02.0D BIO Communities & Ecosystem Dynamics - Biodiversity (PART D)
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Biodiversity
The total of all the genetically based variation in all organisms in the biosphere. Three types include: ecosystem, species, and genetic diversity

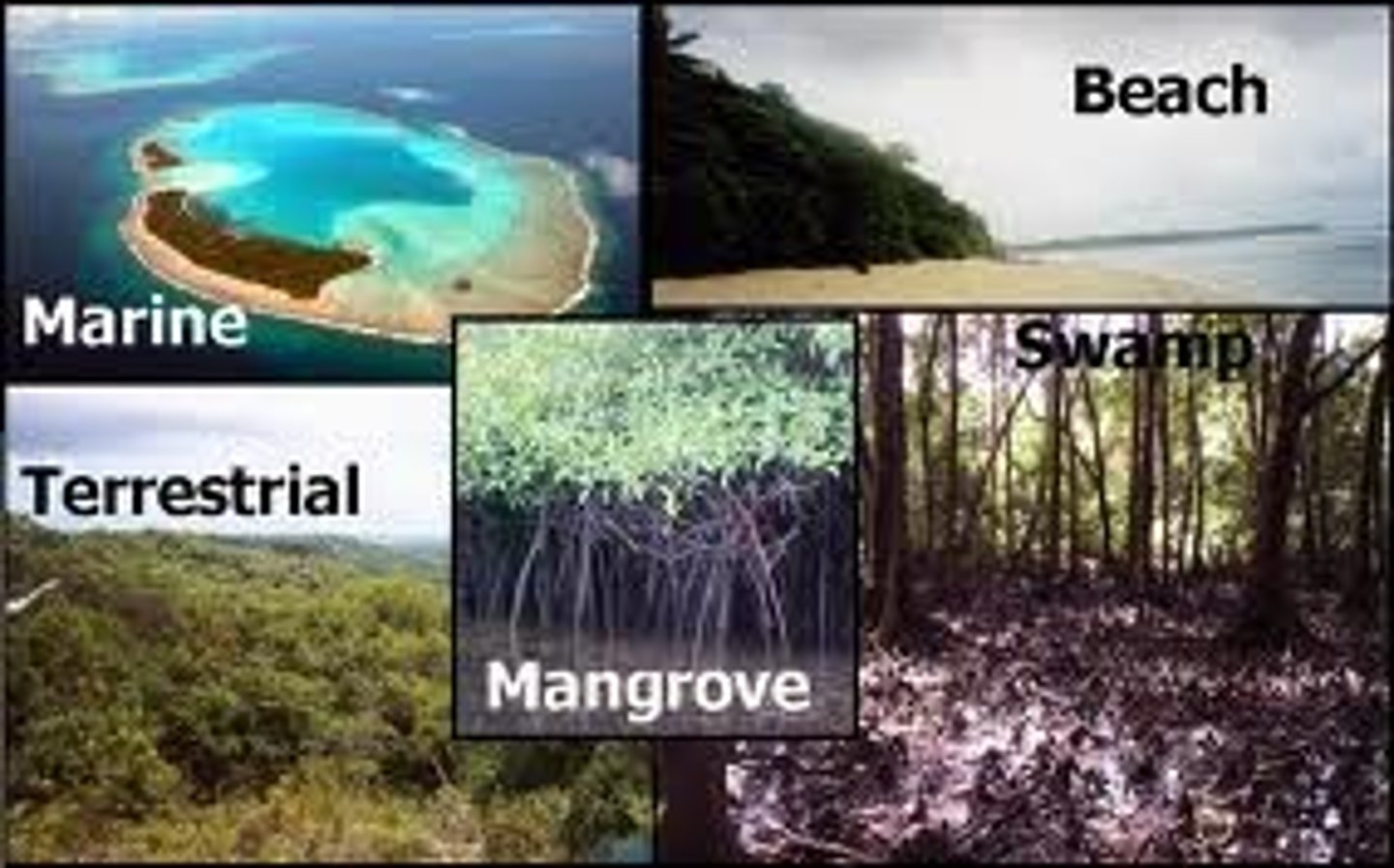
Ecosystem Diversity
Refers to the variety of habitats, communities, and ecological processes in the biosphere.
