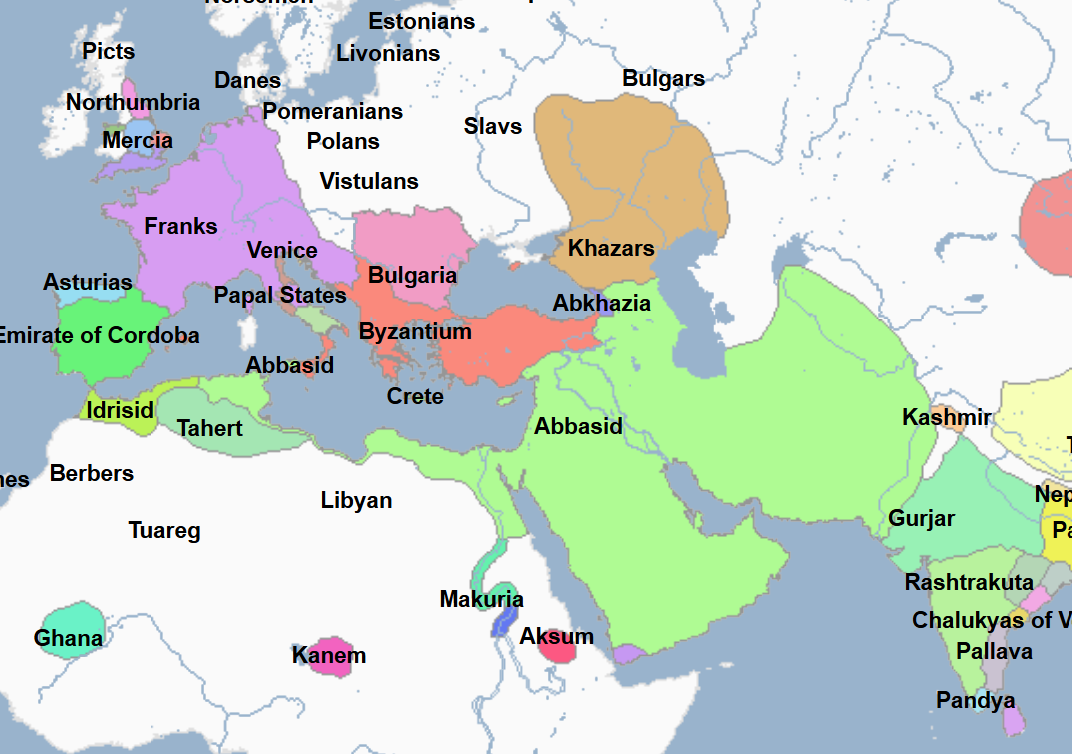
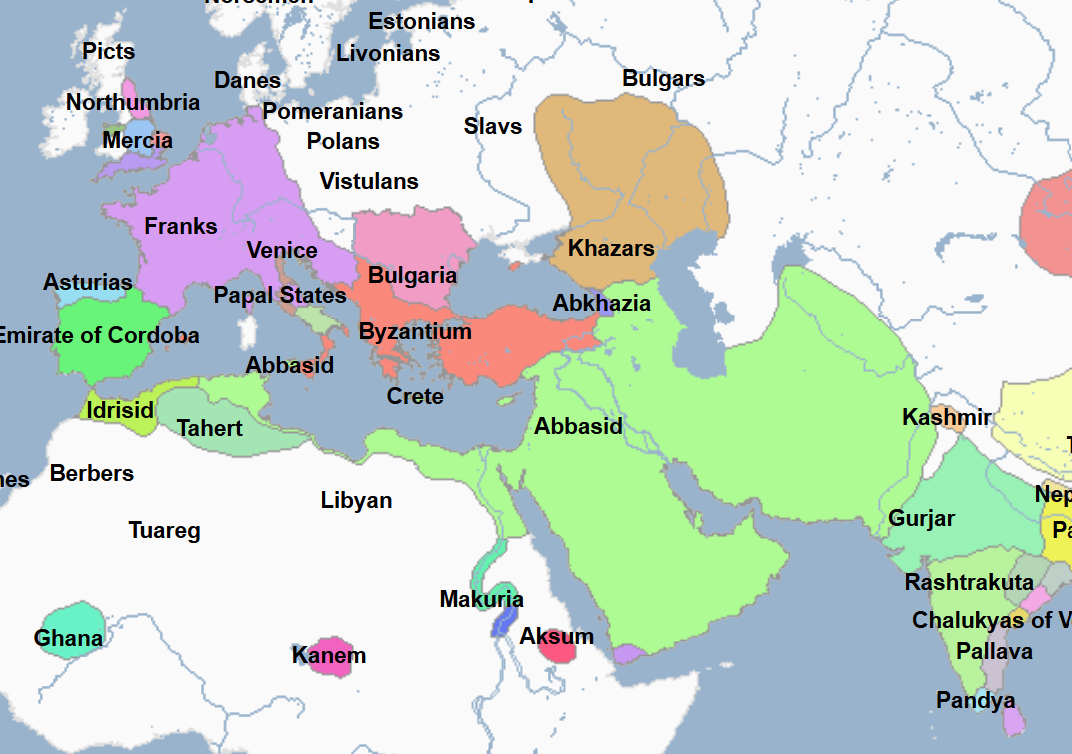
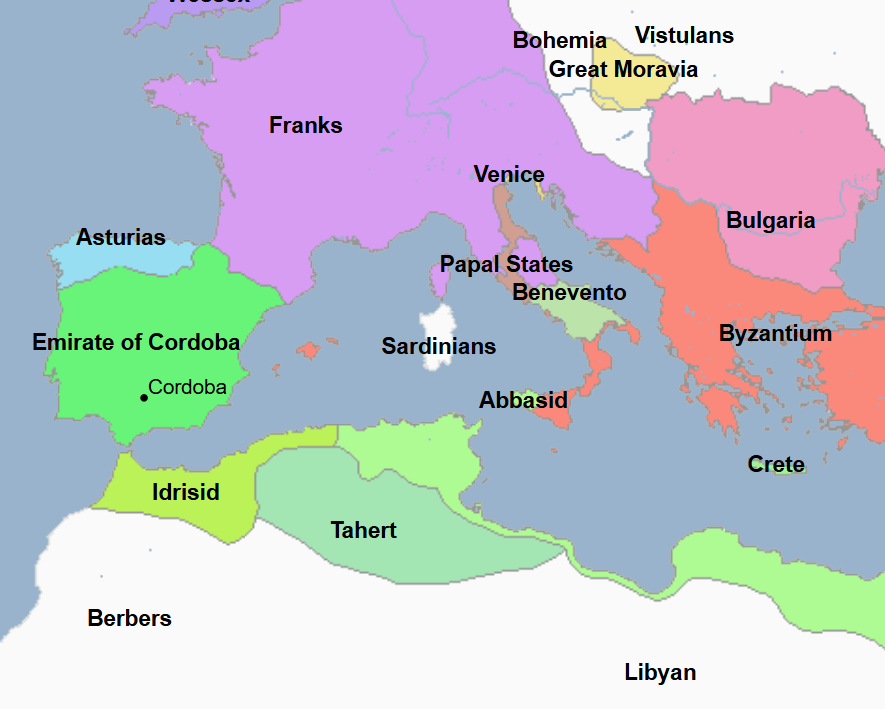
(1) Islamic World: Political History and Notable People
1/105
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Includes Both Notable Religious and Non-Religious Figures | Images show Regimes at their territorial peak unless indicated otherwise
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms

570 - 632 - Muhammad (All Facts)
Born in Mecca
Founder of Islam
He is known as “The Great Prophet”
He was
Born to poor parents and eventually orphaned
He was a preacher of the Quraysh tribe of the Bedouin
He called for an end to the demons and idols of Arab religion or Arab polytheism
He denounced the idols associated with the Kaaba
He called for conversion to the ways of the one true god, Allah
He urged people to turn to Allah, “the One and Only God” who had revealed Himself to the Jews and the Christians, but both of whom had misinterpreted his true word but then had revealed himself to the namesake
He urged people to help the poor
In Mecca, he was married to a wealthy Qurayshi widow with money in the caravan business
He became increasingly unpopular for his teachings and was eventually forced to leave Mecca and take refuge at Medina in what became known as the “Hegira”
He had done this due to his emphasis on helping the poor, which contrasted with the aims of the rich and powerful Meccans, who had become his enemies over the years
While in Medina, he continued to receive revelations from Allah, which began to be recorded
He saw himself as an instrument of Allah and submitted to Allah’s will, and thus established his faith based on this principle, Islam, which is Arabic for “submission”
He eventually left Medina and made a pilgrimage back to Mecca along with his followers for which they were granted permission by the authorities of the time, following the lifting of a siege of Medina by the Meccans
City which eventually accepted his authority as a preacher and Prophet of God
He eventually made peace with and took control of Mecca when they agreed to recognize him as Prophet of God
In exchange, he accepted that the Kaaba, the former temple of polytheism in Mecca, can remain a place of pilgrimage for the new faith of Islam
He raised the status of women in many ways given that he
Treated his wives with love and devotion
Insisted that dowries be paid to the future wife rather than to her father
Forbade female infanticide, a common practice during his time
His wife was educated and owned her own business, which set a pattern for the recognition of Muslim women’s abilities
Upon his death, his closest followers elected his father-in-law to succeed him as leader of the Islamic World
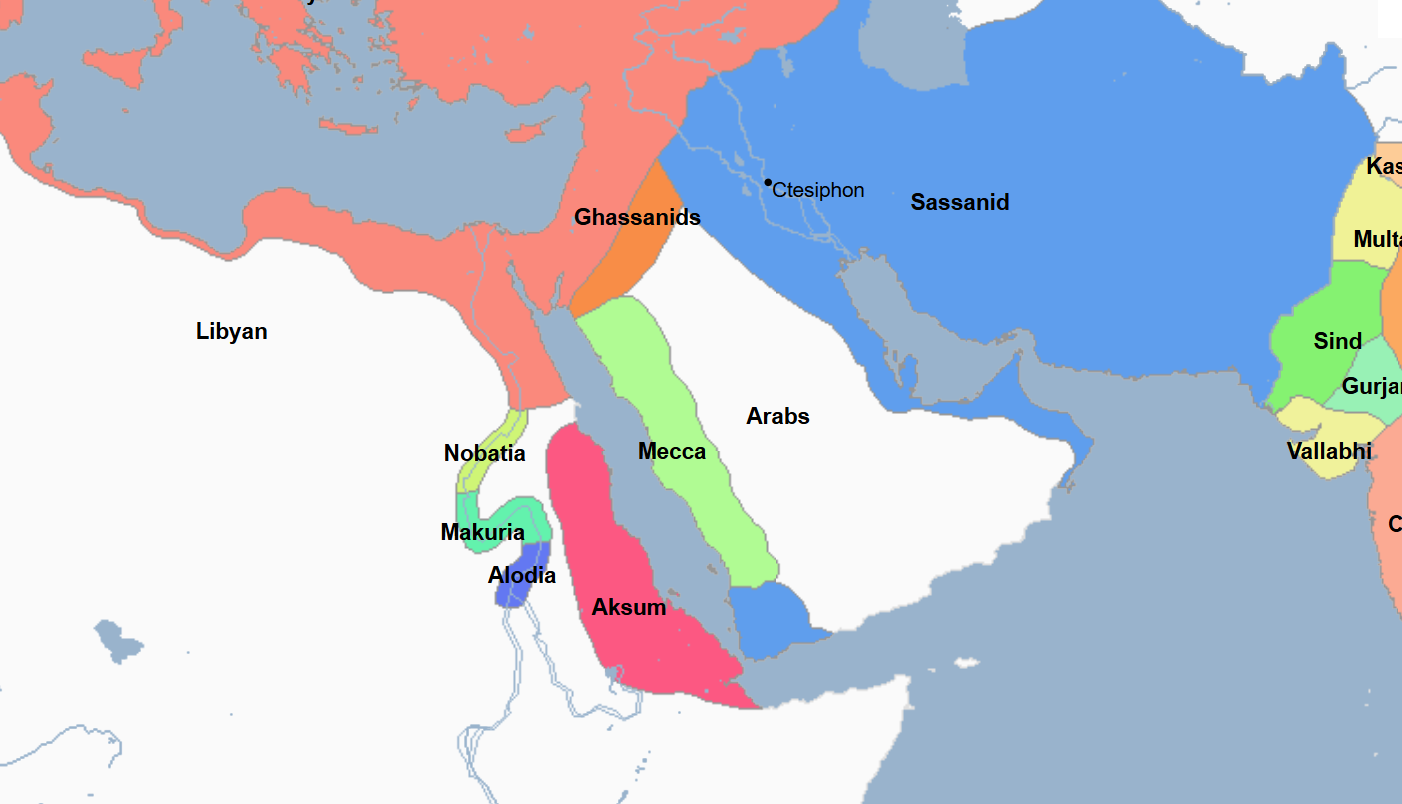
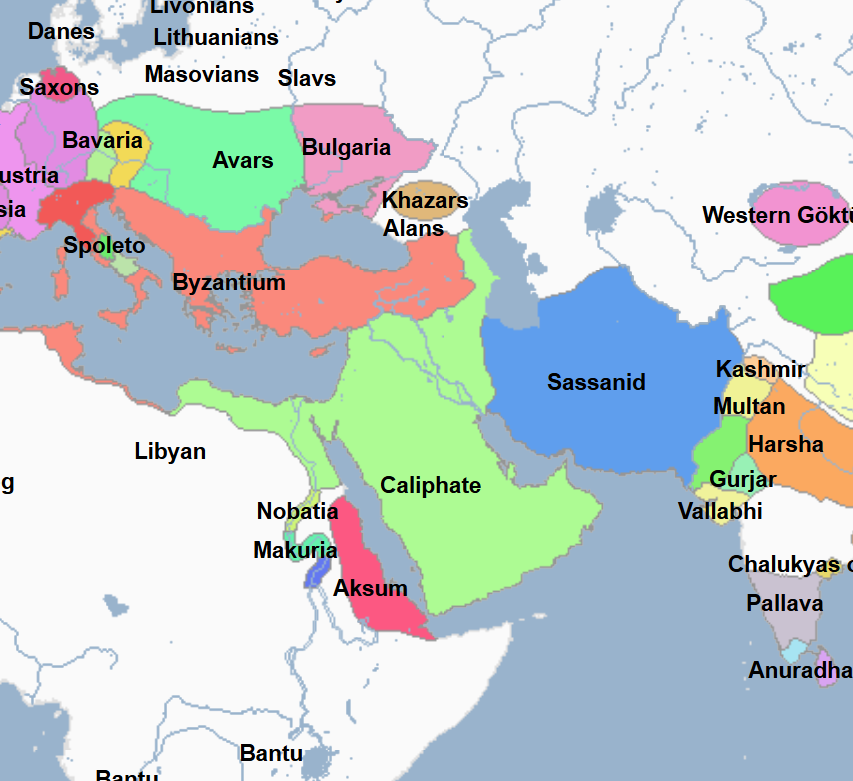
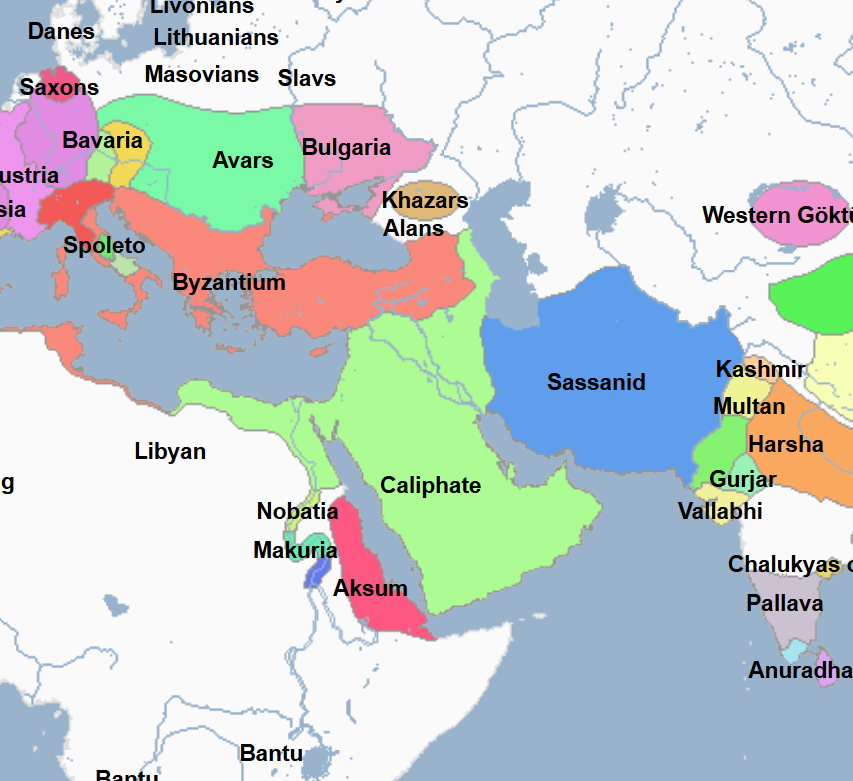
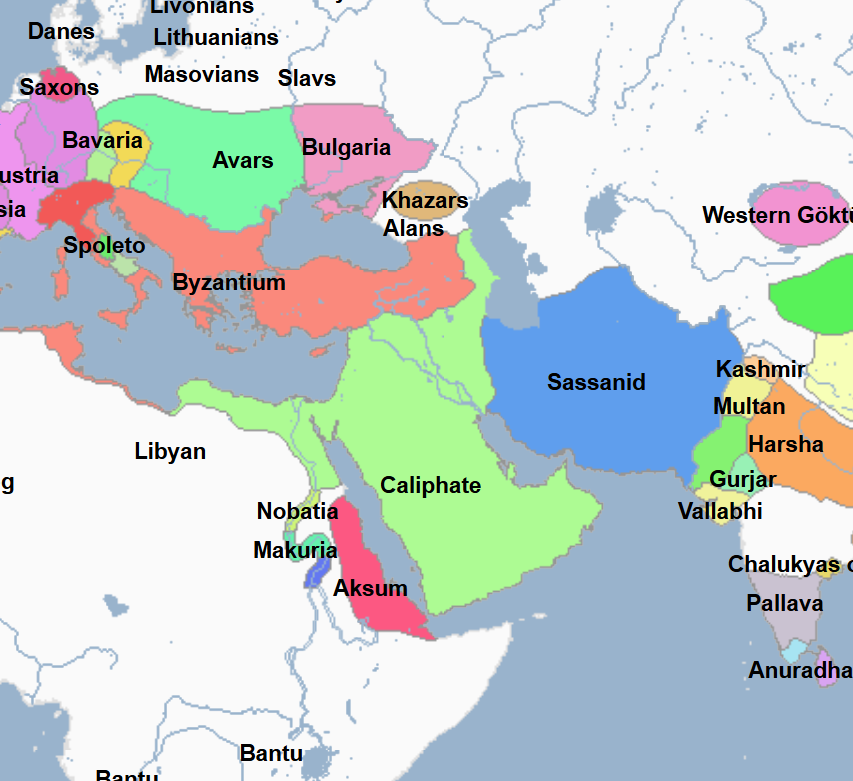
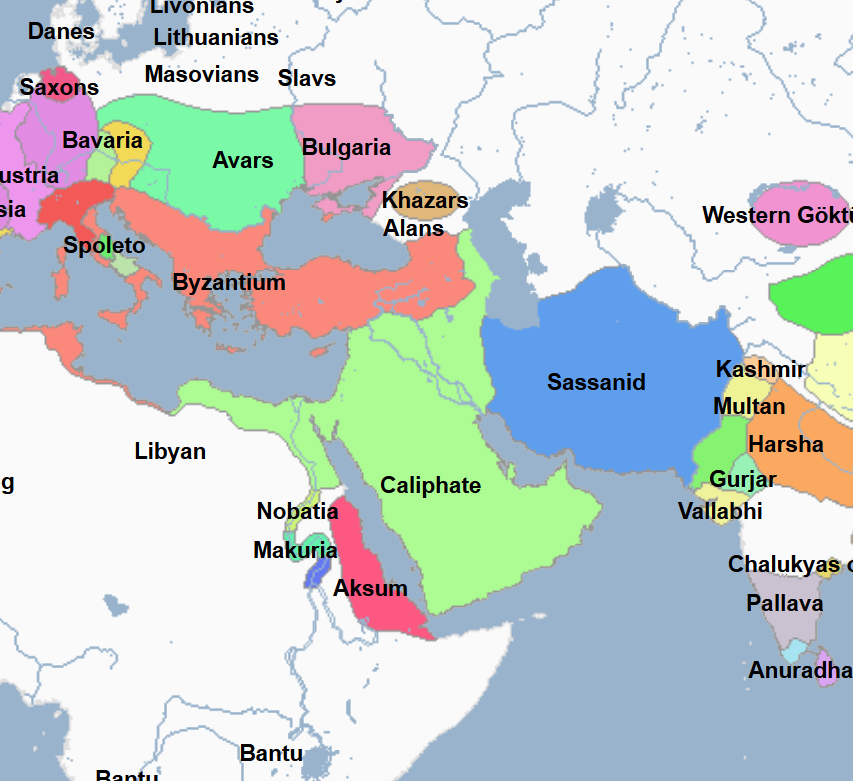
622 - 632 - First Islamic State (All Facts)
Established by Mohammed, it culminated in the defeat of the Meccans and control of Mecca
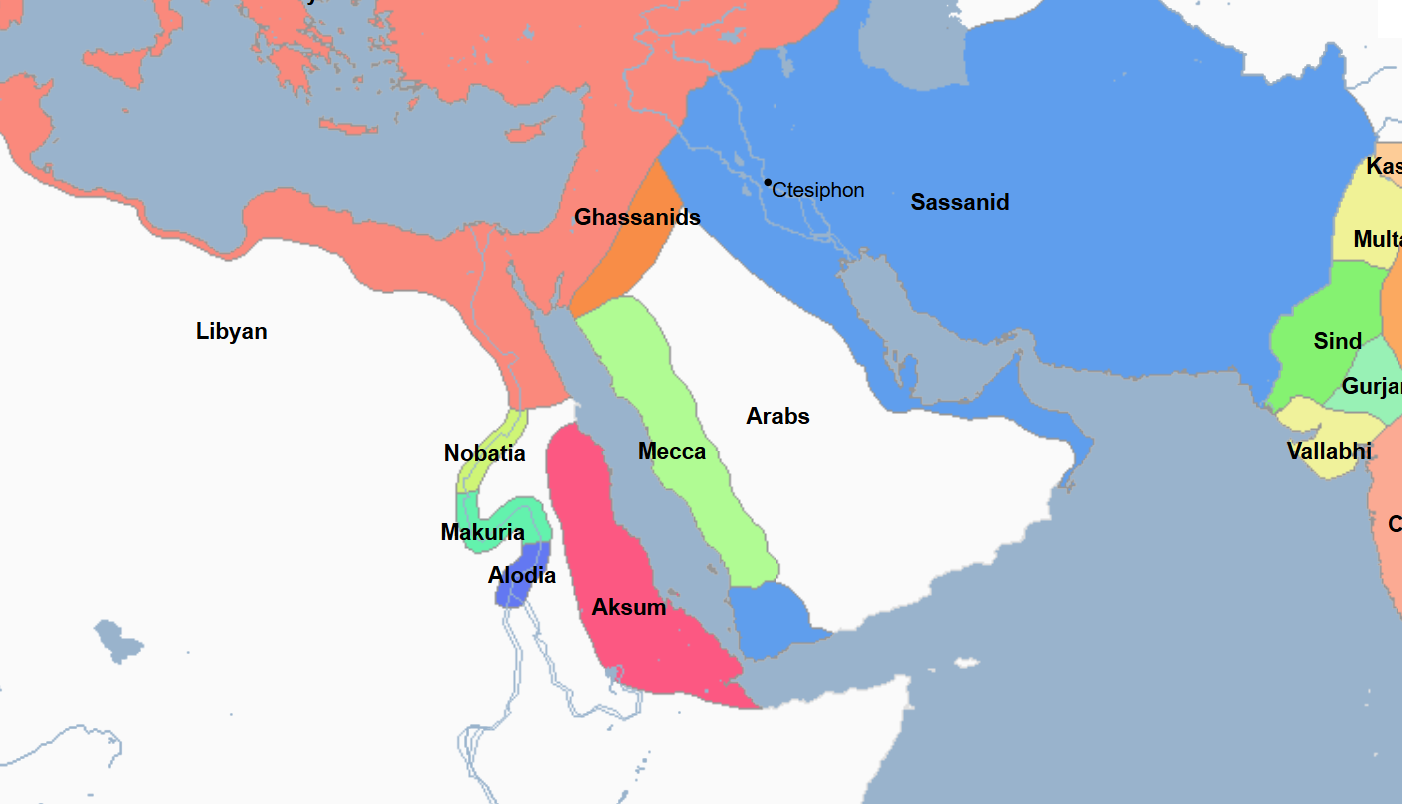
632 - 661 - Rashidun Caliphate (All Facts)
1st Caliphate of the Islamic World
Its capital was Medina, and then later the city of Kufa
Caliphate of many notable Islamic leaders including
Abu Bakr
Umar
Uthman
Ali

632 - 634 - Abu Bakr (All Facts)
1st Caliph and Founder of the Rashidun Caliphate
He was a father-in-law and closest friend to Mohammed the Prophet
He was a mild and courteous old man
He was elected by Mohammed’s closest followers following the Prophet’s death
The claims of Ali being the most faithful follower and successor or caliph instead of his own were brushed aside
He ensured the survival of Islam and achieved much despite his short reign
Under his reign, via his general Khalid ibn-al Walid, the Arab Muslims
Consolidated Arab tribes that rejected the new faith and authority of the Muslim leaders in Medina by launching military expeditions to bring them back into line
Invaded the Byzantine Empire in Syria
Invaded the Sassanid Empire in Mesopotamia

634 - 644 - Umar (All Facts)
2nd Caliph of the Rashidun Caliphate
He was a stern and puritanical figure unlike his predecessor
He was a father-in-law and senior companion of the Prophet Mohammed
Under his reign, the Arab Muslims, via his general Khalid ibn-al Walid
Defeated the Byzantine Empire and took Byzantine-controlled Syria and Damascus in the Battle of Yarmuk
Defeated Yazdegerd III and the Sassanid Empire and took all of its territories in the Battles of al-Qadisiyyah and Nahavand
Under his reign, the Arab Muslims, via his general Abu Ubayda
Invaded, defeated, and took control of Damascus and Byzantine Syria
Under his reign, the Arab Muslims, via his general Amr ibn al-As
Invaded, defeated, and took control of Alexandria and Byzantine Egypt
Under his reign, the Arab Muslims reached Cyrenaica and Tripolitania and also proceeded south after their conquest of Egypt towards Nubia
Under his reign, he oversaw a mass migration of Arab tribes into the fertile lands between the Tigris and Euphrates, the Levant or Sassanid Mesopotamia
Rather than mingle with the local people, the Arab armies set up military encampments in Kufa and Basra on the edge of the desert
From those military encampments, they
controlled and taxed the region
Mounted Bedouin raids into the Sassanid Empire, which they ultimately defeated in the Battle of Nahavand
He was assassinated in Media and succeeded by his successor
629 - 638 - Khalid ibn-al Walid (All Facts)
Muslim General under Umar of the Rashidun Caliphate, he led the Arab Muslims
Invaded, defeated, and took control of Damascus and Byzantine Syria in the Battle of Yarmuk
Invaded, defeated, and took control of Yazdegerd III and Sassanid Mesopotamia in the Battles of al-Qadisiyyah and Nahavand
He was nicknamed “the sword of Allah”
634 - 639 - Abu Ubayda (All Facts)
Muslim General under Umar of the Rashidun Caliphate, he led the Arab Muslims
Invaded, defeated, and took control of Byzantine Jerusalem
640 - 646 - Amr ibn al-As (All Facts)
Muslim General under Umar of the Rashidun Caliphate, he led the Arab Muslims
Invaded, defeated, and took control of Alexandria and Byzantine Egypt

644 - 656 - Uthman (All Facts)
3rd Caliph of the Rashidun Caliphate
He was a son-in-law, second cousin, and senior companion of the Prophet Mohammed
Under his reign, the Quran was written down for the first time
He feared that the conquests of Islam would not last if the new faith did not have a single, unifying sacred text like that of Judaism and Christianity
He appointed a committee under one of the Prophet Mohammed’s old secretaries to assemble the scattered texts
Thereafter, all non-standard versions of the Quran were banned from the namesake’s territories
Under his reign, the Arab Muslims
Had Yazdegerd III of the Sassanid Empire (already permanently destroyed) assassinated
Took the cities of Kabul and Kandahar
Via a man named Muawiya, had assembled a formidable fleet of sea ships and invaded Byzantine Cyprus
Invaded Nubia
Invaded Rhodes, systematically having pillaged the island
He was assassinated and succeeded by his the Prophet Mohammed’s son-in law
He was hacked to death at 82 years of age by Muslim rebels from Mesopotamia who
blockaded his home throughout the hot Hijazi summer, which forced the namesake caliph to suffer from protracted hunger and thirst
broke into his home in Medina while he sat studying the Quran
His death as a notable Islamic scholar had thrown the Islamic World into confusion
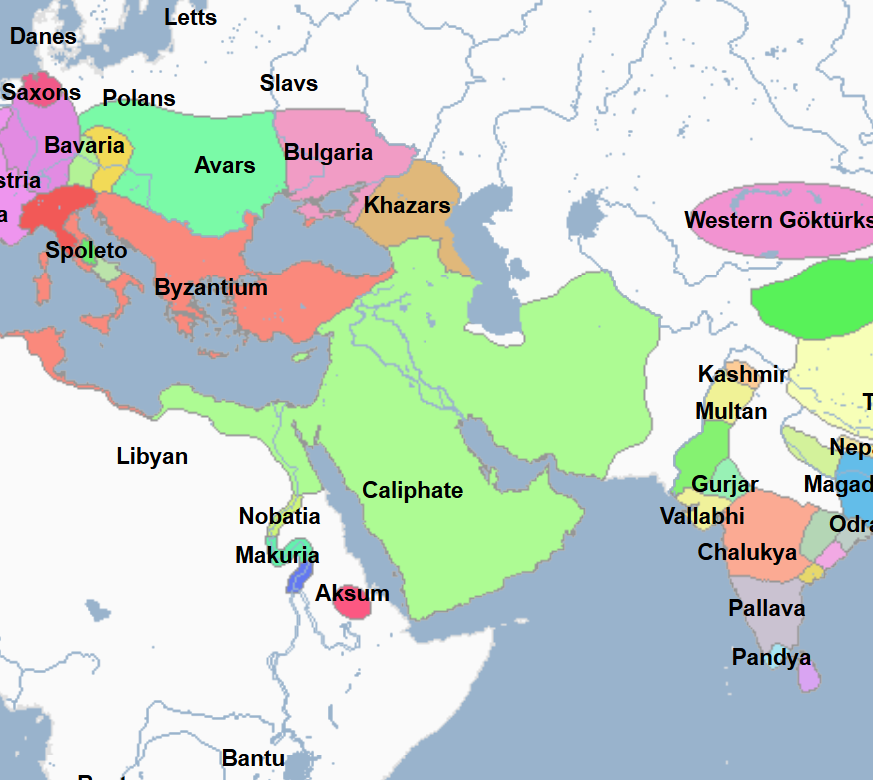

