Forensic Biology Exam 2
1/139
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
140 Terms
True or False: Every person’s handwriting is unique.
True
True or False: A questioned document is any document with handwriting.
True
When was handwriting analysis first used in a US court?
1868
When was handwriting analysis evidence accepted is court?
1923
What is the Daubert standard of evidence?
provides a systematic framework for a trial court judge to assess the reliability and relevance of expert witness testimony before it is presented to a jury
When was the Daubert standard created?
1993
What are the details of Robinson v. Mandell
1868: forged will was exposed
What are the details of the Lindbergh kidnapping and murder?
1932: document examiners testified that Bruno Hauptmann wrote the ransom notes for the
kidnapped son of pilot Charles Lindbergh
What are the details of the DeAutremont brothers case?
1927: postal inspectors used handwriting analysis to identify Hugh DeAutremont, who was wanted for a train robbery.
What can cause variation in handwriting?
different writing instruments, mood, age, illness, use of drugs/alcohol/medications
What are the three characteristics of handwriting?
letterform
line form
formatting
What are the four steps for analyzing a handwriting sample?
Sufficient amount
Obtain exemplars
Compare characteristics
Peer review by another document analyst
How can you minimize conscious writing effort?
don’t show suspect the questioned document
don’t provide any punctuation/spelling guidance
What are some shortcomings of handwriting analysis?
quality of example determines quality of analysis
subjective
relies of expertise of examiner
What is forgery?
The act of falsifying a document or signature with the intent to deceive or defraud.
What methods do banks use to prevent check forgery?
chemically sensitive paper
font size
high-res borders
embedding fibers
What are some ways to detect forgery?
mechanical erasures alter paper fibers that can be seen under microscope
solvents may expose crossed out writing
exposure to UV/infrared light can distinguish between inks
some inks/leads burn slower than paper
How many bank notes are counterfeit?
1/10,000
What is the most commonly counterfeited bill?
$20
True of False: Counterfeit money feels the same as real money
False
True or False: Real money is printed on wood-fiber paper
False
What substance do counterfeit identification pens contain?
iodine
What are some motivations behind the global movement to change currency to plastic?
harder to counterfeit
more durable
less expensive to produce
What Amazon program was launched to help combat counterfeit products?
Project Zero
How do biometric signature pads help prevent fraud?
identity authentication
records signature and biometric data
What methods are used to analyze forgeries?
n-gram tracing
paper analysis
ink analysis
infrared reflectography
What is N-gram tracing?
method of detecting document forgery by examining the repeating patterns of pen strokes within a questioned document, breaking down the handwriting into small sequences of characters
What methods are used to prevent counterfeiting?
banknote technology
Micro-optic lenses within the surface
security thread
What are intelligent banknote neutralization systems?
system that uses a degradation agents to mark stolen banknotes, making them difficult to re-enter circulation
What is SEALGN@TURE?
copy-sensitive code that can be embedded in to the design of banknotes
What are fusion polymer substrates?
material that protects against counterfeiters by embedding level III material into the polymer substrate
What are holograms?
common security feature that has been used on banknotes since 1988
What are RollingStar security threads?
security feature that helps distinguish real banknotes from counterfeits
What are LumaChrome color-shifting foils and threads?
color-shifting material that is difficult to reproduce
What is felonious assault?
attack committed for the purpose of inflicting severe bodily harm or death
What are different names for felonious assault?
aggravated assault, felonious battery, assault with intent to commit murder
What are the four elements of felonious assault?
Attempted to commit an assault or performed an action that would cause a reasonable person to fear immediate assault
Intended to hurt another person or make them fear
Able to commit the assault, appeared able to commit assault, or though he was able to commit assault
Committed assault with dangerous weapon
What is the difference between justifiable and excusable homicides?
Justifiable homicides occur during the performance of legal duties or the exercising of a right, putting the person not at fault. In excisable homicides, the person is at fault but the reason lessens the fault enough that it is not a criminal homicide.
Are all homicides felonious?
No
What is the difference between murder and manslaughter?
Murder requires malice aforethought while manslaughter does not.
What is the medico-legal examination pathway?
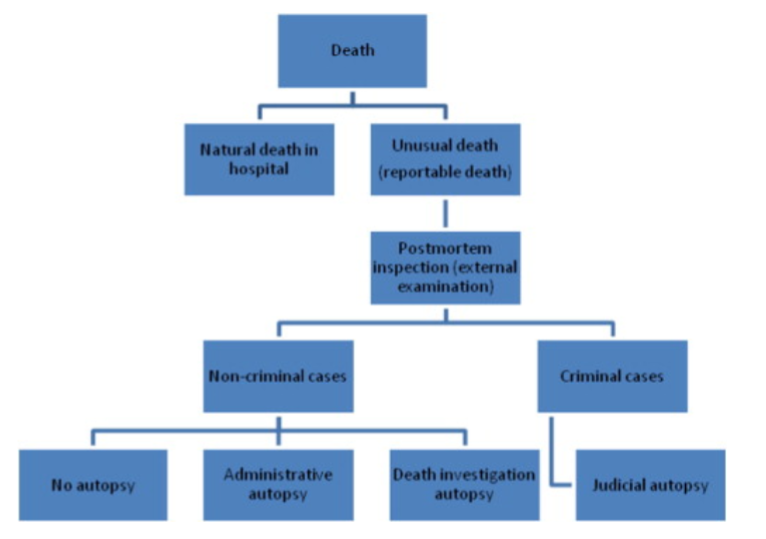
What types of questions can an autopsy answer?
time/cause of death
possible weapons
fatal wounds
direction of attack
signs of struggle/self-defense
signs of rape
toxicology
What is the postmortem interval?
time elapsed from death until discovery and examination
What is the survival period?
time from injury until death
Why is establishing PMI and survival period necessary?
legal questions of alibi and opportunity
True or False: Physico-chemical changes that begin after death progress in an orderly fashion.
