1 — Operating Room Orientation
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
Operating Theatre
This is another name for the operating room
Operating Room
This is a sterile, controlled environment within a hospital where surgical procedures are performed
Operating Room
This is a critical space designed to minimize infection and ensure safety of both surgical teams and patients
Aseptic technique
Zoning
Proper lighting
Ventilation system
Temperature control
Proper equipment
Drugs and other consumables required for routine and emergency use
Important considerations for operating room set up
Anesthesia Machine
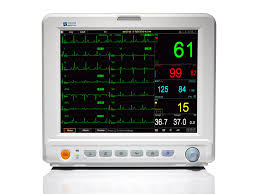
Anesthesia Monitor
Anesthesia Cart
Operating Table
Operating Lights
Defibrillator
Suction Units
Electrocautery Machine
Back Table
Mayo Table/Stand
Prep Table
IV Pole
Kick Bucket
Storage Cabinets
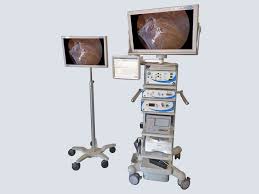
Laparoscopic Tower
Key Components of Operating Room
Anesthesia Machine
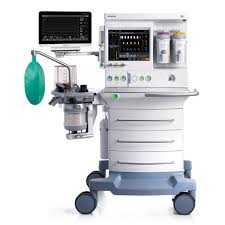
A machine usually checked by the circulating nurse
Patient Monitor
Anesthesia Cart

Operating Room Table

Operating Room Lights

Electro Boperized Machine

Suction Machine

Back Table

Kidney Table

Mayo Table

Prep Table/Cart

IV Pole

Kick Bucket

Steel Cabinet

Laparotomy Tower
Unrestricted
Semi Restricted
Restricted
Three Areas of the Operating Room
Unrestricted Area
Traffic is not limited
Street clothes are allowed
Allows access for communication with the department and the hospital personnel
Semi Restricted
Traffic is not allowed to everyone
Restricted
Traffic is limited
Wearing of scrub attires, caps, and masks are compulsory
Sterile Team
Unsterile Team
Two Components of a Surgical Team
Anesthesiologist
Circulating Nurse
IW/Cleaner/Lifter
Members of the Unsterile Team
Surgeon
Assist
Scrub
Members of the Sterile Team
Only sterile item are used within the sterile field
Principle 1 of Aseptic Techniques in Operating Room
Sterile persons are gown and gloved
Principle 2 of Aseptic Techniques in Operating Room
Table are only sterile at table level
Principle 3 of Aseptic Techniques in Operating Room
Sterile persons touch only sterile items while unsterile OR personnel touch only unsterile items
Principle 4 of Aseptic Techniques in Operating Room
Unsterile persons avoid reaching over sterile field and sterile person avoid touching or leaning over an unsterile area
Principle 5 of Aseptic Techniques in Operating Room
Edges of anything that encloses sterile contents are considered unsterile
Principle 6 of Aseptic Techniques in Operating Room
Sterile field is set-up just before a surgical procedure
Principle 7 of Aseptic Techniques in Operating Room
Sterile areas are continuously kept in view
Principle 8 of Aseptic Techniques in Operating Room
Sterile persons keep well within sterile area
Principle 10 of Aseptic Techniques in Operating Room
Sterile persons keep in contact with sterile areas to minimum
Principle 10 of Aseptic Techniques in Operating Room
Unsterile persons avoid sterile areas
Principle 11 of Aseptic Techniques in Operating Room
Destruction of integrity of microbial barriers result in contamination
Principle 12 of Aseptic Techniques in Operating Room
Microorganisms must be kept to irreducible minimum
Principle 13 of Aseptic Techniques in Operating Room
Hand hygiene
Attire
Prepare the work surface
Open sterile packages
Place sterile items
Maintain sterility
Consider contamination
Timing
Environment control
Monitoring
Key Steps in Preparing a Sterile Field
Cutting tools
Grasping tools
Haemostatic Instruments
Retractors
Commonly Used Surgical Instruments by Category
Cutting Tools
Instruments that are used to make incisions and sever muscle, tendon, cartilage, bone, vessels, and other connecting tissue
Scalpel

Used for making incisions, tissue dissections
Include a blade and a blade holder or knife handle
Blade Holder #4
What blade holder number is used to hold blade sizes #20 and #22 in a scalpel?
Blade Holder #3
What blade holder number is used to hold blade sizes #15, #12, #11, and #10 in a scalpel?
Blade #10 and #20
What blade sizes (there are two mentioned) in a scalpel is used for major surgeries?
Blade #12
What blade size in a scalpel is used to puncture?
Blade #15
This is a smaller version of Blade #20
Scissors
These are used for cutting tissues, sutures, and for dissection
Mayo Scissors
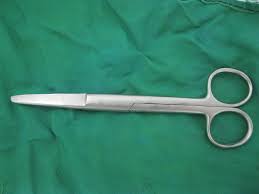
Surgical scissors that primarily used for cutting heavy tissues, sutures, fascia, and dressings during surgery
Metzenbaum Scissors

