NMR Spectroscopy
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
5 Terms
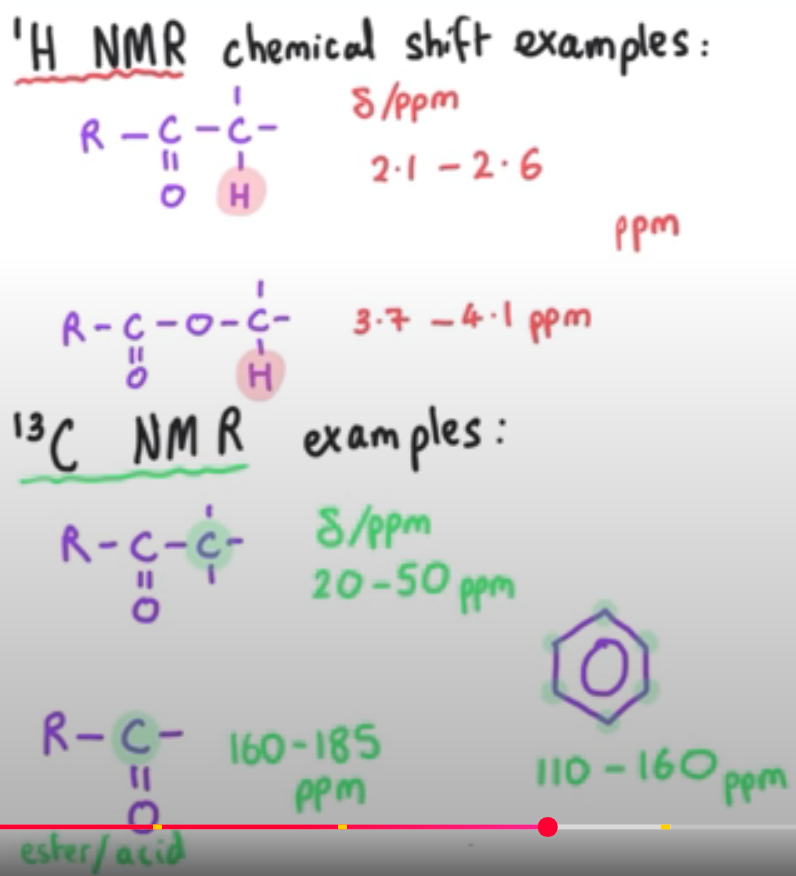
What is chemical shift?
Chemical shift is a measure of the energy difference
Delta means chemical shift in ppm
What does NMR need?
A reference / standard substance
Energy absorbed by sample is compared to the energy absorbed by the standard
Tetramethylsilane Si(CH3)4
all carbons and hydrogens in same environment
Therefore only produce one characteristic peak
Long way away from any other peaks from the sample
Delta = 0ppm for this peak
It is an inert chemical - therefore won’t react w/ sample
Non-toxic
Highly volatile - therefore can remove from sample very easily once you’ve run the NMR spectrum
What determines a chemical shift value?
what atoms are nearby?
Highly electronegative atoms deshield a nucleus, which gives a larger delta value
Common examples: (1H NMR)
Delta/ppm 2.1-2.6ppm - hydrogen attached to a carbon adjacent to a carbonyl group
Shown as a range - because precise values will vary from one molecule to another
Delta/ppm 3.7-4.1ppm - hydrogen attached to a carbon that is connected to the oxygen of an ester group
(13C NMR)
Delta/ppm 20-50ppm - carbon adjacent to carbonyl group
Delta/ppm 110-160ppm - carbon atom in a benzene ring
Delta/ppm 160-185ppm - carbonyl group in an ester or a carboxylic acid will have a carbon which has this peak
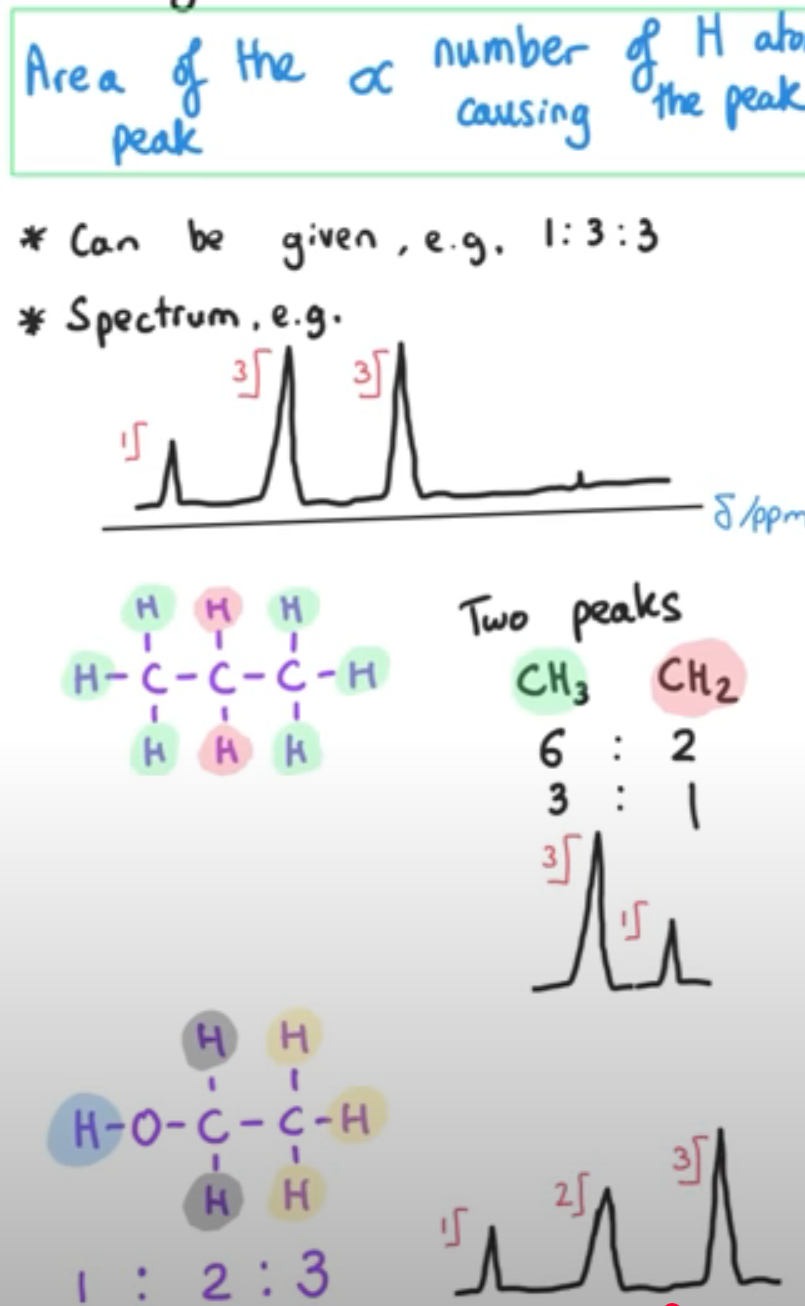
What is the integration trace?
(1H NMR only)
Area of the peak is proportional to the number of hydrogen atoms causing the peak
Splitting pattern - high resolution NMR
