Vertebrate Zoology - 02 Evolution Complete
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Linnaeus Belief of Species
Believed species were fixed and unchangeable.
Understanding of evolution requires three parts:
Fact of evolution
Course of evolution
Mechanism of evolution
Jean-Baptiste de LaMa
French naturalist and later professor at National Natural History Museum in Paris
Philosophie Zoologique (1809) argued all 3 aspects of evolution:
Species changed over time
Organisms started simple, became more “perfect”
Evolution by inheritance of acquired characteristics
LaMarckian evolution
Inheritance affected by use or disuse; Confuses physiology with genetics
Charles Darwin
Voyages on HMS Beagle, describes much biodiversity in South America, islands
Develops theory of evolution by natural selection, sits on it for decades
Prompted to publish when ARW discovers the same mechanism.

Alfred Russel Wallace
4 years younger than Darwin
Poorer background, spent most of career in field
Greatly admired Darwin, sent him his theory for his opinion
ARW also remembered as “father of biogeography”.
Three basic parts of evolution by natural selection:
Inheritable variation under nature
Differential survival and reproduction
Time (generations)
Origin of Species (Darwin 1859)
(With 6 editions) Presented an “abstract” of Darwin’s case
Evidence largely from biogeography, natural history, some paleontology and geology, and analogy with artificial breeding of animals by humans.
Two serious scientific criticisms of Darwin and Wallace’s ideas at the time:
Time: ages of fossils, the Earth unknown then; unclear if the world was old enough for such a slow process
Inheritance: No one knew how traits were passed from parent to offspring, and the hypotheses they did have were wrong.
The modern estimate of the age of the Earth is…
4.54 + 0.05 billion year
Pangenesis
A version of blending, wherein every part of the body contributed to gametes.
(Gregor Mendel) Particulate Inheritance
Transmission of alleles or discrete units of genes.
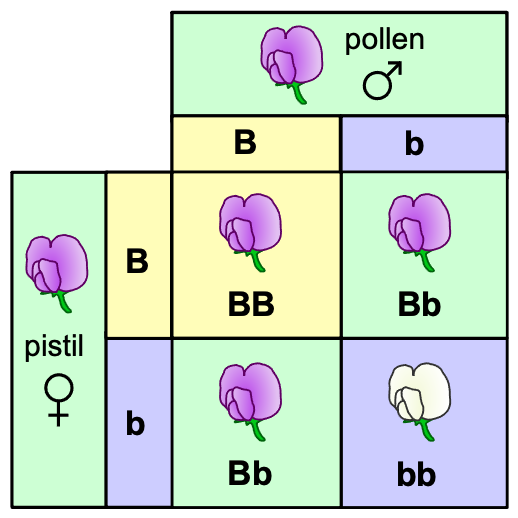
Order of Evolution Takes a Long Time
Life appeared around 4.3-3.8 billion years ago.
Eukaryotes appear by 1.8 billion years ago
Animals appear around 650 Mya
Vertebrates appear ~518 Mya
Mammals appear ~225 Mya
Primates ~66 Mya
Humans ~300,000 years ago.
