Earth's Resources
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Solar Energy
Light energy from the sun are captured using solar panels which are typically made from silicon or another semiconductor material. Once photons are captured it releases electrons which produce an electric charge.
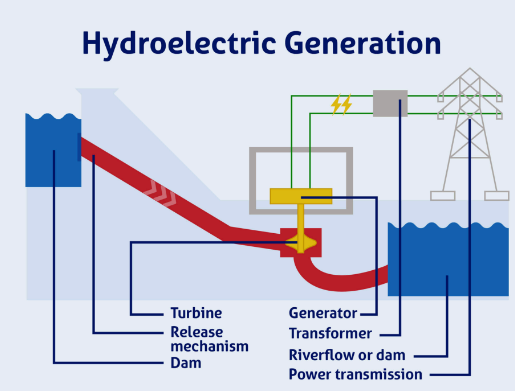
Hydroelectric Energy
Using dams to collect water, and then the water flows into turbines which turns the movement into electricity.
For water plants, water flows into a pipe called penstock which spins the blades of a turbine and this generates electricity.
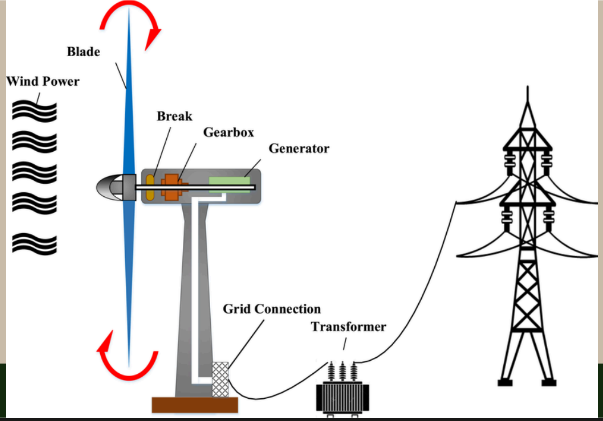
Wind Energy
It uses windmills to create energy. When wind blows all around us, wind turbines capture the wind’s energy and converts it into electricity. Wind flows on the wind blades causing it to turn, these blades are connected to a drive shaft that turns an electric generator.
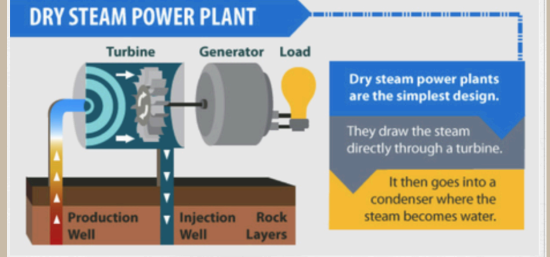
Geothermal Energy
Inside the Earth there is heat that comes from hot rocks. Electricity is generated in geothermal power plants by drawing heat through a well to the surface where it is then converted into steam. The steam powers the turbines to produce electricity.
Fossil Fuels
Formed from ancient plants and animals. This includes coal, oil, natural gas. When these fuels are burned they release energy used to power things, however it also releases pollution and are non-renewable.
Solid Waste
Made up of objects/particles that accumulate on the site where they are produced. Can be categorized into four: Municipal, Agricultural, Industrial, Mining Waste.
Municipal Waste
Includes materials that people no longer want because it’s broken, spoiled, not useful. Comes from households, commercial establishments, institutions and some industrial sources.
Agricultural Waste
Form of waste from farming and poultry. Typically organic and used as fertilizer. Excess agricultural waste is thrown into bodies of water which can cause eutrophication.
Industrial Waste
From industrial sources other than mining such as manufacturing. EX. ash from combustion. If the waste is hazardous it’s disposed in special landfills for isolation and treatment.
Mining Waste
From mining operations, milling operations, and water from mines.
— Large amounts of rock and soil are removed to extract ores.
— The grinding and sorting of materials “tailings” which is dumped in ponds.
