periodontal debridement, sickle scalers, and universal curettes
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
_________ plays a significant role in causing periodontal disease, it is difficult to prevent or control periodontal disease is this is present
calculus
what is calculus
calculus is mineralized plaque covered w a living layer of plaque biofilm
what color does calculus change into as it is found more subgingivally and why
goes from a more yellow color to a black color; gets more black bc it has more hemoglobin in it
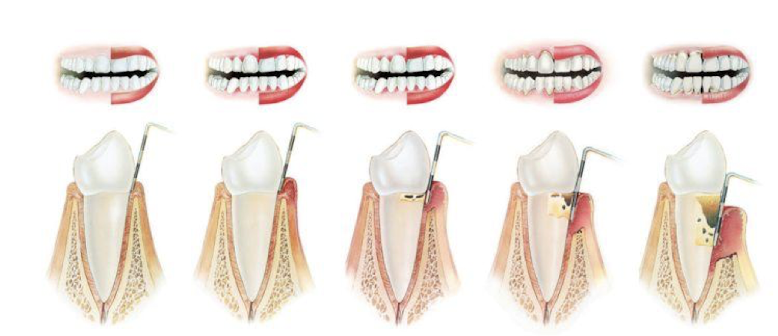
calculus is ________
tenacious
debridement
instrumentation of crown and root surfaces to remove deposits
scaling
descriptive term for calculus removal stroke using scalers or curettes
root planning
descriptive term for smoothing the root to remove infected and necrotic tooth substance (liek necrotic cementum)
3 types of instrument strokes
exploratory
scaling