656 - 661 - Ali (All Facts)
4th and Final Caliph of the Rashidun Caliphate
He was a son-in-law and cousin of the Prophet Mohammed
He was married to Mohammed’s daughter Fatima
He is considered the first Shia imam (caliph)
He moved the capital of the Rashidun Caliphate from Medina to Kufa
His forces defeated a rebellion against him which started with a dispute of his succession in the Battle of Basra / Battle of the Camel
He fought against Muawiya and his forces in the Battle of Siffin, but later agreed to arbitrate the issue that caused the battle in the first place
His concession to negotiate with Muawiya after the battle instead of continuing to fight against him was seen as un-Quranic by some of his supporters, which eventually split off and called themselves Kharijites
They proceeded to rebel against him in the Battle of Nahrawan
He was assassinated in Kufa by an ex-supporter turned Kharijite
Exiled Kharijite rebels assassinated him, in which he died after being stabbed with a poisoned sword as he left the mosque at Kufa in Mesopotamia
They did this after he attack them when they rebelled against him for negotiating rather than killing his opponent, Muawiya
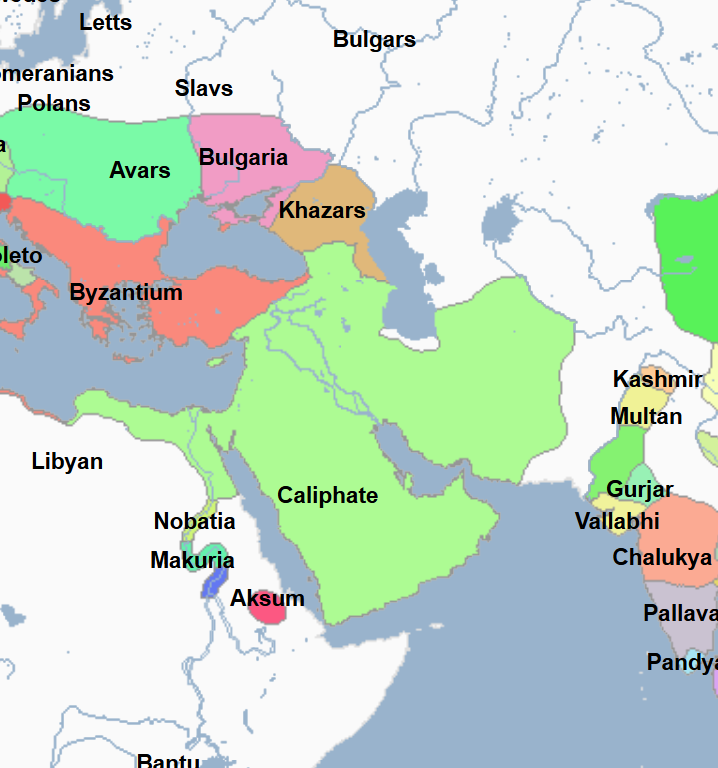
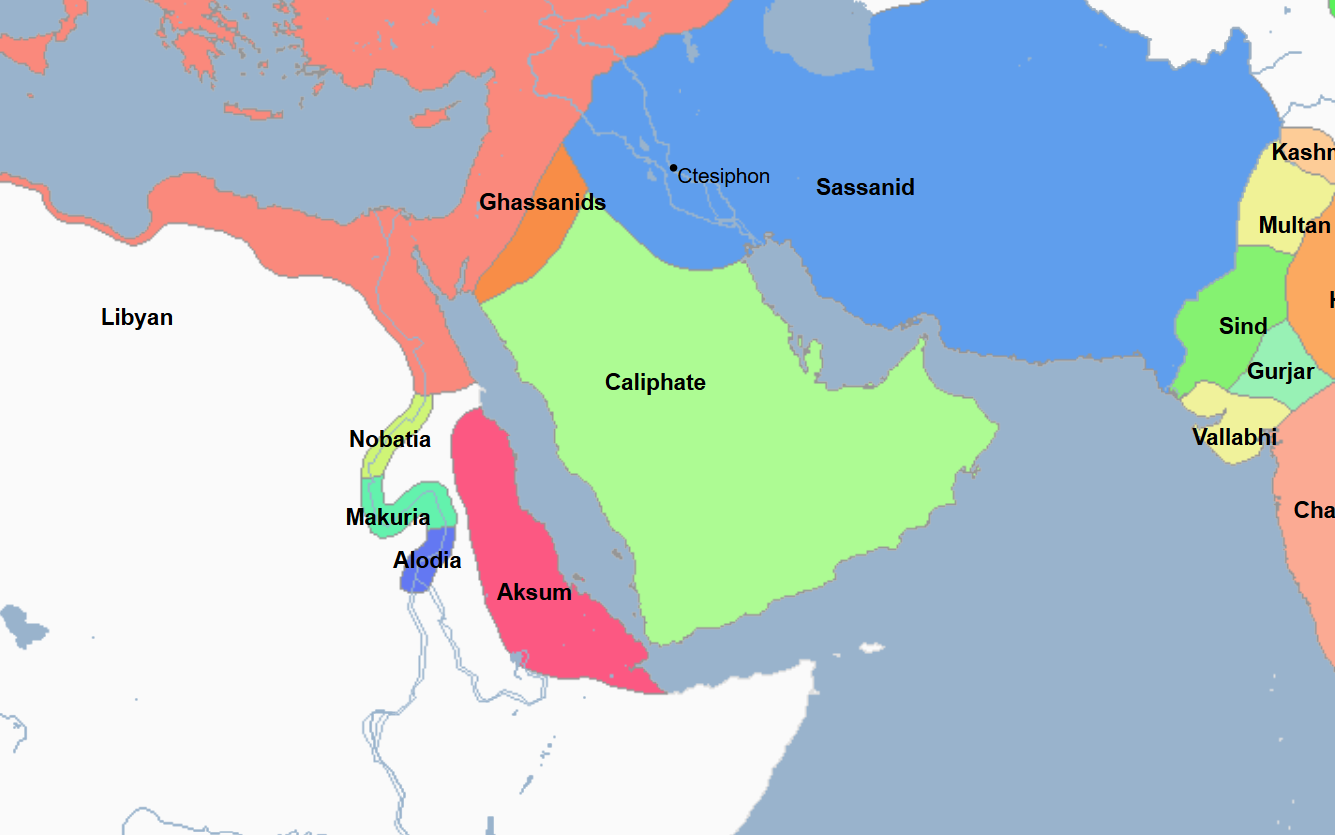
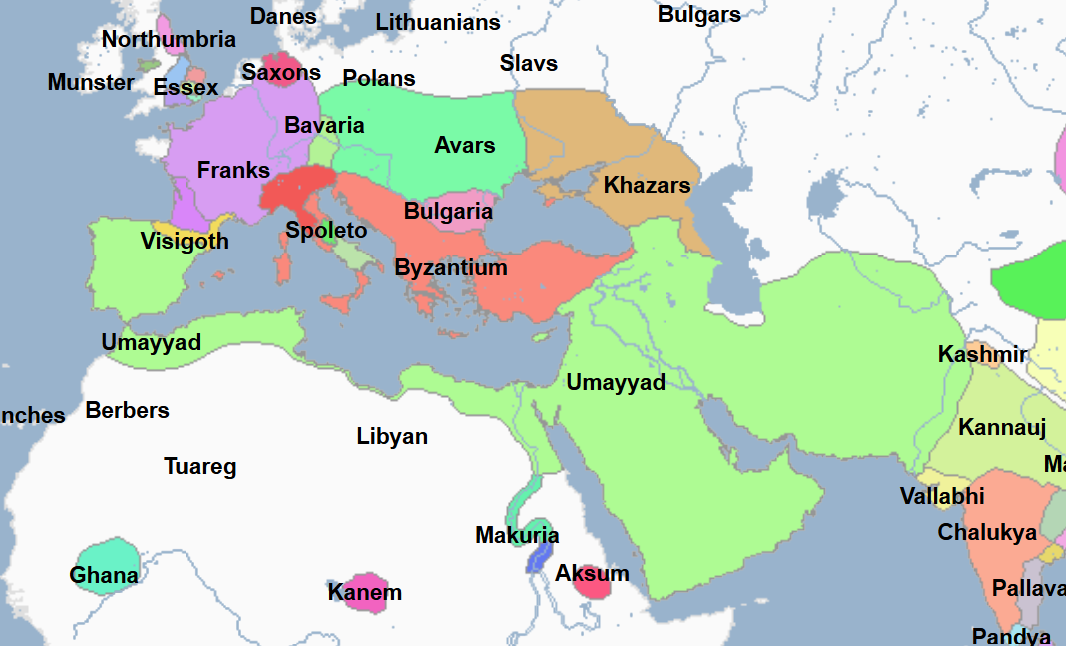
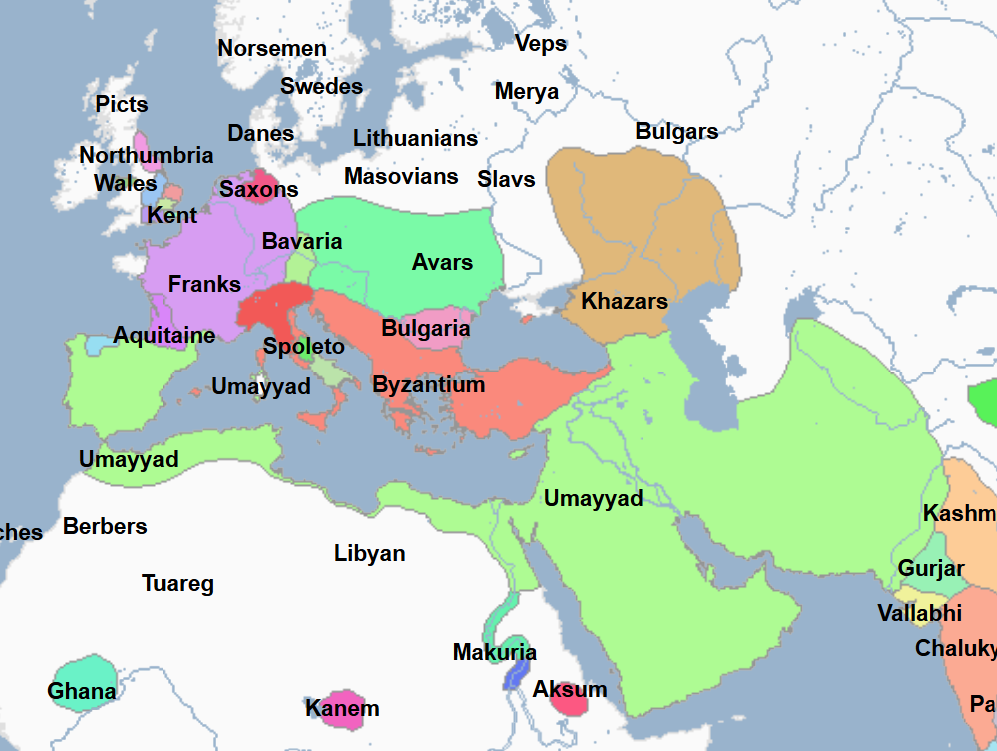
661 - 750 - Umayyad Caliphate (All Facts)
2nd Caliphate of the Islamic World
It was the first Sunni Islamic Caliphate
In the century since the death of Mohammed the Great Prophet, the Arab Muslims under the namesake caliphate carried their faith to the limits of the known world, with the exception of the Byzantine Empire and Northern Europe
At its greatest territorial extent, it stretched from the Atlantic Coast to the Indus River and as far north as the Aral Sea
In this way, its boundaries by this point were wider than that of the Roman Empire
They offered equality to any of their subjects of their invasions if they embraced the Quran, but their assurances were left in complete tatters when jealous conflicts among the Arab settlers and their armies arose
By 740, Muslims from Arabia traded on the coasts with people from Persia
Its capital was Damascus, and then later the city of Harran
Caliphate of many notable Islamic leaders including
Muawiya
Marwan II
Caliphate which fell because they had come to be seen as unworthy rulers
Their ancestors had been among the most bitter enemies of the Great Prophet Mohammed
Their later rulers became godless and debauched
Thus, many had felt that true Islam could only be restored when the family of the Great Prophet Mohammed held the reins of power again

661 - 680 - Muawiya (All Facts)
1st Caliph and Founder of the Umayyad Caliphate
He was initially the governor Syria, who laid waste to Cappadocia in Byzantine Anatolia, upon which he took the spoils back home to Damascus
Prior to his reign, he was known for having led the Arabs in an invasion of Cyprus, which they stormed after he had assembled a formidable fleet of sea ships for the Muslims for the first time
Under his direction, Abu al-Awar and the Rashidun Caliphate defeated Constans II and the Byzantines in the Battle of the Masts, which solidified the Arab Muslim control and command by sea of the Eastern Mediterranean
He fought against Ali and his forces in the Battle of Siffin, but later agreed to arbitrate the issue that caused the battle in the first place
One of Islam’s most respected statesmen due to his
Political maneuvers, which he designed to secure oaths of allegiance from potential rivals for the succession
He insisted that his own son should succeed him
Remarkable flair for administration
Calm and intelligent disposition
Upon his assumption to the throne, he moved the capital from Kufa to Damascus
Under his reign, the Arab Muslims completed their conquest of “Ifriqiyah,” which roughly comprised land stretching from Egypt to Eastern Algeria
By the end of his reign, the Islamic Empire stretched from Kairouan in Tunisia to Kabul in Afghanistan
Under his reign, the Arab Muslims were repelled by the Byzantines from Constantinople from 674 to 678
He consolidated his reign and territory defeating the Umayyads in North Africa and the Near East
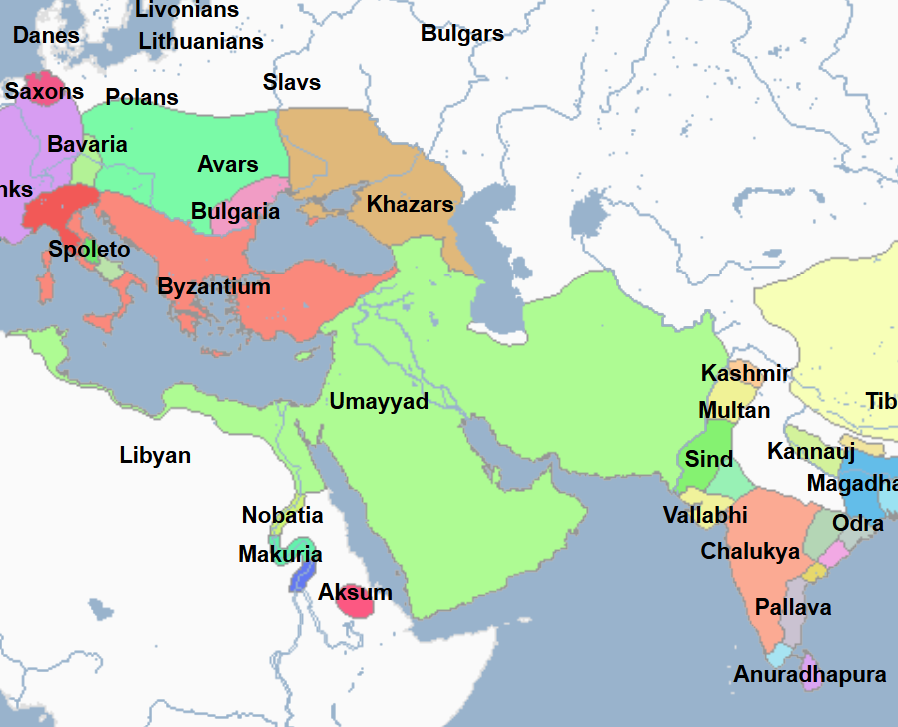

666 - 683 - Uqba ibn Nafi (All Facts)
General under Muawiya of the Umayyad Caliphate
He led the Arab Muslims to invade, defeat, and control North Africa to the Atlantic Ocean, spurring his horse into its waves; taking it from the Byzantine empire
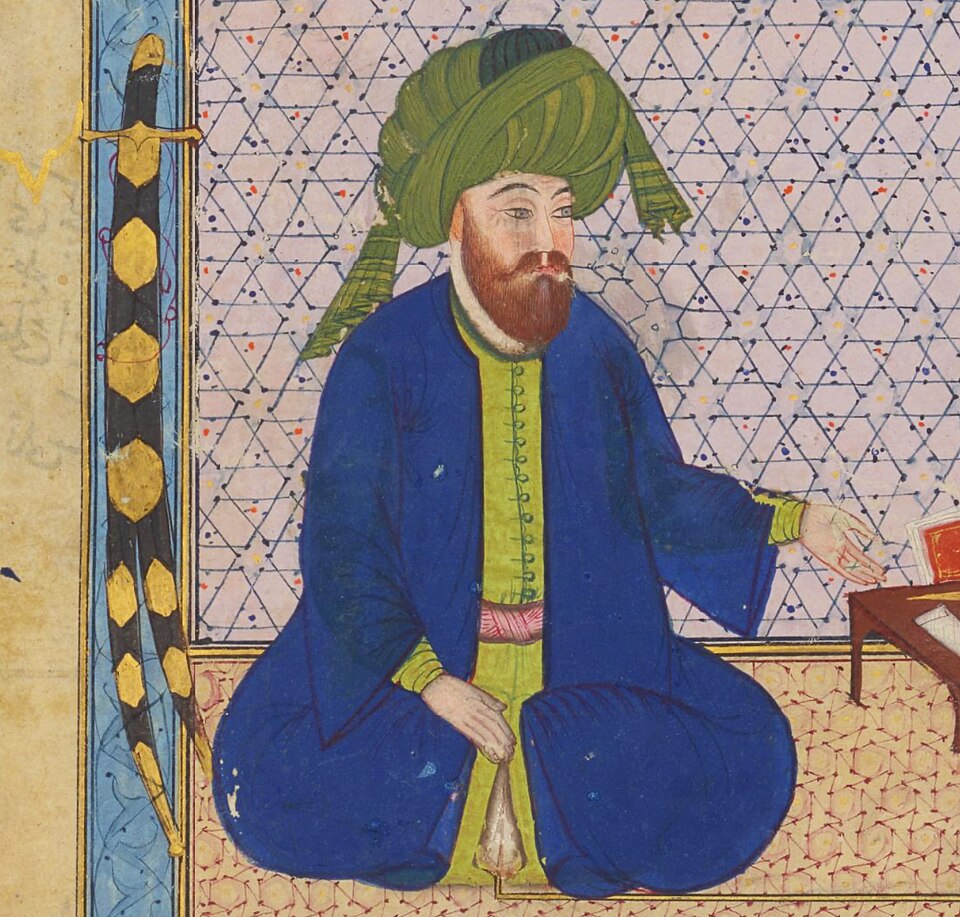

670 - 680 - Husayn ibn Ali (All Facts)
Social, political, and religious leader of Islam in Arabia
He was the son of the Caliph Ali and grandson of the Prophet Mohammed; and rival of Muawiya
He was bought off for an unspecified but substantial sum of money in order not to succeed Ali
He was killed in the Battle of Karbala
His death gave birth to Shia Islam
He is seen as a martyr by Shia Muslims

680 - 683 - Yazid (All Facts)
2nd Caliph of the Umayyad Caliphate
He was initially the governor of Damascus in Islamic Syria
He was the son of his predecessor
His confirmation in office was seen as continuing evidence of the Umayyad Caliphate’s dynastic ambitions
Under his reign, Husayn ibn-Ali led a revolt against him and advanced onto Kufa where his father Ali, the Prophet Mohammed’s son-in-law, has briefly been caliph

684 - 685 - Marwan (All Facts)
4th Caliph of the Umayyad Caliphate
He was a distant cousin of Muawiya

683 - 692 - Abdullah ibn al-Zubayr (All Facts)
Leader of the Zubayrid Caliphate, a usurper Caliphate during the Second Fitna
He was supported by the people of Mecca and Medina
He was acclaimed caliph in Arabia, Mesopotamia, and Egypt
He was supported and acclaimed caliph by the Qais tribe in Syria
686 - 691 - Mus'ab ibn al-Zubayr (All Facts)
Governor of Basra (Iraq), he was the brother of Abdullah ibn al-Zubayr, the usurper or counter caliph that founded the Zubayrid Caliphate
He was defeated and killed by Abd al-Malik and his Umayyad Caliphate forces in the Battle of Maskin during the Second Fitna

685 - 705 - Abd al-Malik (All Facts)
5th Caliph of the Umayyad Caliphate
He oversaw an even greater expansion of the Islamic Empire and the Arabization of the Islamic Empire
Under his reign
The Dome of the Rock or “Qubat as-Sakrah” was built and completed in Jerusalem
It was the first such shrine to be constructed on the orders of an Islamic leader
It commemorates the “binding of Isaac” and the ascent to heaven of the Prophet Mohammed, which supposedly took place at the site on which it was built
The Quran was re-edited with vocalic symbols
During his reign,
He made Arabic as the official language of the Umayyad Empire
He substituted Arabic for Greek as the official language of administration
He made the dinar the official currency, abolishing the previous Byzantine coinage
He comes to an agreement with Constantine IV of the Byzantine Empire whereby they agree to share the taxes from Armenia, Georgia, and Cyprus
However, the Byzantines later break this agreement and he has them defeated at the Battle of Sebastopolis where the Umayyads take Armenia from the Byzantines
He and his forces defeated Mus’ab ibn al-Zubayr of the Zubayrid Caliphate in the Battle of Maskin
His general Al-Hajjaj ibn-Yusuf captured Medina
Under his reign, a Berber revolt in the Aures mountains, in the region the Umayyads called “Ifriqiyah” on the North African coastline, was suppressed
He died in Damascus

692 - 694 - Al-Hajjaj ibn Yusuf (All Facts)
General under Abd al-Malik of the Umayyad Caliphate
He and his forces captured Medina during the Second Fitna
He and his forces ultimately defeated Abdullah ibn-Zubayr and the Zubayrid Caliphate in the Siege of Mecca, thus ending the Second Fitna
He was then made governor of Mesopotamia under Abd al-Malik of the Umayyad Caliphate

705 - 715 - Al-Walid (All Facts)
6th Caliph of the Umayyad Caliphate
Under his reign, he oversaw the construction of the Great Mosque of Damascus
This mosque was enormously expensive
It was built on the site of a Christian Church
Under his reign,
The Islamic religion reached
India in 712
Spain in 715

670 - 720 - Tariq ibn Ziyad (All Facts)
General under Al-Walid of the Umayyad Caliphate
Sent by Musa ibn Nusayr, he led a small Arab Muslim expeditionary force and crossed the Straits of Gibraltar where he took up position on Mt. Calpe which was renamed after him, and defeated Roderic and the Visigoths in the Battle of Guadalete
After this battle, much of Visigothic Spain was given over to the Umayyad Caliphate
After defeating Roderic in the Battle of Guadalete, he took
Toledo
Cordoba
Algeciras
Ecija
Alcala de Manares
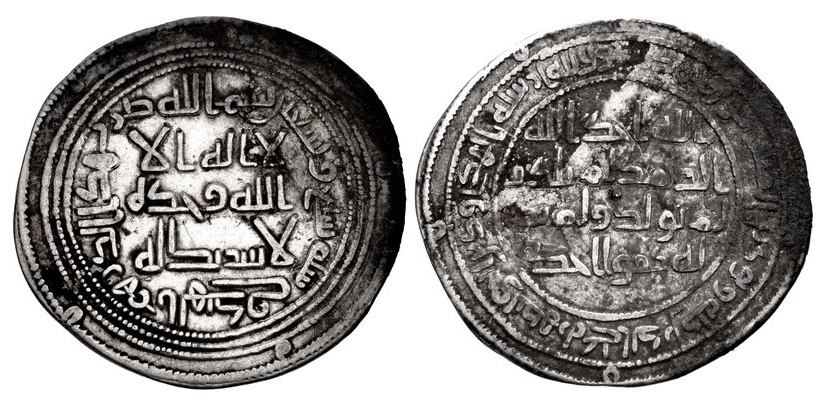