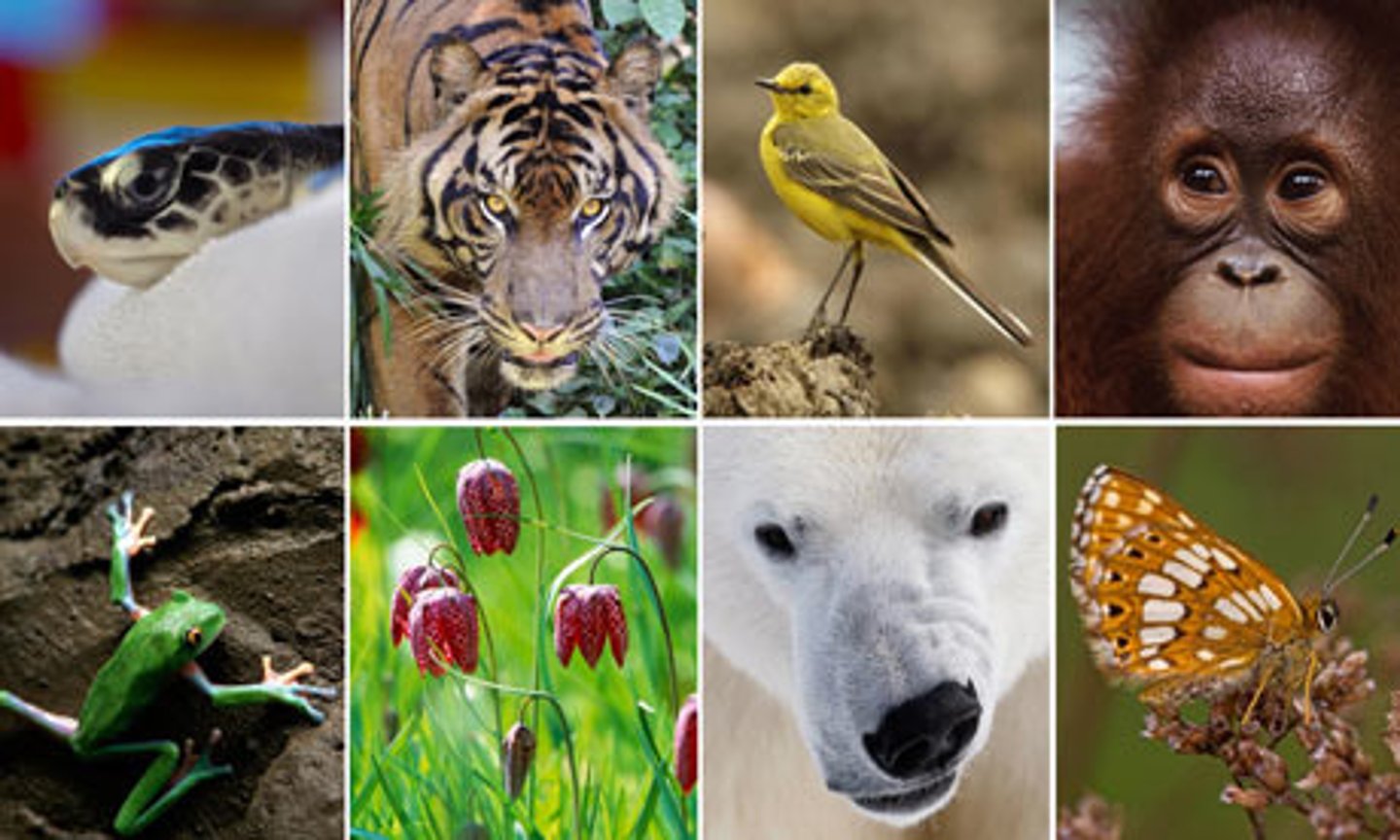
Species DIversity
The number of different species in the biosphere, or in a particular area.