root planning
exploratory stroke and what grasp you have
using a scaling instrument to explore for calculus
light grasp
scaling stroke and what grasp you have
firm grasp is achieved by squeezing the instrument between the thumb, index finger, and middle finger while pushing down on the fulcrum finger
stroke activation occurs w lateral movement of the wrist and forearm
working stroke is a pull stroke
root planing stroke and what grasp you have
strokes are more numerous and lighter than the scaling stroke
rank the 3 types of stroke from least to most heavy handed
exploratory (lightest grasp) → root planing → scaling (most firm)

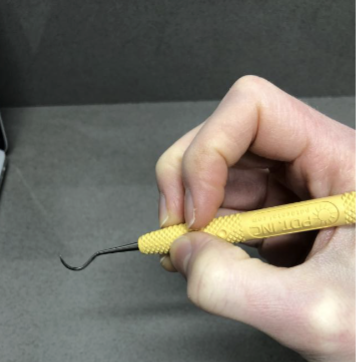
is this a good example of the modified pen grasp
no
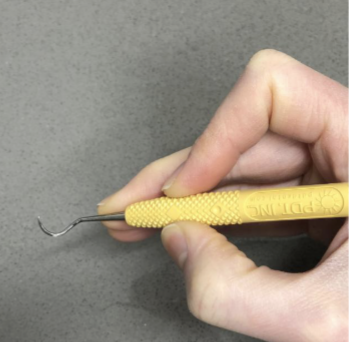
is this a good example of the modified pen grasp
no
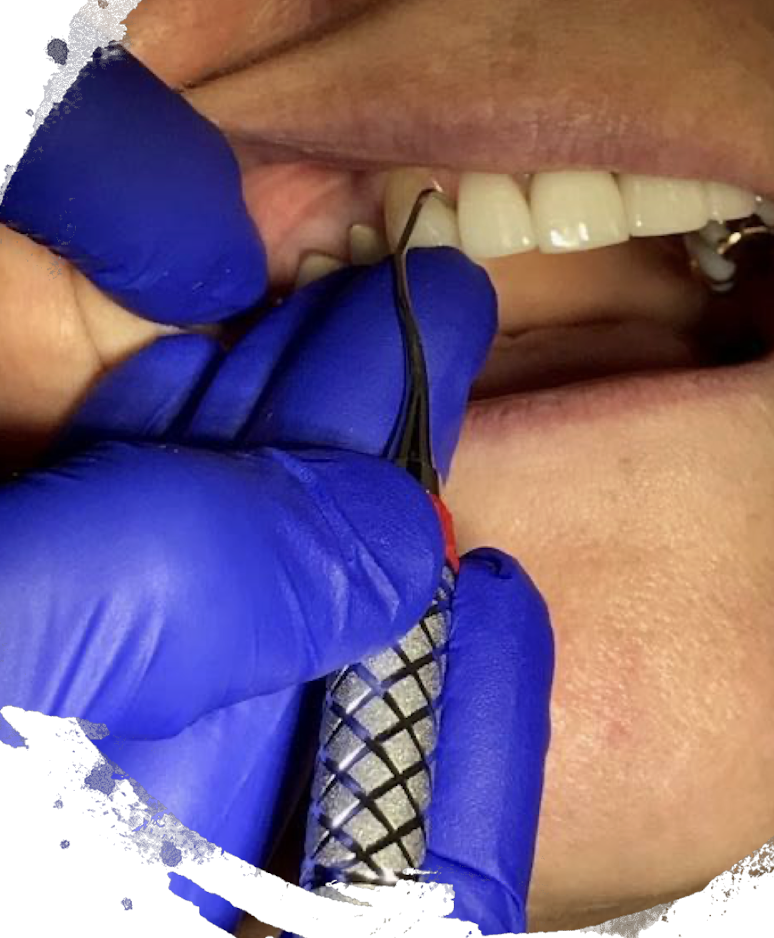
is this a good example of the modified pen grasp
yes

is this a good example of the modified pen grasp