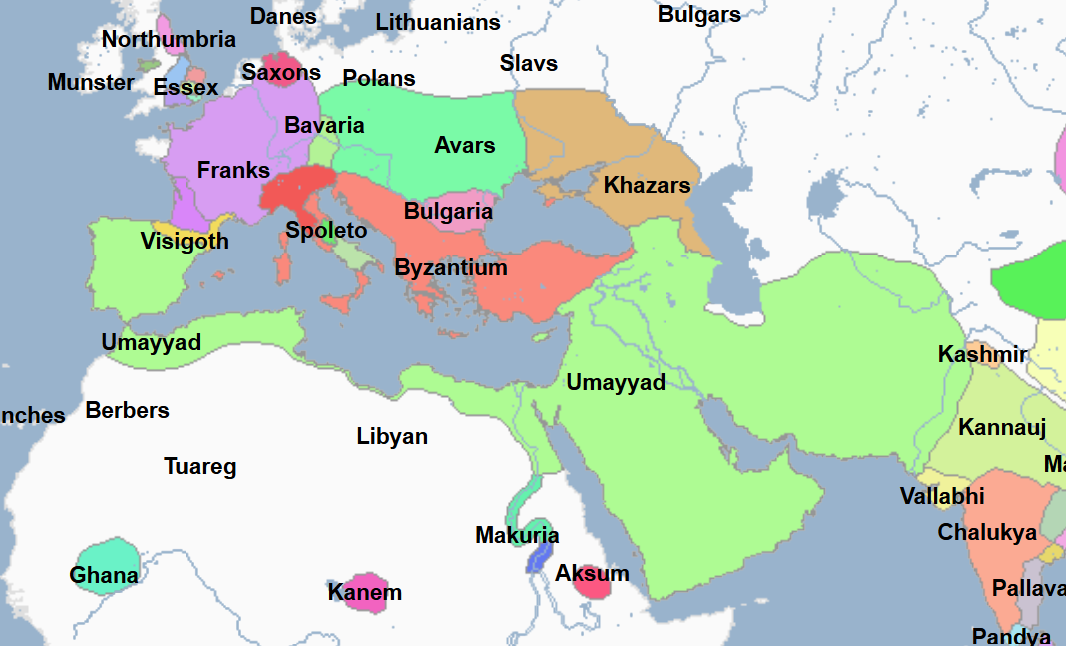
712 - 715 - Mohammed ibn al-Kassim (All Facts)
General under Al-Walid of the Umayyad Caliphate
He led the Arab Muslim invasion of India, in which he and the Arab Muslims came to conquer Sind and part of the Punjab
His army was mustered by the governor of Mesopotamia from the restless Arabs of Kufa and Basra
From the mouth of the Indus River his troops spread over the plains to the capital of Multan
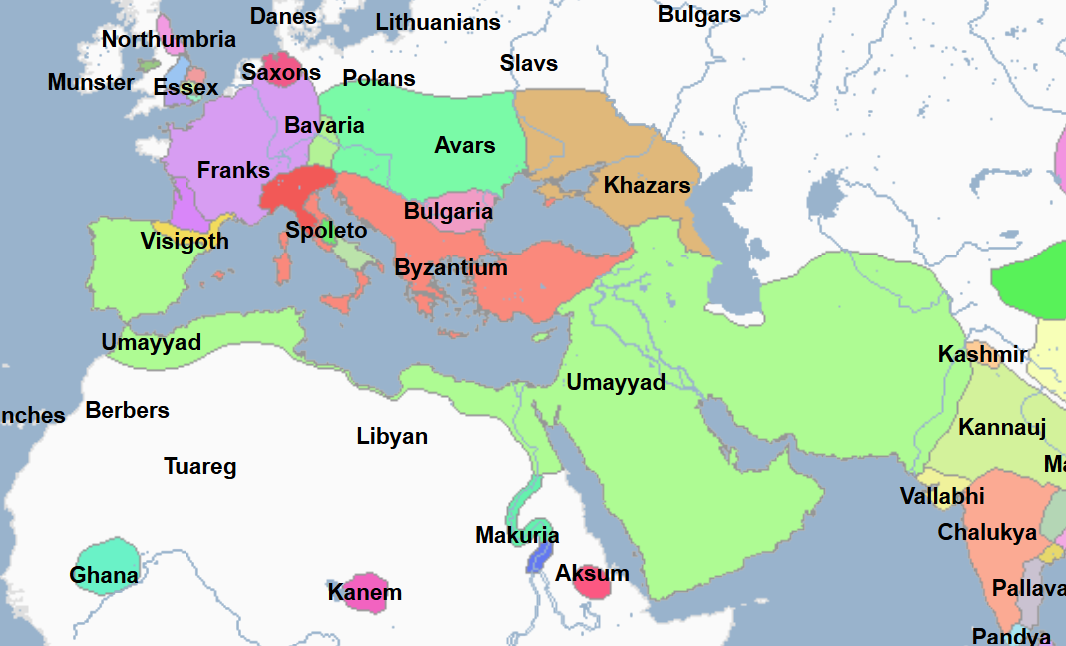
640 - 716 - Musa ibn-Nusayr (All Facts)
General and governor under Abd al-Malik and Al-Walid of the Umayyad Caliphate
He was governor of Ifriqiyah (Tunisia)
He sent a small expedition across the Straits of Gibraltar led by Tariq ibn Ziyad
A few years later he followed Ziyad with new troops and took Spanish towns including
Seville
Merida
Saragossa
Under his watch, the Arab Muslims conquered all of Spain except its northern mountainous region which it had no desire to penetrate
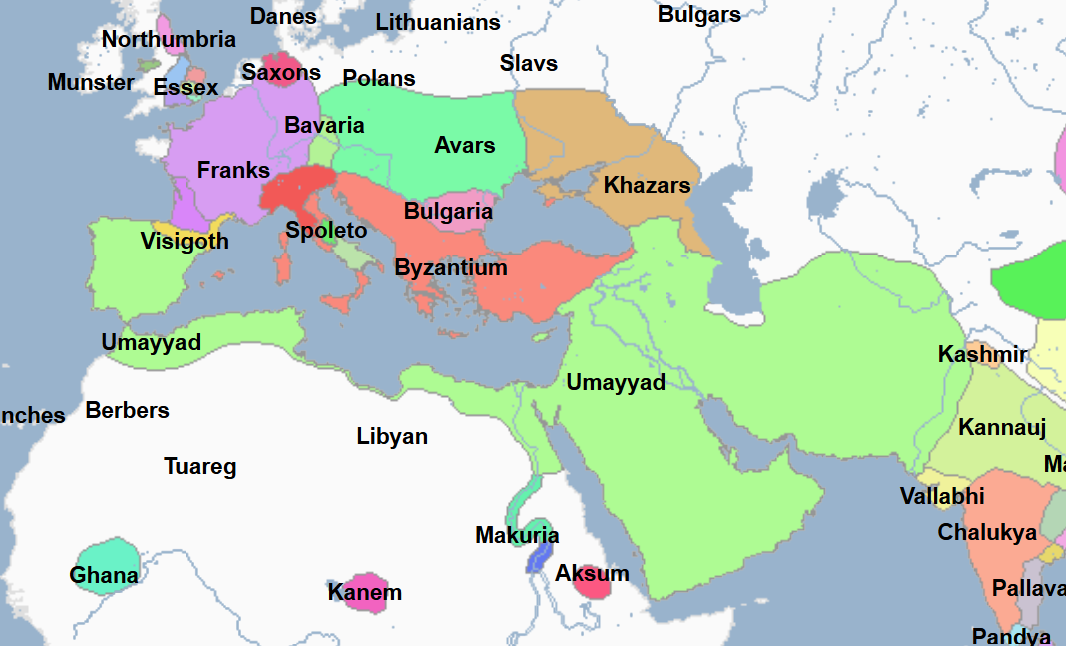
669 - 716 - Qutayba ibn Muslim (All Facts)
General of the Umayyad Caliphate
During his command, the Umayyad Empire stretched from the Atlantic Coast in Spain to the Indus River and as far north as the Aral Sea
In this way, its boundaries were even wider than those of the Roman Empire
Commanded Muslim armies to push east from the Persian plateau into the steppes of Turkestan and the valleys of the Oxus and Jaxartes, where they penetrated into and occupied many cities along the Silk Road from China including
Tashkent
Bokhara
Samarkand
Khwarazm (a fertile oasis on the Aral Sea)
Here, the Muslims first encountered the Turks
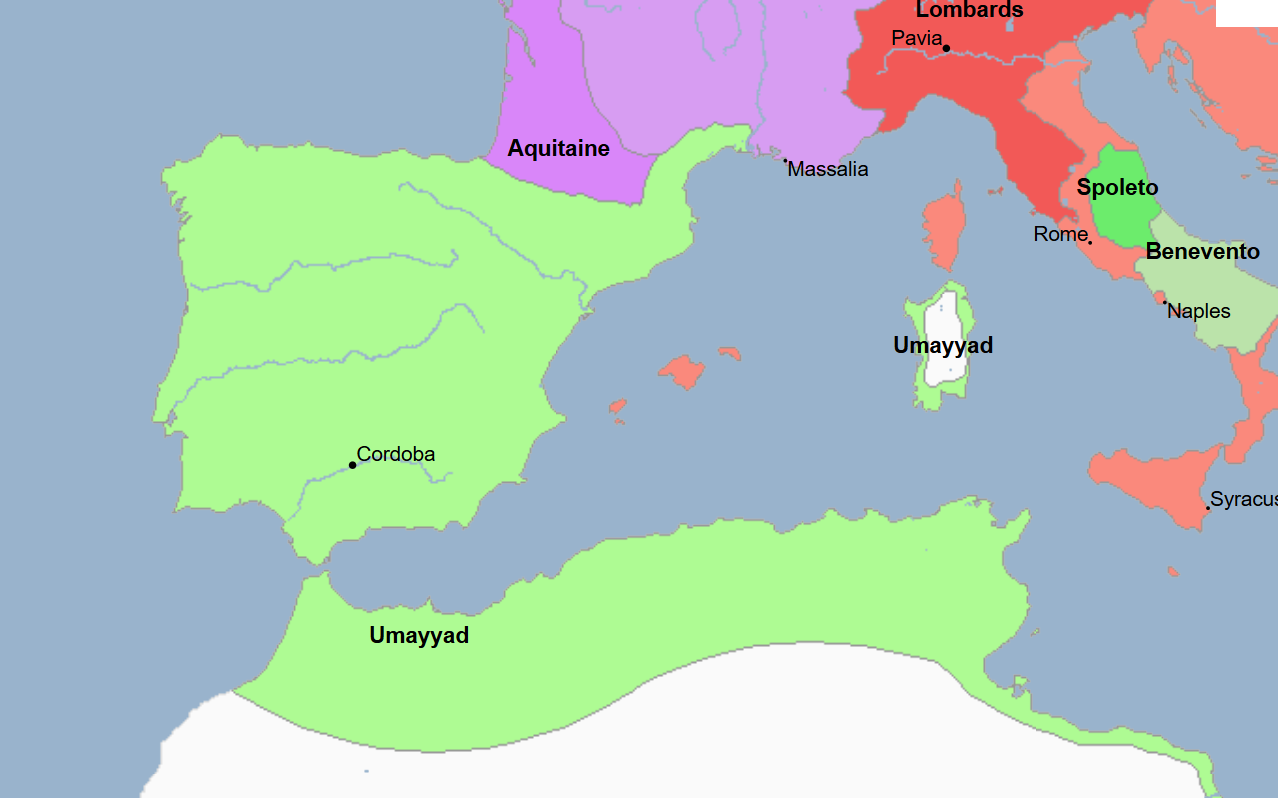
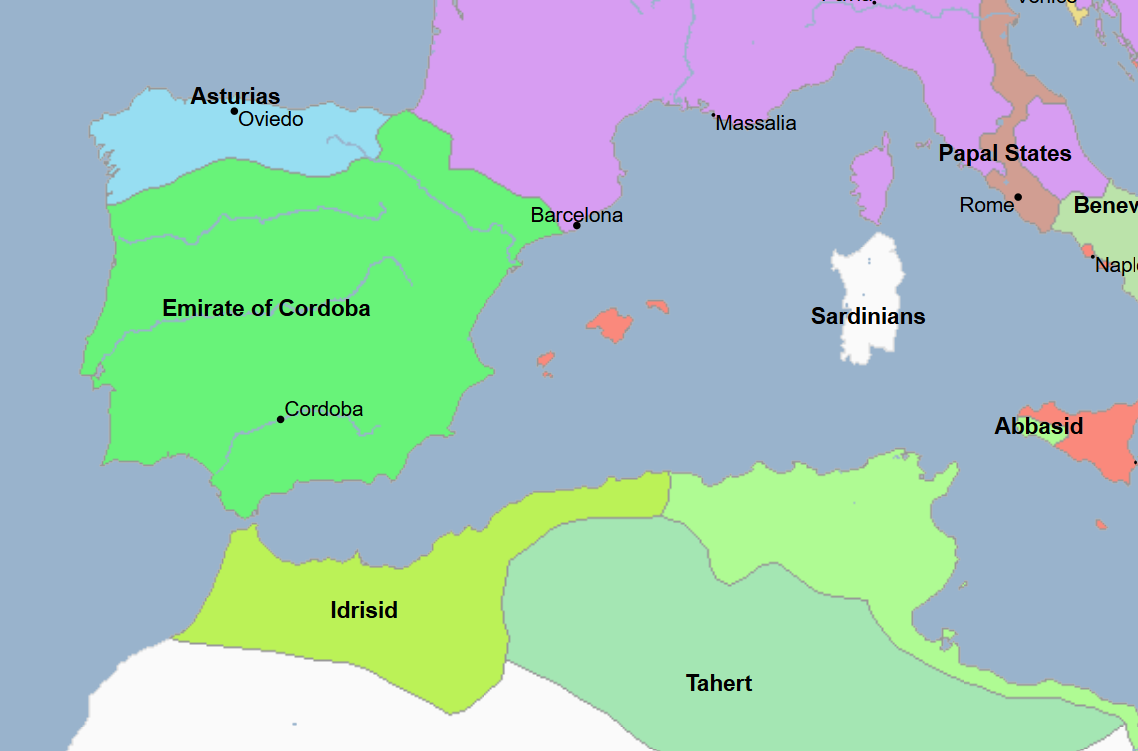
711 - 1492 - Al-Andalus (All Facts)
Title used to refer to the state of Spain under Muslim control, it was the successor state to the Visigothic Kingdom
The Arabs had pacified the country in a relatively enlightened fashion for the time, offering to grant religious freedom to Jews and Christians in return for a town’s capitulation to their rule
In the countryside of the namesake region, most of the peasants ended up adopting the faith of Islam
Thus, like the Abbasids in Baghdad, its Umayyad rulers created a climate of religious toleration allowing Muslims, Christians, and Jews to peacefully coexist
Its rulers promoted trade, having allowed Chinese and Southeast Asian products to enter into Spain and thus into the rest of Europe
It was a center of learning
Cordoba had the largest library in the world at the time
Its people groups, or “People of the Book” (Muslims, Christians, and Jews) not only tolerated one another but also influenced each other
It reached its greatest territorial extent under the Umayyad Caliphate
It was ruled by various Islamic entities including
The Umayyad Emirate of Cordoba
The Umayyad Caliphate of Cordoba
The Almoravid Dynasty
719 - 721 - Al-Samh ibn Malik (All Facts)
General of the Umayyad Caliphate
He was defeated by Duke Odo the Great and the Franks in the battle of Toulouse, preventing his attempted invasion of Gaul
695 - 740 - Zayd ibn Ali (All Facts)
Great-grandson of Caliph Ali of the Rashidun Caliphate
He tried and failed to revolt and overtake the Umayyad Caliphate in favor of his Rashidun ancestors
He was killed in a Shia revolt at Kufa
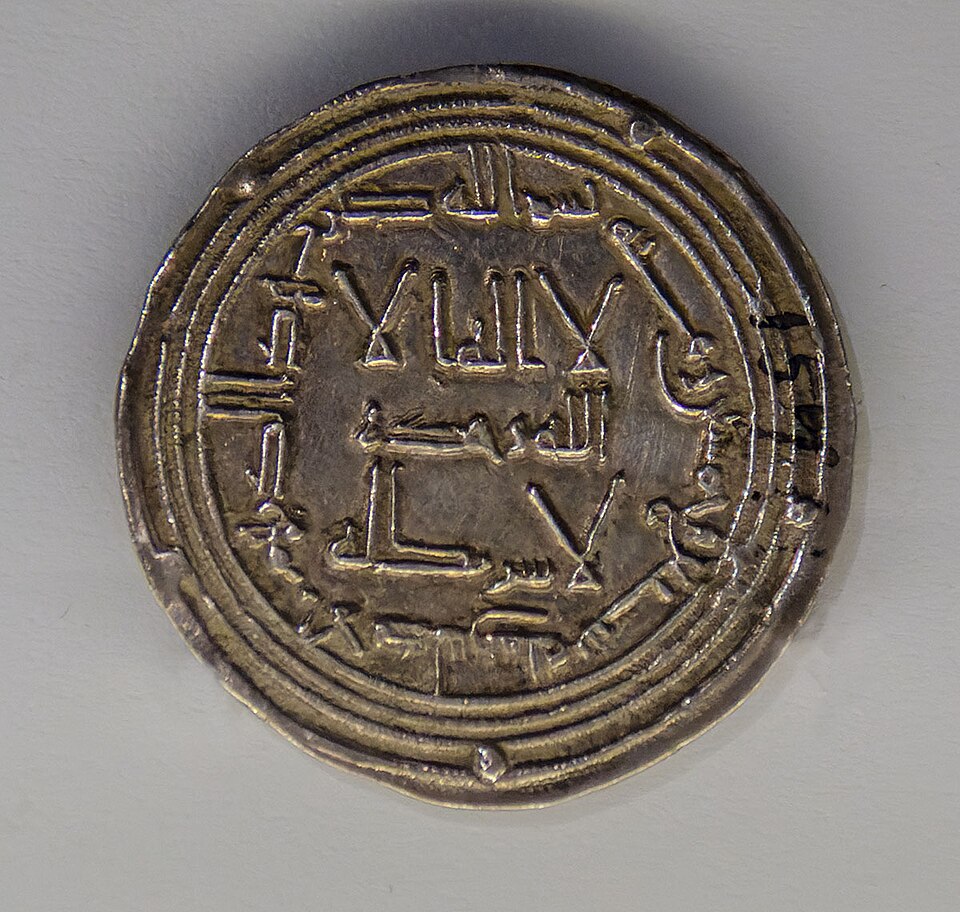

724 - 743 - Hisham ibn Abd al-Malik (All Facts)
10th Caliph of the Umayyad Caliphate
He was shrewd and puritanical
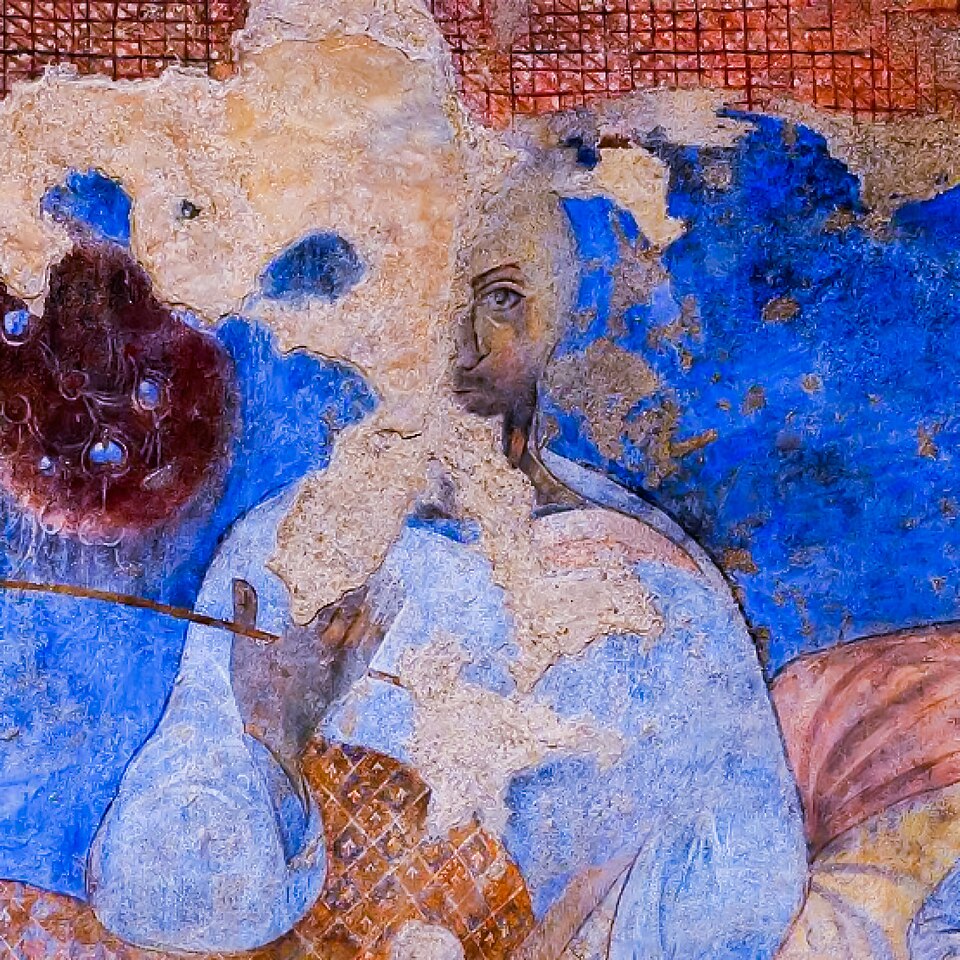

743 - 744 - Al-Walid II (All Facts)
11th Caliph of the Umayyad Caliphate
He was notorious for his impious extravagance, moving from one desert palace to another and spending a fortune on building, poets, and wine (despite wine being forbidden under Islamic law)
One story claims he dived into a pool of wine and drank himself unconscious
He loved hunting
He loved boys and girls
Due to his immoral behavior, his shocked family had him murdered and various factions sought to take advantage of his death

744 - 750 - Marwan II (All Facts)
14th and Final Caliph of the Umayyad Caliphate
He ruled from Egypt
He imprisoned Michael, Patriarch of Alexandria, in retaliation for his and his Coptic Church’s resistance to Muslim rule in Egypt
In response, King Kyriakos of the Christian Makurian Kingdom of Nubia sent an army to Egypt, which picked up more troops on the way in Christian Axum (Ethiopia), and invaded Egypt, occupied Cairo, and released Michael from captivity
He and the Umayyad Caliphate thus capitulated to Kyriakos and the Makurian Kingdom, thus ending the Umayyad Caliphate
He was defeated by Al-Saffah and the Abbasid Caliphate in the Battle of the Zab

718 - 755 - Abu Muslim (All Facts)
General
His name means “Father of Muslims”
He was sent by Al-Saffah (Abul-Abbas) to exploit the unrest and revolt against the Umayyad Caliphate
Taking advantage of the weakening of the Umayyad Caliphate due to the Makurian Invasion of Egypt, he led a revolt of the Abbasids against the Umayyads in Khurasan in what was northeast (Sassanid) Persia
He seized Merv, the capital of Khorasan
Suppressed a revolt in Syria
He was assassinated in Baghdad on the orders of Caliph al-Mansur
Following his death, his supporters in Khorasan revolted against the Abbasids, for whom the namesake had initially fought
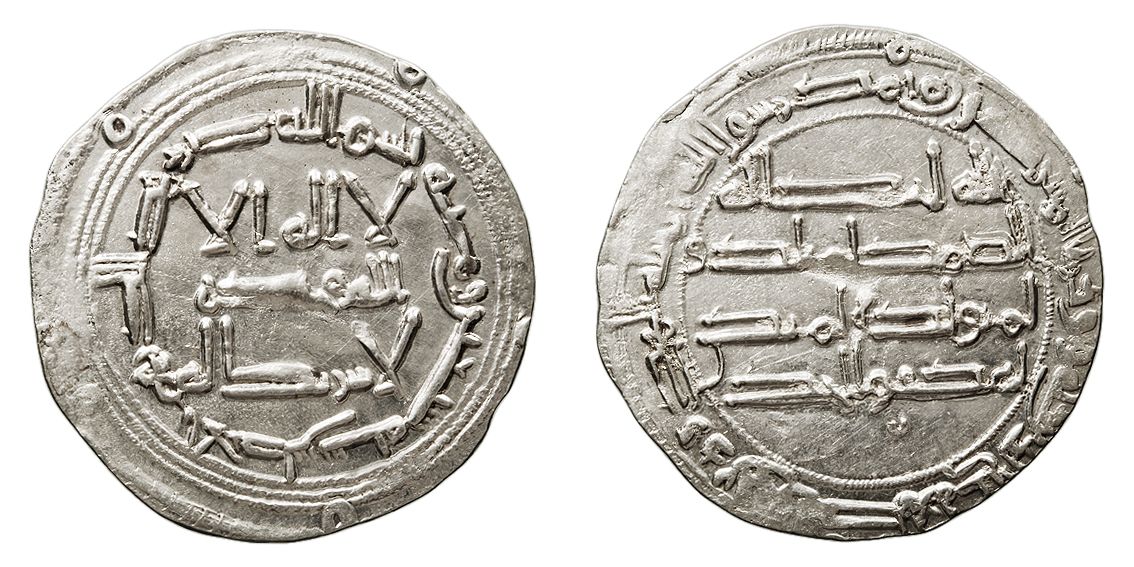

