Economics 11HL Unit 1
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/50
Earn XP
Last updated 12:37 AM on 9/14/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
1
New cards
Factors of Production
Land, labour, capital, entrepreneurship
2
New cards
Land
natural resources
3
New cards
Labour
human resources
4
New cards
Capital
production of goods
5
New cards
Entrepreneurship
management
6
New cards
Scarcity
limited availability of economic resources relative to society’s unlimited demand for goods and services
7
New cards
Efficiency
Maximized production using supply and based off of individual choices (demand) or making the best possible use of scarce resources
8
New cards
Choice
not all needs and wants can be satisfied, so choices have to be made
9
New cards
Oppurtunity cost
what you give up to have something else
10
New cards
Economic cost
accounting/financial cost + oppurtunity cost
11
New cards
Sustainability
ability of the present generation to meet its needs without compromising the ability of the future generation(s) to meet their own needs
12
New cards
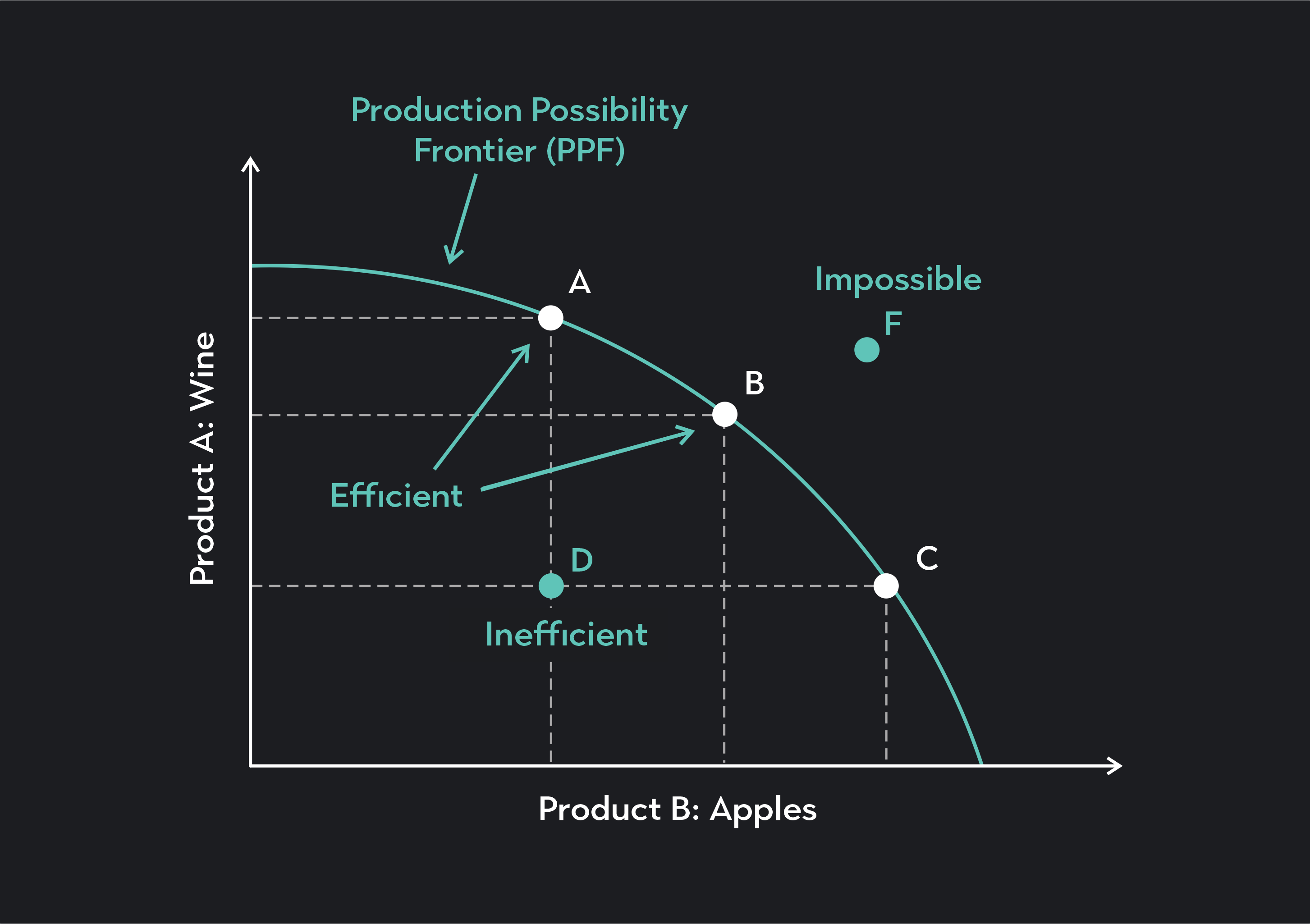
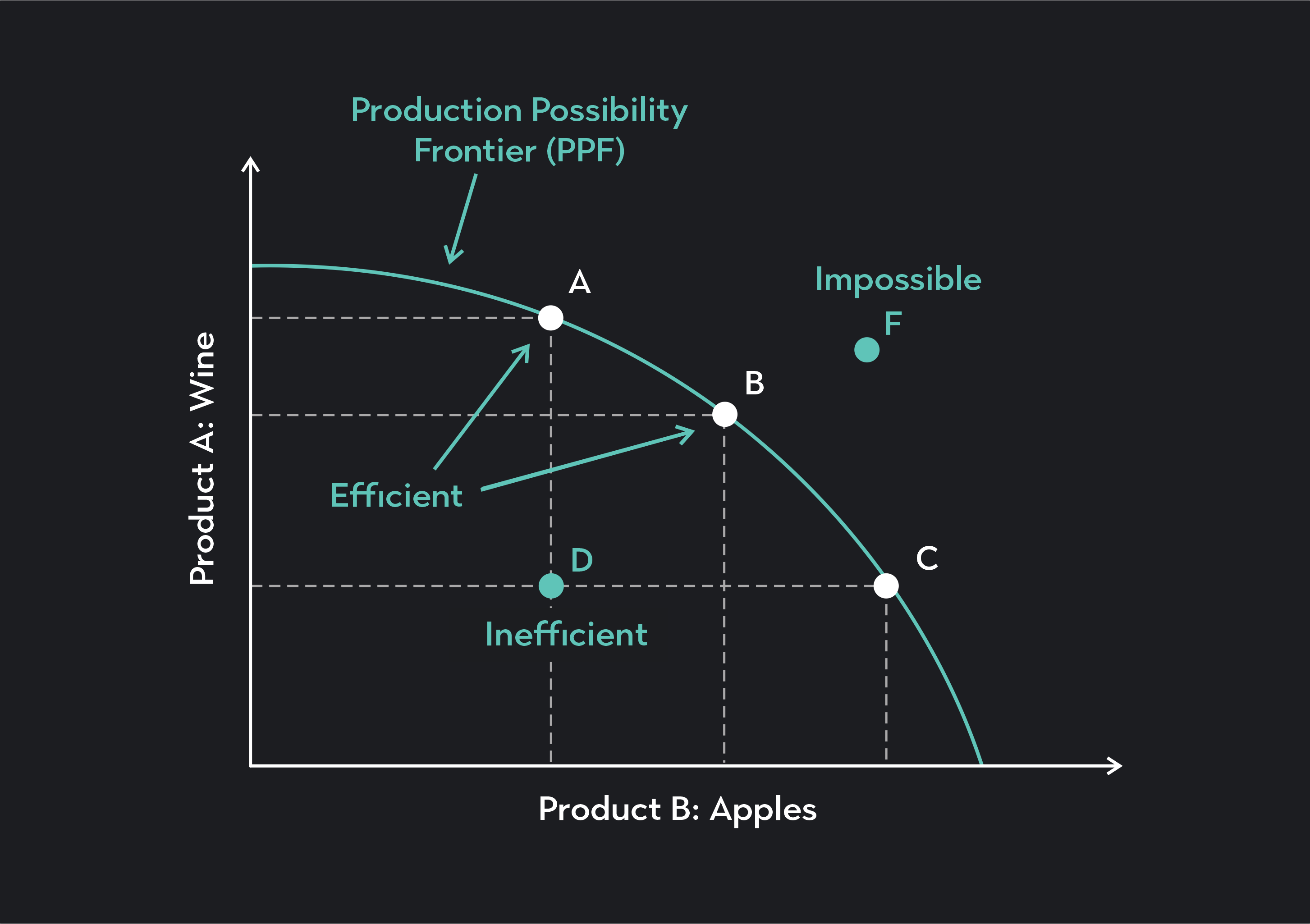
Production Possibilities Curve (PPC)
a graph which indicates the different possible choices a firm can make to maximize profit while maintaining maximum efficiency
Difference between Price 1 and Price 2 is not the same as the difference between Price 2 and Price 3 (oppurtunity cost)
