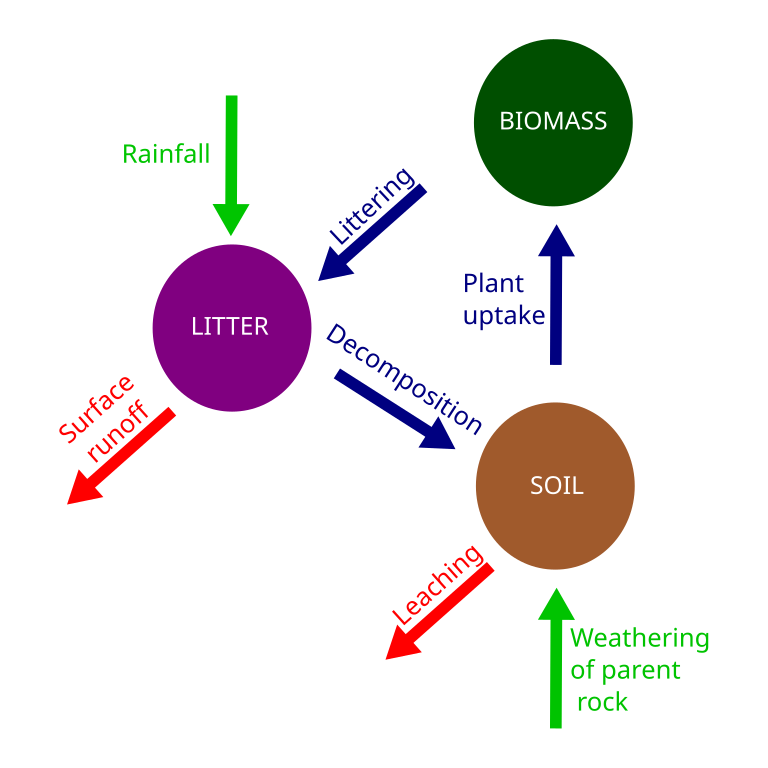
Why is the rainforest nutrient cycling so rapid?
1)The forest floor is hot and damp so this enables rapid decomposition of material.
2) Rapid uptake of nutrients from abudnace of vegetation
What is the greatest store in nutrient cycle
Biomass
What are microclimates and why do they exist?
Microclimates are small regions within a general climate zone that have their own unique climatic conditions. They exist because of local physical features such as mountains and bodies of water or due to human features such as buildings and roads
How do rainforests produce their own waterfall and how is deforestation impacting this?
Water is stored in the trees of the rainforest as biomass. The solar energy from the Sun then heats up the biomass and water exits through the leaves via evapotraspiration. The water vapour in the air rises (because hot air rises) and then as it cools down, it condenses and comes back down as rainfall the cycle then repeats and this is called a convection rainfall.
Deforestation impacts this because when we lose our trees we are losing a source of water in the convection rainfall of the rainforest and without the trees water wouldn't be able to evaporate and transpire into the air as water vapour which alters rainfall. The lack of trees will also cause leaching and for the soil to flood when heavy rain falls. The soil will also be ruined by the intense heat which will bake the soil making it hard to grow as the trees are no longer there to shade the soil
What is the soil like in rainforests and why
Most of the soil in the tropical rainforest are called latosols. The soil is not very fertile and is very thin and poor. Nutrients are concentrated in the upper top soil this is because the the trees have a rapid uptake of minerals before the lower layers of the soils can get it. There is also lots of leaching. The soil is also slightly acidic and grayish red in colour, this red colour is due to the rich iron and aluminium compoundsm. The soil is also poor because nutrients cycling is very rapid and dead Matter decomposes quickly (due to humidity) before the soil can absorb it
What is the structure of a rainforest
There are four main layers of the rainforest. The first one is the shrub layer or the ground layer. This layer is less than 5 meters in height. The next layer is the under canopy which is between five and 15 meters above soil. The next layer is the canopy which is 15 to 30 meters above soil and finally the top layer is the emergent layer which is 30 to 60 meters above soil
Flora and Fauna of a rainforest
Most trees are evergreen to take advantage of the continual growing season. The vegetation cover is also very dense and very little light reaches the forest floor so lots of plants grow on other plants and take nutrients and moisture from the air, for example orchids and ferns. Trees in the emergent layer are very tall and have big wide buttress roots to support trunks and only have branches at their crown where most light reaches them. In terms of fauna the tropical rainforest contains more animal species than any other ecosystem. Many animals are camouflages so they can hide from predators and other animals are nocturnal so they sleep through the day and feed at the night when it's cooler to help them save energy.