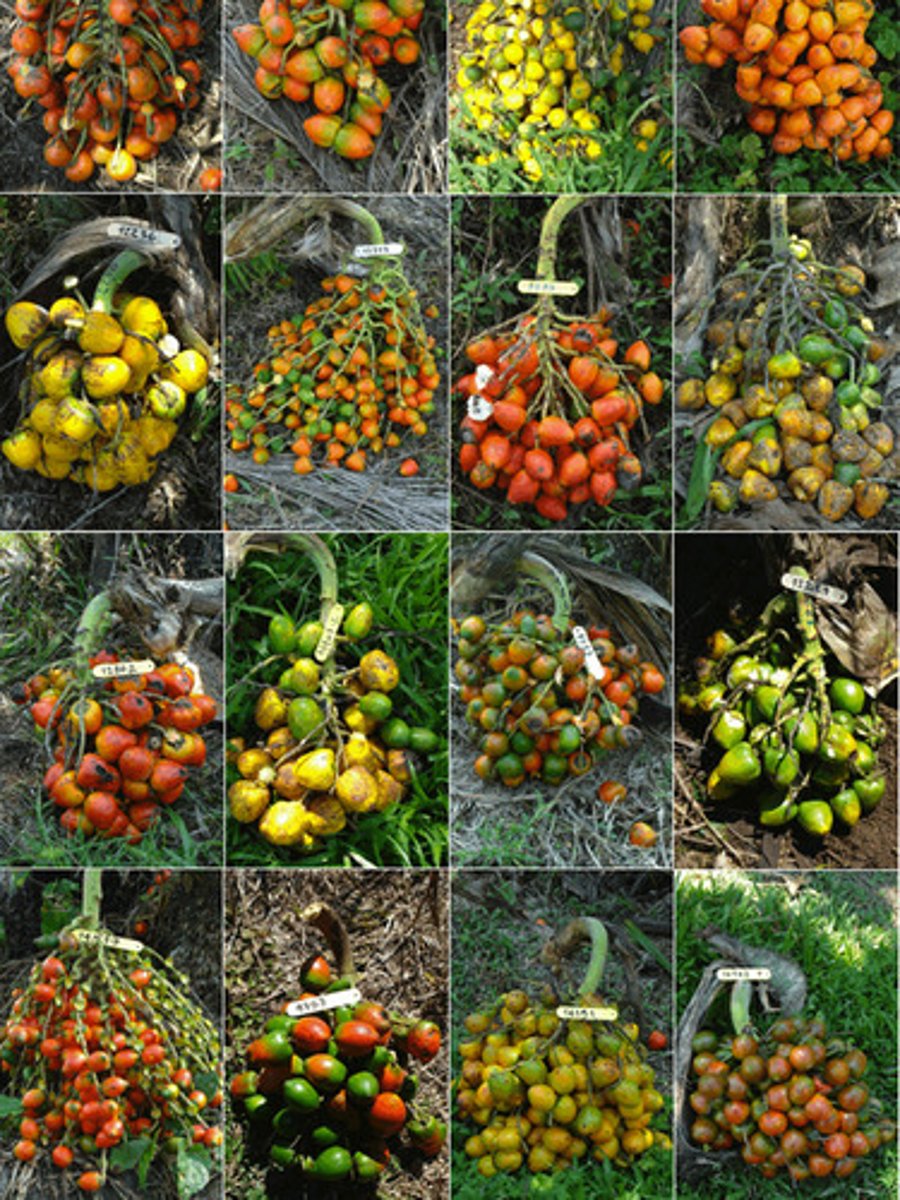
Genetic Diversity
Can refer to the sum total of all different forms of genetic information carried by a particular species, or by all organisms on Earth.

Threats to Biodiversity
Includes altering habitats, hunting, introducing invasive species, releasing pollution into food webs, and contributing to climate change.

