DSA22 Bone Pain (Osteoporosis, Osteomalacia, Rickets, and Paget Disease)
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
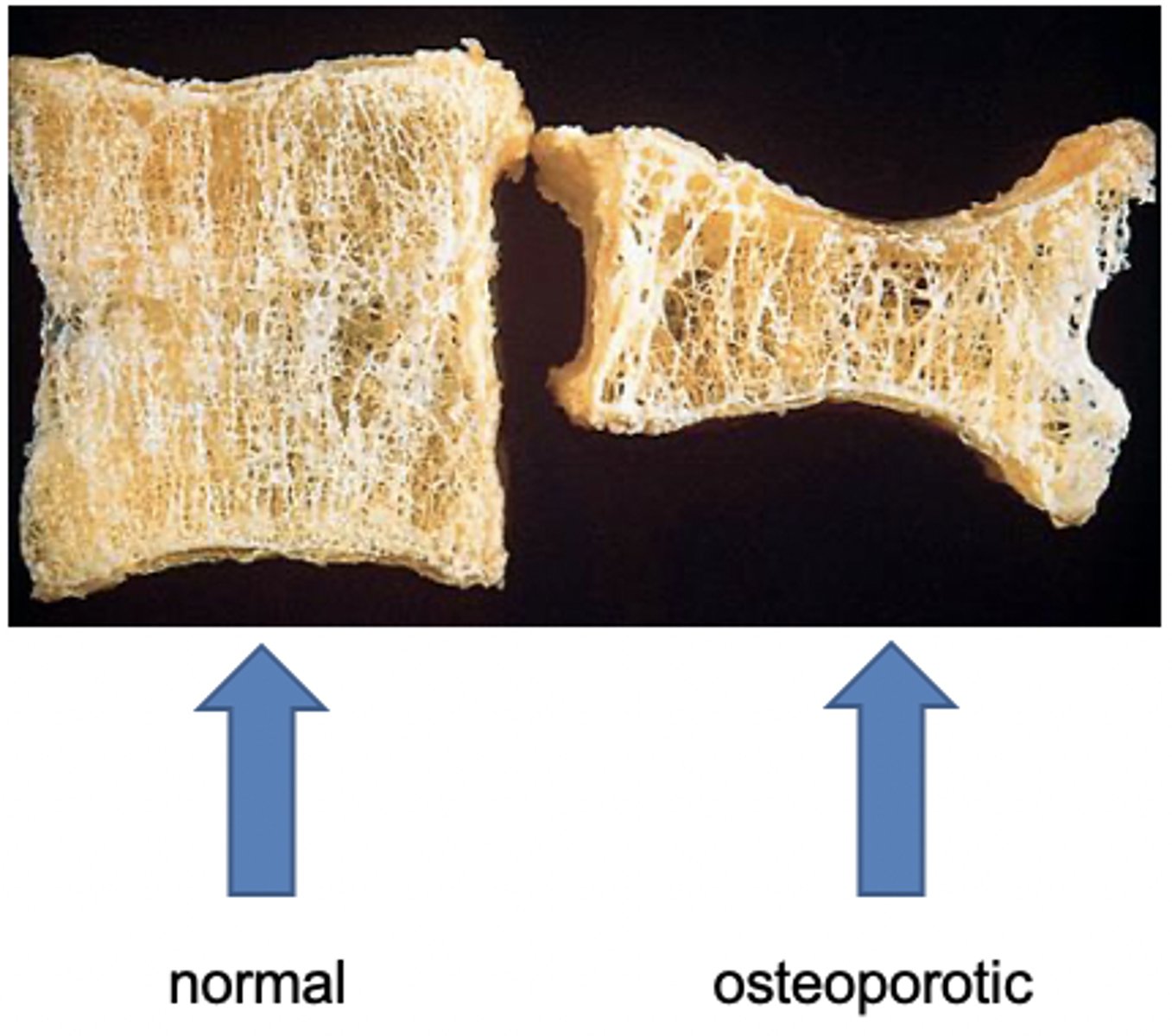
Osteoporosis is characterized by
loss of bone density leading to decreased bone strength/increased susceptibility to fractures
osteomalacia vs rickets
osteomalacia: defective mineralization of osteoid
rickets: defective mineralization of cartilage in the epiphyseal growth plates (so this can only happen in children)
can osteomalacia and rickets occur simultaneously?
yes, but in kids (only osteomalacia in adults)
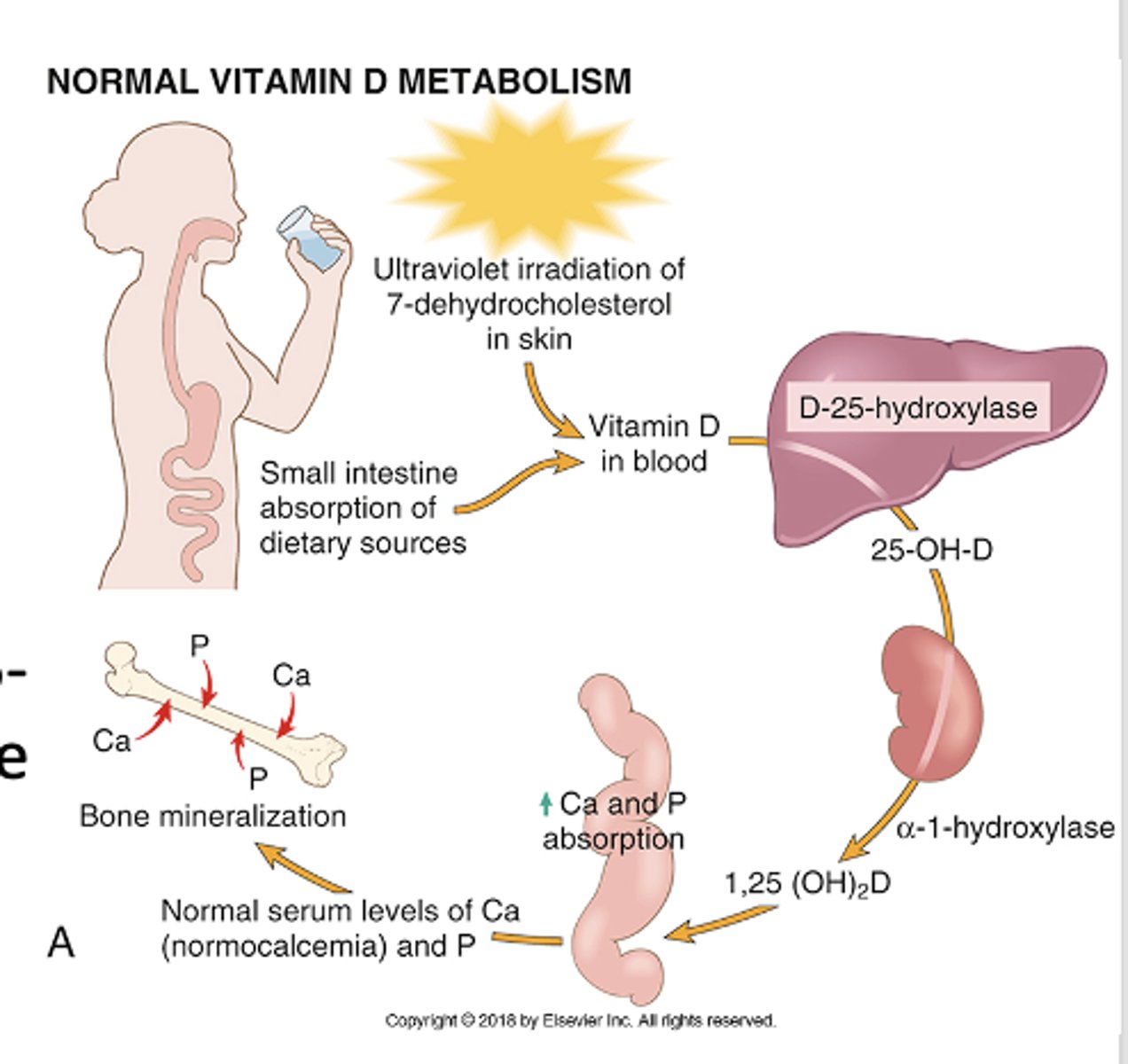
How does vitamin D affect bone turnover?