curve is named PPF (Production Possibility Frontier)
Difference between Price 1 and Price 2 is not the same as the difference between Price 2 and Price 3 (oppurtunity cost)
curve is named PPF (Production Possibility Frontier)
13
New cards
Assumptions of the PPC
technology, time, and factors of production (FOP) is constant
only two goods are produced in this market
all of society’s income goes towards these two goods
only two goods are produced in this market
all of society’s income goes towards these two goods
14
New cards
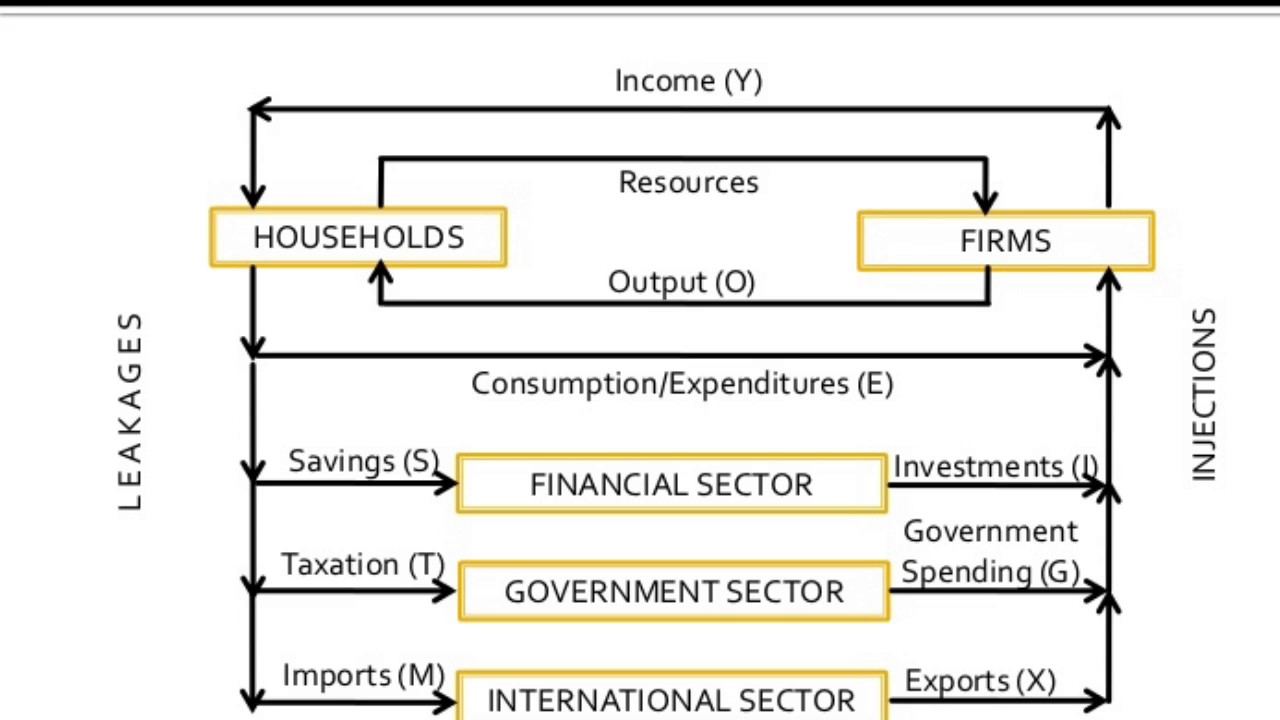
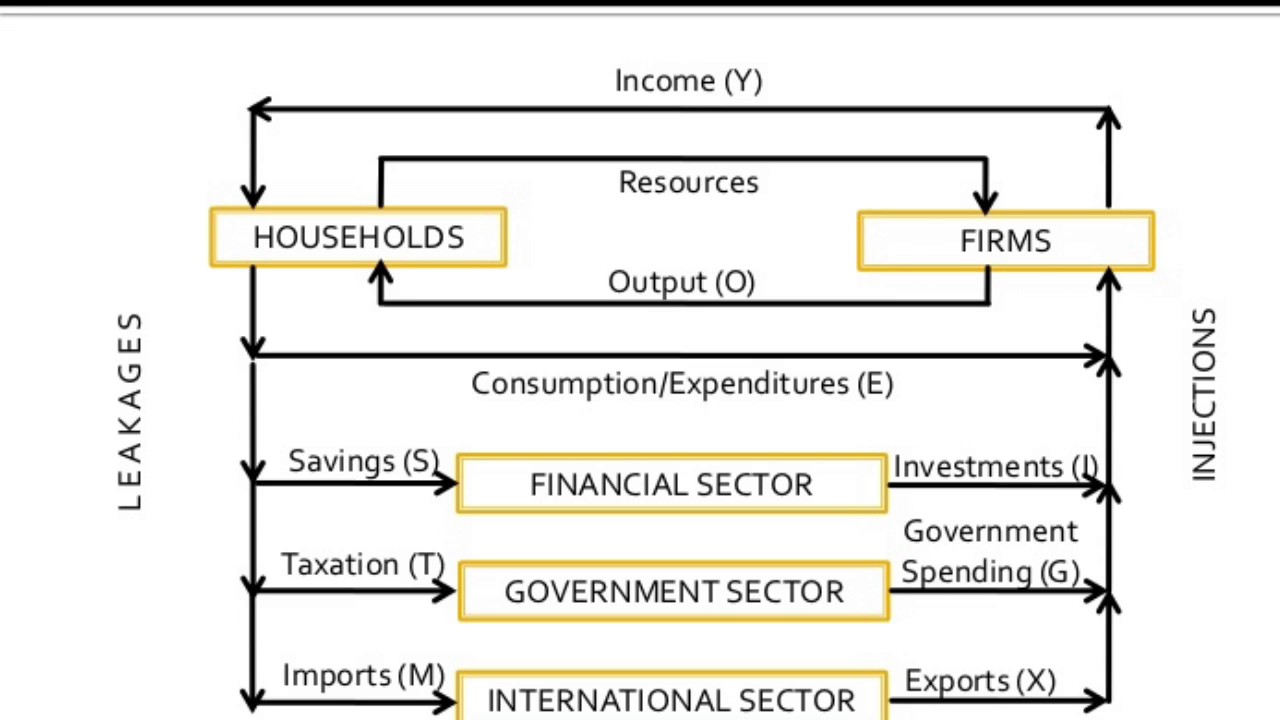
Circular Flow Diagram
GDP = C + I + G + (X-M)
Consumption, Investment, Government, eXports, iMports
Simplification of reality that takes out certain factors and makes them constant
Consumption, Investment, Government, eXports, iMports
Simplification of reality that takes out certain factors and makes them constant
15
New cards
Methodology
Positive and Normative
16
New cards
Positive
Scientific perspective on economics (hypothesis + data)
Verifiable in principle
All other things remain equal (certeris parabus)
Verifiable in principle
All other things remain equal (certeris parabus)
17
New cards
Normative
Subjective value judgement
Cannot be objectively verified/measured
Nonquantifiable adjectives (important, ought to, must, etc.)
Cannot be objectively verified/measured
Nonquantifiable adjectives (important, ought to, must, etc.)