Altered Habitats
When natural habitats are eliminated for agriculture or for urban development, the number of species in those habitats drops, and some species may become extinct.
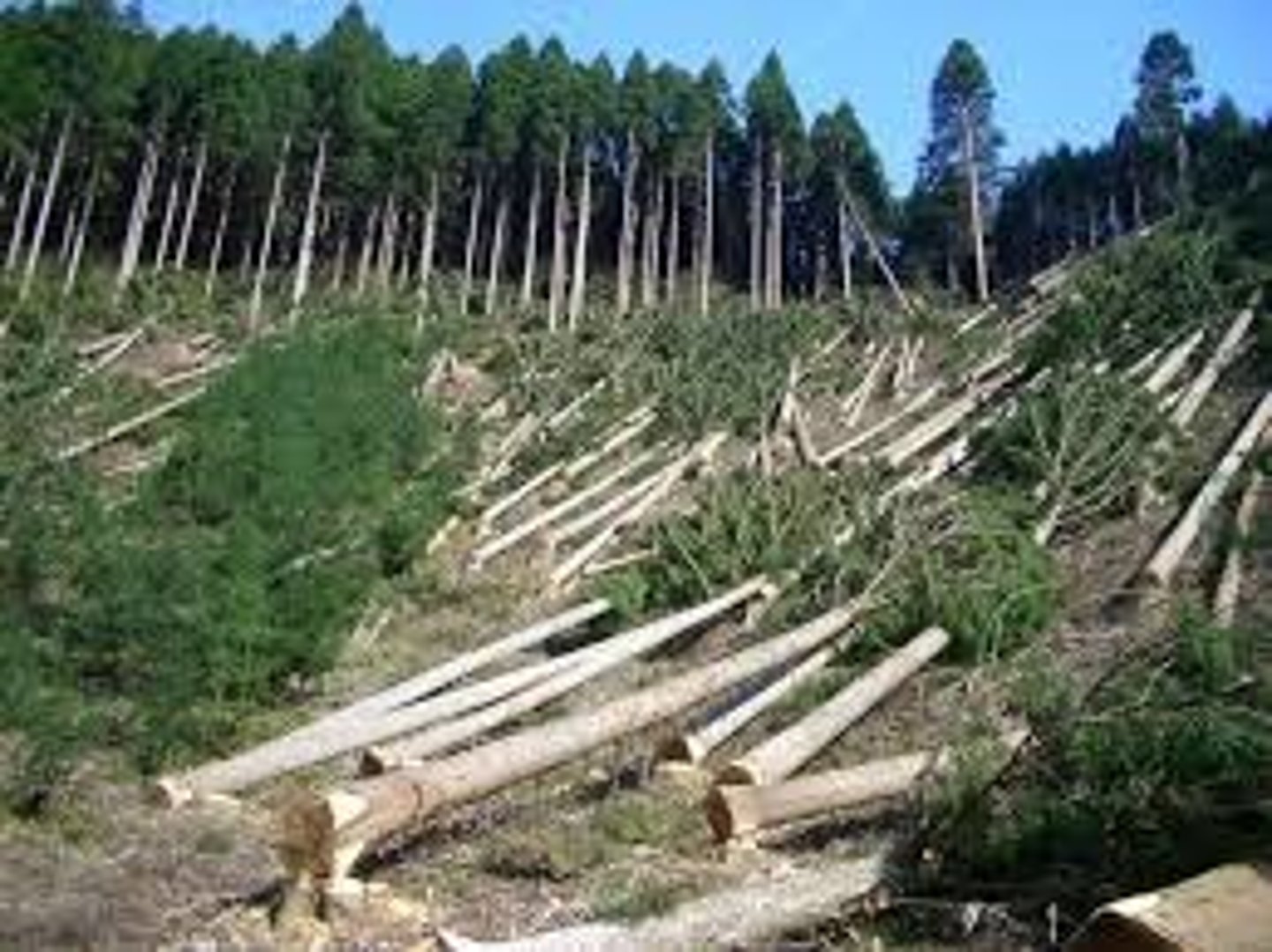

Habitat Fragmentation
A process that splits ecosystems into fragments. For example - deforestation in Florida leading to islands; putting a road through a forest.