Helps mineralize osteoid by:
- Increasing serum calcium,
- Increasing serum phosphate
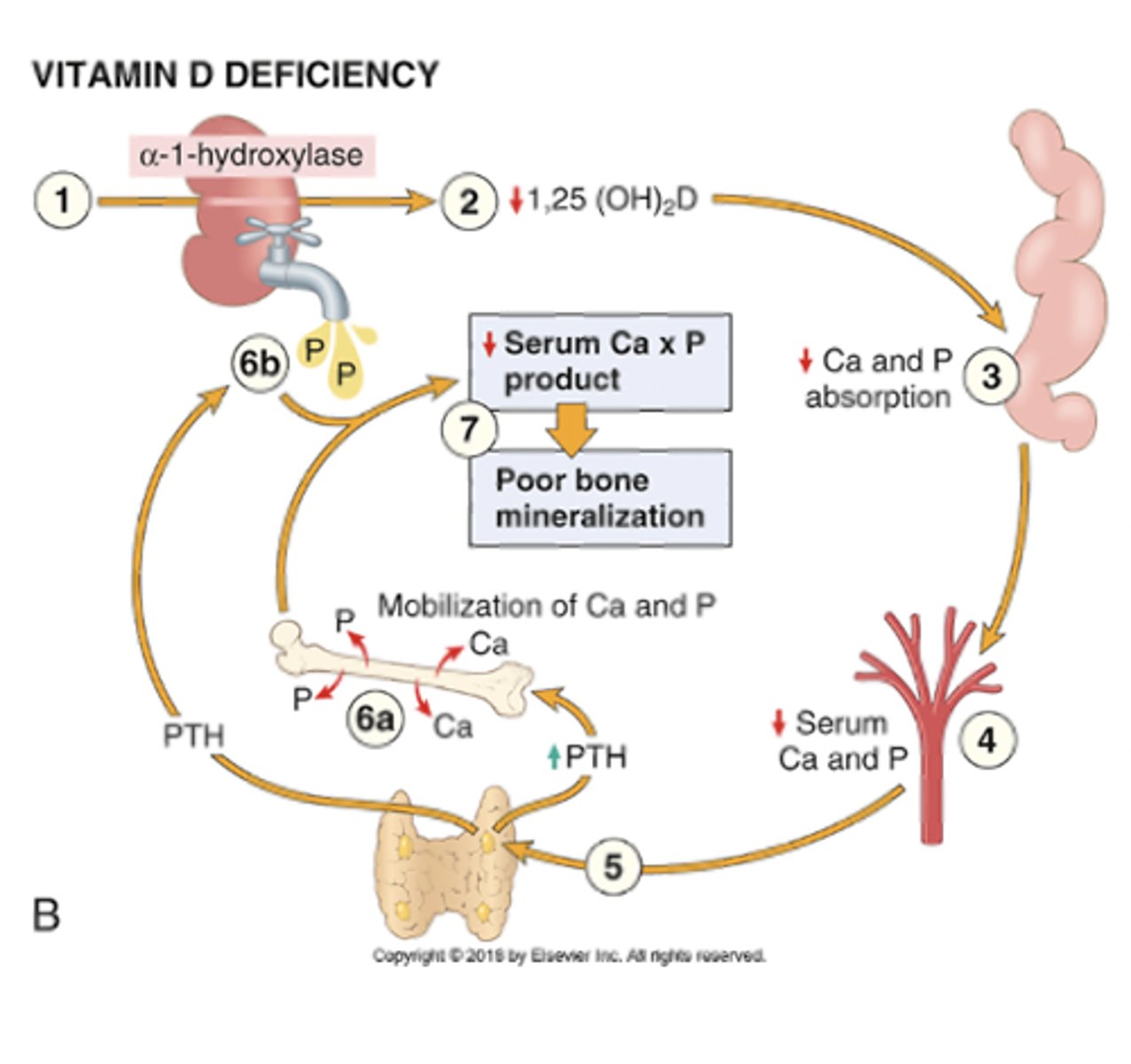
without vitamin D, calcium may be normal due to _______ action, but bone mineralization is still impaired due to low _______
PTH
low phosphate
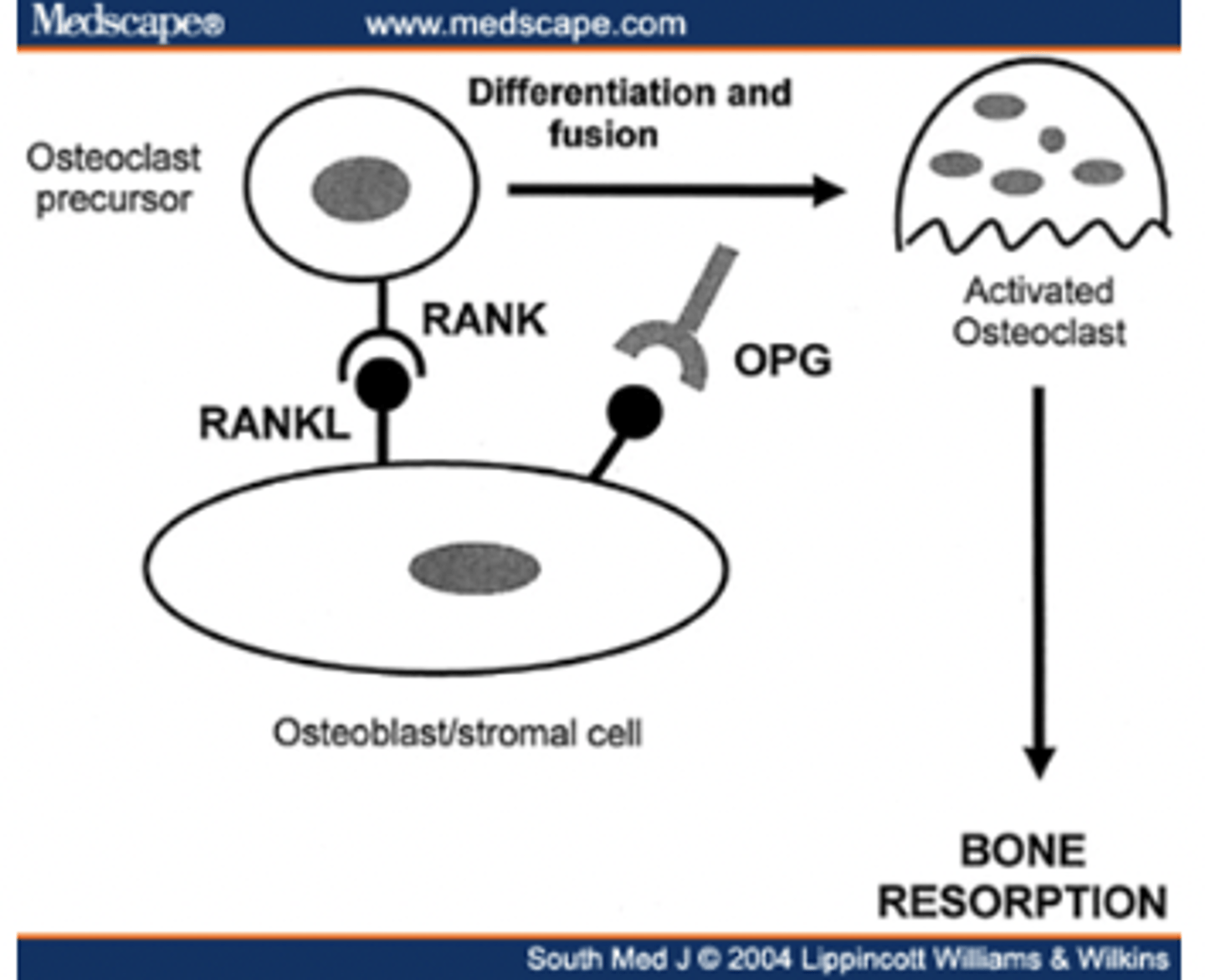
RANK/RANKL function
Binding of RANKL to RANK regulates osteoclast differentiation and activation --> bone reabsorption
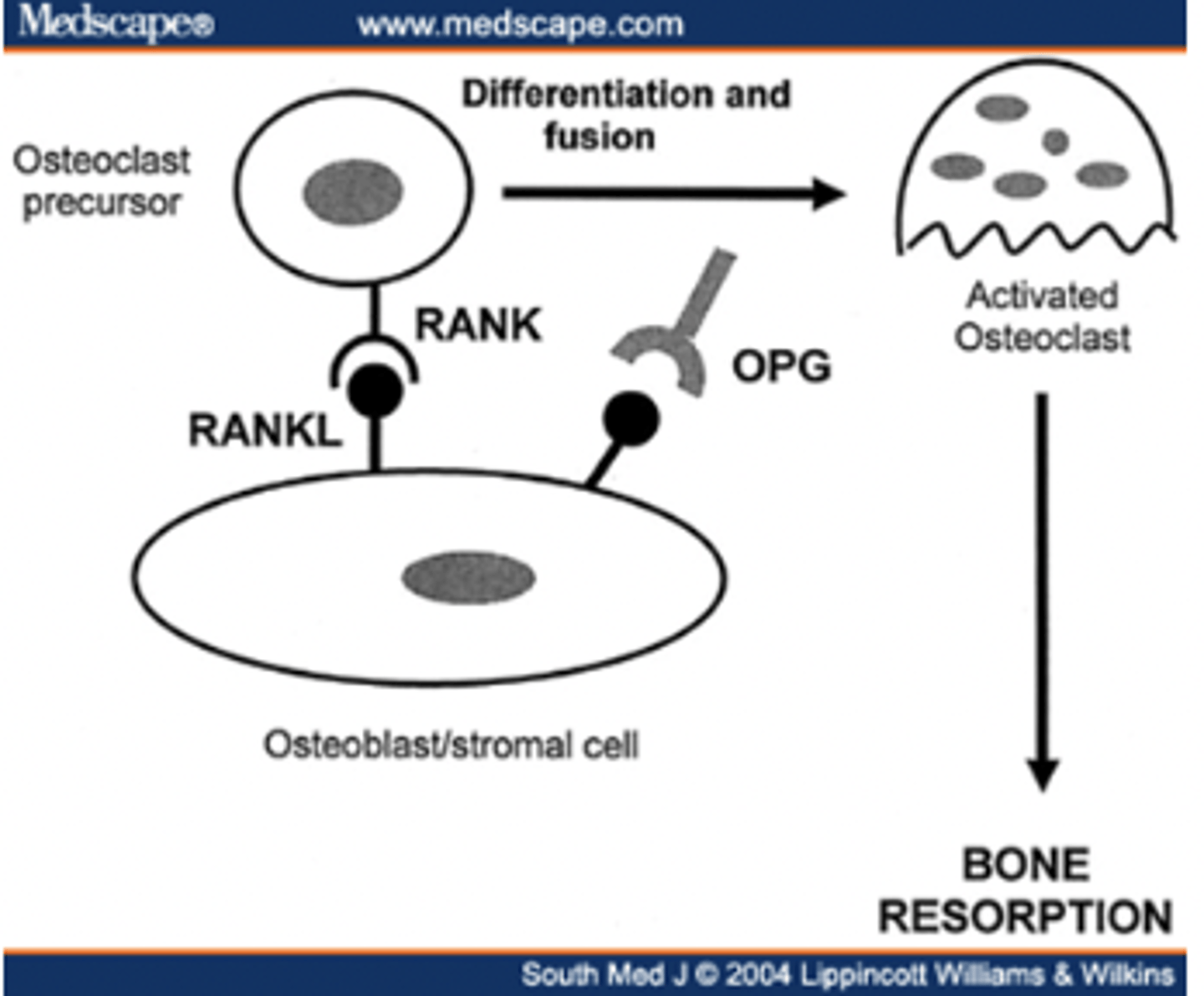
RANK/RANKL is inhibited by ______
OPG
Osteopenia= bone mass _______ standard deviations below the mean
1-1.25
Osteoporosis= bone mass _____ standard deviations below the mean, significantly increases the risk of ________
2.5
fracture
how does estrogen deficiency play a major role in osteoporosis?