731 - 788 - Abd al-Rahman (All Facts)
He founded the Umayyad Emirate of Cordoba in the Iberian Peninsula in retaliation of Abbasid rule following the death of Abu Muslim by Caliph al-Mansur of the Abbasid Caliphate
He was thus proclaimed Emir of Cordoba
He was
A Syrian Prince
A member of a fanatical Muslim sect
He led the Umayyad Caliphate in having sacked Bordeaux and Poitiers, and then advanced them towards Tours with eyes on its monastery of St Martin, one of Christendom’s wealthiest
He and the Umayyad Caliphate were defeated by Charles Martel and the Franks in the Battle of Tours and he was among the dead after the battle
He was the only member of the ousted Umayyad Caliphate to survive the Abbasid massacre of the Umayyads in the Abbasid Revolution
He fled from the Abbasid Revolution and took refuge in Egypt and Kairouan before finally settling down in Al-Andalus with other Arab clans
Profiting from division among Arab Muslims in Al-Andalus at the time, he made his way via Seville to Cordoba, the capital of Al-Andalus at the time
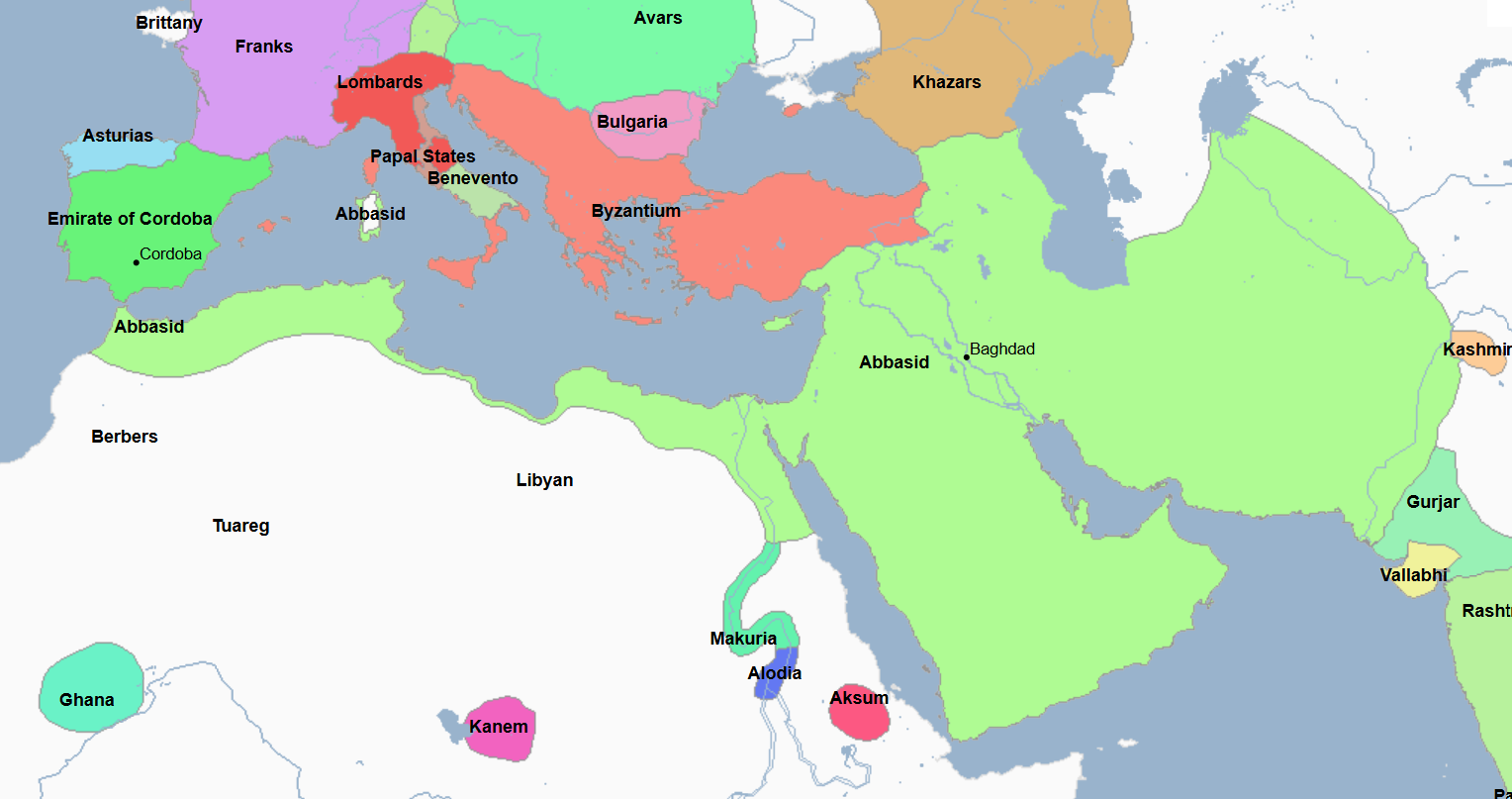
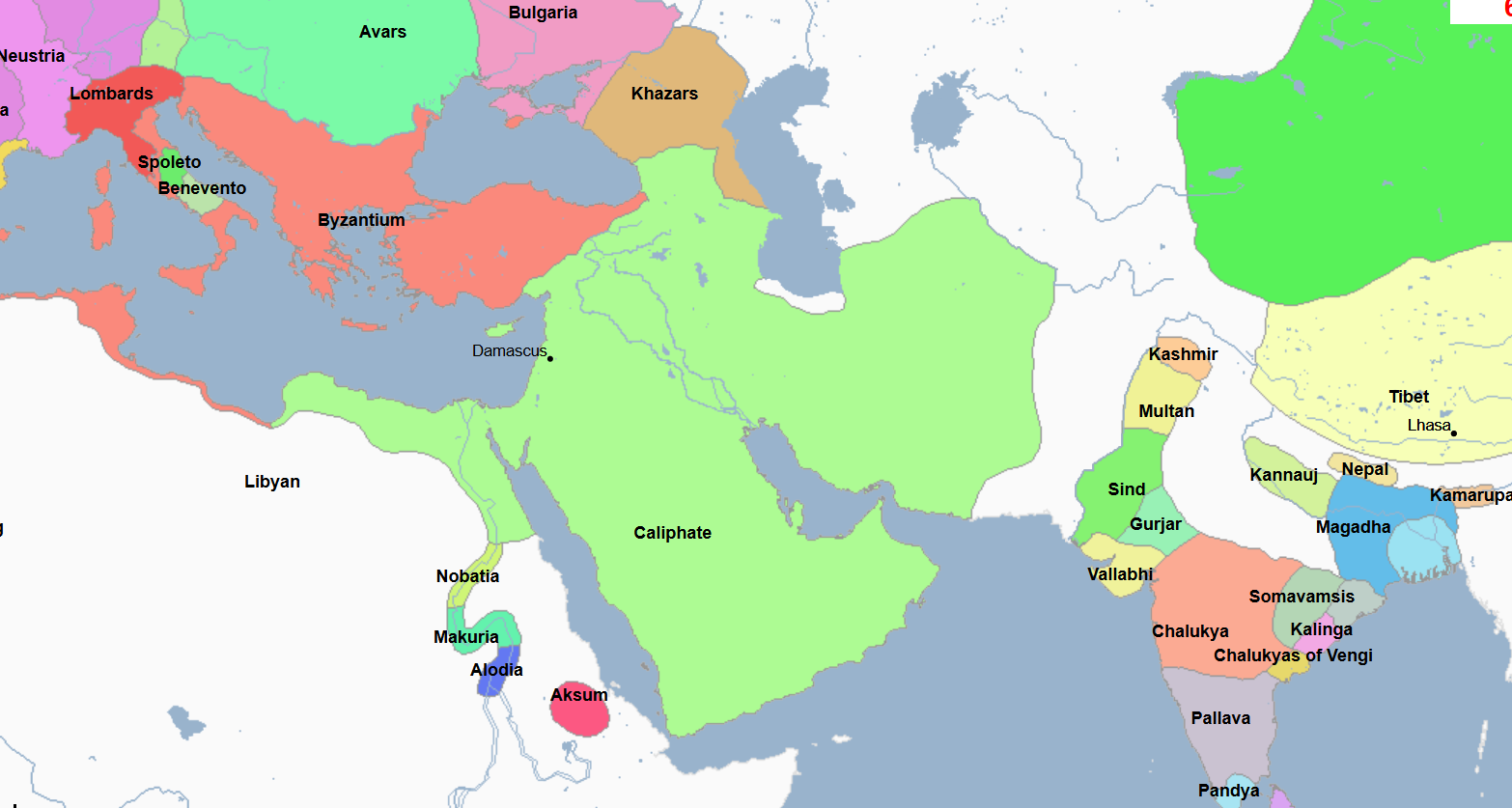
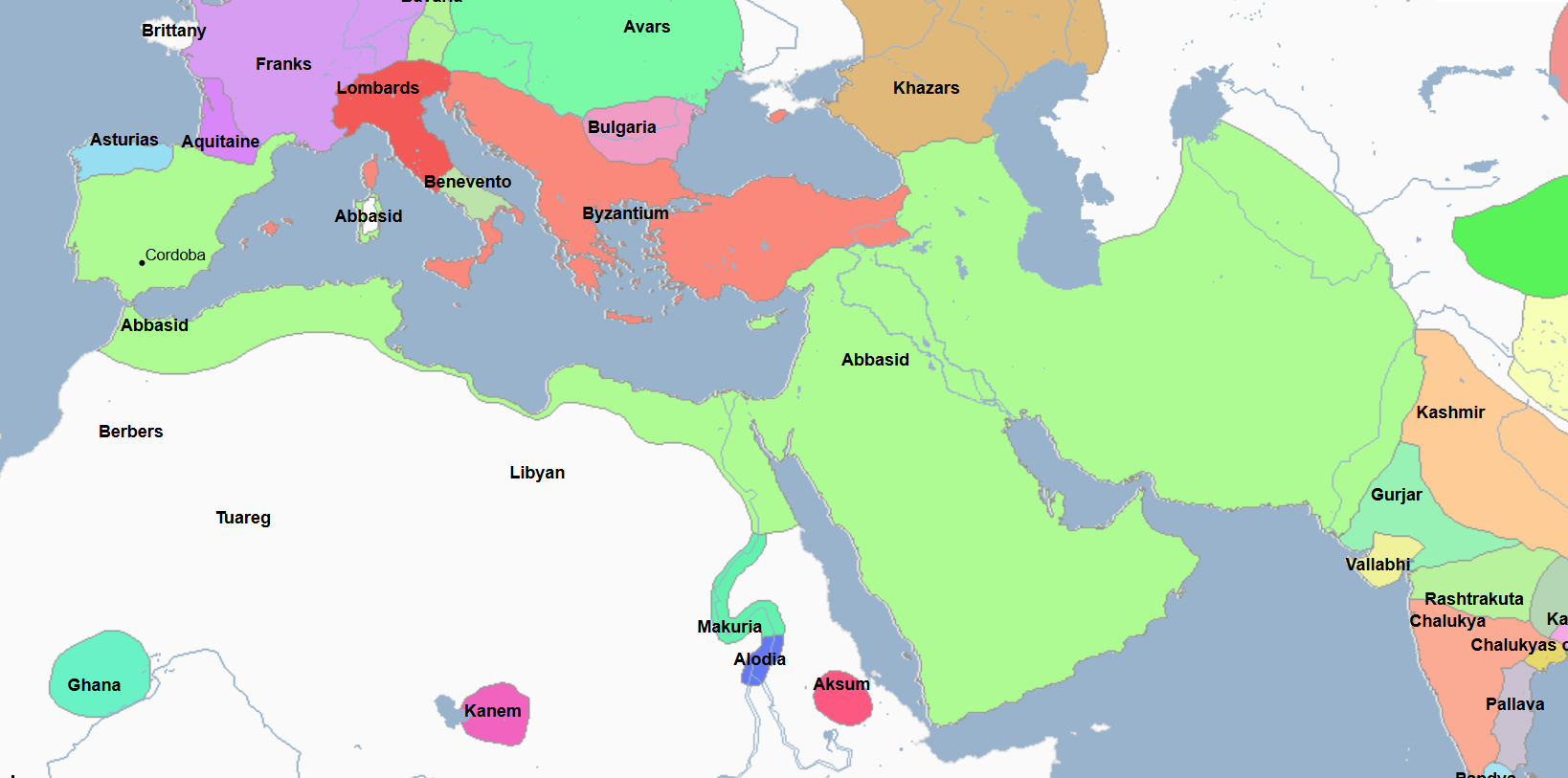
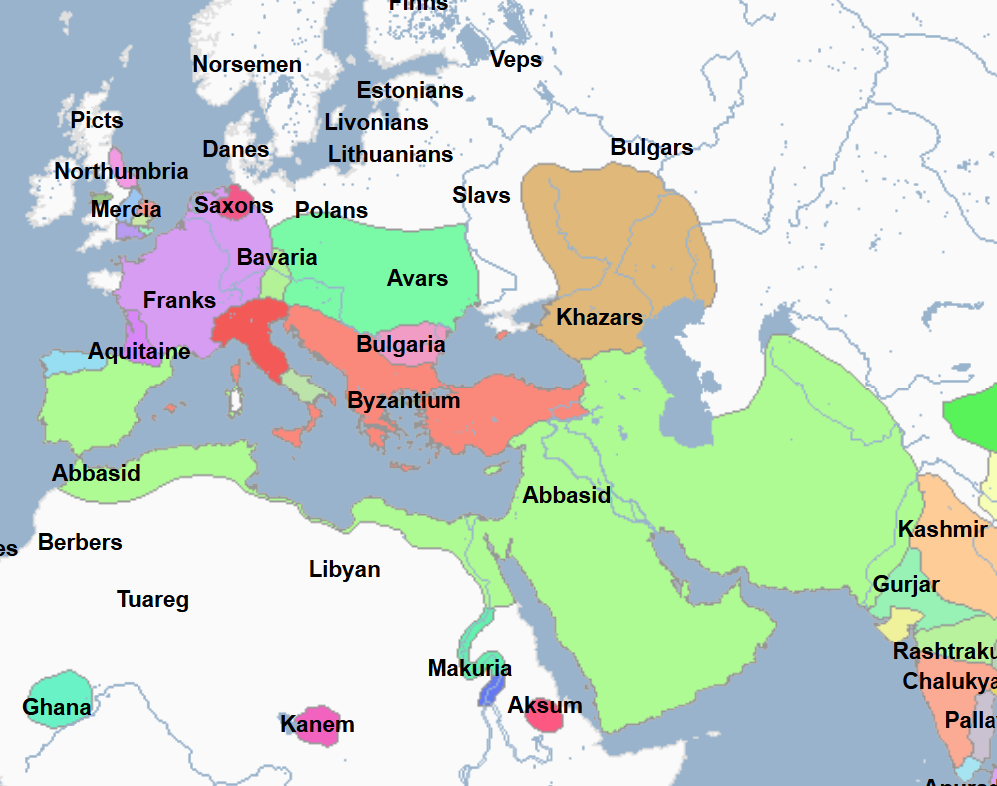
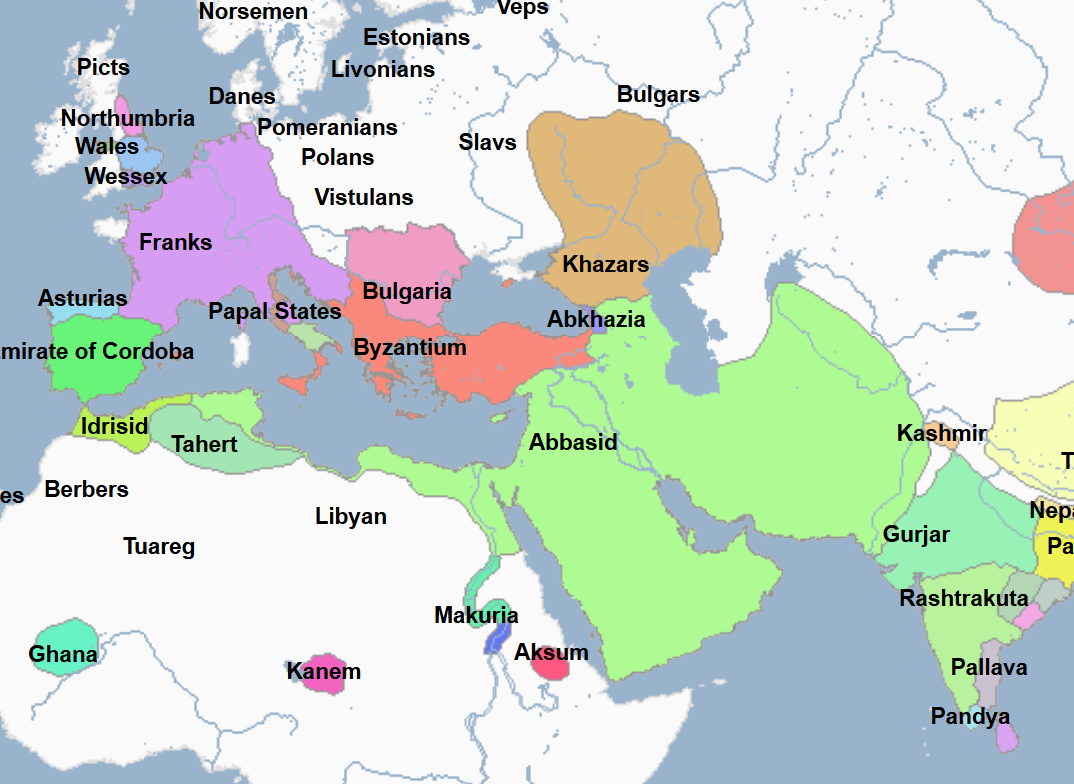
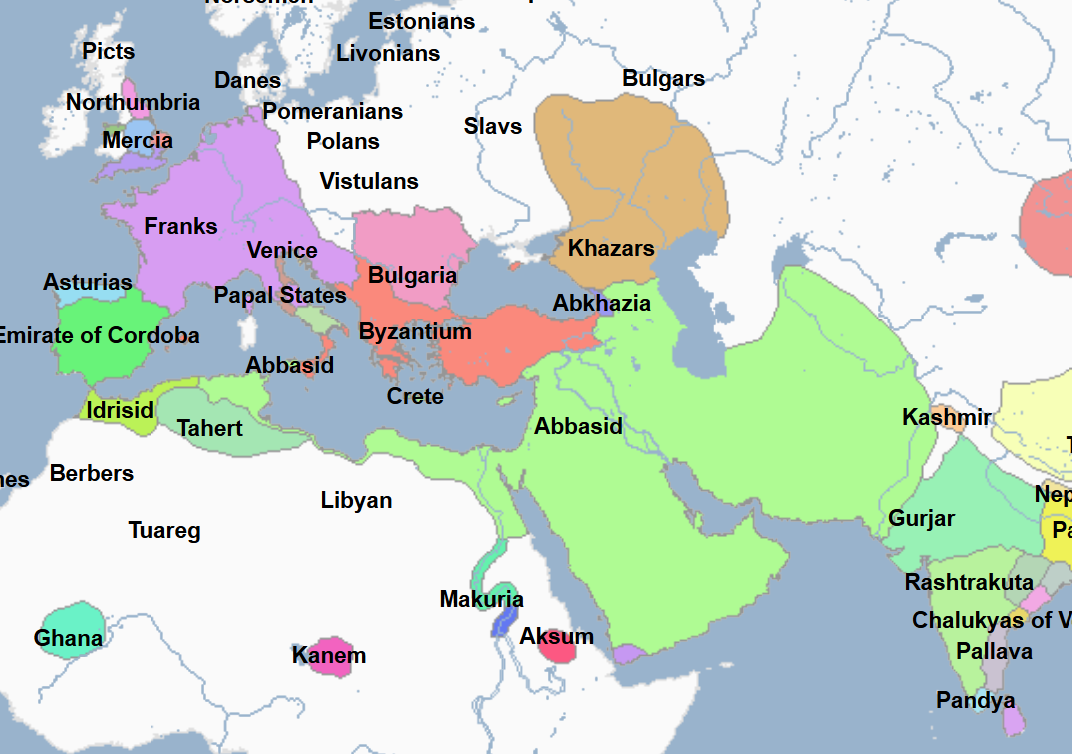
750 - 1258 - Abbasid Caliphate (All Facts)
3rd Caliphate of the Islamic World
They overthrew the preceding Islamic Caliphate in the Abbasid Revolution, in which they gained political and spiritual control of most of the Islamic world
Caliphate which was primarily led by ethnic Arabs and Persians
Legitimized by claiming descent from Muhammad's uncle Abbas
Characterized by its climate of religious toleration, especially amongst and in result towards the peaceful coexistence of Muslims, Christians, and Jews
It served as an important link connecting Asia, Europe, and North Africa in which
Goods and ideas flowed from one region to another on trade routes controlled by them, many of which went through their capital at Baghdad
The presence of a permanent military force that kept order but did not own property allowed life for most of the inhabitants of the countryside to remain virtually unchanged during their reign
It fell due to the
Mamluks / Mamluk Sultanate
Seljuks / Seljuk Empire
Crusaders
Mongols / Mongolian Empire (who conquered the remainder of the caliphate by its end)
Trade routes they controlled slowly shifting on their own farther north, away from Baghdad, which eventually lost its traditional place at the center of trade and lost its wealth and population
Inability to keep its canals repaired
Inability for its farmers to provide enough food for its urban populations
Decay of the infrastructure that had made its center of Baghdad a great city

750 - 754 - Al-Saffah (All Facts)
First Caliph and Founder of the Abbasid Caliphate
He was also known as Abu’l-Abbas
He lived in obscurity in southern Jordan until he took advantage of unrest in Khorasan, in the east of the Umayyad Empire
He sent Abu Muslim to exploit the unrest under and begin an insurrection of the Umayyads during the Abbasid Revolution during the Third Fitna
He sent Abu Muslim, his brilliant but sinister envoy to inspire the people of Khorasan to march west and overthrow the Umayyad Caliphate
He appealed to the Shia Alids for help, but once in power, he negated them
His duping of the Shia Alids would come to be a source of trouble for the namesake caliphate later on when the Shia Fatimid Dynasty was established which would rival the Abbasid Caliphate
He and the Abbasids claimed legitimacy by citing that they were descendants of Mohammed the Great Prophet’s uncle, al-Abbas, upon which the Caliphate is named
At Kufa, he proclaimed himself caliph with the namesake title, which, in Arabic, means “Shedder of Blood”
From there, he had consolidated his power and mopped up the remnants of the preceding caliphate, thoroughly earning the aforementioned title
His armies swept west, obliterating members of the Umayyad family wherever they had found them
His armies even dug up the bodies of the Umayyad caliphs and publicly flogged their remains before scattering their bones back into the earth
He even gruesomely invited the remaining male members of the Umayyad families that survived to a dinner party, where he had them massacred and feasted over their corpses
During his reign,
The Battle of Talas occurred, in which
Islamic influence expanded into Central Asia
The Abbasids learned from Tang Chinese POWs (from the battle) how to make paper, contributing to the Islamic Golden Age under the Abbasid Caliphate and the establishment of the first paper mills in the Islamic World
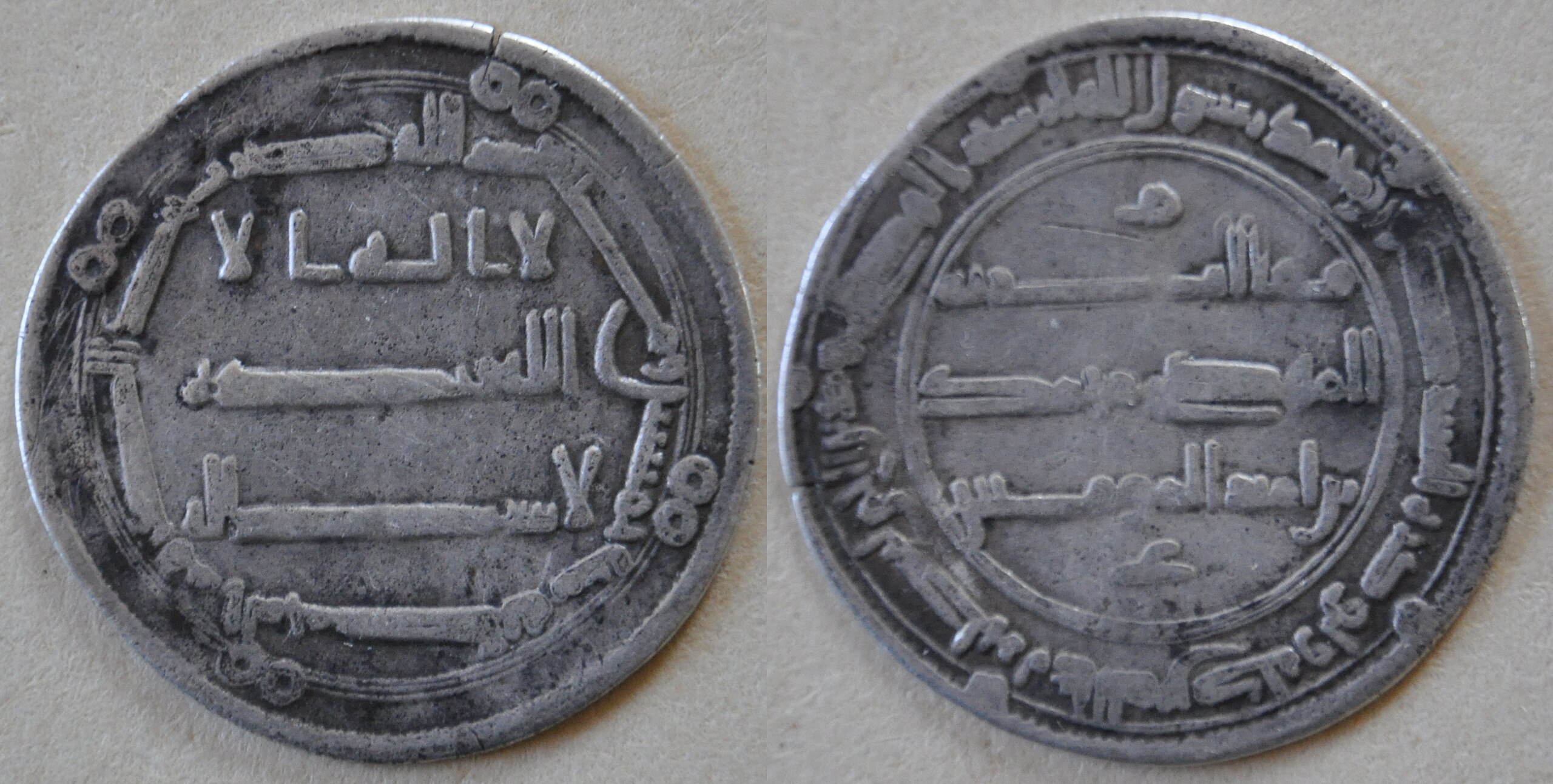
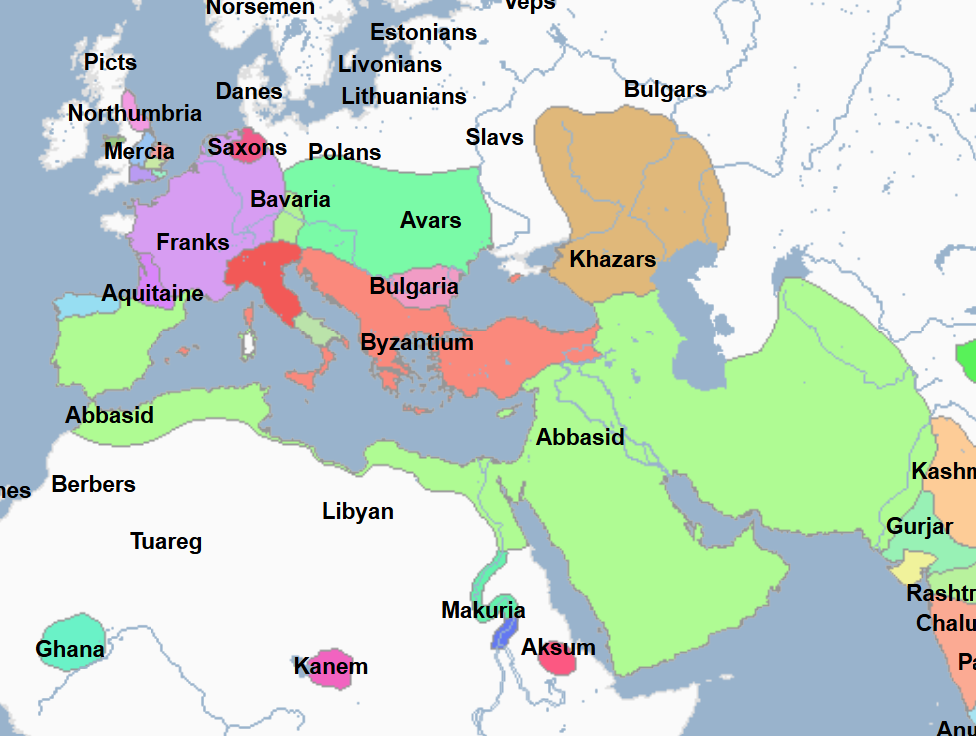

754 - 775 - Al-Mansur (All Facts)
2nd Caliph of the Abbasid Caliphate
He was the brother of his predecessor
He was tall, gaunt, and swarthy
He showed no mercy to his rivals, including the general Abu Muslim who had fought with and for the Abbasids
However, he was supportive to servants and loyal commanders
He ruled during a time when the Abbasids were under pressure from outside and from those who wanted to make the Caliph a puppet
He moved the capital of the Abbasid Empire from Kufa to Baghdad
He had built there a formal and ceremonial round city for his court and army with four vast gates and a mosque and palace at its center
He had Abu Muslim assassinated in Baghdad
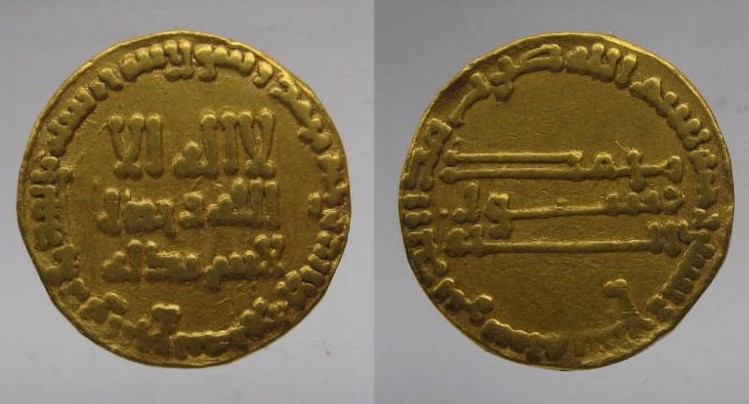
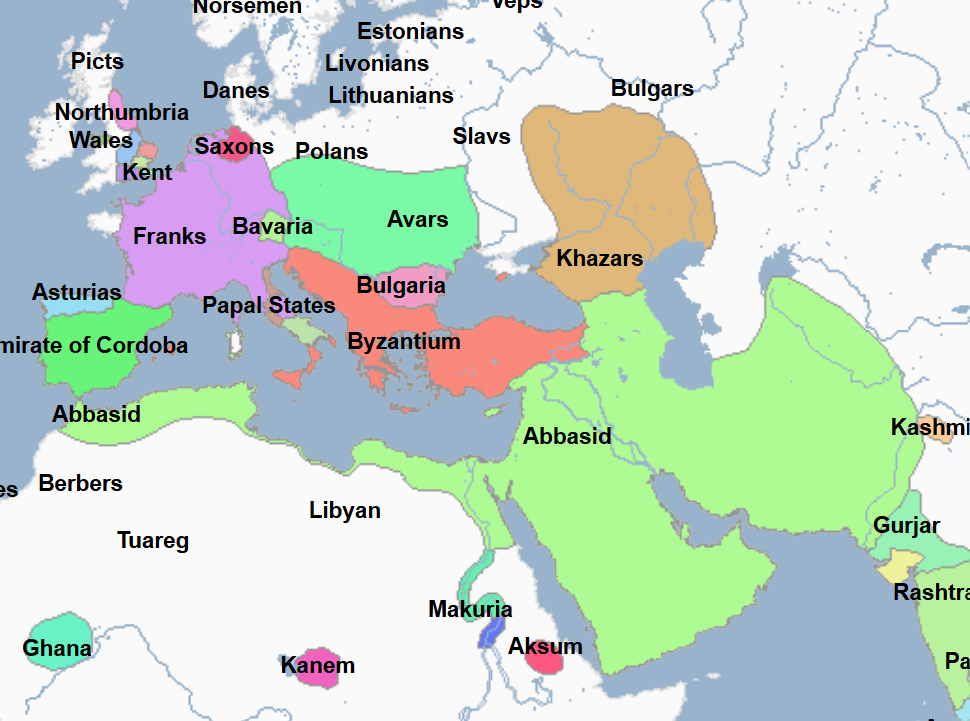

775 - 785 - Al-Mahdi (All Facts)
3rd Caliph of the Abbasid Caliphate
He was the son of his predecessor
Factions which his predecessor had controlled began to re-emerge under his reign
The military backed his dull but competent son to rule
His wife Khayrazun and palace bureaucrats favored Harun al-Rashid to rule over his namesake son and successor
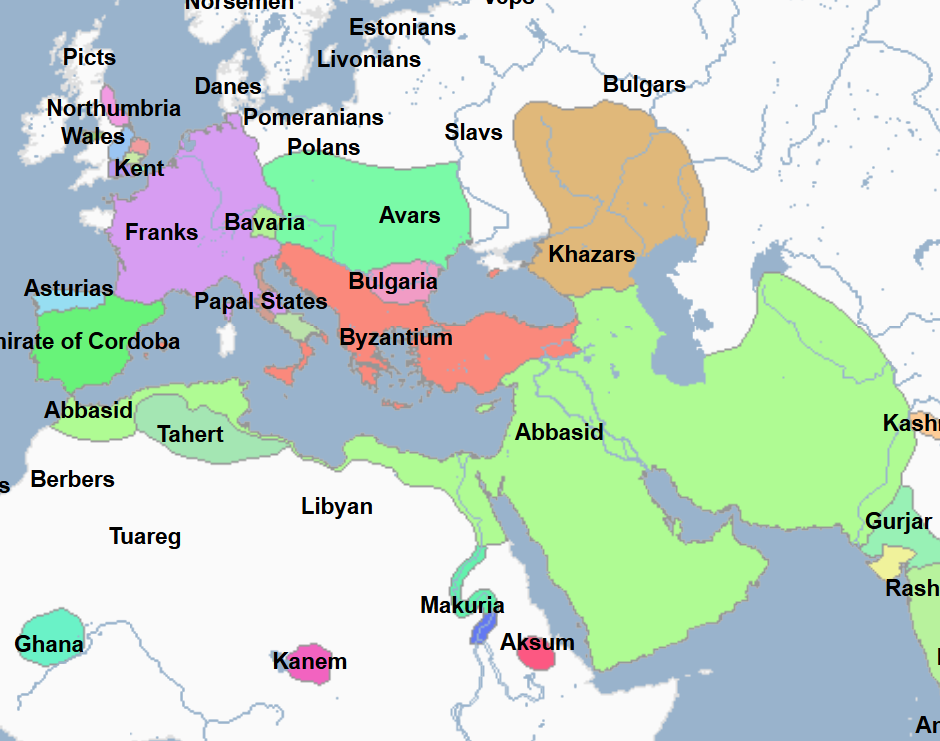
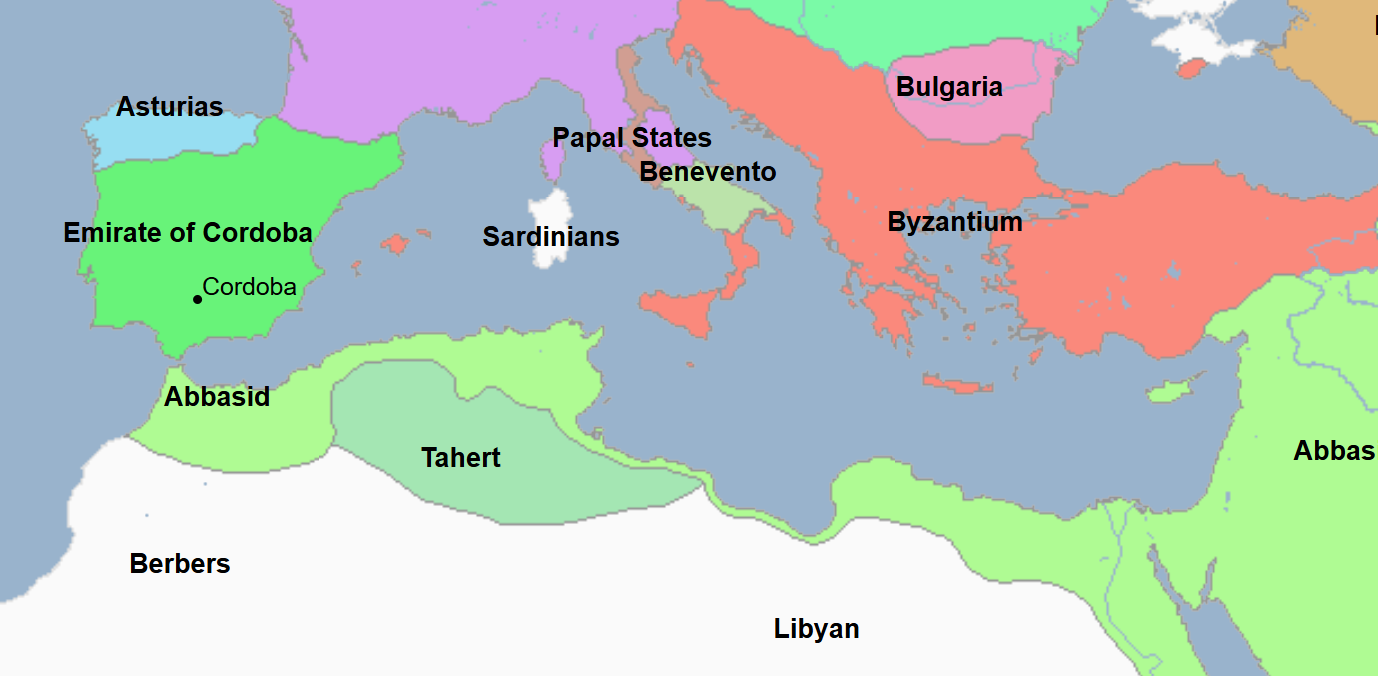
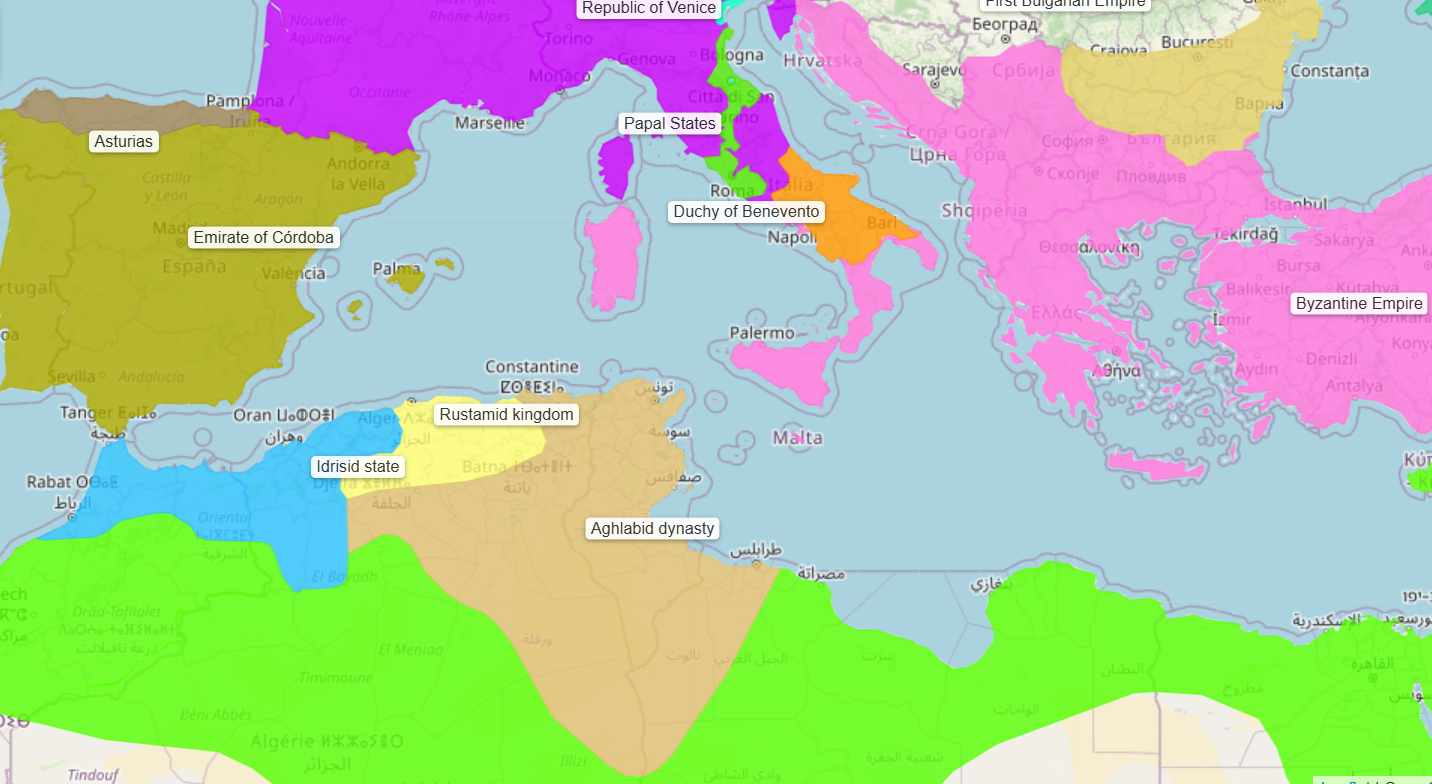
777 - 909 - Rustamid Imamate (All Facts)
Founded by Ibn Rustum
Its capital was at Tahert (on the map it shows Tahert instead of the namesake)
777 - 788 - Abd al-Rahman ibn Rustam (All Facts)
First Ruler and Founder of the Rastumid Imamate
He established the Imamate’s capital at Tahert
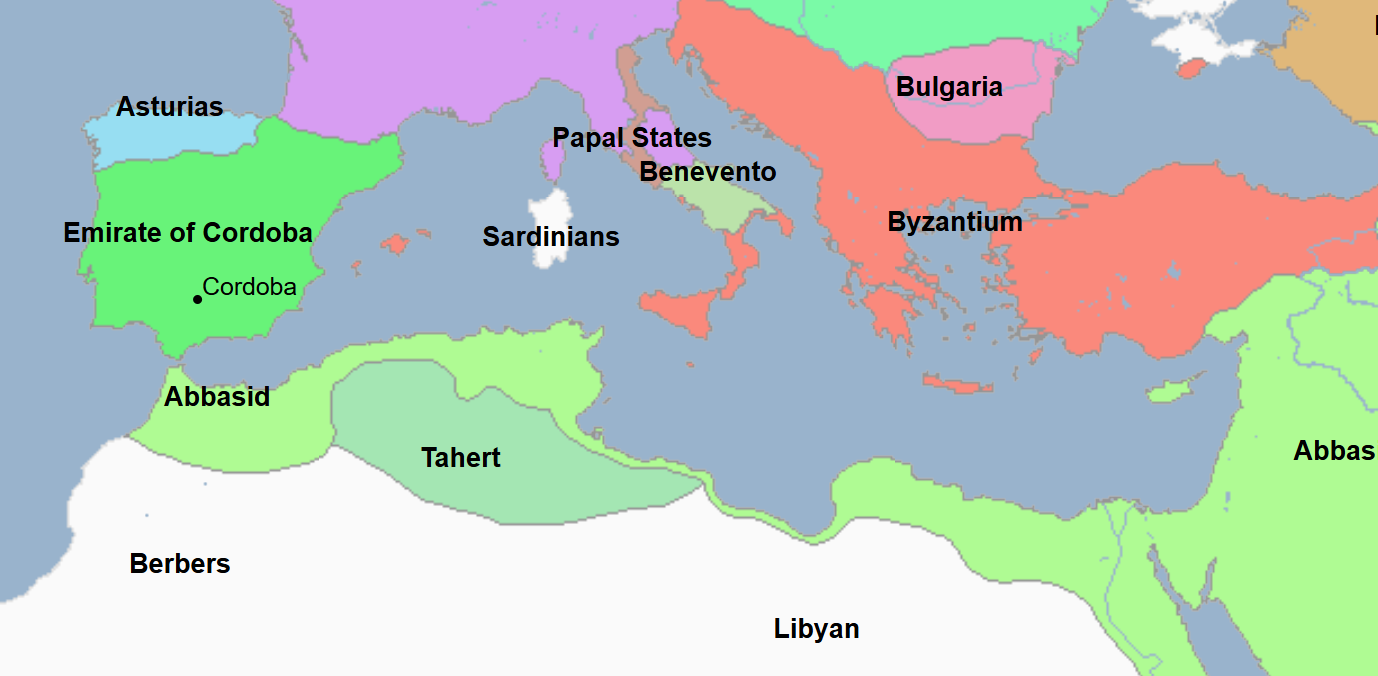