These are lighter surgical scissors used for cutting delicate tissues and blunt dissection during surgical procedures. They are characterized by their long shank and relatively short blades compared to mayo scissors.
Grasping Tools
Used to hold items, both organic tissue (skin, bone, organ) and inorganic materials (surgical towels, sponges, needles), to manipulate, hold in place, or reveal and access the areas beneath
Ratcheted
Non-Ratcheted
Two categories of grasping tools
Clamps / Kelly Forceps

Right-Angle Forceps / Mixter

These are specialized forceps primarily used for clamping, dissecting, and grasping tissues in deep, confined, or hard-to-reach surgical areas to minimize the risk of injury to surrounding tissues.
Schnidt Forceps

This is a surgical instrument used primarily in ENT (ear, nose, and thorax) procedures, especially during tonsillectomy. Their main uses include clamping blood vessels to control bleeding, holding and stabilizing tonsil sponges, and placing surgical packing after the tonsils are removed.
Allis Forceps

This is a ratcheted forceps that is used to grasp and hold tissues during various procedures, and is characterized by its interlocking jaws with teeth.
Sponge / Ovum Forceps

This is surgical that could be used to either hold surgical sponges or gauze to absorb fluids and maintain a clear surgical field, or grasp, hold, manipulate and remove delicate tissues within the uterus — particularly during and after procedures like cesarean sections, hysterectomies, and uterine repair
Babcock / Bobcock (spelling from ppt)

This is a surgical forceps used for grasping and holding delicate tissues, particularly in procedures involving the intestines, uterus, or fallopian tubes.
Pennington Forceps

This is also known as a Duval clamp/forceps. Characterized with its triangular eyelet, this surgical forceps is used for grasping tissues, particularly during intestinal and rectal operations, including some OB/GYN cases like Cesarean sections.
Kocher Clamp/Forceps
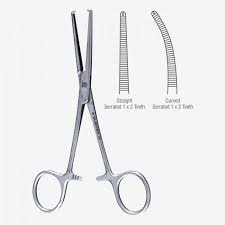
Also known as hemostatic forceps, this surgical instrument is primarily used to clamp and manipulate small to large blood vessels to control excessive bleeding during surgery
Towel Clips / Clamps
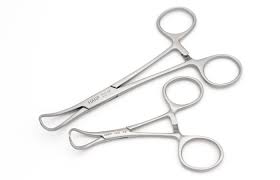
This are surgical forceps that are used to secure surgical drapes to the patient and maintain sterile environment during operations
Needle Holder

These are used as drivers for procedures that require suturing.
Debakey Forceps

This is a non-ratcheted forceps that is used for handling delicate tissues, particularly in cardiovascular and general surgeries.
Tissue Forceps

This is a non-ratcheted forceps used to hold and manipulate delicate tissues during surgical procedures or laboratory work. They are designed with fine tips, often with teeth, to provide a secure grip without causing significant tissue damage.
Haemostatic Instruments
These are surgical instruments that are used to control or cease bleeding
Electrocautery / Bovie
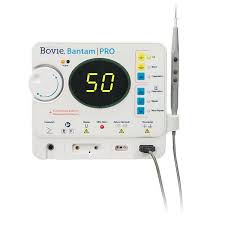
This is a haemostatic device or procedure that uses heat from an electric current to either control bleeding (coagulation), remove diseased or unwanted tissue (cutting and desiccation), and seal blood vessels
Retractors
These surgical supplies are used to hold the incision open, hold back tissues or other objects to maintain a clear surgical field, or reach other structures
Army Navy Retractor

Senn Retractor
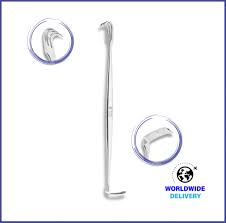
Retractor more commonly used in plastic surgery, small bone and joint surgeries, and thyroidectomies
Deaver Retractors
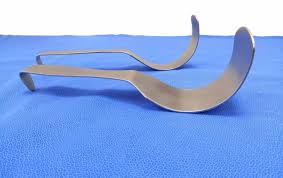
Retractors particularly useful in deep abdominal or thoracic surgeries, but can also be used in a variety of specialties
Bladder Retractor
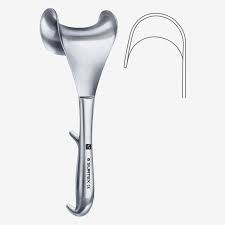
A retractor particularly useful in gynecological, urological, and abdominal surgeries
Richardson Retractor

Balfour Retractor

A self-retaining retractror used during surgeries in which large abdominal incisions need to be held open to provide more visibility to the surgeon such as during a cesarean section