yes
in the modified pen grasp, do you want your middle finger on the upper or lower shank
upper
positives for having a folcrum
provides a stable base for leverage
enhances control- avoids slipping and laceration of tissue
a fulcrum must be located to allow ________ motion
wrist-forearm (want to use big muscles)
what are the 5 types of fulcrums
conventional intraoral
extraoral
cross arch
finger-on-finger
assisted
describe the intraoral fulcrum
ideally establish as close as possible to the working area
middle finger rests against ring finger to create a ‘built-up’ fulcrum
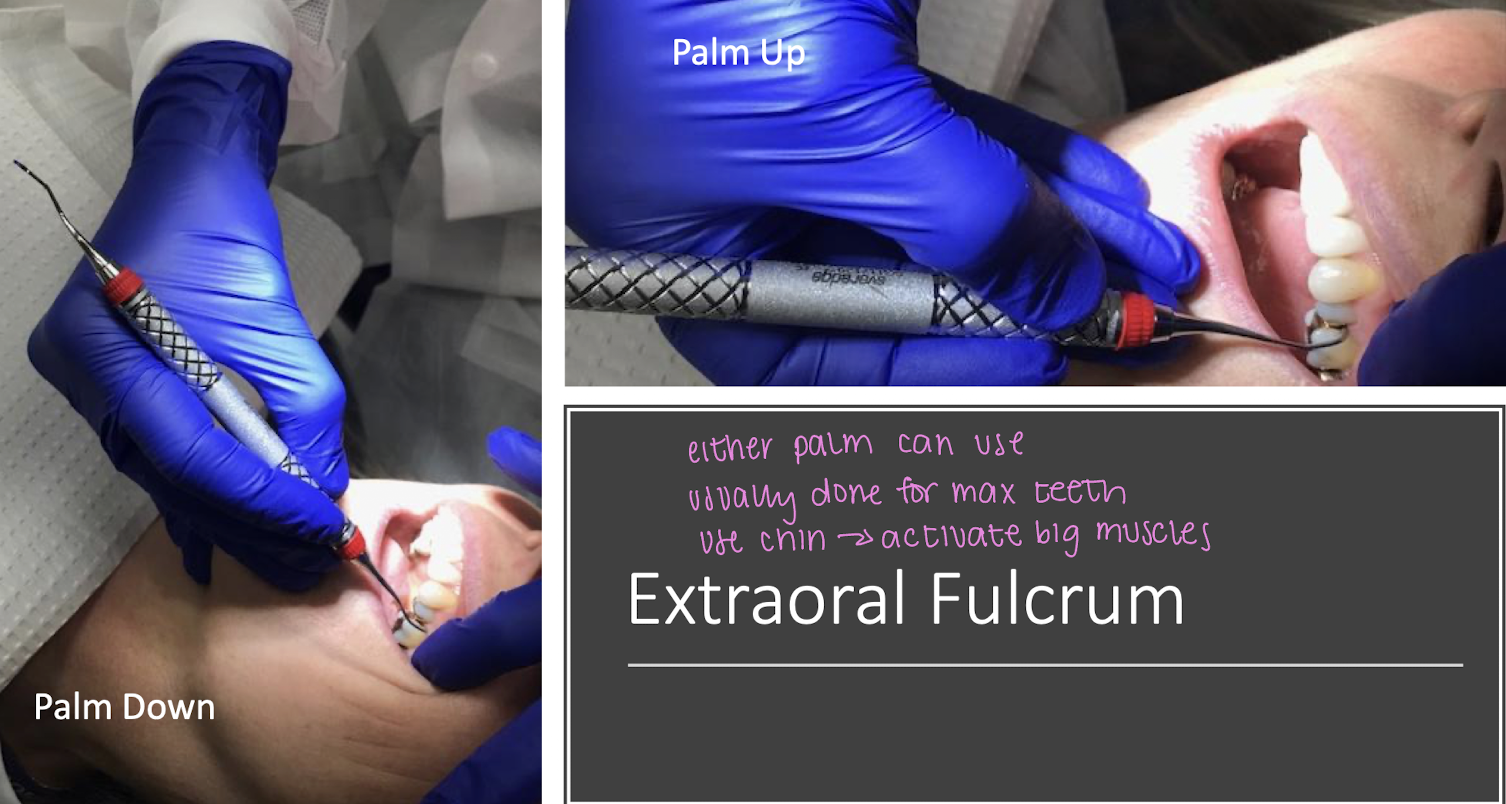
describe the 2 different techniques you can use for the extraoral fulcrum
palm down
palm up
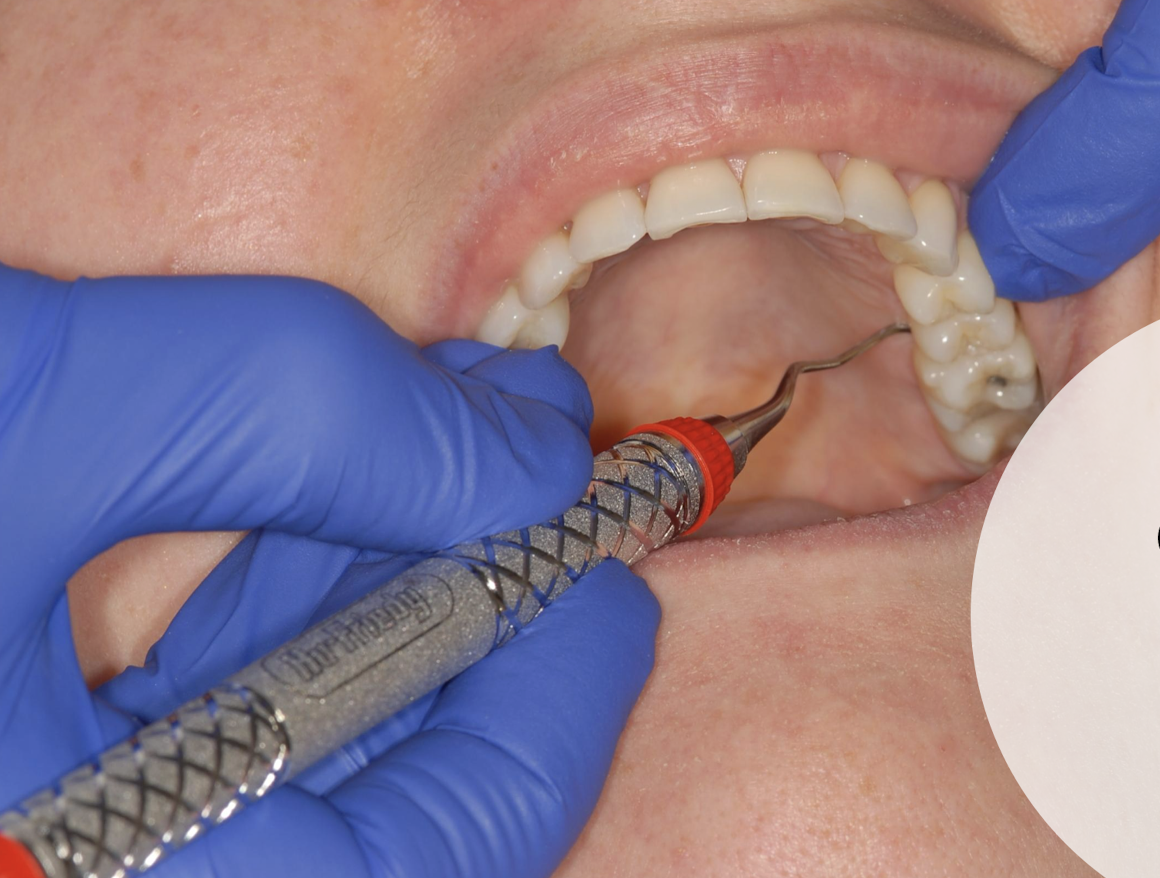
what fulcrum is this
cross arch fulcrum
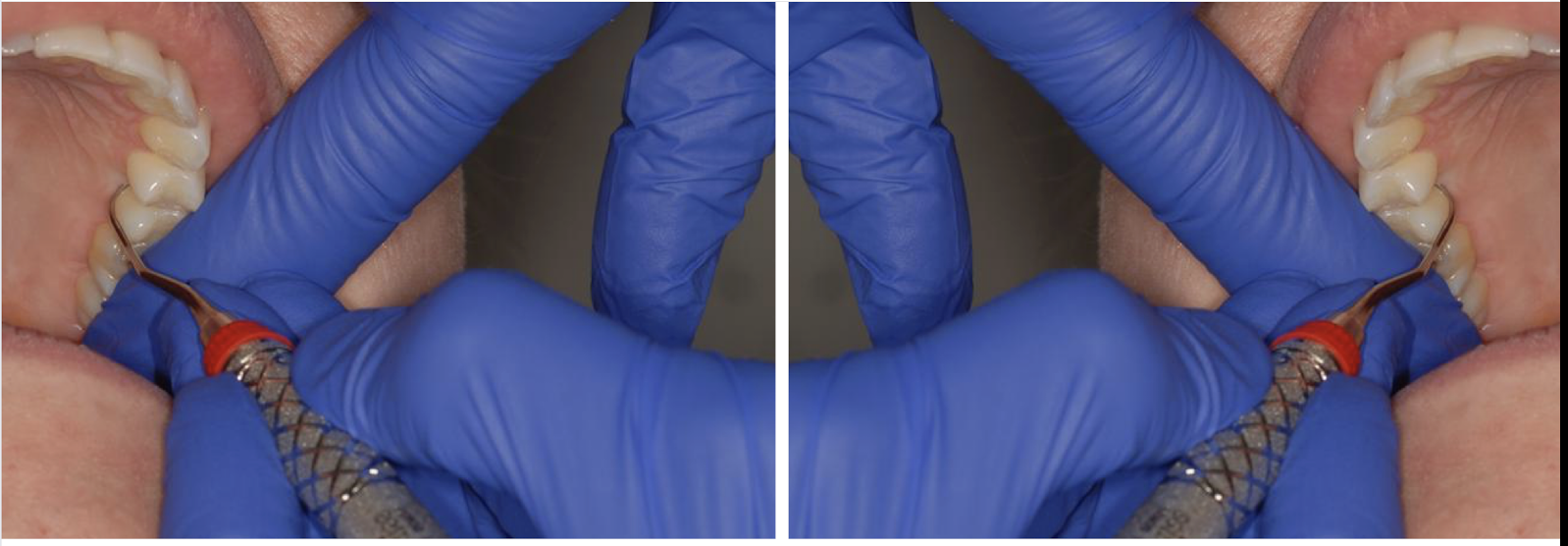
what fulcrum is this
finger-on-finger fulcrum
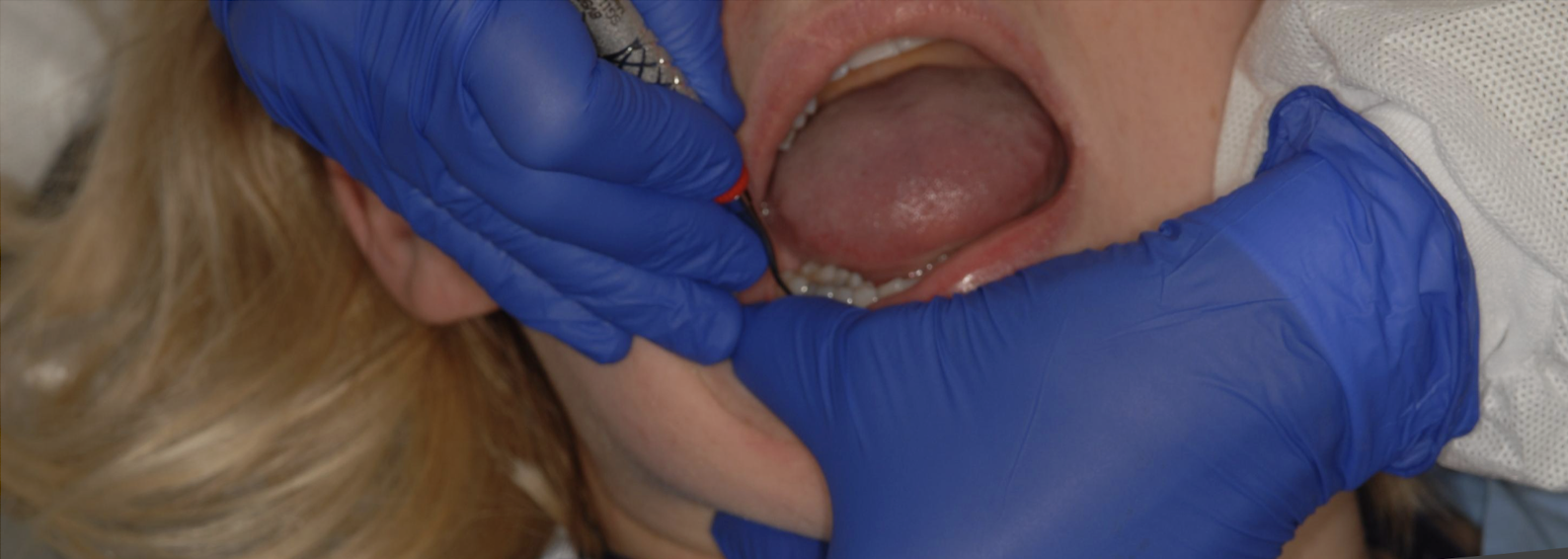
what fulcrum is this
