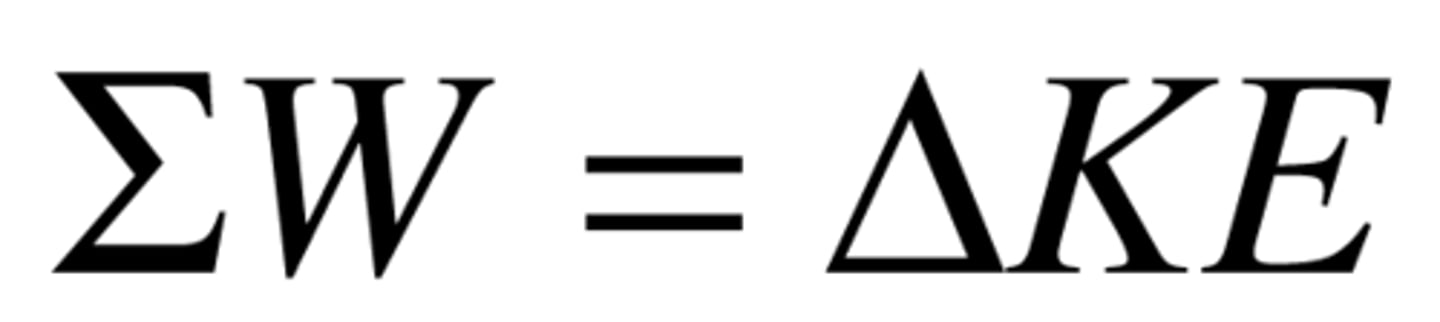AP Physics Key Terms
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
acceleration
how much an object's velocity changes each second.
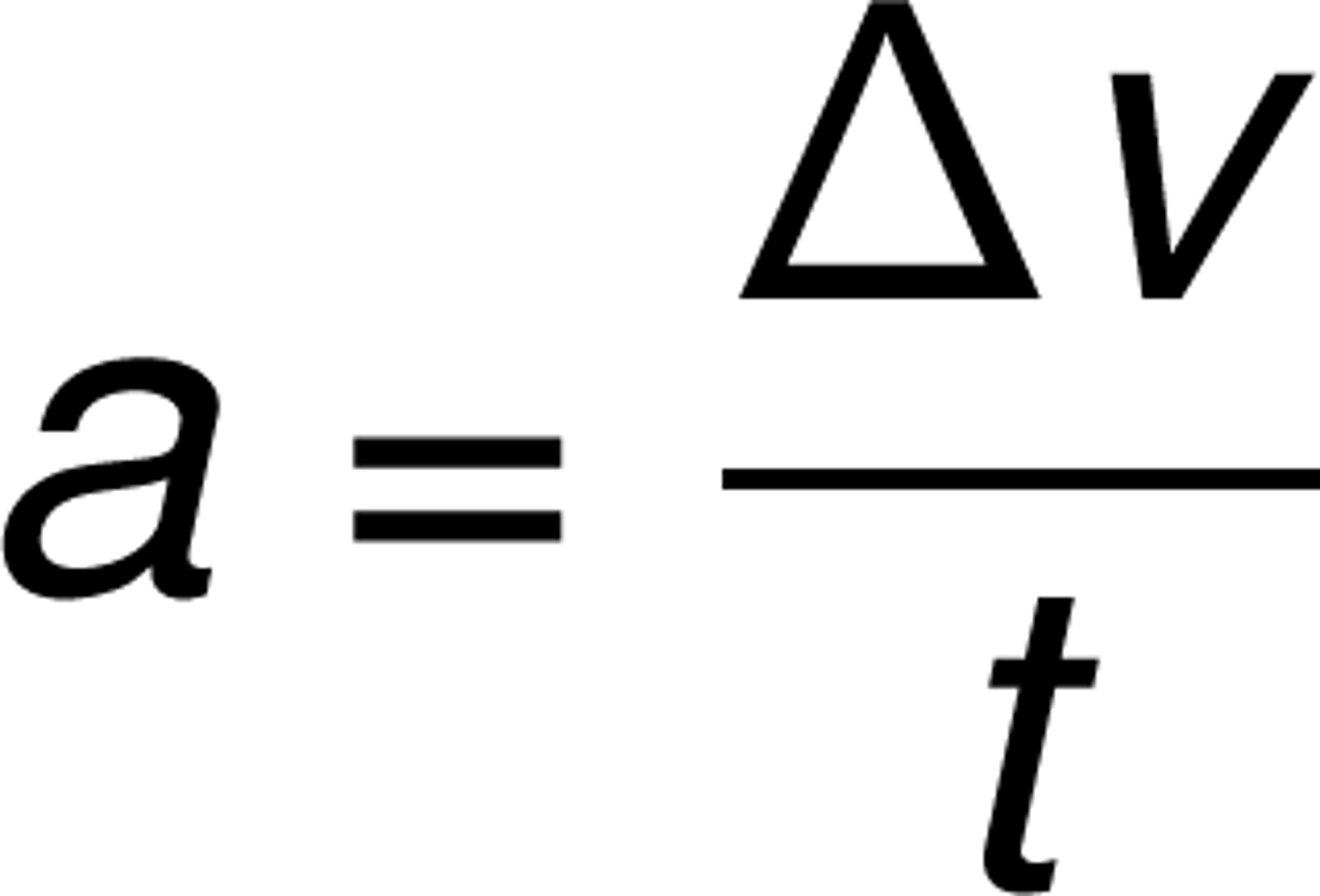
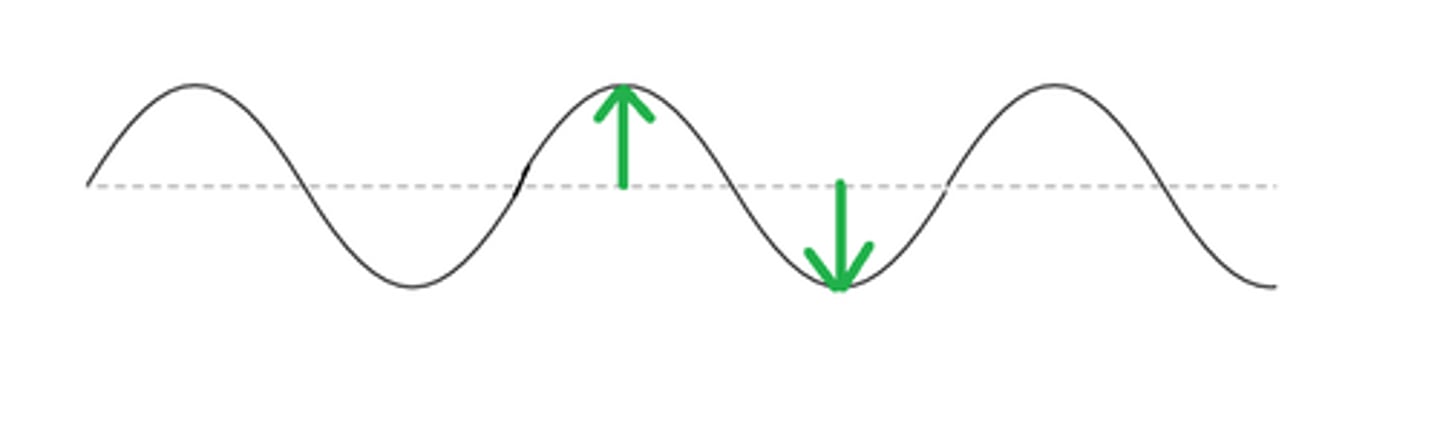
amplitude
the distance from the midpoint of a wave to either the crest or the trough. For an oscillating system, it is the distance between the maximum displacement and the equilibrium position.
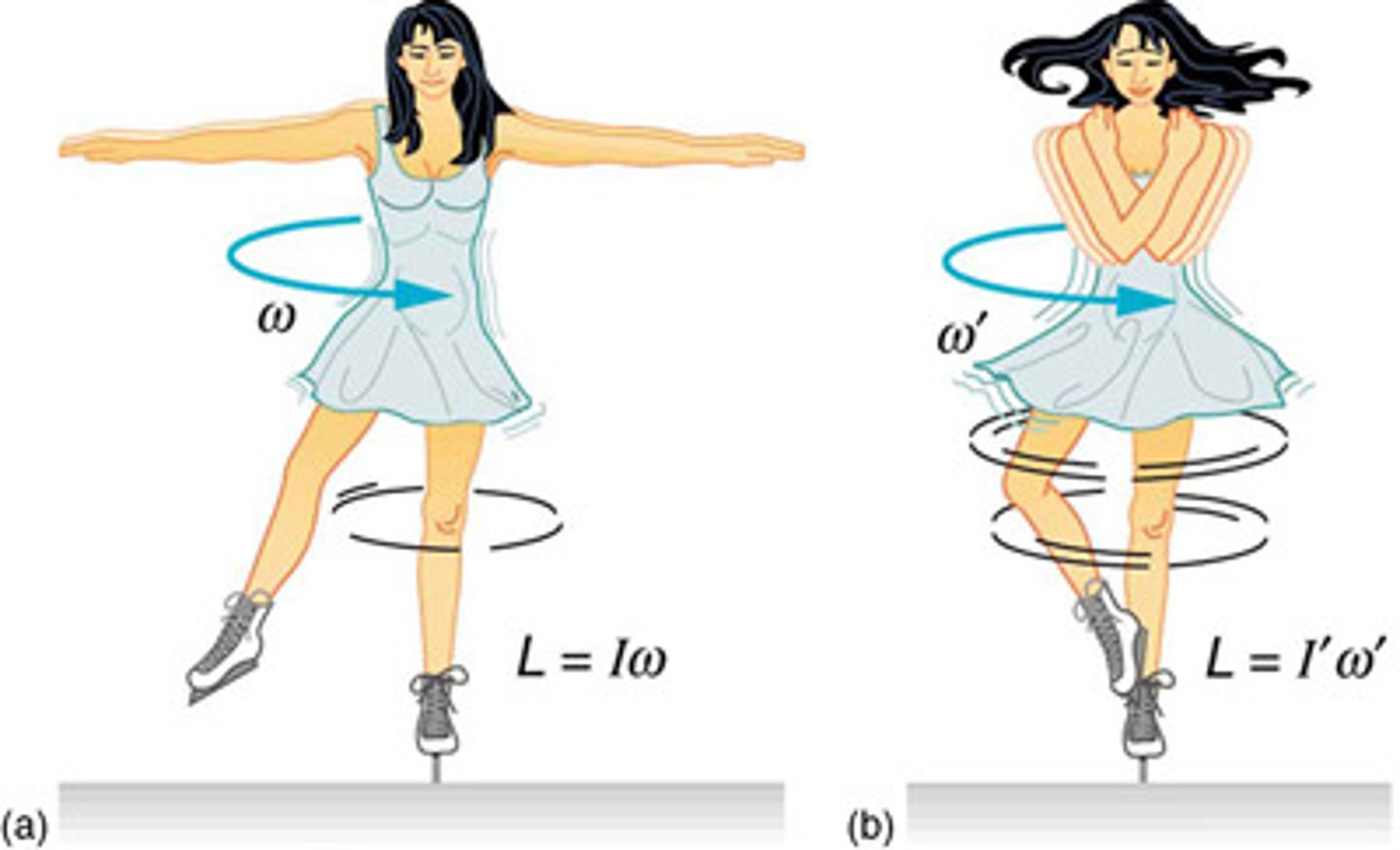
angular momentum
the object's rotational inertia times its rotational velocity. For an object rotating a distance about a central axis of rotation, it is the product of its torque over a given time interval.
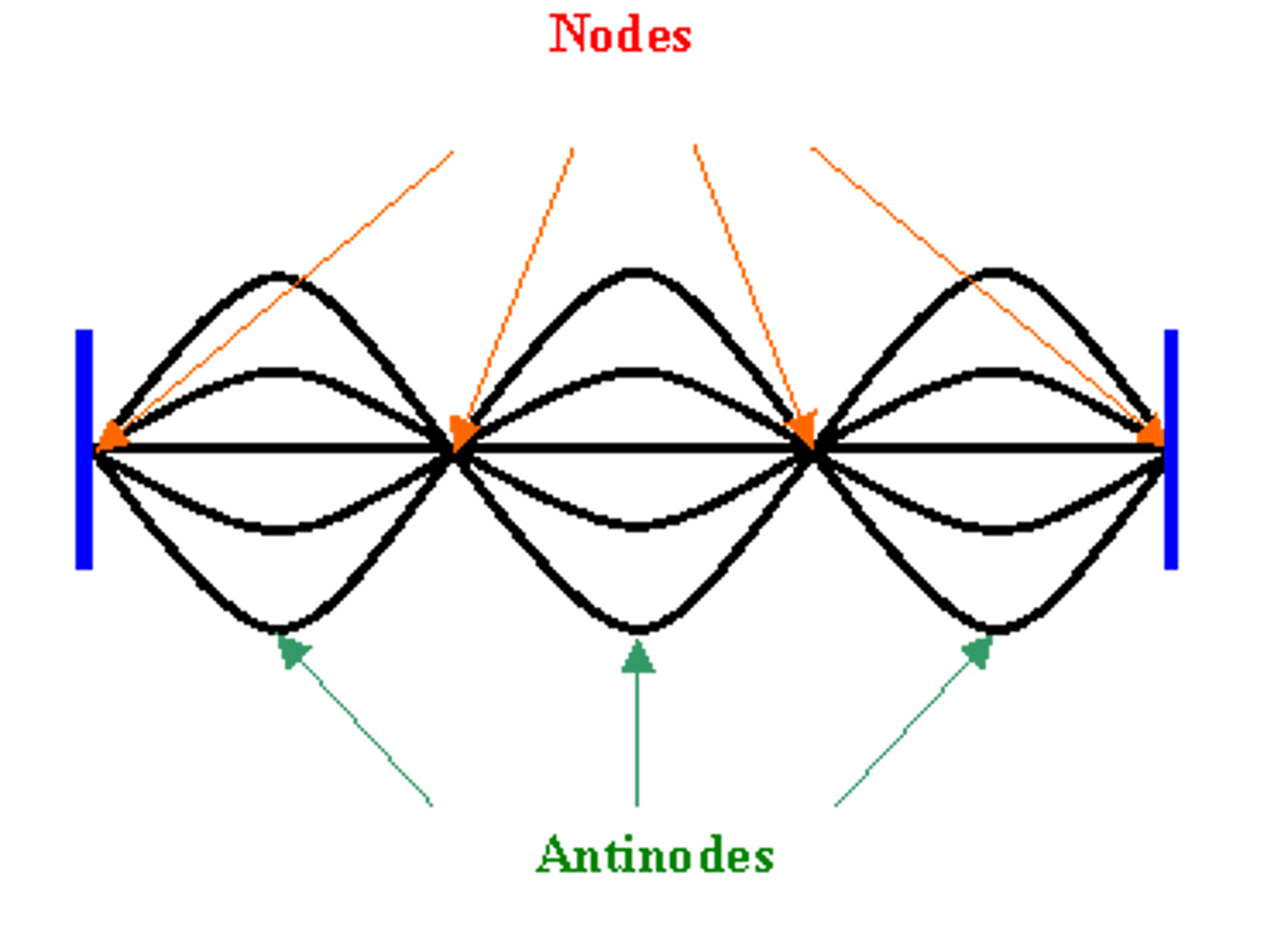
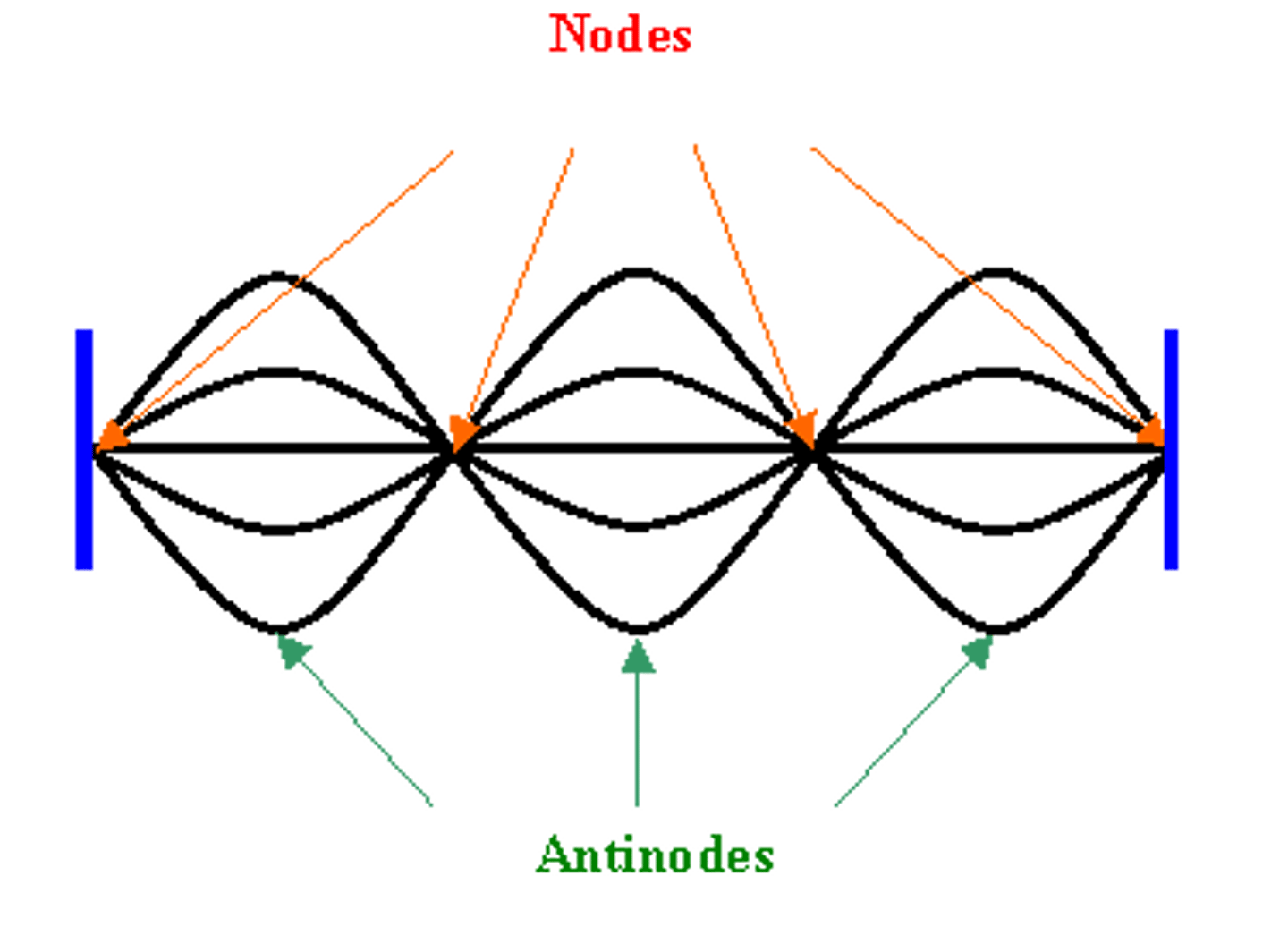
antinodes
positions on a standing wave with the maximum amplitude.
beats
interference that happens when two notes of unequal but close frequencies are played simultaneously.
center of mass
a unique point in an object or a system where one can consider all the mass as being concentrated
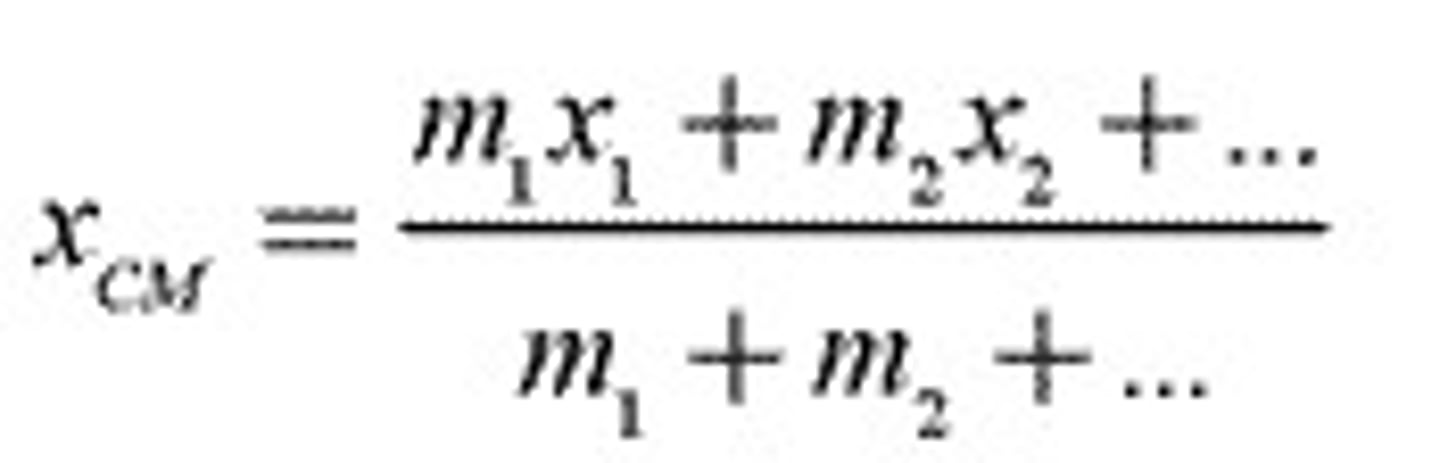
centripetal acceleration
a "center-seeking" acceleration. An object moving in a circle experiences this acceleration directed radially inward.
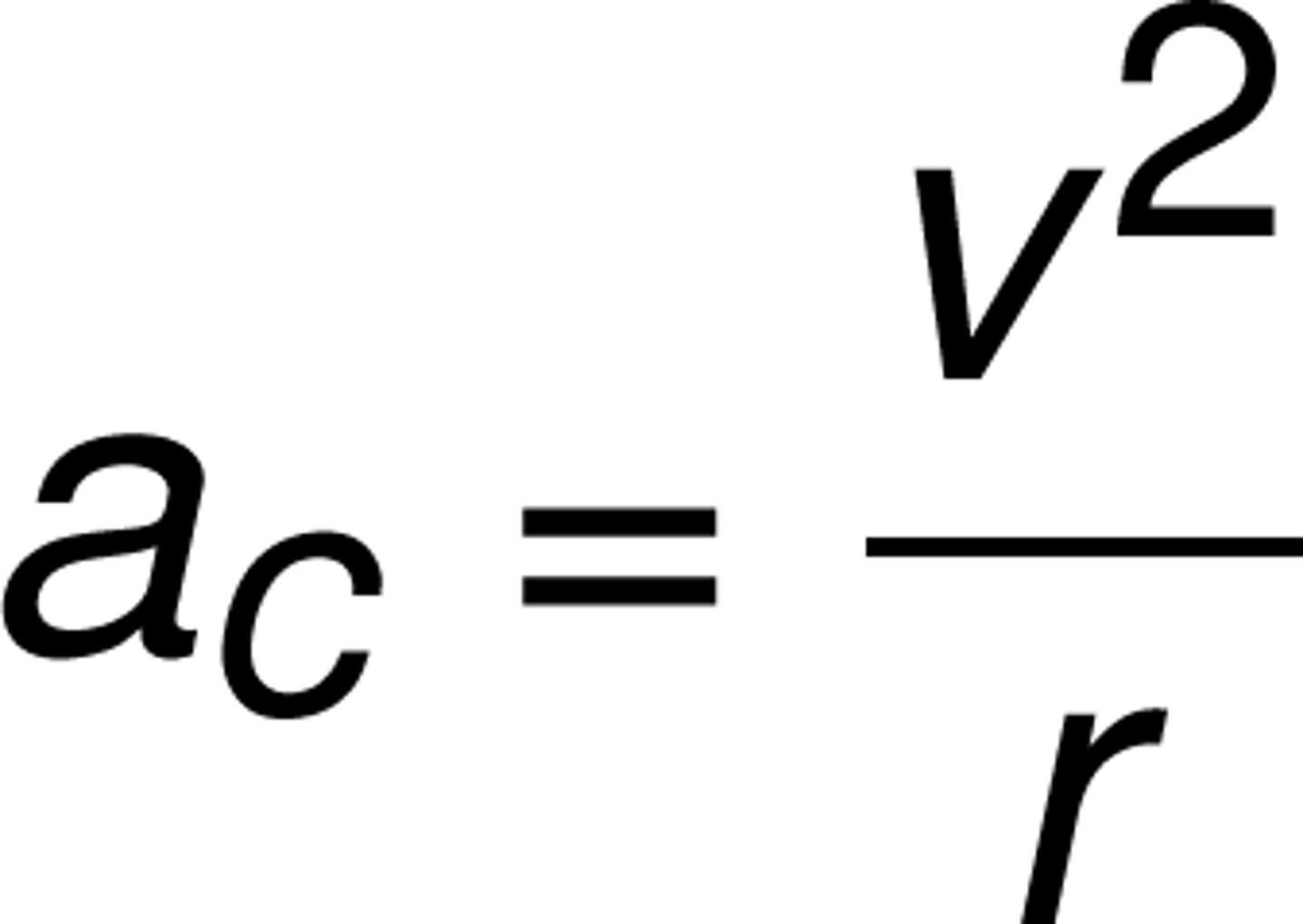
charge
a fundamental property of matter that is affected by an electric field. It is measured by an excess or deficit of electrons on an object.
Symbol: Q
Measured in: Coulombs (C)