Explain how the rainforest ecosystem is interdependent
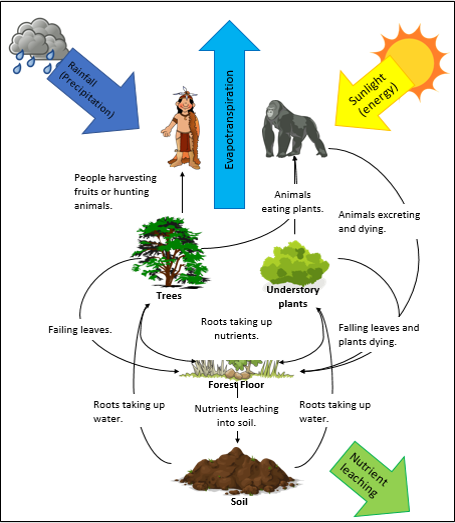
How many indigenous people live in the tropical rainforests
50 million
What is leaching of soil? why does it occur quickly at tropical rainforest soil?
Leaching is when the water washes away minerals and nutrients out of the soil. This happens so quickly because it rains often in the rainforest and the minerals are sitting on the top layer so rain . doesn't have to suck out the nutrients from llower layers of the soil.
Bonus : try find out why it gives it a reddish colour
What is the differences between goods and services
The goods provided by an ecosystem are the physical products and items that can be used by people. The term services on the other hand refers to the unique role or job that the ecosystem plays in its environment. Goods are often locally produced, whereas the tervice role that ecosystem plays can often have a global effect.
What are some goods the tropical rainforest provides us with
Fruits and vegetables such as passionfruit, cane sugar, bananas, citrus fruits and avocados.
Oils such as palm oil, coconut (used in sun tan lotion, candles ), rosewood and ylang - ylang (used in perfumes)
Nuts such as Brazil nuts and cashews
Fibres such as bamboo furniture, rugs, mattress and rattan
Woods such as teak, mahogany, and rosewood
Medicines such as Curare which is used as a muscle relaxant and quinine which is used as an anti malaria treatment. 70% of plants have been proven to have anti-cancer properties found in the tropical rainforest.
Rubber in products such as car tyres and rubber mats
Flavourings like vanilla,coffee, cocoa and tea
Guns and resins in painting products, on golf balls and in chewing gum
What are some services the tropical rainforest provides
Known as the earths sponge because thee trees reduce the rod the flood risk as the leaves intercept and slow down the rain water. This reduces the time it takes for the water to reach the soil and soak into the ground.
They maintain some of the world's most fragile soils protecting them from soil erosion.
The rainforest is a habitat for a wide range of flora and fauna so which are the most endangered like the orangutan.
Rainforest provide a source of income for indigenous people through agriculture and tourism.
Tropical rainforest maintain the water cycle pumping moisture into the atmosphere and providing the Globe with a greater defense against droughts, forest fires and extreme weathers.
They provide the world's rainforest (most of it) and form a cooling band around the equator like a giant thermostat.
Tropical rainforest are often refer to as the lungs of the earth as they absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen. This process of photosynthesis means rainforest are an important carbon sink. Cutting down and burning rainforest and removes this important sink sending vast amounts of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. In fact 25% of the world's emissions now are from deforestation to put this in Context only 14% come from cars planes and factories combined
What is shifting cultivation and how is it sustainable
1) a small area of Forest is cleared by chopping down trees are burning them.
2) seeds are grown in the new clearing and ash from burning trees adds nutrients to the soil.
3) initially the crops grow well but after two to 4 years the soil loses its fertility
4) people move on to other parts of the rainforest and the trees in this clearance slowly regrows
This js environmentally sustainable because it allows for the new growth of trees by not using the land so much they kills the soil. This is socially sustainable because it provides people with jobs. This is also economically sustainable as people can go back and reuse the land instead of it being a one-time use which provides the government with more GPD from sales.
