Sheep Handling and Production
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Large operations own ___ % of sheep. These operations are primarily in these 6 states
80%
•Colorado, Idaho, Texas, California, South Dakota, Wyoming
Oregon is ranked #__ in the country for sheep production
#9
What products do we get from sheep?
Wool, Lanolin (used in moisturizing creams)
Meat
Yarn
Lamb prices are broken down according to these 2 things
USDA top quality grades
Yield Grades
Ethnic Holidays
What are the quality grades for sheep?
What age do we want to slaughter lambs by?
1.Prime , Choice and Good
•Lambs generally <14 months old the most valuable
A yield grad of 1 is the ______ and a yield grade of 5 is the ______ yield
1 is highest yield
5 is lowest yield
How often is wool harvest?
Wool harvested once a year
Is wool a primary or byproduct of the production system?
Can be both
Name the 5 factors affecting quality. Briefly describe them
–Fiber diameter (thickness ) :measured in microns
–Crimp : Natural waviness or bend of wool fiber
–Yield: amount of wool left after scouring (washing)
–Color
–Length and strength
•Sheep grazing grass seed fields stimulate ________ and increases overall ________ production.
•Sheep grazing grass seed fields stimulate tillering and increases overall seed production.
•Sheep benefits from high-quality forage at time when forages are generally _______
scarce
What are some of the main challenges faced with raising sheep?
Predation
Non predator:
Parasites
Lambing Problems
Name the 2 main hair breeds
Dorper and Katahdin
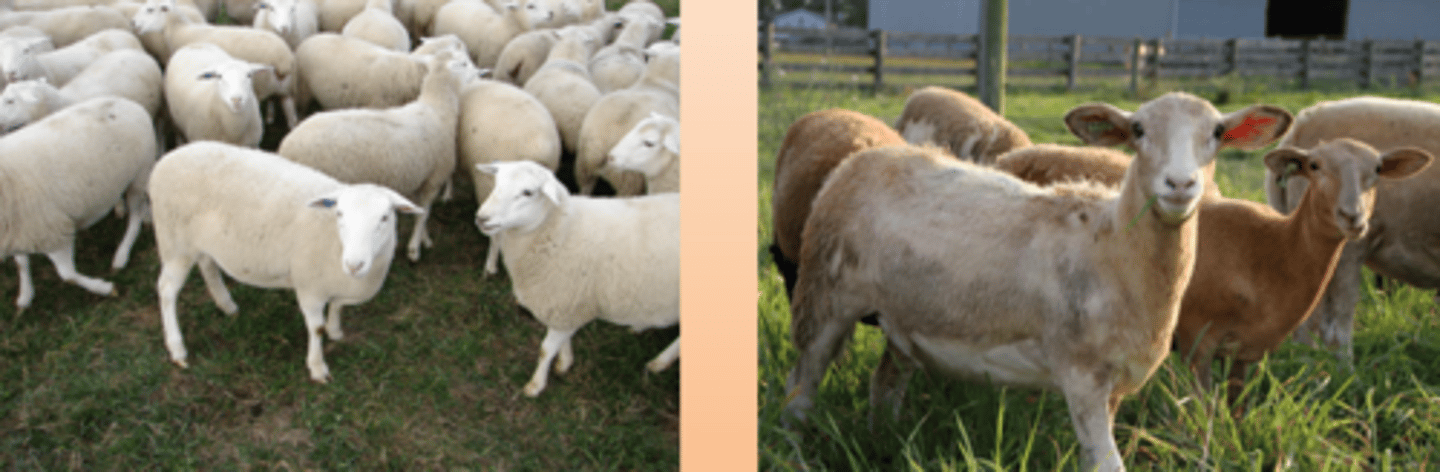

What is a common club lamb breed?
What breed is a superior meat breed?