coefficient of friction
a unitless quantity that tells us how "sticky" two surfaces are when rubbed past one another.
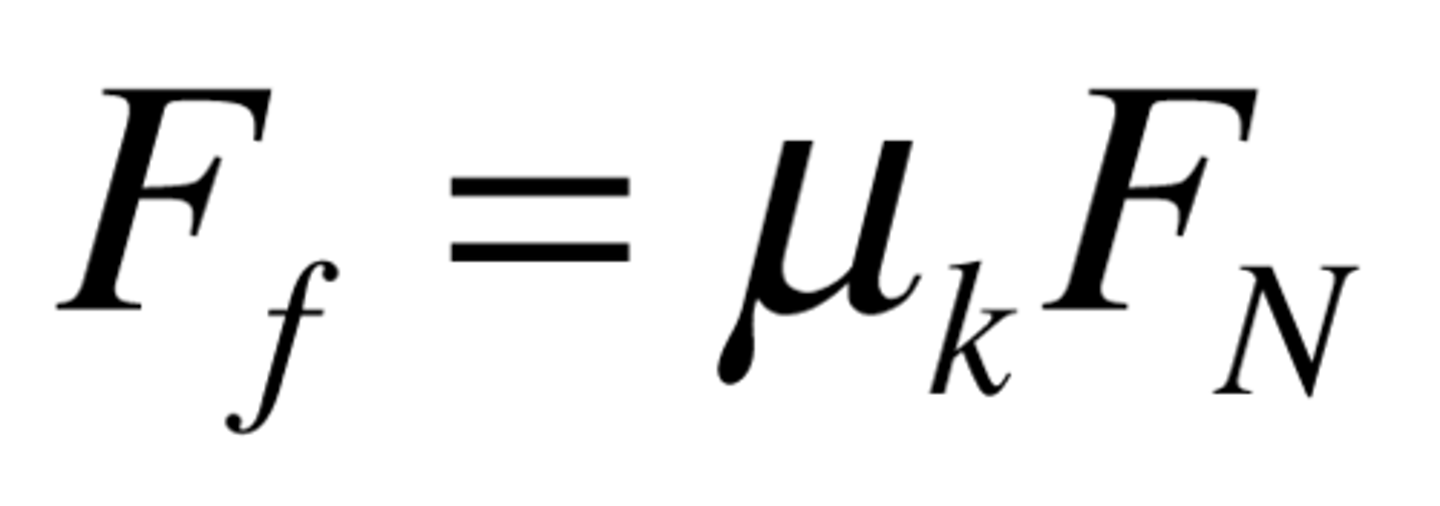
Coulomb's Law
describes the force of attraction or repulsion between two electric charges. The electrostatic force is proportional to the magnitude of the product of the two charges and inversely proportional to the distance between them squared.
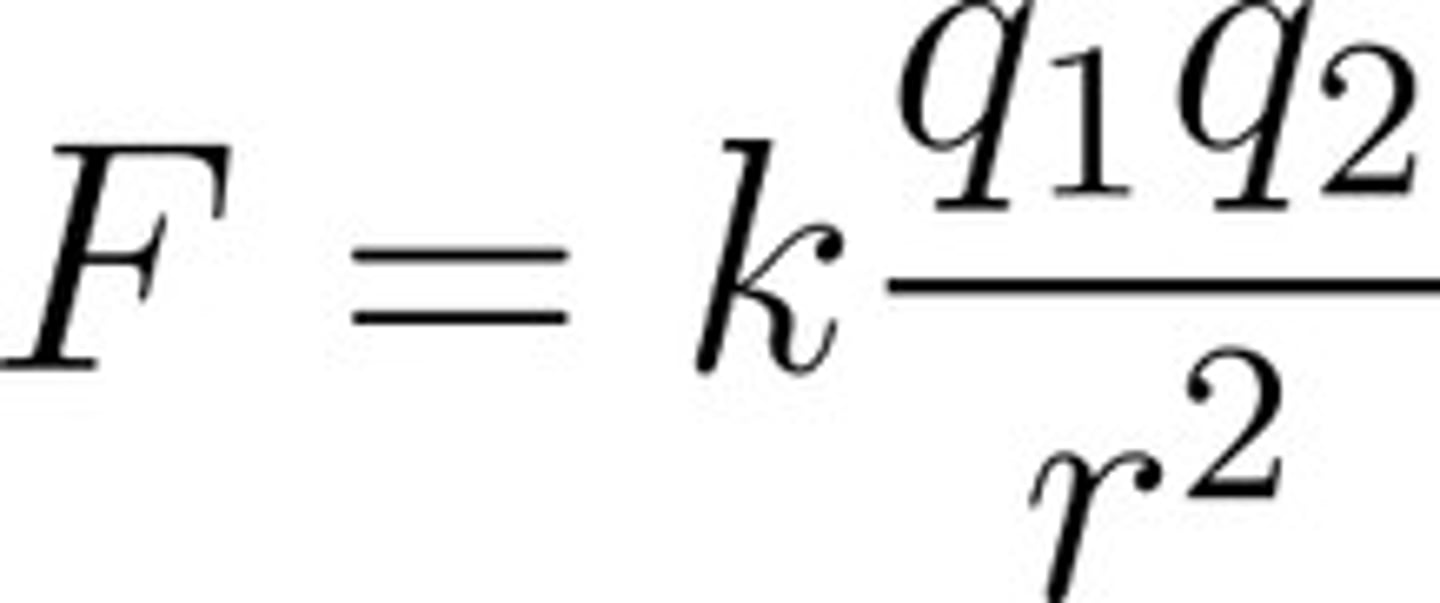
current
the rate of flow of positive charge
Measured in: Amperes (Amps) (A)
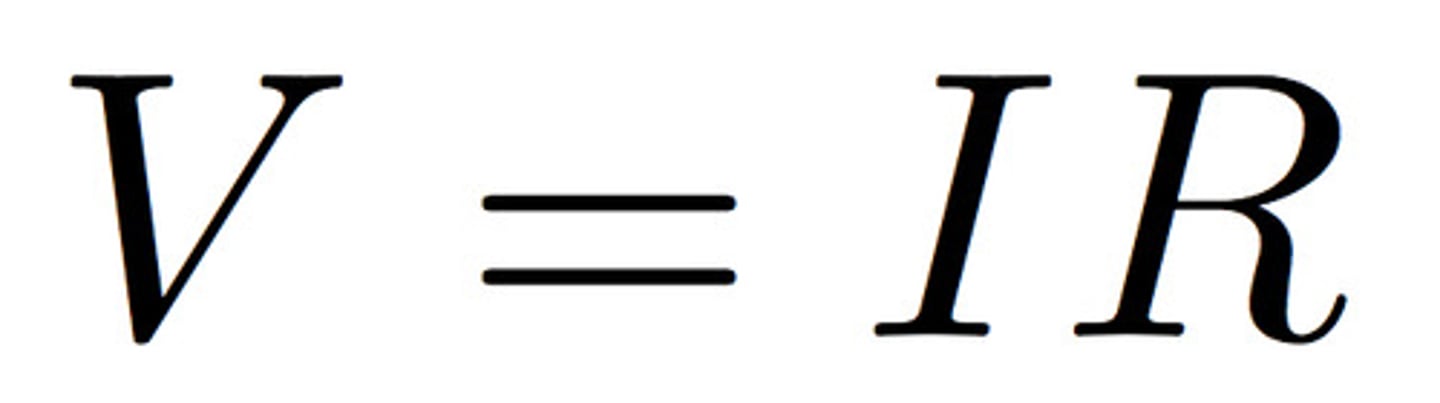
density
the mass per volume of a material, used as a measure of compactness of a substance.
displacement
a vector quantity, measured in meters, which tells us how far an object is from its initial position.
distance
a scalar quantity, measured in meters, telling how far an object has traveled
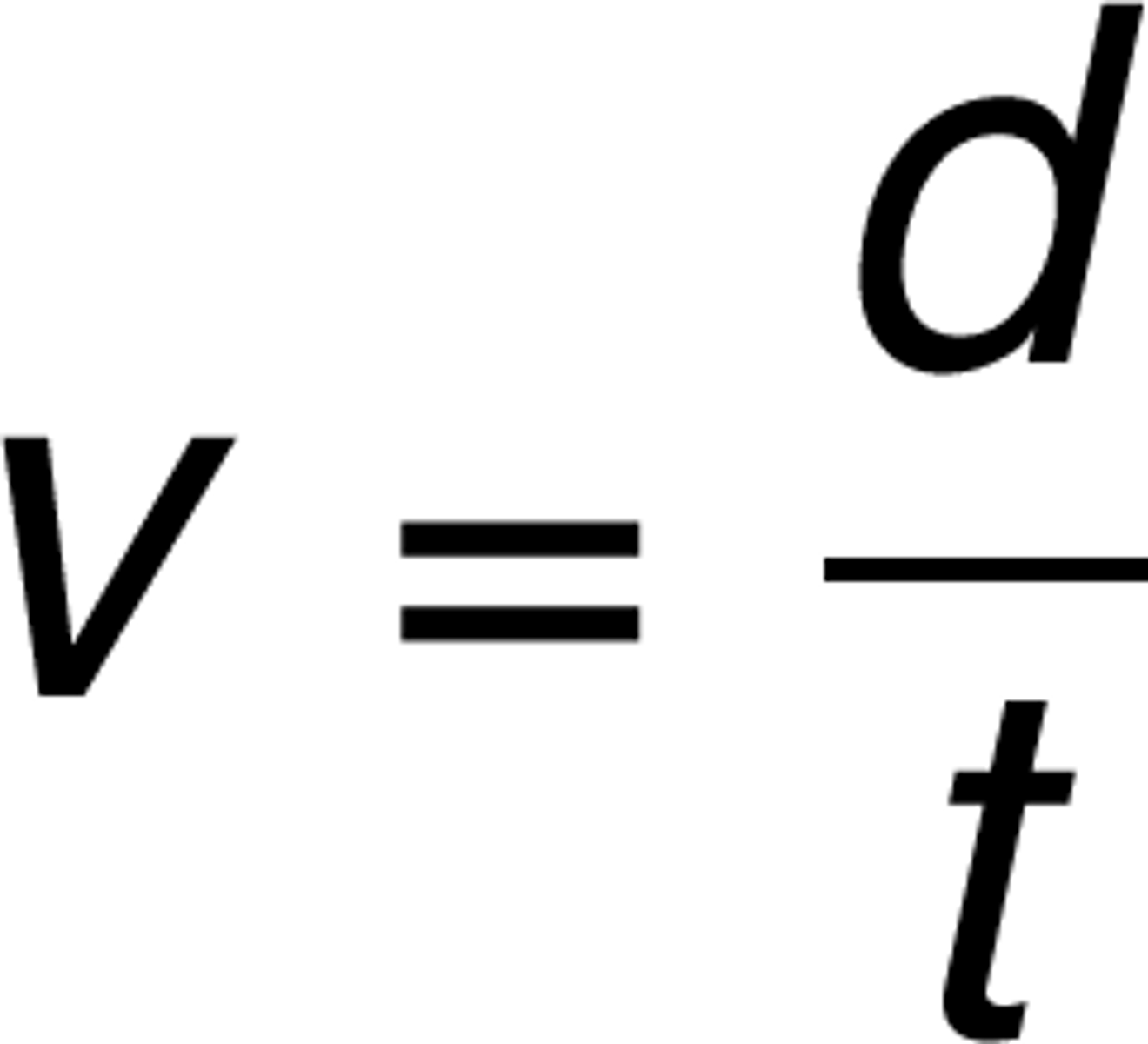
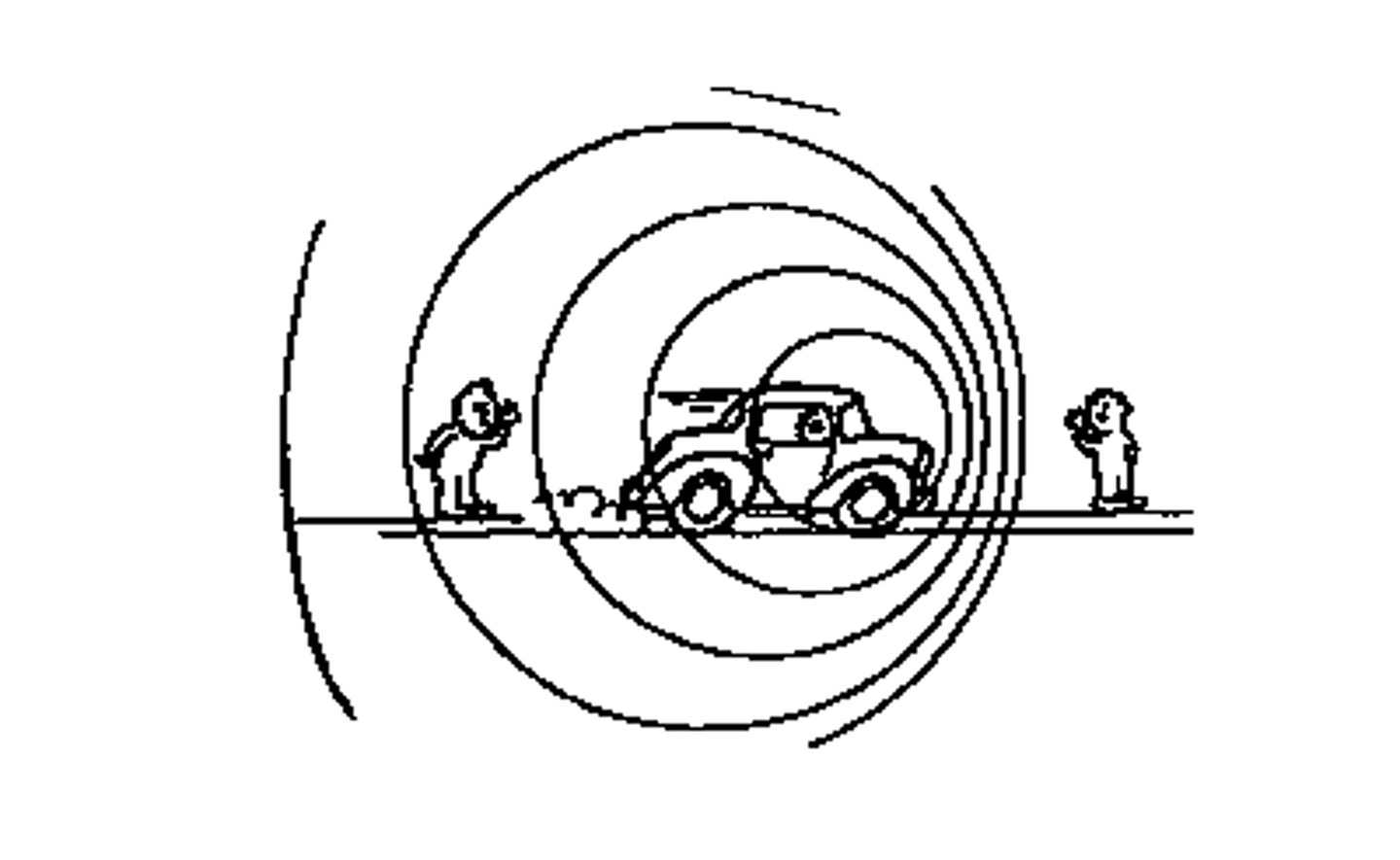
Doppler Effect
the apparent change in wave's frequency or wavelength because of the relative motion between the source of the wave and the observer
elastic collisions
when two objects collide, the momentum and the kinetic energy of the system are conserved. The two objects bounce off each other without any loss of kinetic energy
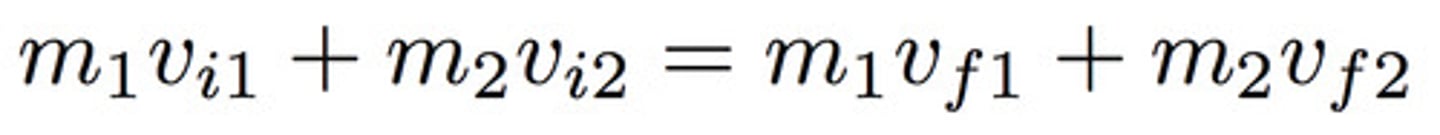
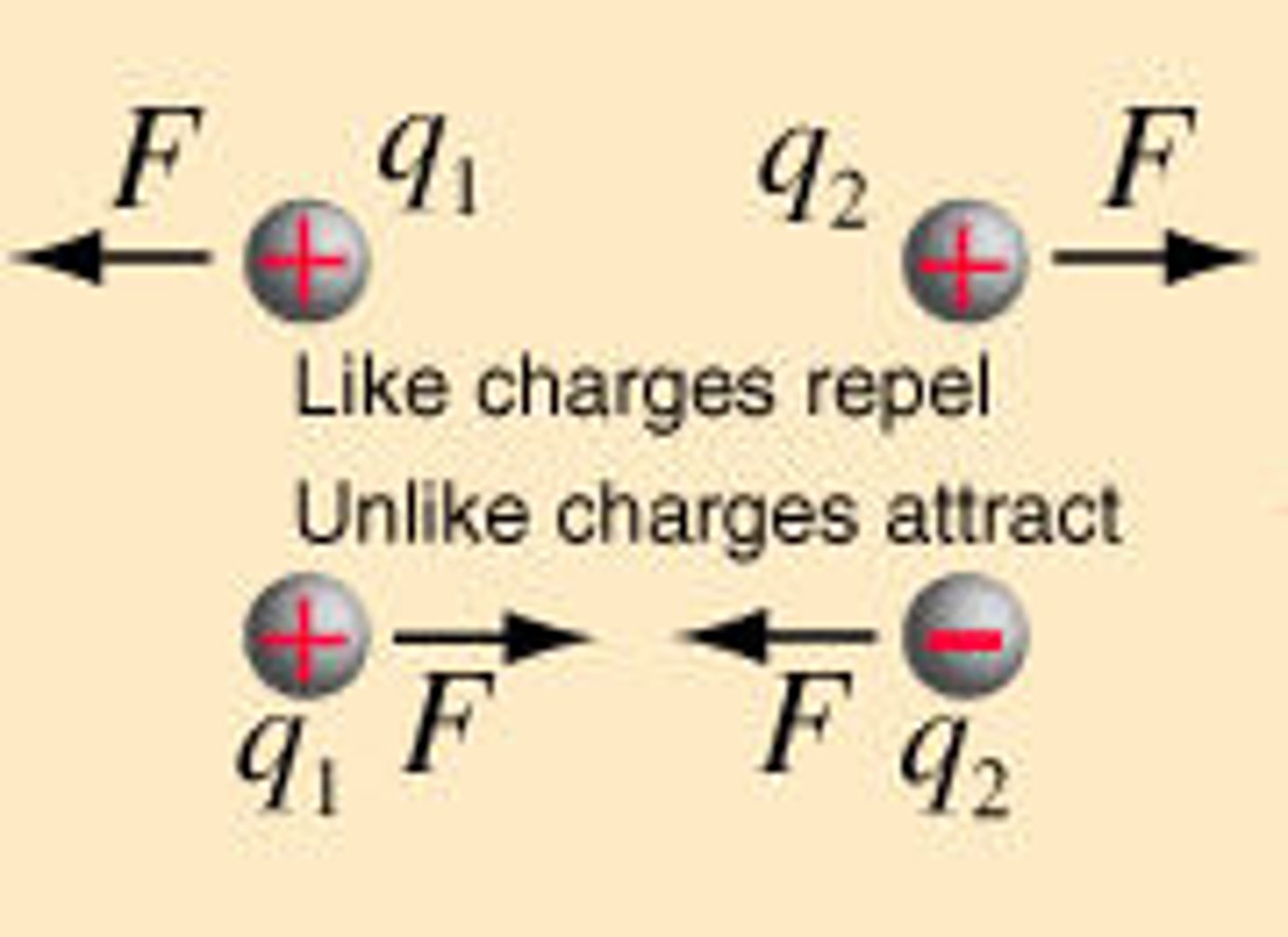
electrostatic force
the force between objects caused by their electric charges. Governed by Coulomb's Law
Measured in: Newton's (N)
force
any push or pull (contact or not) from one object on another which could cause or contribute to the acceleration (or change in velocity) of one or both objects. Vector quantity
Measured in: Newtons (N)
force of gravity
(also called weight) how hard the Earth pulls on you. Depends on the mass of the Earth, your mass, and how far you are from the center of the Earth. g=9.8m/s^2

