Module 3 Quiz 1 - All Vocab
1/121
Earn XP
Description and Tags
LOOK OUT THERE'S A PIPEBOMB
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
122 Terms

The functions of epithelial tissue are to…
mainly serve as protective barrier, absorb substances, secrete molecules like enzymes & mucus, & hold nerve endings for sensing stimuli
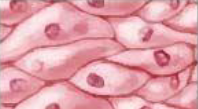
Where can epithelial tissue be found…
on surfaces of organs & outer surface of the body (skin)
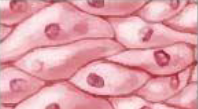
Epithelial tissue cells are…
tightly packed with minimal space between cells
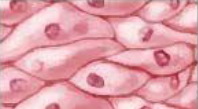
Epithelial tissue consists of:
simple squamous epithelium, stratified squamous epithelium, simple cuboidal epithelium, simple columnar epithelium
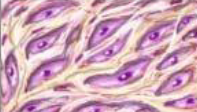
The functions of connective tissue are to…
support & protect organs, connect parts of the body, store energy, & provide immune defense
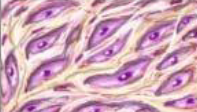
Where can connective tissue be found…
below the skin, around organs, in circulation throughout the body, tendons & ligaments, flexible body structures (ears, nose), covering the ends of bones, & bone in general
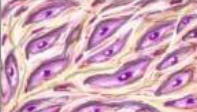
Connective tissue cells are…
widely spaced with material (matrix) between cells
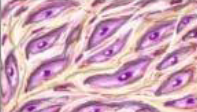
Connective tissue consists of:
loose connective tissue, adipose tissue (fat), blood, dense connective tissue, cartilage, bone
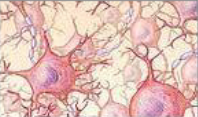
The functions of nervous tissue are to…
receive stimuli, conduct nerve impulses, process information, transmit signals, communicate at synapses (ends of axons), speed up impulses, support complex functions
Where can nervous tissue be found…
central nervous system (brain & spinal cord), peripheral nerves, sensory organs (nose, ears, etc.), & target organs (“response” organs; muscles, glands, etc.)
Nervous tissue cells are…
“neurons”; unique structure with dendrites, a cell body, & axon
Nervous tissue consists of:
nerve cells (neuron), neuroglial cells

The functions of muscle tissue are to…
contract repeatedly & efficiently, produce movement, pump blood, propel substances & regulate organ function

Where can muscle tissue be found…
attached to bones, the heart, in the walls of internal organs (intestines, stomach, blood vessels, various glands, other hollow organs)

Muscle tissue cells are…
oval-shaped, no stripes (smooth); fused, branched & some stripes(cardiac); long, fused & many stripes(skeletal)

