Mineralogy Midterm
1/42
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
True or False?
Most minerals have a single cation or cationic group, while they often have more than one anion.
False.
Most minerals have a single anion or anionic group, while they often have more than one cation.
Crystal Chemistry
relationship of chemical composition to atomic structure
Mineral
A mineral is a naturally occurring solid with a highly ordered atomic arrangement and a definite (but not fixed) chemical composition. It is usually formed by inorganic processes
Steno’s Law
"In crystals of the same species (different specimens), under equal conditions of pressure and temperature, the corresponding dihedral angles are always the same, the number, shape and size of the faces being variable"
The 5 chemical bonds
ionic
covalent
metallic
van der waals
hydrogen
Compounds ending in–ide…
are simple binary compounds containing 2 elements even if there is no metal
Compounds ending in–ate…
means oxygen is present
Ending in –ite…
have less oxygen present than in –ate compounds
4 Crystal Bonding Types
Molecular Crystal
Covalent Crystal
Metallic Crystal
Ionic Crystal
radius ratio
is the ratio of the cation radius to the anion radius
symmetry
Property that makes an object (motif) coincide with another identical one through a movement called the symmetry operation
4 Basic Symmetry Operations
Translation
Rotation
Reflection
Inversion
6 Crystal Systems
Triclinic
Monoclinic
Orthorhombic
Tetragonal
Hexagonal
Isometric
Crystal shape is determined by _______
Atomic arrangement
THE BECKE LINE WILL ALWAYS MOVE ONTO THE MATERIAL WITH THE________ AS THE STAGE IS LOWERED
HIGHER REFRACTIVE INDEX
When the RI of the mineral and the RI of the mounting material are equal, the Becke line…
splits into two lines, a blue line and an orange line.
Anisotropic minerals extinct _____ times
4
Isotropic minerals extinct ___ times
Isotropic minerals are always extinct. This is because they cannot reorient light
What causes extinction?
The direction of vibration of light in the mineral is parallel to the direction of polarization
Uniaxic crystal systems
Hexagonal
tetragonal
biaxic crystal systems
rhombic, monoclinic, triclinic
C axis refers to the…
Optic axis
All uniaxial minerals show ____ extinction
parallel
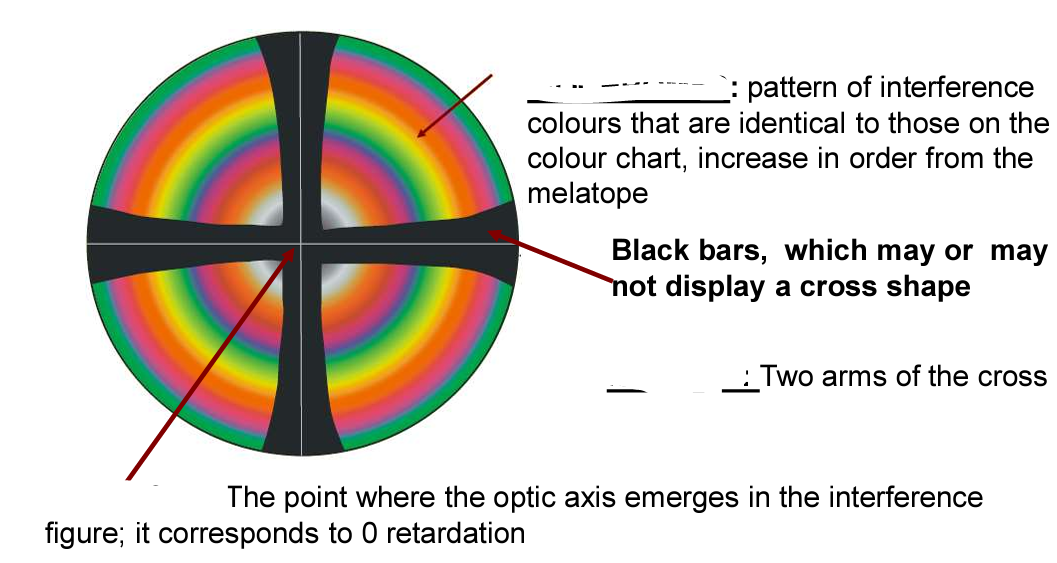
What type of interference figure is this + label the elements
Centered Uniaxial Interference Figure
Isochrome: pattern of interference colours that are identical to those on the colour chart, increase in order from the melatope
Isogeres: Two arms of the cross
Melatope: The point where the optic axis emerges in the interference figure; it corresponds to 0 retardation
The 3 Uniaxial Interference Figures
Optic Axis Figure-OA vertical
Off Centred Optic Axis Figure- OA inclined
Flash Figure- OA horizontal
Which quadrant helps you determine the sign?
