Approach to Kidney Disease
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
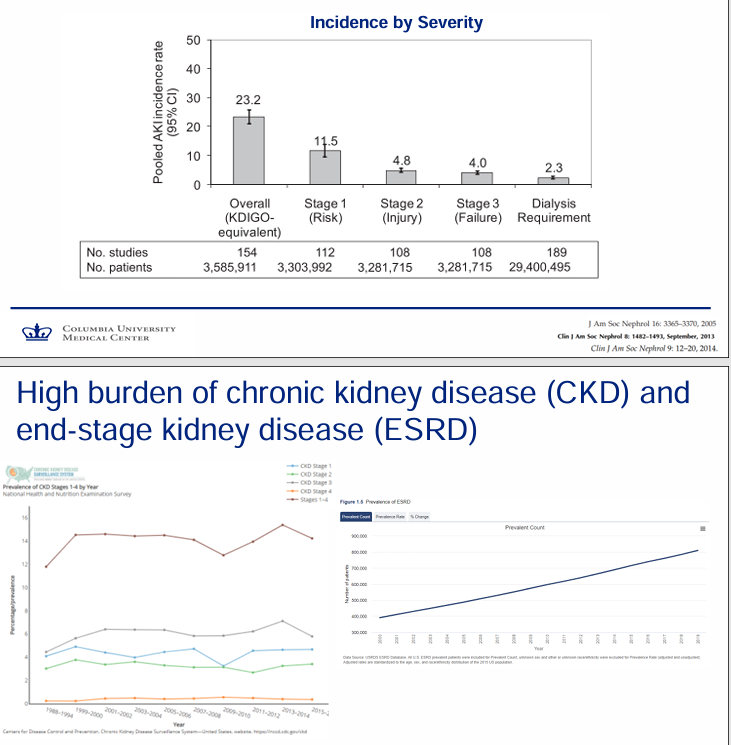
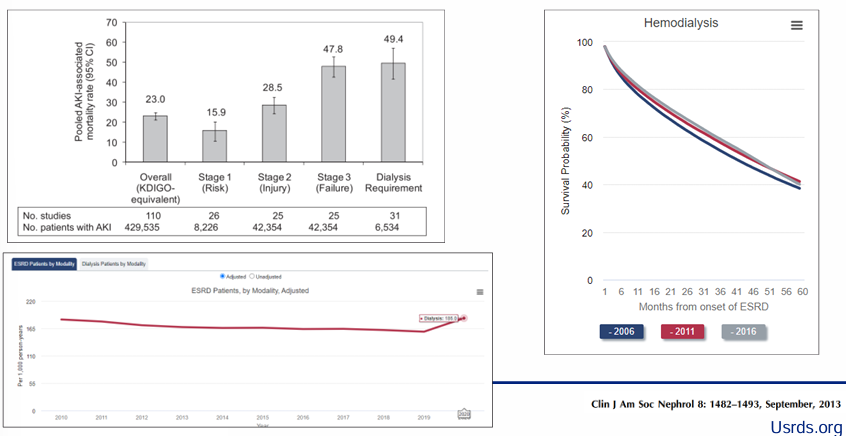
burden of AKI, CKD, and ESKD
renal failure confers
-high risk of mortality
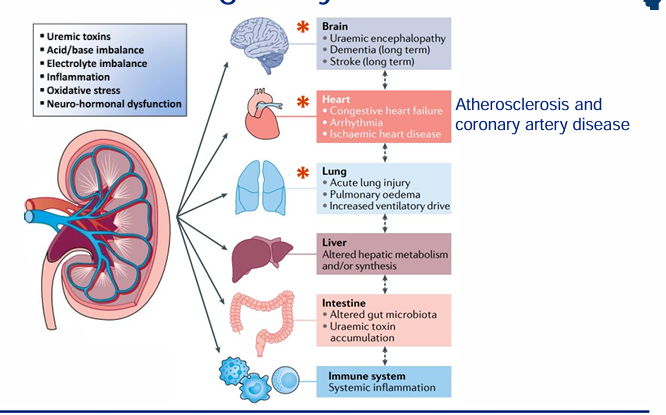
renal failure as a multiorgan, systemic condition
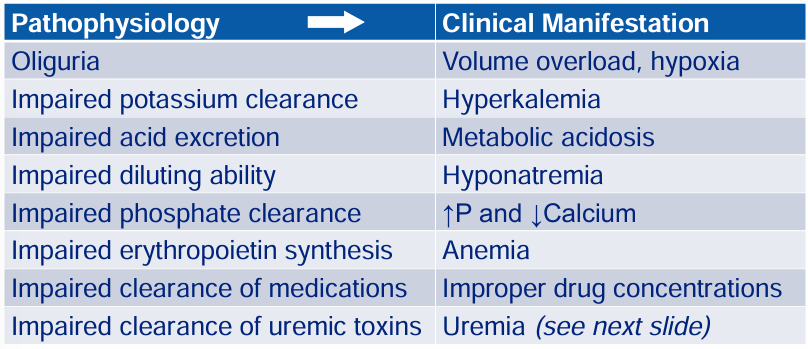
complications of severe renal failure: pathophysiology → clinical manifestation
uremia

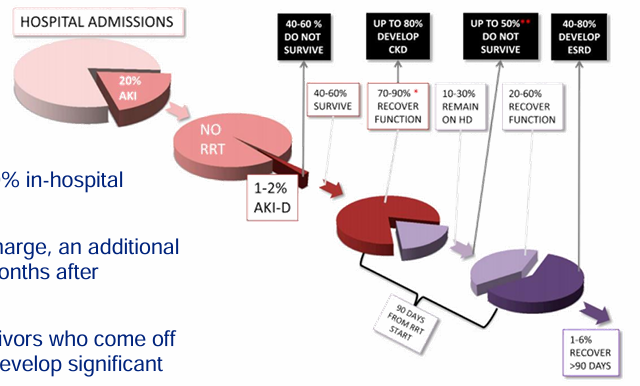
natural history of acute renal failure
-AKI is common
-severe AKI has ~50% in-hospital mortality