1.Suffolk (left picture)
2. Hampshire (right picture)
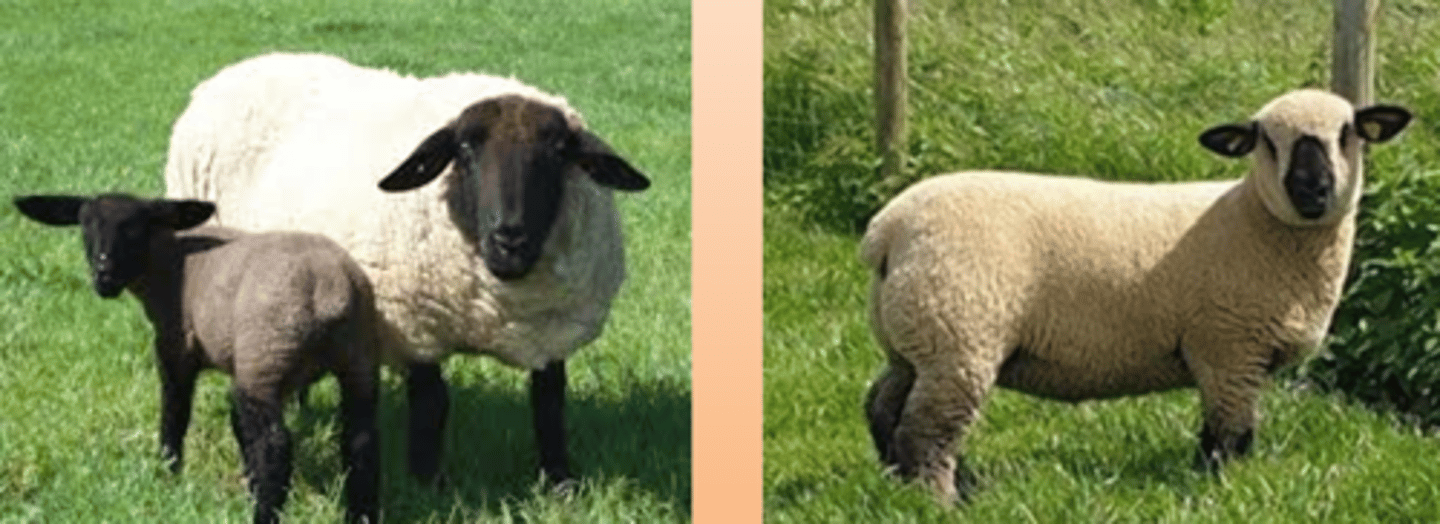

What is the oldest breed of sheep?
What are they typically used for?
Southdown
Market Lamb production
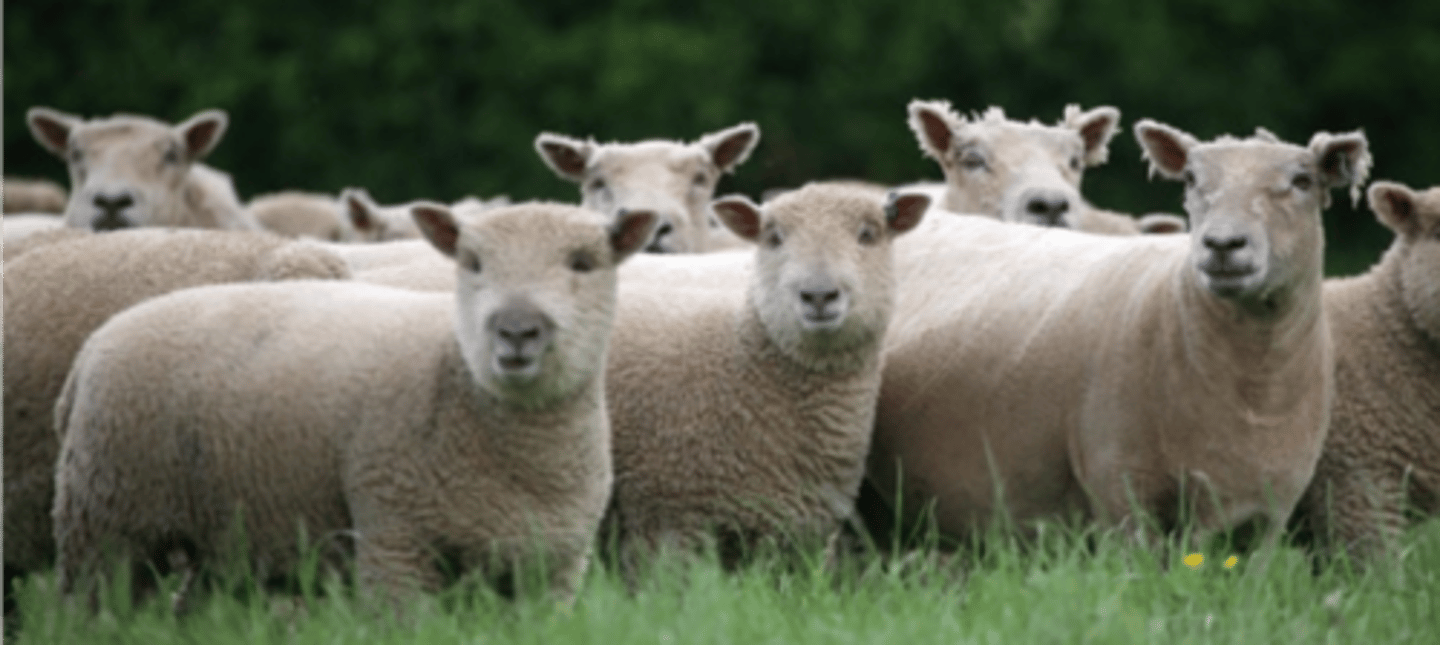

What breed has the ability to breed out of season, can be horned or polled, and is often crossbred with fine-wool ewes?
