ACLS- Acute Stroke Case 2025-2026 latest updated version with expert solutions
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Drugs used during stroke
Approved fibrinolytic agent (rtPA)
Glucose
Labetalol
Nicardipine
Enalaprilat
Aspirin
Nitrprusside
When should IV fibrinolytic therapy be started for a stroke?
As early as possible
-Generally within 3 hours of onset of symptoms (4.5 hours for selected patients)
8 D's of stroke care
Highlight the major steps in diagnosis and treatment of stroke
-Detection
-Dispatch (911)
-Delivery (Rapid EMS, management, and transport)
-Door (triage to stroke center)
-Data (triage, evaluation, and management within ED)
-Decision (Stroke expertise and therapy selection)
-Drug/device (Fibrinolytic or endovascular therapy)
-Disposition (Rapid admission to the stroke unit or critical care unit)
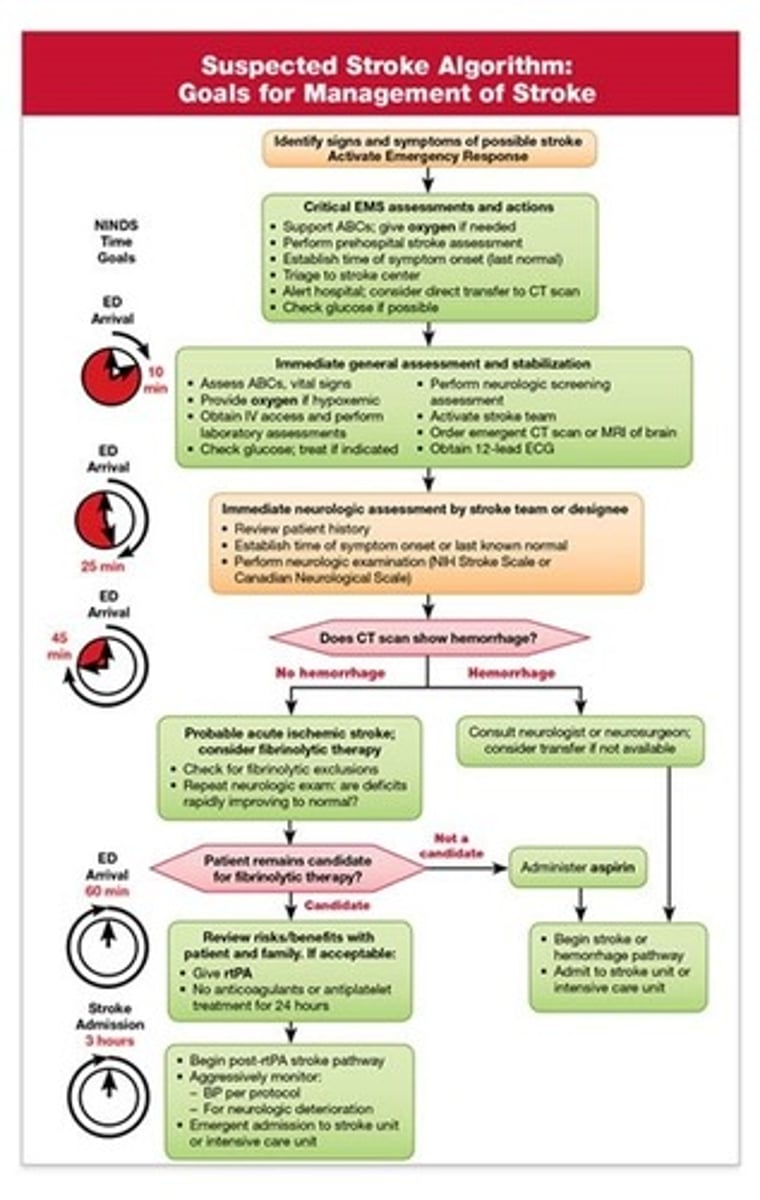
In-hospital time goals for stroke
1. Immediate general assessment by the stroke team/ other expert within 10 minutes of arrival; order urgent noncontrast CT
2. Neurologic assessment and CT scan performed within 25 minutes of hospital arrival
3. Interpretation of the CT scan within 45 minutes of ED arrival
4. Initiation of fibrinolytic therapy therapy in appropriate patients within 1 hour of hospital arrival and 3 hours from symptom onset
5. Door-to-admission time of 3 hours
Critical time periods for stroke
Immediate general assessment: 10 minutes
Immediate neurologic assessment: 25 minutes
Acquisition of CT of the head: 25 minutes
Interpretation of the CT scan: 45 minutes
Administration of fibrinolytic therapy, timed from ED arrival: 60 minutes
Administration of fibrinolytic therapy, timed from onset of symptoms: 3 hours, or 4.5 hours in selected patients
Administration of endovascular therapy, timed from onset of symptoms: 6 hours in selected patients
Admission to a monitored bed: 3 hours
Adult Suspected Stroke Algorithm
Identification of s/s of possible stroke and activation of emergency response (step 1)
Critical EMS assessments and actions (step 2)
Immediate general assessment and stabilization (step 3)
Immediate neurologic assessment by the stroke team or designee (step 4)
CT scan: hemorrhage or no hemorrhage (step 5)
Fibrinolytic therapy risk stratification if candidate (steps 6, 8, and 10)
General stroke care (steps 11 and 12)
Warning s/s of stroke
Sudden weakness or numbness of the face, arm, or leg, especially on one side of the body
Sudden confusion
Trouble speaking or understanding
Sudden trouble seeing in one or both eyes
sudden trouble walking
Dizziness or loss of balance or coordination
Sudden severe headache with no known cause
Cincinnati Prehospital Stroke Scale (CPSS)

To provide the best outcome for the patient with potential stroke, do the following:
Support ABCs- supplementary oxygen to hypoxemic stroke
Perform stroke assessment- (CPSS)
Establish time- Determine last known well (time zero); if patient wakes from sleep with symptoms, time zero is when the patient was last seen normal
Triage to stroke center
Alert hospital
Check glucose (hypoglycemia mimics stroke symptoms)
Fibrinolytic therapy
Higher likelihood of good to excellent functional outcome when rtPA is given to adults with acute ischemic stroke within 3 hours of onset of symptoms
Evaluating for fibrinolytic therapy
If CT scan is negative for hemorrhage, perform further eligibility and risk stratification
Inclusion criteria:
-Diagnosis of ischemic stroke causing measurable neurologic deficit
-Onset of symptoms <3 hours before beginning treatment
-Age ≥18 years
Exclusion criteria for fibrinolytic therapy
Significant head trauma or prior stroke in previous 3 months
Symptoms suggesting subarachnoid hemorrhage
Arterial puncture at noncompressible site in previous 7 days
Hx of previous intracranial hemorrhage
--Intracranial neoplasm, arteriovenous malformation, or aneurysm
--Recent intracranial or intraspinal surgery
Elevated blood pressure (sys>185 or diastolic>110)
Active internal bleeding
Acute bleeding diathesis, including but not limited to:
--Platelets <100,000
--Heparin received within 48 hours, resulting in aPTT >upper limit of normal
--Current use of anticoagulant with INR>1.7 or PT>15 seconds
--Current use of direct thrombin inhibitors or direct factor Xa inhibitors with elevated sensitive laboratory tests (ie, aPTT, INR, platelet count, and ECT; TT; or appropriate factor Xa activity assays)
Blood glucose concentration <50 (2.7 mmol/L)
CT demonstrates multilobar infarction (hypodensity > 1/3 cerebral hemisphere)
Potential adverse effects of fibrinolytic therapy
Major complication= intracranial hemorrhage
Other bleeding complications
Angioedema
Transient hypotension
Intra-arterial rtPA
For patients with acute ischemic stroke who are not candidates for standard IV fibrinolysis
Provide it within first 6 hours after onset of symptoms
Mechanical clot disruption/ stent retrievers
Criteria:
-Prestroke mRS score 0-1
-Acute ischemic stroke receiving intravenous rtPA within 4.5 hours of onset
-Causative occlusion of the internal carotid artery or proximal MCA (M1)
-Age 18 or older
-NIHSS score 6+
-ASPECTS of 6+
-Treatment can be initiated (groin puncture) within 6 hours of symptom onset
General care of all patients with stroke
Begin stroke pathway
Support airway, breathing, circulation
Monitor blood glucose
Monitor BP
Monitor temperature
Perform dysphagia screening
Monitor for complications of stroke and fibrinolytic therapy
Transfer to general intensive care if indicated