-of survivors to discharge, an additional 50% mortality in 3 months after discharge
-majority of survivors who come off of dialysis go on to develop significant CKD or ESRD
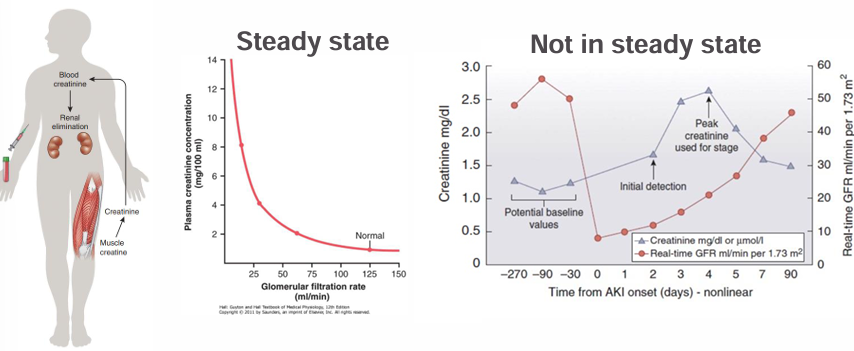
serum creatinine as a biomarker of filtration
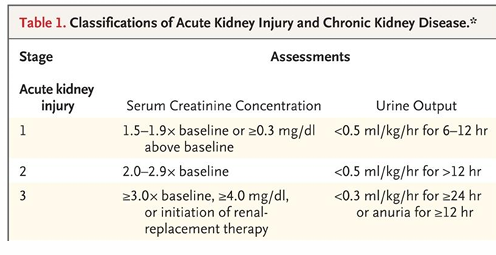
acute kidney injury (AKI)
-relies on EITHER an absolute or relative change in serum creatinine OR on a decrease in urine output over a short period of time
biomarkers in AKI
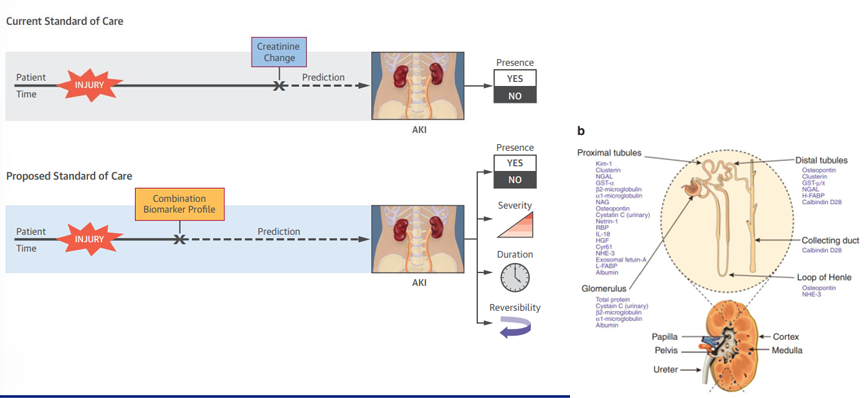
improving AKI definitions
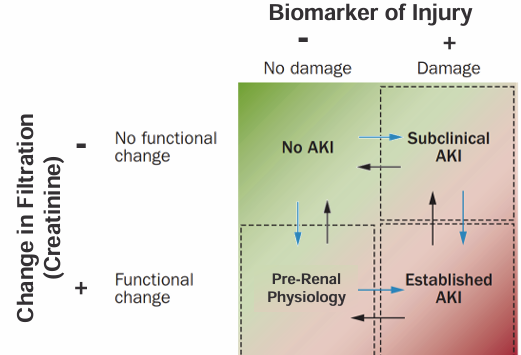
-true AKI can be present without a change in Cr (“subclinical AKI”)