Dorsets

Ram
uncastrated male ovine
Ewe
Female ovine
Wether
male ovine castrated when young
Lamb
Immature ovine, •< 14 mo., not cut its 1st pair of permanent incisors
Yearling
•an ovine, 1-2 yr., with first pair of permanent incisor teeth but not second pair
Sheep
an ovine, > 24 months of age, cut its 2nd pair of permanent incisors
Sheep have an _______ sense of hearing
excellent
Do sheep have a narrow or wide field of binocular vision?
Narrow
Do sheep have a narrow or wide field of monocular vision?
Wide
When does the sheep have a blind spot behind them?
When can the sheep see in all directions?
-Area in back of sheep "blind spot" usually when head raised. If head down animal can see in all directions.
When are 80% of lambs born?
80% of lambs born during first 5 months of the year
What is the weaning age? (its a range)
What is the slaughter age and approximate weight?
-Weaning age: 30-90 days .
-Lamb slaughter: 8-14 moths (120-160 lb body weight)
What is flushing?
•Common management practice of increasing protein and energy content of the diet of the ewes 3 weeks prior and 3 weeks post breeding. It increases BCS and may increase ovulation rate
What are the 3 general phases of the sheep production cycle?
Lactation
Maintenance
Gestation (144 to 152 days)
What are the general guidelines for catching & restraining sheep?
- if possible have sheep in small catching pen
-try to corner the animal
-Grab sheep under the chin
-don't grab wool
-Keep animal's head up
-Stand sheep against fence if possible
Describe the general positioning of castration or tail docking

What are the 5 things we look to observe before getting hands on?
-Attitude
-Respiratory pattern and frequency
-Posture
-Urination/defecation
-Locomotion
Normal TPR
•Temperature: 101.5 - 104 F
•Pulse: 70 - 90
•Respiratory rate: 12 - 20
What are measure parameters to take into consideration when taking TPR?
-Level of fleece in animal
-Outside temperature
-Level of "excitement" / transportation
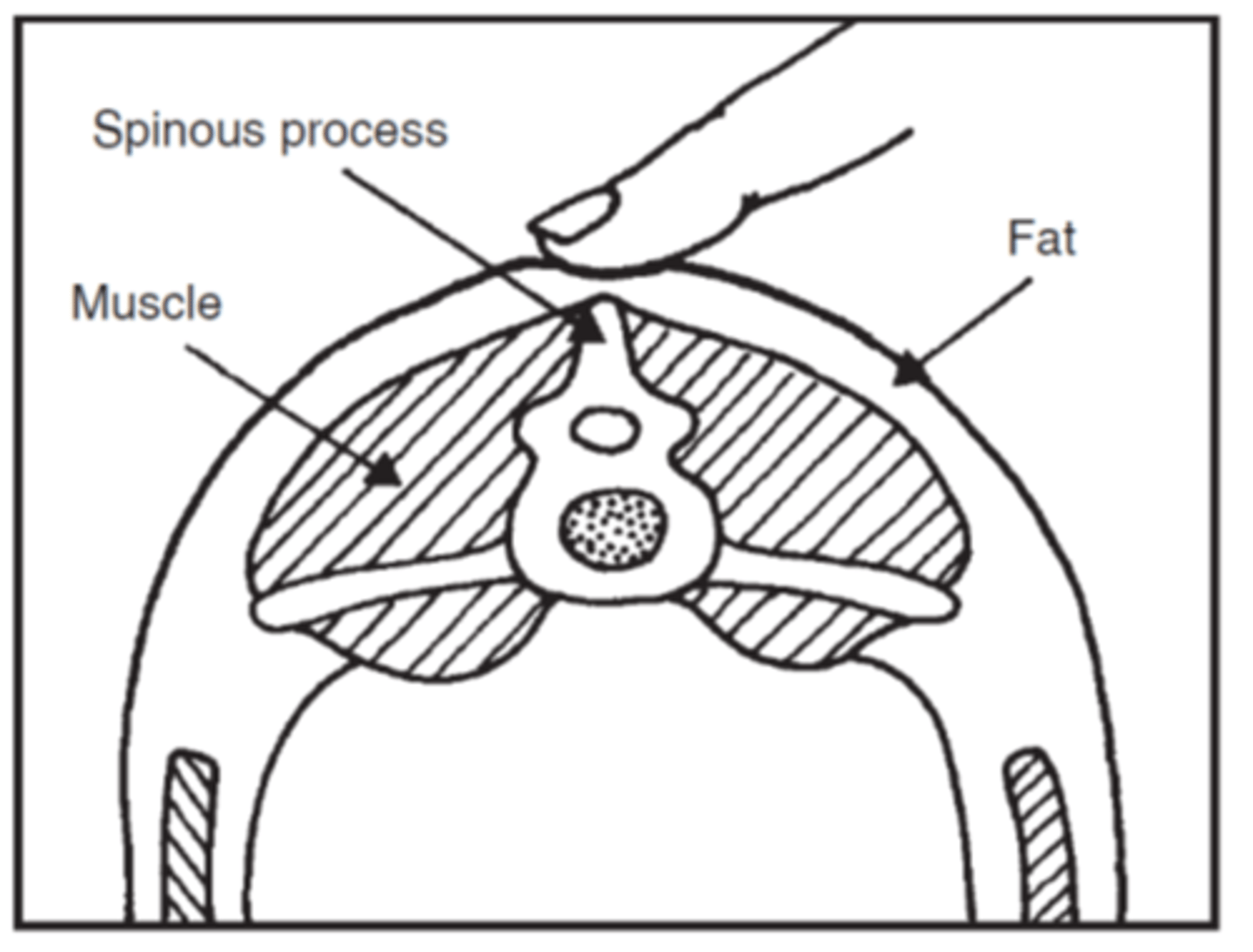
Do you need to touch the animal to evaluate BCS?