What are some methods to sustainably manage an area of tropical rainforest
Agroforestry is growing trees and crops together. Some crops benefit from the shelter of the tree canopy. Trees also prevent soil erosion and crops benefit from the nutrients in the leaf litter.
Selective logging is when trees are only cut down when they reach a certain height. Young trees are allowed to mature so the height of the canopy is maintained.
Reforestation is the replanting of trees to replace the original primary forest that had been lost. This method does not maintain the biodiversity of a natural forest.
Afforestation is growing trees and a place where there wasn't before
Monitoring users satellite technology and photos to ensure that no illegal activities are taken place and that land owners follow guidelines for sustainability
Protecting areas is simply about giving places legal protection and enacting tight laws that stop deforestation in certain places
Evaluate a case study that have attempted to sustainably manage an area of tropical rainforest
Samasati Nature Reserve
Located in Costa Rica in Central America and uses ecotourism to sustainably manage its rainforests
Takes in over 250 acres of primary and secondary rainforest
Environmentally sustainable:
Uses green wood which is wood that has naturally fallen reducing deforestation
Wood was transported by oxen instead of machinery which lowers CO2 emissions
Buildings fit between trees in forest
No heavy machinery used in constructio
Timber uses from afforestation project
Colours of buildings blends in with the landscape so doesn't ruin unique landscape with urban style and doesn't disrupt/conuse wildlife as much
Natural light and ventilation used so energy sources dont need to built
Drinking water comes from natural springs so artificial pipes don't need to be built
No exotic species of fauna or flora have been brought in to avoid alterations to ecosystem
Rainwater is collected in roofs and used for toilets and showers
Toilet excretion can provide nutrients to soil
Only biodegradable soap, detergents and shampoos allowed
Socially sustainable
Only hires locals which provides them with an income and improves quality of life and standard of living
Creates a good relation with tourist and locals
Teaches tourist about rainforests and brings awareness of deforestation
Economically sustainable
Organic waste is sent to local farmers and used as fertiliser which saves farmers money.
Natural ventilation means don’t need to buy AC which reduces money spent
Hires locals so increases GPD per capita
Rainwater is used so dont need to spend money on water
most environmental factors can apply as economic factors
Unsuccessful because tourists can interact with local tribes and wildlife and expose them to harmful diseases which can kill them. Animals can also confuse new construction with their usual habitat and distress them.
Causes of deforestation
1) Logging
2) Cattle ranching
3) Palm oil plantations
4) Mineral extractions
5) Tourism
6) Hydroelectric power and Dam building
7) Road construction
what is the definition of deforestation
the permanent removal of forests to enable the land to be used for something else
Explain logging and its impacts (bonus: use place specific detail)
Logging is when trees are chopped down and the wood is used for things. About half of it is used for feul wood the other uses include building materials, furniture and paper.
(Direct) logging only accounts for 10% of deforestation. It also contributes to global warming as it realeases carbon into the atmosphere.
Two types of logging:
Clear felling - clearing whole areas of forest regardless of use
Selective logging - selecting trees to cut down. Usually selecting bigger/ better value trees then leaving smaller trees to grow. However deforesting one tree can have a knock on effect and many more can be damaged anyways.
Indonesia has 1/10 of the remaining rainforests in the world but is destroying them faster than any other country because the Indonesia government has licensed much of their rainforest for logging in order to grow country’s economy. Two million hectares of indonesian rainforest are disappearing every year. Indonesia covers barely 1% of earths land but accounts for 8% of global carbon emissions due to this.
In contrast, over the last decade illegal logging has decreased by 50%-75% across Cameroon, Indonesia and the Brazilian Amazon
Explain cattle ranching and its impacts (bonus: use psd)
Cattle ranching is the agricultural practice of raising herds of cattle on large open land.
It accounts for 6.5% of deforestation.
Popular because it is low risk and low maintenance in comparison to cash crops such as palm oil. It is also not vulnerable to changes in global prices, climate and environment. It is also in high demand (especially in USA) so farmers make good return.
Causes soil erosion and siltation due to areas of exposed land.
In northern regions of the Amazon basin, cattles have outnumbered people by 10 to 1.
Around 80% of brazils deforsested areas are used for cattle.