785 - 786 - Al-Hadi (All Facts)
4th Caliph of the Abbasid Caliphate
His assumption to the throne ended a decade of uncertainty and rivalry
Although he had been ill, his sudden death sparked rumors that his wife suffocated him, that his son has been arrested, etc. and his namesake successor succeeded him with the task of winning over the military that supported the namesake
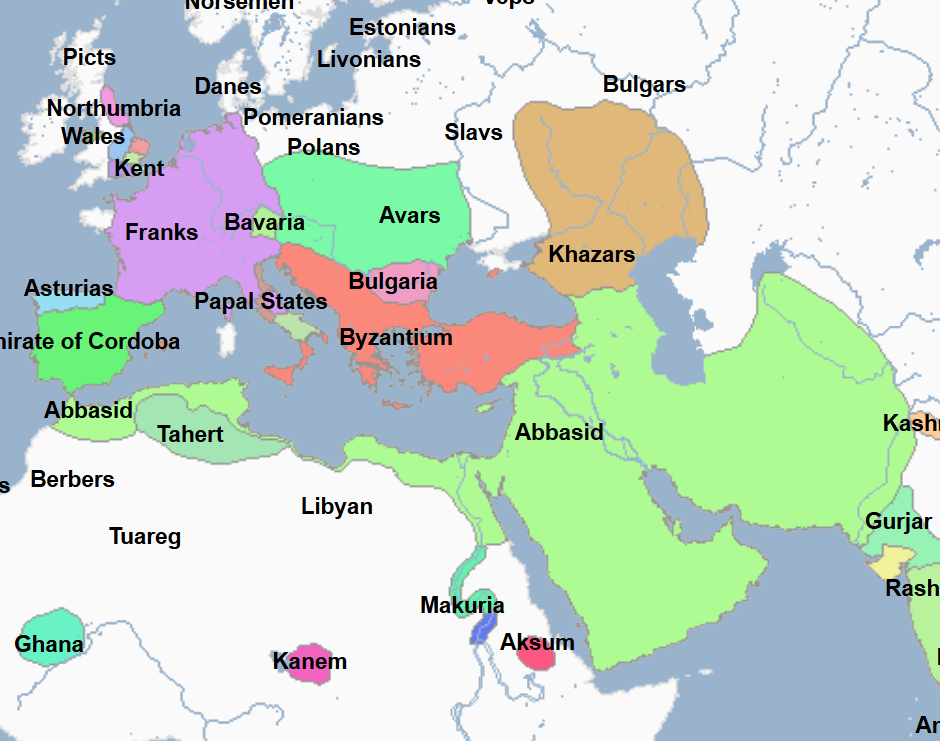
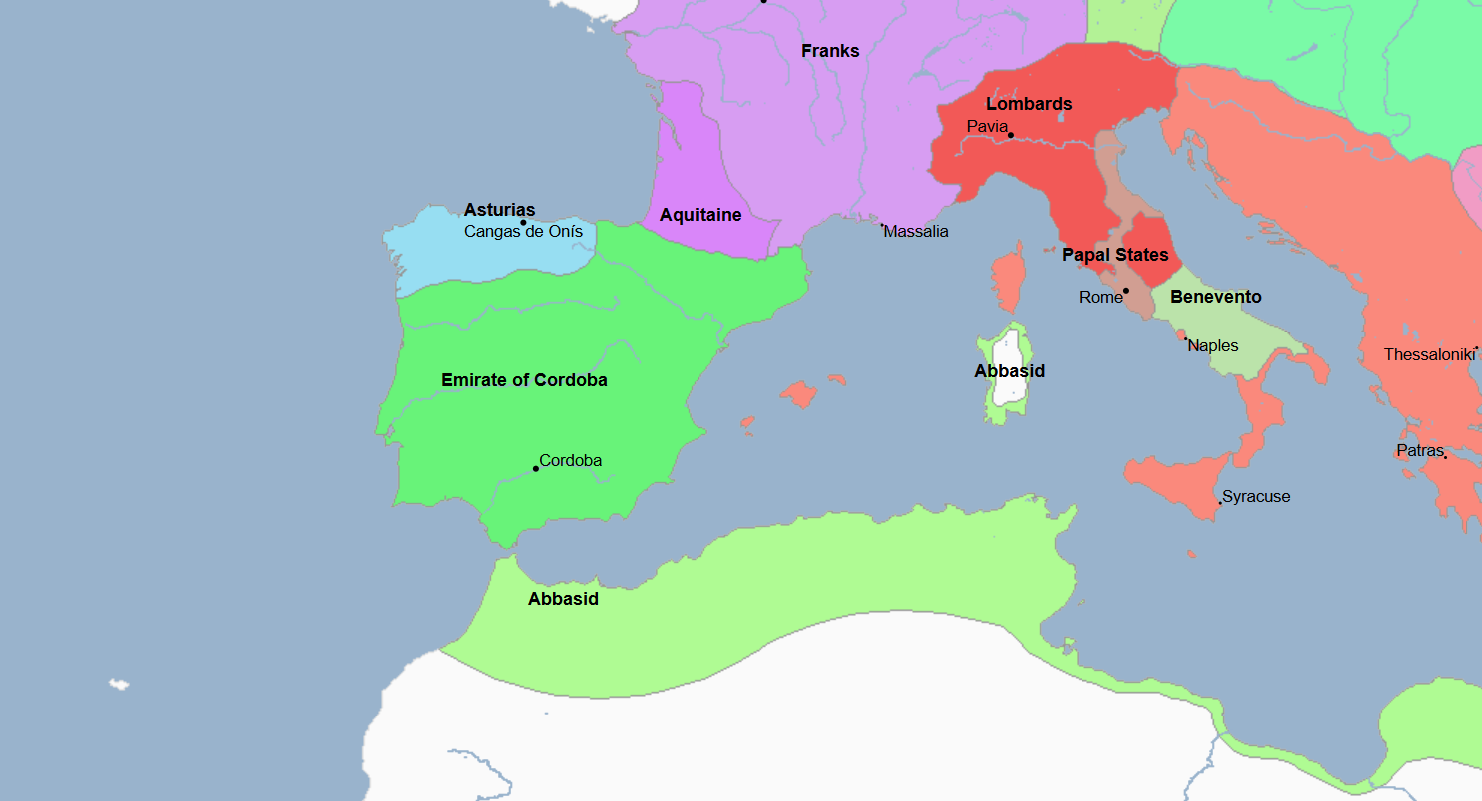
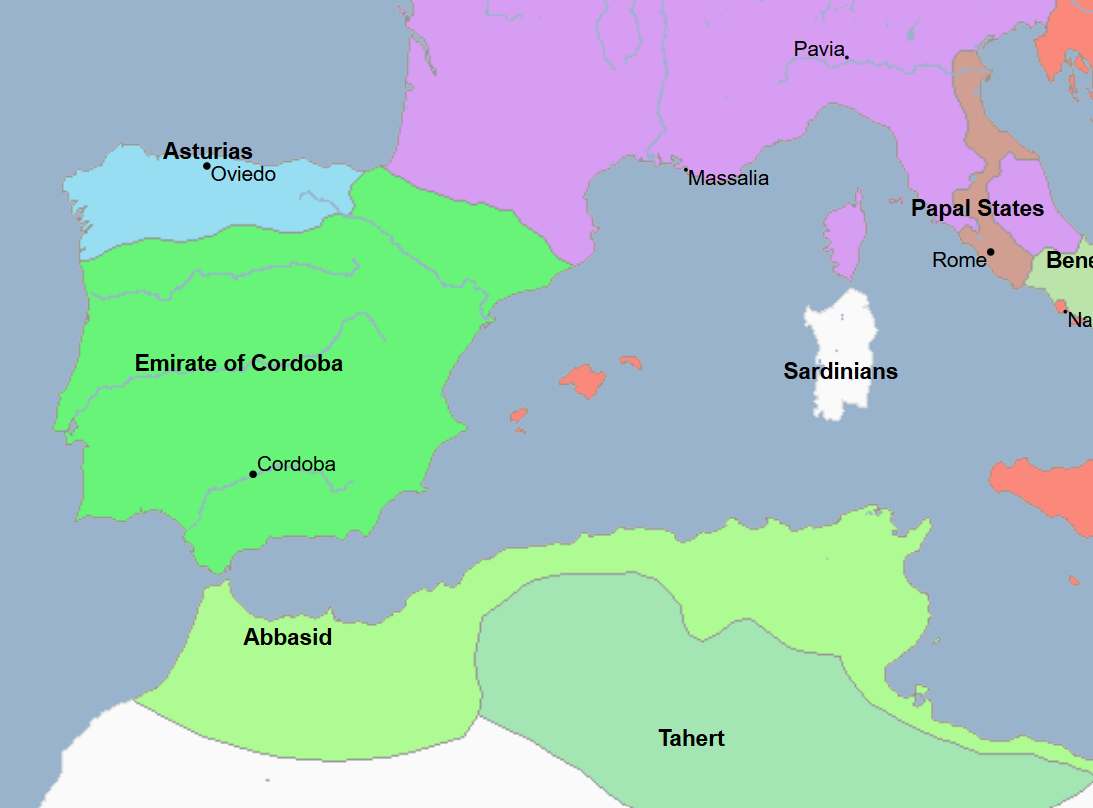
756 - 1031 - Umayyad Cordoba (All Facts)
Arab Islamic state ruled by the Umayyad Dynasty during the rule of the Abbasid Caliphate
In 756, it was founded by Abd al-Rahman
By 929, it proclaimed itself a caliphate but until then was an emirate
Its territory comprised most of Al-Andalus, the Balearic Islands, and parts of North Africa
It eventually dell due to racial and religious tensions / pressures
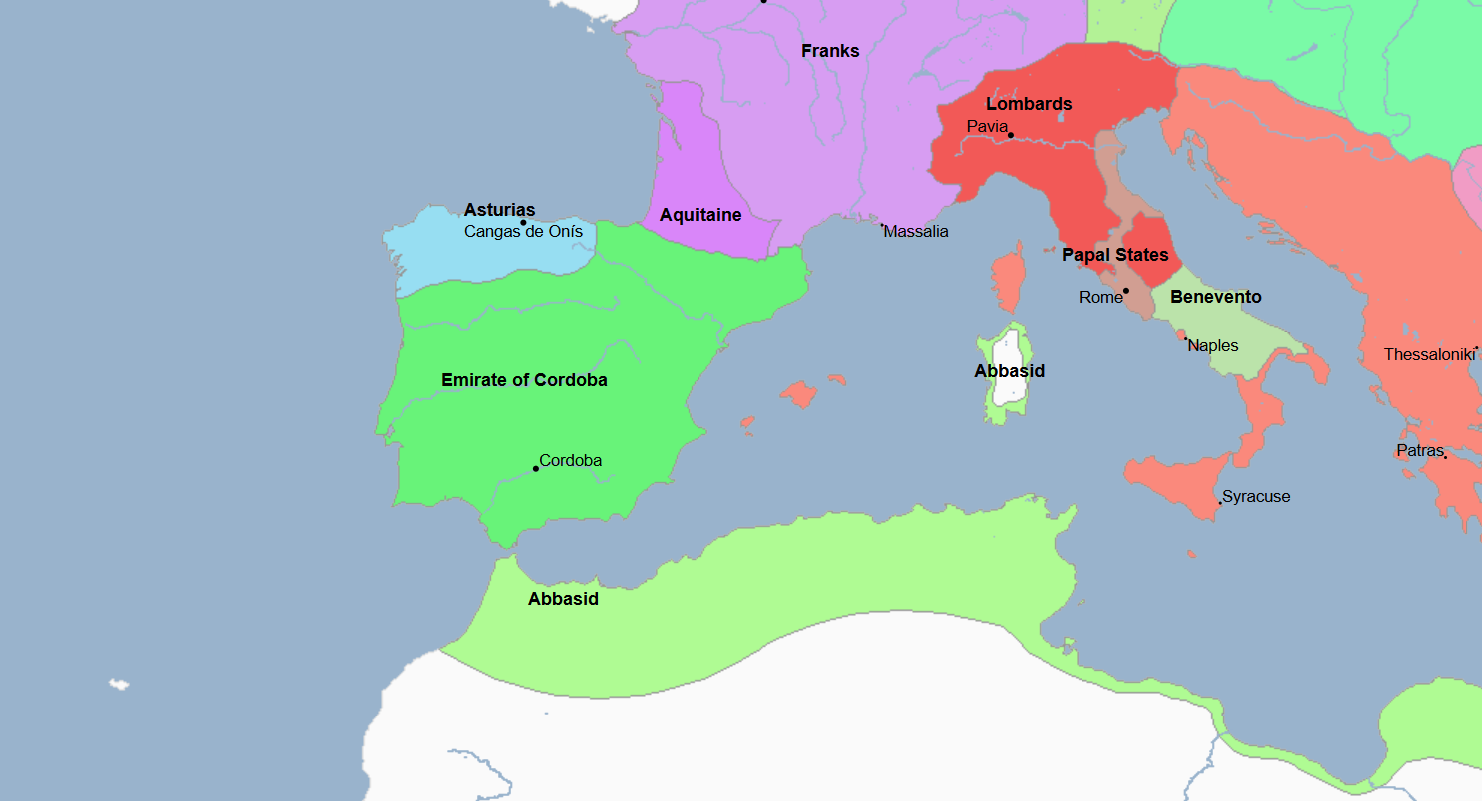
756 - 929 - Umayyad Emirate of Cordoba (All Facts)
Founded by Abd al-Rahman, its capital was at the namesake
Since the Arab Muslim invasion in 711, it had a succession of emirs, but up between the 830s and 930s, it saw a prolonged political crisis of instability which led to the establishment of this same exact state but as a Caliphate instead of the namesake
Emirate which held a policy of religious toleration for Jews and Christians
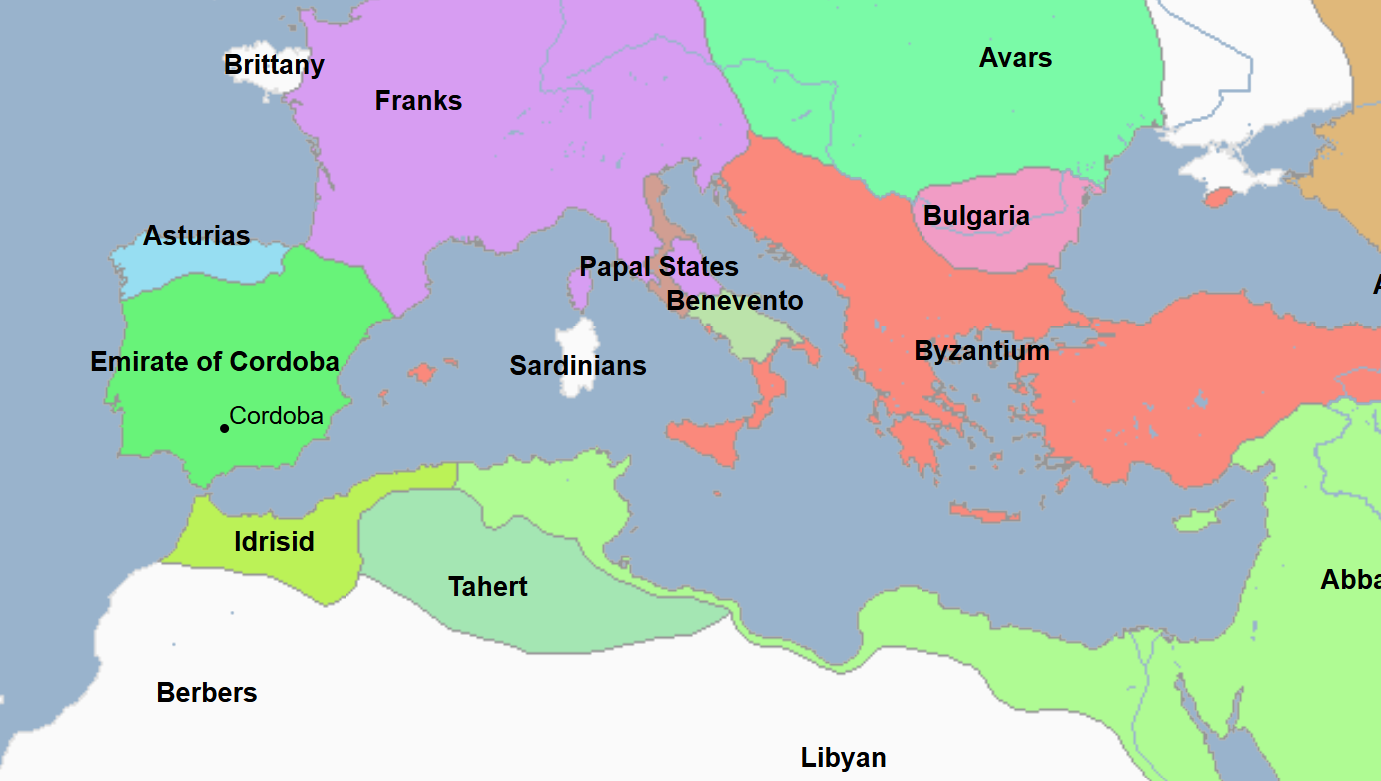
788 - 974 - Idrisid Dynasty (All Facts)
Ruled most of modern-day Morocco and Western Algeria
They were an Alid dynasty that descended from the Great Prophet Mohammed through his grandson Hasan
They were one of many Alid dynasties that vied for power after Al-Saffah had negated the Alids from the Abbasid Caliphate
Founded as a means of refuge from Abbasid persecutions in the east of non-Abbasids like the Alids
Dynasty which played an important role in the early Islamization of Morocco
Dynasty which was founded by its namesake ruler
788 - 791 - Idris (All Facts)
First Emir and Founder of the Idrisid Dynasty
Located in modern-day Morocco and Western Algeria
He founded the kingdom as a means of refuge from Abbasid persecutions in the east of non-Abbasids like the Alids, of which he hailed
He was
Originally from Medina in Arabia
A descendent of the Great Prophet Mohammed through Mohammed’s grandson Hasan
He fought in the Battle of Fakhkh
When the Alids were defeated by the Abbasid Caliphate, he fled in disguise to Egypt and then to Morocco
When he arrived, the Awraba Berbers there hailed him as their Imam (leader)
He established himself in Volubilis, an old Roman town
He died after being poisoned by a toothpick sent by Caliph Harun al-Rashid of the Abbasid Caliphate back in Baghdad
He left no son but one of his concubines was heavily pregnant upon his death

786 - 809 - Harun al-Rashid (All Facts)
5th Caliph of the Abbasid Caliphate
He was the younger brother of his predecessor
He signed a treaty with Ibrahim ibn-al Aghlab of the Aghlabid Dynasty in which
He
Would receive 40,000 dinars
And in return, would give ibn-al Aghlab
Autonomy of the province of Ifriqiyah, which became the Aghlabid Dynasty
The right to hand over the province to his son
He granted the Franks a decree protecting the Holy Places in Jerusalem
Under his reign, Arab music entered its golden age, and his own music tastes were revealed in “The Arabian Knights”
Under his reign and throughout the Islamic Golden Age which it spurred, a style of romantic song flourished
Died at Tus in Eastern Persia
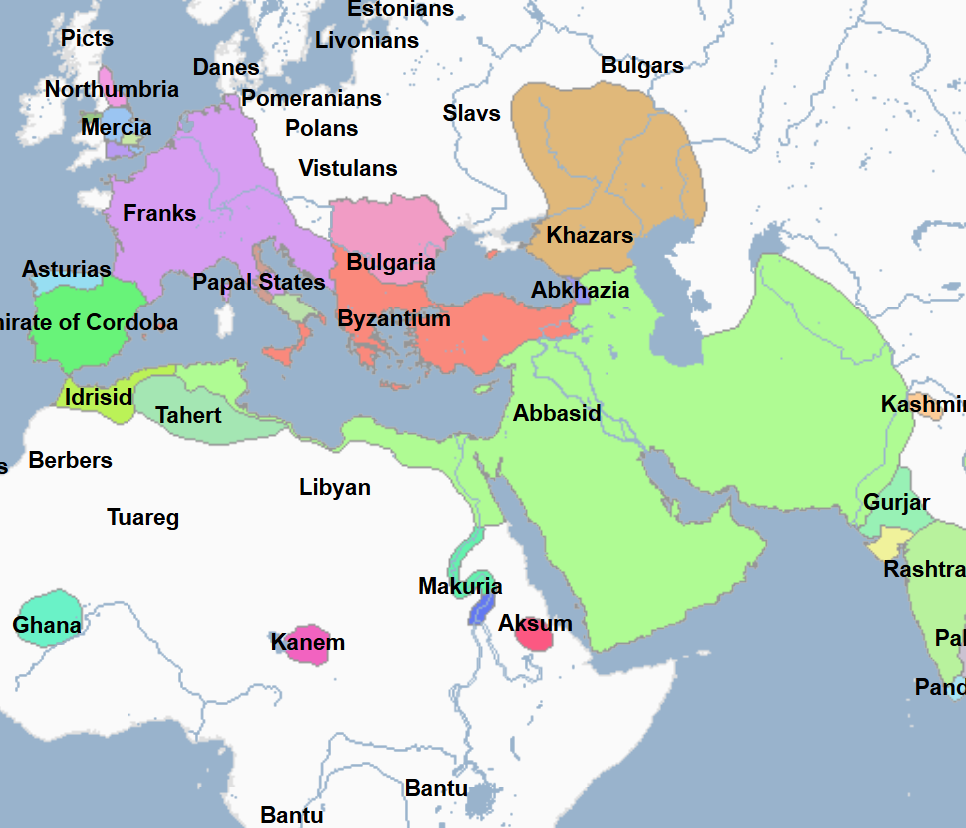
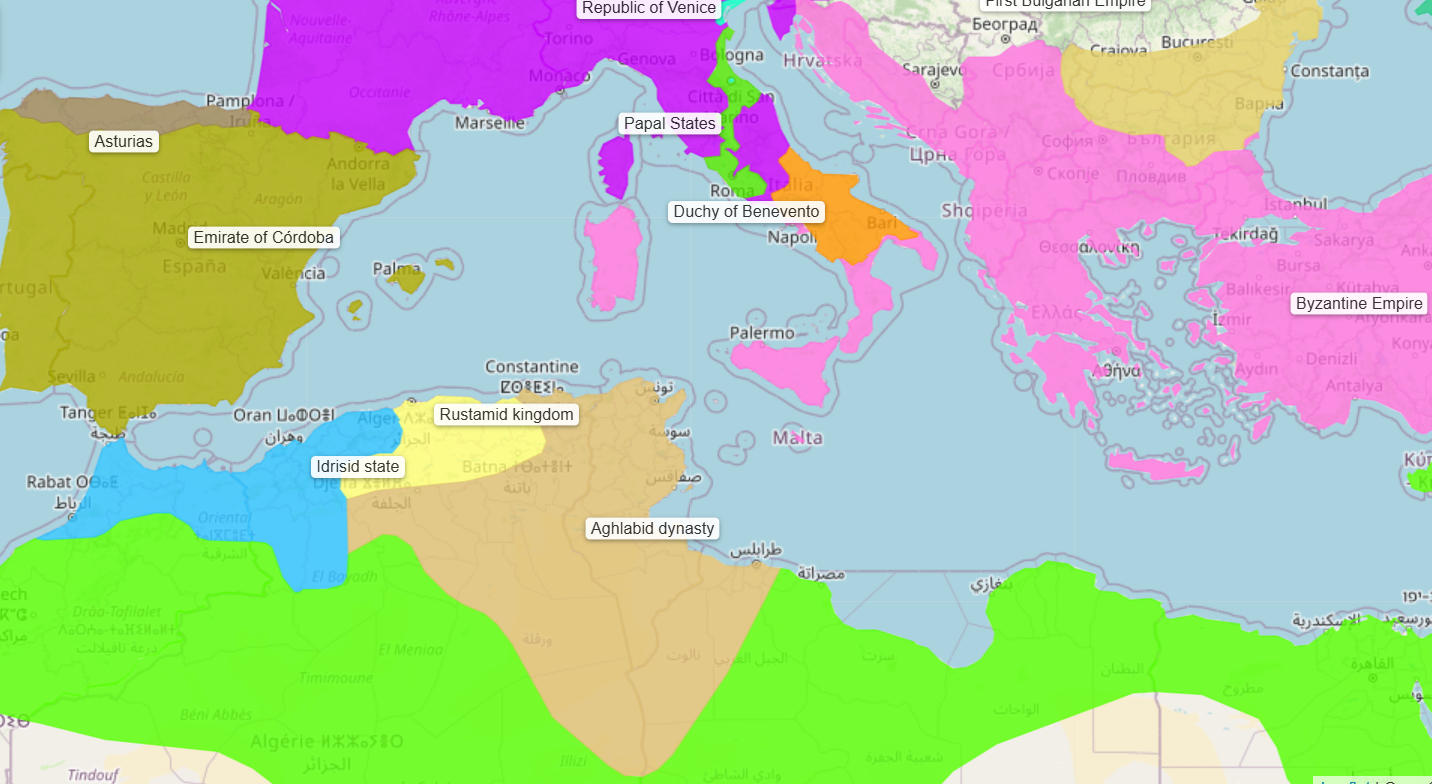
800 - 909 - Aghlabid Dynasty (All Facts)
Founded by Ibrahim ibn-al Aghlab
Formerly a part of the Abbasid province of Ifriqiyah (Tunisia)
Its capital was Kairouan
Fell to Abu Abdallah al-Shi'i and the Berbers

800 - 812 - Ibrahim ibn al-Aghlab (All Facts)
First Emir and Founder of the Aghlabid Dynasty
He was initially the governor of the Abbasid province of Ifriqiyah (Tunisia)
He was energetic in restoring order and calm after a period of turbulence
He oversaw the building up of a guard of Black slaves to help tackle the threat of unrest from subdued Berber tribes and others in Kairouan
His military power derived from this put him in a strong bargaining position with Caliph Harun al-Rashid and the Abbasids
He signed a treaty with Harun al-Rashid of the Abbasid Caliphate in which
He
Would receive complete autonomy
The right to hand over the province to his son
And in return, would give Harun al-Rashid
40,000 dinars