YES- must touch lumbar region, feel for transverse processes
When examining integument, what are we looking for
Ectoparasites
-Lice (chewing/bloodsucking)
-Mange (chorioptes)
-Fly strike (cutaneous myiasis- black blowfly)
Hair loss ( generalized / localized)
In sheep do we palpate lymph nodes?
Yes
What is the standard BCS range?
1-5
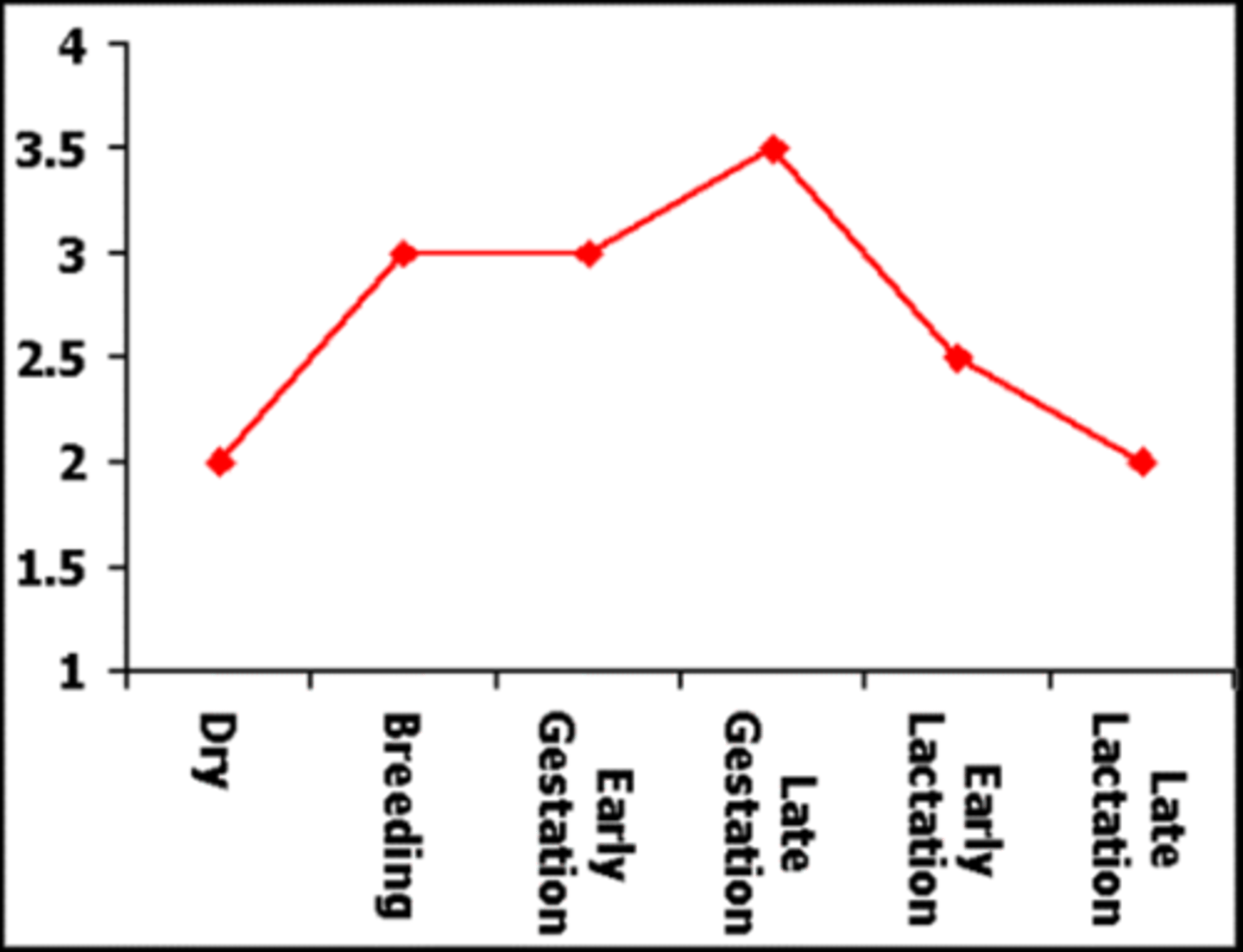
What should the BCS be at the following stages:
a. Breeding
b. Late Gestation
c. Early Lactation-Late Lactation
a.3
b. 3-3.5
c.2-2.5 (2 is not ideal but also not abnormal)
When examining the Head and Neck, what 6 things do we evaluate?