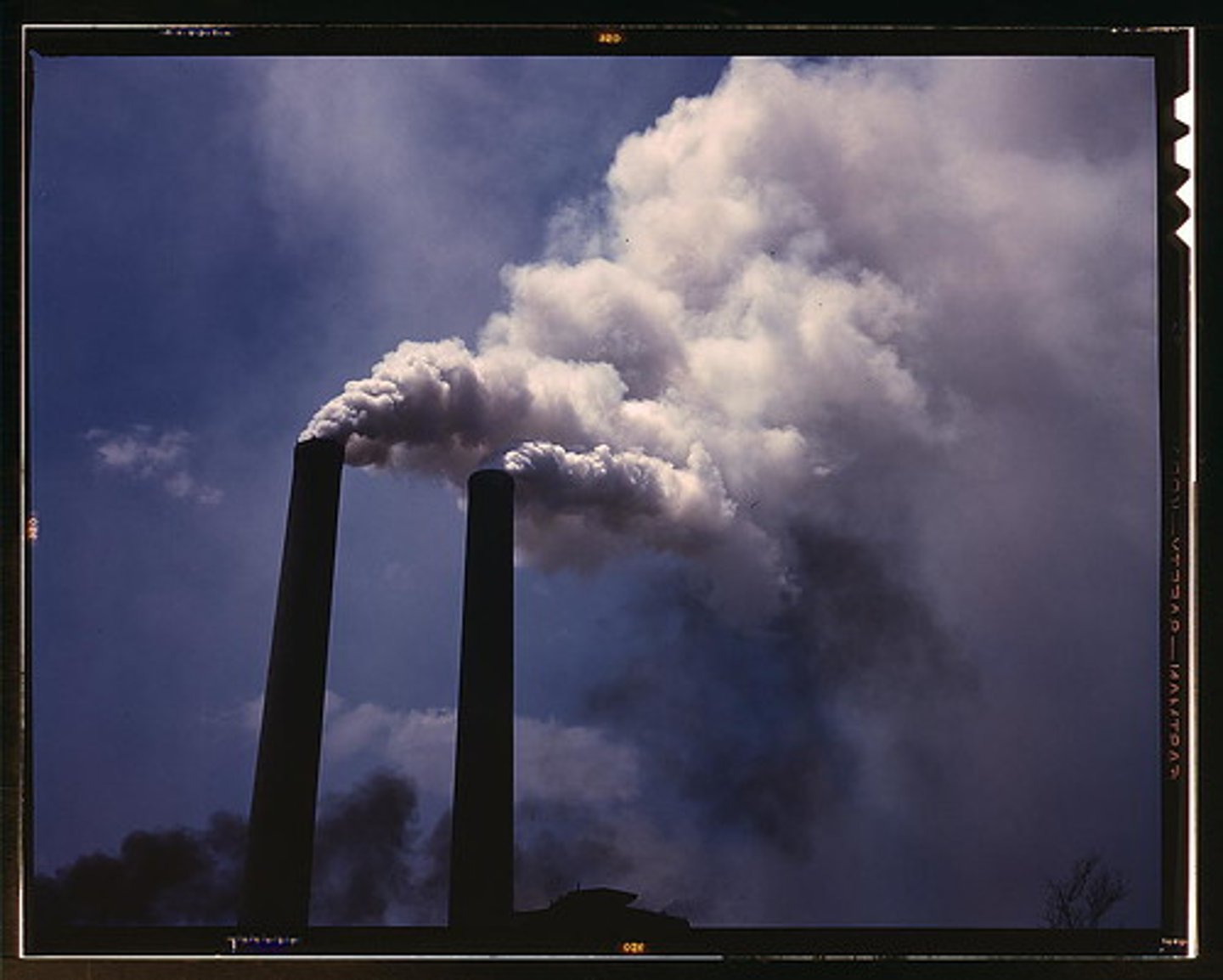
Pollution
DDT, for example, prevents birds from laying healthy eggs.