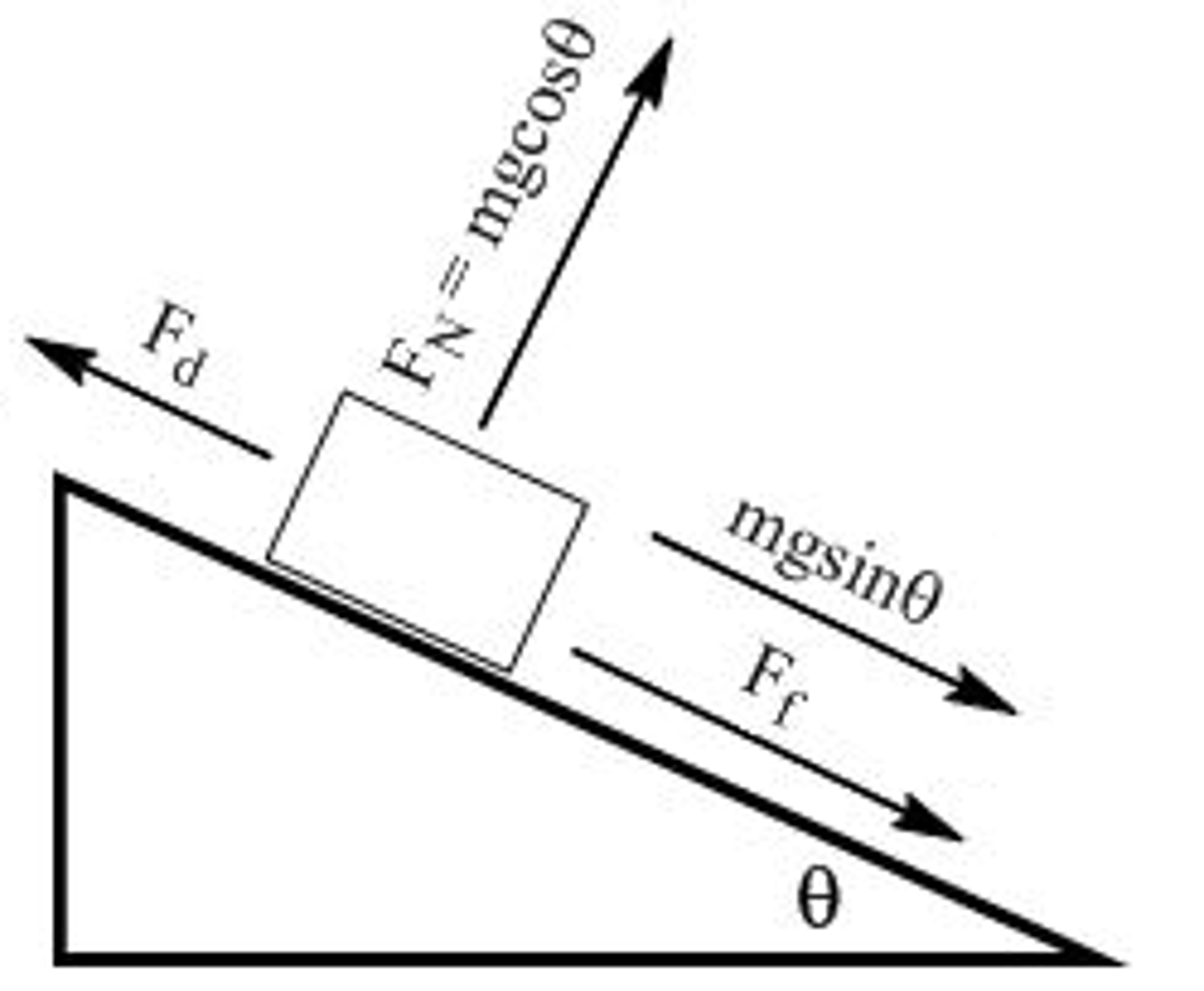
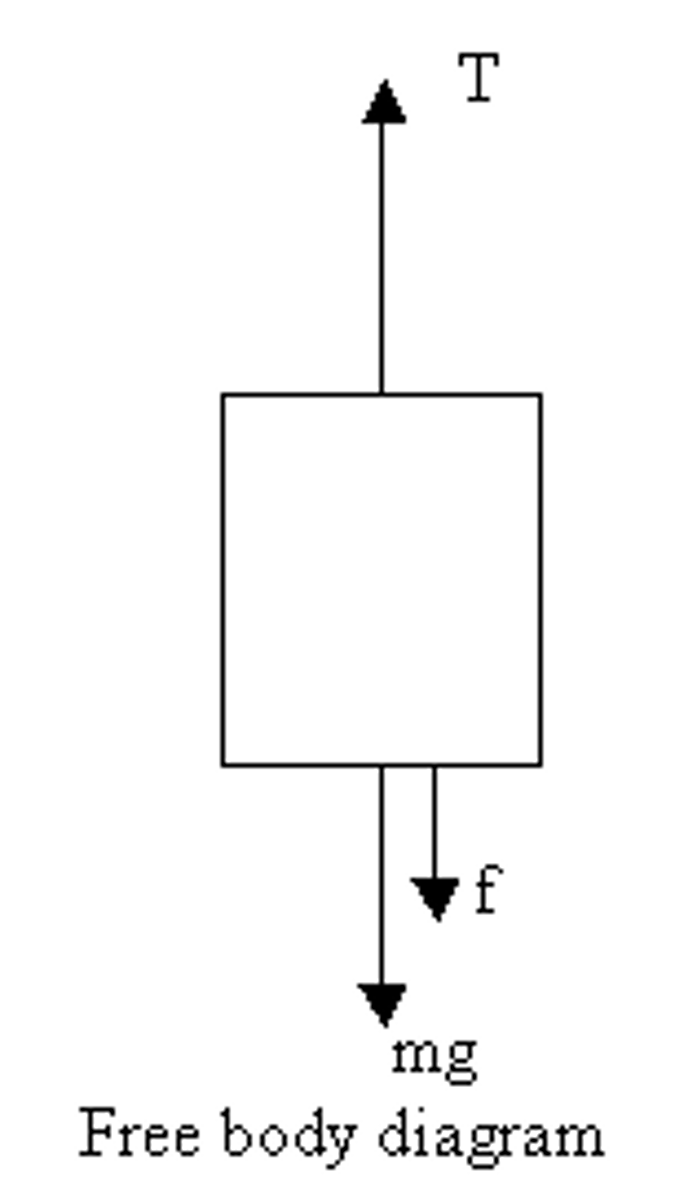
Free Body Diagram or Force Diagram
a diagram showing the magnitude and the direction of all forces acting on an object