Muscle tissue consists of:
skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, & smooth muscle
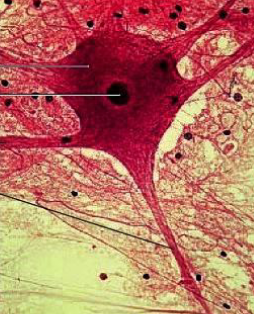
What are neurons?
specialized cells that receive, process, & transmit nerve impulses throughout the nervous system
Simple epithelium
epithelial tissue with a single layer of cells
Stratified epithelium
epithelial tissue with multiple layers of cells
Squamous
thin, flat, scale-like cell shape found in certain epithelial tissue
Cuboidal
cube-shaped cells found in certain epithelial tissue
Columnar
tall, column-shaped cells found in certain epithelial tissue
Pseudostratified
“falsely layered”; cells appear to have multiple layers but are actually single-layered, found in certain epithelial tissue
Absorption
the process of taking in substances (nutrients, water)
Secretion
the process of producing & release substances (enzymes, mucus) from cells or tissues
Osteocytes
living bone cells that maintain the bone matrix, can produce & secrete calcium, and help repair & build new bone
Chondrocytes
living cartilage cells that produce & maintain cartilage matrix proteins (ex. chondroitin: makes cartilage flexible & smooth)
Dense (Fibrous) Connective Tissue
connective tissue; mostly densely packed collagen fibers with few cells; provide strong, flexible support & connection between body parts, resist tension & pulling forces; in tendons (muscle to bone) & ligaments (bone to bone)
Loose Connective Tissue
connective tissue; widely spaced cells & watery matrix with proteins (collagen, fibrin); connects skin to muscles & tissues, provides skin with elasticity & flexibility, contains immune cells; just beneath skin (subcutaneous layer)
Adipose Tissue
connective tissue; composed of fat-storing cells; stores energy as fat, provides insulation for body temperature maintenance, cushions & protects internal organs; beneath skin (subdermal layer), around organs
Nerve Cell Body
“soma”; central part of nerve cell, contains nucleus & most cell organelles; processes information received from dendrites & sends signals to axons
Axon
long, thin extension from the nerve cell body; carry nerve impulses away from cell body to other nerve cells or target organs
Dendrite
branch-like extension from the nerve cell body; helps nerve cell collect info from other cells or environment, receive signals & conduct impulses toward the cell body,
Myelin sheath
fatty layer that wraps around many axons; acts as insulation, speeds up impulse transmission along axon
Node of Ranvier
small gap between sections of myelin sheath on an axon; help speed up impulse transmission
Telodendria
tiny branches at the end of an axon; form connections with other nerve cells or target organs, help transmit nerve signals
Synapse
the small gap between two nerve cells or between nerve cell & target organ; allows nerve signals to pass using neurotransmitters (chemical messengers)
Neurotransmitter
chemical released by nerve cells at telodendria (axon terminals); carry signals across synapse to other nerve cells or target organs
Skeletal Muscle
muscle tissue; attached to bones, for voluntary movement, striated, limited ability to mature & divide once mature, formed by fusion of embryonic cells into muscle fibers
Smooth Muscle
muscle tissue; in internal organs, involuntary, responsible for moves food through digestive system (peristalsis), aids in glandular secretion, limited ability to repair itself; made up of individual, smooth, & non-striated cells
Cardiac Muscle
muscle tissue; ONLY in the heart (myocardium), involuntary, responsible for pumping blood throughout body, composed of fused cells, striated but specialized for endurance & rhythmic activity, limited ability to repair itself
Striated Muscle
striped muscle tissue; consists of skeletal & cardiac muscle
Voluntary Muscle
muscle tissue you can consciously control
Involuntary Muscle
muscle tissue that contracts automatically
Cardiovascular System
body network responsible for blood circulation; consists of heart, blood vessels (arteries, veins, & capillaries), & blood; delivers oxygen & nutrients to tissues, removes waste products from tissues; two types of circulation: systemic & pulmonary
Artery
blood vessel that carries oxygen-rich blood away from heart
Arteriole
small blood vessel that branches off from arteries & lead to capillaries; help regulate blood flow & blood pressure by constricting or dilating
Capillary
smallest blood vessel; connects arteries to veins, site where oxygen, nutrients & waste products are exchanged between blood & tissues
Vein
blood vessel that carries oxygen-rich blood to the heart
Venule
small blood vessel that collects blood from capillaries & carries it to larger veins that return the deoxygenated blood to the heart
Visceral Pericardium
the membrane that’s directly attached to surface of the heart; part of the pericardial sac, protects the heart
Parietal Pericardium
membrane just outside the visceral pericardium, a fluid-filled space separates them (pericardial cavity), surrounds the heart
Atrium
upper chamber of the heart, receives blood returning to heart
Ventricle
lower chamber of the heart, pumps blood out of the heart
Systole
heart cycle phase when heart muscles contract to pump blood out of chambers
Diastole
heart cycle phase when heart muscles relax & chambers fill with blood
Atrioventricular Valve (AV Valve)
located between an atrium & ventricle; prevents blood from flowing backward when ventricle contracts
Tricuspid Valve
located between the right atrium & right ventricle, three flaps
Bicuspid/Mitral Valve
located between the left atrium & left ventricle, two flaps
Aortic Semilunar Valve
located between the left ventricle & the aorta, prevents blood from flowing back into the heart after being pumped out
Pulmonary Semilunar Valve