1. Asymmetry
2.Position of the eyes and presence of ocular discharge
3. Color of mucous membranes (very important!)
4. Nasal discharge
5. Presence of "swellings" or nodules"
6. Dental exam (age)
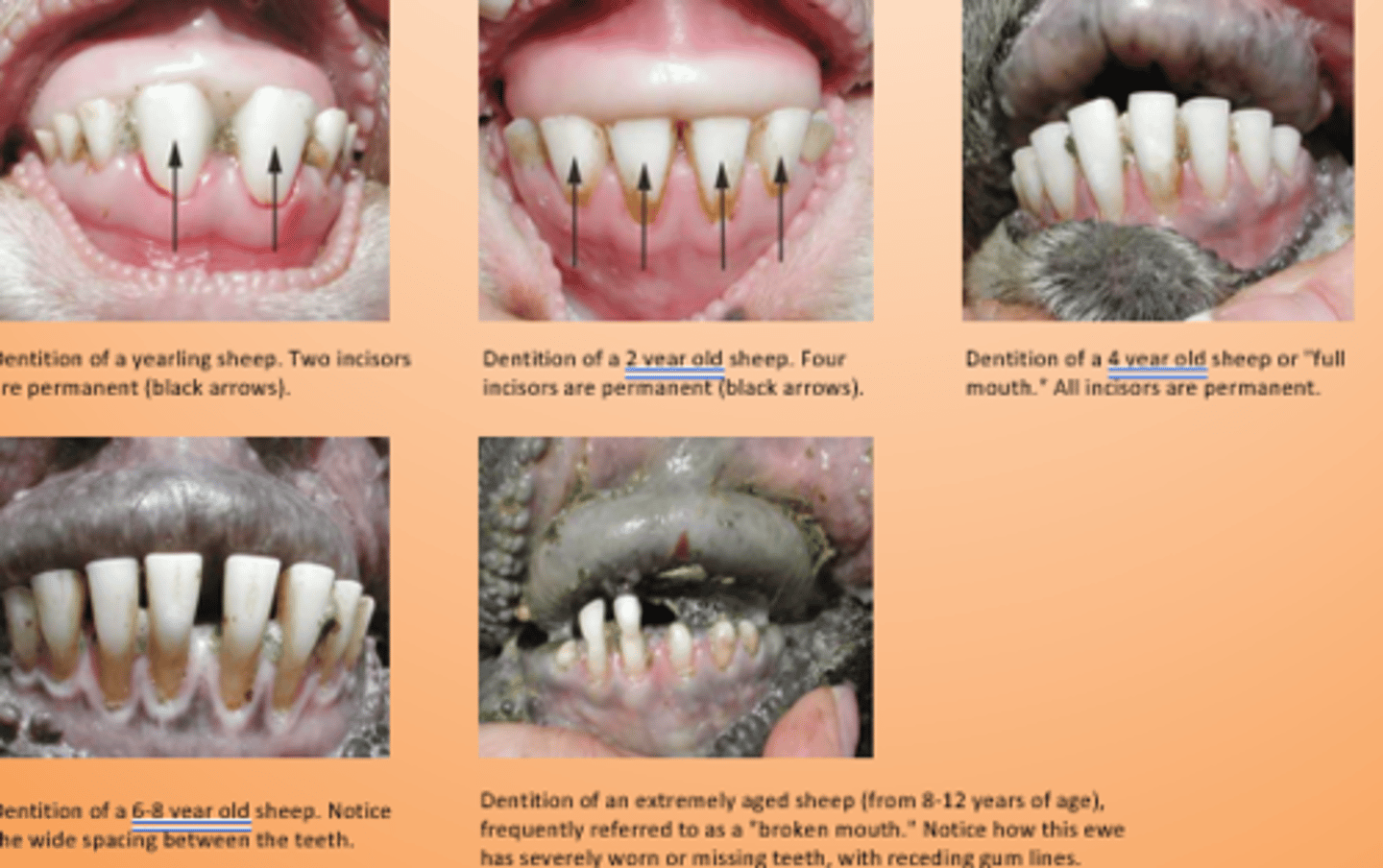
When does incisor 1 erupt?