free fall
an object's movement under the influence of only the force of gravity, where the acceleration is due to gravity (G). Examples of free fall would include an object traveling (for a moment) upward.
frequency
the inverse of period, the number of cycles or of wavelengths passing a position every second.
Measured in: Hertz (Hz)
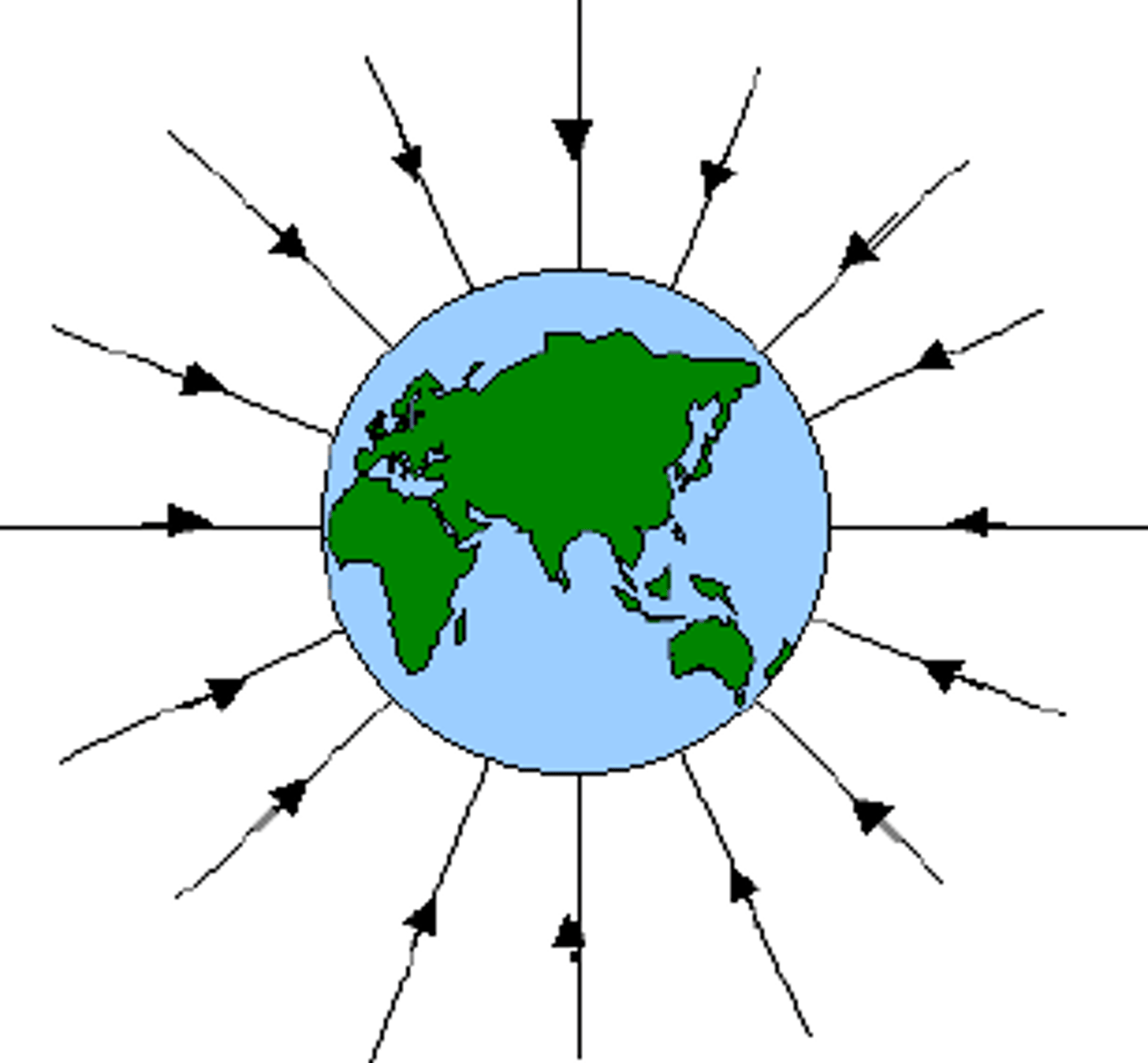
Gravitational Field
a model explaining how massive bodies exert gravitational forces on other bodies. The gravitational force created by a massive central object divided by the mass of any other object at a given distance from the center of the object
Gravitational force
the universal force existing between two objects because of their masses
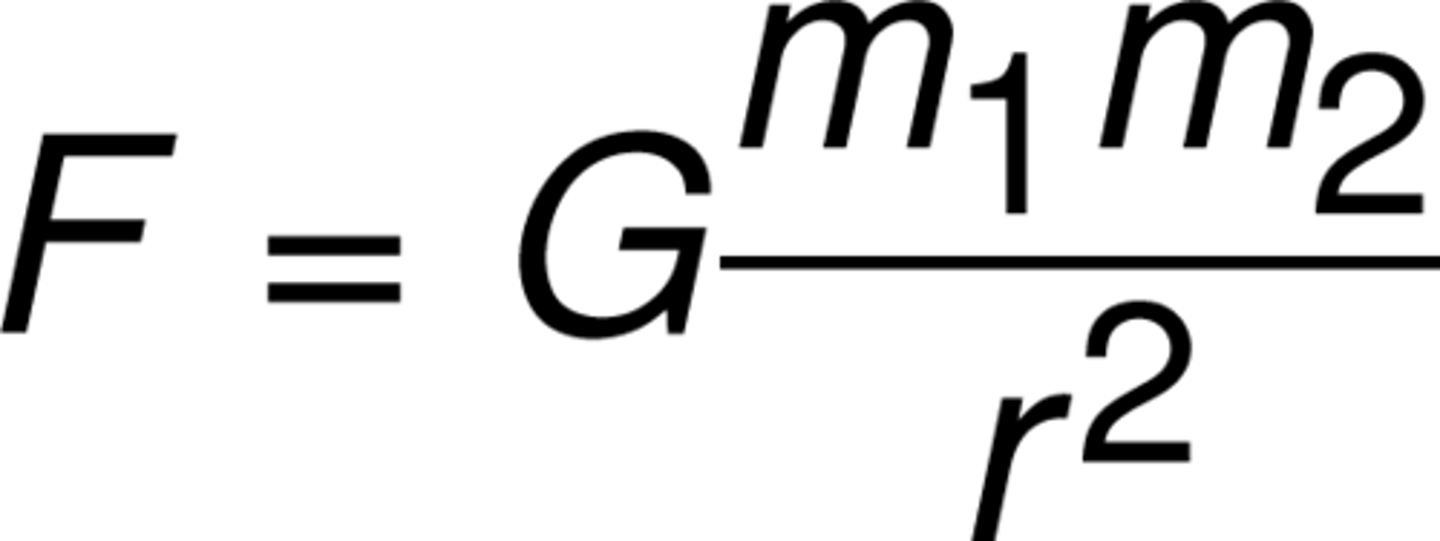
Gravitational Potential Energy
Energy related to the position of an object above or below a reference point. Can not be possessed by a single object; rather it is energy stored between two objects due to their relative positions and masses

impulse
the change in an object's momentum which is equal to the product of the net force on an object and the time interval over which the force is applied.
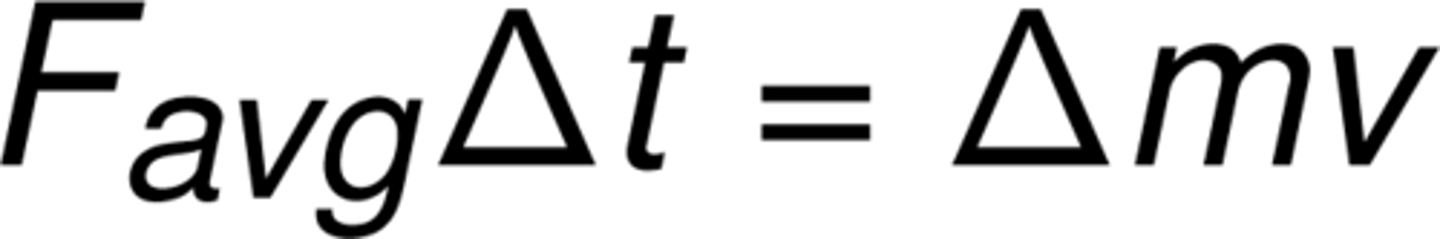
inelastic collision
when two objects collide inelastically, the momentum of the system is conserved, but kinetic energy from the system will be transferred to other non-mechanical forms (such as heat, sound or deformation of the objects).
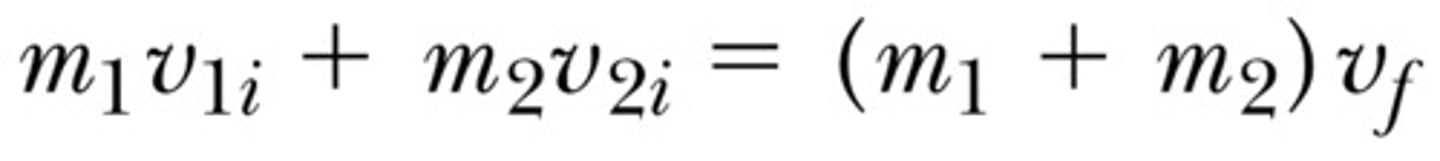
inertia
the property of an object's mass that causes it to move in a straight line at a constant velocity. It may also be thought of as the object's resistance to acceleration used in Newton's Second Law (F=ma)

interference
when two waves cross over and through each other, they will interact with one another.
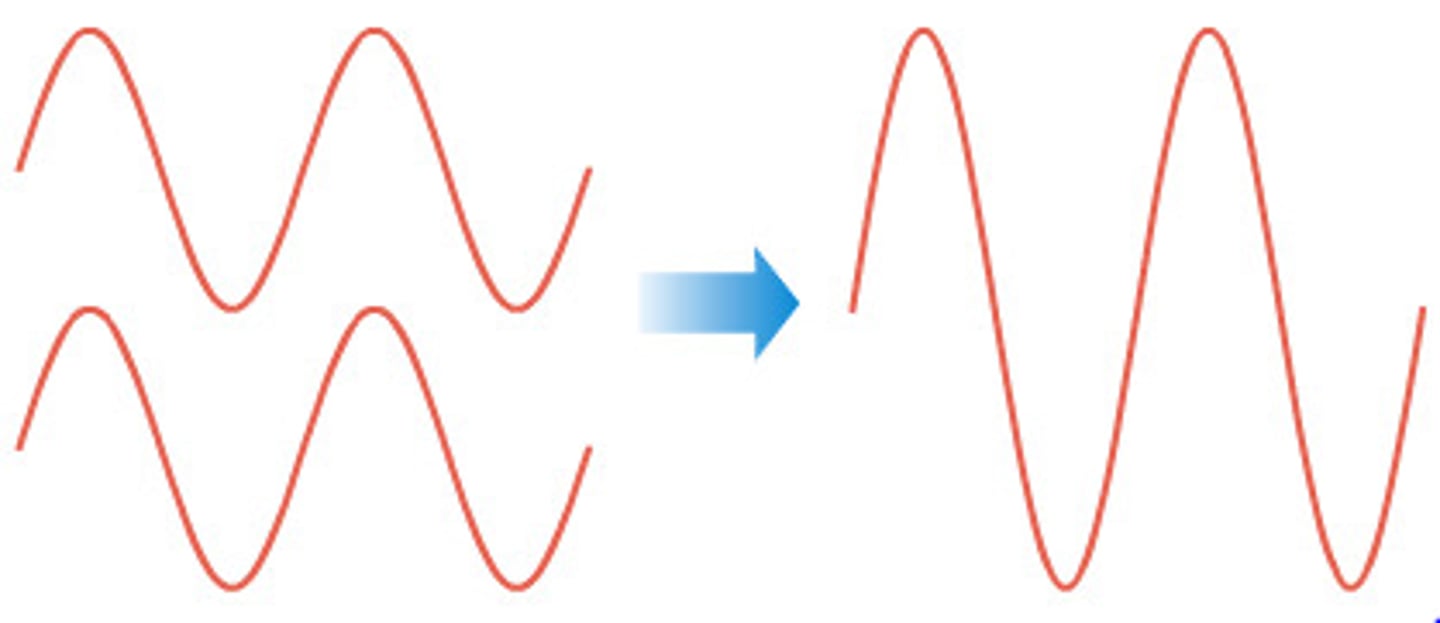
constructive interference
when the crests of two waves meet up, and they add to form (for an instant) a larger wave.
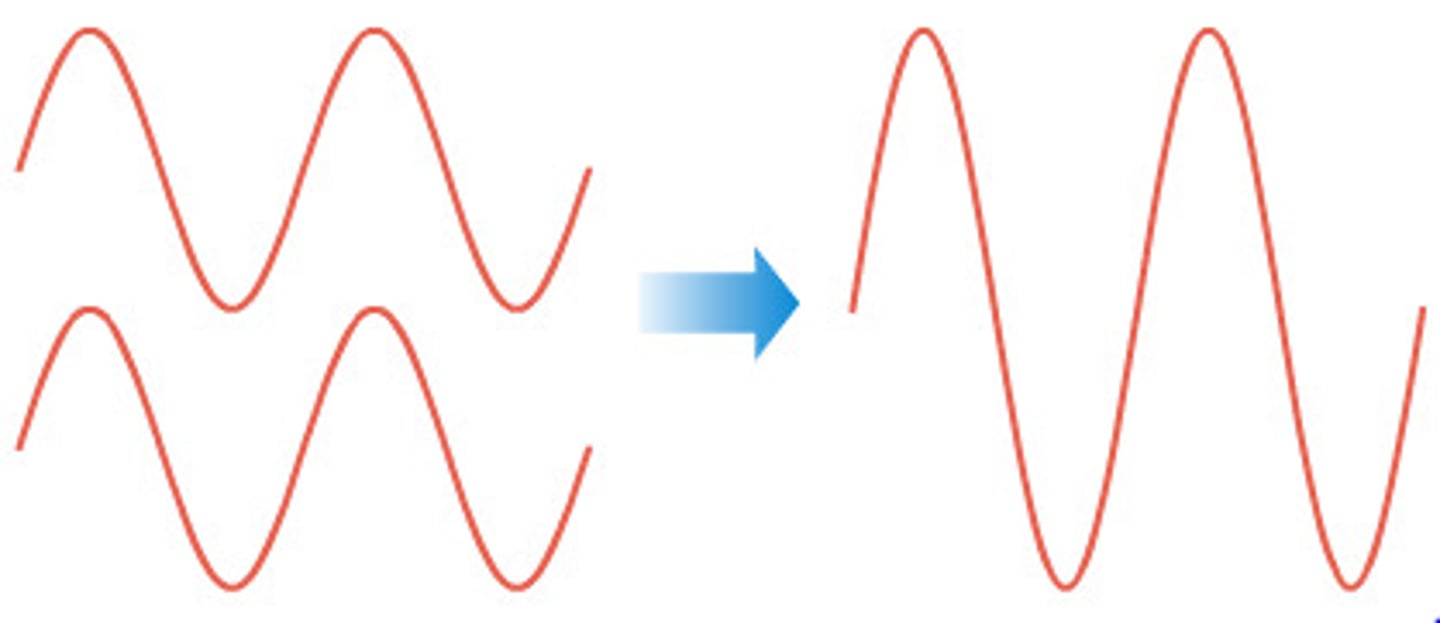
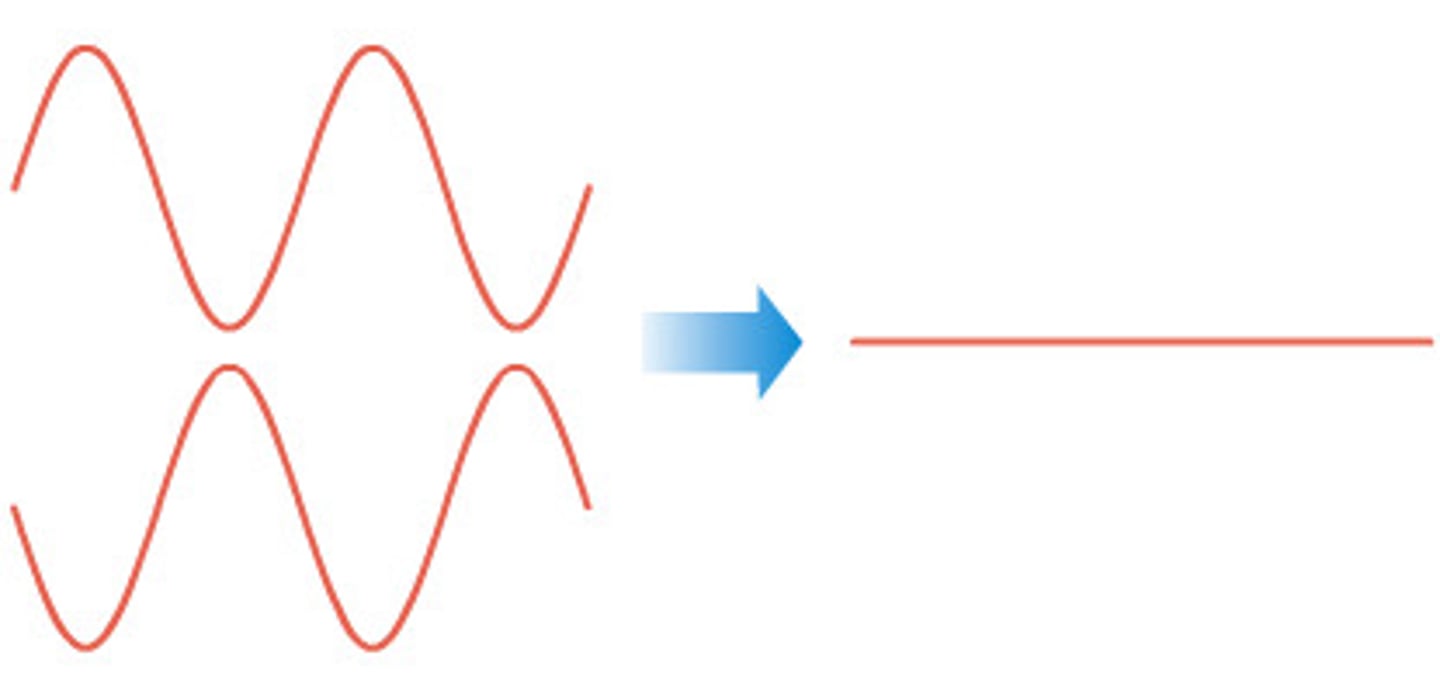
destructive interference
when the crest and a trough from two waves meet up and add to form (for an instant) a much smaller wave.
internal energy
this can have two meanings depending on the situation.
1st: microscopic, related to temperature of the object (for example a box sliding across the floor comes to stop) (heating up the box and the floor).
2nd: referencing the total stored potential energy of the system.
kinetic energy
the energy associated with the motion of an object
Measured in: Joules (J)