assisted fulcrum
funx of sickle scalers
designed for the removal of medium to large supragingival calculus and calculus just below the contact
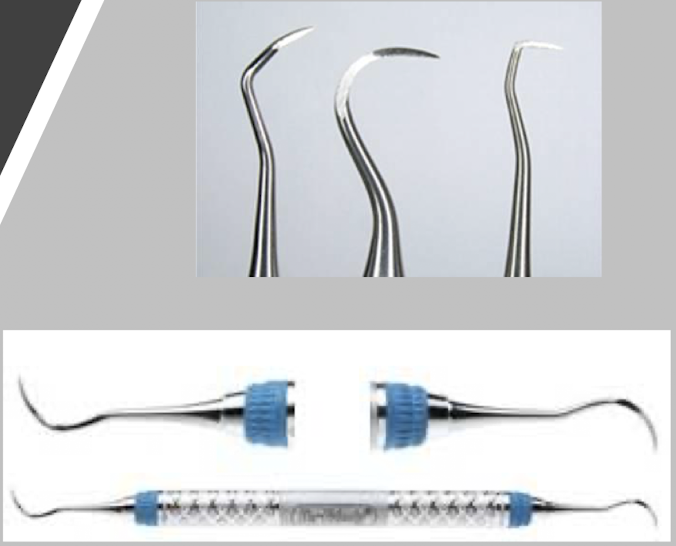
describe the anterior sickle
double ends are 2 different types
describe the posterior sickle
double ends are mirror images
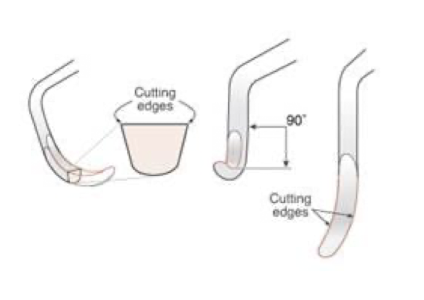
the design of sickle scalers are _________ in cross section
triangular
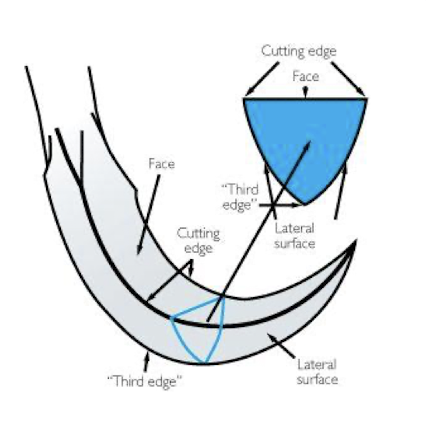
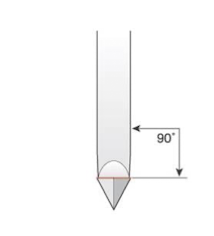
the design of sickle scalers, the face of the blade is at ____ degrees to ______ shank
90 degrees to lower shank
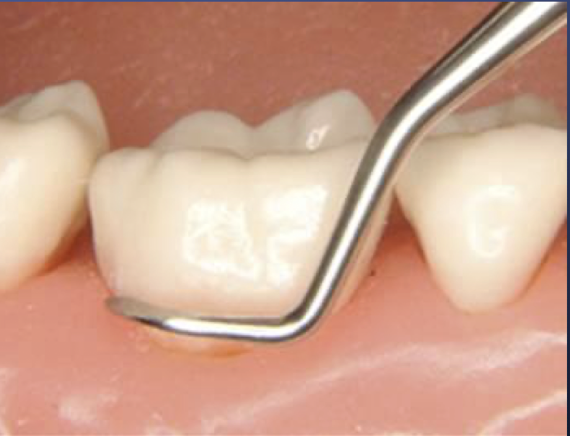
is this the correct orientation of a posterior sickle scaler
NO → should NOT be perpendicular tot he tooth; should be parallel
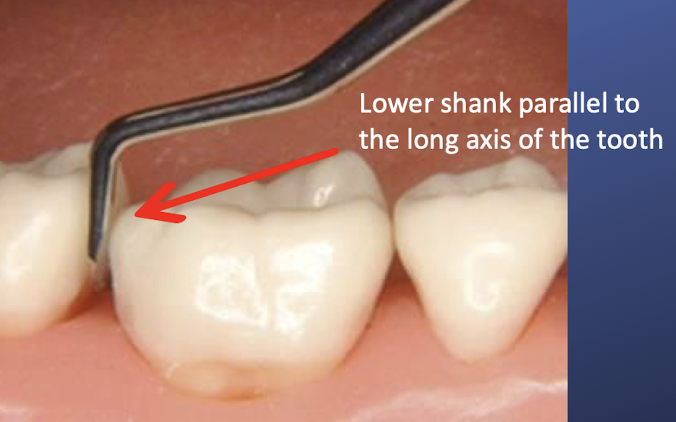
is this the correct orientation of a posterior sickle scaler
yess
how to orient anterior sickle scaler
