Chem 103 Exam 1 review - UW Madison
1/1200
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
1201 Terms
What is an acid?
solution has an excess of H+ ions. a substance that can donate a proton (H⁺ ion), accept a pair of electrons, or increase the concentration of hydrogen ions in a water solution
What is a base?
solution has an excess of hydroxyl ions (OH-)
What is neutralization?
-process where acid and base are mixed until they become neutral and the PH is 7.
What are the two products of a neutralization chemical reaction?
water and salt ( The type of salt depends on acid or base added to neutralize.)
What is a weak acid?
an acid that only partially ionizes in an aqueous solution. This means that not every molecule breaks apart.
pH
is a measurement of how acidic or how basic a solution is.
Why is pH important to biology?
Cells survive in a specific pH range.
Human blood is maintain at 7pH for homostasis.
The stomach has acids to break down food.
Bile from the liver is a base which breaks down fats & grease.
What is a buffer?
a substance to help to neutralize/balance pH levels.
What are pH indicators?
They are used to tell you the pH value.
Examples are phenalphelein and bromthymol blue.
What are the properties of an acid?
taste sour, conduct electricity, corrosive, reacts with metals, turns litmus paper red.
Give examples of acids
HCL which is in your stomack.
Sulfuric acid which is used a lot in industries to make fertilzers, paints, etc.
Tums antacid used to neutralize stomach acids.
What are some uses of bases?
soaps and cleaning products
used in batteries
What are some examples of bases?
lye used to make soap.
Liquid plummer used for clogged drains. Baking Soda and Baking powder
What is the main neutral substance?
water
How is a salt chemically formed?
When you add acid or base to neutralize a solution the products formed are water and salts.
A change in pH units represents a tenfold change in the acidity of the solution (logarithmic scale). If one solution has a pH of 1 and a second solution has a pH of 2, the first solution is not twice as acidic a the second it is ______times more acidic.
ten (logarithmic)
What is a pH scale?
a logarithmic scale that indicates the pH of a solution. It ranges from 0 - 14.
On the pH scale, what numbers represent an acid?
0-6
On the pH scale, what numbers represent a base?
8-14
On the pH scale, what number represents a neutral solution?
7
What is a weak acid?
An acid that only partially ionizes (breaks down) in a solution. Weak acids are close to 7pH
What is a weak base?
A weak base will only parttally ionize in a solution. This means that not every molecule breaks apart.
What is a chemical change?
When a change in composition occurs giving new substances with new properties.
Example when wood changes to carbon. Wood and carbon do not have similar properties.
WHat is a physical change?
When a change does NOT change the composition.
What are indicators of a chemical change?
Observations such as what you see( color change, precipitant (solids in solutions)
Hear-boom Smell Taste-sour/sweet Feel-hot or cold.
Also, bubbles indicate gas..
What is the law of conservation of mass?
Mass is not created nor destroyed.
What is a chemical formula?
-chemical symbols represent molecules with subscripts to represent the number of that element.
NaCl represents table salt.
Reactants are on the right or left of the -> (yield) sign in a chemical equation.
left
Products are on the left or right of the ->(yield) sign in a chemical equation.
right
What does the -> represent in a chemical equation?
yield or to produce
What is a chemical equation?
It represents with chemical formulas a chemical change/reaction.
When one molecule splits apart and switch places this is called a __ reaction.
replacement type of chemical reaction
What is a reactant in a chemical equation?
They are substances that are present before the chemical change takes place. They are what you put into the chemical reaction to cause a chemical change.
What is a product in a chemical equation?
Chemicals that are formed during the chemical change.
When energy is absorbed in a chemical reaction it is a __reaction.
endothermic
When energy is released in a cheicial reaction it is a __reaction>
exothermic ( usually in the form of heat)
What does a neutralization chemical reaction produce?
water and salt
A chemical reaction is when a __ change has occurred.
chemical
What happens to the old molecules in a chemical reaction?
They rearrange into new molecules
What is activation energy?
The energy needed to start a chemical reaction.
What is a coefficient?
The number in front of a chemical formula which tells how many of that molecules is needed to balance the chemical equation.
Chemical reactions will produce
new substances.
A __ represents a chemical reaction
chemical equation
What happens in a chemical reaction?
bonds between atoms are broken and new bonds are formed.
Why are chemical equations balanced?
When chemical equations are balanced they have the same number of the same atom on both sides of the equation. This is because of the law of conservation of matter.
How does a catalyst increase the reaction rate?
by lowering the activation energy
Describe the types of chemcial reactions?
Synthesis A + B -> AB (single product)
Decomposition AB-> A + B ( breaks down into smaller elements)
Single Replacement AB + C -> AC + B
Double Replacement AB + CD -> AD + BC
Neutralization acid + base -> water + salt
What is a synthesis chemical equation?
When two ro more substances combine in a chemical reaction to form another substance .
What is a decomposition chemical equation?
The breakdown of a substance into two or more simpler substances.