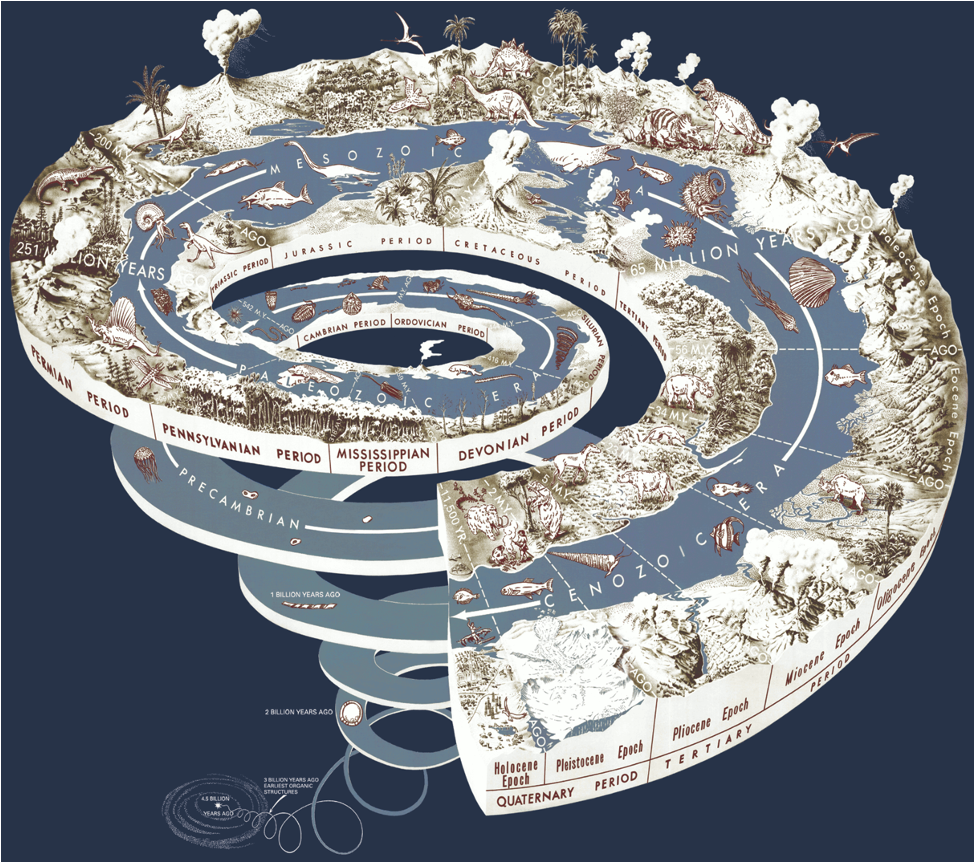
Calendar of Evolution takes a long time.
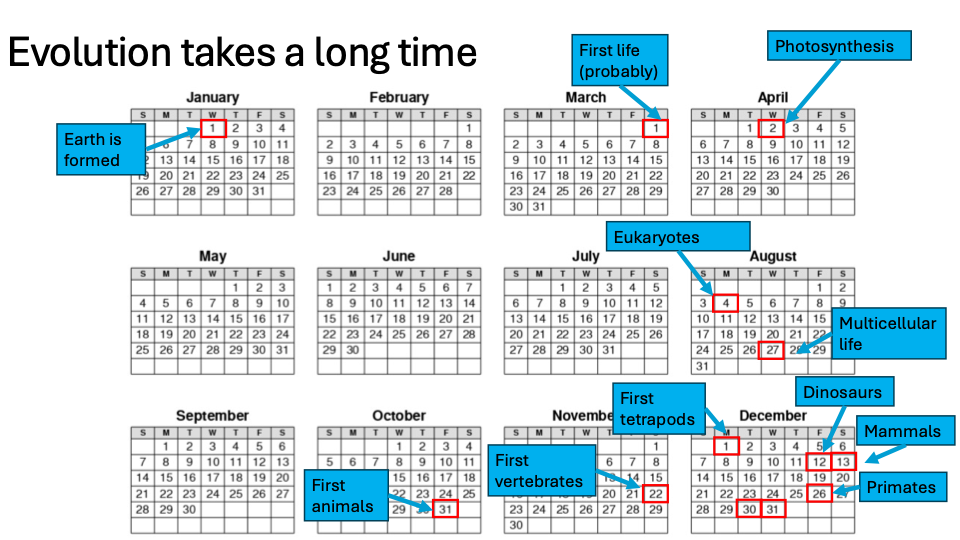
Archaea
Have a nucleus
Amorphea (aka: Unikonta)
One flagellum developed
Opisthokonta
Evolved from protistan ancestors
Multicellular
Evolved independently
Bikonta
A group that includes plants.
