Histology of Endocrine Glands
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
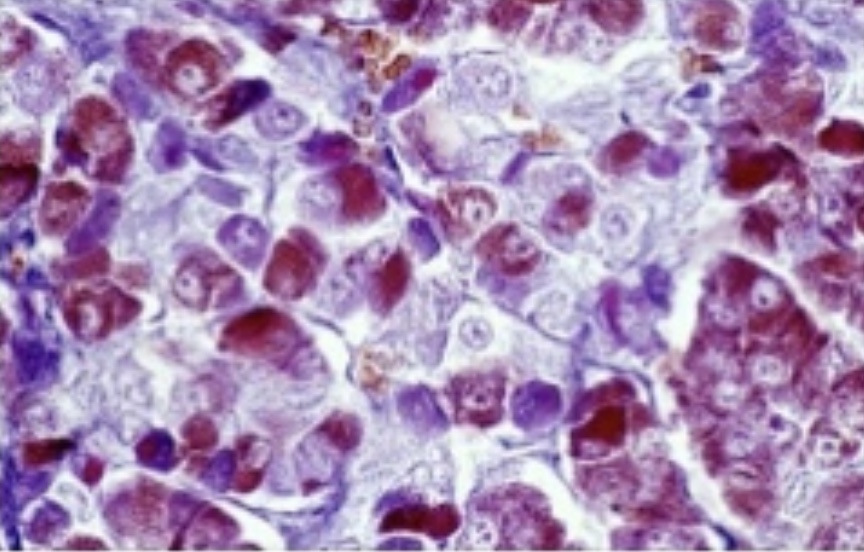
Anterior Pituitary
The anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis) composed of glandular tissue, works w blood vessels
Growth hormone (GH)- cell division, helps w growth of bones
Prolactin (PRL)- milk production after birth
F.L.A.T (Tropic Hormones- Hormones that stimulates other endocrine glands)
Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH)- sexual development, help development of egg in ovaries, in males helps the production of sperm
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH)- regulates the production of cortisol from the adrenal glands. It plays a key role in the body's response to stress.
Luteinizing Hormone (LH)- promotes secretion of male and female sex hormones
Thyroid- Stimulating Hormone (TSH)- stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormones, which regulate metabolism and energy. (T4- thyroxine and T3- triiodoththyronine ).
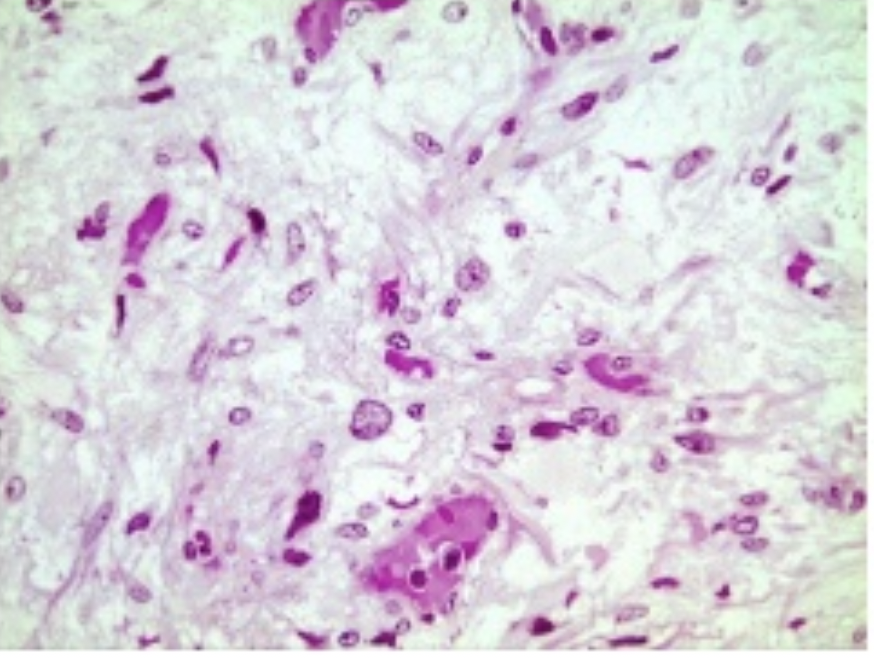
Posterior Pituitary Gland
The posterior pituitary gland (neurohypophysis), works w the nervous system (neurotransmitters)
stores hormones produced by the hypothalamus.