leads to increased bone resorption and formation, but the resorption wins out (high-turnover osteoporosis)
how does reduced physical exercise play a role in osteoporosis?
mechanical force stimulates bone remodeling --> less weight-bearing exercise contributes to decreased bone density
what is senile osteoporosis?
gradual loss of bone mass as pts age (esp over 70 years old)
- osteoblasts activity reduced with age
(low turnover osteoporosis)
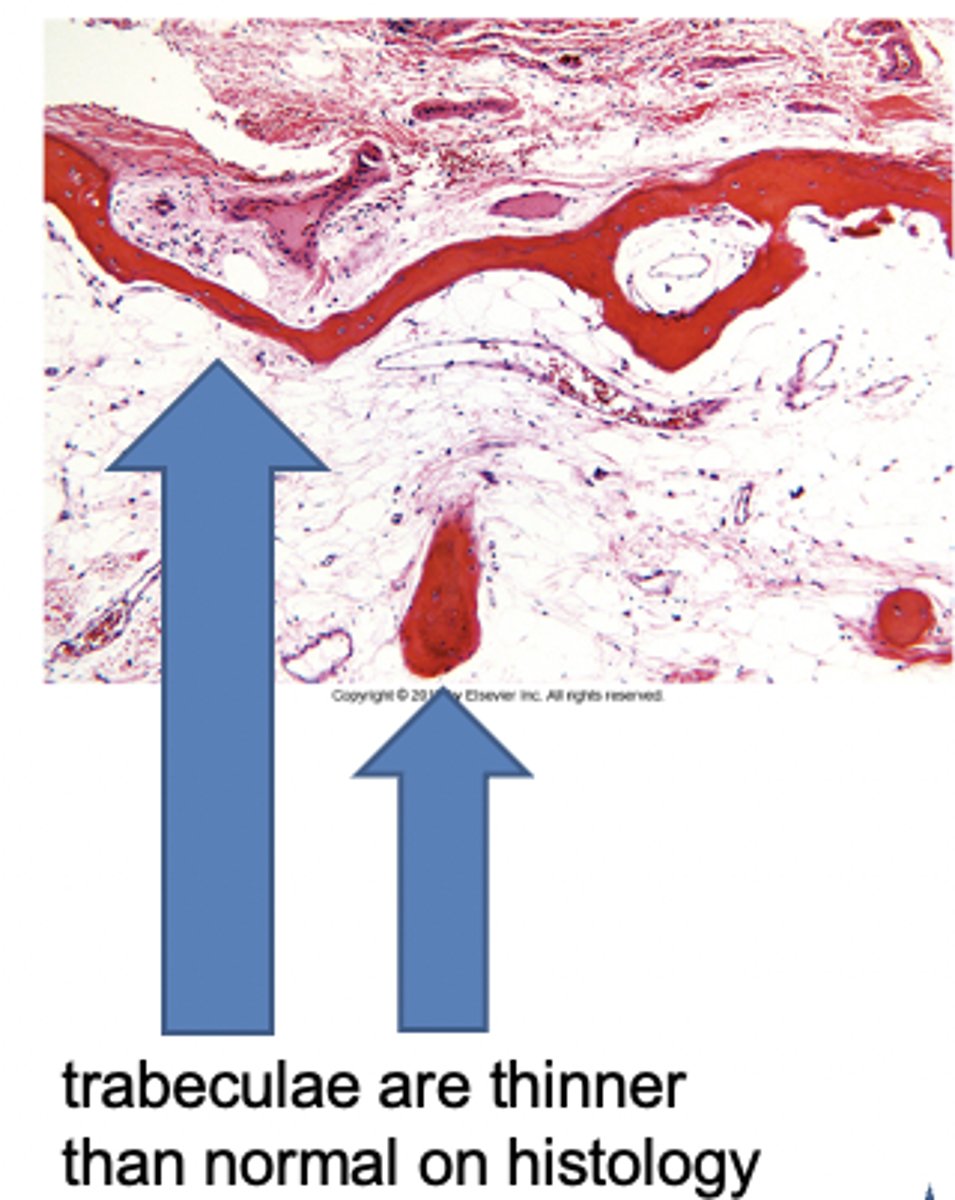
In osteoporosis, the ________ are thinner leading to increased __________ and eventual collapse
trabeculae
microfracture
When you think about osteomalacia and rickets, think defective ___________ due to vitamin D deficiency
mineralization
breastfed infants need to supplement w/ ________ due to significant risk for ________
