MCR3U Properties of a parent function
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
5 Terms
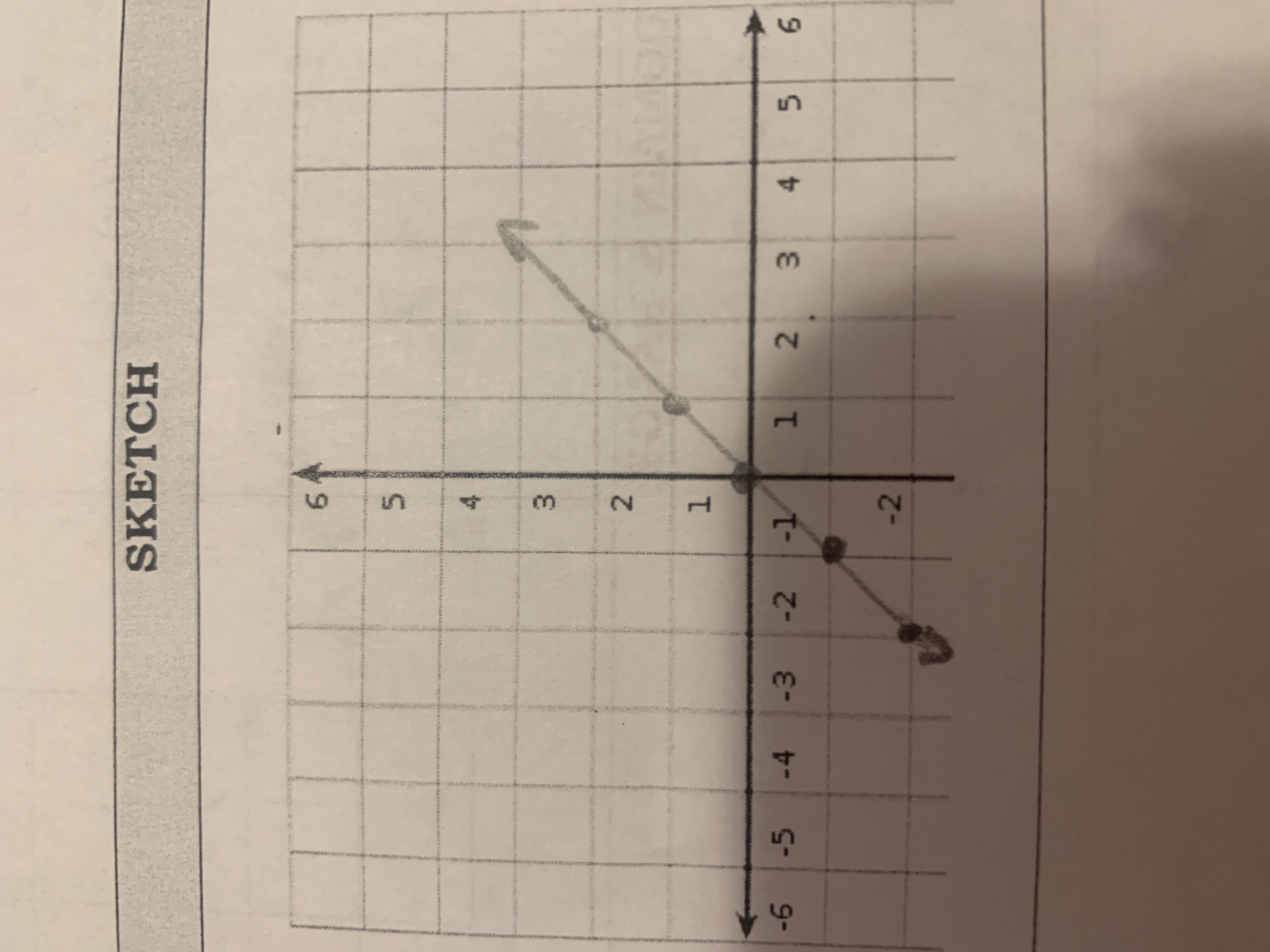
Linear
f(x) = x (ex: f(-2) = -2)
Key points
x= -2,-1,0,1,2
f(x)=-2, -1,0,1,2