— Water pumped from mines flow from piles of rock or tailings.
6 Effects of Improper Waste Management
Water Contamination
Pollution
Extreme Weathers
Harm in Marine and Land Animals
Compromised Human Health
Soil Contamination
What is Soil?
Essential Component of Earth that lets life exist. From the Greek word pedon which means “soil” and sfaira which means “sphere”.
Pedosphere is the living skin of Earth, which is caused by the dynamic interaction from the atmosphere, biosphere, geosphere, and hydrosphere.
Components of Soil
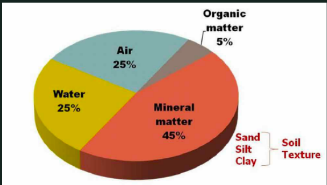
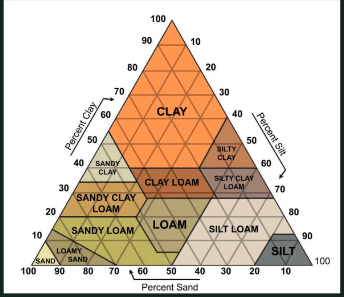
Soil Texture
Relative proportion of the particle sizes in the soil: sand, silt, clay.
Composed of these elements and the proportion which affects other properties like porosity and water retention. The proportions are plotted in the soil texture triangle to determine its soil type based on particle size.
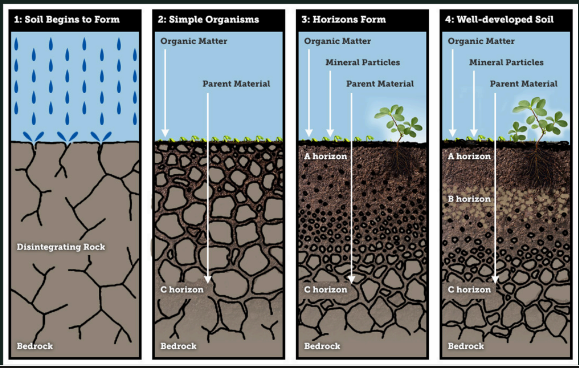
Soil Formation
What can soil provide?
Soil is a resource.
Arable land for Agriculture
Regulating Water and Filtering Potential Pollutants
Nutrient Cycling
Foundation and Support
Mineral Deposits
What is Arable Land for Agriculture
Land that can be plowed. Used to grow crops and sustain animal life.
Regulating Water and Filtering Potential Pollutants
In the water cycle soil plays and important part in storing water. Water and dissolved solutes flow over the land through the soil. Soil’s minerals and microbes are responsible for filtering, degrading, immobilizing and detoxifying organic and inorganic materials.
Nutrient Cycling
Carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, etc. are stored transformed and cycled in the soil.
Foundation and Support
Soil provides a base for plant roots, and provides support for human structures.
Mineral Deposits
Soil contains mineral content such as iron nickel or aluminum. These soils are called laterites.
Soil Erosion
Loss of the topsoil and nutrients in the soil. Most visible effect of soil degradation. Natural process that is made worse by poor human management choices.
Soil Compaction
Reduces the amount of air, water, and space available. Such as repeated traffic on wet soil.
Desertification
Irreversible change of the land to a state that it cannot be used. Characterized by drought and arid conditions as a result of human activities.
Intensive Agriculture
Cultivation that uses large amounts of labor and capital relative to land area. Heavy machinery, deforestation, clearing of land. Leads to the loss of organic matter, soil compaction, and damage of physical properties. Over application of fertilizers and pesticides can lead to soil contamination.
Urbanization
Conversion of arable land to urban centers, generally characterized concrete structures, roads, and pavement.
Conservation of Soil Resources
Increasing Soil Organic Matter
Keeping the Soil covered and vegetated
Avoiding excessive tillage
Managing pets and nutrients efficiently
Promoting crop rotation