vitamin D
rickets
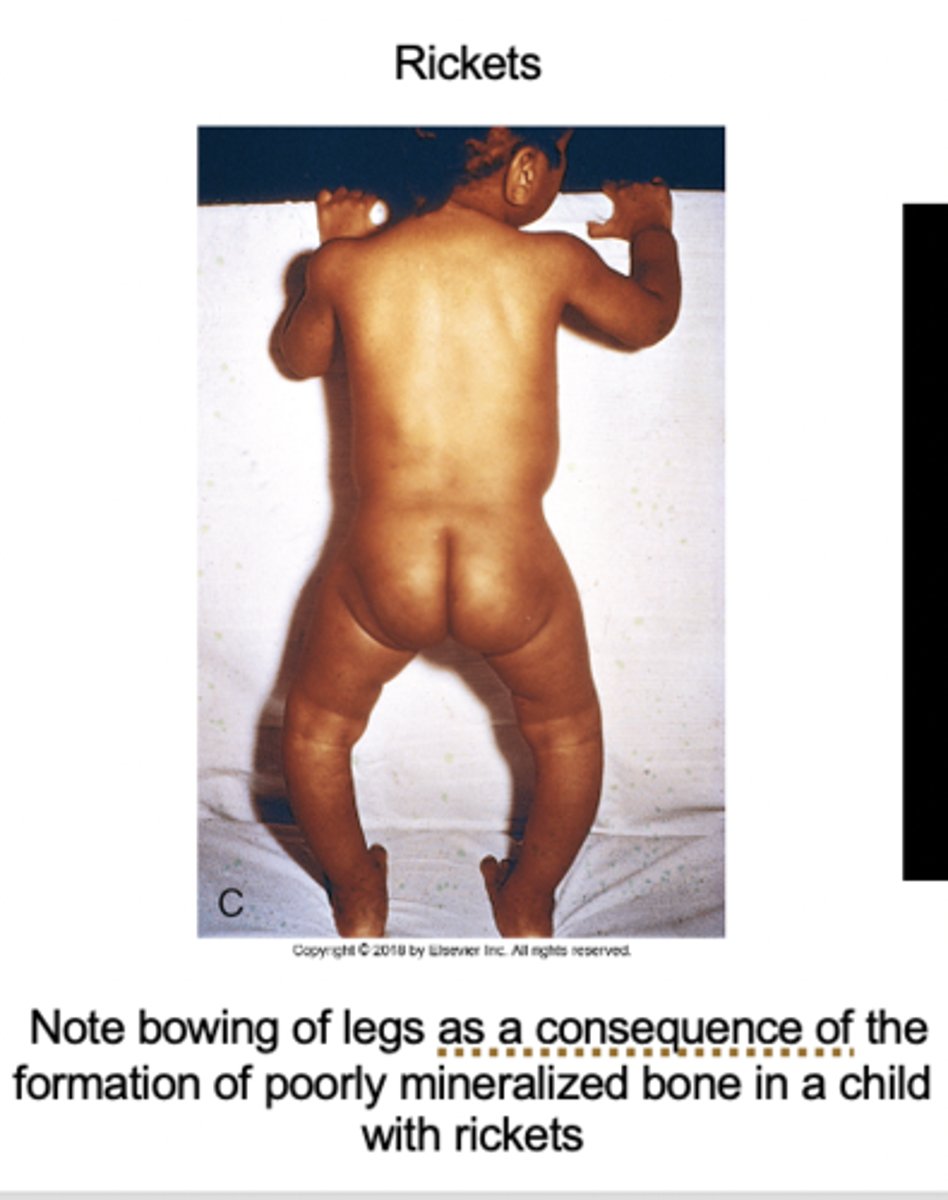
Rickets is characterized by a defect in mineralization and the widening of the __________
epiphyseal plates
osteomalacia is a defects in the mineralization of the _________
bone matrix
What is the most important lab marker in the diagnosis of rickets?
- increased alkaline phosphatase (ALP)
osteomalacia histology
more osteoid (orange) around the bone (green) which has accumulated bc it is not properly mineralized
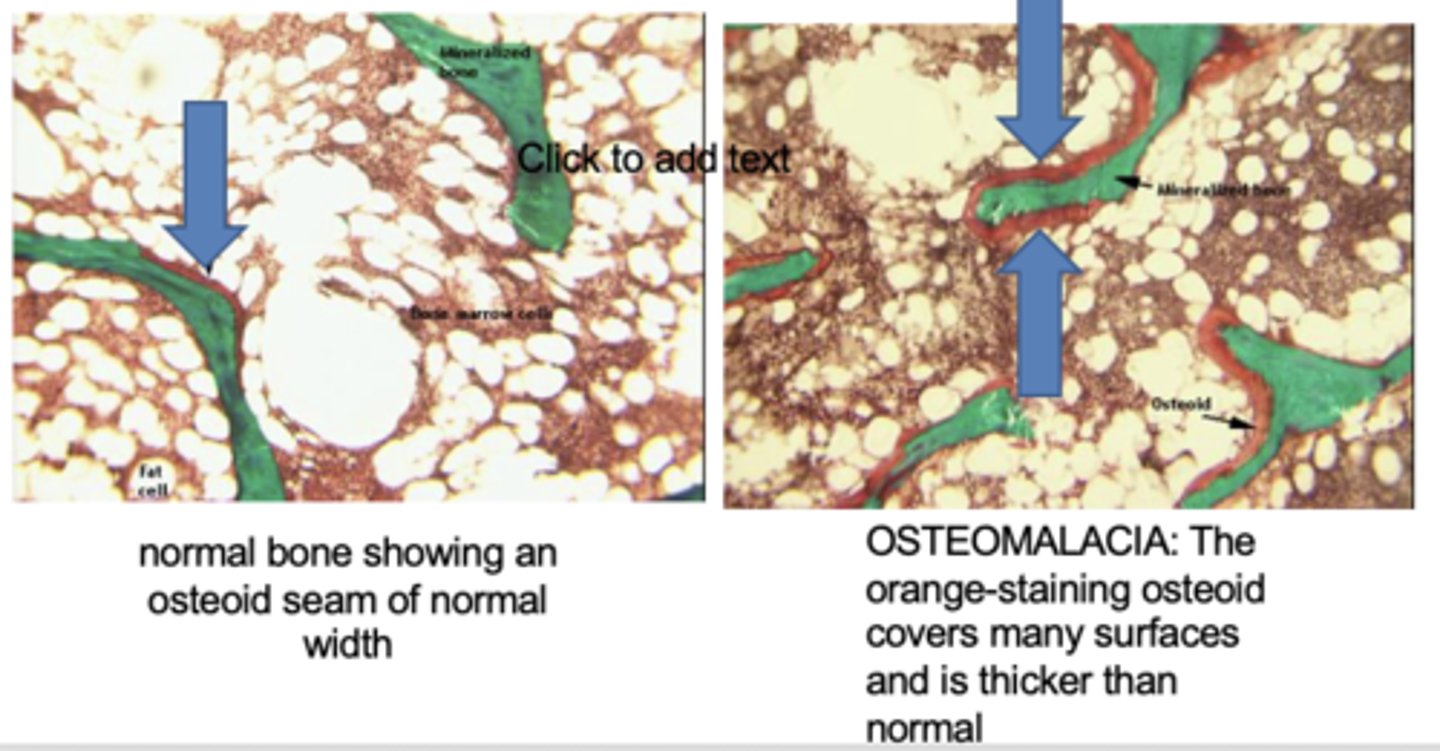
In osteomalacia, the bone is weak and vulnerable to gross fractures or microfractures, which are most likely to affect __________ and __________
vertebral bodies and femoral necks
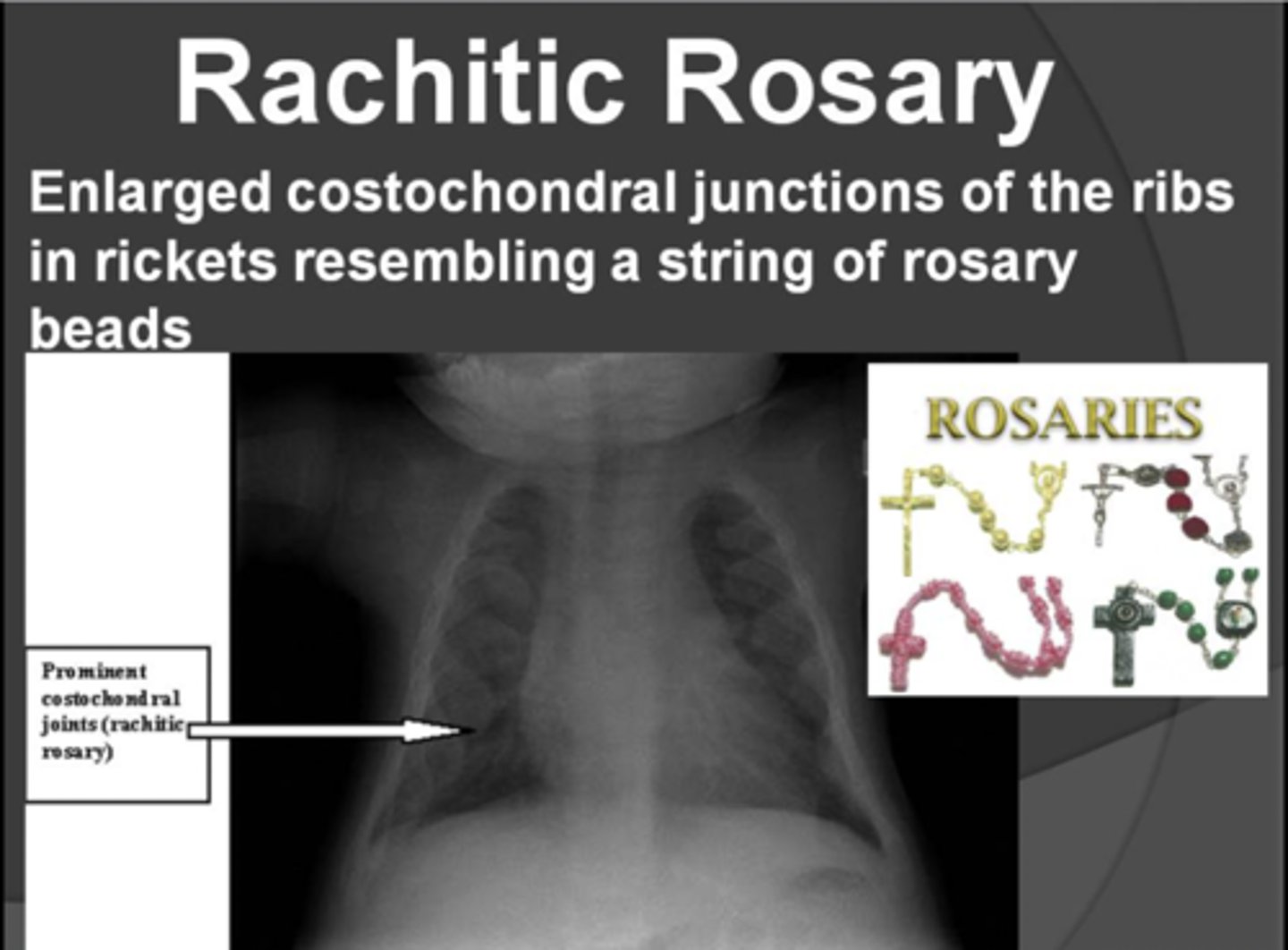