D= {xeR} R= {yeR}
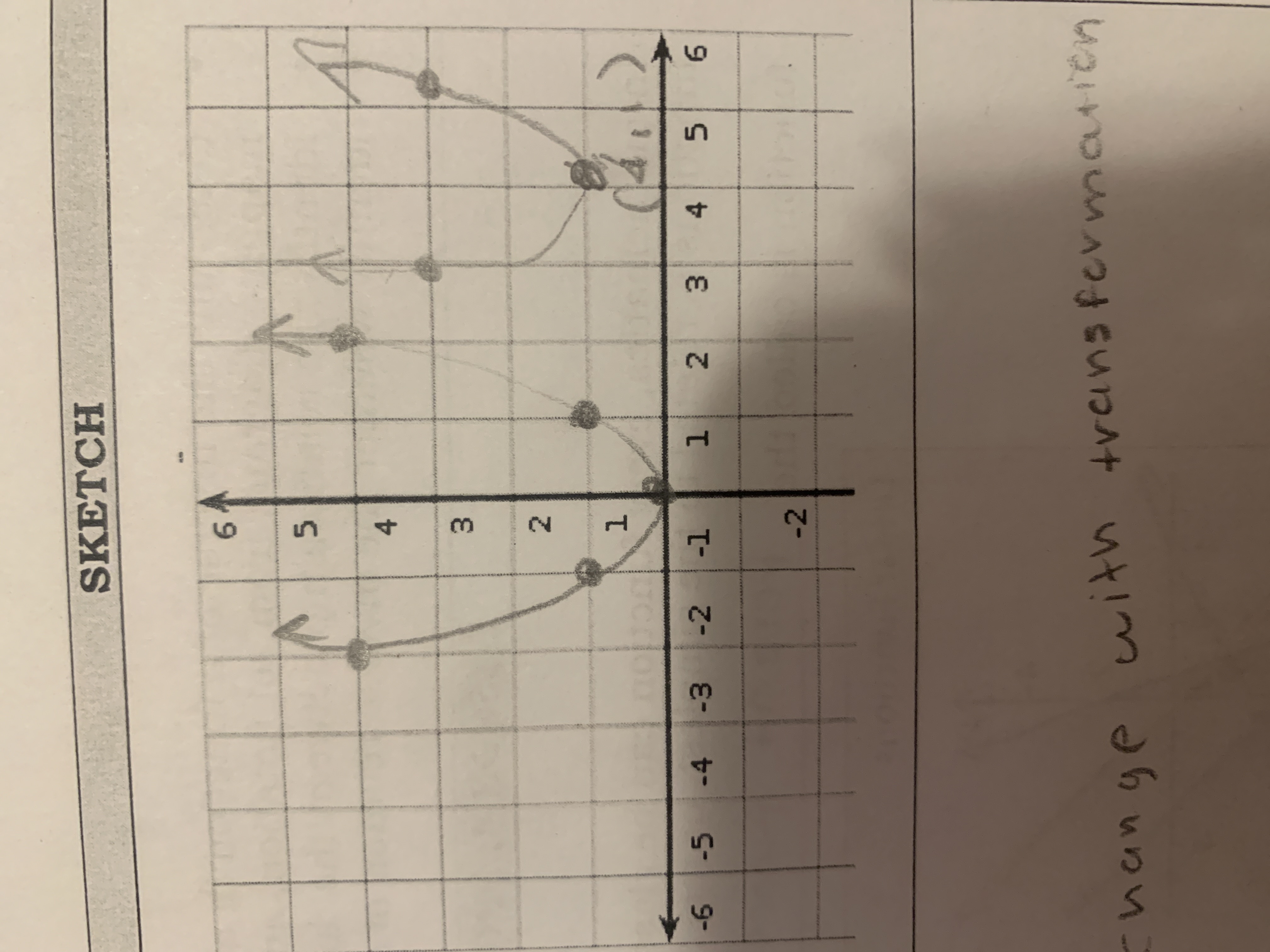
Quadratic
f(x) = x² (ex: f(-2)= (-2)² =4)
x = -2, -1, 0, 1, 2
f(x)= 4, 1, 0, 1, 4
D= {xeR} R={yeR I y ≤ 0} (r will change with transformations)