True
Rates of development of postmortem changes are influenced by what?
unpredictable changes within body and environment
True or False: The longer the PMI, the narrower/more precise the death estimate is.
False
What is algor mortis?
The body cooling to the environmental temperature after death
Where should body temperature be taken to get the most accurate reading?
rectum or liver
What factors affect the rate of cooling?
size of body
clothing/coverings
movement/humidity of air
immersion in water
When do the corneas become cloudy if the eyes are open following death?
2 hours or less
When do the corneas become cloudy if the eyes are closed following death?
12-24 hours
What happened to the corneas three days postmortem?
They become opaque.
What happens to the eyes when gas collects in the body?
They bulge out.
What happens to the eyes during advanced decomposition?
They become endopthalmic, retracting into the body.
What can the stomach contents tell us about death?
time of death and what was eaten shortly before death
What is rigor mortis?
freezing of the joints and stiffening of the muscles
When does rigor mortis set in?
1-3 hours after death
What affects rigor mortis?
body temperature and metabolic rate
How long will a body remain in rigor mortis?
24-36 hours or until rigor is physically broken
What can rigor mortis tell us?
whether or not a body has been moved
What is livor mortis?
Reddish purple coloration in dependent areas of the body due to accumulation of blood in the small vessels of the dependent areas secondary to gravity
When does livor mortis set in?
30 min to 2 hours after death
When does livor mortis reach its maximum?
8-12 hours after death
What are the three reason that livor mortis is important to examine?
estimate time of death
indicate if body has been moved
indicate cause of death
What is a cadaveric spasm?
instant rigor mortis usually caused by sudden death like a gunshot
What happens to the body as rigor mortis passes?
The abdomen turns green, and as the discoloration spreads, the body begins to swell with bacterial methane gas.
What occurs to the body during the bloat phase?
Air is forced from the skin, causing epidermal sloughing and hemoglobin degradation.
What is purging?
When the increased internal pressure of the body forced decomposed blood and bodily fluids out of body orifices.
The rate of tissue deterioration depends on what?
environmental temperature
True or False: Decomposition occurs evenly throughout the body.
False
What can entomology tell us?
if body has been moved
if body was disturbed
position and presence of wounds
Where do bugs gather?
body: in ears, eyes, nostrils; beneath waist; underneath shirt cuffs and pant legs
skeleton: soil; pelvis and sacrum; eyes, ears, cranium
What occurs in dipteran larval development?
Blow flies are used to determine time of death.
The day or the range of days in which the first insects laid eggs on the corpse can be determined by an analysis of the oldest stage of insect on the corpse and the temperature of the region in which the body was discovered.
What occurs in the study of insect succession over time?
Different insect species are involved in each decompositional stage - analyze the insect assemblage associated with the
remains to determine a window of time in which death took place.
Requires the knowledge of insect succession and regional, seasonal, habitat, and meteorological variations.
What types of wounds are encountered in investigations?
firearm wounds
incised wounds
stab wounds
puncture wounds
lacerations
Is the bullet wound smaller or larger than the diameter of the bullet?
Smaller because the skin stretches with the bullet and then retracts.
The combined contusion ring and entrance opening corresponds to what?
the bullet caliber
What is the smudge ring?
a black ring created by small particles originating from the surface of the bullet
What is the main difference between a close-range and a long-range firearm discharge?
Close-range wounds will exhibit smoke deposits while long-range will not.
What size shotgun wound is produced when at close-range vs. longer-range?
contact to 12 in: 0.75 - 1 in
3-6 feet: 1.5-2 in
What is used to determine the gauge of the shotgun and the size of the pellets?
wad and pellets
Do shotgun pellets normally exit the body?
Rarely, except when used in suicide shots to the head
If someone has discharged a handgun, will residues appear on the palm?
No, unless they hold the gun with both hands like police officers.
What are incised wounds?
Wounds that are narrow at the edges and gaping at the center, caused by a sharp-edged instrument.
What determines the severity of incised wounds?
shape and sharpness of weapon
part of body being cut
amount of force used
What causes death from stab wounds?
severe damage to vital organ
internal bleeding
shock
secondary infection
Shape and depth of stab wounds are determined by what?
shape, size, sharpness of blade
manner in which blade is thrust into and pulled out of body
What are characteristics of puncture wounds?
small with little to no bleeding
easily overlooked
cause death similar to stab wounds
What are lacerations?
Open, irregularly shaped wounds caused by clubs, pipes, pistols, or other such blunt objects.
Can be inflicted accidentally.
How do lacerations cause death?
severe head injuries
What determines the severity of lacerations?
amount of force
amount of time over which force is delivered
region struck
amount of body surface over which force is delivered
nature of weapon
True or False: The greater area over which a force is delivered, the less severe the wound will be.
True
What are defense wounds?
Wound suffered by victims attempting to protect themselves from an assault.
Where are defensive wounds commonly found?
palms, fingers, forearms
What is ligature strangulation?
Pressure on the neck is applied by a constricting band that is tightened by a force other than the body weight. Results in a ligature mark that encircles the neck in a horizontal plane across the larynx.
What is the mechanism of death in strangulation?
Occlusion of the vessels that supply blood and thus oxygen to the brain
What can change the appearance of a ligature mark on the neck?
nature of ligature
amount of resistance
amount of force
What is manual strangulation?
Produced by pressure of the hand, forearm, or other limb against the neck, compressing the internal structures of the neck