lower shank must be tilted towards the tooth surface to achiever angulation between 70-80 degrees → lower shank should not be perpendicular but not 100% parallel
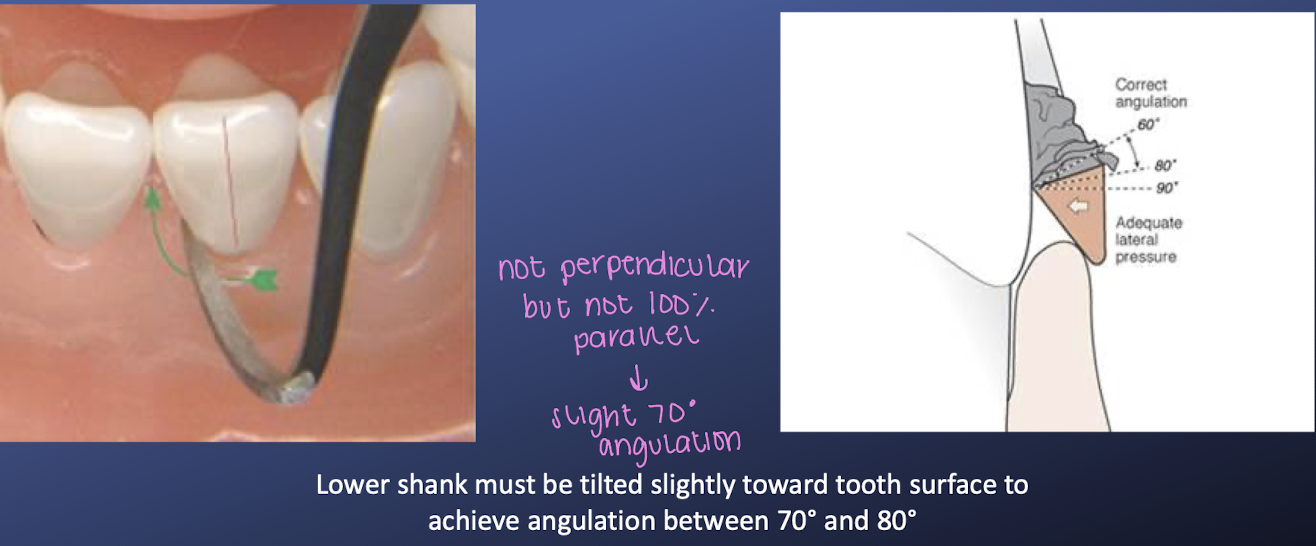
the angulation of a posterior sickle/curette/explorer should be _________ to the long axis of the tooth
parallel

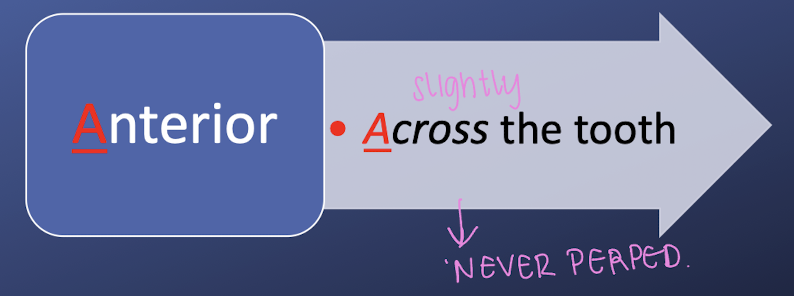
the angulation of a anterior sickle/curette/explorer should be _________ in reference to the tooth
across the tooth
when thinking of stroke activation, you want to maintain adaptation of 1 mm of tip of cutting edge to tooth surface → _________
tangent
when thinking of stroke activation, you want to roll the handle to move ___________
interproximally
when thinking of stroke activation, you want to press down w…
press down w fulcrum finger and rotate wrist /forearm to apply lateral pressure against tooth
when thinking of stroke activation, the tip shoudl be adapted to tooth and should NOT cause….