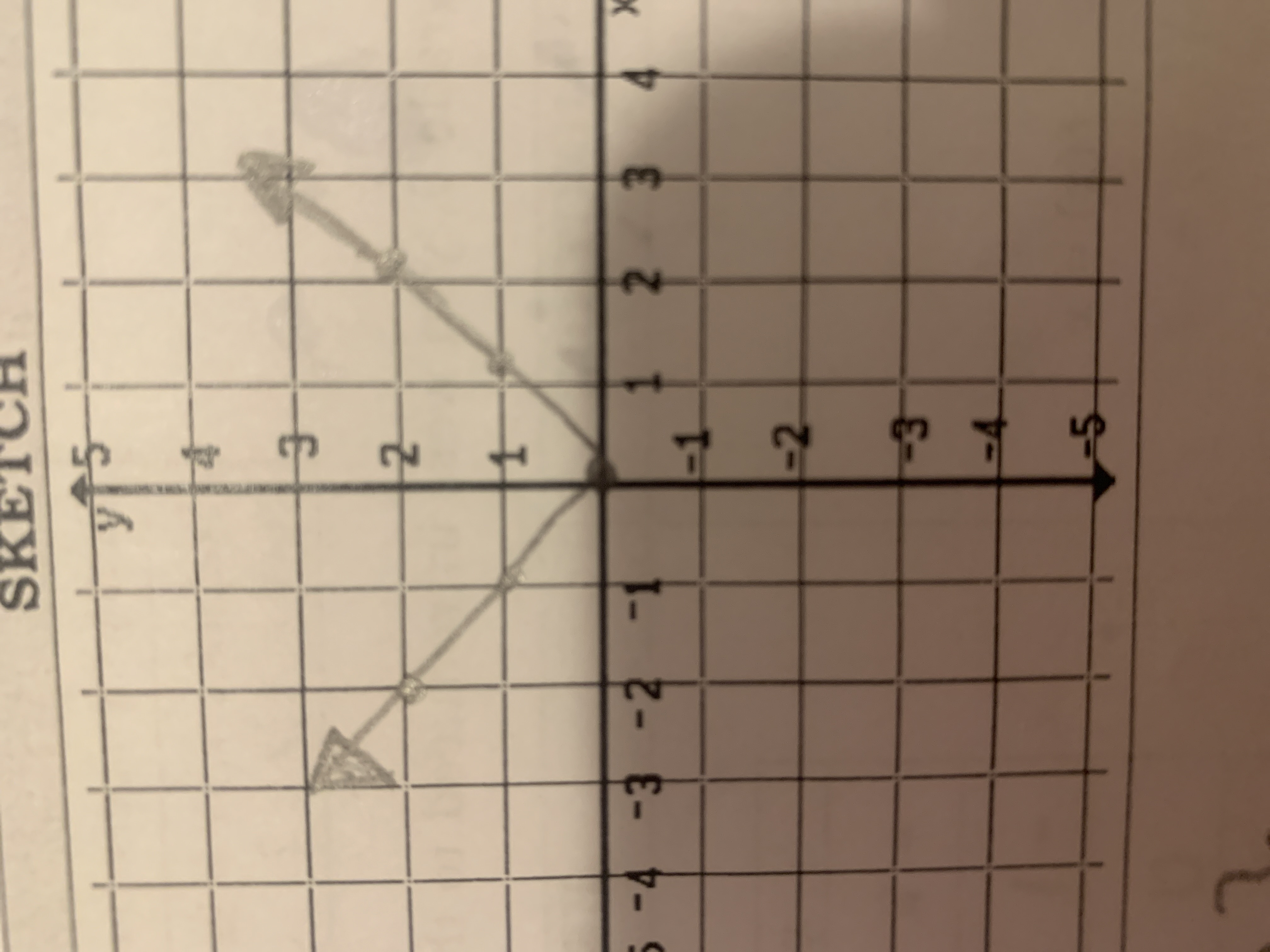
Absolute
f(x) = lxl →two lines take any value and make it +
ex: f(-2) = I-2I = 2
x= -2, -1, 0, 1,2
f(x)= 2, 1, 0, 1, 2
D= {xeR} R={yeR l y ≤ 0} →will change with transformations