Oxytocin- causes muscle contraction of the uterine walls during birth
Vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone, ADH)- cause kidneys to reduce water excretion, helps maintain blood pressure
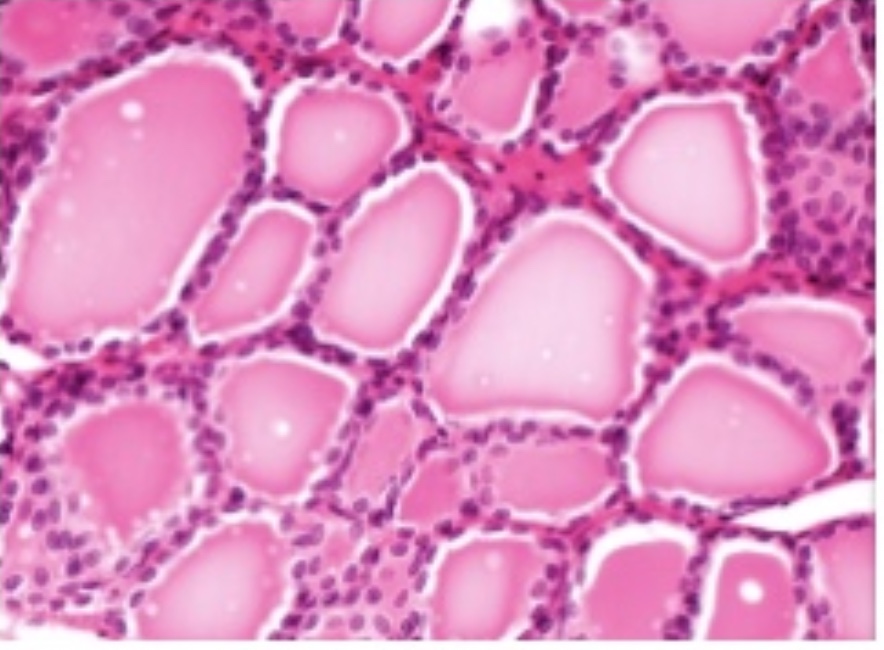
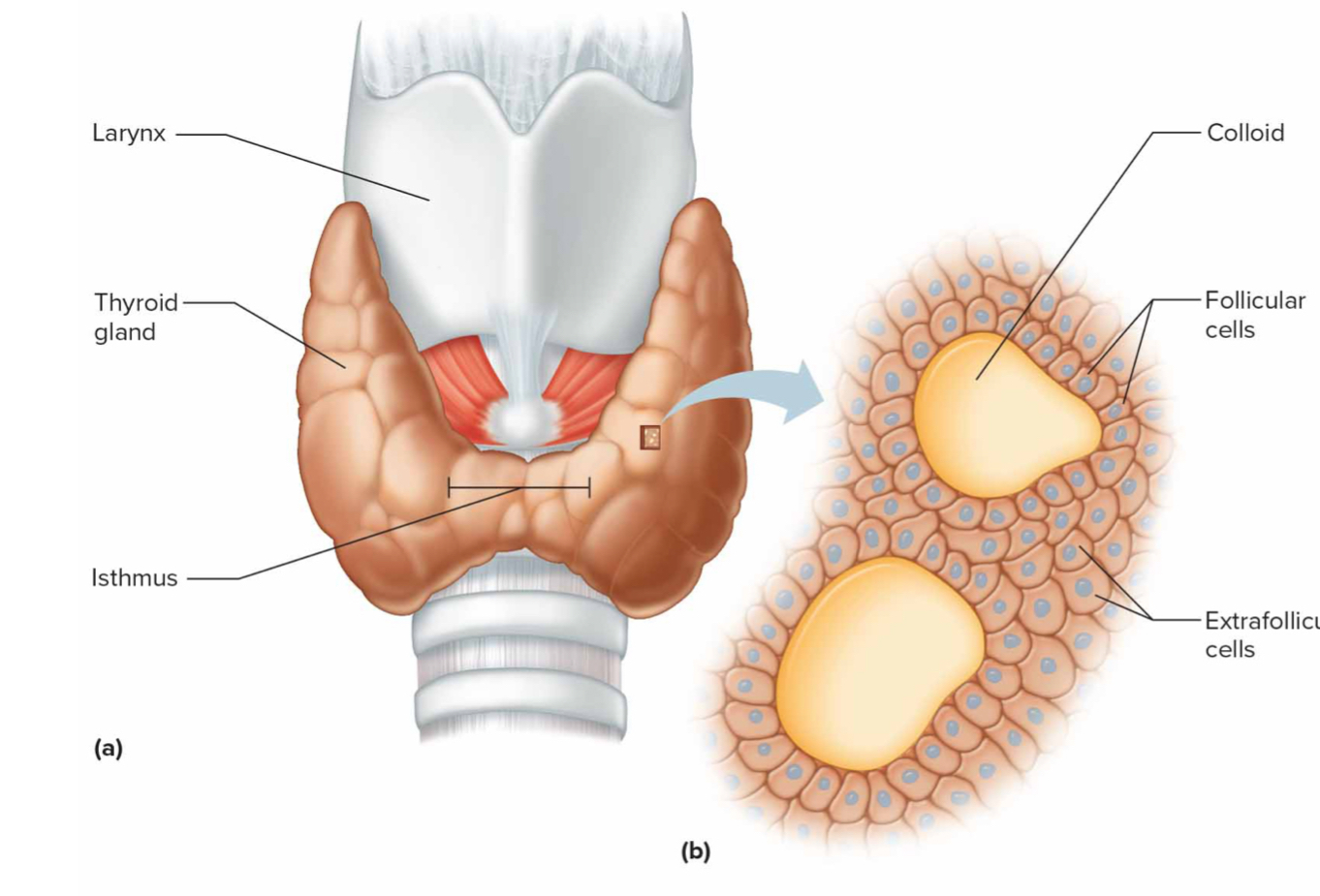
Thyroid Gland
Hormones: thyroid hormones
T3- triiodoththyronine: same as T4 just more potent
T4- thyroxine: increases energy rate, increases rate of protein synthesis, accelerates growth,
calcitonin- Lowers blood calcium and phosphate ion concentration
*has special ability to remove iodine from blood
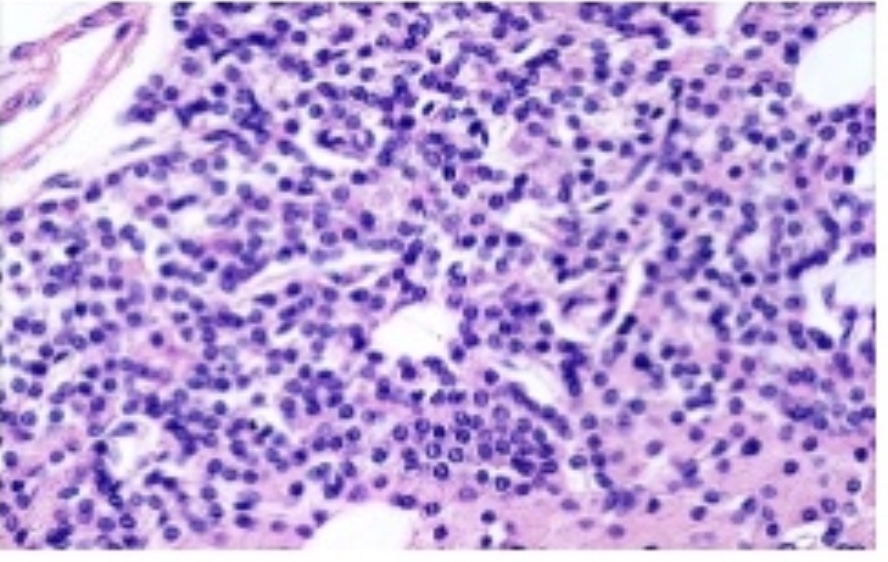