809 - 813 - Al-Amin (All Facts)
6th Caliph of the Abbasid Caliphate
He was the son of his predecessor
He died fleeing from the Siege of Baghdad by his brother and successor
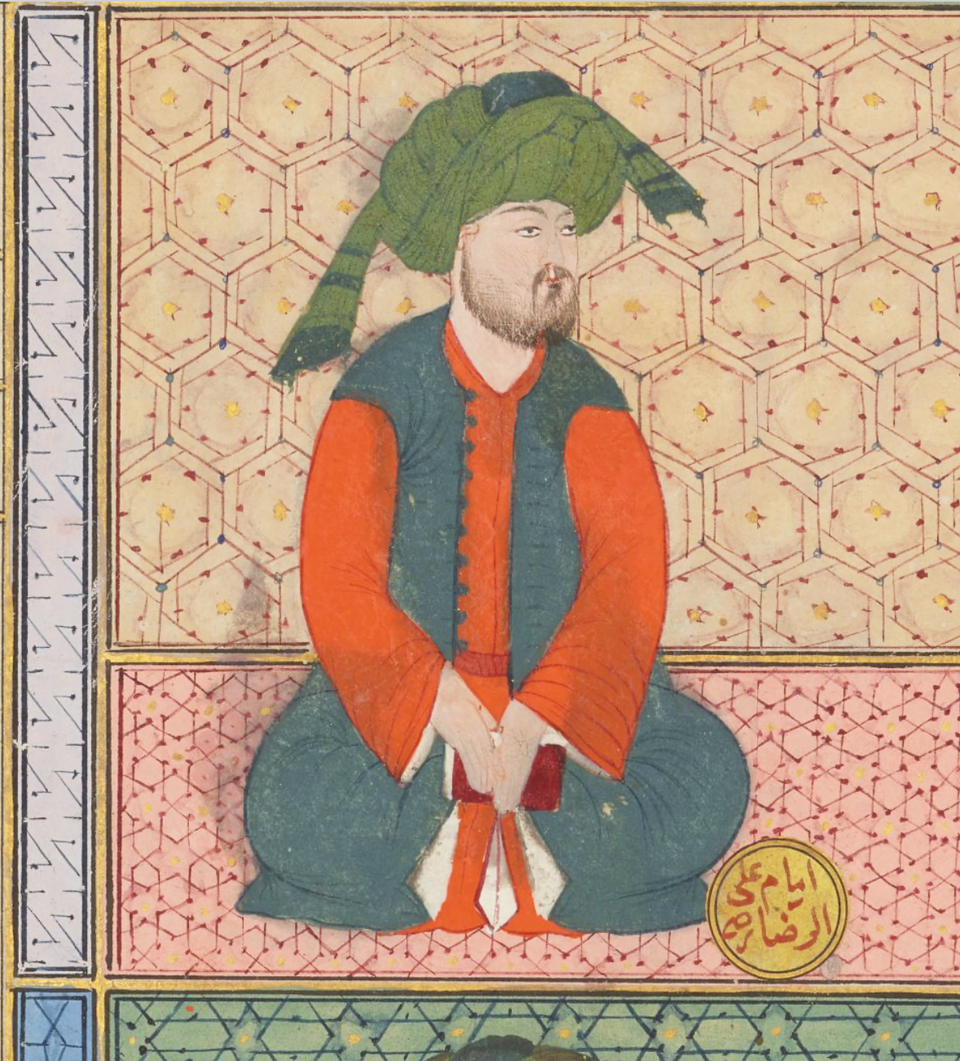

765 - 819 - Ali al-Rida (All Facts)
He was originally designated to succeed Al-Amin as Caliph, but he was mysteriously killed
803 - 828 - Idris II (All Facts)
2nd King of the Idrisid Dynasty (in Morocco)
He established the dynasty’s capital at Fez
This is considered his most notable acheivement
When he died, the Idrisid Dynasty was divided between his sons

813 - 833 - Al-Mamun (All Facts)
7th Caliph of the Abbasid Caliphate
He oversaw and encouraged the most glorious epoch of the Abbasid Caliphate
Under his reign, the Abbasid Caliphate (and its culture) reached new heights in that there was an expansion in commerce and industry
During his reign, international trade extended to Africa, Europe, China, and India
He founded the scholarly “House of Wisdom” / “House of Knowledge” in Baghdad
This was done to support efforts to translate ancient Greek wisdom into Arabic
The texts were not translated from the original Greek but from versions in Syriac
Greek authors translated included Galen, Ptolemy, Aristotle, and Dioscorides
Texts on history, poetry, and drama were considerably neglected
The translators themselves were mostly Christians
He advocated Mu'tazilism
He did this to boost his authority and win over the family of Ali (The Great Prophet’s son-in-law), who had already claimed in the past that Muslims can supplement the Quran with their own comments
He launched an inquisition to ensure all the officials under him agreed with this doctrine
He was initially supported by the Persian military against his brother Al-Amin during the Fourth Fitna
He ruled as governor of Persia
However, he soon left Persia for Baghdad (the capital of the Abbasid Caliphate)
As a result, many Persians, especially military generals who did all they could to install the namesake as caliph over his brother like Tahir, felt that the namesake had abandoned him / them
Under his reign,
Khurasan became independent

821 - 822 - Tahir ibn-Husayn (All Facts)
He was the governor of Khurasan during the reign of Al-Mamun of the Abbasid Caliphate
When Al-Mamun stayed in Persia but then left for Baghdad and the the namesake and other Persians had done everything they could to install him over his brother Al-Hadi as Caliph during the Fourth Fitna, they felt betrayed
He eventually renounced the Al-Mamun’s authority by omitting his name from Friday prayers
By the next day, Al-Mamun’s agents had him killed
However, political pressure forced Al-Mamun to appoint the namesake’s son Talha to succeed him
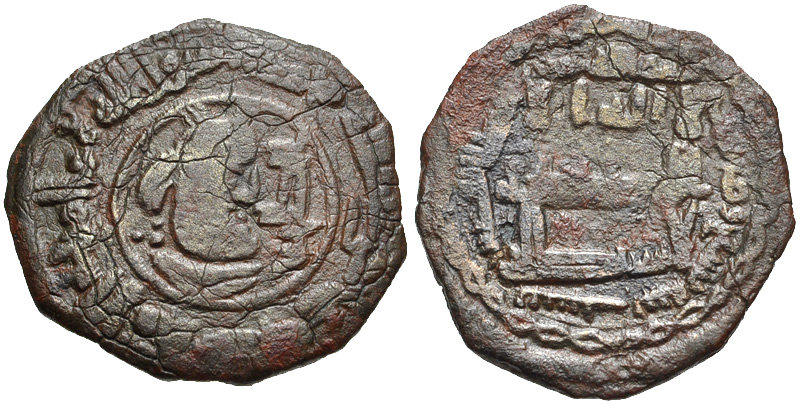

822 - 828 - Talha ibn Tahir (All Facts)
First native Persian ruler of Persia since the conquest of the Sassanid Empire by the Rashidun Caliphate

817 - 838 - Ziyadat Allah (All Facts)
3rd Aghlabid King of Ifriqiyah (Tunisia)
By the start of his reign, the Aghlabids were completely independent from the Abbasids
During his reign, he launched an expedition to capture Sicily from the Byzantine Empire via his general Asad ibn al-Furat
759 - 828 - Asad ibn al-Furat (All Facts)
Religious magistrate of Kairouan famed for his spiritual fervor and military energy
Under the reign of Ziyadat Allah and the Aghlabids, he was sent to capture Sicily from the Byzantine Empire
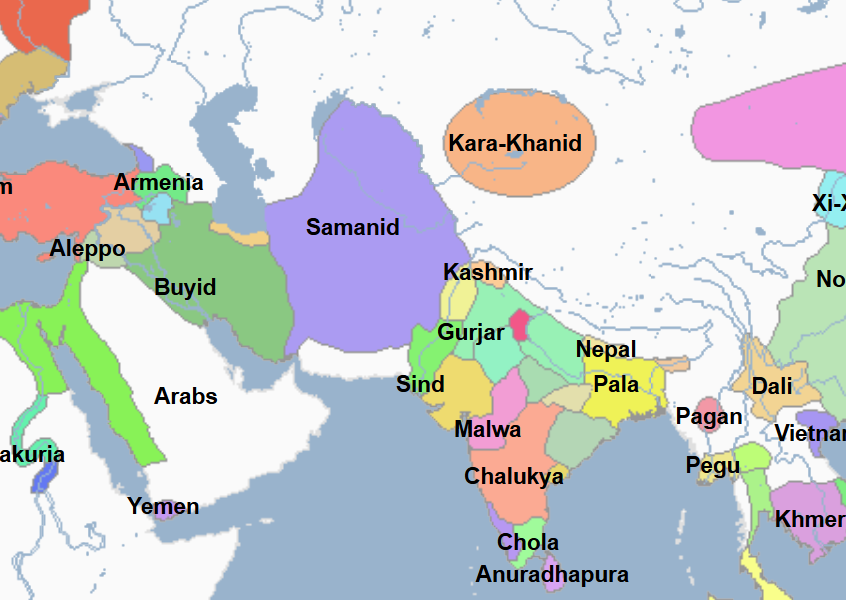
819 - 999 - Samanid Empire (All Facts)
Persian Sunni Muslim Empire
It was centered in Khorasan and Transoxiana (east of the Oxus River)
It was based on the namesake dynastic family that ruled it
It was located in the region between the Caspian Sea and the Hindu Kush
Its rulers and inhabitants were originally Persian landowners from Samarkand
Over time, they increased their power to form the dynasty and empire
Its capital was at Bokhara
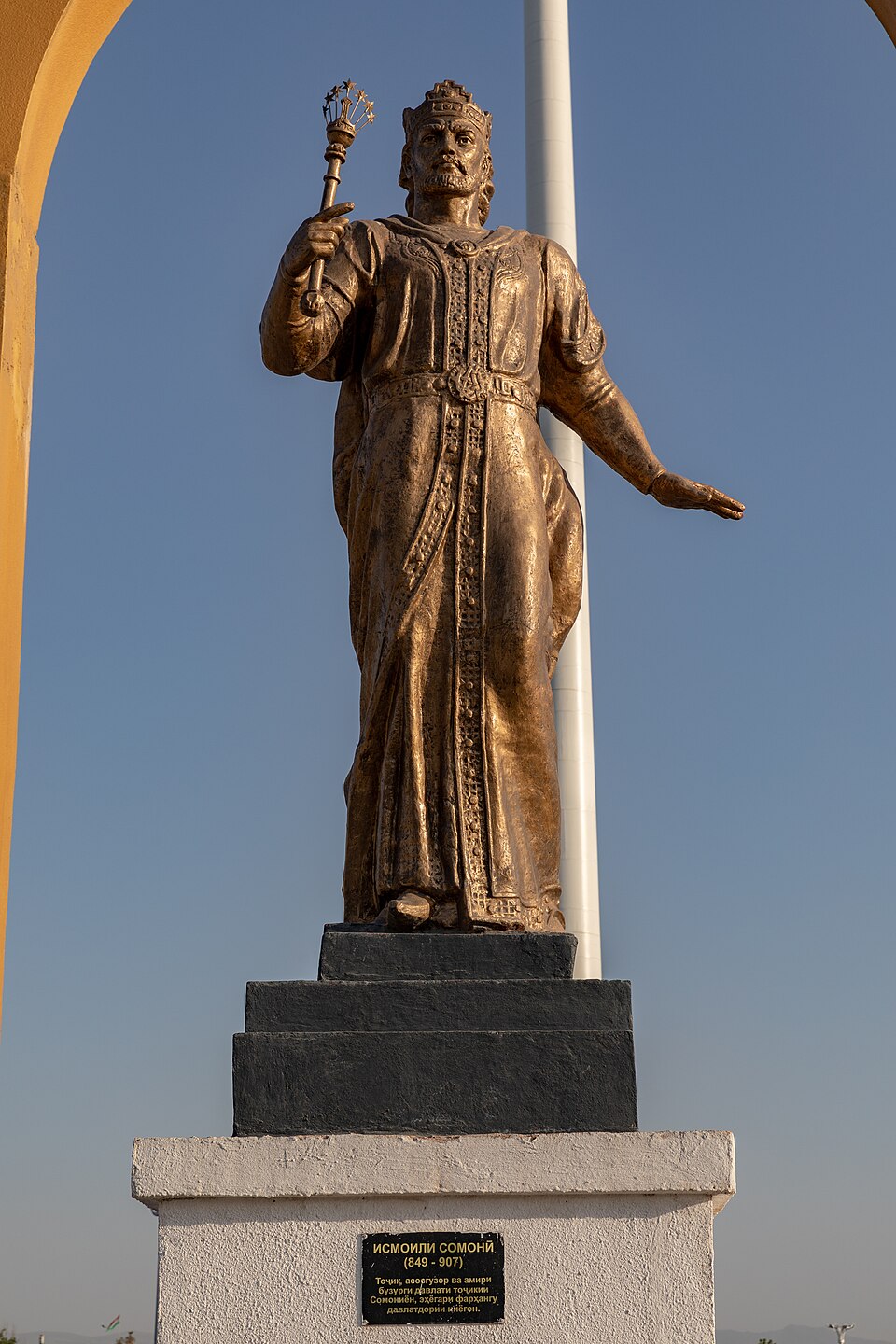

892 - 907 - Ismail Samani (All Facts)
First Emir and Founder of the Samanid Empire
As a people-group, the Samanids were ruled by others prior to him
He was the head of the Samanid family dynasty who defeated his local rivals to consolidate his power and rule
The Abbasid Caliphate had formally recognized him as ruler of Transoxiana
He established the Empire’s capital at Bokhara
During his reign, the Samanid Empire became and continued after his reign to be a rich trading center for goods from China and the from the far north
They traded gold and silks with the Rus for furs and iron along the Volga River
He was a patron of Persian poetry
He oversaw the construction and completion of his namesake family mausoleum in Bokhara
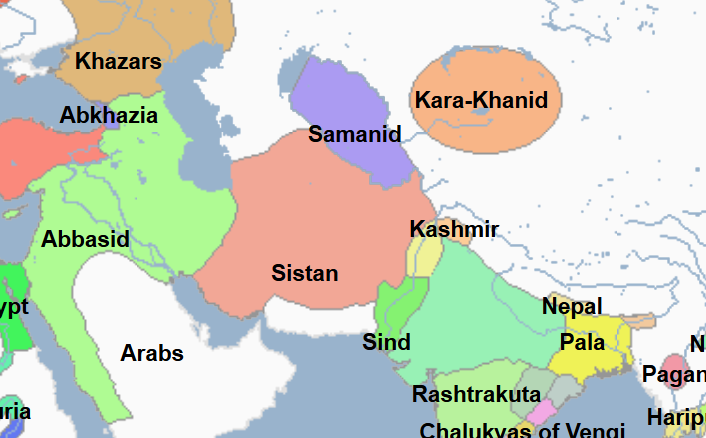

833 - 842 - Al-Mutasim (All Facts)
8th Caliph of the Abbasid Caliphate
He was the brother of his predecessor
He was the son of a Turkic slave woman
He rose to power by recruiting an army of Turks from the eastern borders of the Islamic World who enabled him to sidestep his nephew and become caliph
He integrated the Turks into the Abbasid Caliphate and Islamic World, many of whom had converted to Islam under his reign
He oversaw the construction and completion of the Great Mosque of Samarra
He had built this in order to attract the recently-converted Turkic Muslims to the new town to get them away from Baghdad
At the time of its construction, it was the world’s largest mosque
He moved the Abbasid capital from Baghdad to Samarra
He did this because of growing unrest in Baghdad due to the integration of the Turks, many of whom were becoming Muslim, with the Arab Muslims and the resentment and violent clashes that followed as a result
He founded the new capital to take the Turks out of Baghdad
He organized Samarra in such a way that the Turkic mercenaries used by the caliph did not mix with the Arab Muslims already living there in order to prevent the resentment and violent clashes that had occurred in Baghdad
Initially, only soldiers and bureaucrats made the move, but others soon followed
The town initially did not have running water, but this problem was soon resolved
He had Babak Khorramdin brought to and cruelly executed in Samara
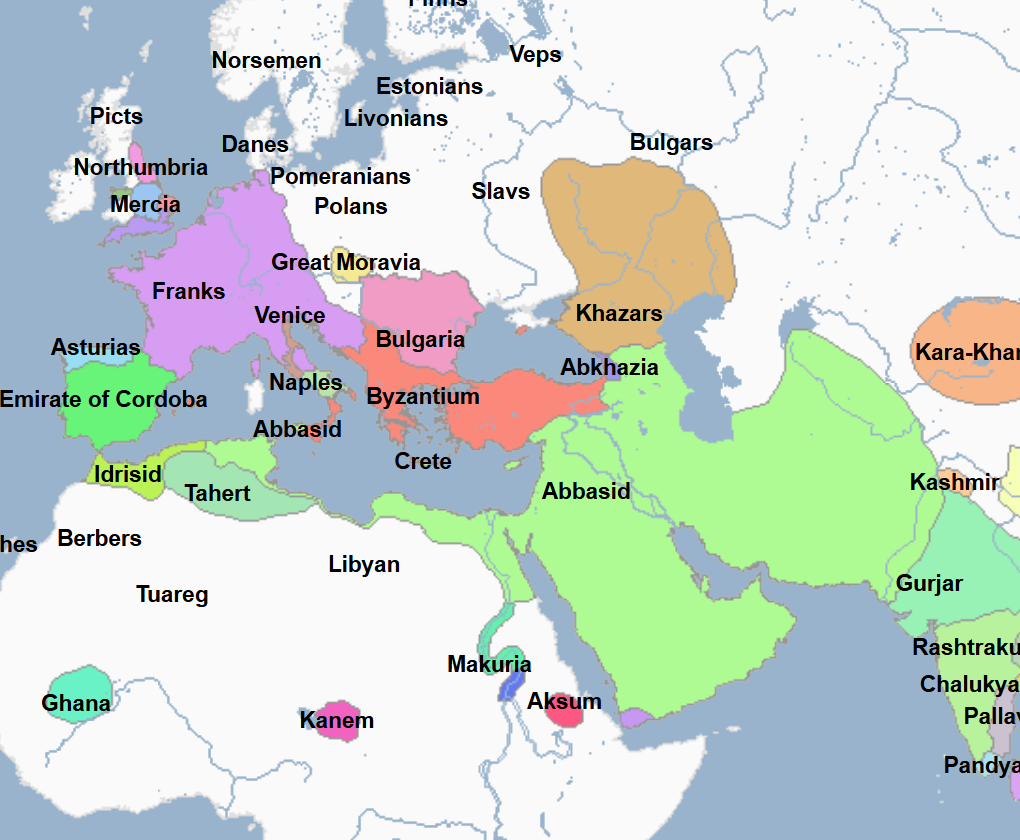

847 - 861 - Al-Mutawakkil (All Facts)
10th Caliph of the Abbasid Caliphate
He tried to restore Abbasid authority by winning the support of the orthodox Sunnis
He persecuted the Mutazilites and Shia as a result
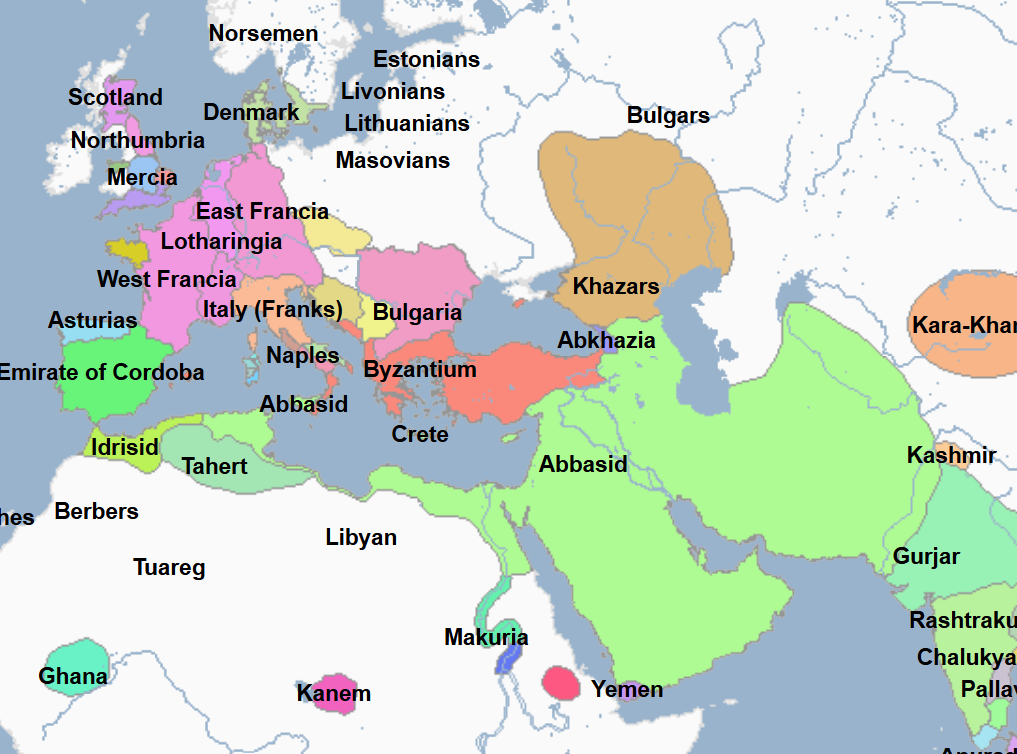

870 - 892 - Al-Mutamid (All Facts)
15th Caliph of the Abbasid Caliphate
Under his reign,
Egypt became independent once again and established its Tulunid Dynasty
Armenia broke free from Arab-Muslim domination, despite having to continue to pay tribute to the Abbasid Caliphate
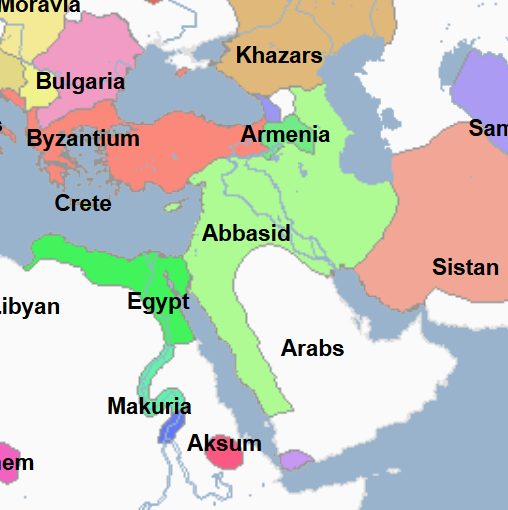
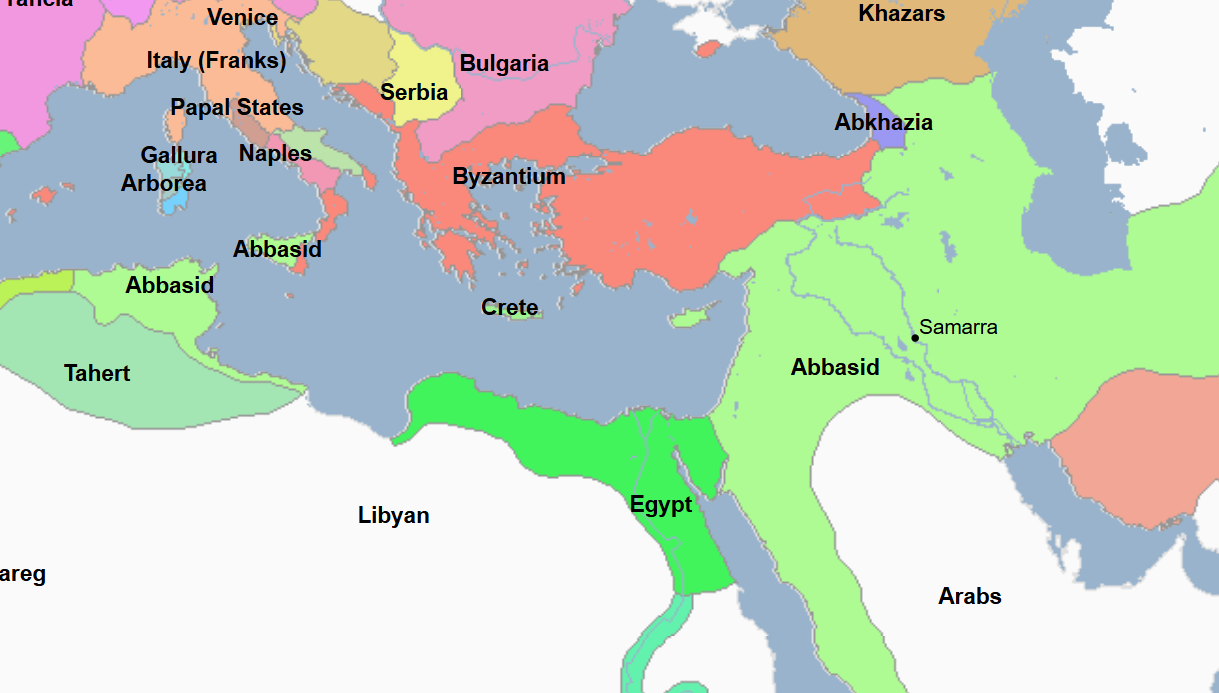
868 - 905 - Tulunid Dynasty (All Facts)
Dynasty which ruled Egypt independently during the years of the Abbasid Caliphate
This was the first time Egypt had been fully independent since the reign of Cleopatra and the rulers of the Ptolemaic Dynasty
868 - 884 - Ahmad ibn-Tulun (All Facts)
First Emir and Founder of the Tulunid Dynasty in Islamic Egypt, which essentially ruled Egypt independently of the Abbasid Caliphate, the first time Egypt had been fully independent since the reign of Cleopatra and the rulers of the Ptolemaic Dynasty
He was born to a Turkic slave
He became a soldier in the caliph’s army at Samarra and rose quickly through the ranks
He then became governor of Egypt under the Abbasid Caliphate
However, he defeated an attempt by Al-Mutamid, the caliph of the Abbasid Caliphate at the time, to remove the namesake from his office
He had pressed home his military advantage in Egypt and gone on to take over Syria as well
He became ruler of Egypt by winning over the loyalty of the people there due to his various administrative reforms, in which he
Stopped the drain of Egypt’s wealth to Al-Mutamid and the Abbasid Caliphate
Built up Egypt’s army, making it stronger
He established his namesake dynasty of Egypt’s capital at Fustat (modern-day Cairo)
He oversaw the construction and completion of his namesake mosque there
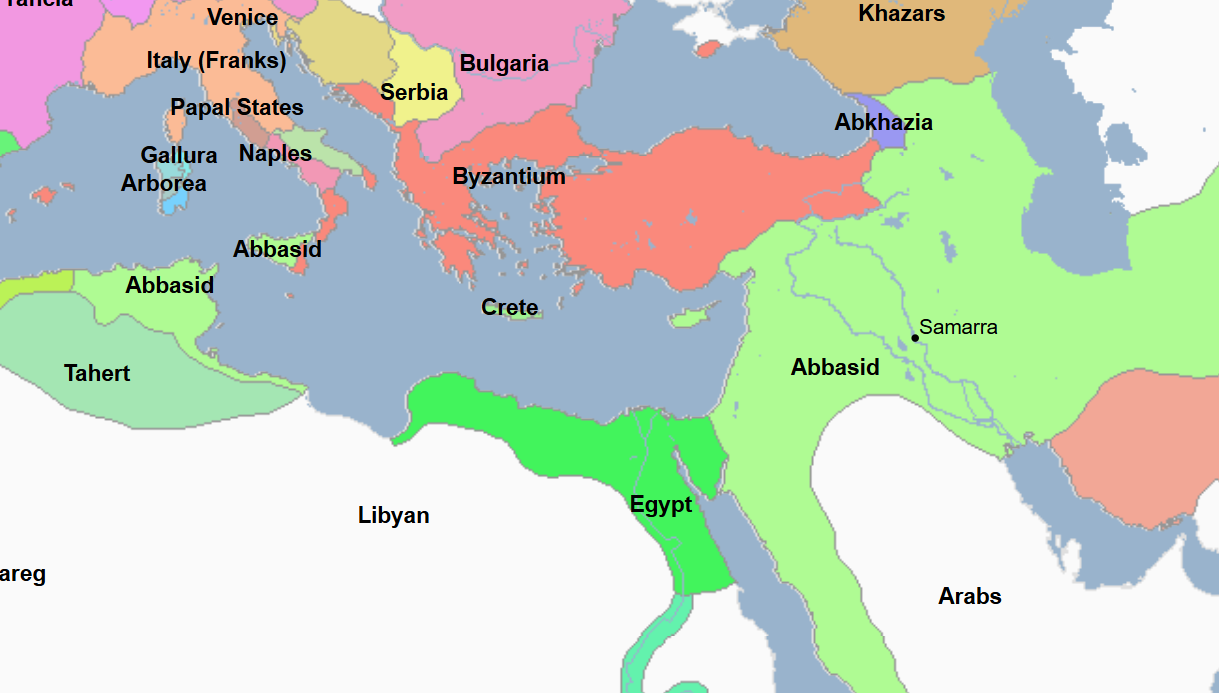