The NE quadrant
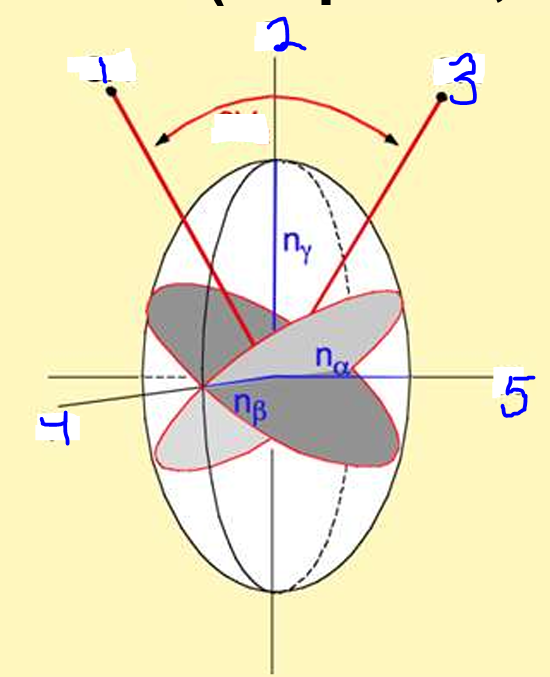
Label 1-5
Optic Axis
Z axis
Optic Axis
Y
X
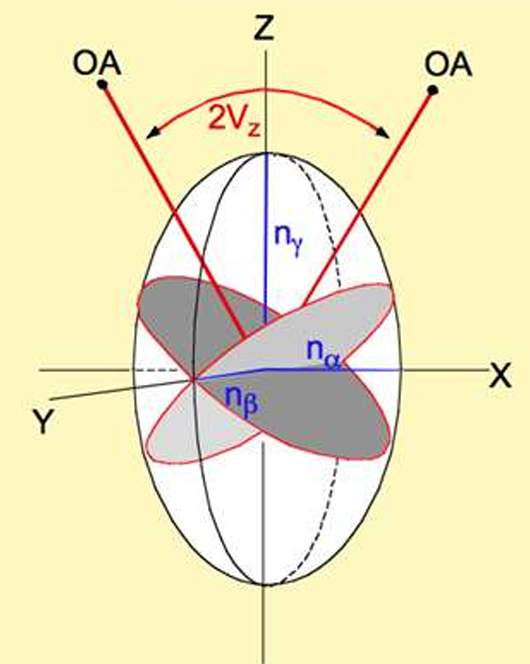
direction X = ?
direction Y = ?
direction Z = ?
direction Z = nγ (highest)
direction X = nα(lowest)
direction Y = nβ (intermediate; ray of circular section)
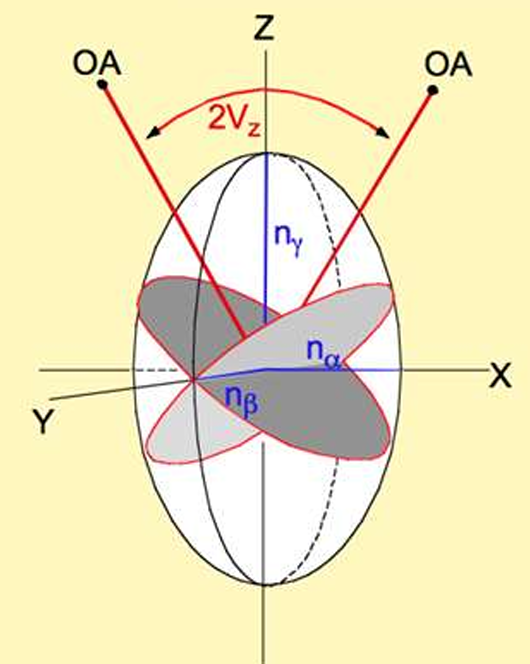
How is 2V measured?
Using the interference figures
Bxa stands for…
Acute Bisectrix
OA stands for…
Biaxial Optic Axis
Bxo stands for…
Obtuse Bisectricx
ON stands for…
Biaxial Optic Normal or Flash Figure
The appearance of the interference figure is dependent on the ____ of the mineral grain and its corresponding______
orientation ; indicatrix
Isotropic
speed of light is the same in any direction.
Vibration direction will always be perpendicular to the propagation direction
only ONE index of refraction
Anisotropic
speed of light varies depending on the direction the light is traveling in
more than one index of refraction
“Cross Nichols” refers to…
adding the analyzer (XPL)
Pleochrism
minerals ability to change its color when its position is changed on the stage
The slow ray in an anisotropic mineral will have a _____ than the fast ray
higher index of refraction
The fast ray is the ______ and is _______ when going through the mineral
extraordinary ray ; not deviated
The slow ray is the ______ and is _______ when going through the mineral
ordinary ray ; slowed down + deviated
the sign of elongation is POSITIVE if the ____ beam vibrates ____ to the maximum length of the crystal
slow ; parallel
the sign of elongation is NEGATIVE if the ____ beam vibrates ____ to the maximum length of the crystal
fast ; parallel