1-1.5 yrs
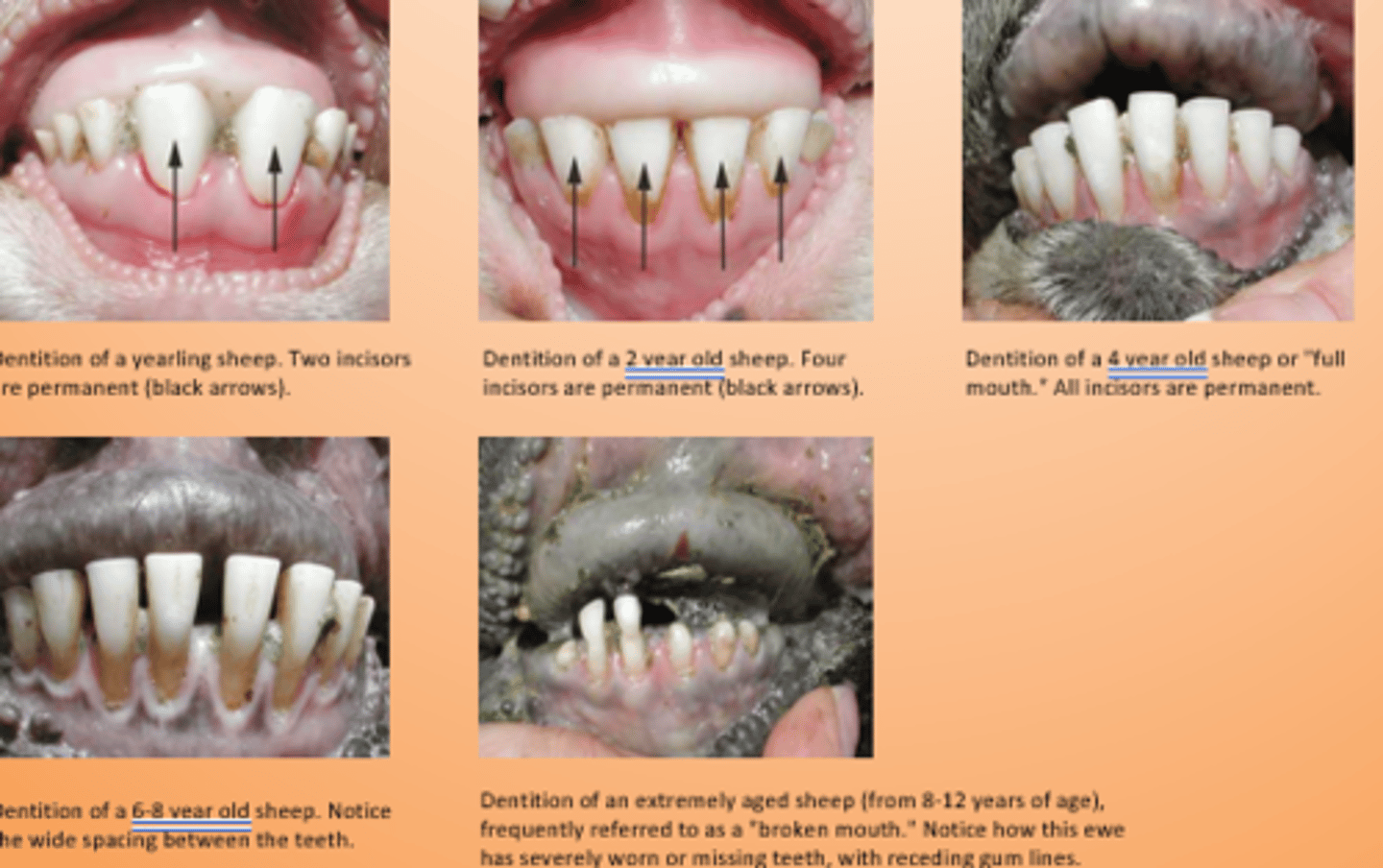
When does incisor 2 erupt?
