Biology unit 2: Enzymes and Proteins
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
What happens to a non-ionized amino acid in water?
The H proton from OH moves to N, resulting in ionization.
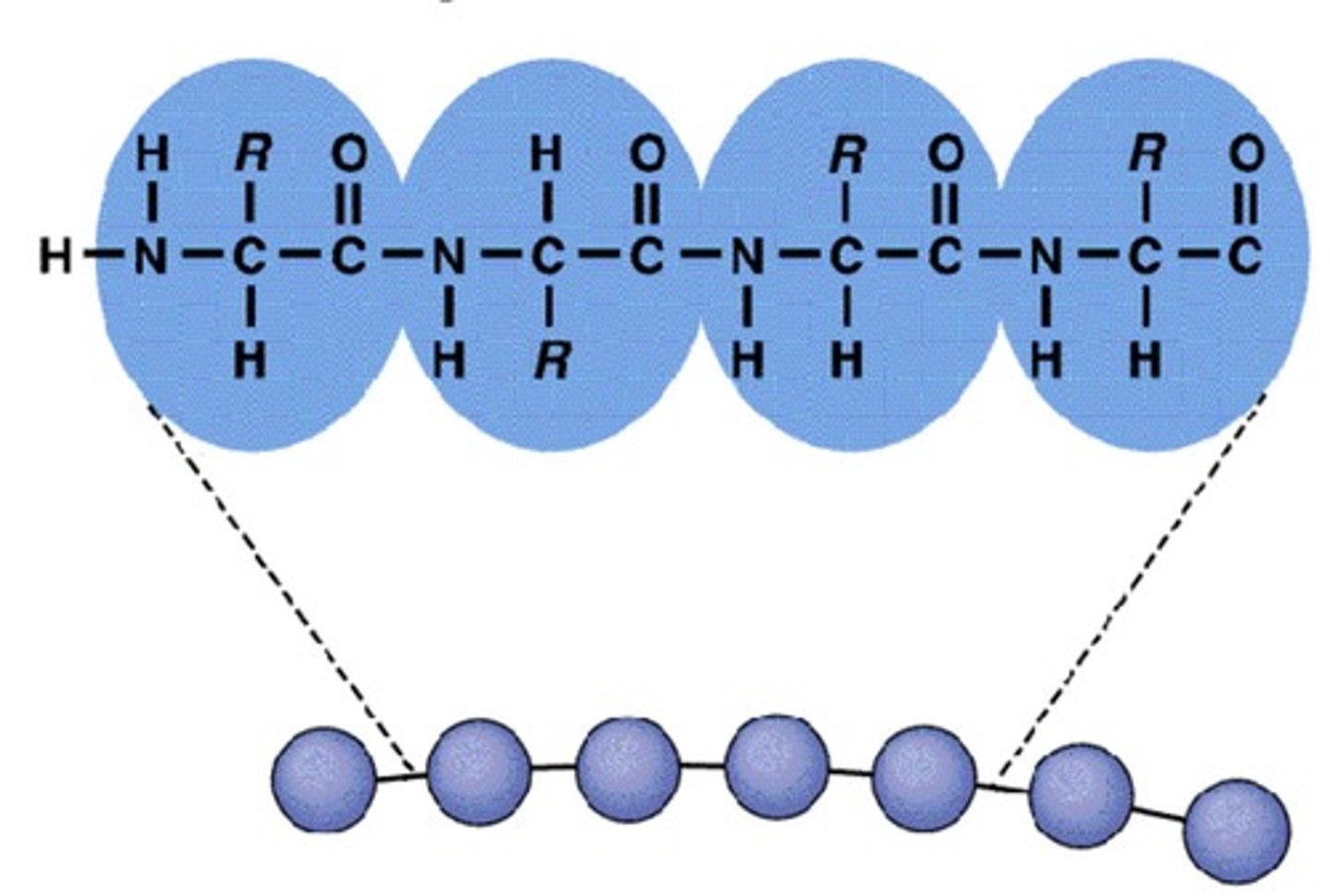
Primary Protein
Single straight line with alpha carbon, carboxyl, side chain, and amide
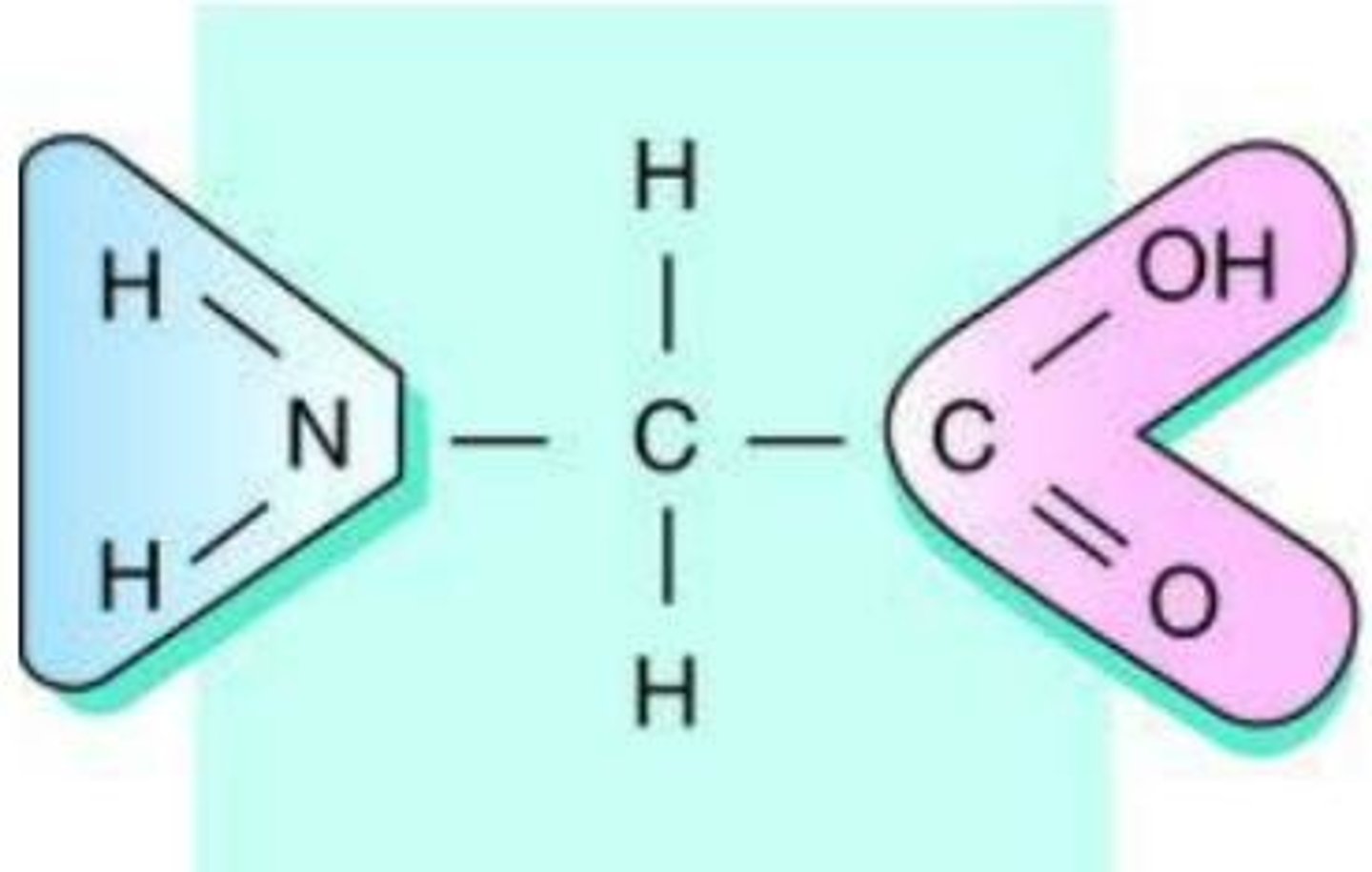
Amide Group
a carbonyl group (C=O) is bonded to a nitrogen atom (N)
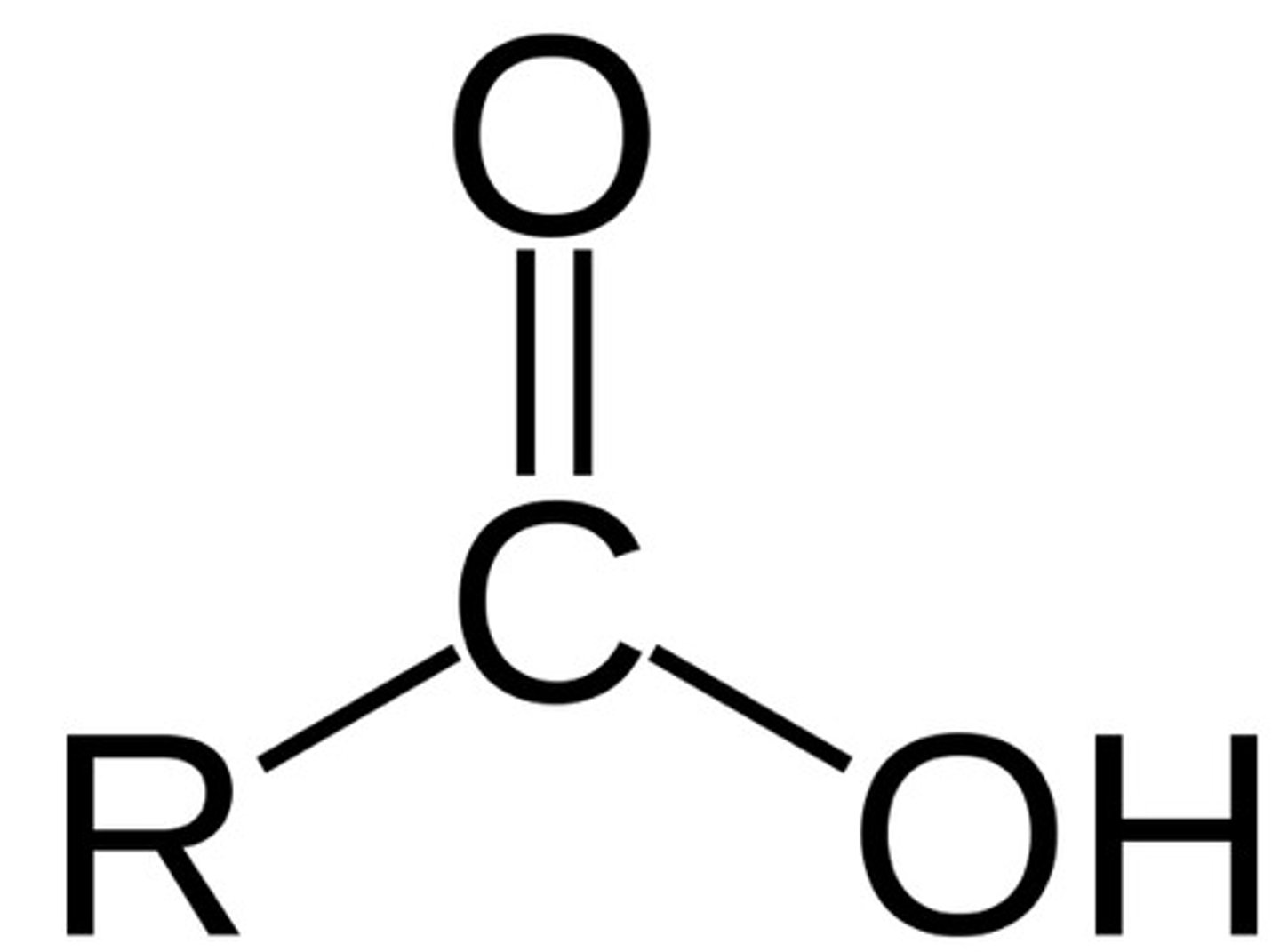
Carboxyl
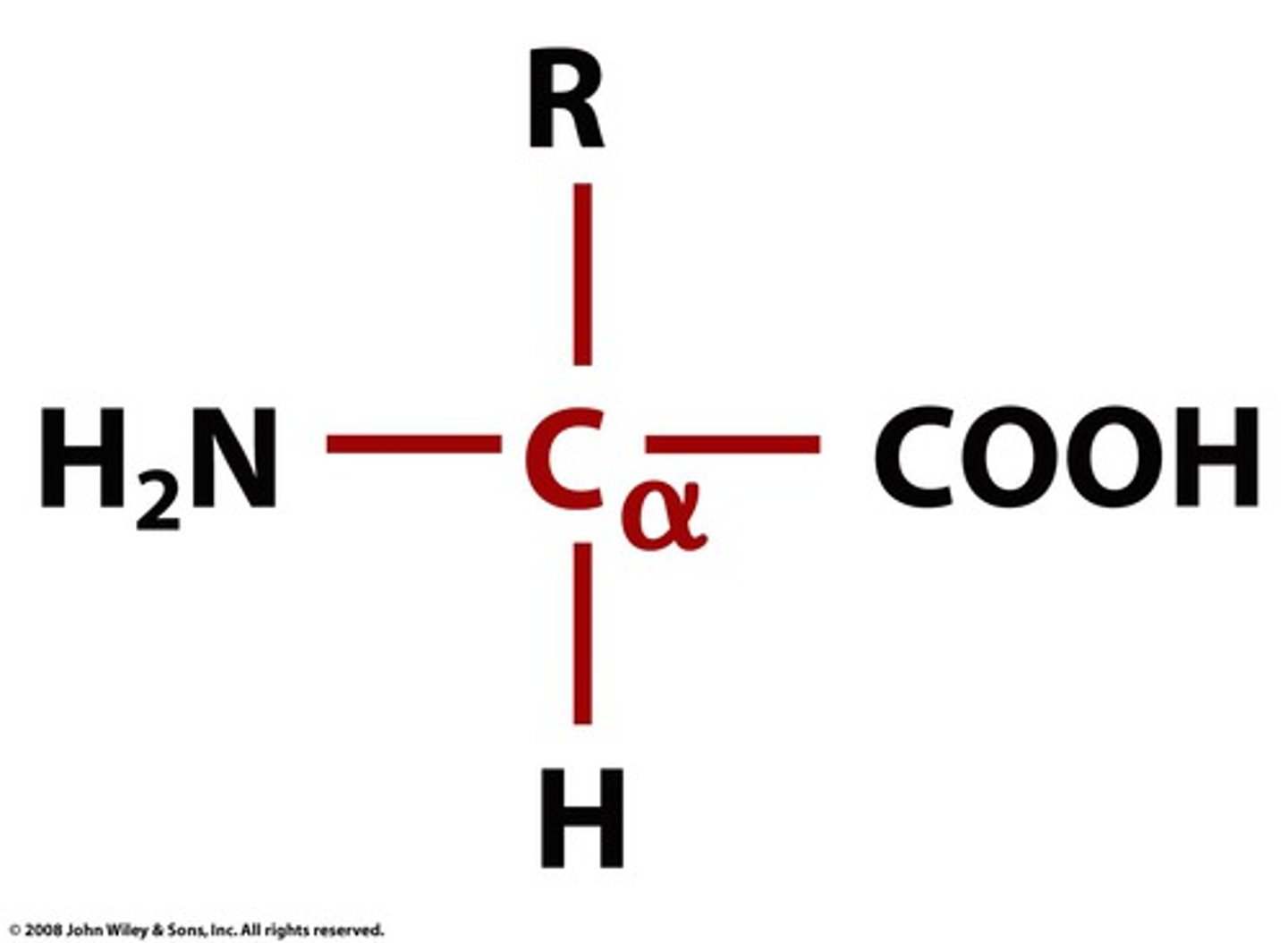
alpha carbon (the red)