kinetic frictional force
a resistive force that opposes the sliding motion of an object. This force exists between the surface and the sliding object when the object is moving relative to the surface. Force is parallel to the surface and opposite to the direction of motion.
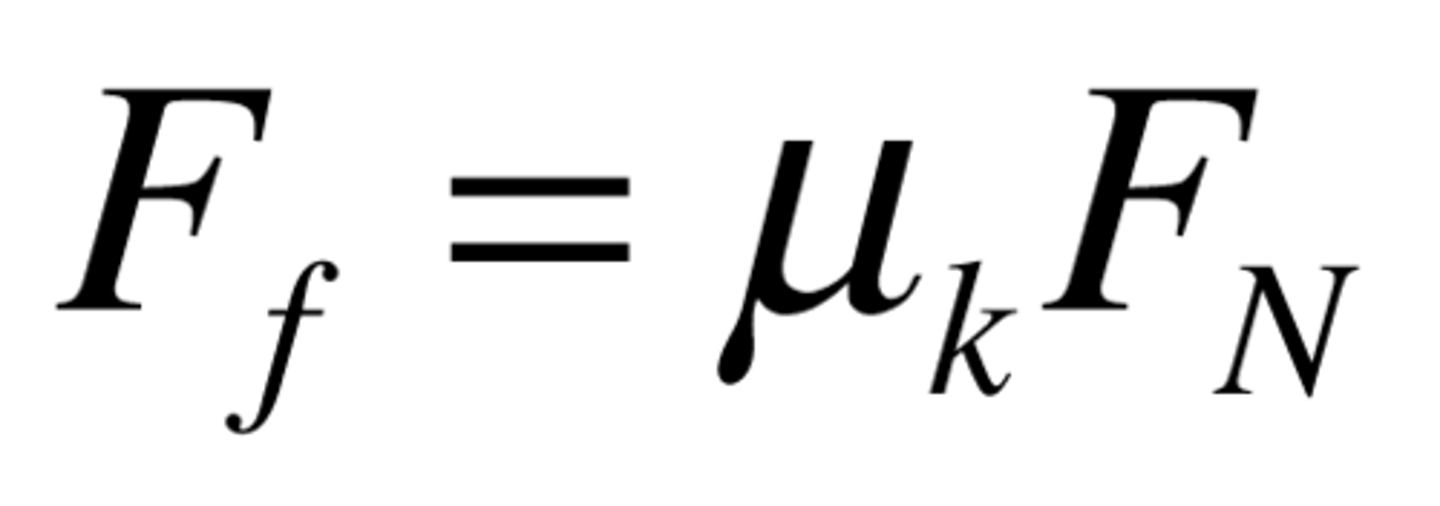
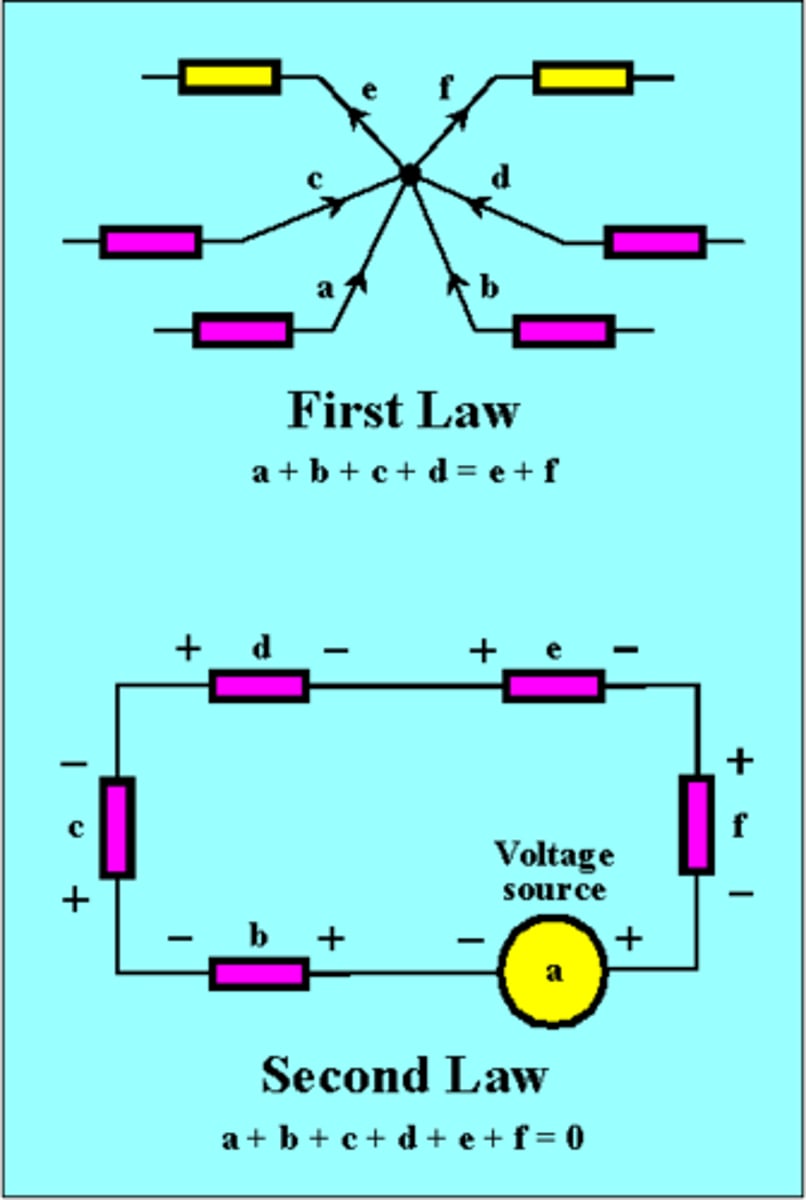
Kirchhoff's Laws
these laws are used to describe current flow and potential difference throughout DC circuits. They simplify to conservation laws, specifically conservation of energy and conservation of charge.
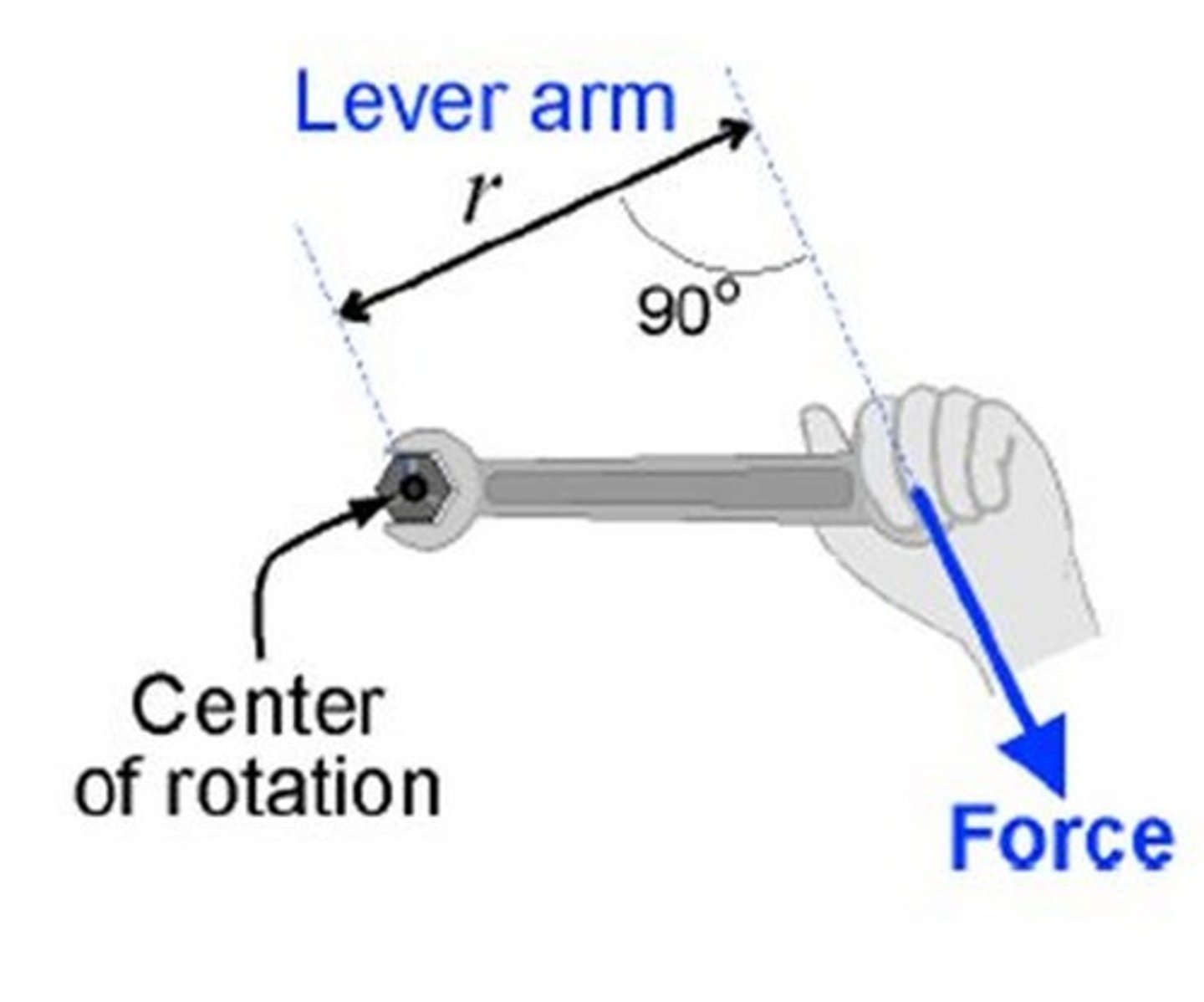
lever arm
(also called the moment arm) is a quantity used in rotating systems and is defined as the distance between the rotation point and where a given force is applied
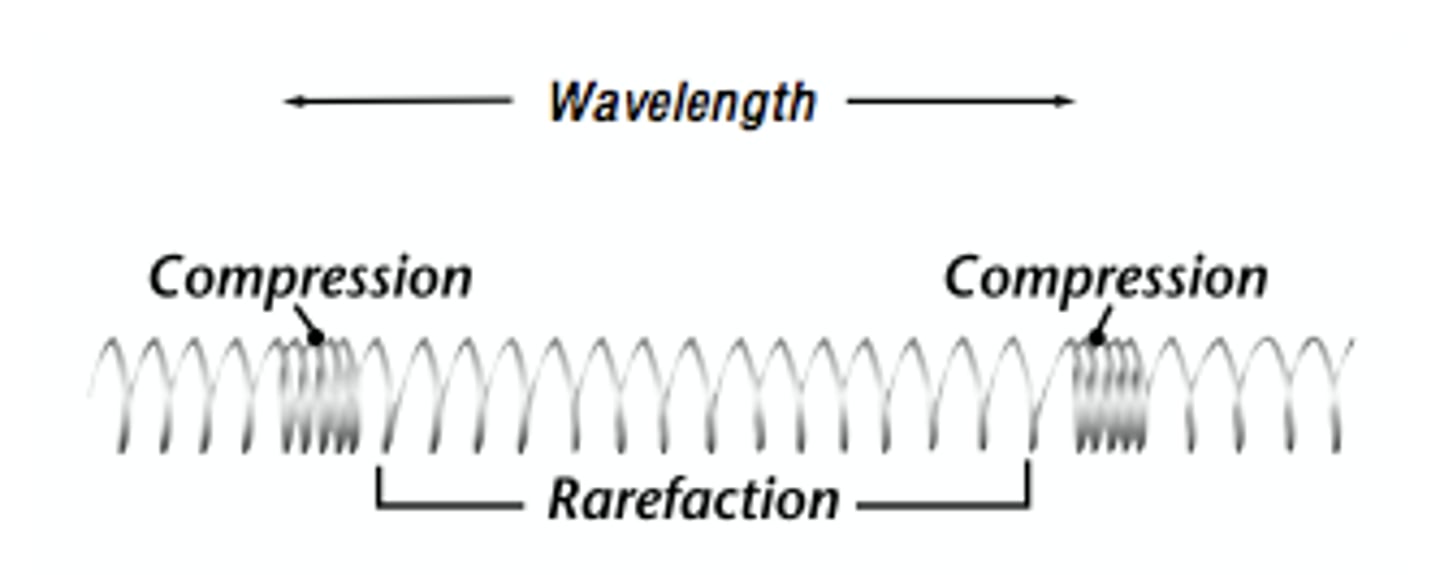
longitudinal wave
carries energy by vibrating the particles of the medium parallel to the direction that the energy is being carried through the medium
mass
the amount of matter in an object and will be the same no matter where you travel in the universe
Measured in: Kilograms (kg)

mechanical energy
the sum of the kinetic and potential energies of a system. Deals with the energy associated with an object's motion and relative position within a system
momentum
the product of its mass and velocity. It is a vector quantity. Always the same direction as the object's velocity.
Measured in: kg x m/s
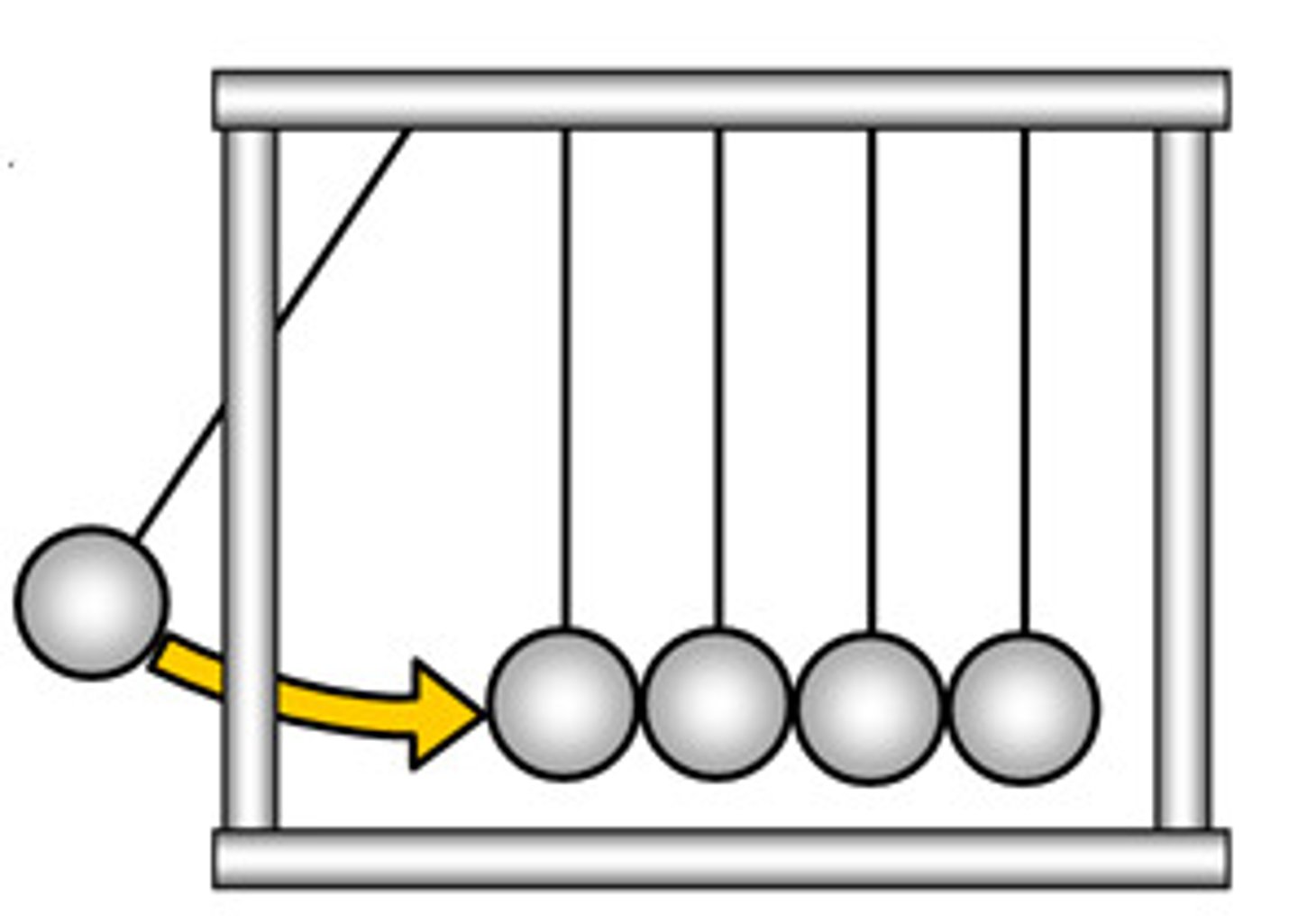
Newton's First Law of Motion
Also called the Law of Inertia, states that an object at rest will remain at rest, and an object in motion will remain in motion, at a constant velocity, unless acted on by an outside force.
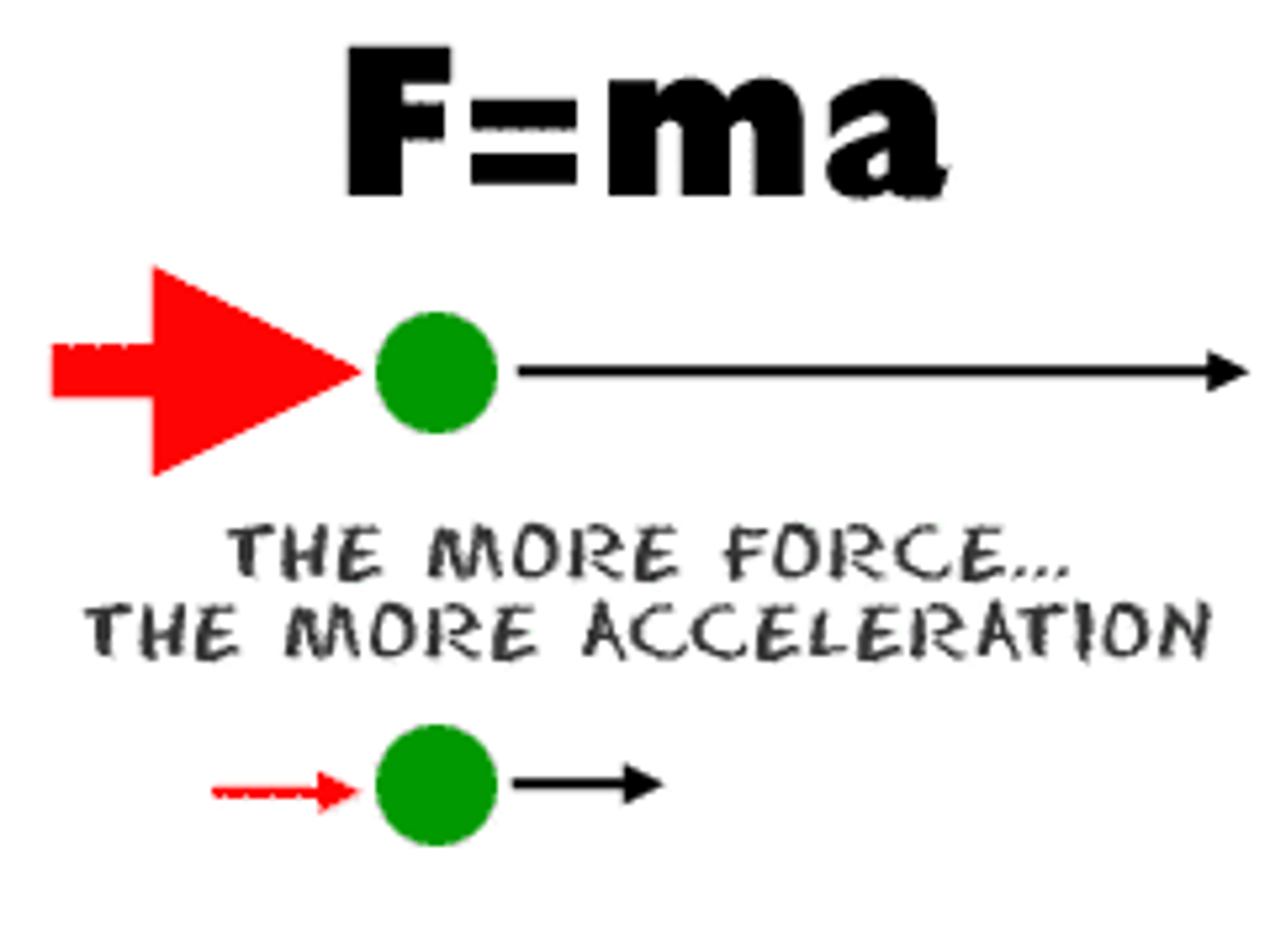
Newton's Second Las of Motion
This law states that the net force (or the total force) on an object will cause an acceleration that is proportional to the force and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. This acceleration is always in the direction of the net force. For any system of constant mass, a larger net force will produce a larger acceleration. With a given net force, the resulting acceleration will be less for a more massive object.
Newton's Third Law of Motion
This law states that every action has an equal an opposite reaction. In other words, the force that object A exerts on object B is the same size and in the opposite direction to the force that object B exerts on object A. Action-reaction pairs act on different objects and NEVER cancel out.

