SCI ♡ Astronomical Events
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Known to Men Before the Advent of Telescopes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Ancient Astronomy and Calendars
before telescopes, humans relied on their senses to understand the universe
Babylonians, Assyrians, & Egyptians
knew the length of the year
Egyptians adopted a calendar based on 365 days
tracked the yearly cycle of the star Sirius, linked to the Nile's flooding
Chinese Civilizations
observed comets, meteors, and Sun's dark spots
Mayan Civilization
developed a calendar based on the movements of Venus
Polynesians
utilized the stars for navigation
Diurnal Motion
daily motion of stars and other celestial bodies across the sky due to Earth’s rotation
observed as the sun rising in the east and setting in the west
Fixed Stars
Greek astronomers have described these as moving in the sky at the same arrangement and speed as most of the stars are
Wandering Stars
stars whose movements deviate from what seems to be fixed stars
Planetes in Greek
seven wandering stars
Sun, moon, Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, & Saturn
Eclipse
occurs when the Earth or Moon casts a shadow on the other
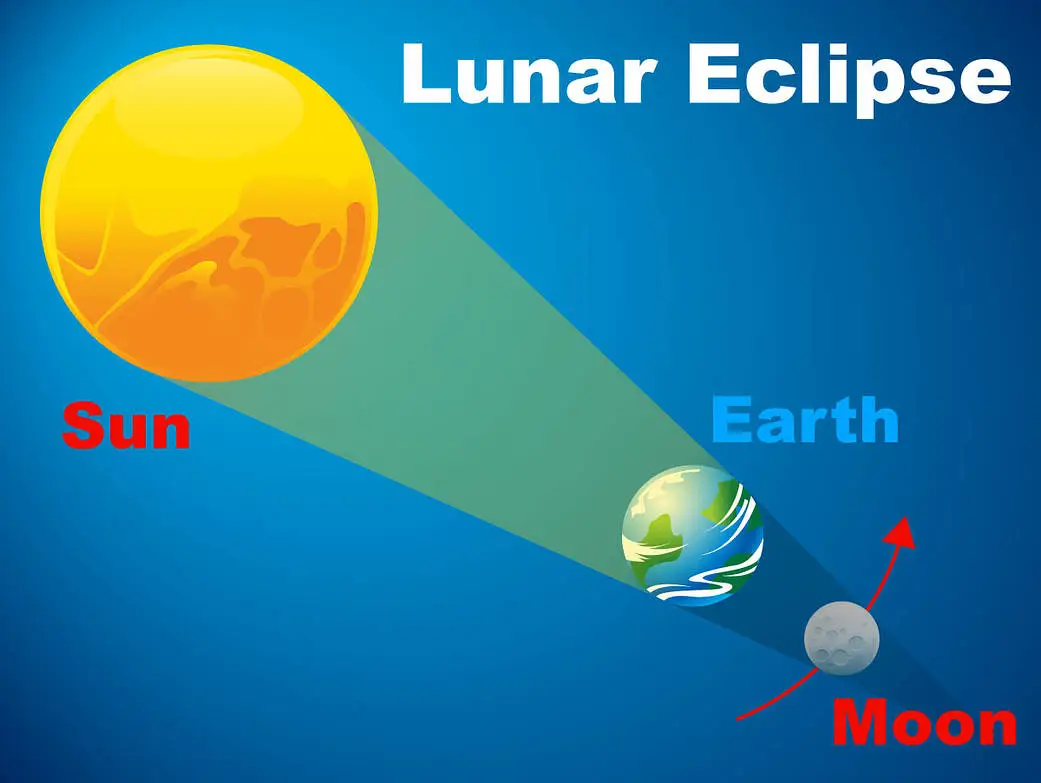
Lunar Eclipse
earth is directly aligned between the sun and moon
the earth casting a shadow on the moon
only occurs during the full moon phase
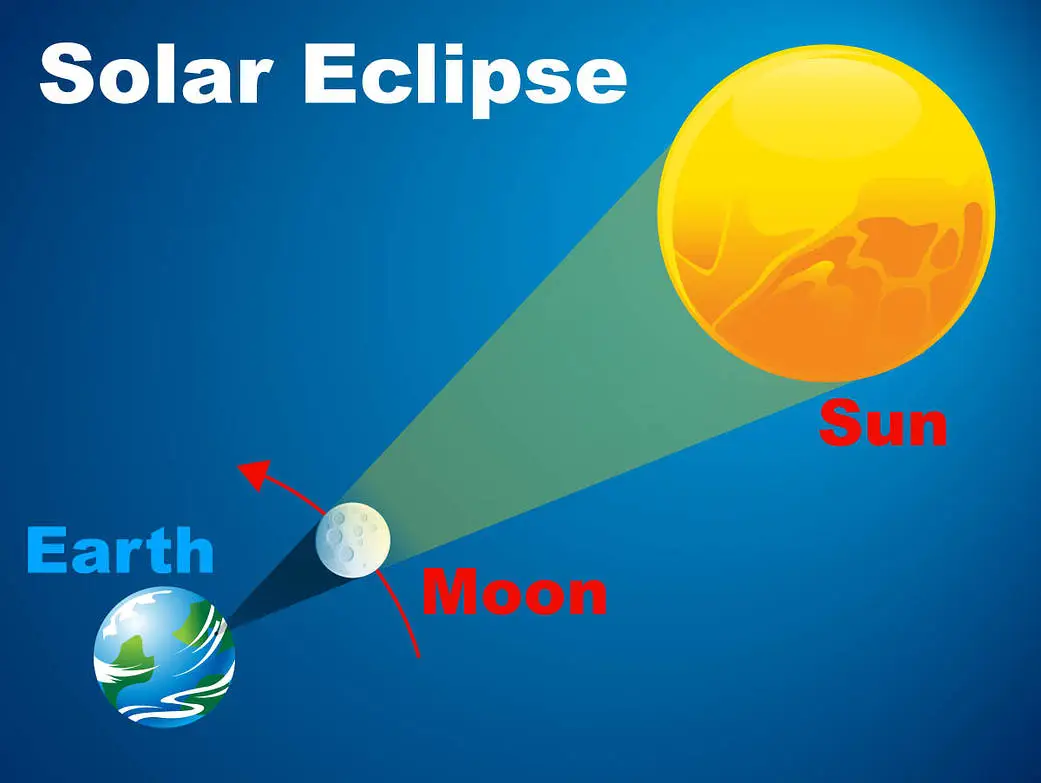
Solar Eclipse
happens when the moon passes between the earth and sun