892 - 902 - Al-Mutadid (All Facts)
16th Caliph of the Abbasid Caliphate
He moved the capital of the Abbasid Caliphate back to Baghdad from Samarra
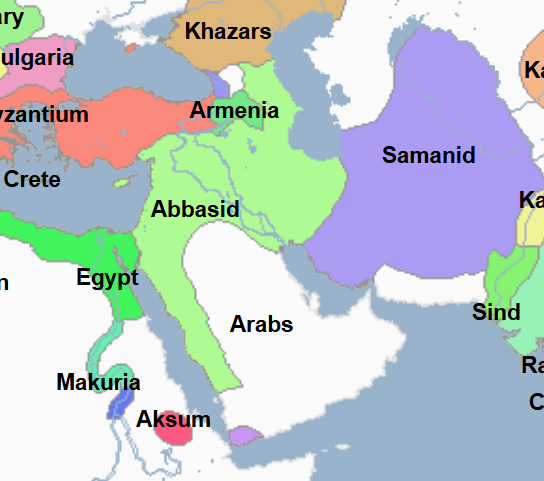
897 - 1091 - Emirate of Sicily (All Facts)
900s - Abu Abdallah al-Shi'i (All Facts)
Islamic missionary who roused up the Berbers to revolt against and overthrow the Aghlabid Dynasty of Ifriqiyah (Tunisia)
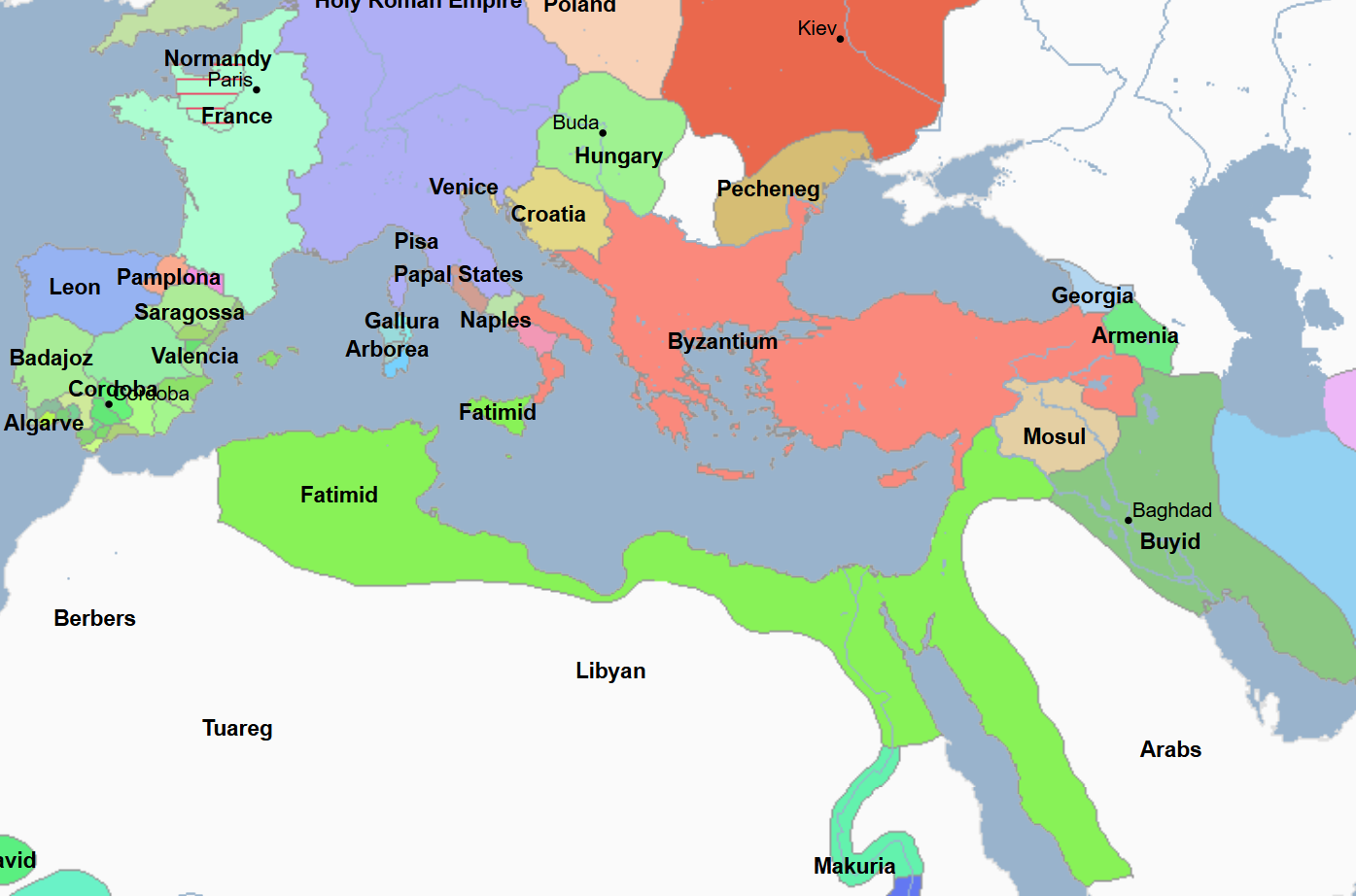
909 - 1171 - Fatimid Caliphate (All Facts)
Caliphate founded by Abd Allah al-Mahdi Billah
Caliphate that was Shia Muslim that coexisted alongside the Abbasid Caliphate (which was Sunni)
Only major historical caliphate that was Shia Muslim
Caliphate which grew out of the discontent by the Shia Alids, whom the first caliph of the Abbasid Caliphate, al-Saffah, had initially appealed to for help in overthrowing the Umayyad Caliphate, but then negated them after establishing Abbasid rule and consolidating his rule power
Caliphate which was legitimized by its having traced its ancestry to the Great Prophet Mohammad's daughter Fatima, whom lends her name to the namesake caliphate; and her husband Ali, who lends himself to the namesake caliphate’s religion since he was the first Shia imam (caliph)
Its first capital was at Mahida in Ifriqiyah (Tunisia)
When they conquered Egypt, Cairo became their new capital
Responsible for colonizing the island of Zanzibar from the Gulf

909 - 934 - Abd Allah al-Mahdi Billah (All Facts)
First Caliph and Founder of the Fatimid Caliphate
He was nicknamed “Mahdi” meaning “Prince of the Faithful”
He was raised in Syria
When he traveled west, he was imprisoned at Sijilmassah
He later settled in Ikjan, where he won over the people there
From there, he proceeded into Aghlabid territory
He overthrew the Aghlabid Dynasty
He was helped by Abu Abdallah al-Shi'i and the Ketama Berbers
He crushed the Aghlabid army in Rakkaba
The Ketama Berbers became the base of the namesake’s caliphate’s military
He styled himself as “caliph” as a direct challenge to the authority of the Abbasid Caliphate in Baghdad
He legitimized his reign by claiming descent from the Great Prophet Mohammed’s daughter and first Shia Imam (caliph) of Ali’s wife Fatima, who lends herself to the Fatimid Caliphate’s name
He established Mahida in Ifriqiyah (Tunisia) as the capital of the Fatimid Caliphate
Shortly before his reign, the Arab-Muslims settled in modern-day Somalia for the first time
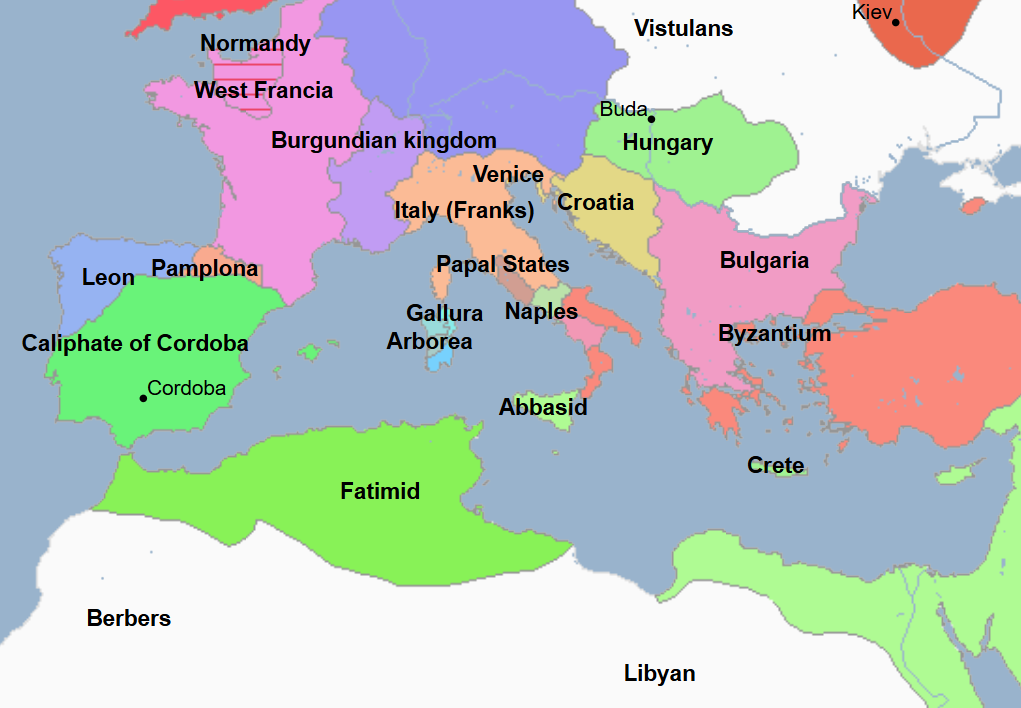
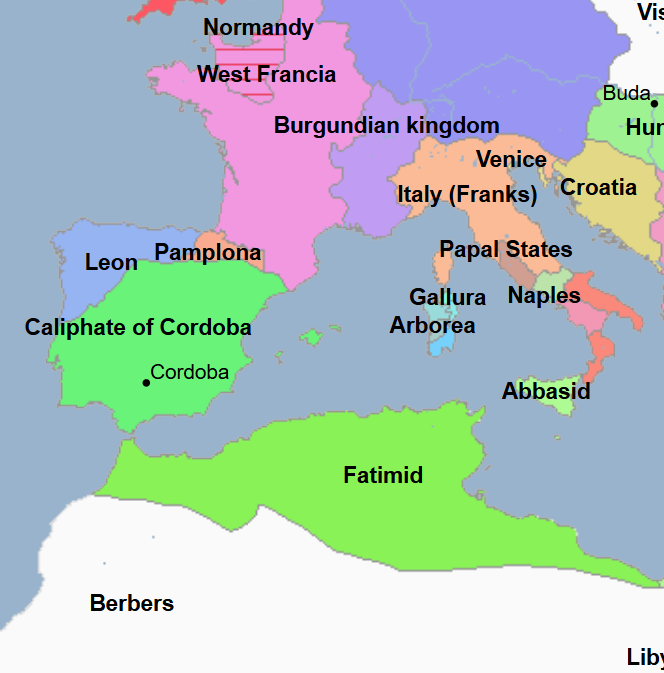
929 - 1031 - Umayyad Caliphate of Cordoba (All Facts)
Founded by Abd al-Rahman III

929 - 961 - Abd al-Rahman III (All Facts)
First Caliph and Founder of the Umayyad Caliphate of Cordoba
He proclaimed himself caliph
He reestablished the Islamic Iberian Peninsula (Spain) as a major Islamic power and independent rival to the (expansionist) Fatimid Caliphate of Ifriqiyah (Tunisia)
He crushed his rivals and reestablished the authority of Cordoba, the capital of the caliphate, in order to end the political crisis of the preceding emirate and consolidate his rule and power
He oversaw a regime with flourishing commerce, fertile agriculture, and thriving intellectual life
During his reign, he took Morocco from the Fatimid Caliphate
Established Madmat az Zahra as an additional capital to Cordoba
Under his reign
Umayyad culture reached its peak
Cordoba, as a center of Islamic science, reached its peak
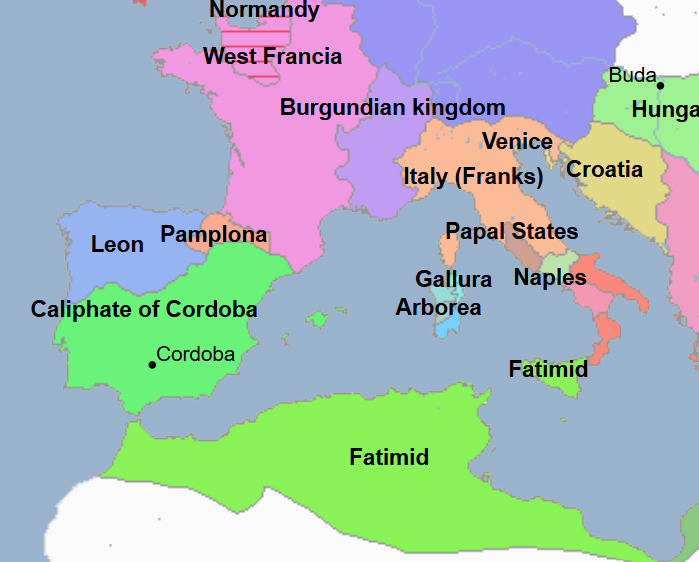
941 - 942 - Ibn-Raiq (All Facts)
Military adventurer who ruled the Abbasid Caliphate after the actual caliph at the time gave his office up to him

944 - 946 - Al-Mustakfi (All Facts)
22nd Caliph of the Abbasid Caliphate
He was blinded, deposed, and replaced by Ahmad ibn Buya / Mu'izz al-Dawla of the Buyid Dynasty
The succeeding Abbasid Caliphs served as vassals under Ahmad ibn Buya / Mu'izz al-Dawla and his successors of the Buyid Dynasty
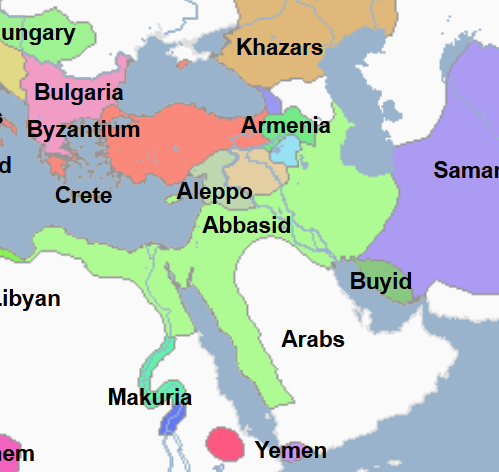
945 - 947 - Abu-Yazid (All Facts)
Led a major revolt against the Fatimid Caliphate in Ifriqiyah (Tunisia)
He was inspired to revolt against the Fatimids after studying the Kharijites and their egalitarian and regional doctrines
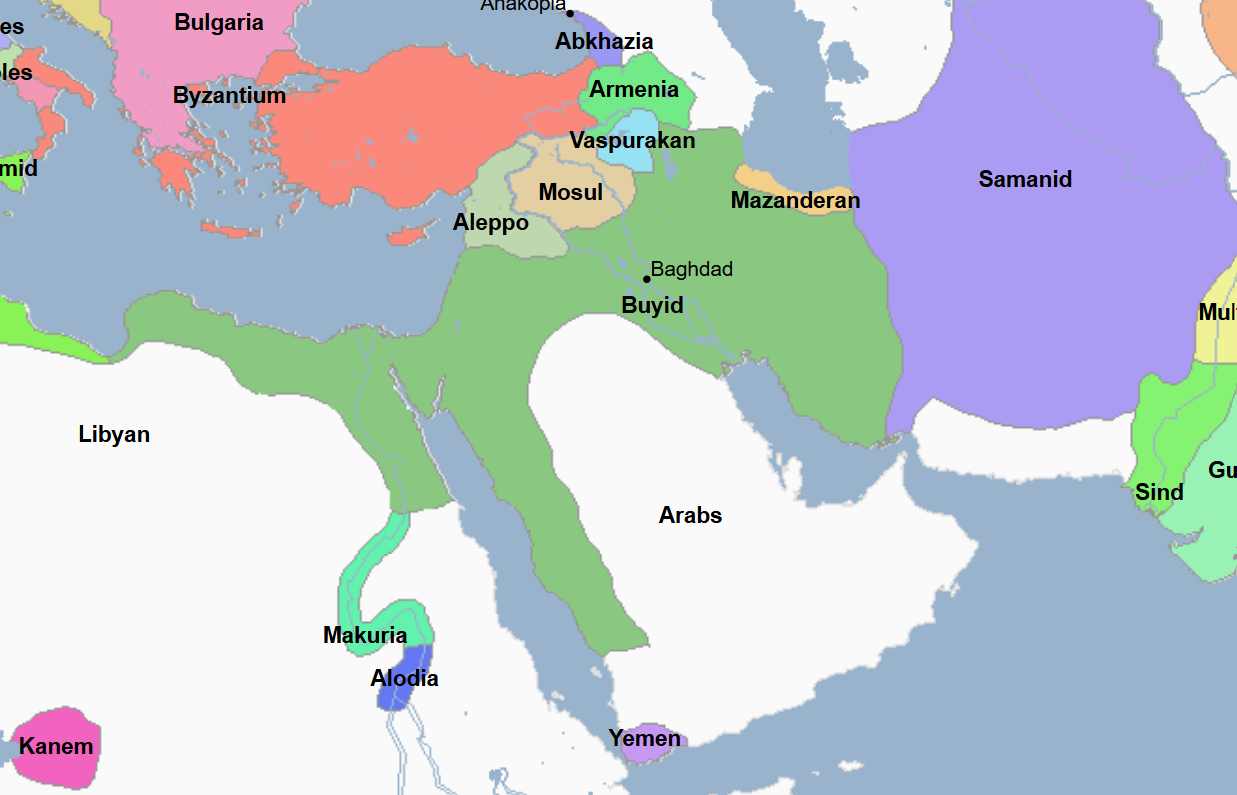
934 - 1062 - Buyid Empire (All Facts)
First Persian (Iranian) Muslim Dynasty, it was Shia
Its creation represented the continued decline in the power of the Abbasid Caliphate
Real power in the region was in the hands of local warlords who had been ravaging the Persian countryside
It fell to Tughril and the Seljuk Turks, who took Baghdad from them and redeclared the Abbasid realm to be Sunni instead of Shia

945 - 967 - Ahmad ibn Buya / Mu'izz al-Dawla (All Facts)
First Emir and Founder of the Buyid Dynasty in Iraq
He was nicknamed the latter namesake title “He who makes the state mighty”
He was born in northern Persia and raised as a fisherman to a father who claimed descent from ancient Persian kings, which he used for his own legitimacy upon assuming the throne
He exploited the chaos in the countryside and took most of Western Persia but eventually tried to restore peace in the region
He decided to keep the caliph as a figurehead
He established the Buyid Dynasty, the first of many distinctly Persian (Iranian) Muslim Dynasties
Like the contemporary Fatimid Caliphate, it was also Shia
He blinded, deposed, and replaced Al-Mustakfi of the Abbasid Caliphate
The succeeding Abbasid Caliphs served as vassals under the namesake and the Buyid Dynasty
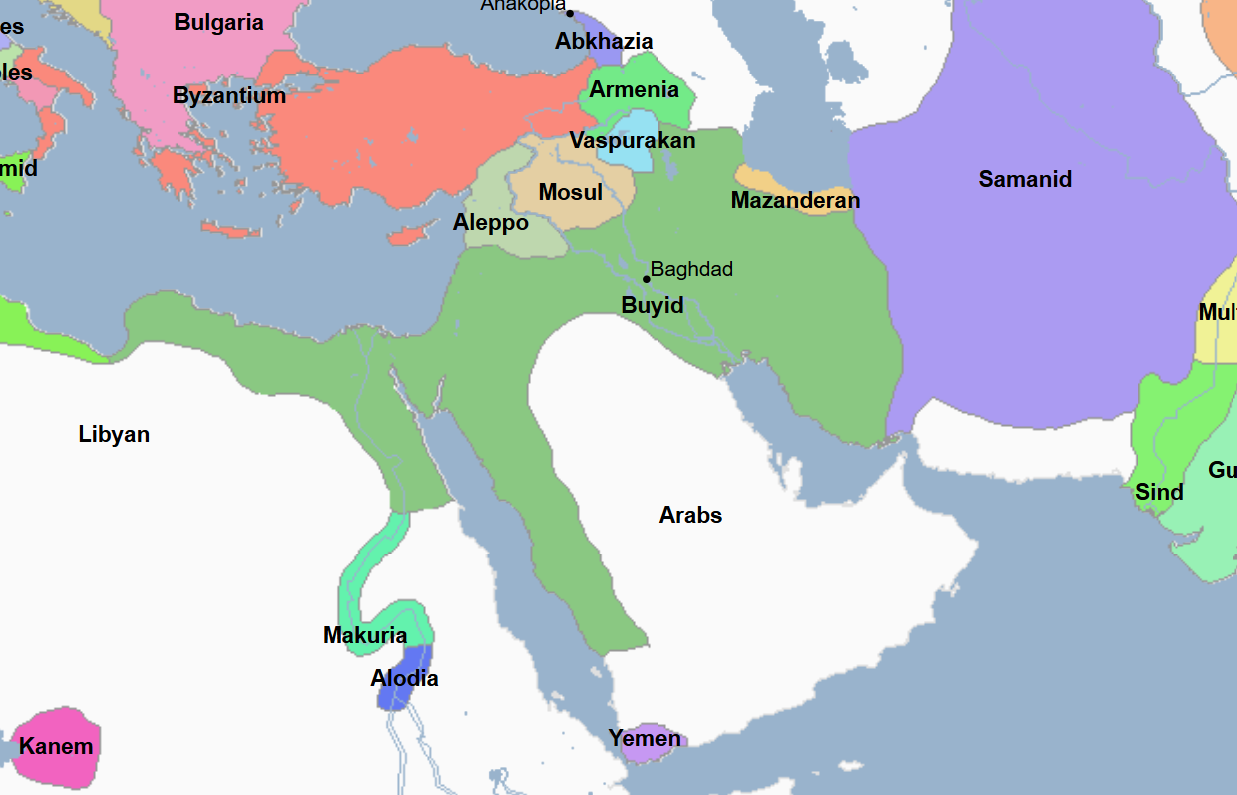
957 - 1513 - Kilwa Sultanate (All Facts)
Sultanate founded by Ali ibn al-Husain ibn Ali located on the southern coast of modern-day Tanzania
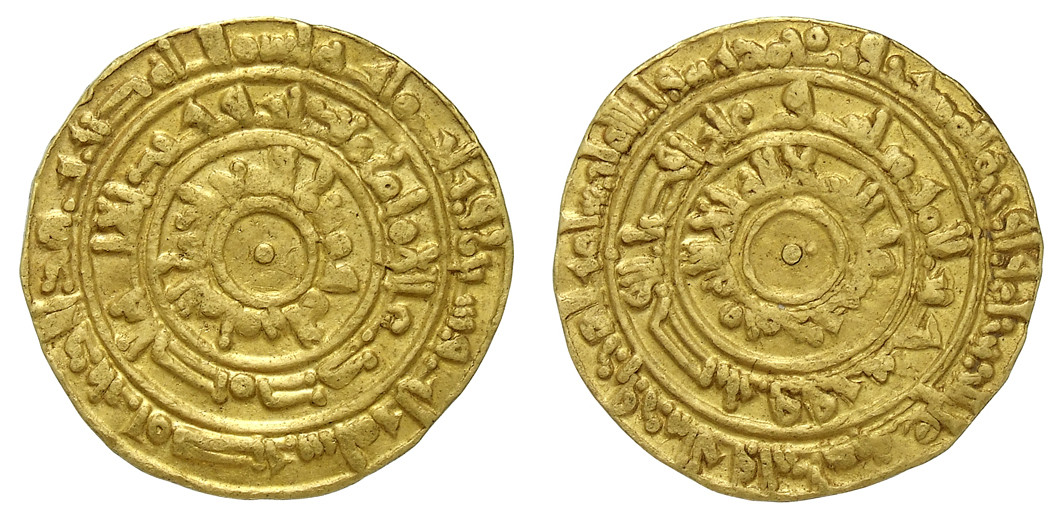

953 - 975 - Al-Mu'izz li-Din Allah (All Facts)
4th Caliph of the Fatimid Caliphate
Under his reign, the Fatimid Caliphate
Conquered much of Egypt
Established Cairo, in Egypt, as their (new) capital and one of the most important cities in the Islamic World for two reasons:
To sever the local Sunni Muslim population from their links with the Abbasid Caliphate in Baghdad
They still owed allegiance to Baghdad given their religious affiliation
To create a center of Shia Muslim learning and education comparable to those in Baghdad
Under his reign, the Al-Azhar Mosque was constructed and completed in Cairo, it served as both a palace and as a university
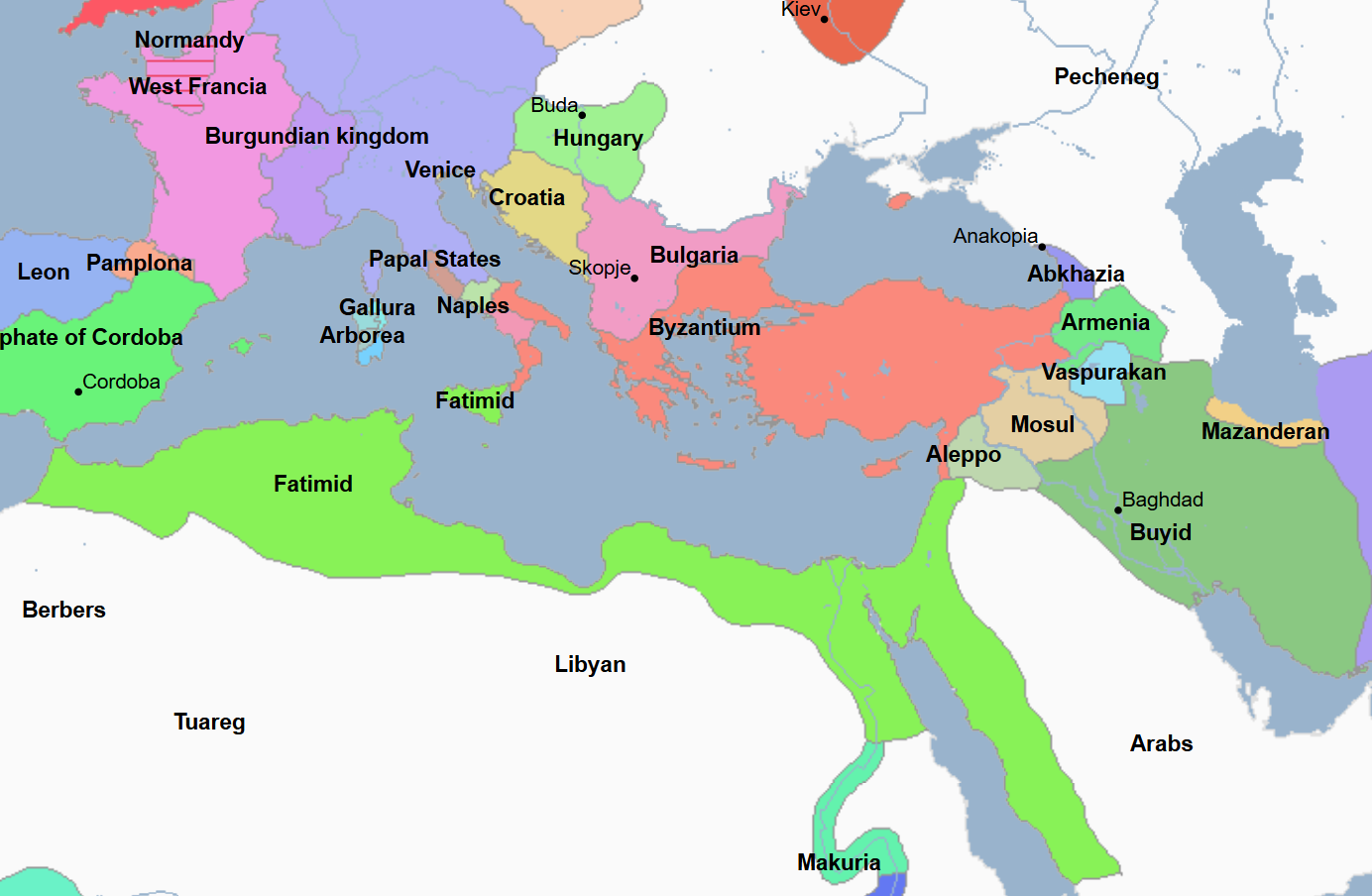
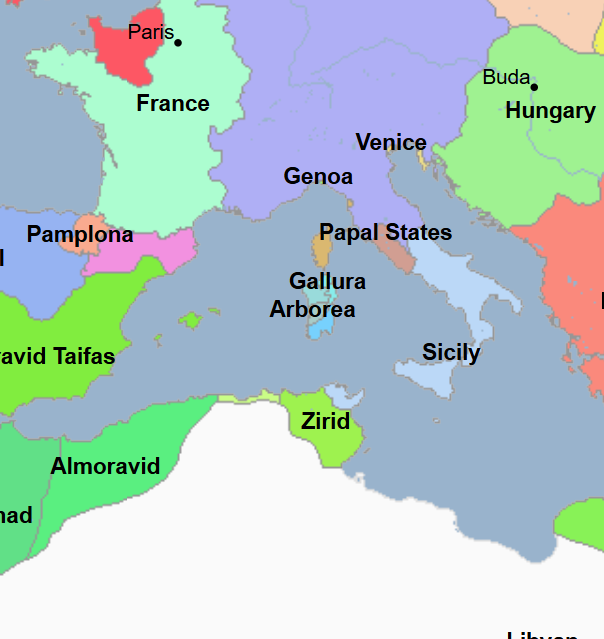
972 - 1148 - Zirid Emirate / Dynasty (All Facts)
Sanhaja Berber dynasty established by the Fatimid Caliphate that ruled modern-day Algeria and the central Maghreb to Ifriqiyah (modern-day Tunisia)
Emirate in which the Genoese and the Pisans obtained trading privileges as the result of their successful expedition against Mahdia in Tunisia
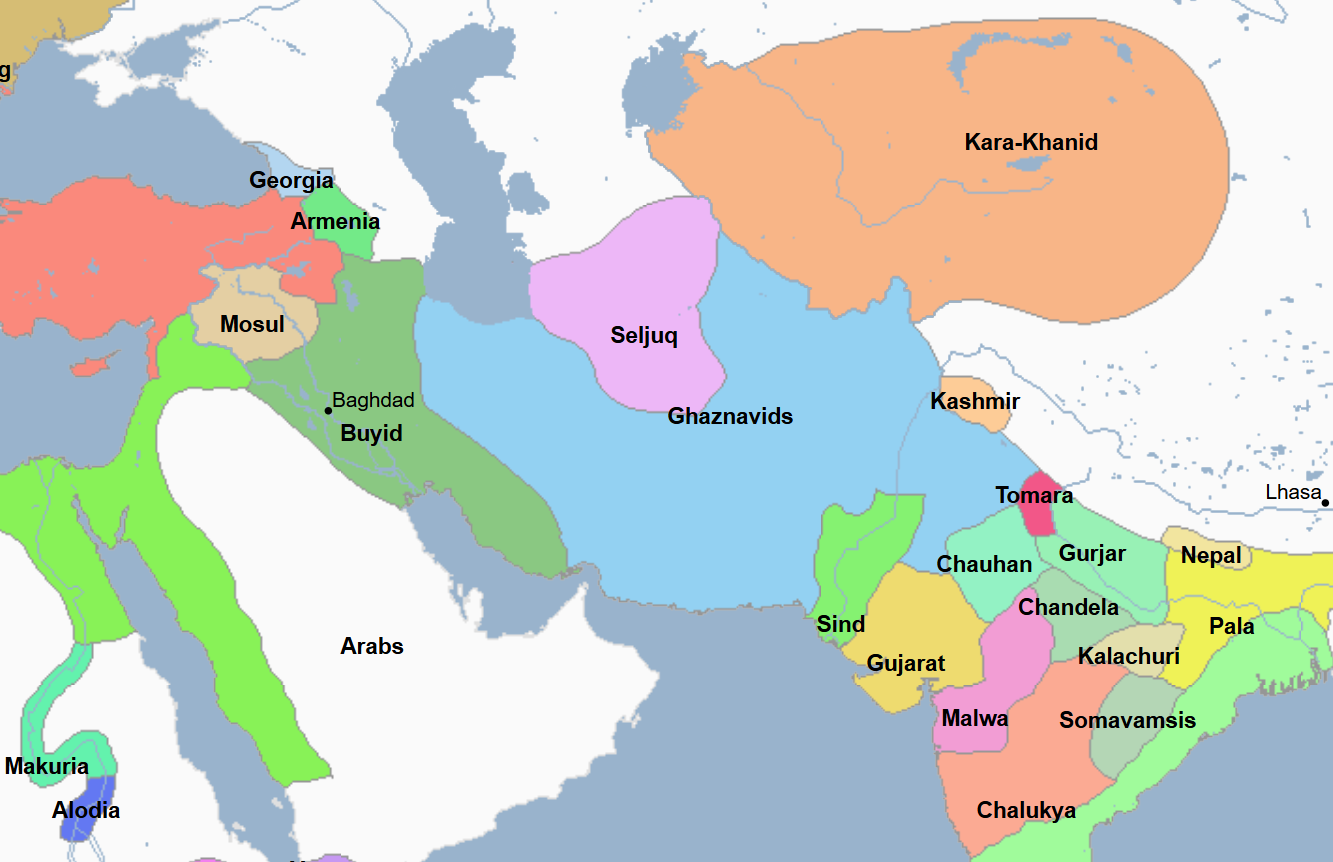
977 - 1186 - Ghaznavid Empire / Dynasty (All Facts)
Turkic-Persian Muslim Dynasty established by Sabuktigin of Ghazni in Kabul in modern-day Afghanistan
At its greatest extent, it stretched from the Oxus River to the Indus River
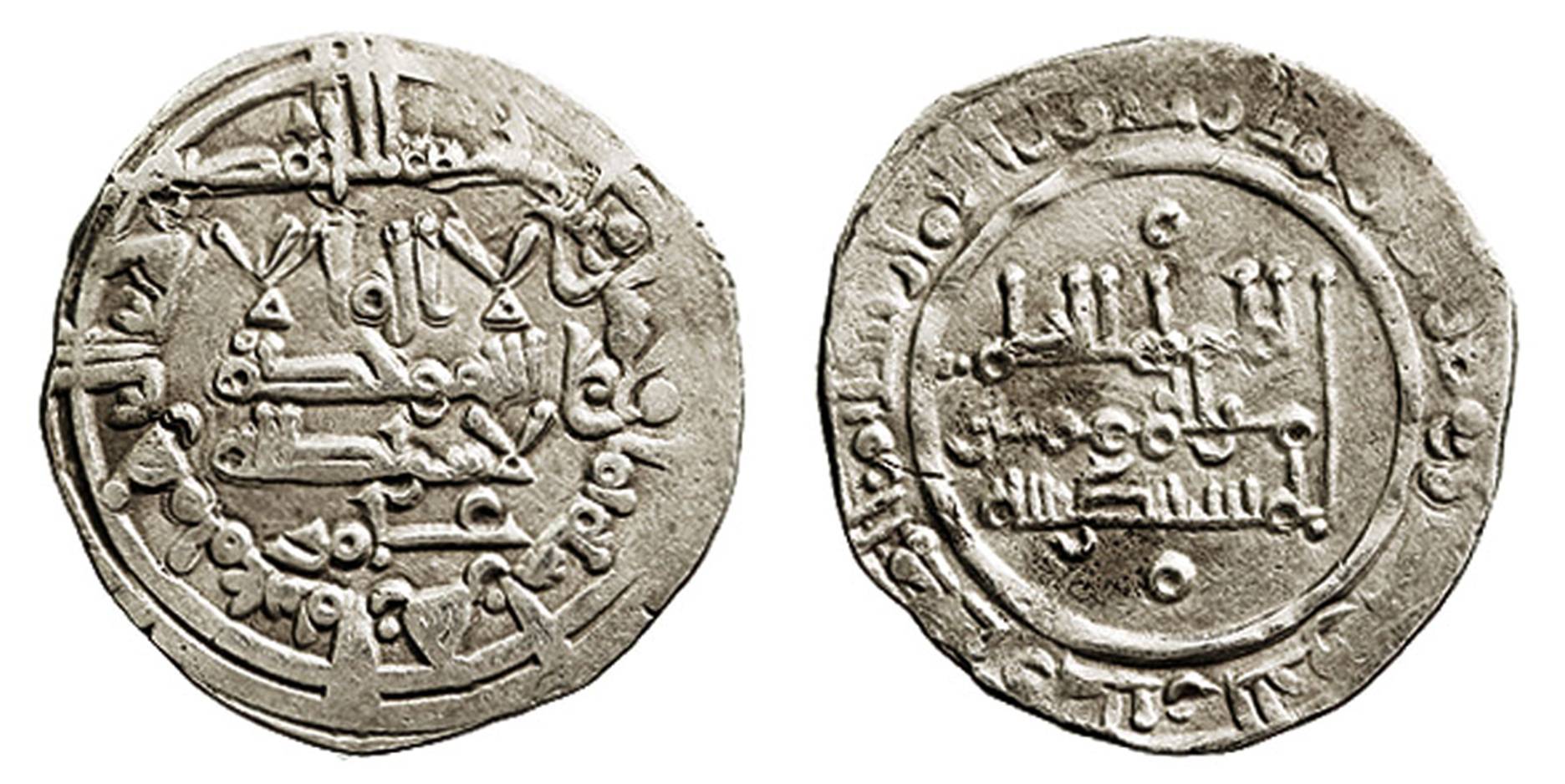