nodes
The stationary point(s) on a standing wave where the amplitude is a minimum.
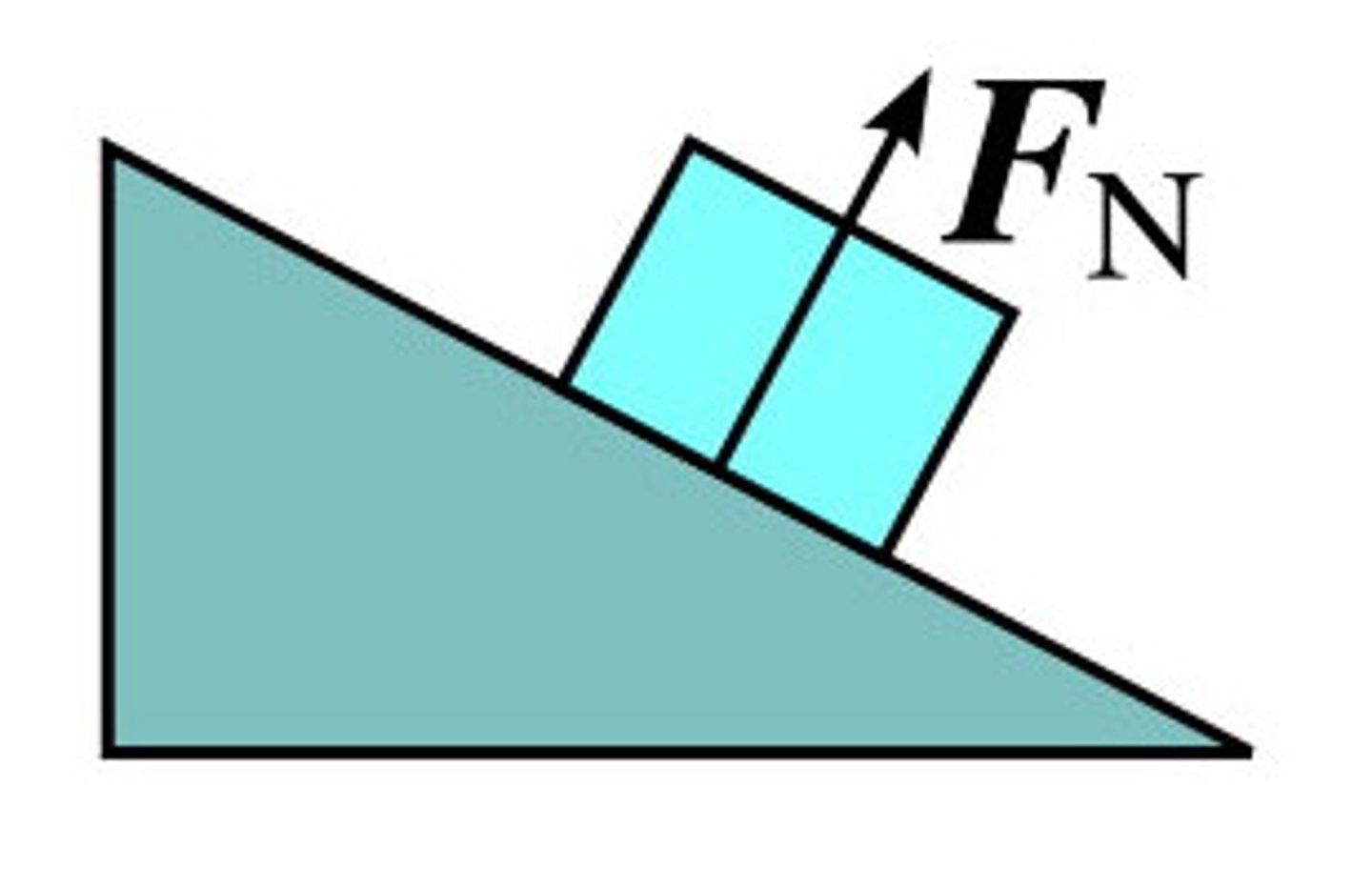
normal force
a contact force existing between two objects that keeps one object from invading another object's space. Normal means perpendicular, and the normal force, by extension, is a force perpendicular to a surface.
object
a physical body of collection of matter

parallel
circuit elements are connected where the path for the current splits and then comes back together. Elements connected will have the same potential difference across them.
period
the time for a complete cycle or the time for a full wavelength to pass a position.
Measured in: Seconds (s)
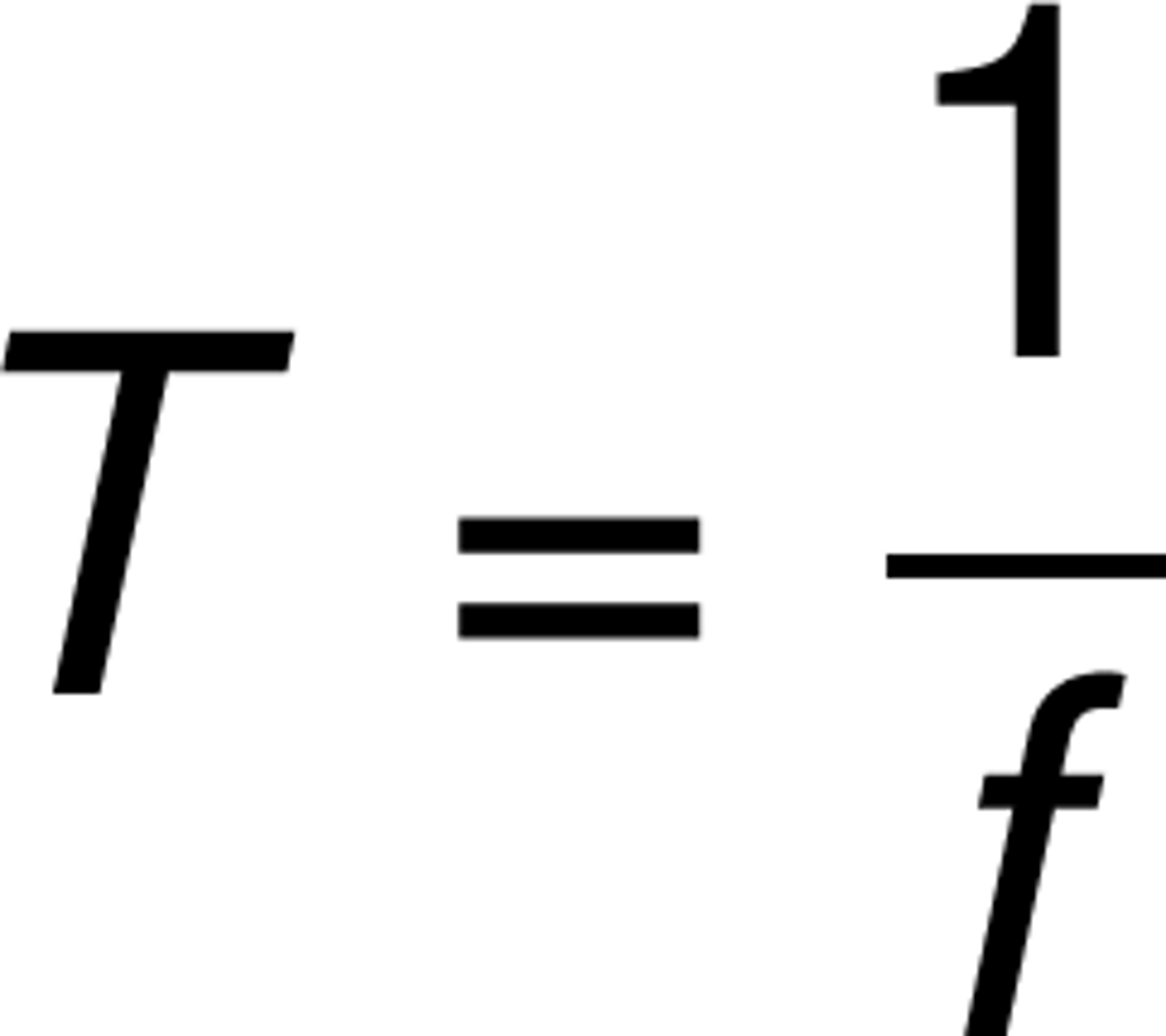
position
the location of an object is relative to a chosen or given coordinate system.
Measured in: meters (m)
power
the rate at which work is done, or energy is used per second. This can be simplified to the product of force and velocity.
Measured in: Joules/seconds or Watts (W)
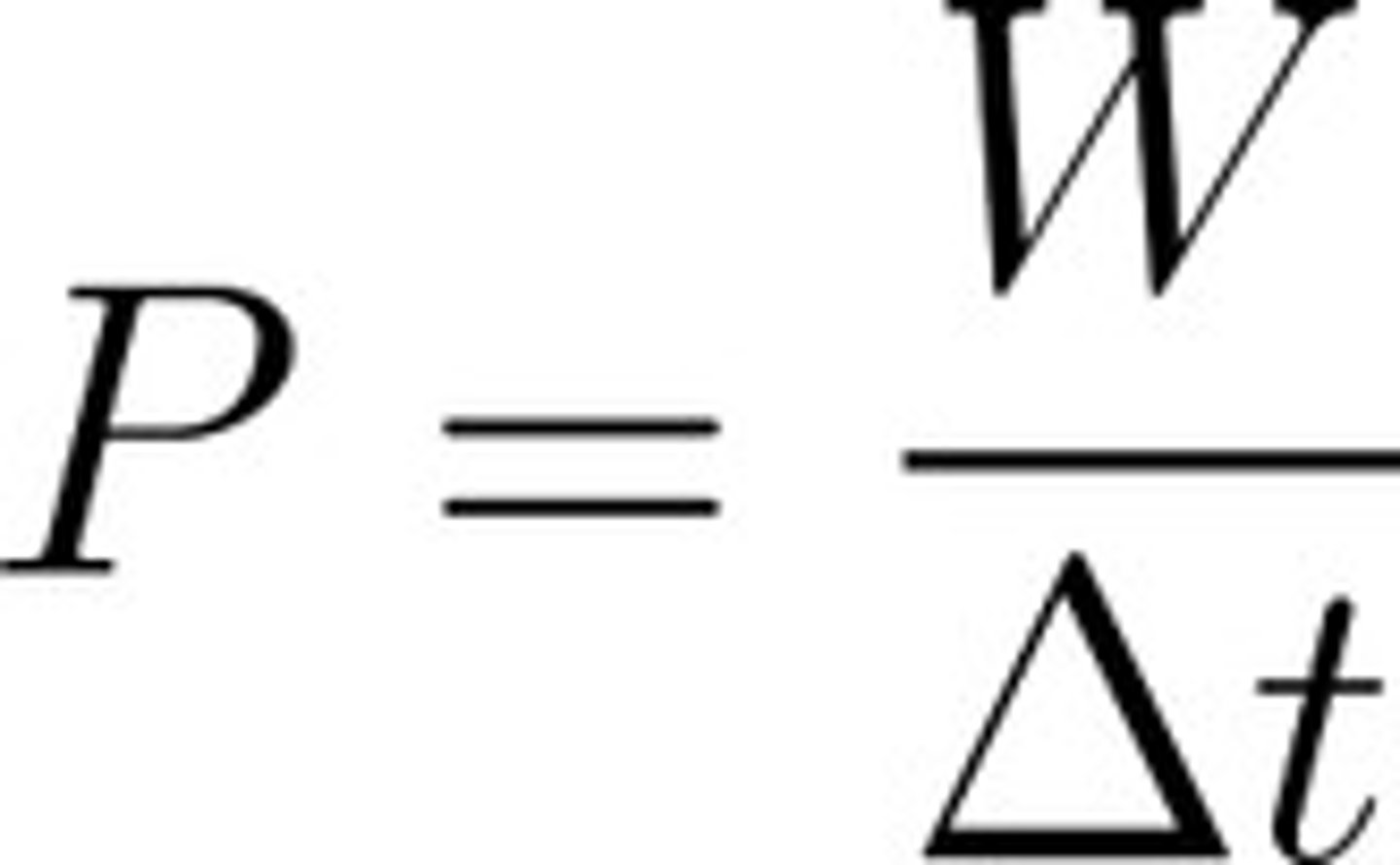
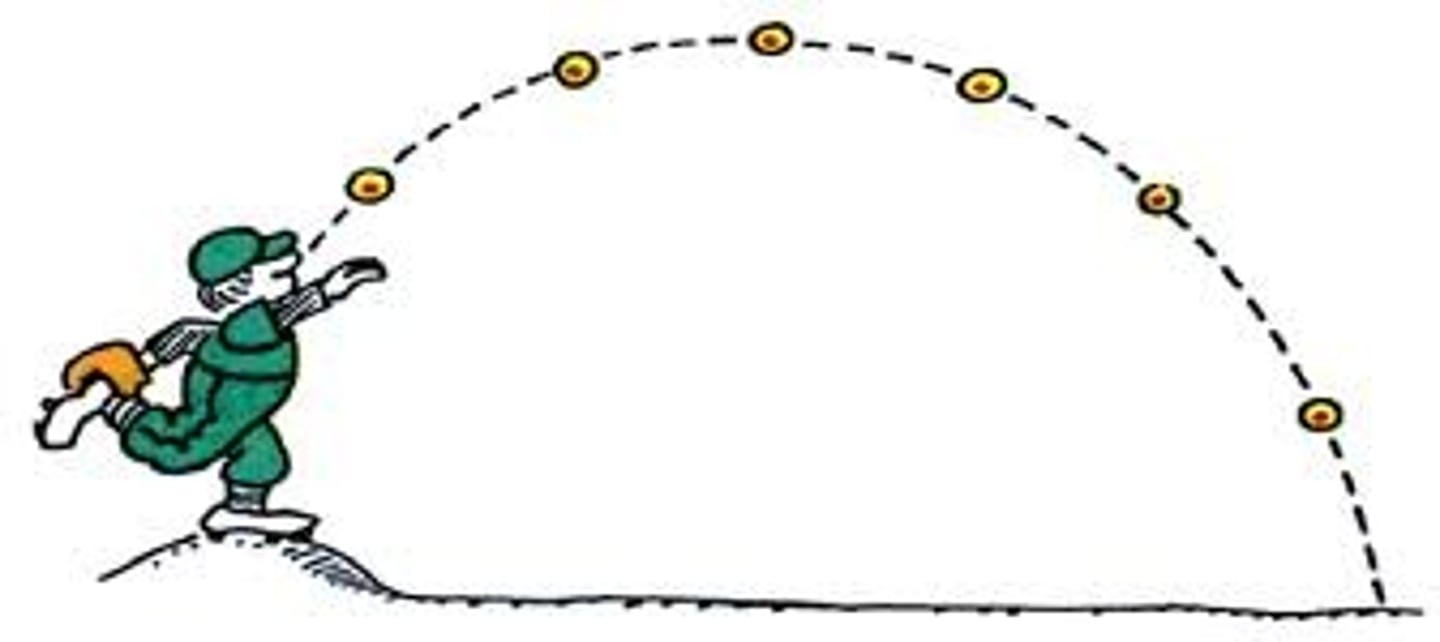
projectile motion
an object in free fall that also has a horizontal component of motion, so that it travels horizontally with a constant velocity while undergoing an acceleration at the same time.
resistance
the opposition to the flow of electric charge through a circuit element. Can be affected by the material, the length, area, or temperature through which the charge flows.
Measured in: Ohms
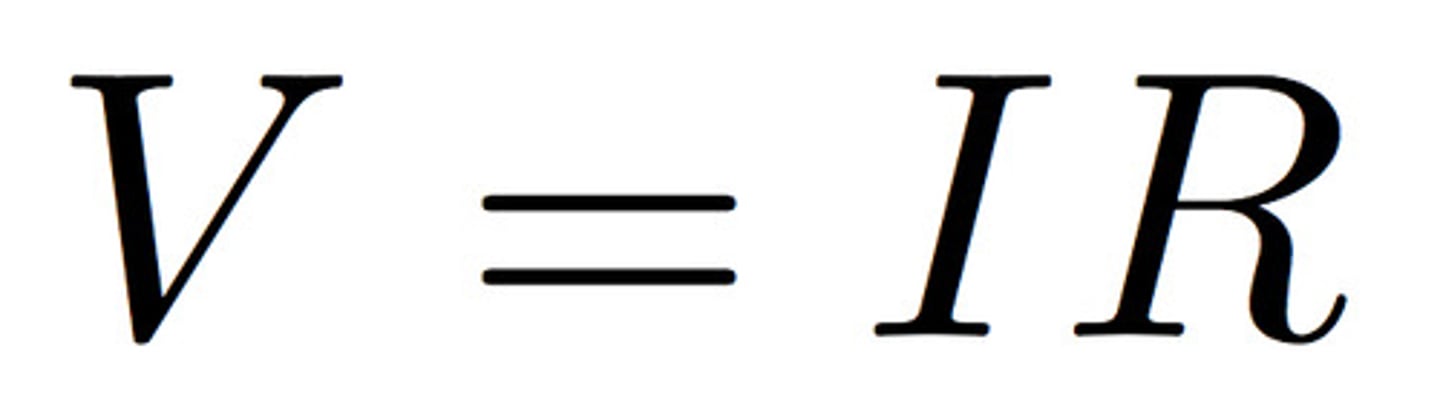
resistivity
the property of a material that tells us what the resistance would be of a cubic meter of that material. Based on the physical dimensions and material of an object.
Measured in: Ohm meters
restoring force
any force that pushes an object back toward an equilibrium posistion
rotational acceleration
analogous to liner acceleration. It is the rate of change of angular velocity
Measured in: radians /s^2