18
New cards
Adam Smith
“the invisible hand” is a metaphor for efficient allocation of resources by society
laissaz faire
laissaz faire
19
New cards
Karl Marx
labour theory of value
decreasing rates of profit and increasing concentration of wealth
more caring towards the masses
decreasing rates of profit and increasing concentration of wealth
more caring towards the masses
20
New cards
Keynes
counter-cyclical government and multiplier
argued that governments had an important management role in macroeconomics
provided a foundation for modern macroeconomics
full employment is a special case and is not frequently occuring
incentive to invest is too weak and the urge to hoard cash is too strong
without necessary investment, the economy maximizes the unfull employment which increases productivity
argued that governments had an important management role in macroeconomics
provided a foundation for modern macroeconomics
full employment is a special case and is not frequently occuring
incentive to invest is too weak and the urge to hoard cash is too strong
without necessary investment, the economy maximizes the unfull employment which increases productivity
21
New cards
19th century classical economic ideas
Bentham, Jevon, Menger, Walras
22
New cards
Bentham
utilitarianism - most happiness among greatest number of people
utility - property in any object tends to produce benefits/advantages/pleasure/good/happiness or to prevent the opposite
utility - property in any object tends to produce benefits/advantages/pleasure/good/happiness or to prevent the opposite
23
New cards
Margin
theory of how prices are derived
derived from consuming something
not total utility, but extra utility of consuming
derived from consuming something
not total utility, but extra utility of consuming
24
New cards
Say’s Law
unemployment cannot exist for long periods because production would create its own demand
25
New cards
Jevon’s Paradox
as technological advancements increase efficiency of labour, demand will increase thus not changing efficiency and waste
26
New cards
Carl Menger
subjective theory of value - in an exchange, both parties always profit as they trade something they think is less valuable for something they think is more valuable
27
New cards
Leon Walras
Walras’ Law - the existence of excess supply in one market must be matched by excess demand in another market so that both factors are balanced out
28
New cards
Milton Friedman
economic theory should be subject to empirical corroboration to test its relevance to the real world
prediction is a key factor
not the realism of the assumptions but the accuracy
prediction is a key factor
not the realism of the assumptions but the accuracy
29
New cards
Robert Lucas Jr.
individual’s rational expectations of inflation and government policies
30
New cards
Friedman + Lucas
the role of markets in bringing the economy back to a situation where there is full employment without any government intervention
31
New cards
Free Sector Diagram
Injections - investment (I), government spending (G), exports (X)
Leakages - savings (S), tax (T), imports (M)
if injections = leakages, the economy is in equilibrium/static
Leakages - savings (S), tax (T), imports (M)
if injections = leakages, the economy is in equilibrium/static
32
New cards
Assumptions made in behavioural economic graphs
1. People are rational/consistent
2. Utility is maximized
3. People have access to all information at all times
33
New cards
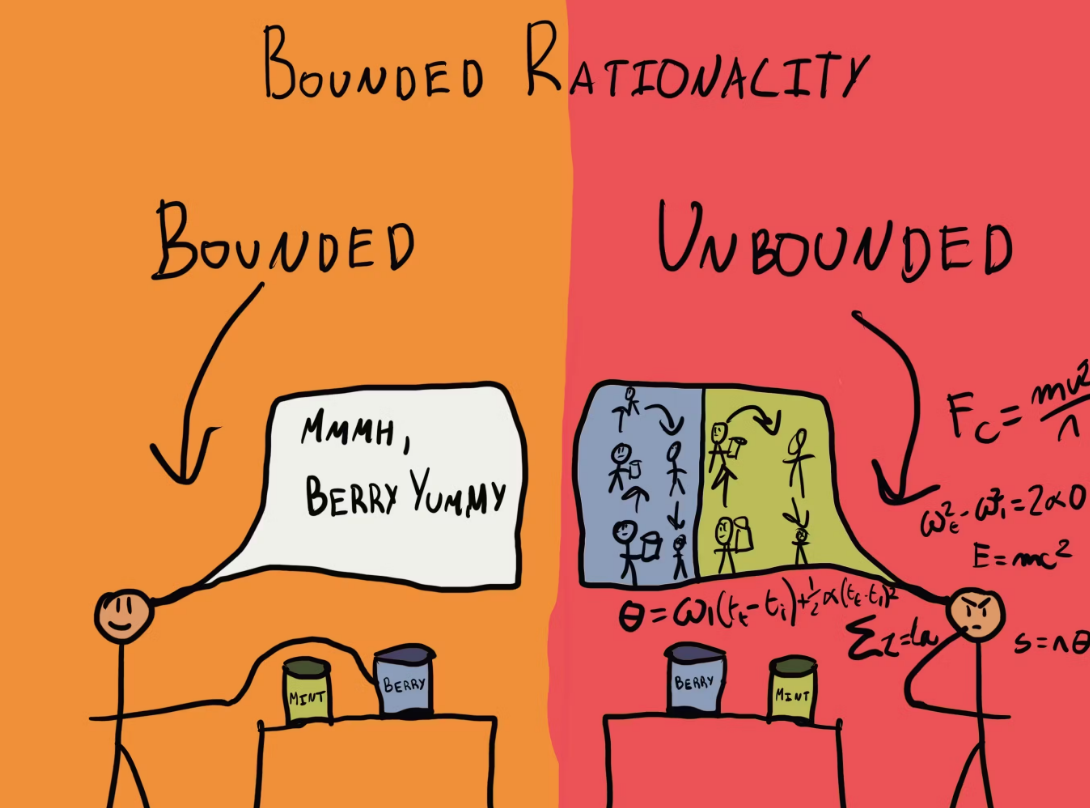
Bounded Rationalism
all rationality is lost past a certain point
34
New cards
Thinking Fast/Slow
heuristics where people use rule of thumb to make quick decisions
35
New cards
Present Bias
people under-invest because the benefits come in the future, and people generally would want benefits in the present
36
New cards
Representative Individual
one person is recorded/measured and “cloned” to create a larger demographic