961 - 976 - Al-Hakam II (All Facts)
Caliph of the Umayyad Caliphate of Cordoba
Under his reign, Al-Andalus’ reputation for learning benefited as the namesake left an important intellectual legacy
He was an enthusiastic bibliophile, having collected some 400K volumes in a library that covers every aspect of Islamic scholarship from theology to science
His library was a center for many scholars, although local Muslim fundamentalists feared that many of its works it included may be heretical and sought to purge the library as a result
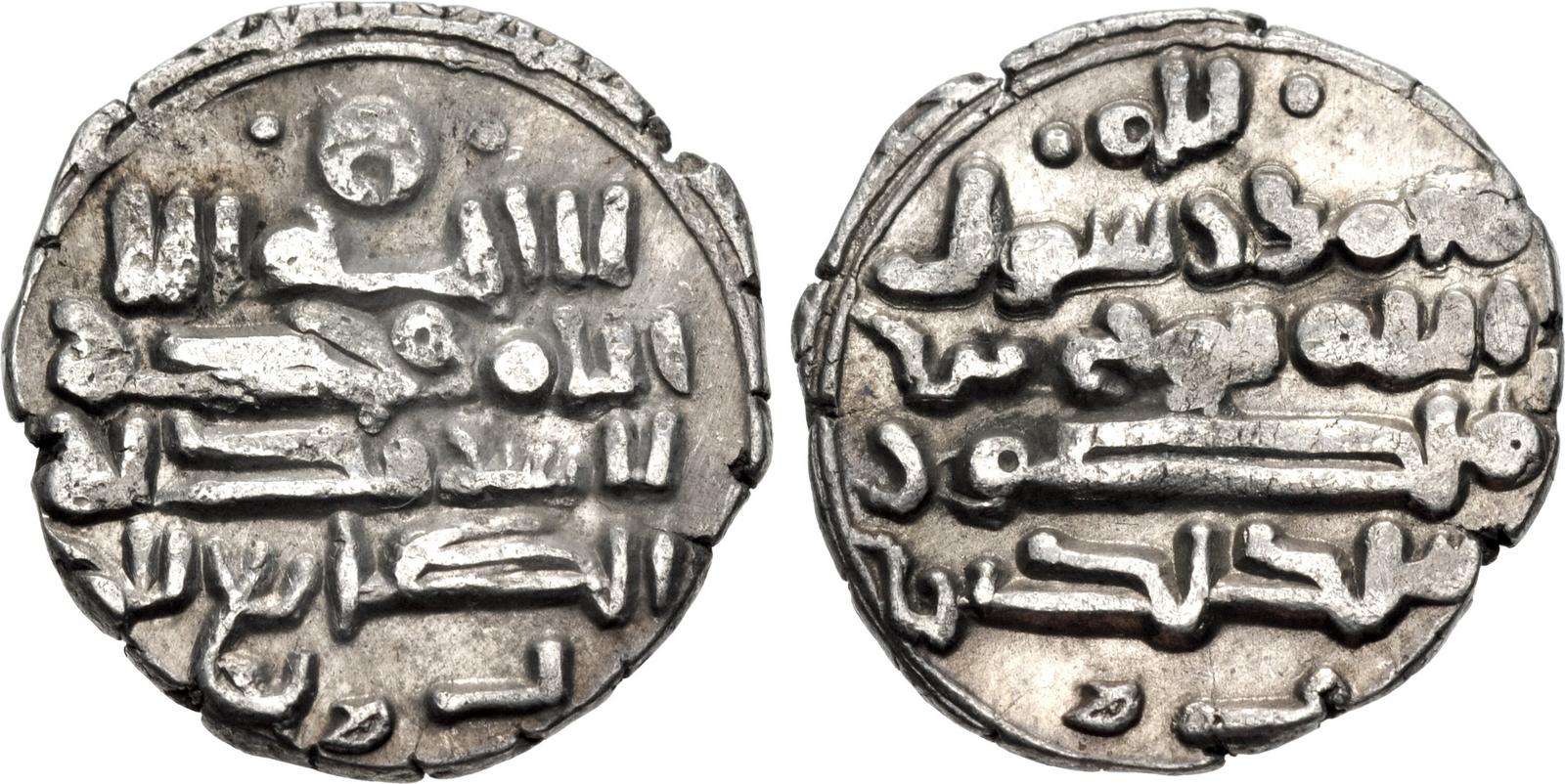

977 - 997 - Sabuktigin (All Facts)
First Sultan and Founder of the Ghaznavid Empire / Dynasty
He occupied Kabul to established Ghaznavid power
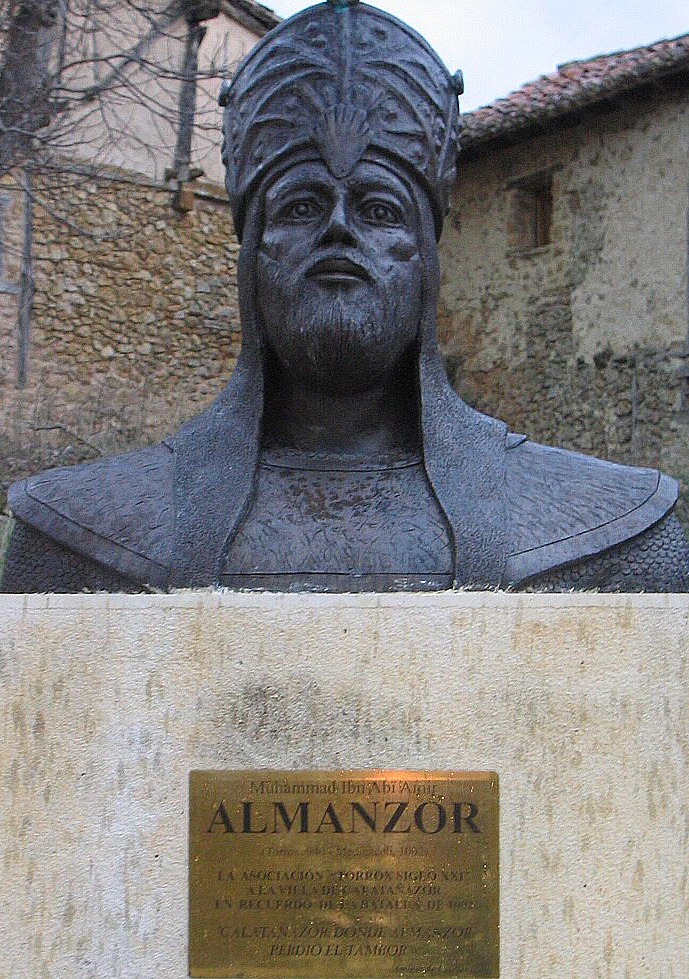
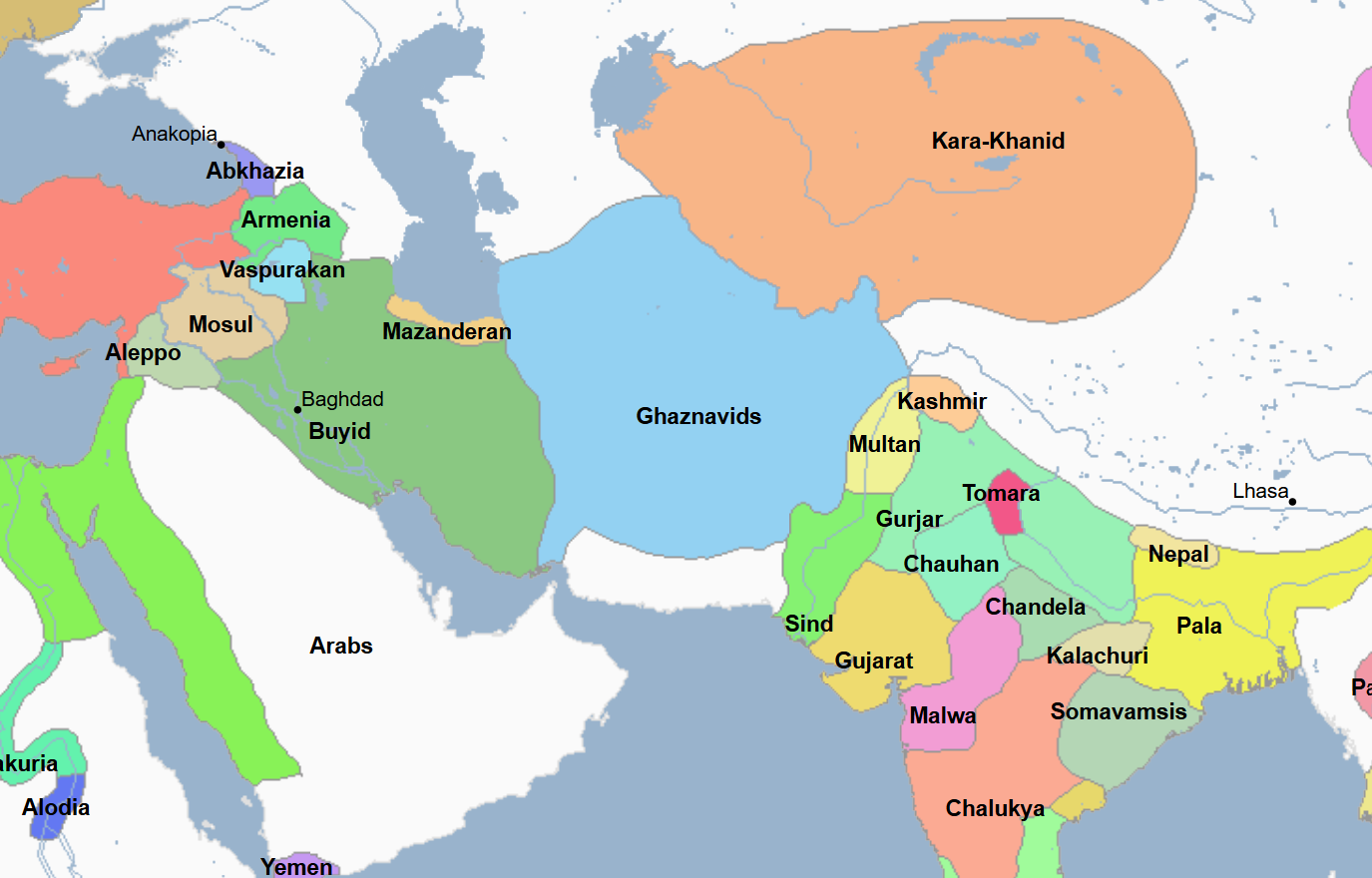

978 - 1002 - Al-Mansur (All Facts)
Chief Minister of Caliph Hisham II, he was the effective ruler of the Umayyad Caliphate of Cordoba
He was nicknamed “The Victorious”
Under his reign, Al-Andalus reached unprecedented importance
He served as chamberlain to Caliph Hisham II and was backed by the caliph’s Basque mother Aurora to become ruler
He was essentially dictator of Al-Andalus for 25 years, however he did not abuse his power and instead worked to increase the influence of Al-Andalus
He expanded the Umayyad Caliphate of Cordoba’s power, in which he took Leon and Compostela in the north away from the Christians and in which he expanded the power of Al-Andalus into the western Maghreb in the south
He died at Medinaceli
He left no apparent heir and a power vacuum ensued following his death

976 - 1009 - Hisham II (All Facts)
Caliph of the Umayyad Caliphate of Cordoba
Under his reign, dictators ruled including Al-Mansur

996 - 1021 - Al-Hakim (All Facts)
Caliph of the Fatimid Caliphate in Egypt
He
Outraged Christians by having ordered the destruction of the Church of the Holy Sepulcher, apparently in a fit of madness
This prompted calls for a Christian Crusade to recover the Holy Land from the Arab Muslims
Made decrees at whim to
Ban chess
Keep markets open at night
Carried out sudden and brutal executions
He disappeared and was eventually murdered
Clothes last worn by him were found slashed by a dagger on the Mukattam hills outside Cairo
Many believe his sister Sitt al-Mulk decided to kill him to put to an end what many saw as a cruel and capricious leader
The Syrian Druze believed he was a divine monarch who had gone into hiding and were simply awaiting his return

1025 - 1029 - Salih ibn Mirdas (All Facts)
Emir / Governor of Aleppo
He besieged the city of Marras

998 - 1030 - Mahmud of Ghazni (All Facts)
3rd Sultan of the Ghaznavid Empire
He was the son of a Turkish slave
He defeated his elder brother to seize the throne
He assumed the throne of the Turkic Ghaznavid people and started new conquests
He expanded the Ghaznavid Empire into Persia and India, defeating and overtaking Hindu states and peoples, in which
He and his forces raided from his mountain fastness down into the rich agricultural plain of Punjab, a region which he plundered and annexed
He and his forces swept through India, defeating the armies of a Hindu confederacy on the plain of Peshawar
He and his forces invaded Kashmir, but were forced to retreat
He sacked Kanauj and broke the power of the Hindu states
He led a campaign in India which took him to the shores of the Indian Ocean, where he horrified the Hindus by destroying the Temple of Siva at Somnath in Gujarat and carried away its celebrated golden gates along with vast treasure and slaughtered over 50K Hindus
His army thus occupied most of northern India
He occupied Transoxiana
His conquests were not just territorially but also religiously motivated
He was a zealous Muslim who worked to
Destroy Hindu temples and carry off their treasures
Force Hindu monks to convert to Islam
He oversaw the construction of
The Celestial Bride Mosque at Ghazni
He founded the great mosque at Ghazni, capital of the Ghaznavid domains
Splendid palaces at Bust and Ghazni
He was a patron of literature and art
The greatest scholars of the age lived at his court
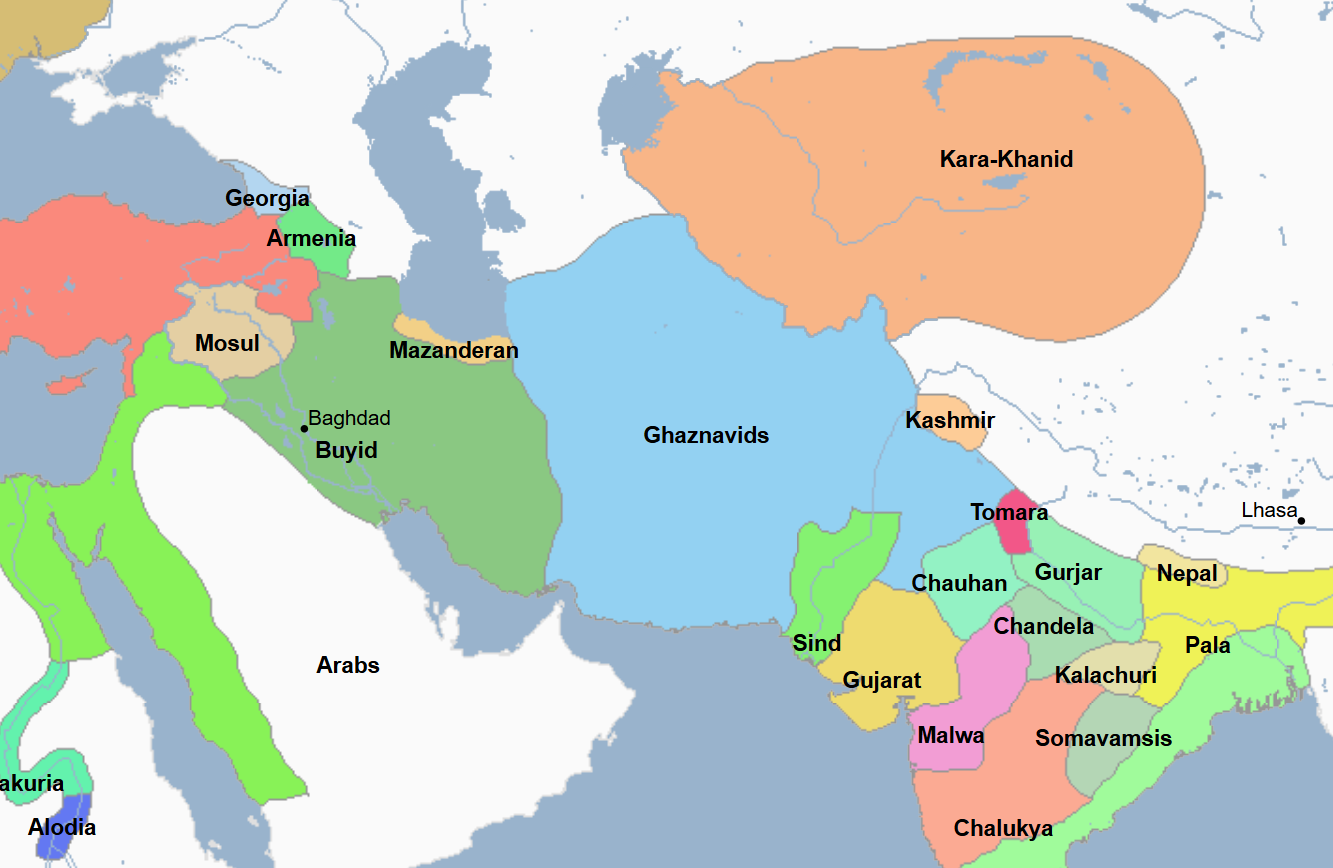

1030 / 1040 - 1041 Muhammad of Ghazni (All Facts)
4th and 6th Sultan of the Ghaznavid Empire
He was blinded and replaced by his brother and successor
He succeeded his brother after he was murdered and ruled again
1027 - 1031 - Hisham III (All Facts)
Final Caliph of the Umayyad Caliphate of Cordoba
When he was deposed, the Umayyad Caliphate of Cordoba was brought to an end
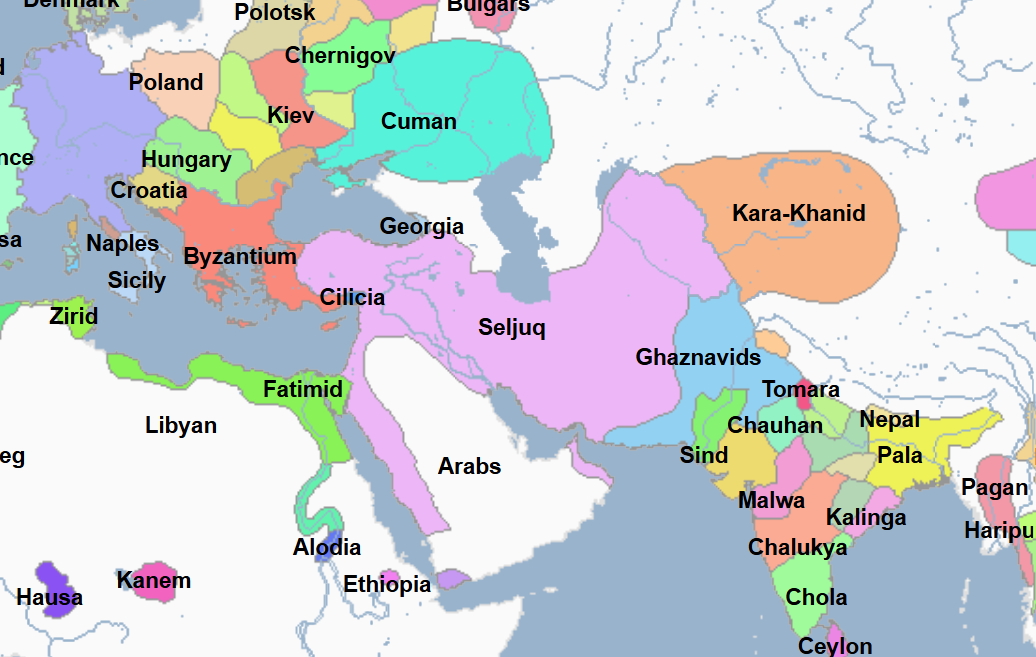
1037 - 1194 - Seljuk Empire (All Facts)
Established by Tughril and the namesake group of Muslim Turks in the Middle East
They began conquering parts of the Middle East in the 1000s and eventually extended their power almost as far east as Western China
In 1040, they took the northwestern part of the Ghaznavid Empire
In 1052, they seized Isfahan
In 1067, they took Caesarea in Cappadocia in the Byzantine Empire
Their rulers called themselves sultans
They limited the travel of and fought to suppress the Crusaders, unlike the Abbasids, who allowed Christians to travel easily to and from their holy sites
They gradually split into separate regencies (by 1100)

1030 - 1040 - Masud (All Facts)
5th Sultan of the Ghaznavid Empire
He blinded and replaced his brother and predecessor
He and his forces were defeated by the Seljuk Turks
On his return to Ghazni, he was murdered and succeeded by his brother
1000s - 1059 - Abdullah ibn Yasim (All Facts)
Founder of the Almoravid Dynasty
He founded the Almoravid Movement, which preached holy war and spiritual renewal
He united the tribes of the western Sahara and advanced into Morocco with 30K zealots
1050 - 1147 - Almoravid Dynasty (All Facts)
Founded by Abdullah ibn Yasin
They were originally a movement of Muslims comprised of nomadic Berber tribesmen
They were based in Morocco, the first region which they invaded
Their empire stretched from the Niger to the Ebro River in Spain
They extended their empire into modern-day Algeria, which they ruled from
They grew via a series of conquests in which they
Seized Awdaghost (Mauretania) in 1055
Conquered Zanata in Morocco in 1061
Seized the Ghana Kingdom in 1077
Thousands of the namesake Saharan nomads swept through Ghana, destroying what was the richest empire in West Africa at the time
Occupied its gold-rich mines and becoming richer than the degenerate sultans they voted to overthrow
Crossed the Straits of Gibraltar into Spain, where they annexed Islamic Spain by 1086
Carved an empire covering western North Africa and Islamic Spain
Their reign in Spain was weakened over time by
Material luxury
Self-interest
Financial problems
The launching of raids by Christian rulers
Revolts in the final years of its reign in Islamic Spain

1037 - 1063 - Tughril (All Facts)
First Sultan and Founder of the Seljuk Empire
He entered Baghdad as the liberator and protector of the Abbasid Caliphate against the Shia Buyid Empire, restoring Sunni Islam and installing himself as the temporal master of the caliph
So he replaced the Abbasid Caliphate politically, but maintained its religious identity

1063 - 1072 - Alp Arslan (All Facts)
2nd Sultan of the Seljuk Empire
He and his forces defeated Romanos IV Diogenes and the Byzantine Empire in the Battle of Manzikert
He and his forces captured Romanos IV Diogenes
Thus, under his reign, the Turkification of Anatolia began

1056 - 1087 - Abu Bakr (All Facts)
Amir of the Almoravids
Under his reign, the Almoravids founded the city of Marrakesh
He invaded Spain

1061 - 1106 - Yusuf ibn Tashfin (All Facts)
4th Amir of the Almoravids
He assumed the throne upon the Almoravid conquest of Zanata in Morocco
He completed the conquest of the Maghreb (in North Africa), ruling an empire four times bigger than Spain at the time
He and his Almoravid forces defeated Alfonso VI and his forces in the Battle of Sagrajas, coming to the aid of the Arab princes of Spain
After the battle, carts loaded with Christian heads were sent to the chief cities of Spain and the Maghreb to show them that the Christians were longer to be feared by the Almoravids
He was not strong enough to occupy parts of Islamic Spain resettled by Christians, such as Toledo, before he died

1106 - 1143 - Ali ibn-Yusuf (All Facts)
5th Amir of the Almoravids
He and his forces were defeated by Alfonso “The Battler” and his forces in the Conquest of Zaragoza
This battle represented the first major loss in the fortunes of the Almoravids
Under his reign,
The Berbers preferred Spanish luxuries to battle
Disaffection spread among the Berber-Almoravid troops
The Almoravid regime’s unruly soldiers and growing financial difficulties led to widespread disloyalty amongst the people
This culminated in his and his forces’ defeat in the Conquest of Zaragoza by Alfonso “The Battler” and his Christian forces
1121 - 1269 - Almohad Caliphate (All Facts)
Founded by Abd Al-Mumin
They were originally a movement of Muslims comprised of nomadic Berber tribesmen
It essentially replaced the Almoravid Caliphate territorially and ideologically
They steadily eroded Almoravid power in Africa
They expanded further, back into Islamic Spain
They expanded to the east against Roger II of Sicily and his kingdom

1080 - 1130 - Ibn Tumart (All Facts)
Founder of the Almohad Movement
He called for a “holy war” against the Almoravids

1124 - 1146 - Imad al-Din Zengi, Atabeg of Mosul (All Facts)
He took the city of Edessa
This led to calls for another crusade against him
He conquered Muslim northern Syria
He fought against Damascus
He was murdered