rickets clinical features
- craniotabes (soft skull)
- frontal bossing
- "rachitic rosary" (chest deformity)
- bowed legs, lumbar lordosis
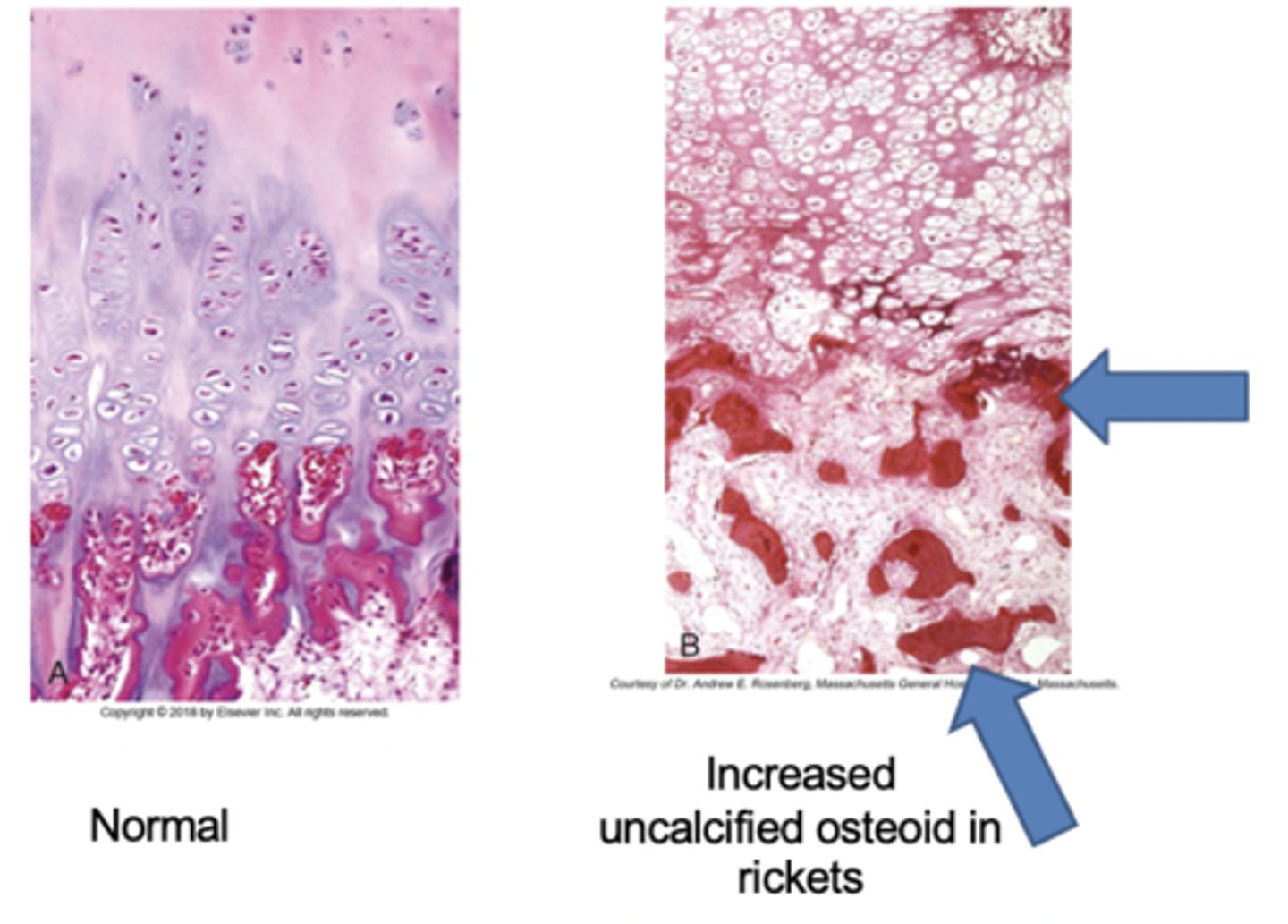
rickets histology
- Normal (L): costochondral junction of a young child illustrates formation of cartilage pallisades and orderly transition from cartilage to new bone
- Rickets (R): Detail of rachitic costochondral junction in which the palisades of cartilage is lost; darker trabeculae are well-formed bone; paler trabeculae consist of uncalcified osteoid
primary hyperparathyroidism
hypercalcemia results from abnormally active parathyroid glands
Secondary hyperparathyroidism
hypocalcemia leads to reactive overproduction of PTH
Primary hyperparathyroidism is usually due to...
