Appendicular System -- bones, joints, fractures
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
appendicular skeleton
126 bones
limbs
shoulder and pelvic girdles
bone functions
attachment for muscles
mechanical basis for movement
protection of internal organs
support frame for body
storage for calcium, phosphorus, and other salts
production of red and white blood cells
classification of bones
long, irregular, short, and flat bones
long bones
limbs
compact bones
spongy bones
periosteum
only bones found in appendicular system/limbs
consist of body and two enlarged articular ends
irregular bones
limbs
peculiar shape (vertebrae, facial bones, and pelvic bones)
short bones
carpal and tarsal bones
consist mainly of cancellous bone with a thin outer layer of compact bone
flat bones
calvarium, sternum, ribs, and scapulae
consist of two plates of compact bone
middle layer of cancellous bone called diploe
sesamoid bones
very small and oval
develop inside and beside tendons
protect the tendon from excessive wear
largest is patella
general bone features
bone marrow produces red and white blood cells and is also really sensitive to radiation
yellow marrow stores fat cells
medullary cavity
periosteum
endosteum
medullary cavity
central cavity of long bones
contains trabeculae filled with yellow marrow (important to see during an x-ray, meaning it was properly exposed)
red marrow found in the ends of long bones
periosteum
tough, fibrous connective tissues that covers bone, except at articular ends
endosteum
lines marrow cavity and helps with growth and repair of bone
ossification
term that applies to the development and formation of bones
begins in the second month of embryonic life
two processes:
intramembranous
endochondral
intramembranous ossification
flat bones are formed from this type of ossification
endochondral ossification
short, irregular, and long bones are created by this type of ossification
occurs form two distinct centers of development:
primary
secondary
primary ossification
begins before birth and forms long central shaft in long bones (diphysis)
secondar ossification
occurs after birth when separate bones begin to develop at both ends of long bones
metaphysis
epiphyseal plate/growth plate
ends are called epiphyses
processes or projections
extend beyond or project out from the main body of a bone
depression
hollow or depressed areas
fissure, foremen, fossa, groove, meatus, notch, sinus, sulcus
fractures
a break in bone
condyle
rounded process at an articular end
coracoid
beaklike process
coronoid
crownlike process
crest
ridgelike process
epicondyle
projection above a condyle
facet
small, smooth-surfaces articular process
hamulus
hook-shaped process
head
expanded end of a long bone
horn
hornlike process
line
linear elevation; not as prominent as a crest
malleolus
club-shaped process
protuberance
projecting prominence
spine
sharp process
styloid
long, pointed process (radius and ulna)
trochanter
either of the two large, rounded, and elevated processes of the proximal femur
tubercle
small, rounded, and elevated process
tuberosity
large, rounded, and elevated process
fissure
cleft or deep groove
foramen
hole in a bone or transmission of vessels and nerves
fossa
pit, fovea, or hollow space
groove
shallow linear channel
meatus
tubelike passageway
notch
indentation in the border of a bone
sinus
recess, groove, cavity, or hollow space
sulcus
furrow or trench
classification of joints
structural: classified by tissue type
fibrous, cartilaginous, synovial
function: classified by function
synarthrodial, amphiarthrodial, diarthrodial
fibrous
held together by fibrous tissue
not all joints are immovable, some are slightly moveable and some are limited movement
mostly classified are immoveable
syndesmosis and suture
cartilaginous
held together by cartilage
not all joints are slightly moveable, some are immovable
symphyses and synchondroses
synovial
synovial fluid in joint capsule
are freely moveable, if movement is restricted it is because of tendons and ligaments preventing the movement
7 movement types
diarthordial
plane
gliding movement
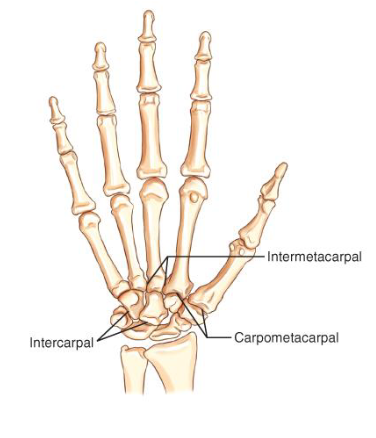