Acid rain places stress on land and water organisms.
Increased carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is dissolving in oceans, making them more acidic, which threatens biodiversity in marine ecosystems.

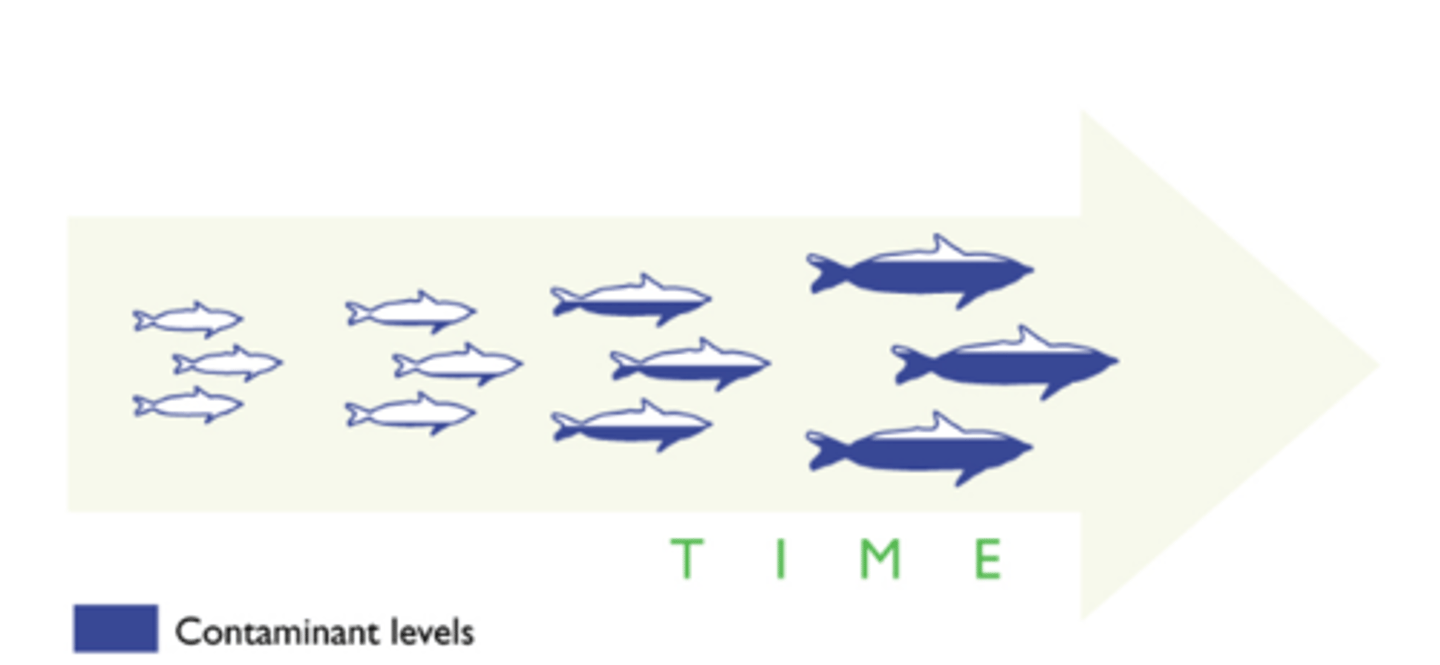
Biological Accumilation
A process in which concentrations of harmful substances like DDT or other pollutants INCREASE in organisms over time.