What is a macromolecule?
They are large molecules which are needed for a living organism. They are fats, proteins, nucleic acid (DNA, RNA) and carbohydrate.
Carbon is unique and causes the formation of long chains in macromolecules because of its __
four valence electrons
What is the word chemical equation for photosynthesis?
carbon dioxide + water -> glucose and oxygen gas
What are the reactants in photosynthesis?
carbon dioxide and water
What are the products in photosynthesis?
glucose and oxygen gas
What factors influence the rate of chemical reaction?
pH concentration pressure, surface area, temperature
What is the name of the white horse on my farm?
Ghost
Atoms
-the submicroscopic particles that constitute the fundamental building blocks of mater
-each has its own unique properties (mass, physical characteristics)
Molecules
-two or more atoms joined in a specific geometric arrangement
-properties of molecules depend on the composition of those molecules
Chemistry
-the science that seeks to understand the behavior of matter by studying the behavior of atoms and molecules
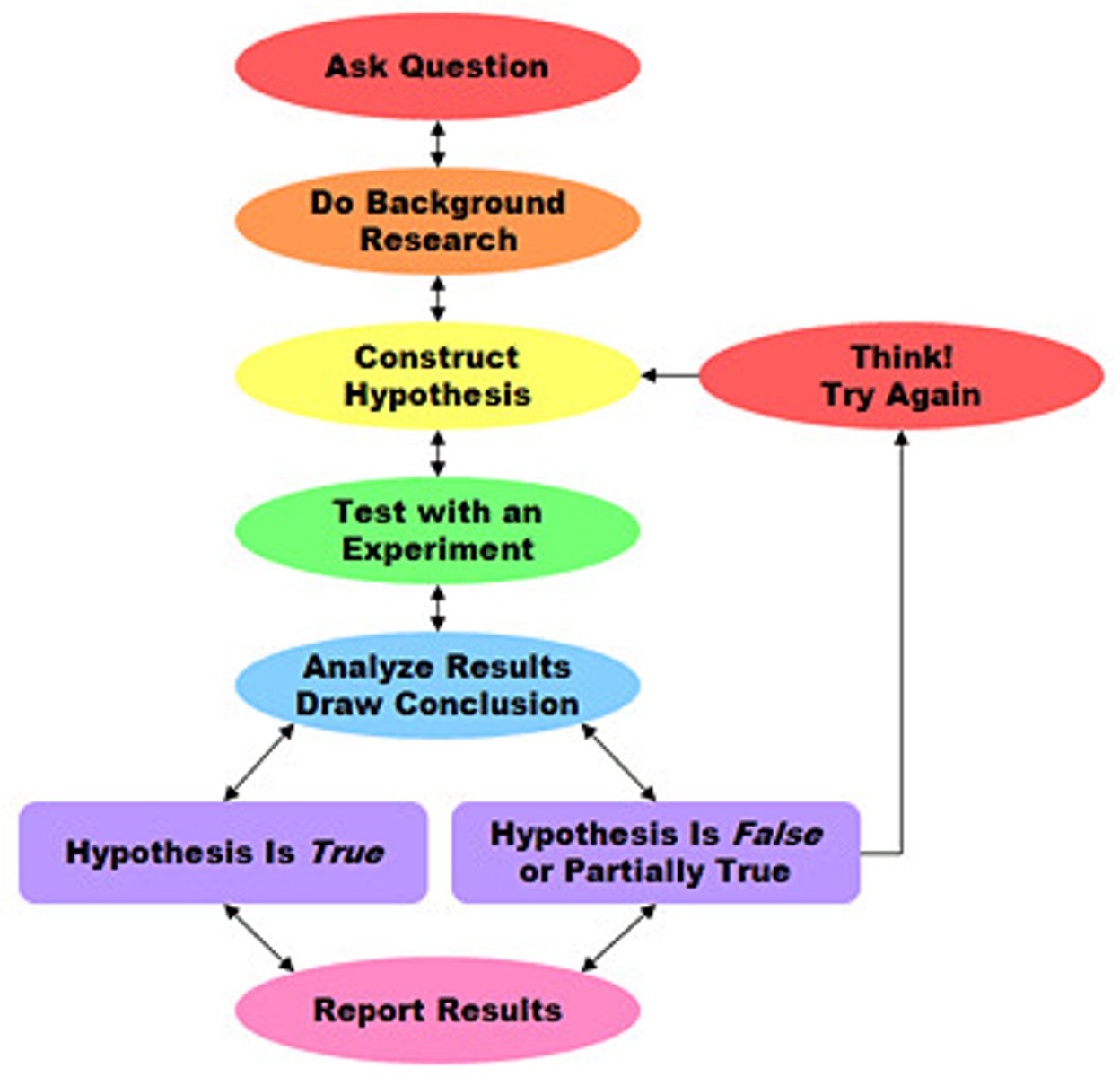
The Scientific Method
-the guidelines for the practice of science