a parathyroid adenoma
secondary hyperparathyroidism is usually due to...
renal disease
In secondary hyperparathyroidism, chronic renal disease commonly leads to ________ due to inability of the kidney to make active _______ which impairs _____ absorption
In secondary hyperparathyroidism, chronic renal disease commonly leads to hypocalcemia due to inability of the kidney to make active vit D which impairs Ca absorption
renal osteodystrophy
Bone lesions due to secondary hyperparathyroidism due to chronic renal disease (hypocalcemia --> increased PTH)
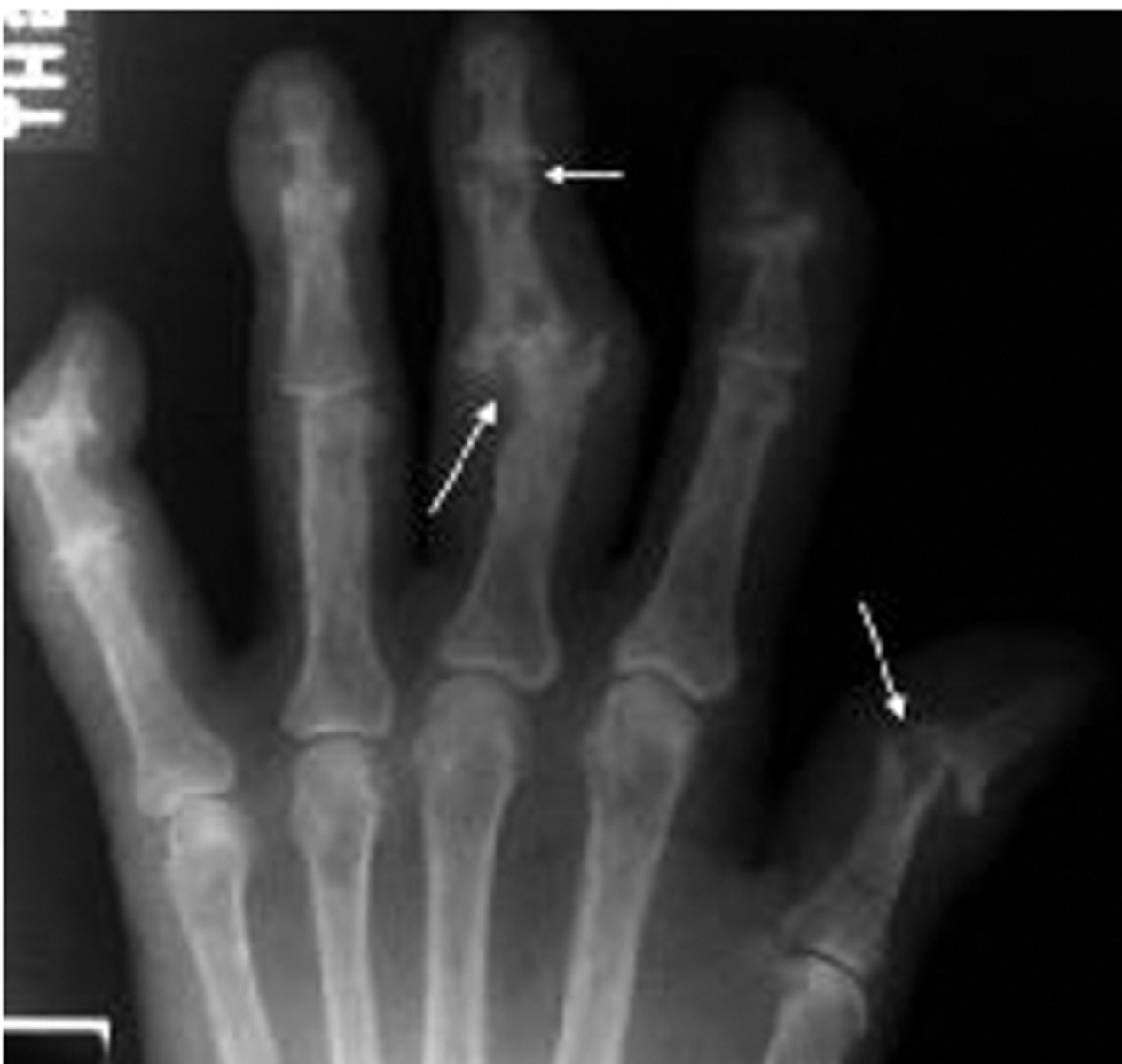
x-ray findings in hyperparathyroidism
subperiostal resorption typically seen at radial aspect of the middle phalanx of the index and middle fingers
dissecting osteitis is associated with...
hyperparathyroidism
(I think this is just a word for lots of osteoclast activity?)
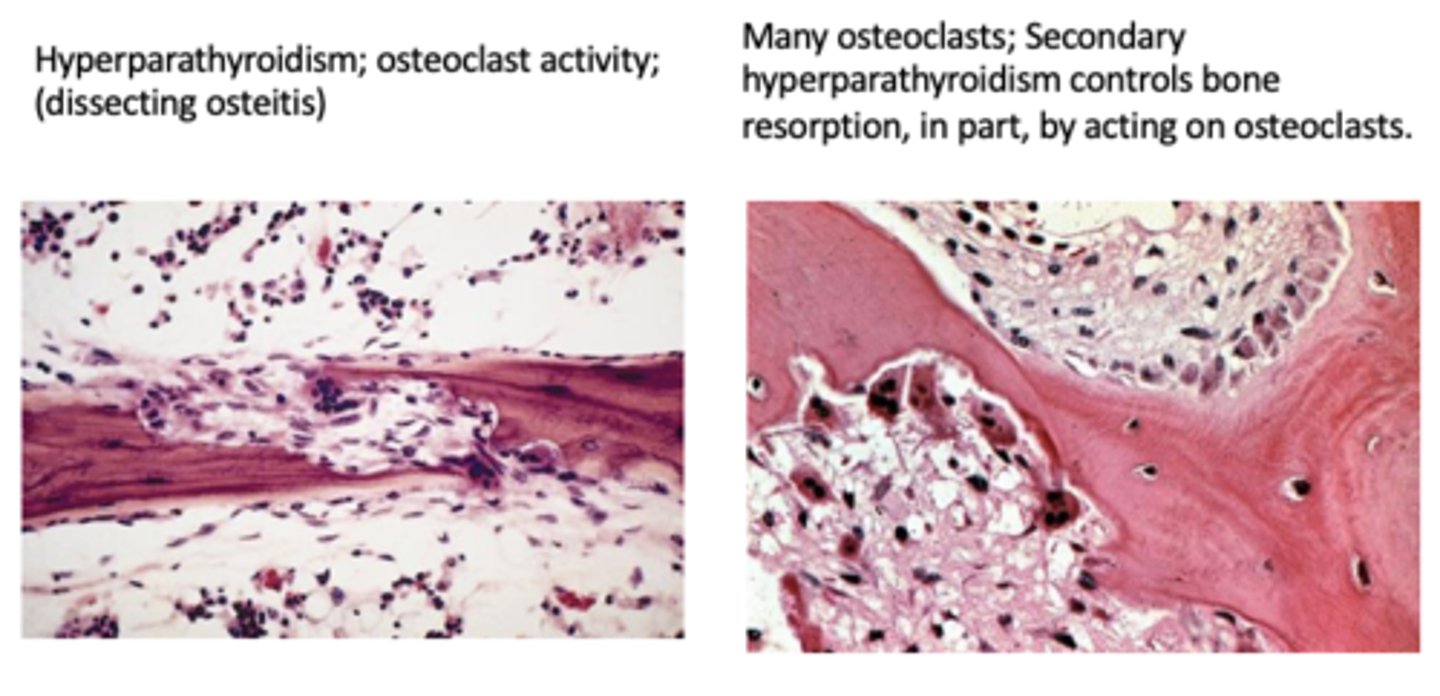
What are brown tumors?
