Neuroscience final exam
1/84
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ch 1-10 review. ADD exam 3 review!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
neuroscience
_____ the scientific study of the nervous system, including in humans and animals.
It is interdisciplinary, often involving researchers trained in other fields.
It is not the same as neuropsychology or neurology, though related
independent, dependent, confounding
_____ variable: the variable you manipulate.
_____ variable: the outcome you measure.
_____ variable: other variables that may influence the outcome.
transcription, translation
______: DNA → RNA. A segment of DNA is copied into mRNA or tRNA.
______: RNA → Protein. Ribosomes use mRNA to synthesize proteins by linking amino acids.
tRNA
____brings the correct amino acid to the ribosome based on the codon.
gene expression
______ is the type and amount of proteins a cell makes, regulated at many points in this process.
grey matter, white matter
_____: neuronal cell bodies, dendrites, glial cells. Found in outer cerebrum (cortical GM) and subcortical nuclei.
_____: mostly myelinated axons and glia. Tracts connect neurons across the brain.
CNS, PNS
Functional divisions of the nervous system
______: Brain and spinal cord. Receives, integrates, stores information; controls output to PNS.
______: Ganglia and nerves. Detects and relays sensory info to CNS; carries motor commands to body.
parasympathetic, sympathetic
_____: rest and digest (homeostasis)
_____: fight or flight response
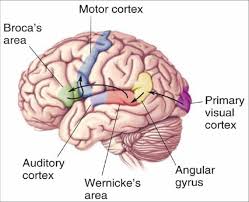
frontal lobe
Voluntary motor control, language production, executive function, working memory, attention.
parietal lobe
Somatosensation, spatial integration, posterior parietal cortex helps guide movement
temporal lobe
Auditory and olfactory info, speech comprehension, memory, emotion, visual processing (ventral stream)
occipital lobe
Primary visual cortex (V1) and extrastriate areas (V2–V4); involved in processing visual input
meninges
Three protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord: dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater.
ventricles
Cavities in the brain filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF); lined by ependymal cells; includes lateral, third, and fourth ventricles.
cranial nerves
12 nerves (I–XII); most emerge from the brainstem. Include somatic, visceral, special sensory, motor, and autonomic fibers.
phospholipid bilayer, hydrophilic, hydrophobic, negative
Composed of phospholipids: _____ (polar) head and _____ (fatty acid) tails.
Forms a selectively permeable membrane:
▪ Impermeable to macromolecules and ions due to hydration shells.
▪ Maintains ___ charge inside the membrane at rest.
dendrites, spines
Receive information, taper to an end, contain synapses with presynaptic terminals.
Contain dendritic ____ — sites of most excitatory glutamate synapses; can change shape/size.
soma
Contains organelles like nucleus, ER, Golgi; integrates signals
axon, terminal
Sends action potentials; ends in axon terminal where neurotransmitters are released.
Begins at axon hillock; initial segment rich in voltage-gated sodium channels.
Can be myelinated or unmyelinated, branched or unbranched.
_____ = presynaptic terminus/synaptic button
synapse
Site where information is transferred to another neuron, muscle, or gland.
astrocytes
type of glial cell.
Most abundant glia in CNS.
Provide structural and metabolic support; regulate extracellular ion concentration.
Participate in the blood-brain barrier (end feet).
Modulate synaptic transmission via gliotransmitters (e.g., ATP).
Respond to injury and form glial scars.
oligodendrocytes
Myelinate multiple adjacent axons.
Provide trophic support and inhibit axon regeneration.
schwann cells
Myelinate a single axon (or support unmyelinated axons).
Promote axon regeneration.
microglia
Immune cells of the CNS.
Scavenge damaged neurons, plaques; defend against infection.
Implicated in dendritic spine removal.
ependymal cells
Line ventricles and central canal; produce and circulate cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
Form choroid plexus with capillaries.
pericytes
Support blood-brain barrier; regulate capillary blood flow
enteric glia
Found in GI system; regulate fluid secretion, motility, neurotransmission, immune signaling.
leak channels
Always open; ions move based on electrochemical gradient (e.g., resting K⁺ channels).
voltage gated channels
Open in response to changes in membrane potential; responsible for action potentials (Na⁺, K⁺, Ca²⁺).
ligand gated channels
Open when a neurotransmitter binds; selective for cations or Cl⁻.
mechanosensitive channels
Transduce physical stimuli into electrical signals; respond to stretch or mechanical forces.
Na, Cl, K
Concentrations of ions inside vs. outside neuron at rest:
Higher outside: __⁺, Ca²⁺, __⁻
Higher inside: __⁺
Summary: A neuron is like "a banana in a salty milk pool."
electrochemical driving force
membrane potential (Vm) – equilibrium potential (Ex).
▪ Determines ion movement direction and magnitude.
equilibrium potential
The voltage at which there is no net movement of a particular ion.
▪ Calculated using the Nernst equation.
▪ Balance between chemical (diffusion) and electrical gradients
depolarization, hyperpolarization
_____: Membrane potential becomes less negative (e.g., Na⁺ influx).
_____: Membrane potential becomes more negative (e.g., Cl⁻ influx or K⁺ efflux).
resting membrane potential
~-70 mV
Inside is more negative than outside.
resting state, depolarization, rising phase, falling phase, undershoot, resting state, absolute refractory, relative refractory
stages of action potential:
____: Voltage-gated channels closed; resting potential maintained.
____: Threshold reached, voltage-gated Na⁺ channels open → rapid Na⁺ influx.
____: Na⁺ continues to enter; membrane potential becomes positive.
____: Na⁺ channels inactivate; K⁺ channels open → K⁺ efflux.
____: Membrane potential becomes more negative than resting (hyperpolarization). Return to ____: Channels reset, membrane returns to -70 mV.