rotational displacement
analogous to liner displacement, it is how many radians an object has rotated through as it rotates.
Measured in: radians
rotational inertia
also called the moment of inertia. It is a scalar that is dependent on the mass of the object and how that mass is arranged. It is the measure of an object's resistance to a change in its rotation around a given pivot point
Measured in: kg x m^2
rotational kinetic energy
the energy associated with the rotational motion of an object. It is proportional to an object's moment of inertia times the square of the angular velocity
Measured in: Joules (J)
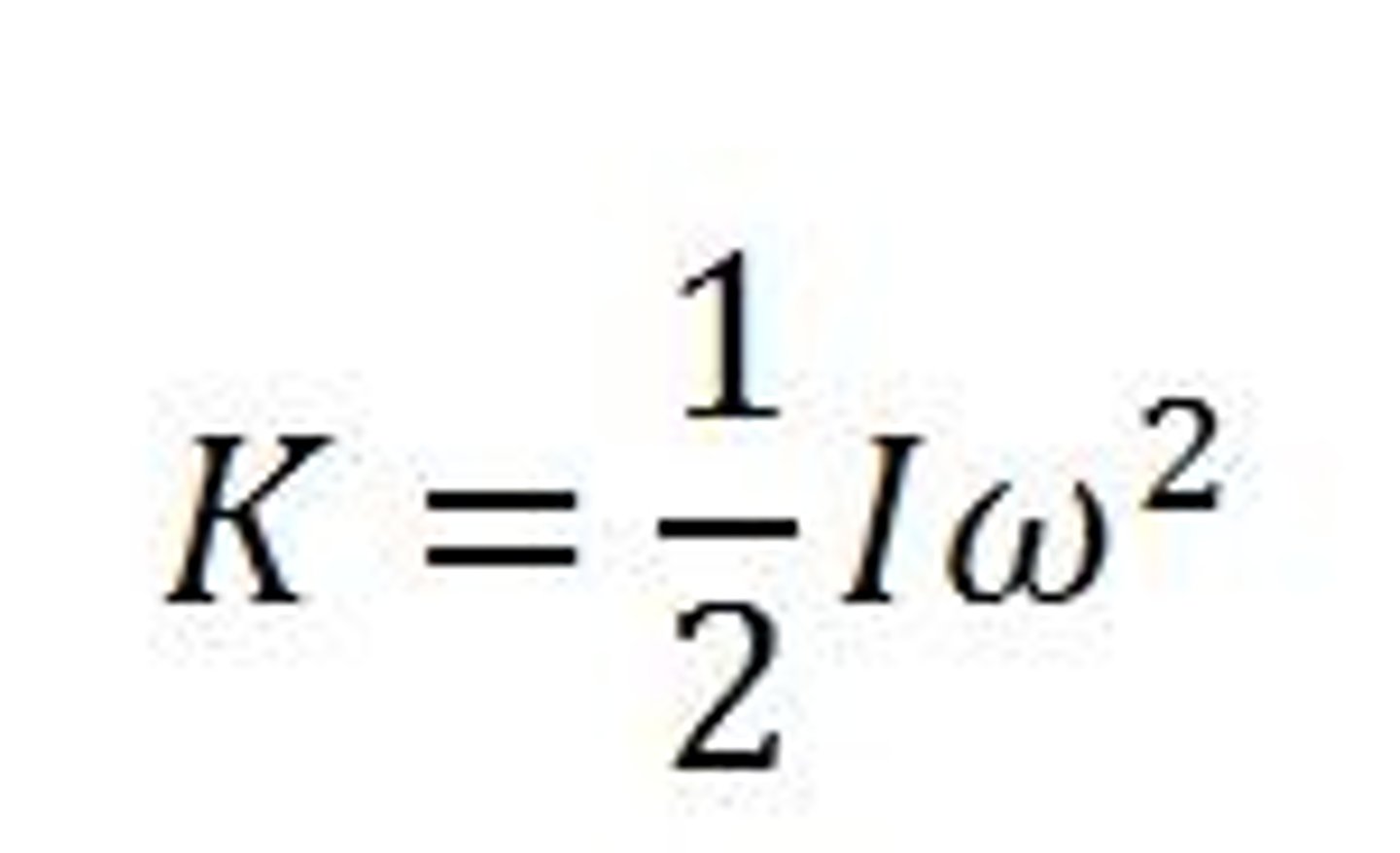
rotational velocity
the rate of change of angular position
Measured in: radians / s
scalar
a number without direction. This quantity has magnitude only

series
circuit elements connected in series form a single path for the current to flow through
speed
the distance traveled per unit of time. Scalar quantity and is a measurement of how fast an object is going but does not indicate direction
Measured in: m/s
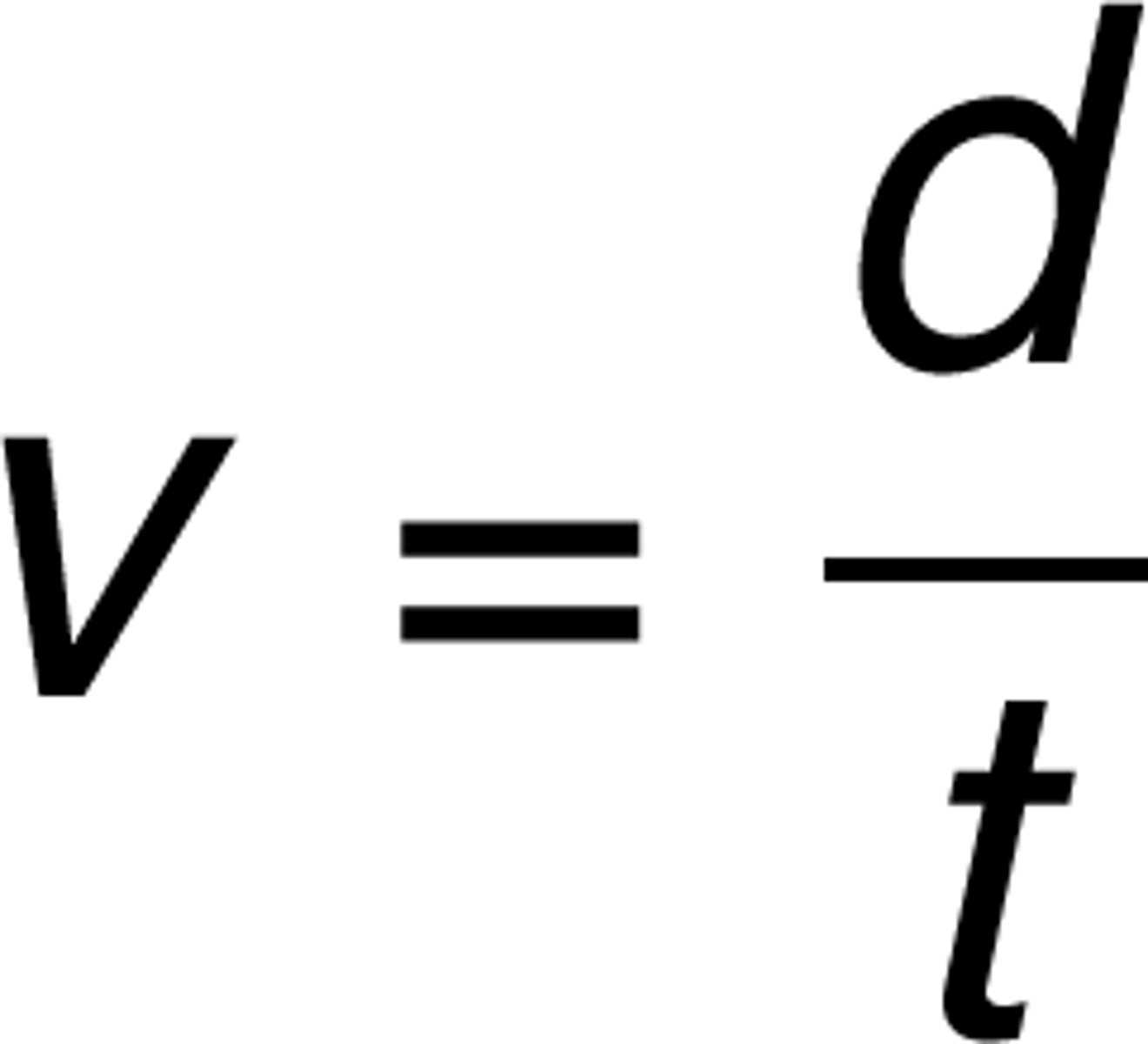
spring constant
tells us how stiff or tough a spring is; the larger the k value for a spring, the more difficult it is to stretch that spring
Measured in: N/m