Carbon at the center of the side chain, carboxyl, and nitrogen
Enzyme
biological catalyst, dramatically speeding up biochemical reactions within living organisms without being consumed itself
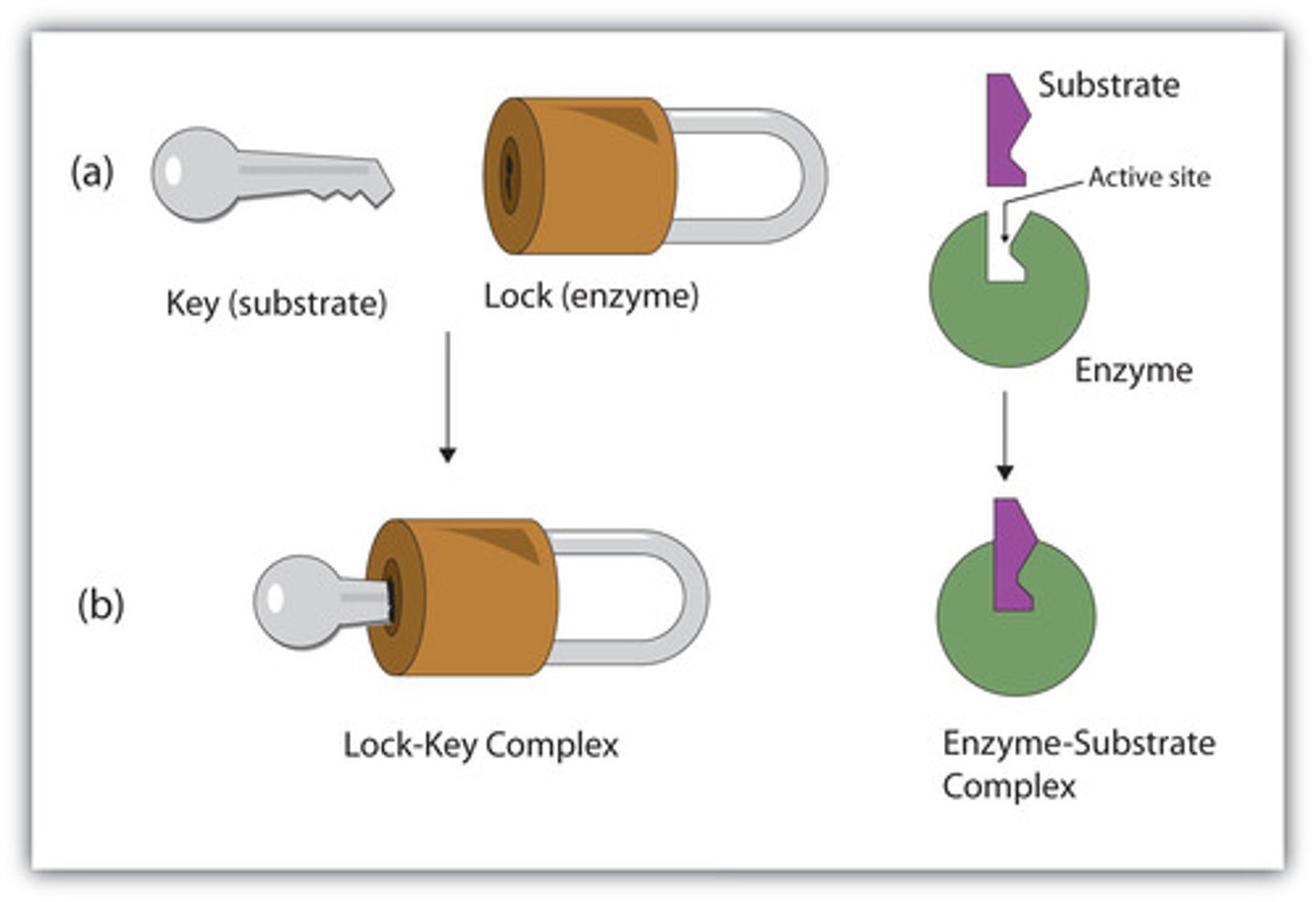
Lock and Key
The substrate fits perfectly into the enzyme
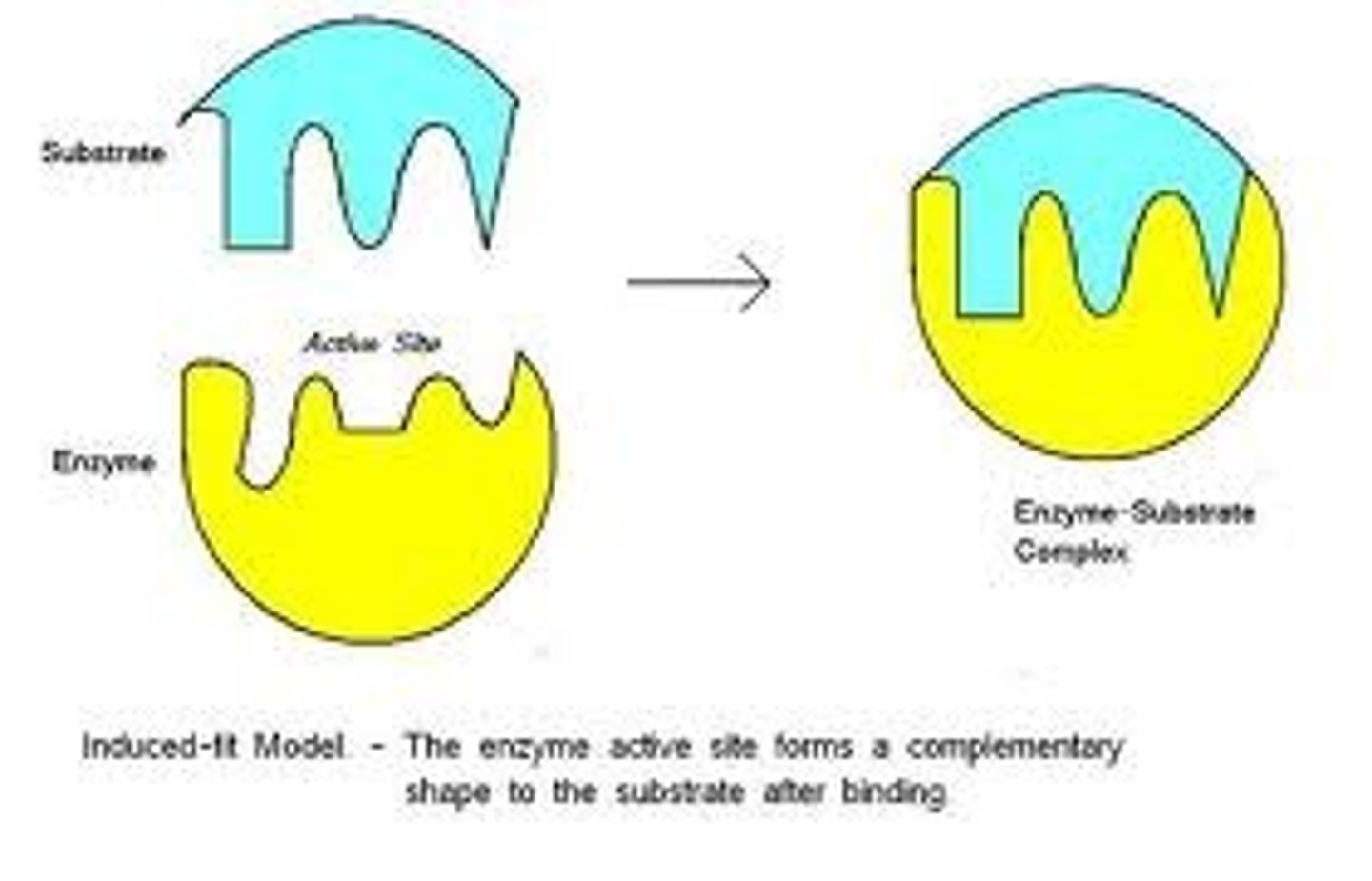
Induced fit
The enzyme absorbs the substrate around it
What is the role of the R side chain in amino acids?
The R side chain allows for hydrogen bonds.
What is a peptide bond?
A bond formed when H2O is removed during a dehydration reaction, linking C and N.