lytic lesions due to high PTH levels (brown due to hemorrhage)
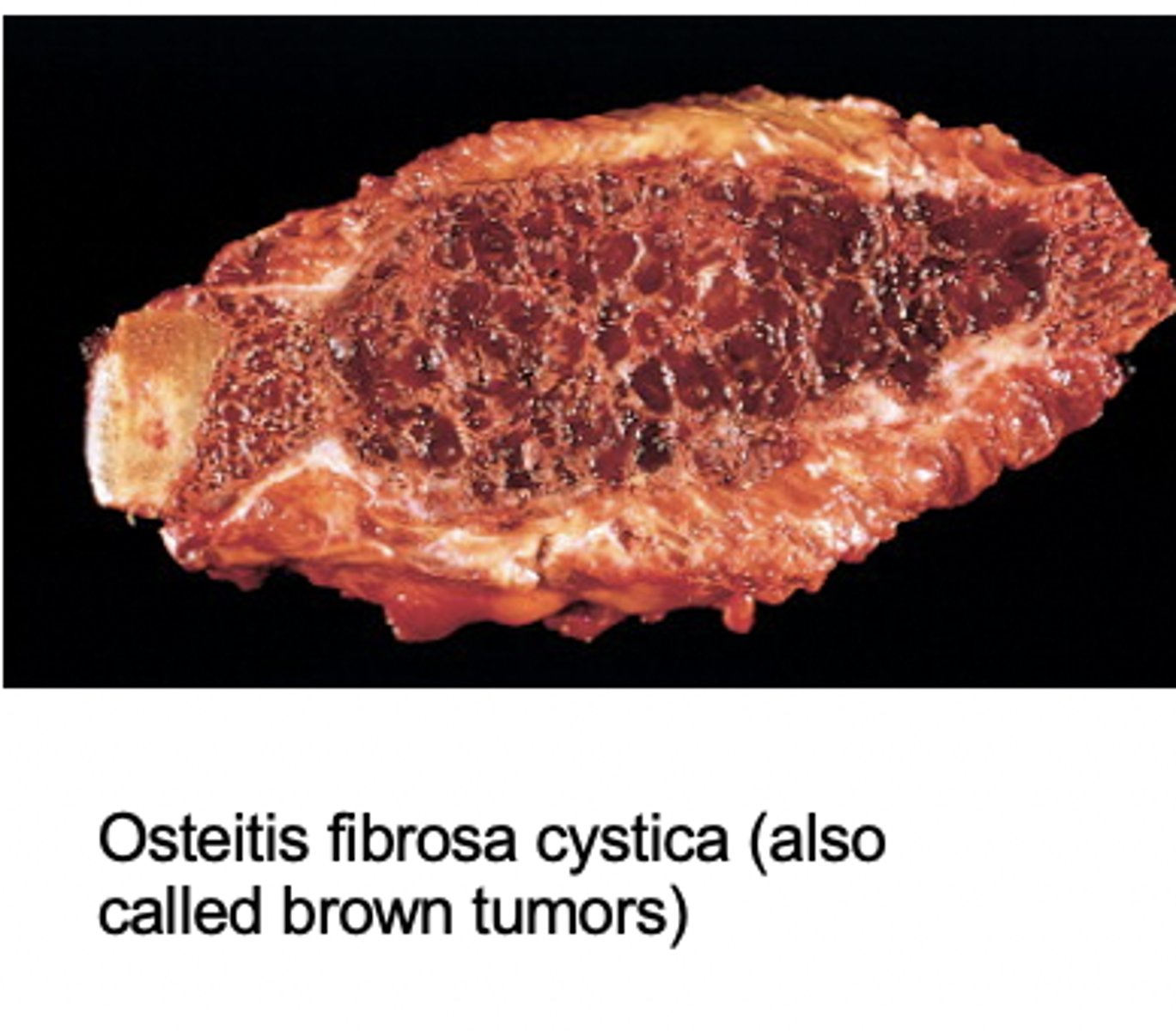
brown tumors are more likely to occur in primary or secondary hyperparathyroidism?
primary hyperparathyroidism
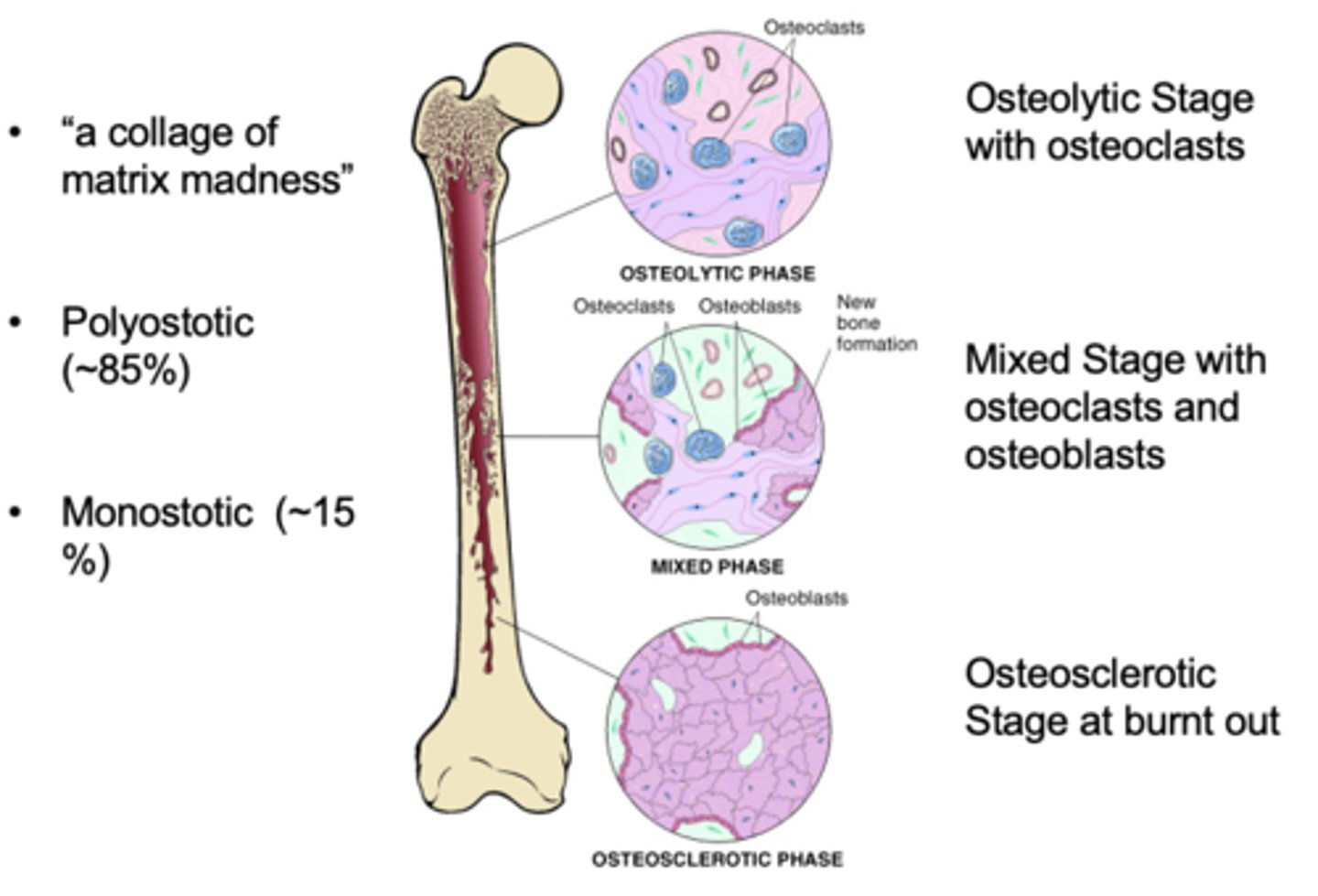
What is Paget's disease?