tissue to blanch
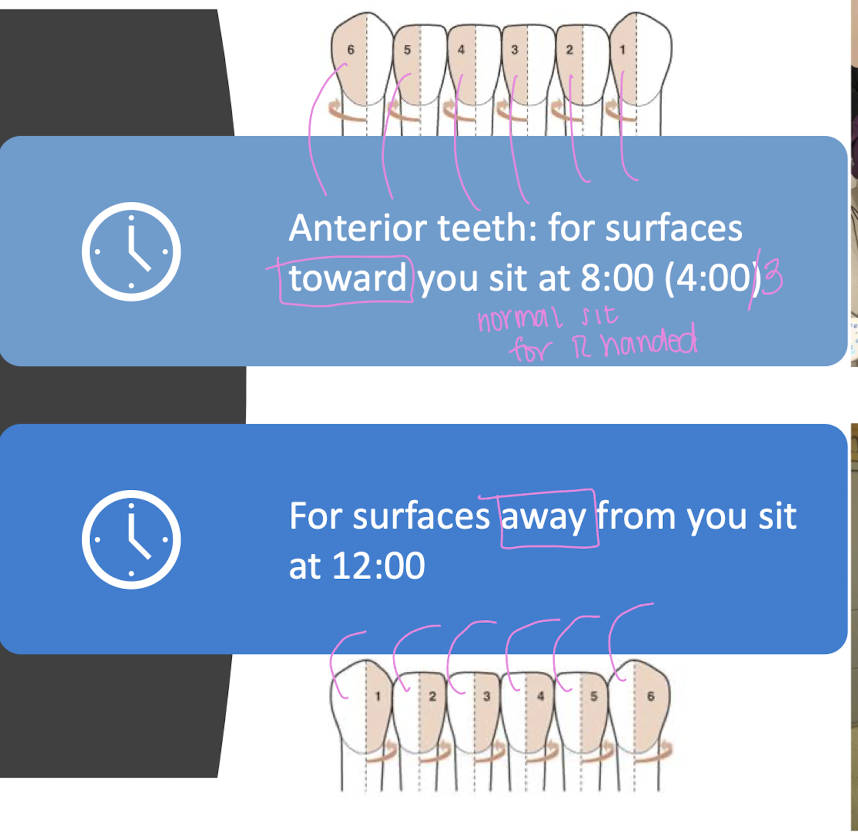
for anterior teeth, how do we refer to surfaces of teeth
surfaces toward you when sititng at 8:00 (for R handed)
surfaces away from you when you sit at 12:00
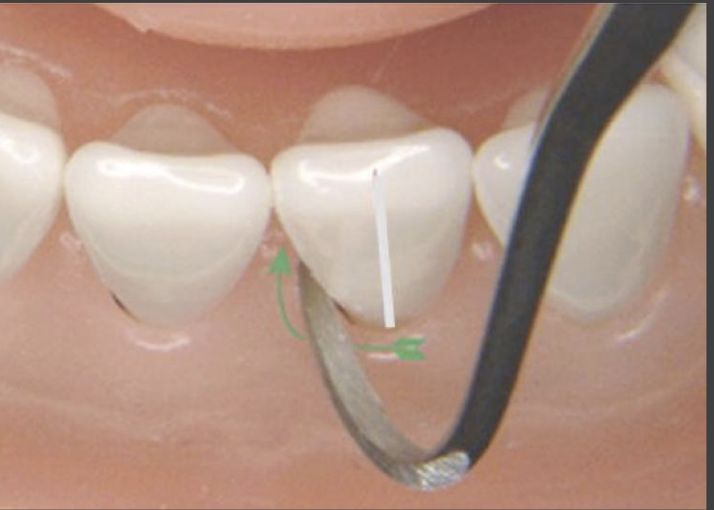
_________ is key for the activation stroke
leverage
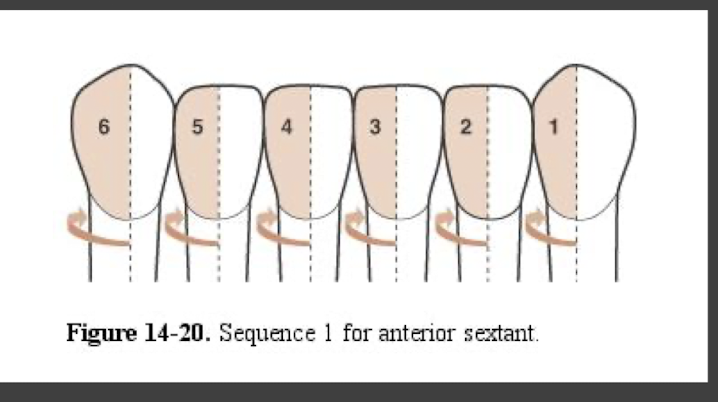
what is the sequence of efficiency
do all surfaces B/L that are towards you
then do away surfaces
sickles are NOT recommended for…
use on root surfaces
universal curettes are designed to use throughout…
the mouth
funx of universal curettes
can be used supra and subgingivally to remove small to medium sized calculus
universal curettes have ___ cutting edges per working end, like sickle
2
universal curette blade is ___ degree to lower shank
90 degrees
what are the 3 types of curettes in an SRP kit, and “*” the ones we have in our kit
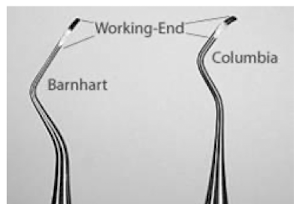
columbia 13/14
4R/4L**
McCall 17/18**
uses for columbia 13/14
smaller
designed for use on anterior teeth and premolar
uses for 4R/4L (in our kit)
larger
designed for use on molars
uses for McCall 17/18