Holomycota
Includes Fungi
(Group) Bilateria
Left and right side possessing bilateral symetry
Protostomia
First mouth (only one opening)
Deuterostomia
Two openings (butt and mouth chordata)
Gnathostomata
Jaws
Osteichthyes
Bones
Sarcopterygii
Two bones in limbs
Tetrapoda
Possesses four legs (Example: Amphibia)
Amniota
Generates amniotic fluid for reproduction (Reptile; birds)
Sauropsida
Group that includes “Reptiles” and birds
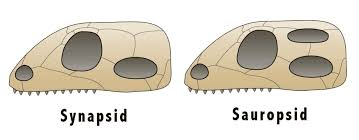
Synapsida
Group that includes no hole in the back of the skull
The first vertebrate ancestors appear in _______ period ~518 Ma; Resembled modern-day Cephalochordata (lancelets): marine filter feeders without jaws or bones
Cambrian period
What is a chordate?
Notochord (cartiligous cord for structure)
Dorsal, hollow nerve cord
Postanal tail
What is a vertebrate?
Segmented vertebral column (fully or partially replaces notochord)
Multi-chambered heart
Inner ear with semicircular canals
Brain with >=3 sections (Cranium with brain)
Discrete sense organs
Nostrils (defines clade Olfactores)
Gut with digestive organs

Cambrian World
538-486 Million years ago
Most of the land was in southern hemispher
No known land, few animals (arthropods)
Cambrian Explosion: modern animal phyla first appear in fossil record 538-525 (approx. Mya)
Chordates and vertebrates appear

Ordivician period
486-443 Million years ago
Highest sea levels of Paleozoic
Molluscs and arthropods dominate the oceans
First terrestrial plants appear
Jawed fishes may have appeared in late Ordovican
Ended in mass extinction (2nd worst in history)
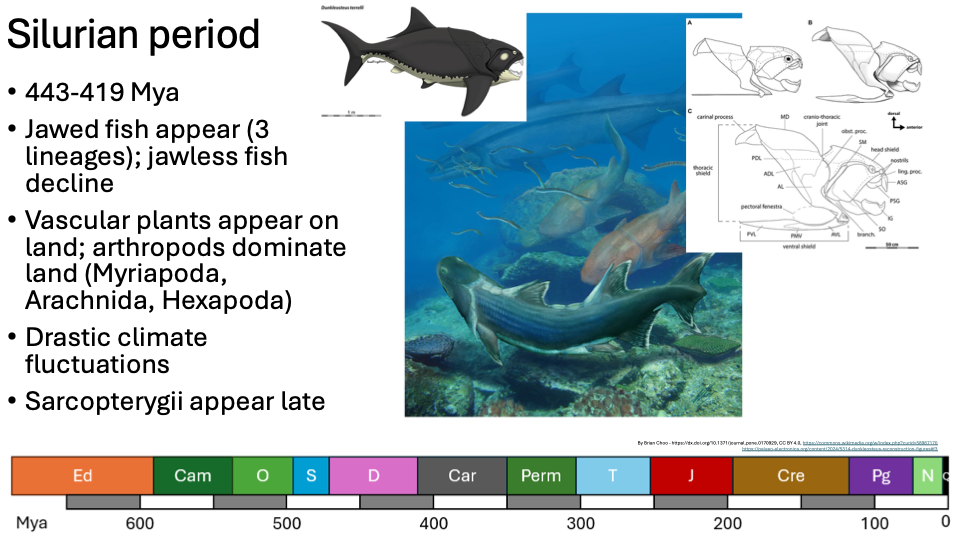
Silurian Period
443-419 Mya
Jawed fish appear (3 lineages); jawless fish decline
Vascular plants appear on land; arthropods dominate land (Myriapoda, Arachnida, Hexapoda)