spring force
the force exerted on an object by a compressed or stretched spring. It is a restoring force, which means it is oriented towards equilibrium
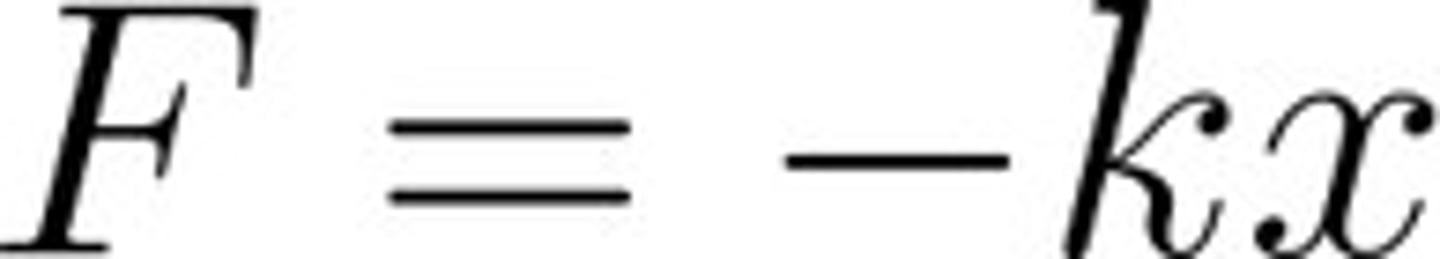
Hooke's Law spring
a special spring where the restoring force is proportional to the distance the spring is stretched or squished
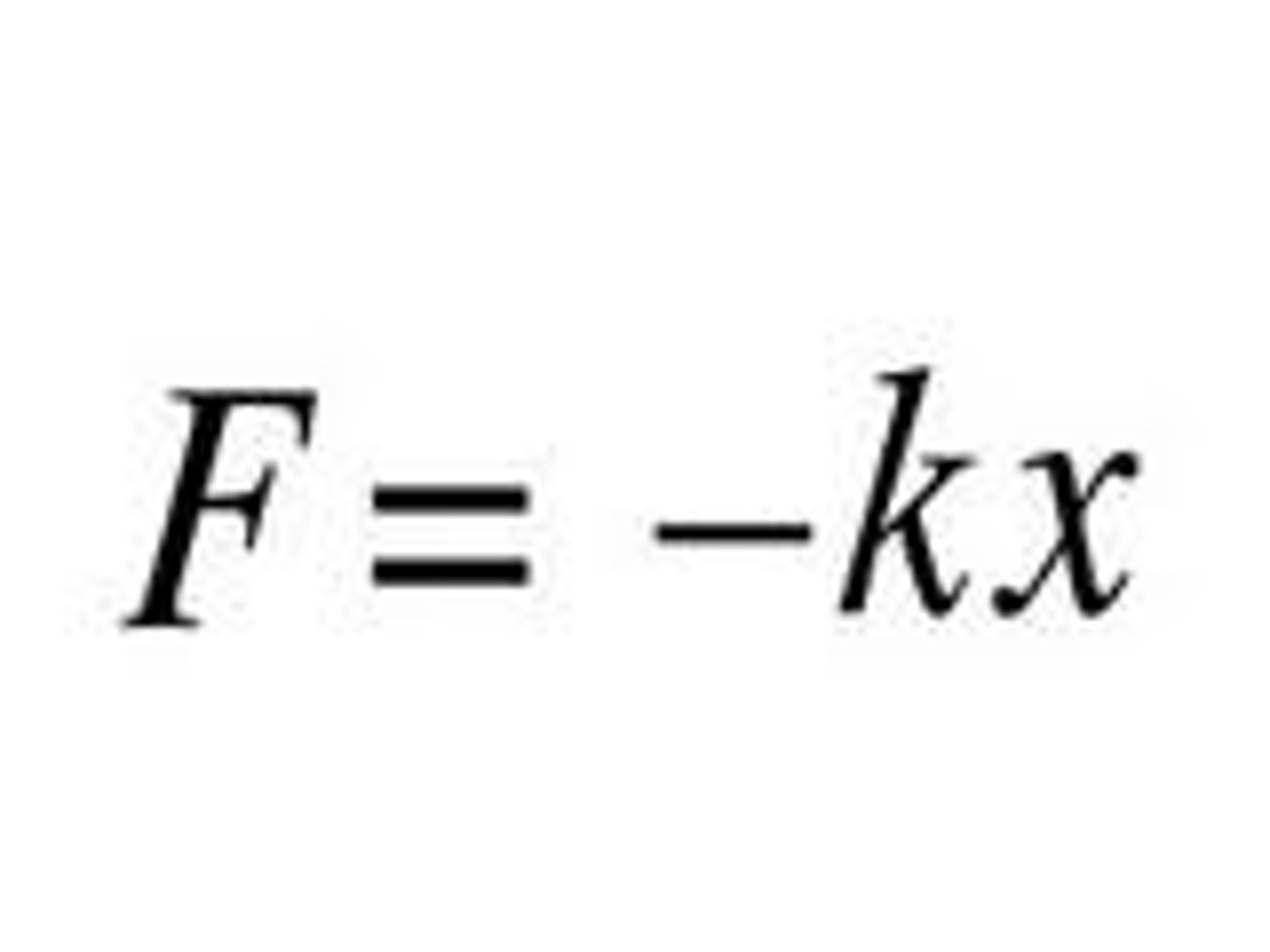
spring potential energy
also known as elastic potential energy. This energy is equivalent to the work done to deform the elastic object, such as a spring, and occurs when it is stretched or compressed and is related to the spring's relative displacement. Stored between the spring and the object
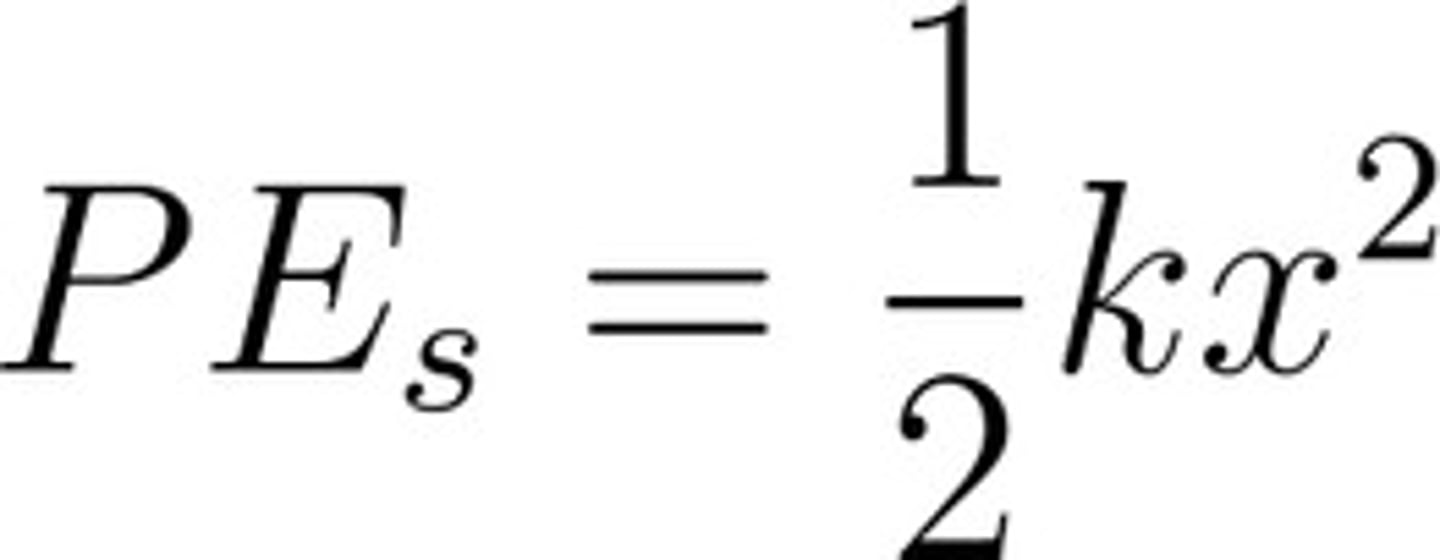
standing waves
a wave that appears to stay in one place on a string instead of moving up and down the string. Formed from interference.
static frictional force
a resistive force that opposes the sliding motion of an object. This force exists between the surface and the sliding object when the object is at rest relative to the surface. Parallel to the surface and opposite to the direction of motion.
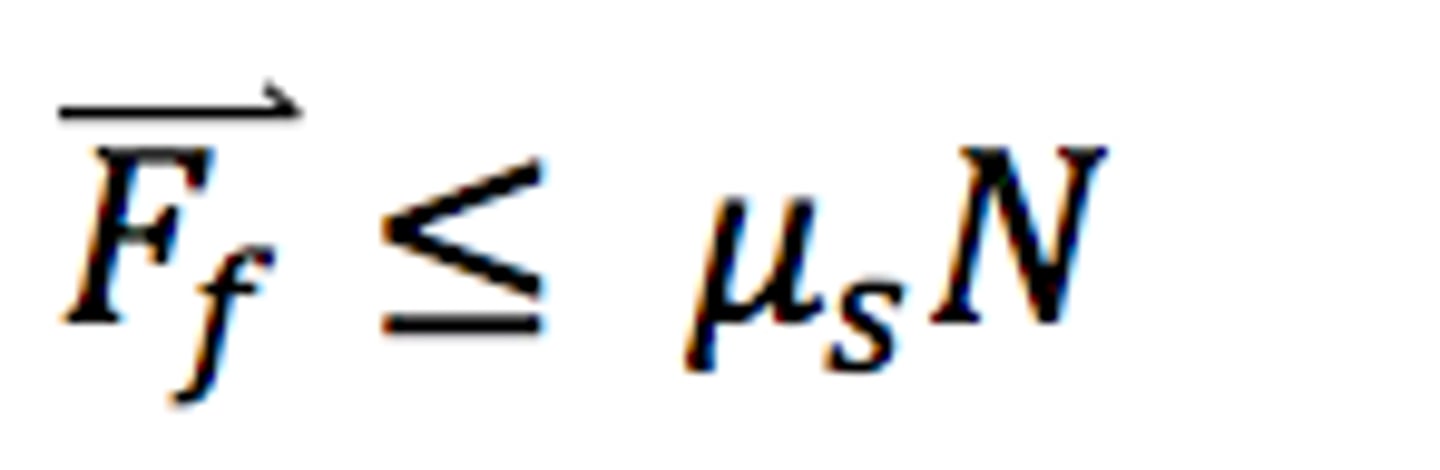
superposition
the principle that allows us to add and subtract waves forms that constructively or destructively interfere with one another
system
a group of objects that can be treated as a single object
tension
a pulling force exerted by a string or a rope. This force is transmitted through the string when the string is pulled at both ends. The force is directed along the string and pulls equally on the objects on either end of the string.
torque
tells us how much rotational acceleration will be caused when a certain force is applied at a given distance from the axis of rotation.
Measured in: N x m (not joules)
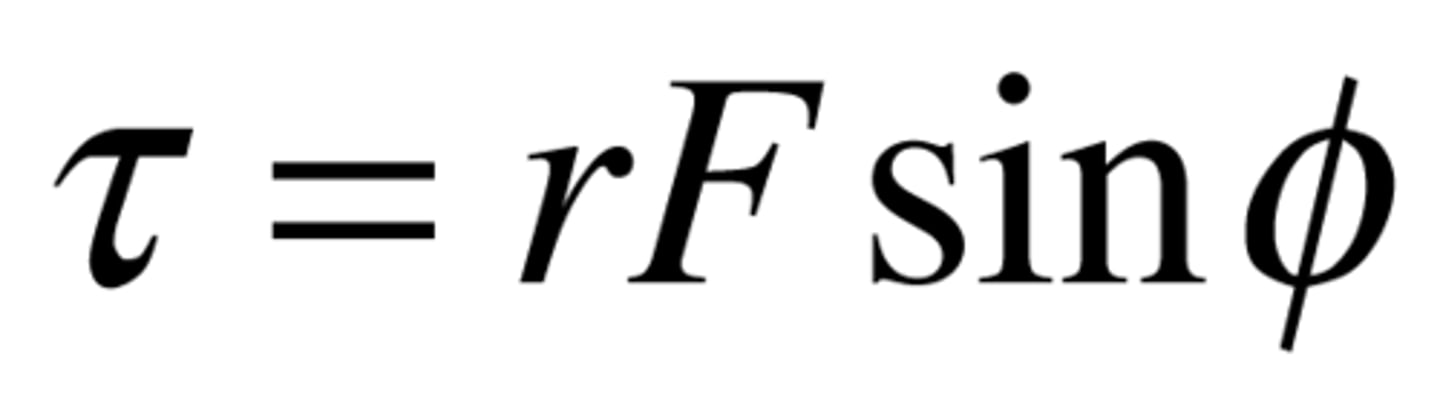
translational kinetic energy
the energy that is associated with translational motion, which occurs when an object's center of mass moves. It is proportional to an object's mass times the square of the velocity
transverse wave
a wave that carries energy by vibrating the particles of the medium perpendicular to the direction that the energy is being carried through the medium
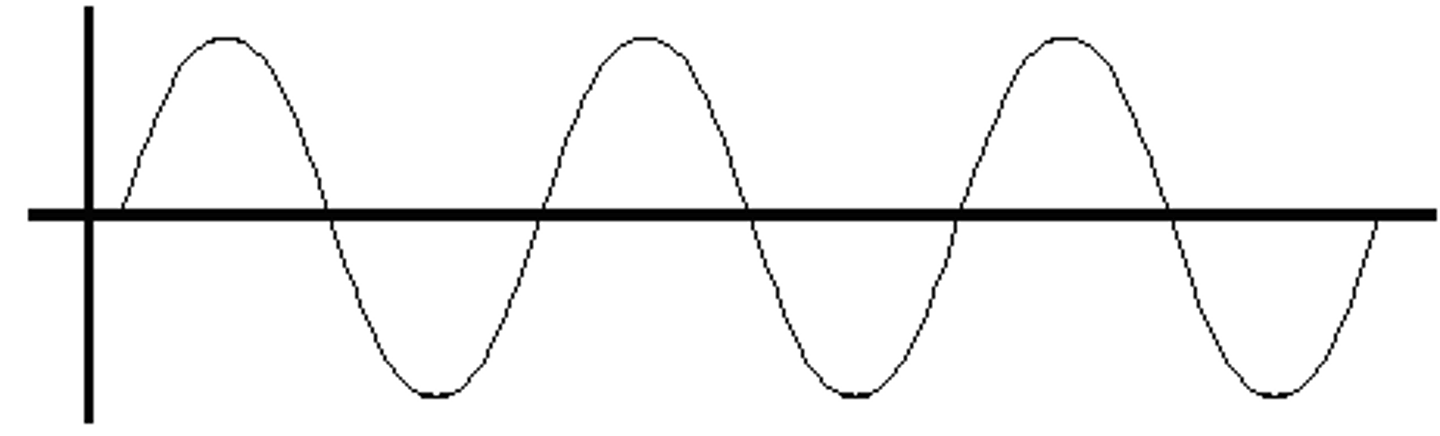
Universal Gravitational Constant
G is equal to 6.67 X 10^-11 N(m^2)/kg^2
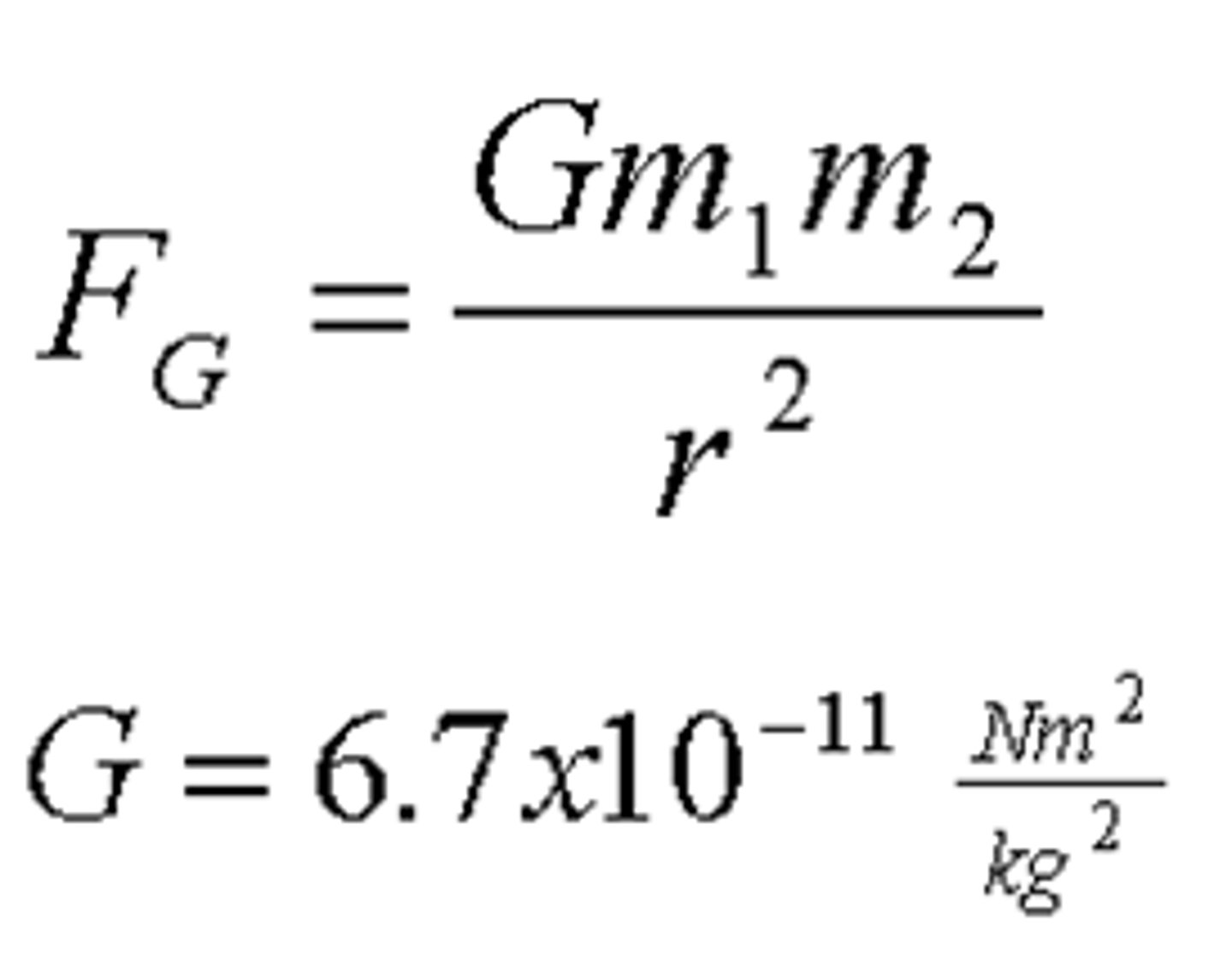
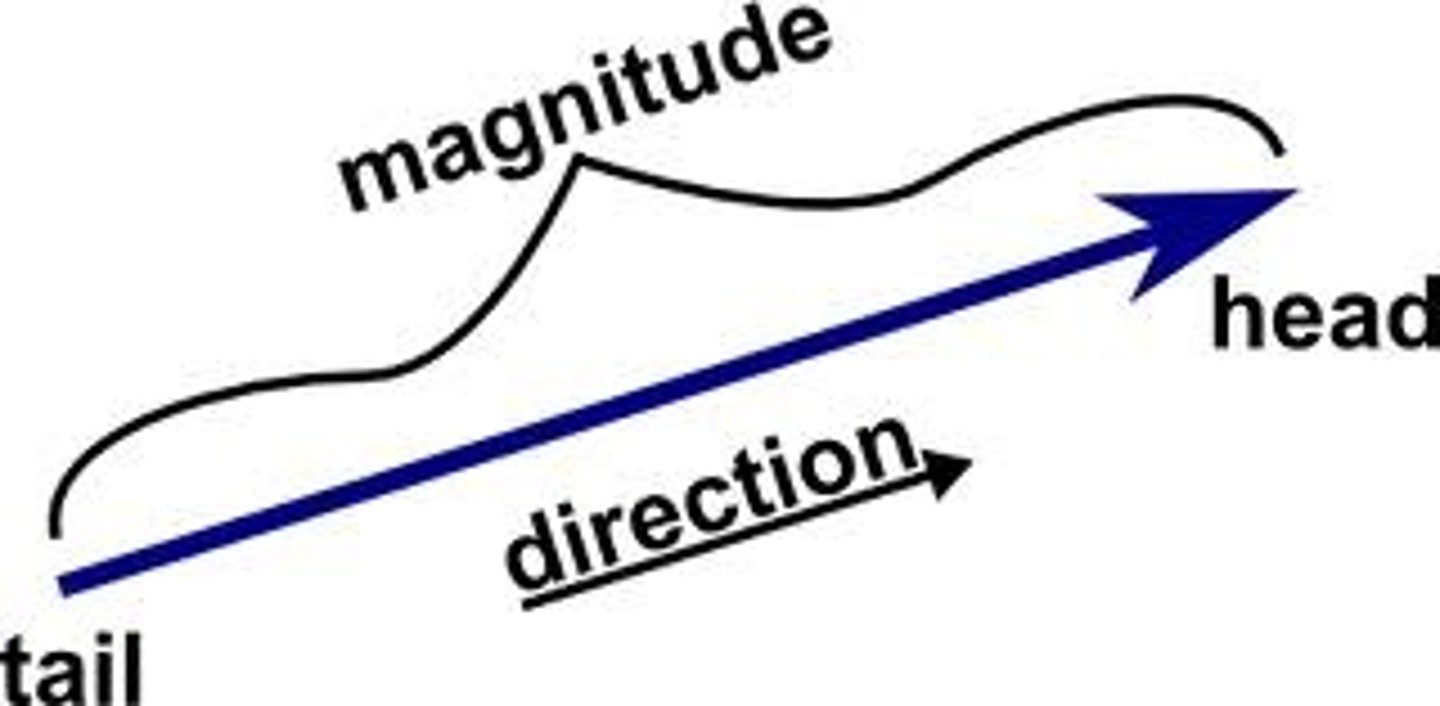
vector
a quantity that has magnitude and direction
velocity
the rate of change of displacement. It is a vector. It tells how fast something moves and the direction in which it moves.
Measured in: m/s
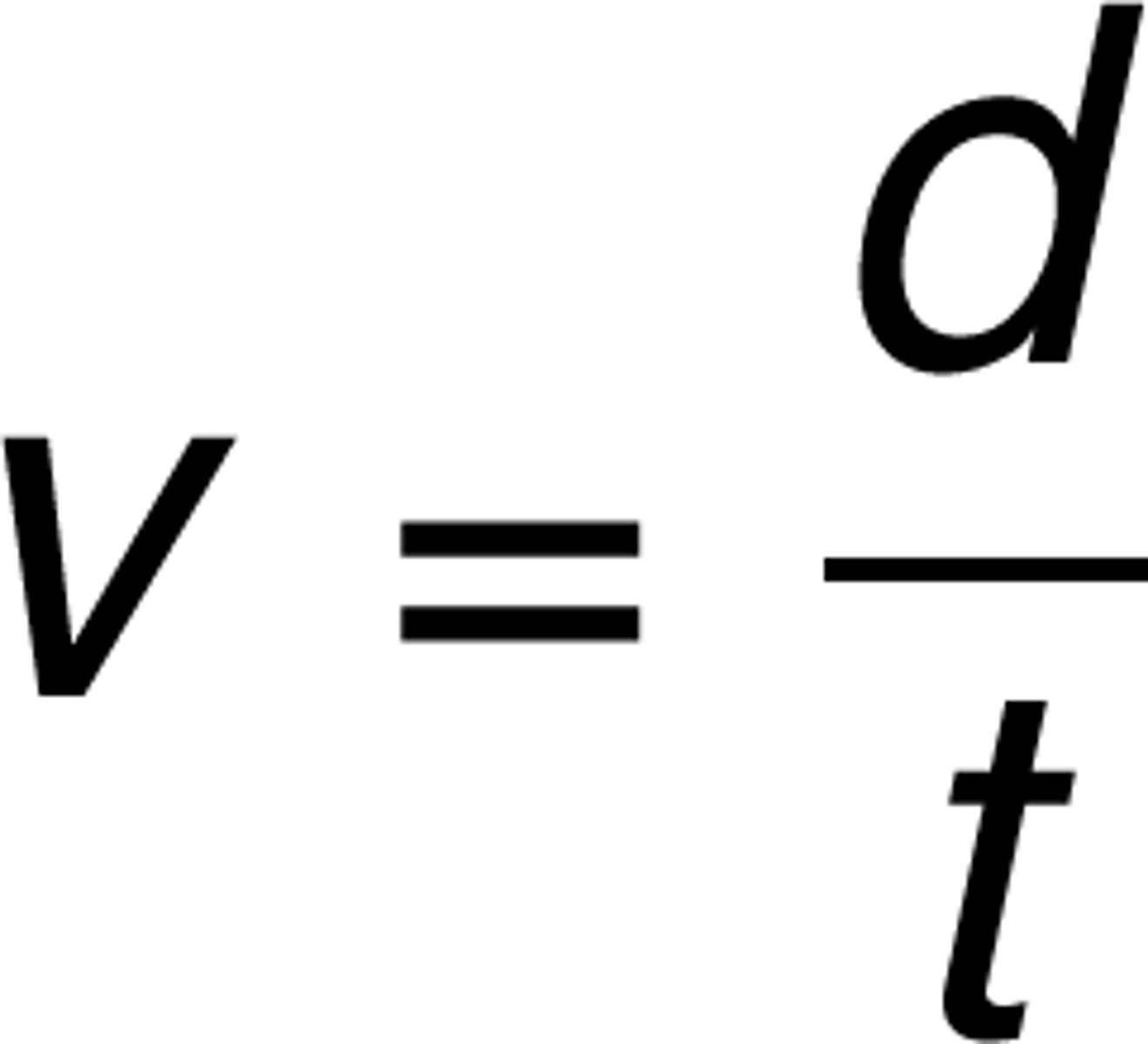
voltage
a measurement of the electrical potential energy per coulomb of charge. It is related to the amount of work done to move a charge through an electric field.
Measured in: Volts (V)

wave
a disturbance in a medium. The disturbance carries energy through the medium without permanetly disturbing the matter in the medium
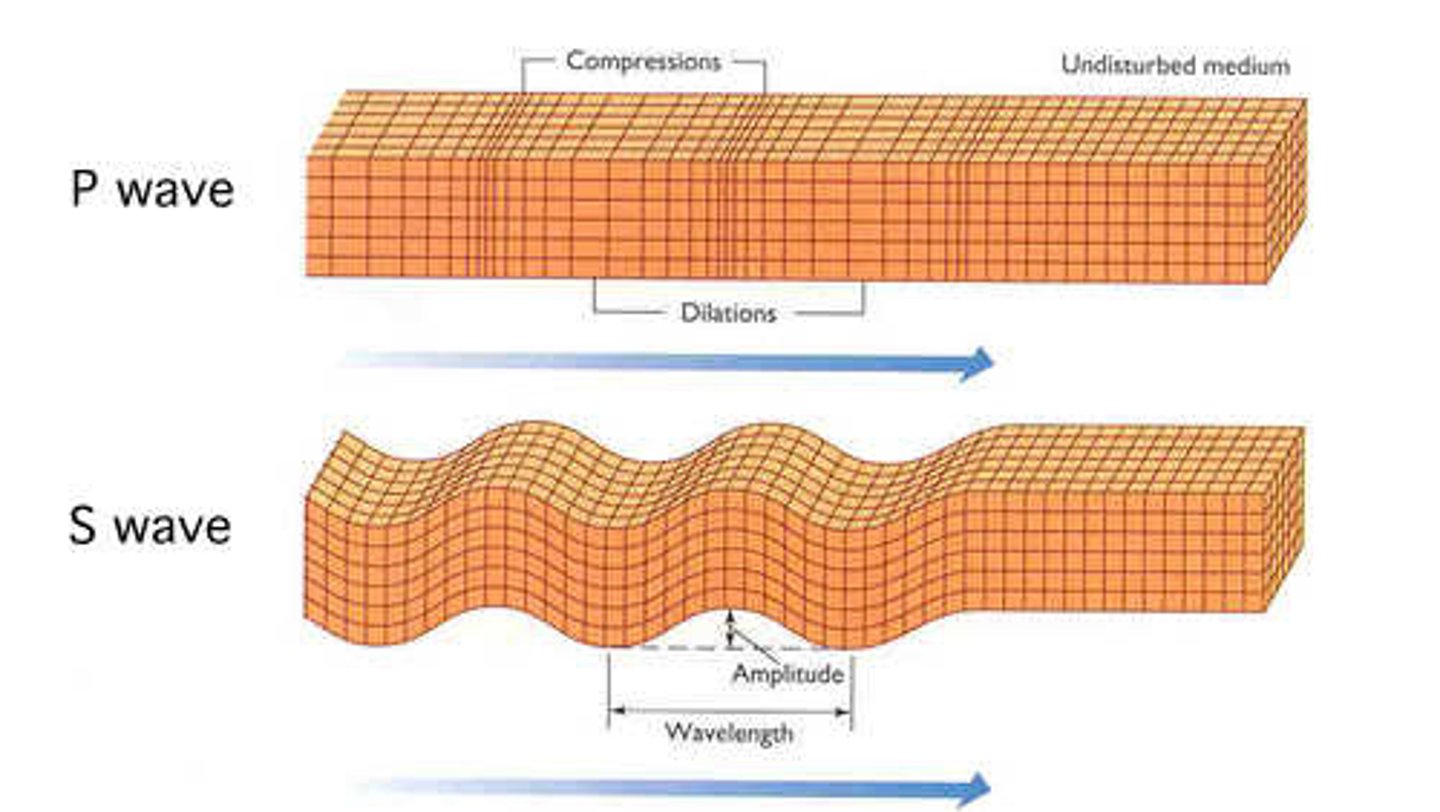
wavelength
the measured distance from peak to peak, or trough to trough, on a wave.
Measured in: meters (m)

weight
the force of gravity on an object. This is different that mass. How much the Earth pulls on that mass.
Measured in: Newtons (N)

work
the change in energy of a system. Equal to the net force acting on an object times the distance over which that force is applied.
Measured in: Joules or Newtons x meters

Work Energy Theorem
when a net force works on an object, it causes the kinetic energy of the object to change. The amount of work done on the object is equivalent to the change in the object's kinetic energy.