Cattle Ranching in the Amazon rainforest is responsible for 340milliom tonnes of carbon per year. It also takes up 8.4 million hectares of land.
What is siltation
Siltation is where the soil is blown away due to soil erosion. it blows into rivers and raises the riverbed and as a result increases risk of flooding
Explain cash crops and its impacts
Cash crops are agricultural crops that are planted for the purpose of selling on the market or for export to make profit.
It accounts for 16.5% of deforestation
Palm oil is one of the most profitable cash crops and is foud in around half of all products sold in supermarkets. It also used to create fuel known as biofuel.
Indonesia has the world's largest palm oil plantation and it provides employment for 3 million people.
Areas of trees need to be cleared but a plantation can be created and it is cut down in a process callrd sladg and burn where the trees are cut down and burnt. The ash ftom the burnt trees provide shirt term nourishment for the soil. However once the palm oil have been harvested the land is useless
Explain how tourism can aid deforestation
Unsustainable mass tourism results in the building on hotels in vulnerable areas and can have a negative impact on the relationship between communities and local government. It can also encourage construction of roads to allow better access to areas for touristsm.
Inm Indonesia, tourists have offered indigenous ape communities food which exposes them to human diseases and causes them to become ill
Explain the impacts of Hydroelectric power + Dam building
Common along rivers such as the Amazon in South America and the Mekong is Laos. It forces thousands of people out of their land (displacement). Large swathes of rainforest are also flooded upstream of the dam. The dam creates Hydroelectrical power which can cause other causes of deforestation such as logging and road building. Silt is also held back by the dam meaning fewer nutrients are supplied downstream for small scale agriculture.
It has some positives as it creates jobs and supplies people within the area with hydroelectrical power energy.
What impacts does road construction have (use psd)
Can be argued that it is vital to help poorest communities gain a better standard of living and can create land available for hiusing and urbanisation but most roads aren't used for that.
The Trans- American highway linked Belem in the Amazon rainforest to the city of Brazil, Brasilia. It began with a very thin cut through the rainforest but lead to a 400km wide expanse of rainforest destruction.
In Congo, a 50,000km project led to many more km of illegal roads branching from the main road which has opened their tropical rainforest to illegal logging.
Flora and Fauna in Polar ecosystems (Artic and Antarctica)
Flora - very few plants like lichens and mosses on rocks and few grasses on coast where it is waemer. plants grow slowly and not tall.
Fauna- Relatively few species compared to other ecosystems. Antarctica has mostly sea animals but Artic has both. Animals adapted to live in extreme conditions. For example polar bears have thick fur coat. Black nose and feet to absorb any heat/light easier. Small surface area to volume ratio to reduce heat loss. Large feet to distribute weight and increase grip on ice. Greasy coat on fur that sheds water after swimming. Penguins huddle to keep warm etc etc

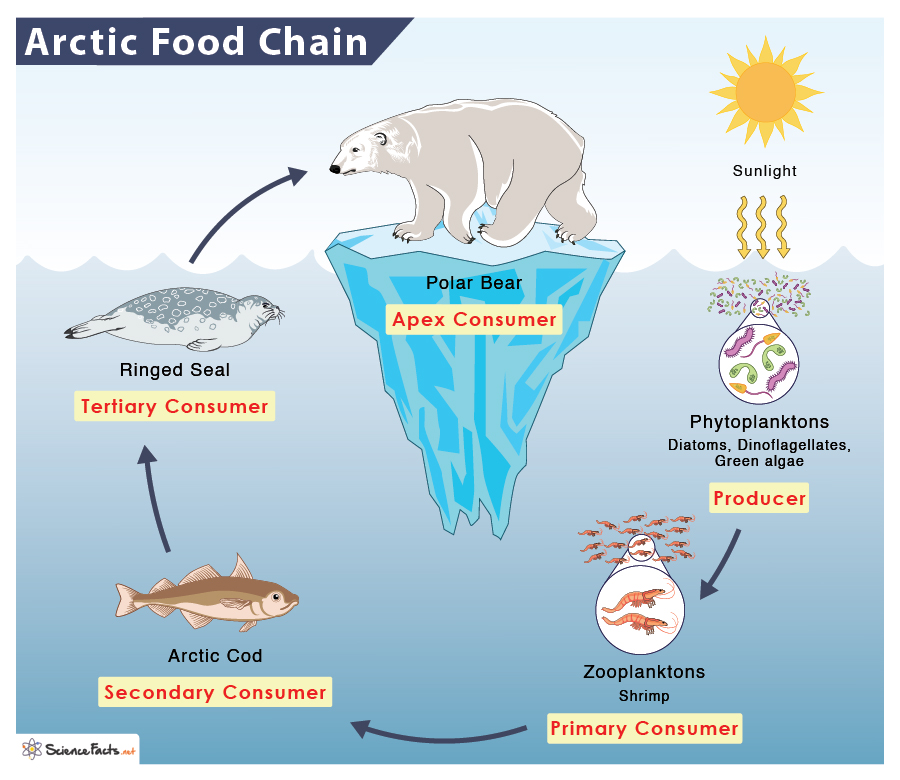
What is the food web like in Polar regions
Producer = phytoplankton, zooplankton
primary consumer= fish (and zooplankton)