Drastic climate fluctuations
Sarcopterygii appear late
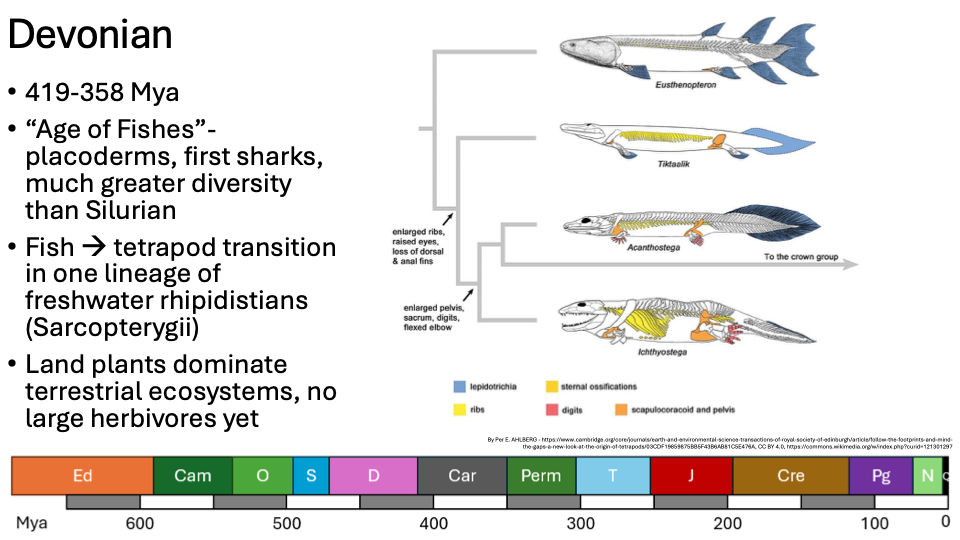
Devonian Period
419-358 Mya
“Age of Fishes”-placoderms, first sharks, much greater diversity than Silurian
Fish à tetrapod transition in one lineage of freshwater rhipidistians (Sarcopterygii)
Land plants dominate terrestrial ecosystems, no large herbivores yet
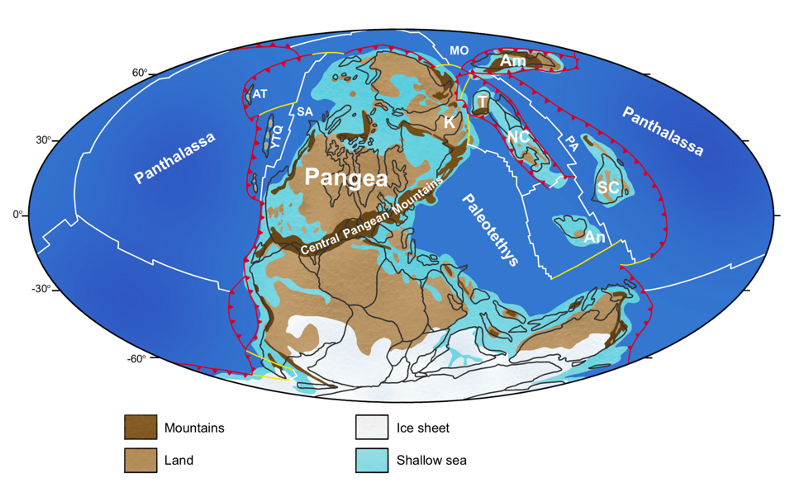
Carboniferous Period
358-298 Mya
Terrestrial vertebrates become more established
Age of Amphibians” – high diversity of early amphibians, esp. labyrinthodonts
Amniotes appear and diversify into sauropsid and synapsid lineages
Many global coal beds laid down during this period
Pangea begins to assemble

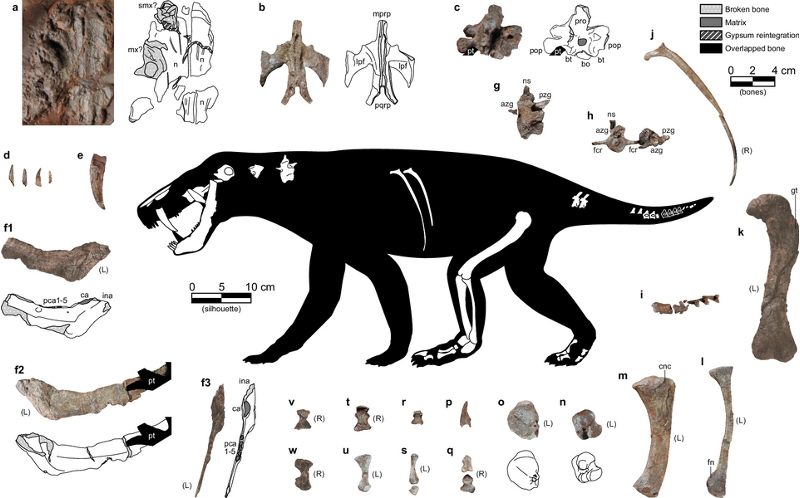
Permian Period
298-251 Mya
Synapsid amniotes were dominant for most of Permian