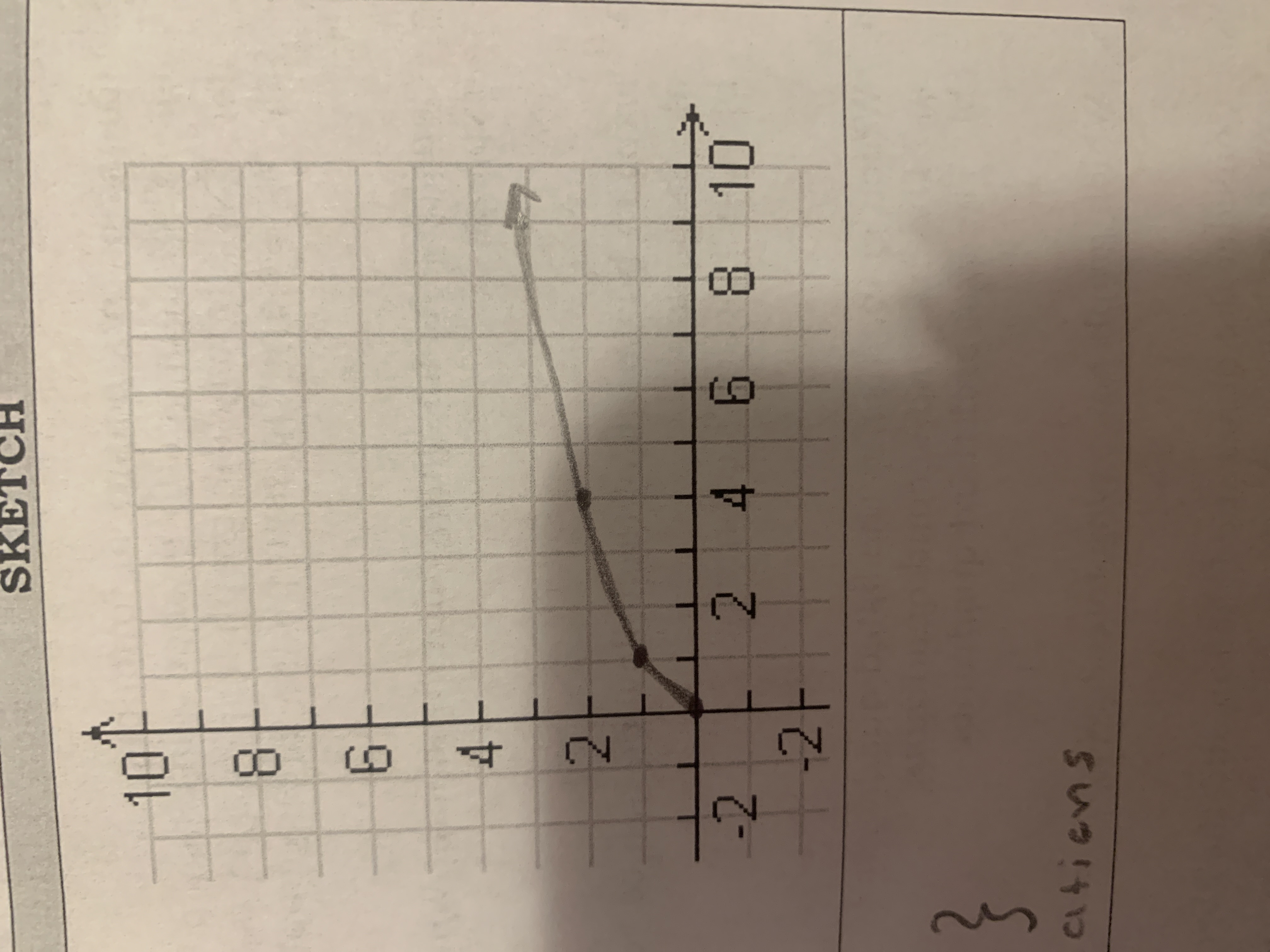
Square root
f(x)√x
(ex: F(4)=√4=2)
x= 0, 1, 4, 9, 16
f(x)= 0, 1, 2, 3, 4
D={xeR l x greater than less than 0}
R={yeR I y greater than less than 0}
