1.4 Review Foundational Pathology Terms
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Pathology
Pathology is the study of the changes in cells, tissues, and organs that underlie disease. Pathology is a bridge between science and medicine.
What are the four core aspects of pathology?
Aetiology, Pathogenesis, Morphological changes, Clinical manifestations
Signs
Objective measures from another person.
Symptoms
Subjective statements from the patient.
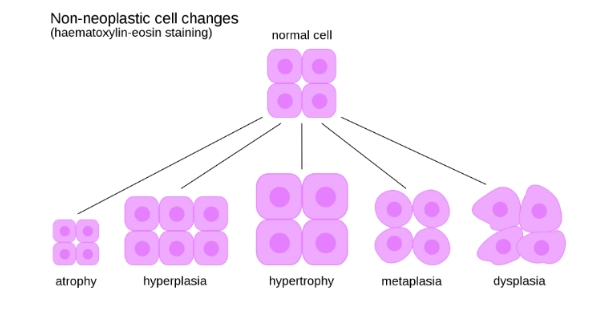
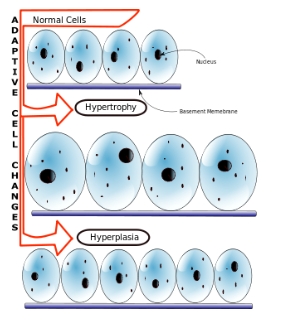
Cellular adaptation
Physiological or pathological responses of cells to changes in their environment, allowing them to survive in adverse conditions. This can involve changing the number of cells or their morphological appearance. It can be physiological, where it occurs in normal tissues or organs, or pathological, i.e. occurring in disease states.
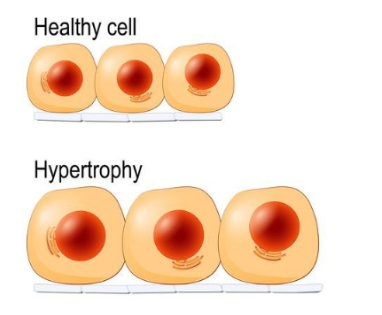
Hypertrophy
An increase in the size of a tissue or organ due to the increased size of the cells.

Physiologic hypertrophy
Increased demand hormones/growth factors.
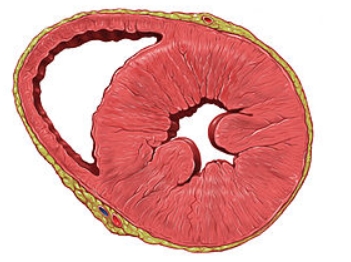
Pathologic Hypertrophy
Ventricular hypertrophy driven by increased blood pressure or ventricular volume Leads to heart failure, arrythmias.
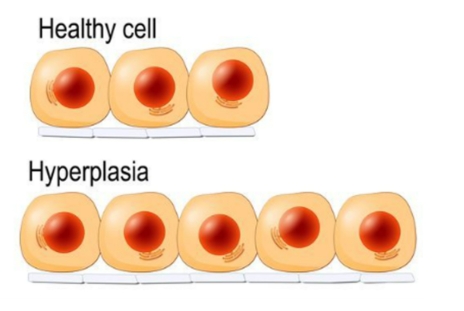
Hyperplasia
Increased size of a tissue or organ due to increased number of cells.
Hyperplasia pathologic
Excessive actions of hormones/ growth factors.

Atrophy
A reduction in size of a tissue or organ due to a decrease in cell size and number.

Metaplasia
A reversible change in which one differentiated cell type is replaced by another cell type.
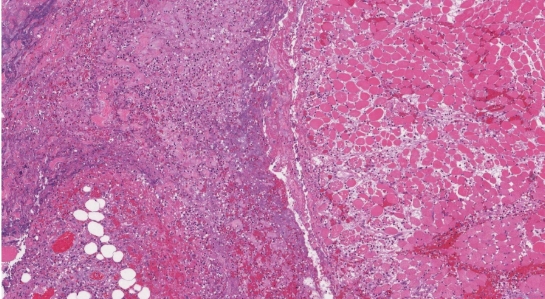
Necrosis
Cell ‘homicide’. A form of cell death characterized by the unregulated breakdown of cells, often resulting from injury or infection.
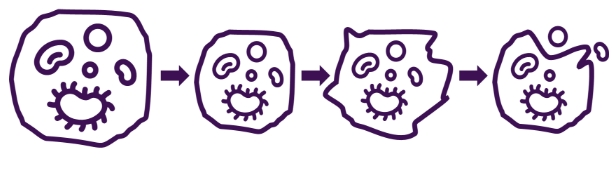
Apoptosis
Cell ‘suicide’. A regulated process of programmed cell death that occurs normally in development and homeostasis.