-Cr can be elevated without any tubular injury (“pre-renal physiology”)
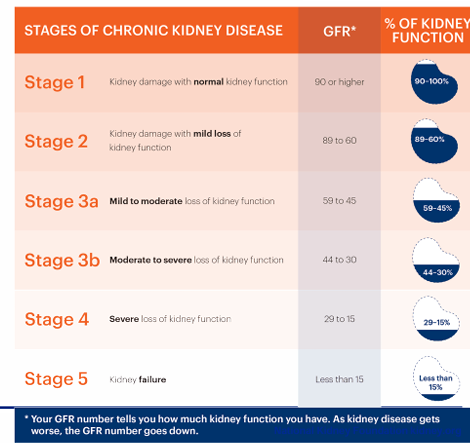
chronic kidney disease (CKD)
-decreased GFR or kidney damage for >3 months
-progressive stages with more severe loss of kidney function
-upcoming dedicated lecture on CKD and complications
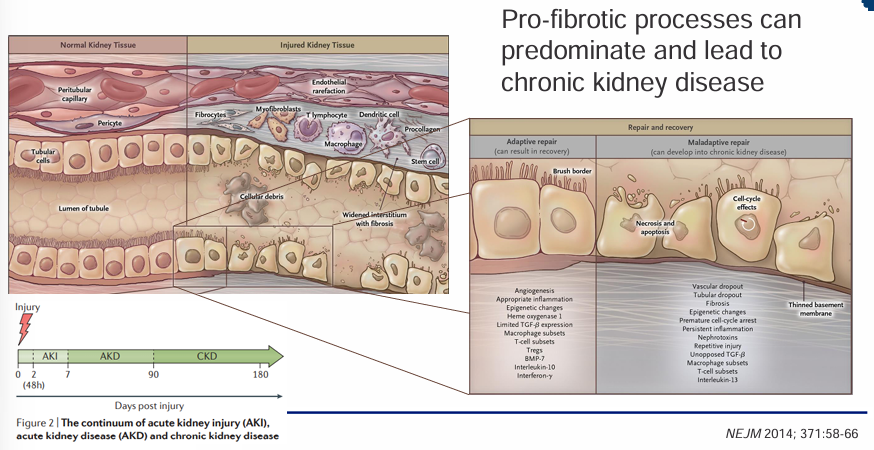
AKI to CKD continuum
AKI v CKD- chronicity
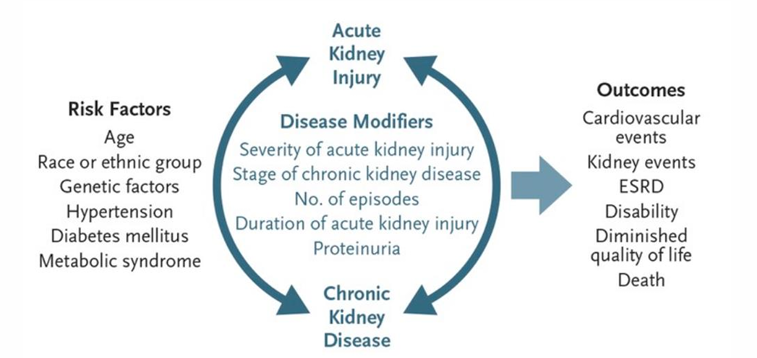
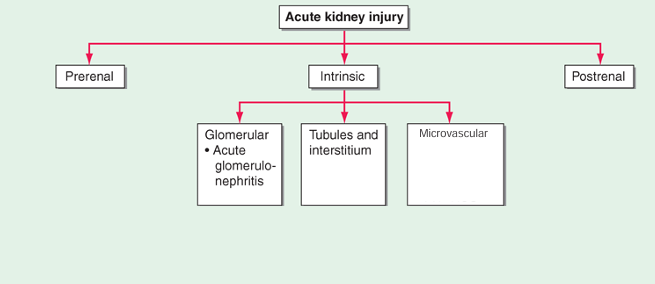
framework for approaching renal failure
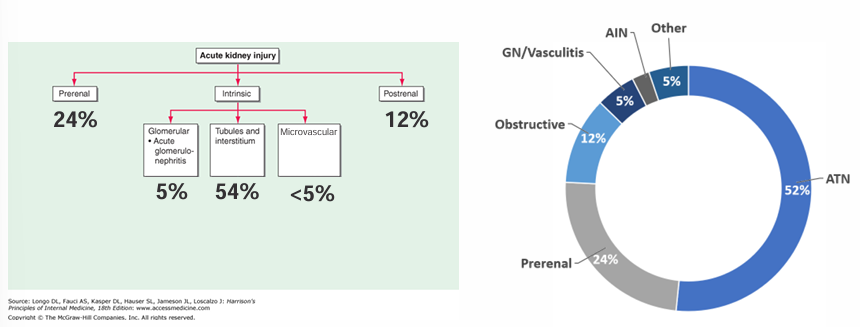
determining the cause of AKI
-history
-BUN:Cr ratio
-urinalysis and urine sediment