ex: intermetacarpal, intercarpal, carpometacarpal
ginglymus
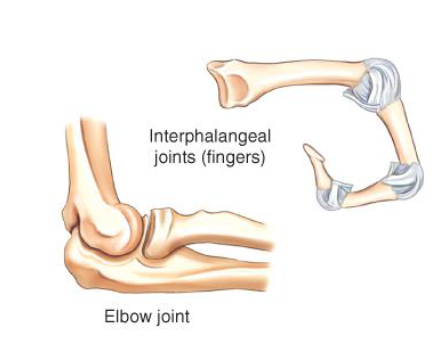
hinge that allows for flexion and extension
ex: interphalangeal/elbow joint
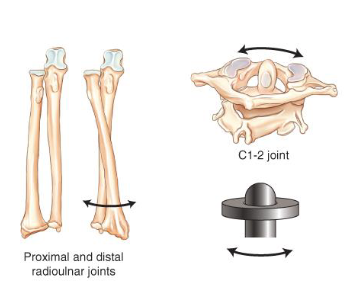
trochoid
pivot that allows for rotation or rolling on an axis
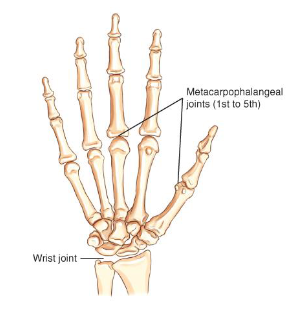
ellipsoid
condyloid — allows for adduction and abduction as well as flexion and extension
sellar
saddle
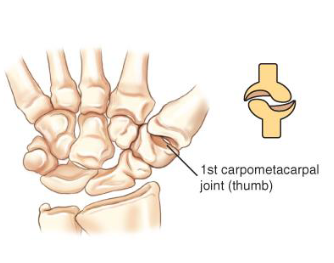
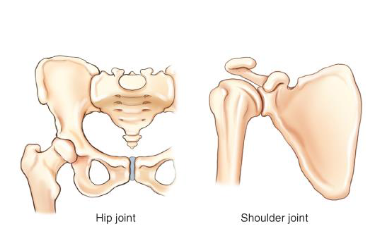
spheroidal
ball and sock — have the greatest range of movement but prone to dislocation
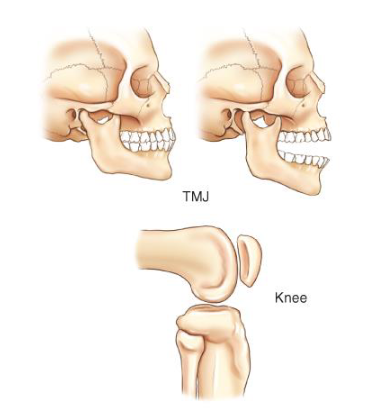
bicondylar
2 condyles on top of each other
subluxation
partial dislocation of joint
dislocation or luxation
displacement of bone from joint
contusion
a “bruise” type injury without a fracture or break in the skin
sprain
forced wrenching or twisting of a joint, resulting in partial rupture or tearing of supporting ligaments, presents with a lot of swelling
fracture types
incomplete fracture, simple fracture, compound fracture, complete fractures, comminuted fractures
incomplete fracture
fracture does not transverse through entire bone
ex: torus or buckle, greenstick, plastic fracture
simple fracture
bone does not break through skin, closed fracture, usually a transverse fracture
compound fracture
bone protrudes through skin, an open fracture
complete fracture
breaks into two pieces
ex:
transverse —- broken straight across
oblique — broken @ an angle
spiral fracture — breaks and turns when broken
comminuted fracture
breaks into two or more fragments
ex:
segmental — fractures in multiple places
butterfly
splintered fracture — splinters into multiple pieces when broken
impacted fracture
one fragment driven into another end of a bone
colles’ fracture
most common type of fracture
posterior displacement of distal radius
lateral projection will confirm
reverse colles’ fracture is an anterior displacement
monteggia’s fracture
proximal ulna fracture along with dislocation of radial head
pott’s fracture
ankle fracture of distal fibula with frequent fracture of medial malleolus
compression fracture
vertebral body collapses or is crushed
stellate fracture
fracture lines radiate from a center point of injury
tuft fracture
comminuted fracture of distal phalanx
osteogenesis imperfecta
nicknamed “brittle bone disease”
an inherited generalized disorder of connective tissue by multiple fractures and an unusual blue color of the normally white sclera of the eye
battered-child syndrome
multiple, repeated, physically induced injuries in young children caused by parent or guardians
also known as suspected nonaccidental trauma (SNAT)
imaging professionals have a legal responsibility to report suspicious cases to their supervisors
facility is legally obligated to notify authorities
osteoarthritis
degenerative joint disease
non-inflammatory
most common type of arthritis
rheumatoid arthritis
chronic systemic idiopathic disease
appears primarily as a noninfectious inflammatory arthritis of the small joints of the hands and feet
bursitis
inflammation of the small fluid-filled sac located near the joints that reduce the friction caused by movement
causes:
repeated physical activity (most common) — tennis elbow
trauma
rheumatoid arthritis
gout
infections
osteomyelitis
bacterial
an inflammation of the bones and marrow caused by a variety of infectious organisms
infectious organisms reach bone by hematogenous spread, extension from an adjacent site of infection, or direct introduction of organisms (after trauma or surgery)
osteoporosis
generalized or localized deficiency the mass of bone
its causes include aging and postmenopausal hormonal changes (most common in women)
a decrease in kVp is required to obtain quality image
simple bone cyst
true fluid-filled cyst with a wall of fibrous tissue, which most often occurs in the proximal humerus or femur at the metaphysis
it is asymptomatic
often discovered either incidentally or after pathologic fracture
neoplasm
cancerous or non-cancerous (benign)
bone metastisis (cancerous)
many types
can be osteolytic (bone destructive) or osteoblastic (bone constructive)