Understanding Acids, Bases, and the pH Scale
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Acids
Substances that dissolve in water to produce hydrogen ions (H+).
Bases
Ionic compounds that dissociate into cations and hydroxide ions (OH-) in water.
Arrhenius acids
Acids that produce hydrogen ions (H+) in aqueous solution.
Arrhenius bases
Bases that produce hydroxide ions (OH-) in aqueous solution.
Bronsted-Lowry acids
Substances that can donate a hydrogen ion (H+) to another substance.
Bronsted-Lowry bases
Substances that can accept a hydrogen ion (H+).
Conjugate acid
The molecule or ion that forms when one H+ ion is added to a base.
Conjugate base
The molecule or ion that differs by one H+ ion from an acid.
Strong acids
Acids that dissociate completely in water, e.g., HI, HBr, HCl, H2SO4, HNO3.
Weak acids
Acids that do not dissociate completely in water, e.g., HF, H2CO3, H2S, H2O.
Strong bases
Bases that dissociate completely in water, e.g., NaOH, LiOH, Ca(OH)2, Ba(OH)2, KOH.
Weak bases
Bases that do not dissociate completely in water, e.g., NH3.
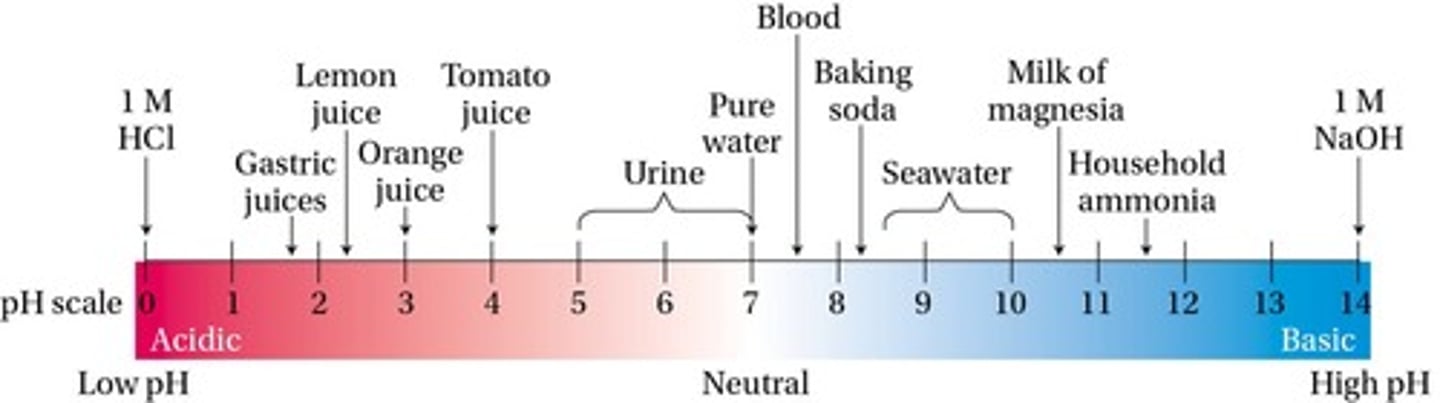
pH scale
A scale that goes from 0 to 14, used to represent the concentration of acids and bases.
pH calculation
pH = -log[H+], where [H+] is the molar concentration of hydrogen ions.
Acidic solutions
Solutions with a pH less than 7.0.
Basic solutions
Solutions with a pH greater than 7.0.
Neutral solutions
Solutions with a pH equal to 7, having equal concentrations of acid and base.
pOH calculation
pOH = -log[OH-], where [OH-] is the molar concentration of hydroxide ions.
pH and pOH relationship
pH + pOH = 14.
Example of pH calculation
For [H+] = 1.0 x 10^-2 M, pH = 2.
[H+] concentration calculation
For pH = 8.25, [H+] = 10^-8.25 = 5.6 x 10^-9 M.
HCl dissociation
HCl (g) → H+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) in water.
NaOH dissociation
NaOH (s) → Na+ (aq) + OH- (aq) in water.