moon casting a shadow on the Earth’s surface
only occurs during the new moon phase
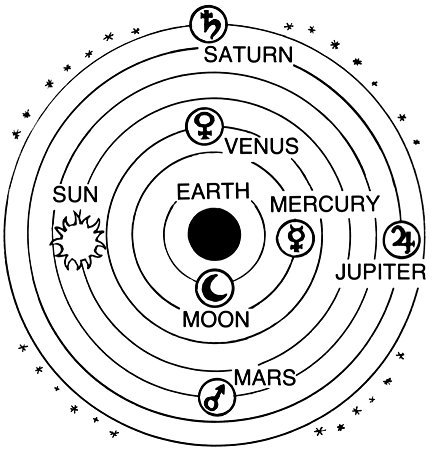
Ptolemaic System
Claudius Ptolemy
center: EARTH
all other celestial bodies revolve around the earth
stars are located and fixed in the outermost celestial sphere
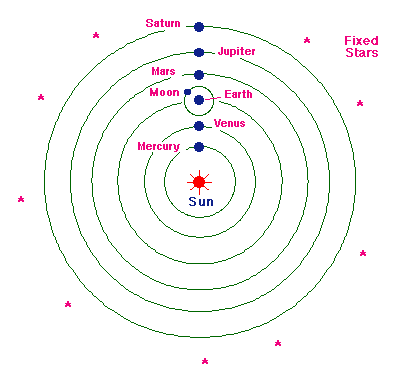
Copernican System
Nicholas Copernicus
center: SUN
all planets including earth revolves around the sun
only the moon revolves around the earth
stars are located and fixed in the outermost celestial sphere
Tychonic System
Tycho Brahe
center: EARTH
moon and sun revolve around earth
all other planets revolve around the sun
stars are located and fixed in the outermost celestial sphere
retrogade: same as Copernican System
Johannes Kepler’s 3 Laws of Planetary Motion
Law of Ellipse
Law of Equal Areas
Law of Harmony
Law of Ellipse
orbits of all the planets are elliptical with the sun at one focus of the ellipse
an ellipse is a somewhat flattened circle
a closed curve in which the sum of the distances from any point on the ellipse to foci (two points inside) is constant
Law of Equal Areas
line joining a planet and the sun sweeps out equal areas in space in equal intervals of time
thus, a planet moves fastest when it is nearest to the sun
Law of Harmony
the square of a planet’s orbital period (years) is proportional to the cube of the semimajor axis of its orbit (in astronomical units or au)
thus, the larger the orbit’s size, the longer it takes to orbit the sun