What are the two ends of a polypeptide chain called?
The N-terminus (base) and C-terminus (acid).
What is the transition state in enzyme catalysis?
The least stable point between reactants and products, with partially broken and formed bonds.
What is the difference between the lock and key model and the induced fit model?
The lock and key model suggests a perfect fit, while the induced fit model involves the enzyme reshaping around the substrate.
What is allosteric inhibition?
A regulatory molecule temporarily binds to an enzyme, changing its shape and stopping the reaction.
What does hydrolase do?
It catalyzes the hydrolysis of larger molecules into smaller ones.
What characterizes tertiary protein structure?
It involves disulfide bridges, hydrogen bonds, and ionic bonds.
What is competitive inhibition?
A regulatory molecule competes with the substrate for the active site, slowing the reaction without stopping it.
What determines the folding of a protein?
Hydrophilic residues go on the outside, while hydrophobic residues are on the inside.
What is the secondary structure of proteins primarily stabilized by?
Hydrogen bonds.
What are the two common forms of secondary protein structure?
Alpha-helix and beta-pleated sheets.
What is quaternary protein structure?
The arrangement of four protein subunits together.
What is the difference between hydrolysis and dehydration reactions?
Hydrolysis breaks down molecules, while dehydration builds them up.
What is the active site of an enzyme?
The region where substrates bind and undergo a chemical reaction.
What occurs during the initiation phase of enzyme action?
Substrates form an enzyme-substrate complex.
What is metabolism composed of?
Anabolism (building up) and catabolism (breaking down).
What is the function of synthase enzymes?
They catalyze the dehydration reaction to combine two monomers into a larger molecule.
What is the role of kinase enzymes?
They transfer phosphate groups, usually from ATP to another molecule.
What happens to proteins at high temperatures?
They can denature, altering their 3D structure and activity.
What are prions?
Misfolded proteins that can cause deadly brain diseases.
What is the role of chaperonins?
They assist with the refolding of misfolded proteins.