Pelycosaurs, later therapsids and cynodonts were apex predators
Archosauromorphs appeared
The “Great Dying: Permian-Triassic mass extinction, 81% of marine and 70% of terrestrial species.
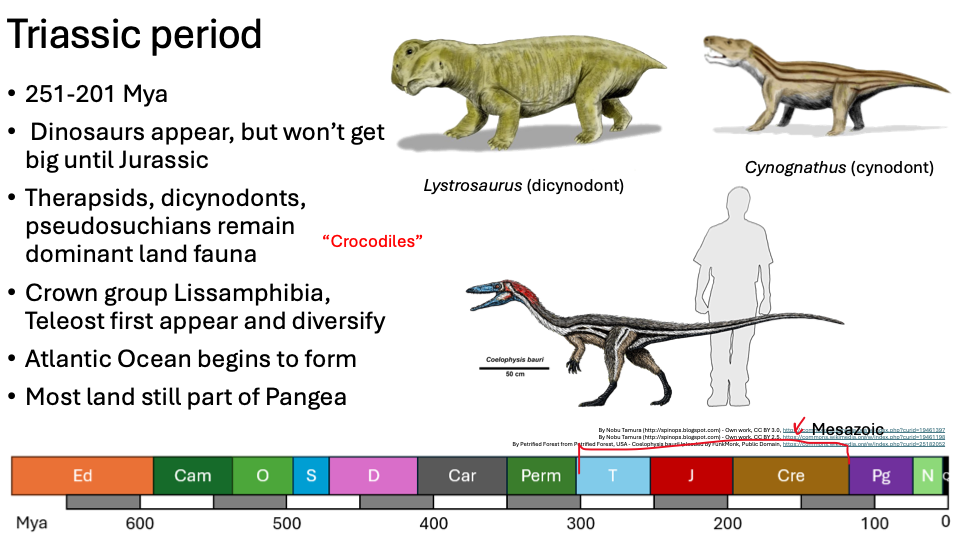
Triassic period
251-201 Mya
Dinosaurs appear, but won’t get big until Jurassic
Therapsids, dicynodonts, pseudosuchians remain dominant land fauna
Crown group Lissamphibia, Teleost first appear and diversify
Atlantic Ocean begins to form
Most land still part of Pangea
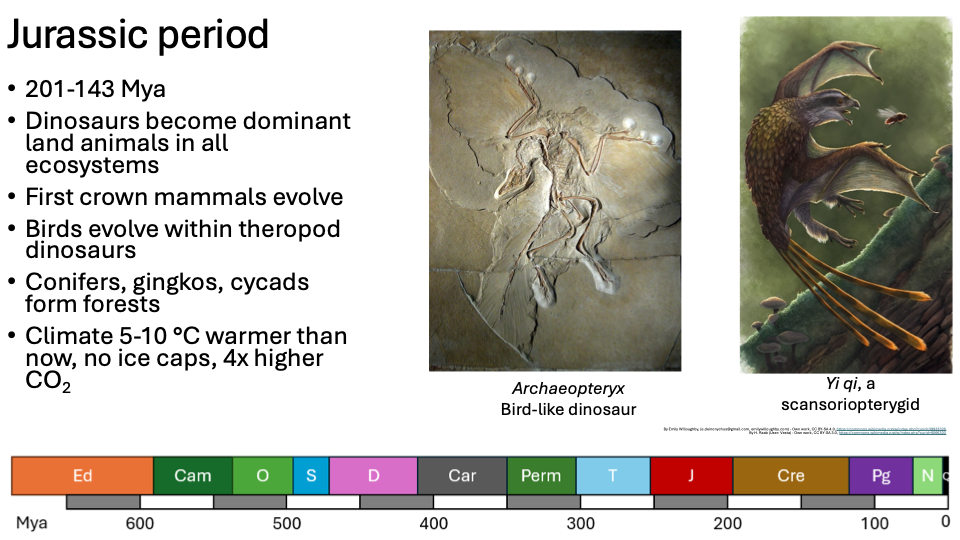
Jurassic Period
201-143 Mya
Dinosaurs become dominant land animals in all ecosystems
First crown mammals evolve
Birds evolve within theropod dinosaurs
Conifers, gingkos, cycads form forests
Climate 5-10 °C warmer than now, no ice caps, 4x higher CO2
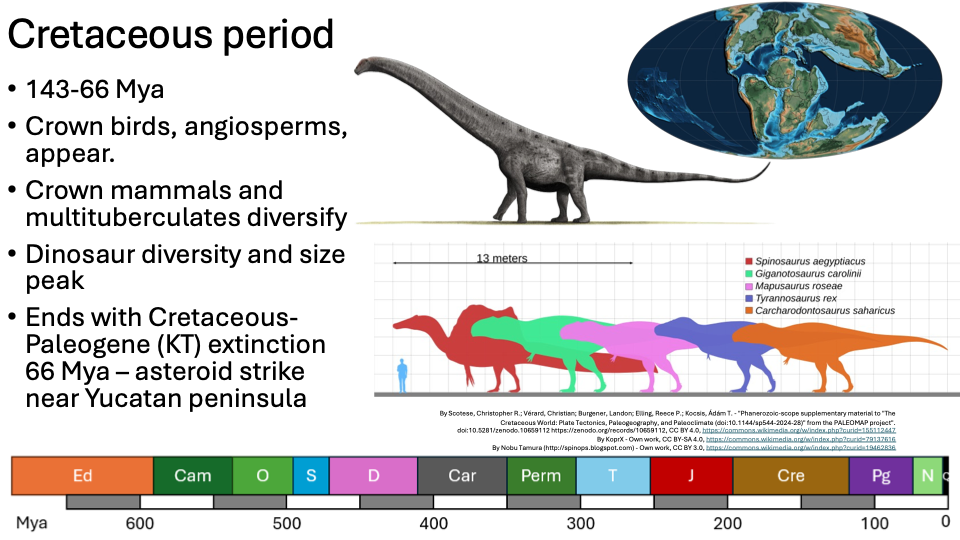
Cretaceous period
143-66 Mya
Crown birds, angiosperms, appear.
