Bot-Lab (Sem-1) - Exercise 3: Fungi
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
kingdom mycetae/fungj
types of eukaryotic organisms characterized by the presence of chitinous cell wall chemically made up of β-4 linkages of N-acetylglucosamine; ergosterol in cell membrane instead of cholesterol
β-4 linkages of N-acetylglucosamine
chemical make up of the chitinous cell wall of fungi
ergosterol
steroid-type protein found in the cell membrane of fungi; similar in configuration to adrenal hormones and testosterone
mycelia
interwoven hyphae adapted for absorption
wind-disseminated
all fungi reproduce by means of spores which are ____-____________
heterotrophic and absorptive
type of nutrition in fungi
pathogens
many fungi are _________ of other organisms like plants and animals
endophytes
fungi that live inside leaves or other plant parts without causing harm; produce secondary metabolites for protecting their hosts
Division
a taxonomic rank in biological classification that is used differently in zoology and in botany. In botany and mycology, division refers to a rank equivalent to phylum
Division Zygomycota (bread molds)
the fungi under this division have hyphae that are coenocytic
coenocytic hyphae
absence of septation
Rhizopus stolonifer
Zygomycetes species commonly known as black bread mold
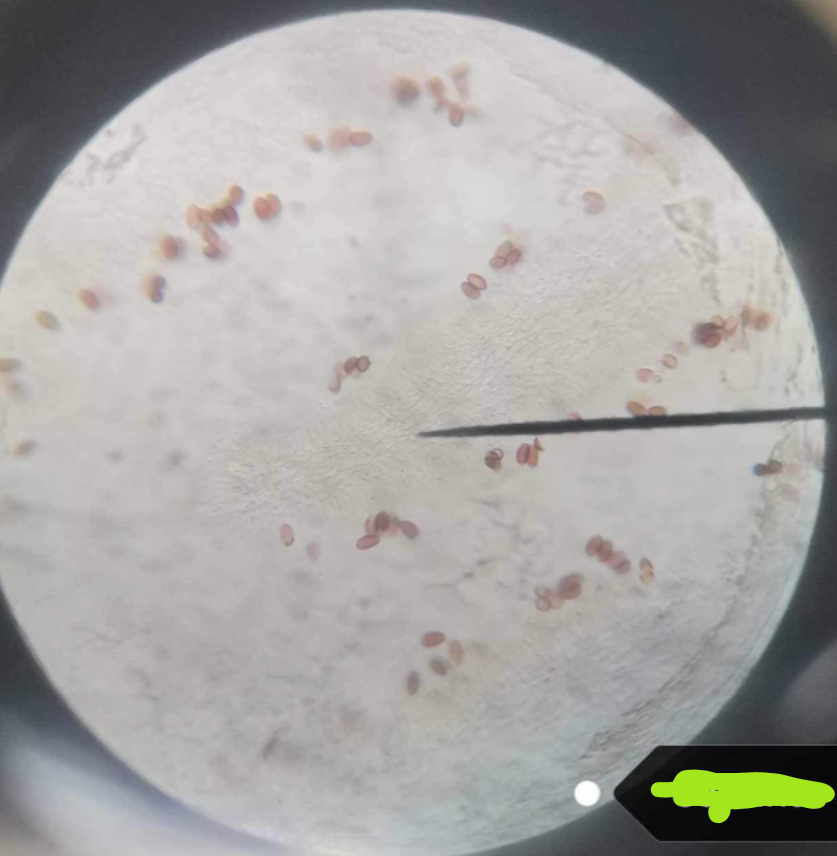
sporangium
the asexual fruiting body of Zygomycota
sporangiophore
the filament that bears the sporangium
sporangiospore
an asexual fungal spore formed within a sporangium
zoosporangium
sexual phase of Zygomycota; a sporangium or spore case in which zoospores are produced.