secondary consumer = krill, squid, jellyfish, seals
tertiary consumer = sea birds, polar bears, whales
Describe the artic soil
Above the soil there is a permafrost layer which is soil, rock or sediment that is frozen for more than 2 consecutive year. Above the permafrost there is an active layer which is areas not overlain by ice and exists beneath a layer of soil rock or sediment which freezes and thaws annually
How are homes in the artic adapted
Built on stilts so when active layer thaws, the sediments in the active layer can move freely while the house stays in place. It also prevents yourself being trapped in house when there is higher levels of snow/ice. It also reduces the heat transfers from house to permafrost to avoid melting the land.
Windows are small to trap heat inside and reduce heat loss and to manage light coming in and out.
Roofs slope steeply so ice can slide of easily
Explain the connection between climate change and oil and gas exploration in the Artic
In 2009 it was discorved that the seabed under the Artic ocean holds 30% of the worlds remaining untapped gas resources and 13% of the untapped oil resources. Ice melting due to temps increasing made these resources much more accessible to large companies such and Shell and ice melting also created more trade routes which increases the people that can go there.
Drilling for oil/gas releases carbon dioxide which is a harmful greenhouse gas futher contributing to climate change. It creates a positive feedback loop as burning fossil fuels = temp increase = ice melting = easier access to burn fossil fuels. (A positive feedback loop is a loop leading away from the norm). Less ice also means warmer atmposhere as ice reflects sun radiation (albedo effect) bc it is white.
Why are oil spills an issue (use psd)
Polluted the water
Biomagnifcation
Costly (cost 2billion to clean the excon valdez oil spill in 1989)
Impossible to clean
Blocks light getting to ocean which affects of phytoplankton and affects food chain
Kills wildlife
Gets washed up on shores and impacts coastal landscapes
Took over 2 decades for environment to recover with excon valdez oil spill
Tell me about a small scale example of sustainable management in either the Antarctic or the Artic
Clyde River Managment Sanctuary
Started in 2008 in Artic
Located at Clyde River at the coast of Baffin Island in Northern Canada
The Clyde River is 109-mile long river and is 601 metres deep and almost 2 miles wide
Banned commercial fishing and mineral exploration
Area extends 12 nautical miles from coast and covers 3360km²A
A sanctuary ( a sanctuary is an area designed for protection of wild animals by preventing human hunting and reserving the environment) for the conservation of up to 2000 bowhead whales every year on their migration route around the coast of northern canada
It includes two deep offshore troughs that are rich in phytoplankton where the whales can feed on.
Other animals such as polar bears, narwhals, seals, fish, geese and ducks can also benefit from this sanctuary
Allows the 1000 Innuit people that live there to continue with sustainable whaling traditions (only a few not endangered whales a year) because without it they would struggle to find food sources as it is hard to grow crops in Artic region
Not successful as we can’t stop whales from leaving protected area on their migration route
It prevents large cruise ships from entering the area (bc it disrupts whales) which reduces tourist revunue
Reduces jobs (mineral extraction, commercial whaling) which reduces GNI for people in Canada.