both will change with transformation
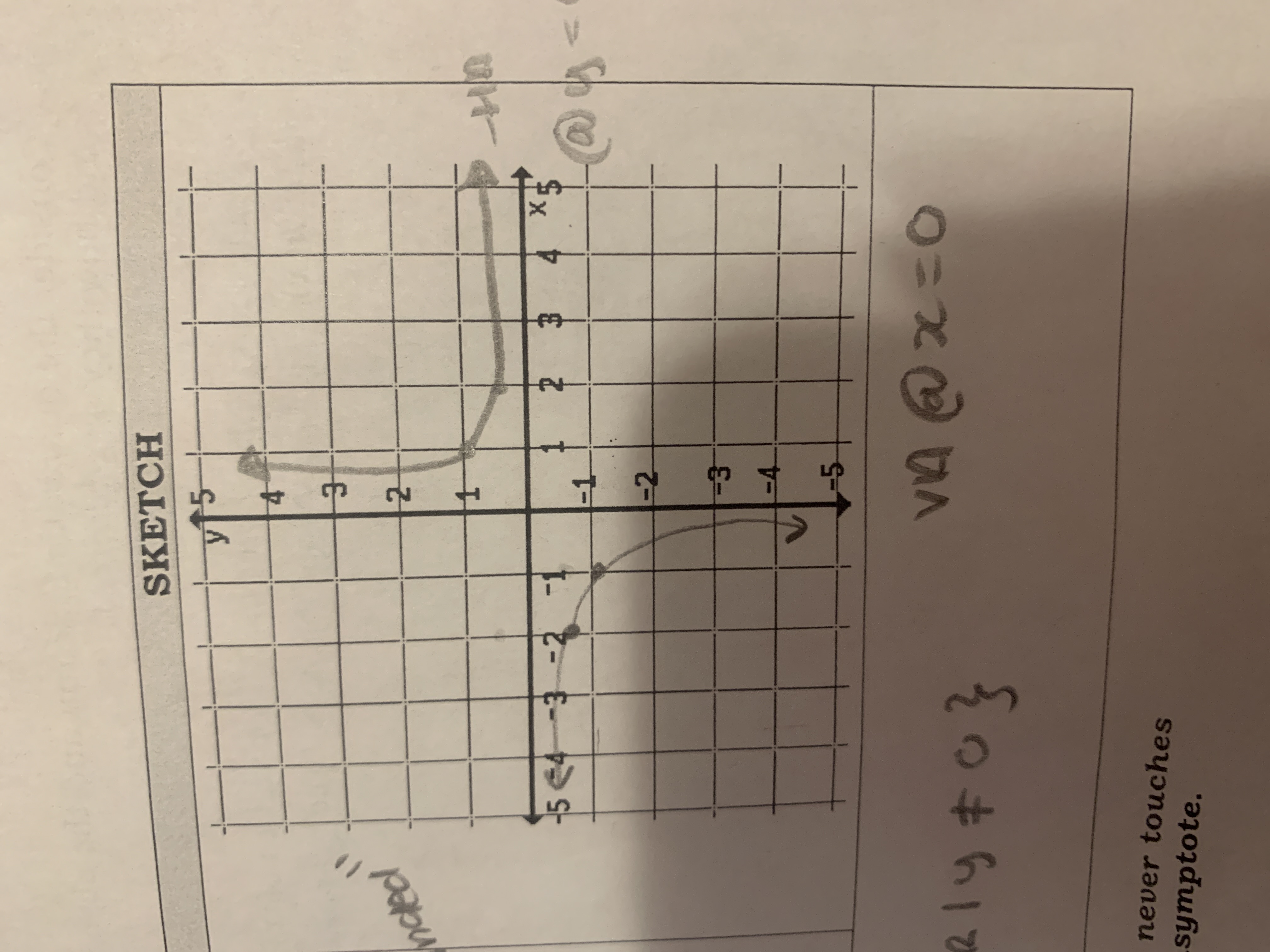
Reciprocal
f(x)=1/x
ex: f(-2)=1/-2 = -0.5
x=-2, -1, 0, 1, 2
f(x)=-0.5, -1, UD, 1,0.5
D={xeR l x≠ 0} R = {yeR l y ≠ 0}
HA = at y =0
VA = at x = 0