1.5-2 yrs
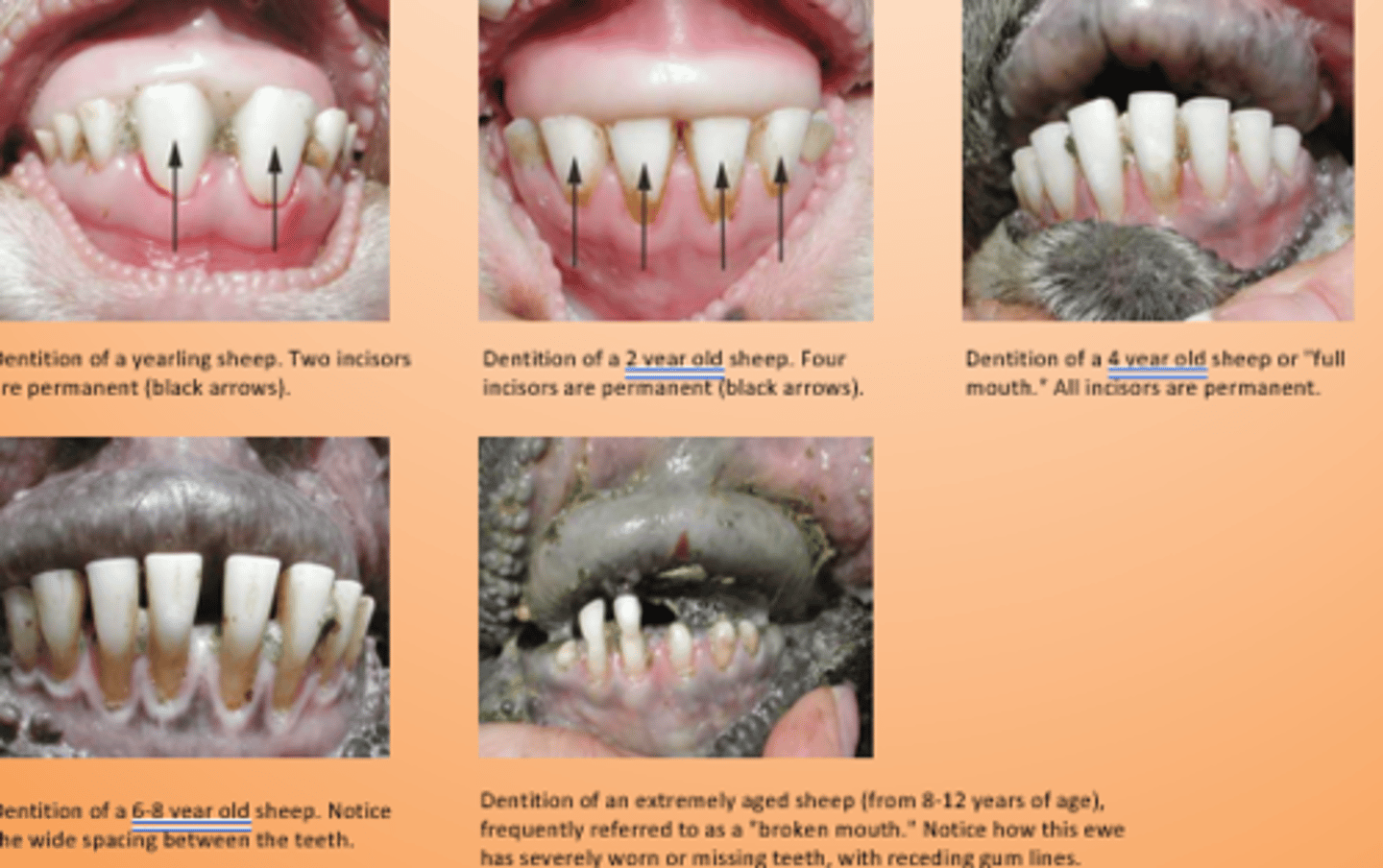
When does incisor 3 erupt?