Successful because bowhead whales can breed safely and increase in number
Who are the Innuit and how were they sustainable
The Innuit people are a small indigenous group living in Barrow in Alaska. (Barrow is on the coast of Alaska which means it maintains a good link too neighbouring countries for trade and food can be provided from the ocean since it is along the migration route of many marine animals . Artic weather is also warmer towards the coast)
The Innuit people make the most of the animals they hunt and don't just use it for meat for example they use the animal's fur/skin as coats and they do whaling on a very small scale.
Assess a global example of a sustainanble management in either the Antarctic or the Artic
The Antarctic treaty started in 1961 is a global sustainable management in Antarctica with over 56 countries that meet regularly to protect the ecosystem. It has 14 rules which include
No military activities are allowed besides scientific research or other peaceful purposes this is socially sustainable as a eases tension between countries and avoids wars. There have been no armed conlicft in Antarctica since treaty was signed
Freedom of scientific investigation is allowed is economically sustainable as it keeps people in their jobs and environmentally sustainable as issues of global concerned can be researched and solved. For example the Ozone depletion. However much of the science conducted in the Antarctica is poor and is done to disguise territorial claims (socially unsuitable) are potential rights to mineral exploitation which can lead to oil spills which is economically and environmentally unsustainable
No territorial claims are allowed which is socially sustainable (same reasons as no military activities)
Nuclear explosions and radioactive waste disposal aren't allowed which is environmentally sustainable as it protects the land from toxic materials
Doesn't allow the hunting of native animals and wildlife which prevents extinction of animals such as polar bears which are unique to polar regions. All visitors must fill in a EIA (Environmental Impact Assessment) to ensure this. However no marine reserve was created due to competing fishing interests
Unsustainable because the Antarctic treaty ends in 2048. Also can't control on what goes outside of Antarctica and it’s surrounding oceans and also it doesn't protect Antarctica from inevitable global climate change. The Treaty doesn't provide countries with enough fund for scientific research upkeep which is economically unsustainable
How are climate and soil interdependent in the Artic and Antarctic
Colds temps causes plants to grow and decompose so soil is low in nutrients. Plants absorb sun (climatic) for photosynthesis which prevent permafrost below from thawing.
As climate increase, active layer thaws.
Why does the Antarctic matter to people living in the UK
Affects global climate via global warming or ocean currents which affects us
Define landscape
Landscape is the visible features that make up the surface of the land
What are the different elements that make up a landscape. Give examples
Human such as buildings and other man-made structures
Physical/natural which include mountains, coastlines, rivers, climate, geology
Variable such as weather, cloudscapes, smells and sounds. They can also be temporary such as frost in the morning
Biological which is living things like vegetation and wildlife but also habitats such as salt marshes and hedges
What is a built landscape
Landscape with more human than physical features overall
What is a natural landscape
A landscape with more physical than human features overall
What is a distinctive landscape
Having specific landscape qualities that set it apart from others
What are igneous rocks
Igneous rocks are volcanic rock made from molten material brought up to the Earth's surface and cooled into solid rock. There is intrusive igneous rock which is where the magma is cooled within the Earth's crust and is below the surface and extrusive igneous rock is above the surfacw when the magma is cooled on top of Earths surface.
They are harder than sedimentary rock but not as hard as metamorphic rock.
Examples: granite basalt, pumice,obsidian
What is Sedimentary rock
Made up from broken fragments of rock that have been worn down by weathering on earth’s surface. It is deposited in layers called strata and they are often found underwater.
They can contain fossils within their layers
They are the only rock that are porous so they allow water to pass through them.
Examples: sandstone,coal, lime stone
What is metamorphic rock
Metamorphic rock is folded and distorted by heat and pressure as Earth’s tectonic plates move
They are denser and more compact and are hard.
Examples are slate, marble and serpentine
What is hydraulic action
The force of water acting against the bed and banks causing material to be dislodged and carried away
Define erosion
Erosion is the wearing away of the land
What is abrasion
This is the process by which the bed and banks are worn down by the river/sea load. The river throws its particles against the bed and banks sometimes at high velocity
What is attrition
Material carried by waves/river/sea bump into each other and so are smoothed and broken down into smaller particles
What is corrosion
This is the chemical action of the river water. The acids in the water slowly dissolve the bed and the cliffs banks.