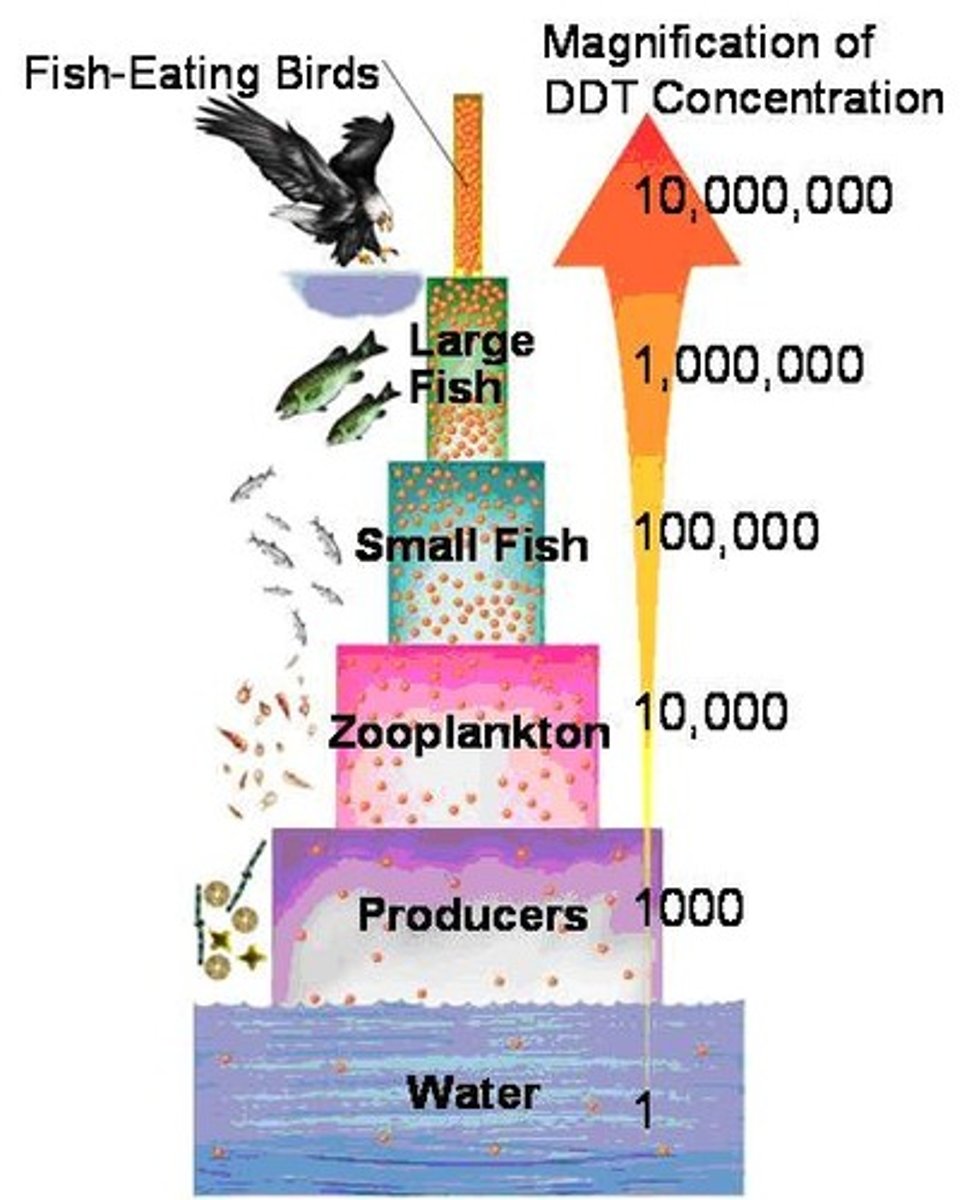
Biological Magnification
A process in which concentrations of harmful substances increase in organisms at higher trophic levels in a food chain or food web. Affects the entire food web, although the top-level carnivores are at the highest risk.