designed for use on 2nd and 3rd molars
good for line angles and buccal, and lingual surfaces
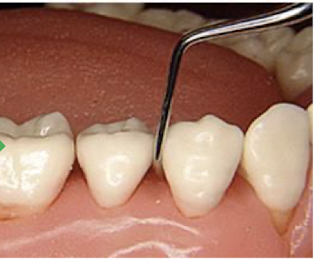
good or bad and why
good: lower shank is parallel to long axis of tooth
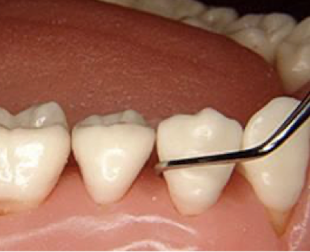
good or bad and why
bad:lower shank NOT parallel
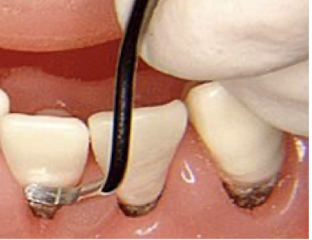
good or bad and why
bad: is parallel but blade should be toward tooth, not tissue
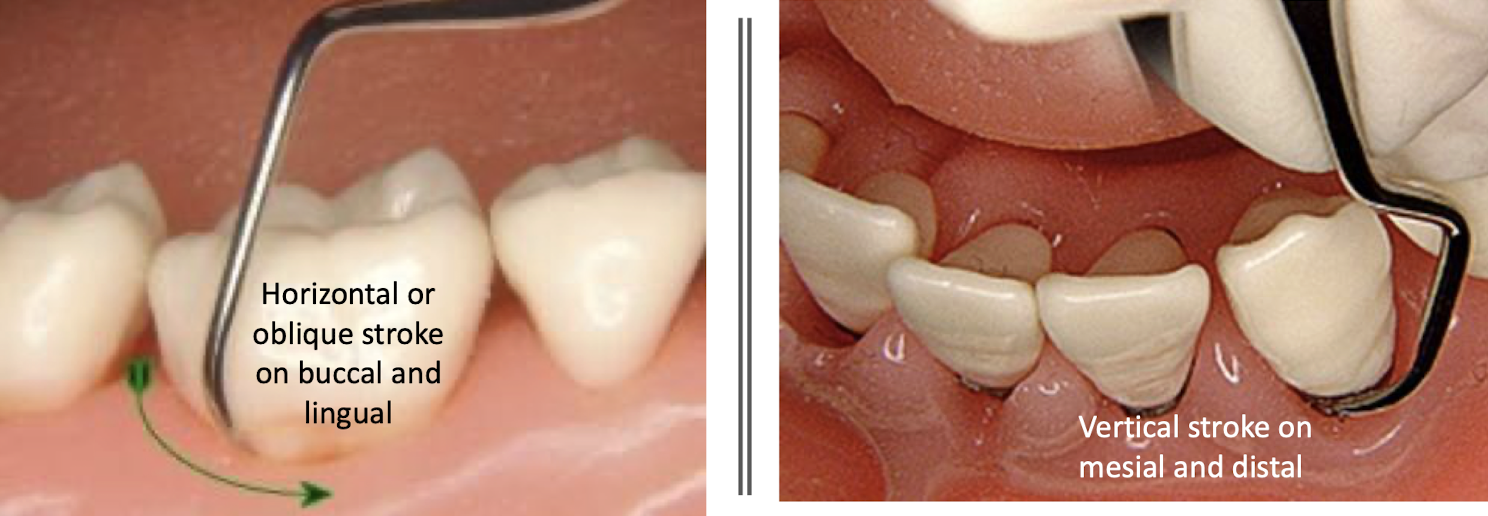
orientation os stroke
face of working end is at 90 degrees to lower shank
blade slightly rotated toward tooth and is slightly closed
B/L stroke: horizontal/oblique stroke
M/D surfaces: vertical stroke
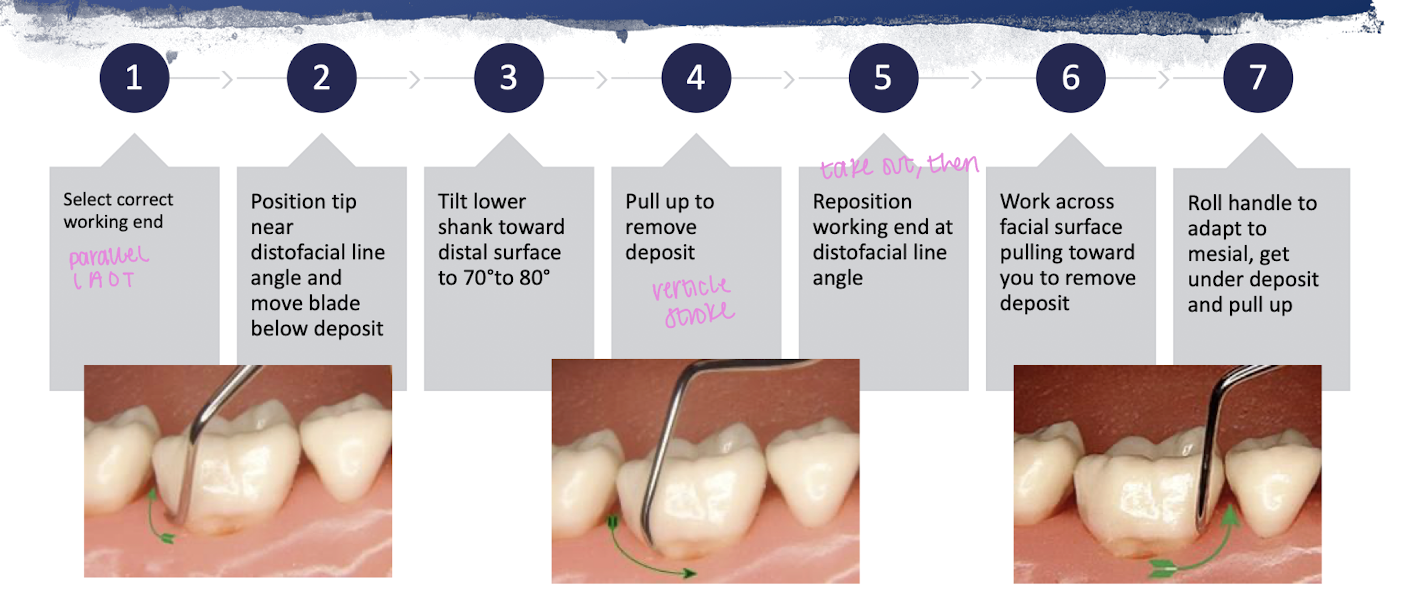
7 steps of mandibular molar stroke
select correct working end
position tip near distofacial lien angle and move blade below deposit
tilt lower shank toward distal surface to 70-80 degrees
pull up to remove deposit
reporsition working end at distofacial line angle
work across facial surface pulling toward you to remove deposit
roll handle to adapt to mesial, get under deposit and pull up
_______ (wet/dry) calculus is more visible than ____ (wet/dry)
dry is more visible than wet