Division Ascomycota
the fungi under this division have septated hyphae
conidium
the tip of the hypha of the asexual fruiting body of Ascomycota
conidiospores
spore produced by Ascomycota during asexual reproduction
conidiophore
a type of hypha that bears asexual spores called conidia
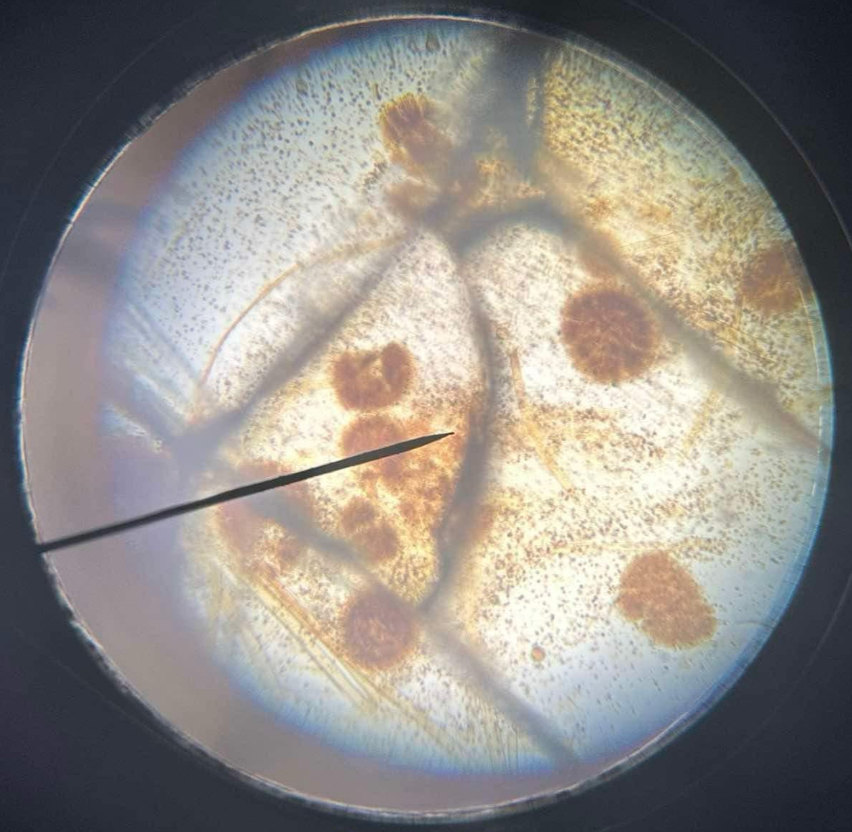
Aspergillus sp.
Ascomycota; look like dandelions; septated hyphae
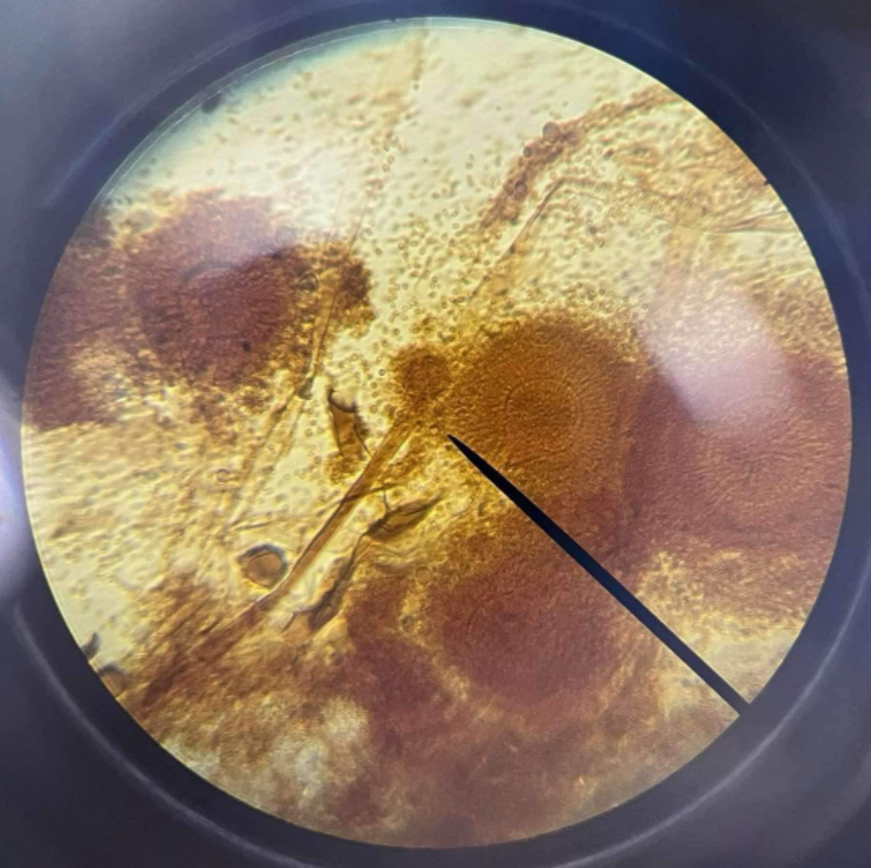
Penicillium sp.