What is traction
Large boulder-like particles are pushed along the bottom of the river/sea bed by the force of the water
What is Saltation
Saltation is pebble sized particles (bigger than suspension particles) are bounced along the river/sea bed by the force of the water
What is suspension
Small particles are carried along by the water. They are “suspended” in the water and don’t touch the river/sea bed
Whar is solution (transportation process wise)
Soluble materials dissolve in water and are carried along
What is glaciation
The process or state of land being covered by ice sheets
What are U-shaped valleys
Land that has been shaped by glaciation, where the ice has carved huge amounts of upland areas. They have steep, straight sides and a flat bottom and are formed when a glacier travels across and down a slope, carving the valley by the action of scouring
What is the Quaternary period
The time period in Earth’s history that began about 2.6 million years ago and continues todaay; includes the Pleistocene epoch and the Holocene epoch
What is river deposistion
When a river loses energy, it will drop/deposit some of the material it is carrying.
Deposition may take place when a river enters an area of shallow water or when the volume of water decreases - for example after a flood or during times of drought.
Deposition is most common towards the end of a rivers journey at the mouth. Deposition at the mouth of a river can form deltas
What is coastal deposition
When the sea loses energy, it drops the sand, rock particles and pebbles it has been carrying. Coastal deposition happens when the wash in stronger than the backwash and is associated with constructive waves.
Coastal deposition is likely to occur when waves enter an area of shallow water or a sheltered area (e.g cave, hook, bay), when there is little wind or when there is a good supply of material
how is igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rock spread across the UK
Igneous - Scotland, Northern Ireland, Wales and Lake district
Sedimentary - England, Wales and lowland Scotland
Metamorphic - Scotland and North Wales
What is freeze thaw weathering
A type of mechanical weathering
1) Rainwater falls in between cracks of rocks and settling within the crack unable to seep through it
2) Temperature change occurs and water freezes into ice. As water freezes it expands pushing the rocks out futher from eachother
3) The ice continues to expand until the rock splits into multiple pieces and breaks down.
What is chemical weathering
Process of which rocks are broken down by chemical reactions
Rain dissolves CO2 in the air, forming weak carbonic acid, acid rain.
Limestone and chalk both composed of calcium carbonate, slowly dissolve in acid
This can create limestone pavements like the one seen in Malham Yorkshire
What is biological weathering
Weathering caused by plants or animals. For example
Tree roots can force their way into rocks splitting them apart.
Smaller plants, like mosses, grow on the surface of the rock, slowly making it crumble.
Animals burrow into softer rocks and people also have an effect with their trampling feet
What is mass movement and the two types of it
Mass movement refers to the sudden movement of materials down a slope due to the pull of gravity.
Heavy rain soaking into permeable rocks can add weight to them and the water can also lubricate the boundaries where material meet so that flow is more likely as the cliff ‘fails’.
1) Rotational slumping occurs om soft cliffs where the base moves and other materials slumps down the face as the bottom moves outwards
2) Rockslides happens where the failure occurs along a geological boundary within the cliff. A section falls down due to gravity and may dislodge other materials on its way. Caused by prolonged wet weather or alternately dry weather where clay shrinks.
Whats the difference between erosion and weathering
Weathering happens in situ (in one place) whereas erosion removes the material from an area
What are the two main type of waves and explain their characteristics
Destructive waves
Large wave height and short wavelength
Weak wash because they break down with great force
High frequency (13 to 15 waves per minute)
Strong backwash due to strong downward energy
Anything one metre or above
Constructive waves
Flat and low in height
Strong wash carries material up the beach
Low frequency (6 to 8 waves per minute)
Wave energy dissipated over it’s wide area which results in weak backwash
Anything under a metre
What is longshore drift
The overall movement of material along a beach, consisting of swash (movement of material onto the beach) in the prevailing wind direction and backwash (movement of material off the beach) at a 90° due to gravity
What is a beach profile
A cross section of the beach from the top of the beach (part closest to land) to the seashore (part closest to sea). It shows how steep the beach is depending on how steep the profile gradient is. Sandy beaches usually have flat gentle profiles while pebble beaches tend to have much steeper profiles.