chronic metabolic disorder characterized by increased bone turnover and breakdown secondary to excessive and disorganized osteoclastic and osteoblastic activity
Hallmark of Paget's Disease
mix of osteolytic and osteoblastic phases
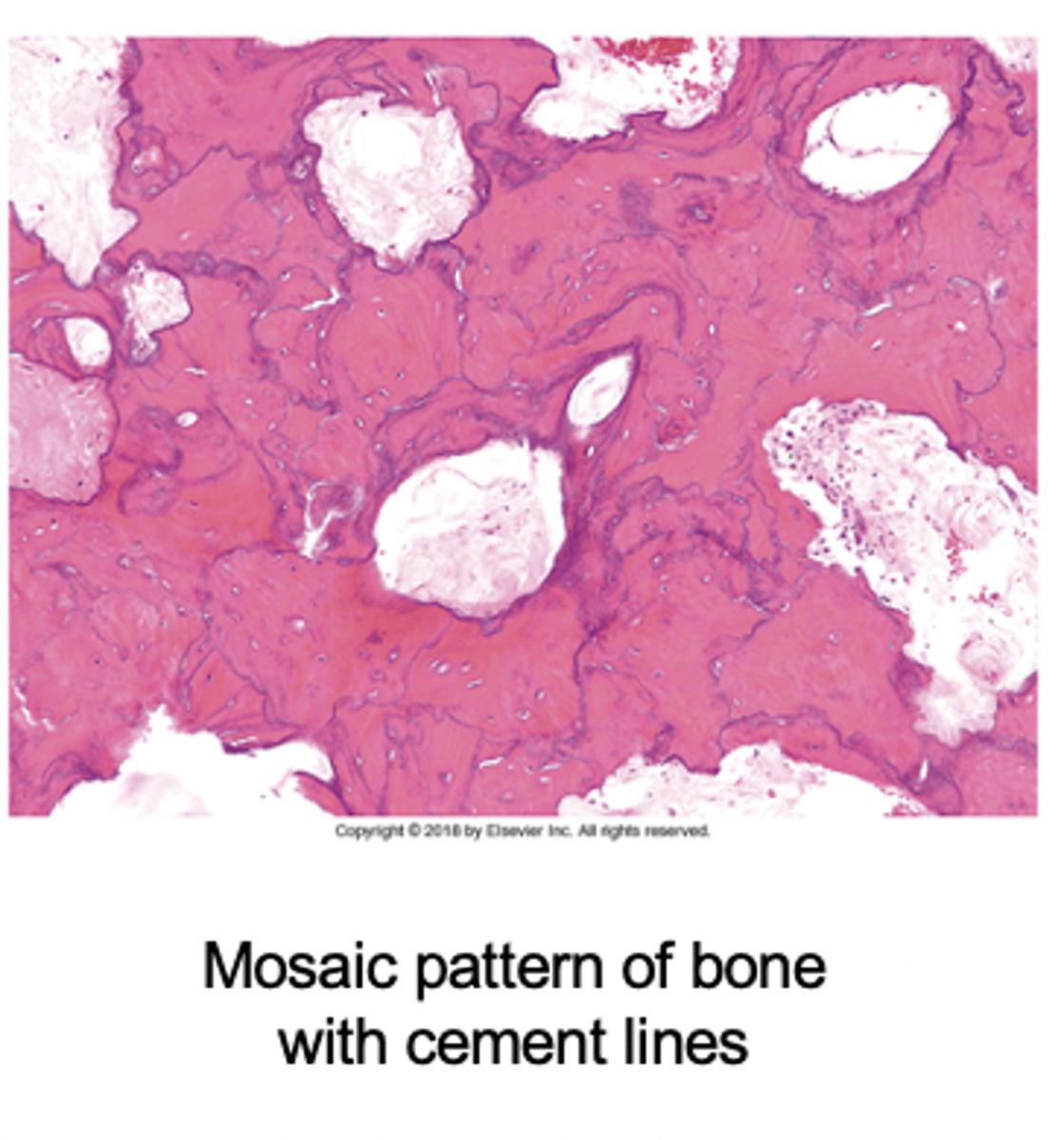
Paget's disease histology
The "mosaic" pattern outlines irregular patches of sclerotic lamellar bone reflecting previous waves of bone resorption and reformation.
Paget's disease labs
- Increase alkaline Phospahatase
- normal Ca
- normal Phos
What is a feared complication of long-standing Paget's disease?
osteosarcoma
Paget's disease facial clinical features
- enlargement of craniofacial skeleton (may produce leontiasis ossea (lion face))
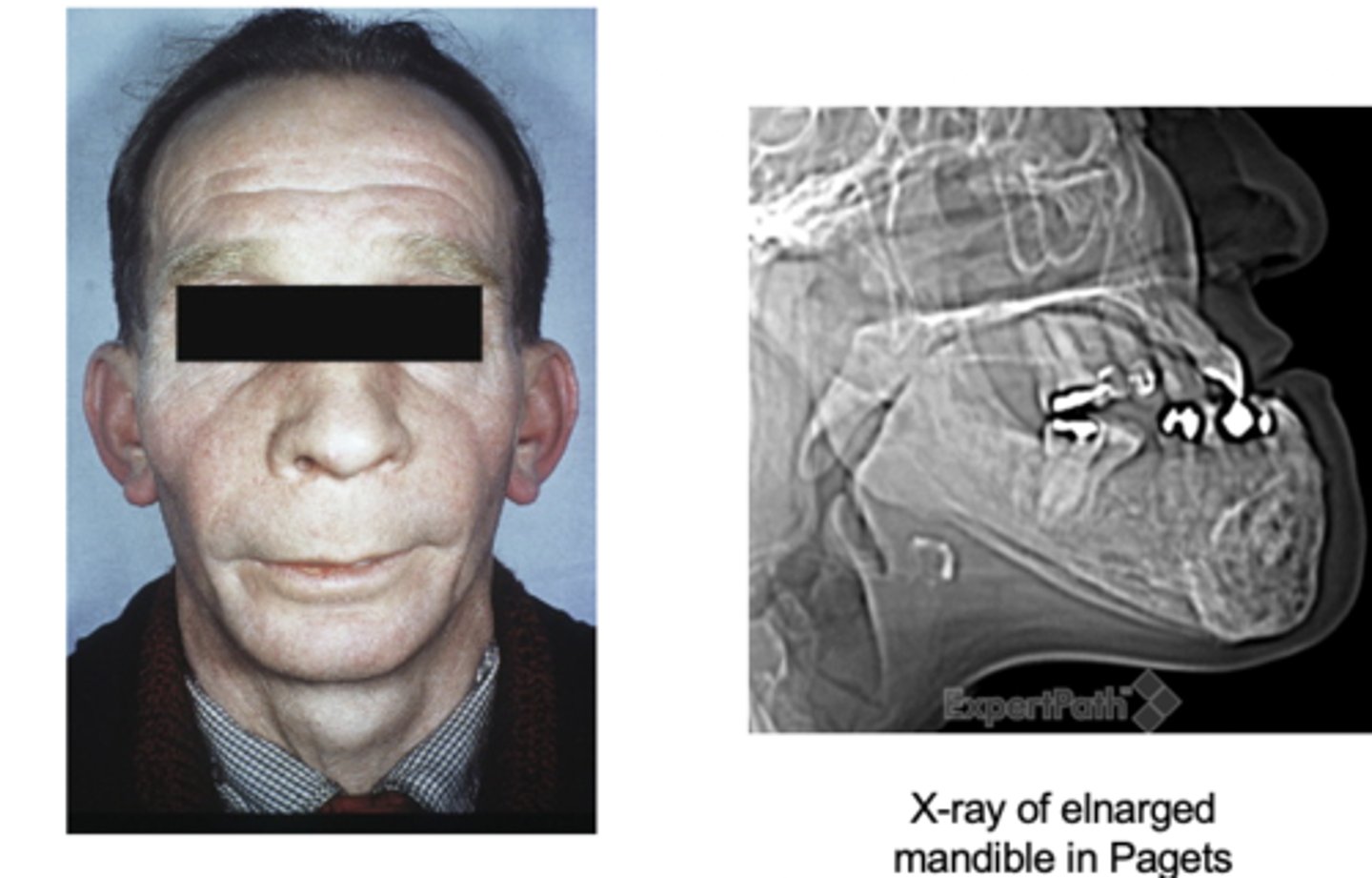
Pagets disease predominantly involves the __________ and __________
axial skeleton and femur