37
New cards
Nudging
preserving freedom but helping people make decisions when they can’t/don’t (default)
38
New cards
Hot-hand fallacy
belief that a winning streak leads to further success
39
New cards
Bias 1 - overconfidence
a belief that one’s skill/judgement are better than they truly are, or that probability of success is higher than it actually is (health club membership example)
40
New cards
Bias 2 - Hyperbolic Discounting
tendency of people to make the present much more important than even the near future while making economic decisions (example: credit cards)
41
New cards
Bias 3 - Framing effects
Endowment effect - possessing a good makes it more valuable
Loss aversion - a framing bias in which consumers choose a reference point around which losses hurt more than gains feel good
Anchoring - a framing bias in which a person’s decision is influenced by specific pieces of information given
Loss aversion - a framing bias in which consumers choose a reference point around which losses hurt more than gains feel good
Anchoring - a framing bias in which a person’s decision is influenced by specific pieces of information given
42
New cards
Bias 4 - Sunk cost fallacy
the mistake of allowing sunk costs to affect decisions
example: Robert Griffin III (NFL, Washington Redskins)
example: Robert Griffin III (NFL, Washington Redskins)
43
New cards
Degrowth communism
the economy is big enough already, when is the stopping point for growth?
focus growth on more important aspects such as healthcare and not consumption as it raises healthcare costs
focus growth on more important aspects such as healthcare and not consumption as it raises healthcare costs
44
New cards
Interdependence
a consideration of possible economic consequences of interdependences is essential when conducting economic analysis
nothing in the economy is self-sufficient, so they interact with one another (the greater the scale of interaction, the greater the interdependence)
nothing in the economy is self-sufficient, so they interact with one another (the greater the scale of interaction, the greater the interdependence)
45
New cards
Linear economy
Take → make → waste
resource extraction → production → distribution → consumption → disposal
resource extraction → production → distribution → consumption → disposal
46
New cards
Circular Economy
Take → Make/remake → Distribute → Use/re-use/repair → Selectively dispose → Enrich/recycle → Take
aims to minimize waste and promote a sustainable use of natural resources
aims to minimize waste and promote a sustainable use of natural resources
47
New cards
Problems with the circular economy
1. No clear definition (too vague in the definitions and different defitions clash with one another)
2. Ignores scientific principles (you cannot create or destroy matter/energy)
3. Lack of scale (hard to scale up to a global level)
48
New cards
Systems Perspective
taking into account all of the behaviours of a system as a whole in the context of its environment
49
New cards
Economic efficiency
socially constructed concept with its politics and its political implications
public goal, competing with other public priorities
to improve the state of one party, you must hurt another
society gets maximum net benefits
public goal, competing with other public priorities
to improve the state of one party, you must hurt another
society gets maximum net benefits
50
New cards
Eco-efficiency
production of goods/services while using fewer resources and creating less waste and pollution
creating more value through an increase in resource productivity and a decrease in resource intensity
leads to less resource consumption
creating more value through an increase in resource productivity and a decrease in resource intensity
leads to less resource consumption
51
New cards
Economic Well-being
refers to levels of prosperity, economic satisfaction and standards of living among the members of a society