-urine protein and urine albumin to urine Cr ratios
-FENa or FEUrea (select cases)
-imaging (select cases)
-serologies (select cases)- complement levels, ANCA, anti-GBM, ANA, ENAs, cryoglobulins, SPEP/UPEP with IFE, SFLC, hep serologies, HIV, ASLOP
-kidney biopsy (select cases)
urinalysis- color
-light yellow (dilute) to dark yellow (concentrated)
-red urine should prompt an evaluation for red blood cells, hemoglobin, or myoglobin in the urine
-various medications, genetic disorders, foods, and medical conditions can change the color
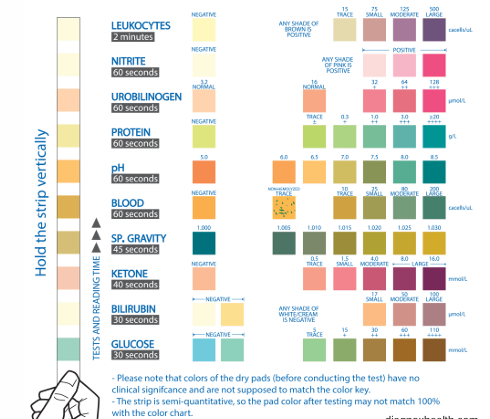
urinalysis
-specific gravity
-pH
-leukocytes