2.5-3 yrs
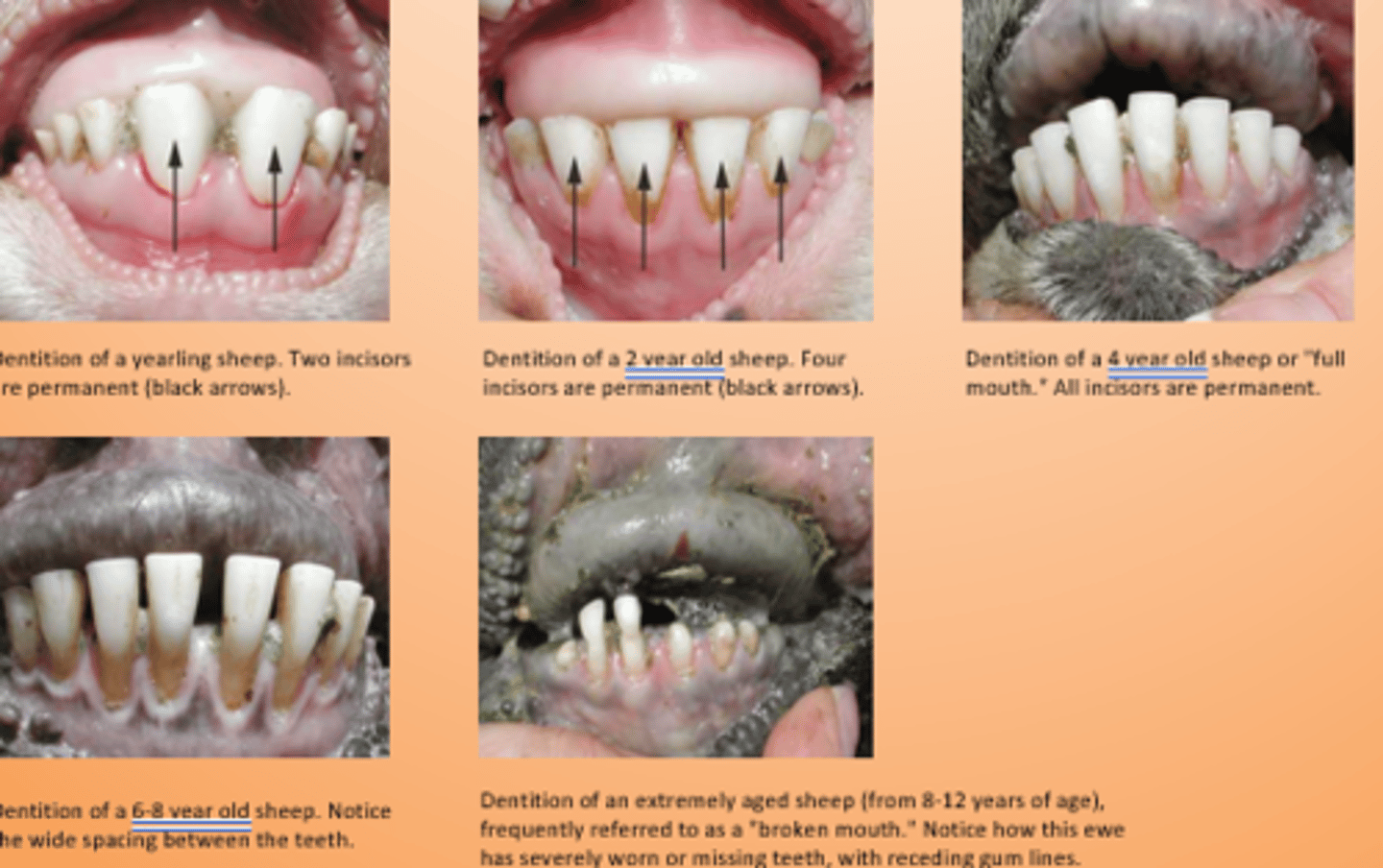
When does incisor 4 erupt?
3.5-4 yrs
What system is commonly used to evaluate Mucous membranes?
What does this system potentially help indicate the presence of?
FAMACHA system
-haemonchus contortus "barber pole worms"
What is the Technique to check the mucous membranes in the eye?
-Cover
-Push
-Pull
-Pop
What should normal mucous membranes look like?
What do abnormal mucous membranes indicate?
Normal: Pink, moist
Abnormal: Pale, could indicate extensive parasites, anemia
What is contagious Ecthyma?
Who does it affect?
Symptoms?
Contagious, zoonotic disease affecting goats and sheep - parapoxvirus
Usually affects young animals (<1 year)
Proliferative, crusting lesions:
-Mouth
-Eyes
-Nose
What is Caseous Lymphadenitis?
What are the symptoms?
•Chronic contagious disease affecting sheep and goats
•Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis
•Swelling of superficial and internal lymph nodes
Is auscultation of the lungs indicative of severity of respiratory disease? Why?
Often not indicative of severity of respiratory disease. Difficult and extremely subjective in small ruminant.
What do we look for that is more indicative of respiratory disease?
Respiratory pattern and effort, nasal discharge, temperature
What locations do we auscultate?
Heart
Lungs
Rumen
In females, what do we need to examine? Be specific in how you examine the location
•Examine the Udder
-Visual inspection - symmetry, swelling, skin changes
-Palpation
-Milk evaluation
What is the animal positioning for hoof trimming in sheep?
Goats?
Sheep: sitting or standing
Goats: standing
Hoof Trimming
Begin trimming around the ________ of the hoof
Avoid cutting large portions at a ______ ________
Preserve the ______.
Stop as horn looks "_____"
Foot should have a parallelogram "_______" shape
•Begin trimming around the perimeter of the hoof
•Avoid cutting large portions at a single point
•Preserve the heels.
•Stop as horn looks "pink"
•Foot should have a parallelogram "boxy" shape
What is the gestation length?
When can we do a transabdominal ultrasound?
avg 147 (144-152)
- ultrasound day 35-50 after breeding
What are some signs of pregnancy at ultrasound?
•Presence of amniotic vesicle
•Placentomes
•Fetus