located between the right ventricle & the pulmonary artery, prevents blood from flowing back into the heart after being pumped out to the lungs
Pulmonary Artery
carries deoxygenated blood from right ventricle of heart to lungs for oxygenation
Pulmonary Vein
carries oxygenated blood from lungs of heart to left atrium of the heart
Pulmonary Circulatory System
part of the circulatory system that carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs & returns oxygenated blood back to the heart
Systemic Circulatory System
part of the circulatory system that carries oxygenated blood from the heart to the rest of the body & returns deoxygenated blood back to the heart
Heart Rate
number of times the heart beats per minute
Cardiac Output
amount of blood the heart pumps out in one minute
Sino-atrial (SA) Node
“pacemaker”; located in the upper wall of right atrium; generates impulses that initiate each heartbeat —> causes both atria to contract almost simultaneously
Atrioventricular (AV) node
located in the lower wall of right atrium; receives electrical signal from SA node, briefly delays it, then sends impulses to ventricles → ventricles contract almost simultaneously
Bundle of His
carry electrical impulses from AV node down into ventricles, help coordinate contraction
Purkinje fibers
fibers that spread electrical impulses throughout walls of the ventricles
Capillary Exchange
the process where oxygen, nutrients, & waste products pass between blood in capillaries & surrounding tissues
Kwashiorkor is a…
nutritional disorder caused by severe protein deficiency despite calorie intake → body breaks down muscle tissue to produce essential proteins
Symptoms of kwashiorkor include:
very thin arms & legs from muscle loss, swelling/fluid accumulation in abdomen (edema) → “pot belly”, blood vessel fluid leakage into tissues due to lack of plasma proteins to maintain osmotic pressure
Hemophilia is a…
genetic disorder where blood is unable to clot properly; caused by recessive gene on X chromosome, more common in males, females usually don’t show symptoms unless both x chromosomes are carriers
Symptoms of hemophilia include:
excessive bleeding from injuries (external & internal)
Sickle Cell Anemia is a…
genetic disorder where hemoglobin changes shape → RBC’s become sickle/crescent-shaped; sickle-shaped cells struggle to pass through capillaries → can block blood flow; caused by inheriting two copies of sickle cell gene (one gives you resistance to malaria)
Symptoms of sickle cell anemia include:
reduced oxygen delivery to tissues, impaired gas exchange
Atherosclerosis is a…
circulatory disorder where fatty plaques build up inside the arteries; plaques start with saturated fats & cholesterol → plaques thicken & narrow the artery → plaques collect confused white blood cells & platelets → can lead to complete blockage; associated with high-fat diets & genetic factors
Symptoms of atherosclerosis include:
heart attacks, strokes, & organ damage due to reduced blood supply
Hypertension is…
chronic high blood pressure, blood pressure is consistently above 140/90 mmHg; makes the heart work harder which could lead to heart problems; can be caused by lack of exercise, poor diet, genetics, & obesity; medication is provided to help lower blood pressure
Symptoms of hypertension include:
organ damage, atherosclerosis, other heart problems
Coronary Artery Disease is a…
condition where arteries supplying blood to the heart become narrowed or blocked; caused mainly by atherosclerosis, yadda yadda same symptoms; risk factors = diabetes, high cholesterol, smoking, & sedentary lifestyle; can lead to heart muscle damage & heart failure
Cholesterol
lipid (fat) essential for stabilizing cell membranes & producing certain hormones; the body can make it
High Density Lipoproteins (HDL)
“good” cholesterol, helps remove cholesterol from the blood
Low Density Lipoproteins (LDL)
“bad” cholesterol, can promote plaque buildup in arteries
Plasma
the liquid portion of blood; makes up 55% of blood’s volume & is more than 90% water; solvent that carries substances such as ions & electrolytes, plasma proteins, nutrients, metabolic waste products, respiratory gases, & hormones; acts as transport medium
Formed (cellular) elements
the cellular components of blood; makes up about 45% of blood’s volume; consists of erythrocytes (red), leukocytes (white), & thrombocytes (platelets)
Erythrocytes
“red blood cells”, “RBC’s”; carry oxygen & carbon dioxide with the help of hemoglobin
Erythropoietin
hormone produced mainly by kidneys, stimulates production of RBC’s in bone marrow, helps regulate RBC levels in response to oxygen available in the body
Leukocytes
“white blood cells”, “WBC’s“; involved in immune responses to fight infections
Basophil
type of WBC; produce & release histamine which causes blood vessels to dilate (vasodilation), helps during allergic reactions & inflammation
Neutrophil
type of WBC; act as phagocytes → engulf & digest bacteria + other pathogens to protect body from infection
Eosinophil
type of WBC; immune defense against parasitic worms, also play a role in allergic reactions
Monocyte
type of WBC; act as phagocytes → digest pathogens & debris, also present pathogen pieces to other cells to help activate them
Macrophage
type of WBC; large, develop from monocytes, act as phagocytes → engulf & digest pathogens, dead cells, & debris, key role in tissue cleanup
Lymphocyte
type of WBC; play a central role in immune system, recognize & respond to foreign substances; consists of T Cells & B Cells
T cell
type of WBC; destroy infected or abnormal cells & help regulate the immune system
B cell
type of WBC; produce antibodies to target specific pathogens
Thrombocyte
“platelets”; help with blood clotting & maintaining blood vessels