Crown mammals and multituberculates diversify
Dinosaur diversity and size peak
Ends with Cretaceous-Paleogene (KT) extinction 66 Mya – asteroid strike near Yucatan peninsula
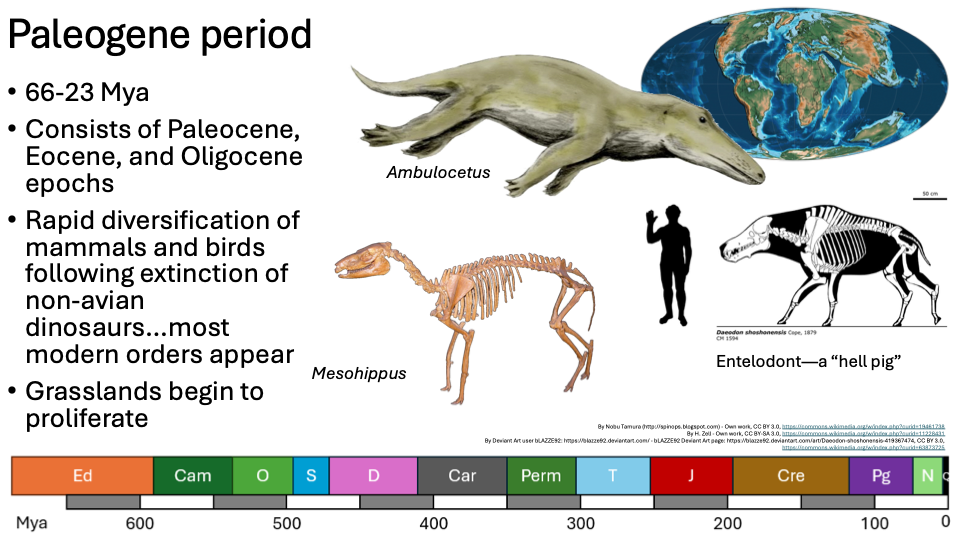
Palogene Period
66-23 Mya
Consists of Paleocene, Eocene, and Oligocene epochs
Rapid diversification of mammals and birds following extinction of non-avian dinosaurs…most modern orders appear
Grasslands begin to proliferate
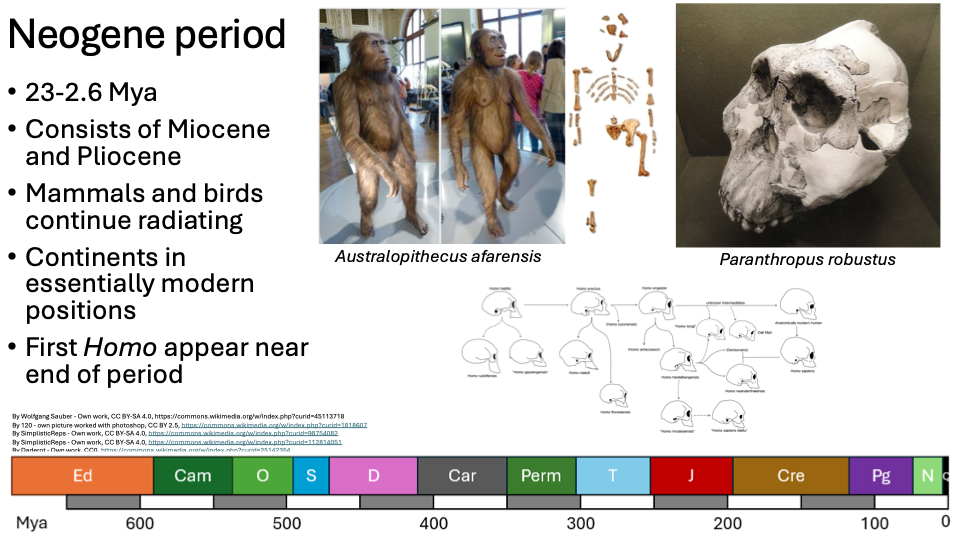
Neogene period
23-2.6 Mya
Consists of Miocene and Pliocene
Mammals and birds continue radiating
Continents in essentially modern positions
First Homo appear near end of period
Quarternary Period
2.6 Mya – present
Pleistocene and Holocene epochs
Some claim new “Anthropocene” epoch has started, but this is controversial and not widely accepted
Repeated ice ages in Pleistocene drove evolution of Pleistocene megafauna
Pleistocene megafauna driven to extinction by climate change and humans
Modern humans evolve about 300,000 years ago (Pleistocene)