Explain the formation of a beach
Deposition is the main process that creates a beach
Deposition occurs where waves have limited energy so beaches often form in sheltered areas such as bays where the waves are likely to be constructive so material is deposited and overtime this material will accumulate. Beaches are under constant change via processes such as longshore drift
Explain the formation of Criccieth bay
Criccieth has a discordant coastline made up of alternating bands of hard rock ( volcanic rock at castle headland and igneous intrusion of Basalt at black rocks headland) and soft rock (soft glacial till at the bay). Erosion happens at the coast by processes such as hydraulic action and abrasion but the soft glacial till is unconsolidated and less resistant so erodes at faster rate of 1 metre every 10 years. This creates an area of retreated land, Criccieth bay.The hard rocks beside the bay is more resistant and erodes at a slow rate of 1mm every 100 years which leaves the black rocks headland and the castle headland jutting out to sea
Where is Criccieth
North wales
What is the fetch of Criccieth bay
It’s exposed to a 7,000km fetch across the Atlantic meaning the waves carry a large amount of enegry
How are wave-cut platforms formed. Give a place where this is seen
1) Weathering such as freeze thaw weathering weakens the top of the cliff
2)The sea attacks the base of the cliff by hydraulic action and abrasion which forms a wave cut notch
3) The notch increases in size causing the cliff to collapse
4) The backwash carries the rubble back to the sea forming a wave cut platform
5) The process repeats itself and the cliff continues to retreat
Seen in Seven Sisters in Sussex and Black Rocks headland in Criccieth has wave cut notches but no visible wave cut platform
Explain formation of caves, arches, stacks and stumps. Give a psd of where this can be found
1) The sea attacks small cracks at the base of the headland/cliff via hydraulic action.
2) The crack gets larger due to weathering and more erosion developing into a wave-cut notch and then into a cave.
3) Erosion on both side of the headland depends the cave and if two caves are aligned, the caves break through via abrasion and forms an arch
4) The roof of the arch is worn away over time by weathering processes such as freeze thaw weathering, biological and chemical. This makes it unstable and eventually it collapses under it’s own weight to form a stack.
5) The base of the stack is attacked by erosional processes such as abrasion, solution and hydraulic action causing it to topple over.
There is a stack to the east of black rocks headland and a stump to its eastern end. There is also caves on black rocks headland. There is also a stack at Old Harry along the Dorset coastr
Explain the formation of a spit. Name a place where a spit can be found
1) Longshore drift moves material along the coastline in the direction of the prevailing wind
2) If the coast changes direction, the material will still be moved via longshore drift but in shallow sea. This means material will be deposited
3) This buildup of material is called a spit.
4) Over time the spit grows and if there is a short term change in wind direction further out, it develops a spit.
5) Wave can not get past a spit so a sheltered area is created where silt is deposited and mud flats or salt marshes can be formed
It can be found in Spurn Head along the Holderness coast in Humberside
What is a tombolo and bar
Tombolo is where a mainland joins an island via a spit
A bar is where a spit connects two parts of mainland.
What are some coastal managment strategies at Criccieth and explain them.
Timber Crib wall and Rock Amour Revtment - Located at the west end of Criccieth shore. the timber Crib wall is composed of grid wooden planks with stones behind it that that are around 5cm in diameter. it hold the cliff in place but allows saturated clay to drain to prevent slumping and mass movement. the crib wall alone doesn’t offer total protection so a rock amour is built at base of the timber Crib wall. It consists of large boulders imported from Norway, around 1m in diameter and it breaks up and disssipates wave energy before they reach the base of the crib wall. For both it cos £271,000 for an 80m stretch of coastline but it protected £1.6 million worth of properties.
Groynes - Found on the western side of the castle headland. Traps sediment being moved by longshore drift which enarges beach and promotes tourism. The larger beach then absorb wave energy and prevents land behid. However due to the interruption in longshore drift, there is more erosion somewhere futher along the coast.
Breakwater - Reflects wave energy away form shore and turns destructive waves into constructive waves through wave refraction. Was built in 1900s but would cost over £500,000 to build today. It promotes fishing
Other:
Victorian sea wall
Recurved sea wall
Do nothing (soft engineering) - at more resistant parts of Criccieth coast
What is a drainage basin
It is the area which is drained by a river and it’s tributaries. It is an open sytsem
What is a catchment
The area of land from which the water drains into a particular basin.
What is a watershed?
The boundary dividing one drainage basin from another
What is a river source
The upland area where the river begins
What is a tributaryu
A river which joins a larger river