-blood/hemoglobin
-nitrites
-ketones
-bilirubin
-urobilinogen
-glucose
-protein
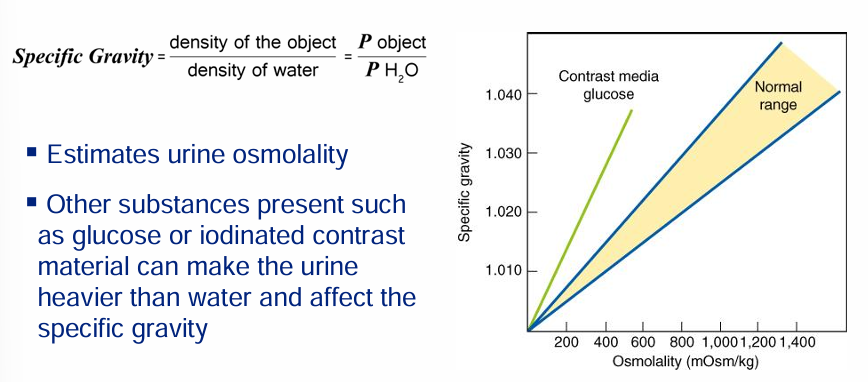
urinalysis- specific gravity
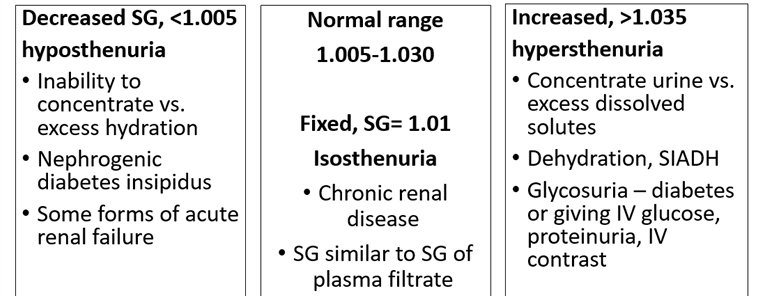
urinalysis- specific gravity: decreased SG, normal range, increased
urinalysis- blood
-hematuria = RBCs in the urine
-hemoglobinuria = free hemoglobin in urine (normally present INSIDE RBCs)- intravascular hemolysis or lysis of RBCs in urine
-myoglobinuria = free myoglobin in urine (normally in intact muscle cells)- rhabdomyolysis (muscle breakdown)
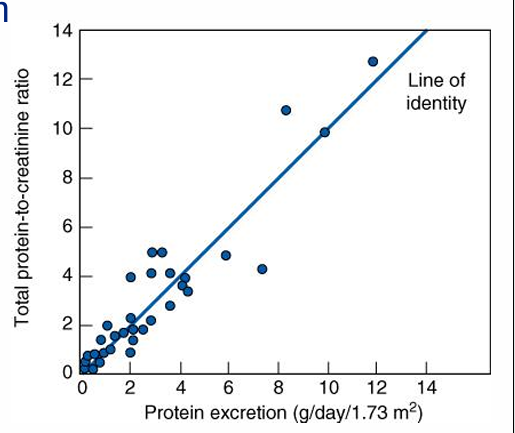
proteinuria estimation