air can deflect free gingiva to see…
subgingival calculus
the use of compressed air can remove saliva that ultimately leads to…
greater visibility
the use of compressed air can make it easier to see what type of caries
root caries
pre-debridement, what are the 7 things you need to do first
health history update
evaluate radiographs
operator position
pt positioin
oral exam
probe
explore
ergo principle #1
neutral posture promotes a balance of muscle forces in the body → workers should minimize time spent in awkward positions
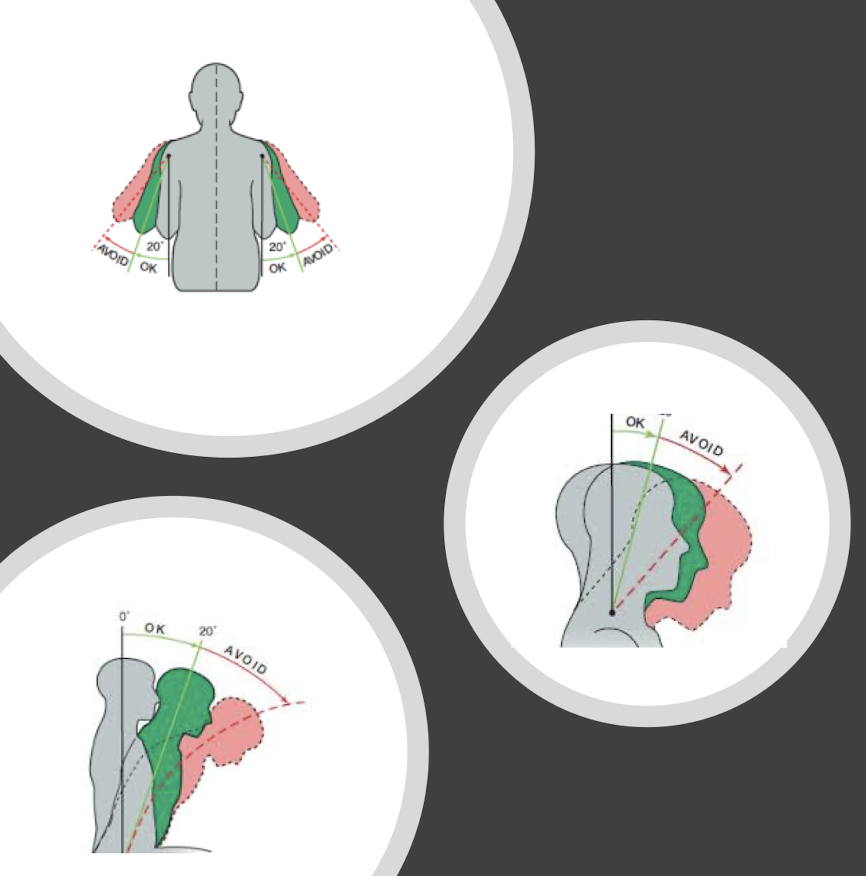
neutral head position
ears above shoulders
head tilt 0-15 degrees
in the neutral operator position, upper arms are parallel to…
long axis of the body
in the neutral operator position, forearms are parallel to…
the floor
in the neutral operator position, weight is…
evenly distributed
in the neutral operator position, knees are slightly…
below the hips
in the neutral operator position, your seat height should be positioned low enough so that…
your heels are on the floor
in the neutral operator position, you want to pivot from your…
hips (not your back)