Ascomycota; fungus that produces penicillin
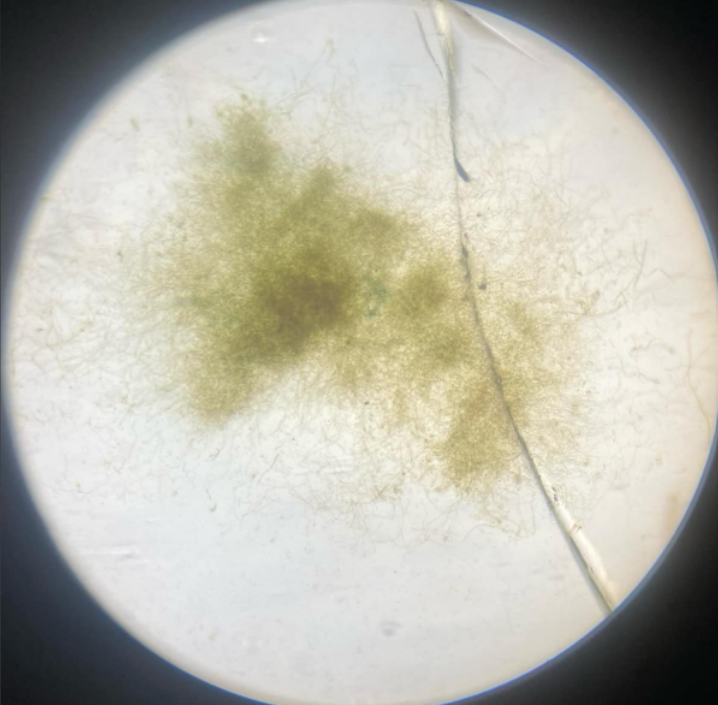
ascocarp
sexual fruiting body of ascomycetes
asci
the sac in ascomycetes in which the sexual spores are formed
ascospores
sexual spore produced within the ascus of ascomycetes
Peziza sp.