-gold standard is 24 hours urine collection (cumbersome)
-a spot urine protein in isolation is meaningless
-normalizing it to spot urinary Cr is used clinically (assuming average muscle mass where daily Cr production ~1000 mg/day)
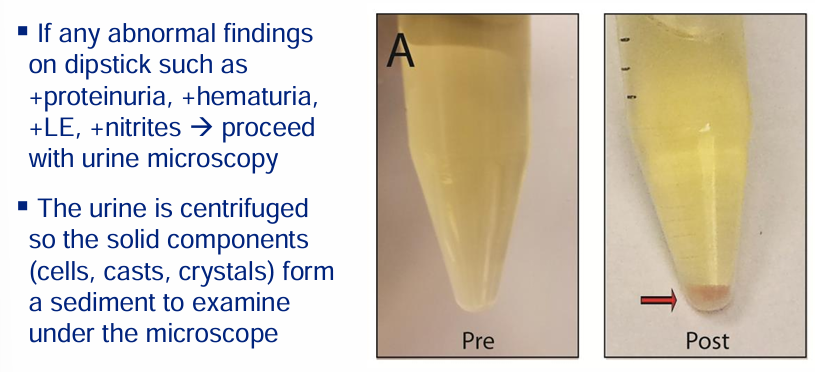
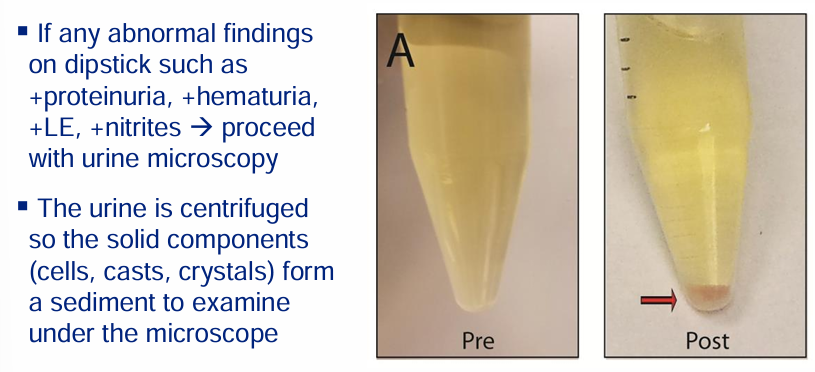
urine sediment
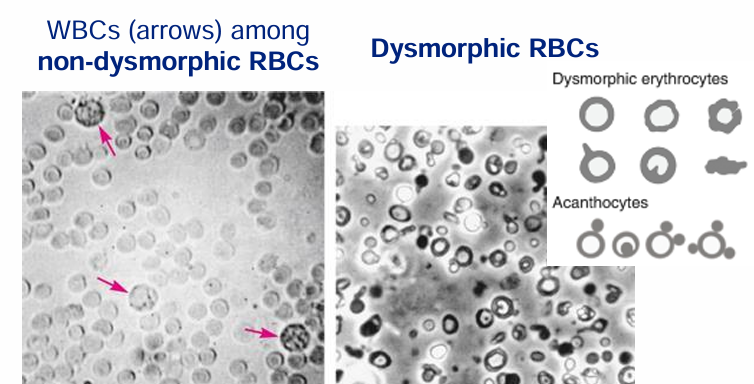
urinary sediment constituents
urine sediment- cells
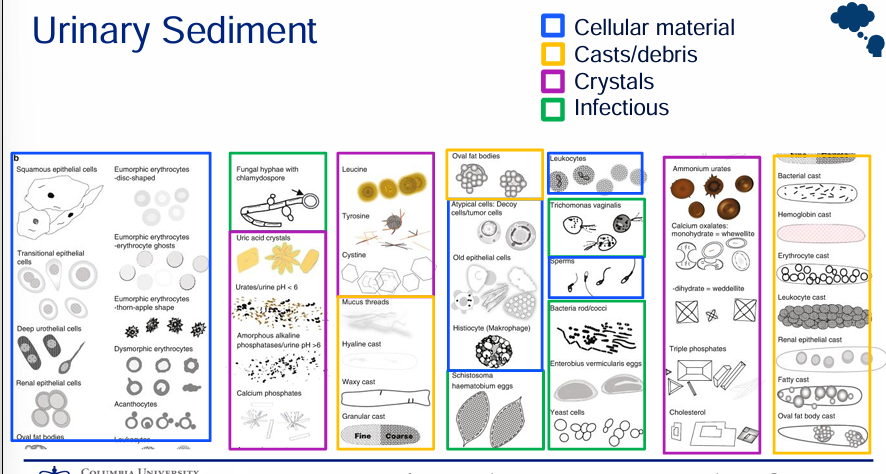
urinary sediment- casts
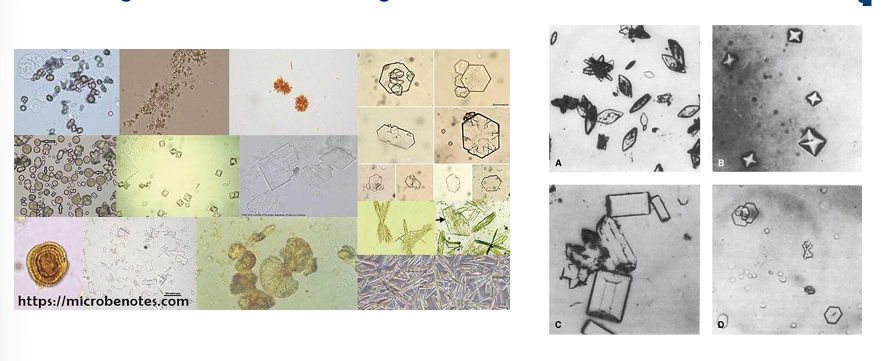
urinary sediment- crystals
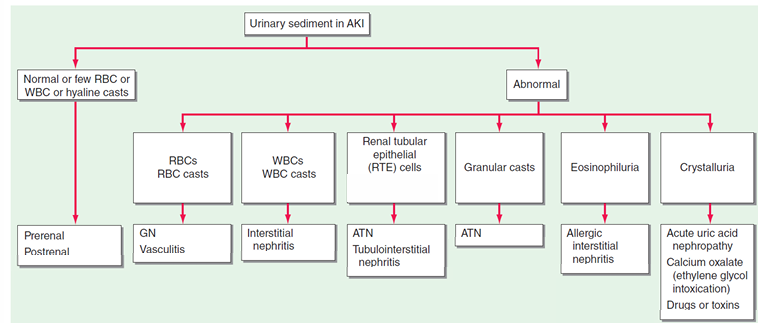
urinary sediment- differential diagnosis