_____ period: Na⁺ channels inactivated; no new action potential possible.
_____ period: Na⁺ channels resetting; new action potential possible but requires stronger stimulus.
electrical, chemical
____ synapses: Use gap junctions (connexons made of connexins).
Allow direct flow of ions and small molecules between neurons.
Very fast; can synchronize activity of neurons.
____ synapses: Use neurotransmitter release from presynaptic neuron into synaptic cleft.
Slower than electrical synapses.
More versatile: can excite or inhibit, modulate gene expression, etc.
ionotropic, metabotropic
____ receptors: Ligand-gated ion channels.
Fast/direct synaptic transmission
____ receptors: G-protein-coupled receptors (or receptor tyrosine kinases). Slow/indirect synaptic transmission (neuromodulation)
can change cell metabolism, excitability, or gene expression
receptor, properties
the effects of a neurotransmitter depend on the ____, not the neurotransmitter itself.
It is determined by the ____ of the receptor
fMRI
Measures blood oxygen-level dependent (BOLD) signal.
Noninvasive; shows areas of brain activity during tasks.
Invented in 1992.
EEG
Measures electrical activity from surface electrodes on the scalp.
Cortical activity only.
Good temporal resolution; less spatial precision than fMRI.
Records event-related potentials (ERPs).
Been used for about 100 years.
Electrophysiology
Measures and manipulates electrical properties of neurons directly.
Often done using microelectrodes guided by microscopy.
Provides precise information about potentials inside/outside neurons.
Can be done in vivo or in vitro.
photoreceptors, bipolar, horizontal, amacrine, retinal ganglion
_____ (rods and cones): Capture light, release glutamate
____ cells: Receive glutamate, activate amacrine and retinal ganglion cells
____ cells: GABAergic, modulate photoreceptor to bipolar signal
____cells: Lateral inhibition; GABA, glycine, ACh, neuropeptides
____ cells: Sole output; axons form optic nerve and project to brain
optic nerve, optic radiation
pathway of visual processing in brain:
Retina -> _____ -> Optic chiasm -> LGN of thalamus -> _____ -> Visual cortex
ventral, dorsal
____ stream ("what" pathway): V1 -> V2-V4 -> inferior temporal cortex -> Object identification, parvocellular input
____ stream ("where"/"how" pathway): V1 -> V2 -> V5 -> V6 -> posterior parietal cortex -> Visuospatial information, magnocellular input
hair, brainstem, auditory
pathway of auditory processing:
____ cells -> Spiral ganglion cells/CNVIII -> _____ -> Thalamus -> _____ cortex
temporal
where is the auditory cortex located?
In the _____ lobe, specifically the superior temporal gyrus.
otolith organs, semicircular canals
____: Sense linear movement; hair cells respond to otoconia
____: Sense head rotation; hair cells respond due to inertia
thalamus, cortex
What is unique about the olfactory system's pathway?
Olfaction is the only sensory modality that does NOT relay through the ____ before reaching ____
GPCR, GPCR, ion channels, ion channels, GPCR
What are the receptor types for the five primary tastes?
Sweet- ____
Umami- ____
Salty- ______
sour- _____
bitter- ______
insula
Where is the gustatory cortex located?
globus pallidus, substantia nigra
What regions are part of the basal ganglia?
striatum
_____
subthalamic nucleus
_____
acetylcholine
What neurotransmitter is released at the neuromuscular junction?
tolerance
What is it called when the same dose of a substance has less effect overtime?
antagonist
what molecule blocks a ligand from binding by blocking the receptor?
dopamine
what neurotransmitter system do nearly all drugs of abuse affect?
nicotine
which drug of abuse binds to cholinergic receptors?
hepatic portal system
What system transports substances from the digestive tract to the liver?
circadian rhythm
what is the 24 hour biological cycle called?
light/darkness
what is the main influence on melatonin release?
wernickes area
damage to what area results in fluent but incomprehensible language?
adenosine
which neurotransmitter may cause sleepiness
corpus callosum
name one white matter tract connecting the brains hemispheres
habituation
what is the suppression of a reflexive behavior after repeated stimulation?
concept cells
what neurons respond to highly specific stimuli across senses?
encoding, retrieval
what are the three phases of memory processing
____, consolidation, _____
striatum
what brain region is involved in habit formation?
inferotemporal cortex
what area is involved in visual memory, including faces and places?
default mode network
which brain network is active at rest and deactivated during tasks?
reticular formation
what brainstem network is necessary for alertness?
neglect
what condition results from damage to the right parietal lobe, leading to attention to only one side?
lateral intraparietal cortex
which brain area creates a priority map from attentional inputs?
integrated information theory
which theory says consciousness arises from cause-effect complexes?
amygdala
what brain region is key in fear conditioning?
hypothalamic, pituitary, adrenal
HPA axis stands for what
dopamine
what neurotransmitter is most implicated in schizophrenia?
cannon bard theory
which emotion theory states feelings and physiological responses happen simultaneously?
negative symptoms
what are diminished emotion, pleasure, and motivation symptoms in schizophrenia called
parietal
what lobe is shown in yellow
functional magnetic resonance imaging
which neuroimaging method measures bold signal in awake humans
sodium
which ion rushes into the cell during an action potential
premotor area
which motor cortex region activates before movement for novel tasks?
diencephalon
from which neural tube vesicle does the thalamus form
wernicke-geschwind model
name this language model