Ascomycota; a large genus of saprophytic cup fungi that grow on the ground, rotting wood, or dung
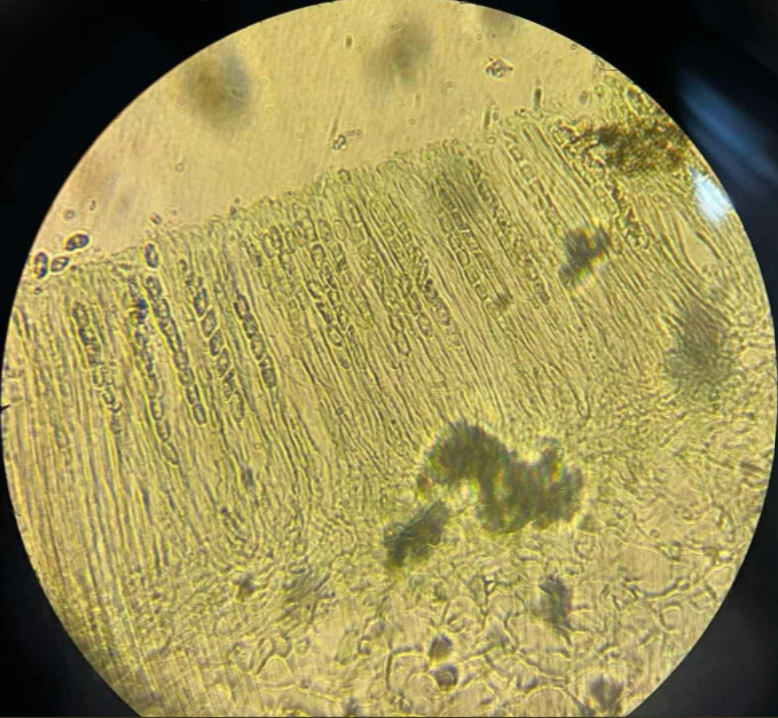
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Ascomycota; Baker's yeast; species of yeast; instrumental in winemaking, baking, and brewing since ancient times; believed to have been originally isolated from the skin of grapes
Division Basidiomycota
the fungi under this division produce septated hyphae; the fusion of two vegetative hyphae produce the dikaryon that fuse and give rise to the basidium
dikaryon
hyphae with cells having 2 different nuclei in each cell.
basidium
club-shaped structure where meiosis occurs
basidiospores
spores produced in the basidia of basidiomycetes during sexual reproduction
Polyporus sp.
Basidiomycota; a hard woody fungus containing pores at the ventral part of the pileus
Puccinia graminis
Basidiomycota; wheat rust; fungus that produces five known types of spores: basidiospores, spermatia, aeciospores, urediniospores, and teliospores
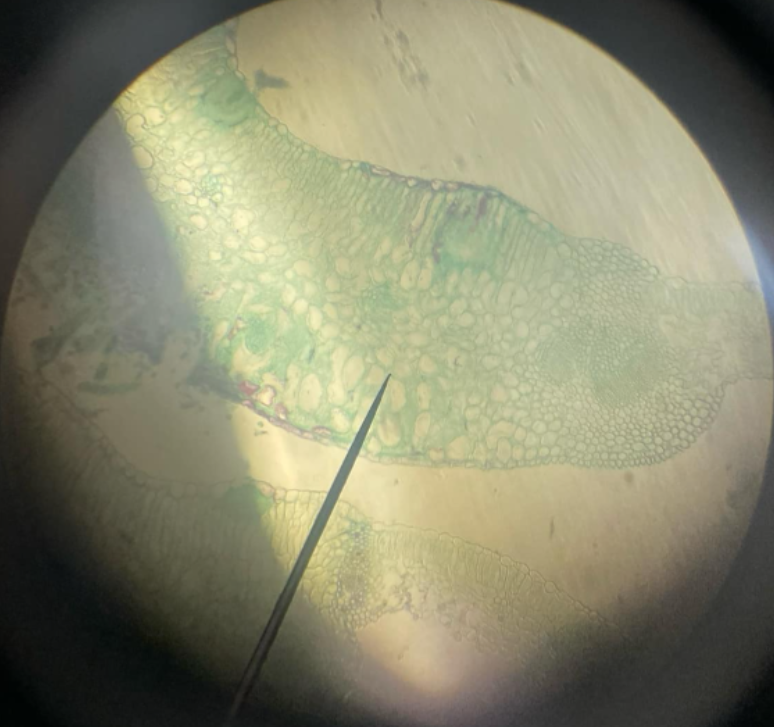
spermatia
a nonmotile cell functioning as a male gamete in certain fungi and lichen
aeciospores
are one of several different types of spores formed by rusts; have two nuclei and are typically seen in chain-like formations in the aecium
urediniospores
thin-walled spores produced by the uredium, a stage in the life-cycle of rusts
teliospores
thick-walled resting spore of some fungi, from which the basidium arises
Coprinus sp.
Basidiomycota; contains a natural compound that mimics insulin, making this mushroom excellent for balancing blood sugar levels