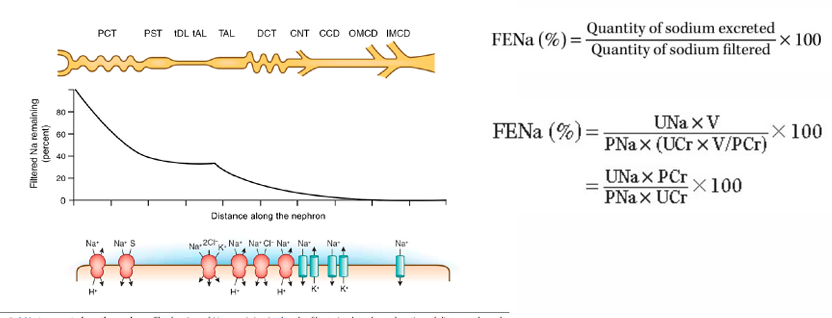
fractional excretion of sodium

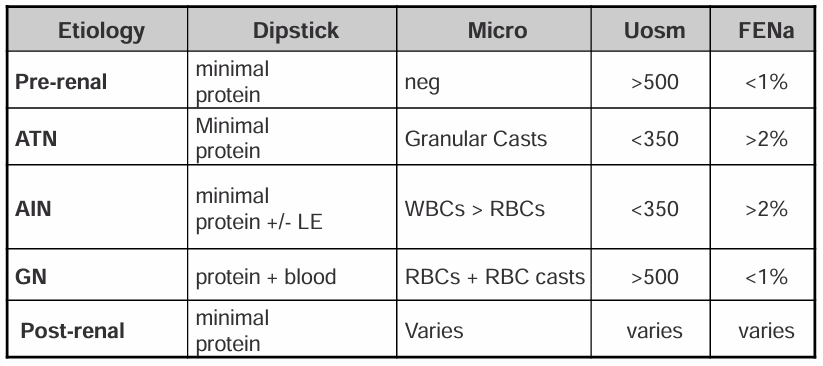
urinalysis and urine chemistries- etiology, dipstick, micro, Uosm, FENa
framework for approaching renal failure
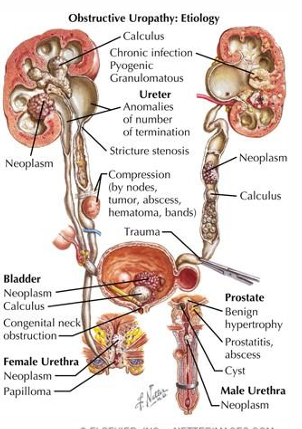
urinary tract obstruction and AKI- post-renal
-ureteral: bilateral stones, papillary necrosis, blood clots, external compression from malignancies, RP fibrosis (IgG4), iatrogenic ligation
-bladder: stones, blood clots, BPH, bladder cancer, prostate cancer, neuropathic
-urethral: stricture, phimosis
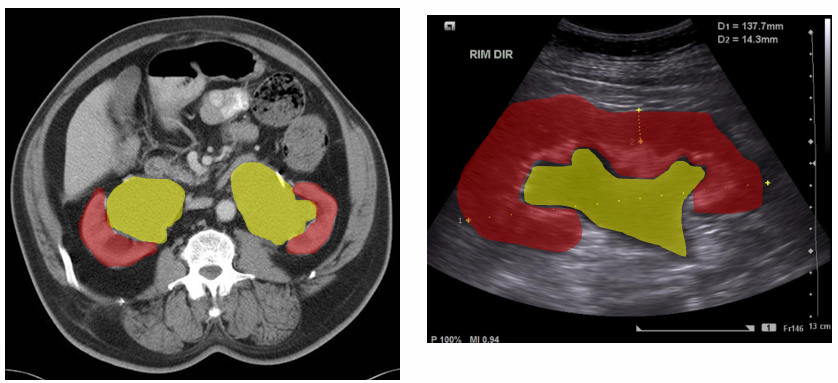
-urinary obstruction on imaging