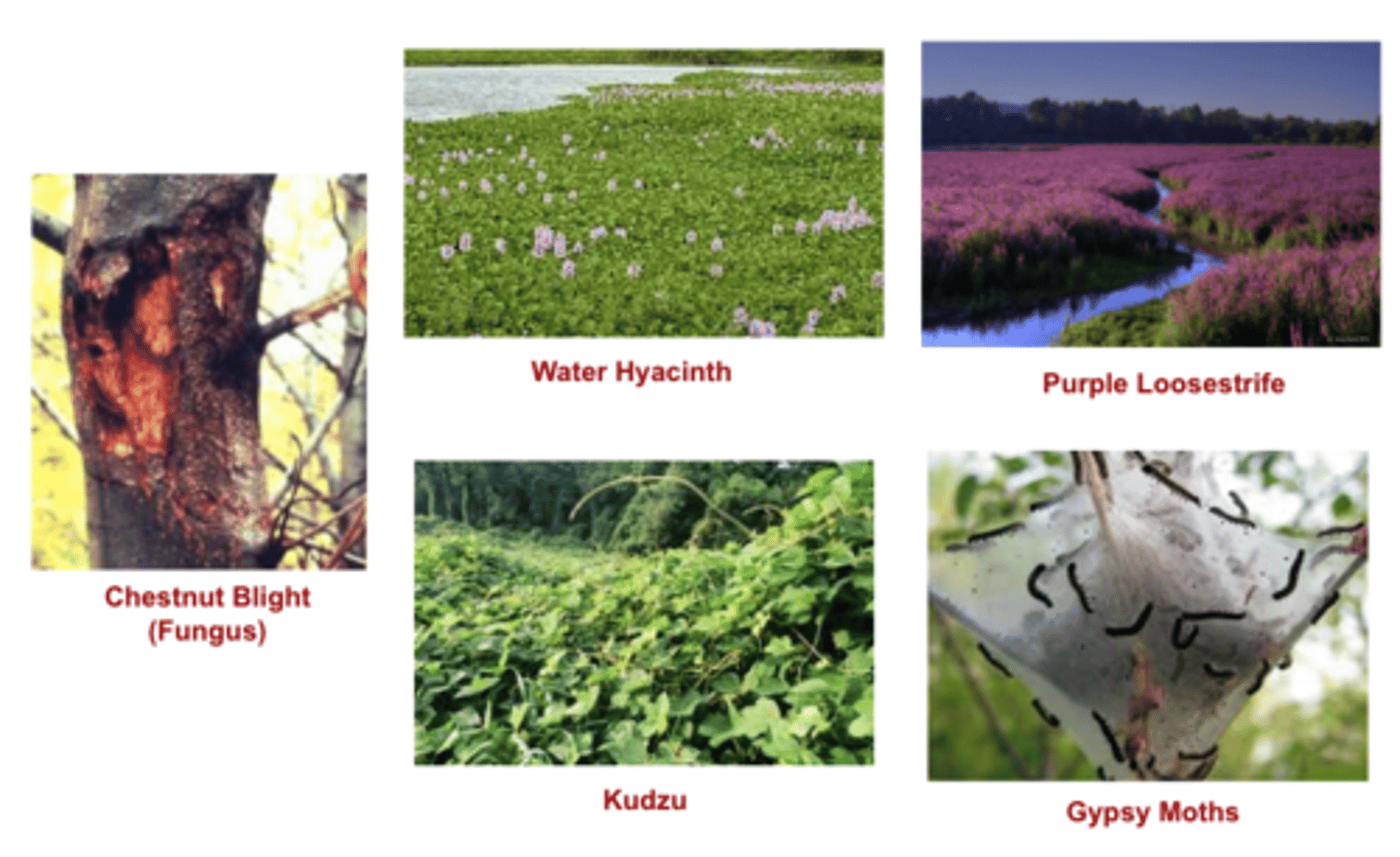
Introduced Species / Invasive Species
Species reproduce rapidly because their new habitat lacks the parasites and predators that control their population "back home". (Australian Rabbit, Hyrdrilla, Kudzu vine, etc)

Conservation
Efforts to protect individual species, preserve habitats and ecosystems, and make certain that human neighbors of protected areas benefit from participating in conservation efforts.