Parathyroid Gland
On posterior side of thyroid gland
Hormones:
parathyroid hormone (PTH: Parathormone)- increases blood level of calcium, decreases phosphate
-acts on bone, kidneys, intestines
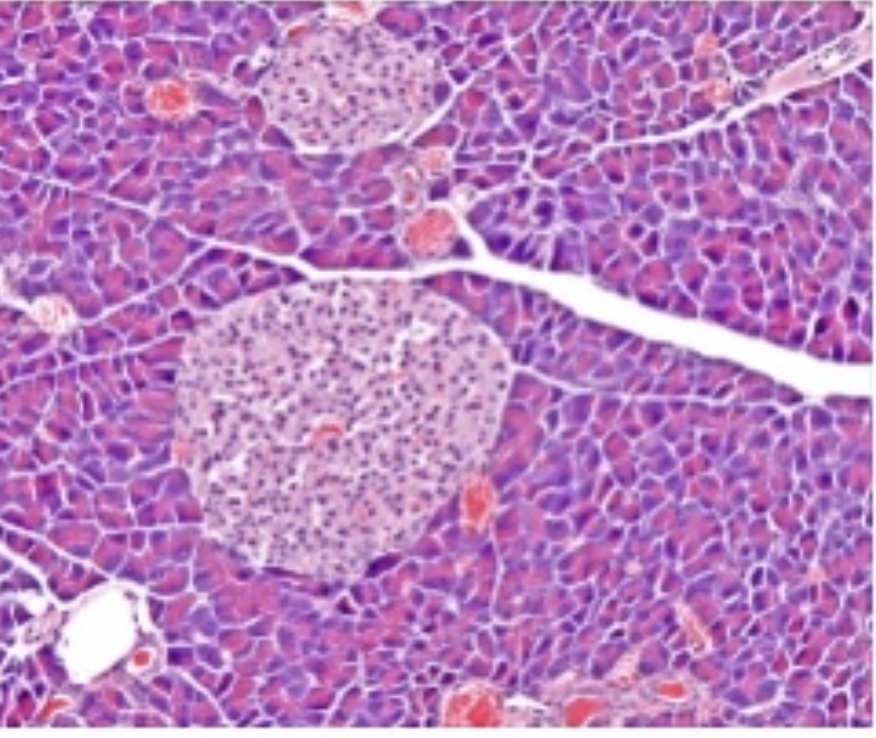
Pancreas
Both Endocrine & Exocrine
Endo- hormones into body fluids
Exo- Juices though Pancreatic Duct
Hormones:
Glucagon: Alpha cells- increase blood glucose
Insulin: Beta cells- decreases blood glucose
Somatostatin: Delta cells- Inhibits (holds back) secretion of insulin and glucagon
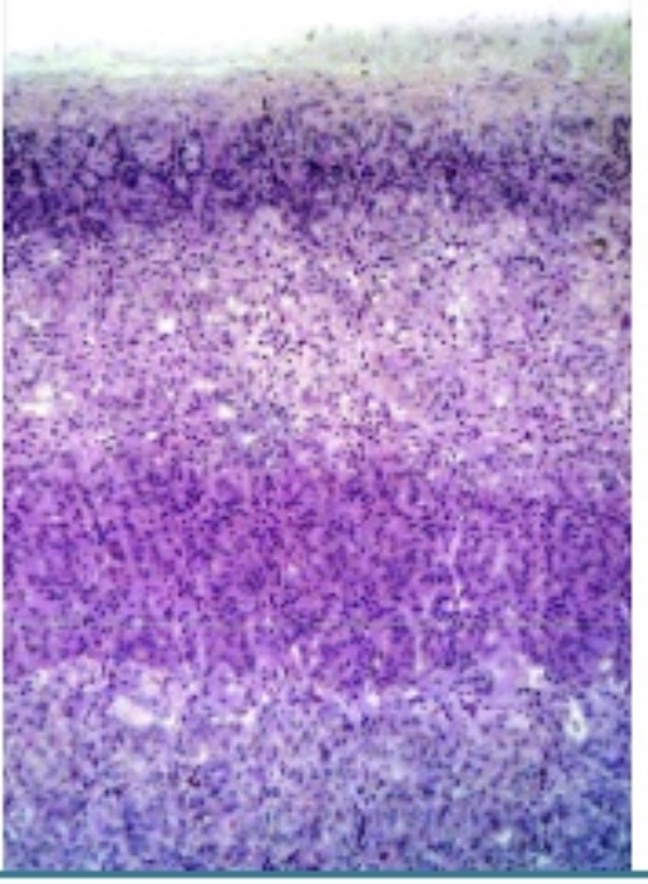
Adrenal Cortex
Out portion of Gland
Hormones:
Aldosterone (ALD)- regulates electrolytes by conserving sodium ions and excreting potassium ions
Cortisol - decreases protein synthesis, increase fatty acid, stimulates glucose synthesis
Estrogen
Testostron
Adrenal Medulla
Central portion of gland
Hormones:
Epinephrine 80%- (adrenaline) “fight or flight response
Norepinephrine 20%
What hormones does thymus gland have?
Thymosin- production/matyration of T cells, which fight infections
Thymopoietin- promotes different T cheeks and enhances immune response
Thymulin- regulates development/function of T cells and has anti-inflammatory properites
GH Factor 1- supports growth and differentiation of T cells