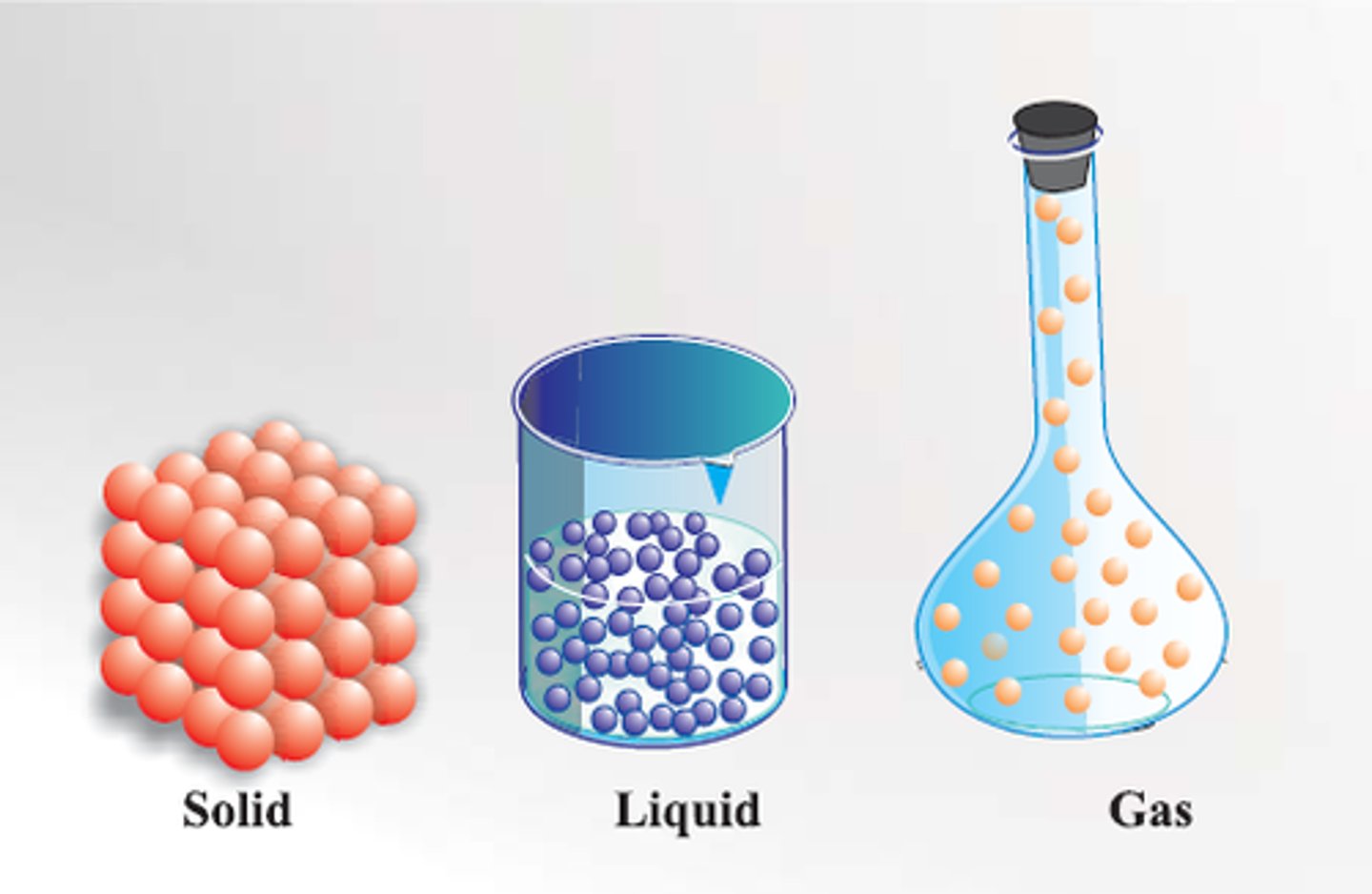
States of matter
-solid, liquid, and gas
Matter is classified by its ____________ or by the ______________
1. state
2. composition
Gas (macroscopic)
1. no fixed volume
2. compressible
Gas (microscopic)
1. gas molecules are far apart, moving fast
Liquid (macroscopic)
1. fixed volume
2. no fixed shape
3. moderately compressible
Liquid (microscopic)
1. In translational motion
2. closer together than gases
3. short range order, long range disorder
Solid (macroscopic)
1. fixed volume and shape
2. incompressible
Solid (microscopic)
1. molecules are packed closely together in fixed positions
crystalline
atoms and molecules are arranged in an ordered repeating pattern. Both short and long range order
-ex: diamond
amorphous
have short range order, but long range disorder. No repeating pattern of atoms/molecules
-ex: charcoal
Pure substances
matter with fixed composition and distinct proportions of atoms
Elements
cannot be decomposed into simpler substances (only one kind of atoms)
-elements vary in abundance
Compounds
-combinations of elements
-compounds have very different properties from the elements that make them up.
Mixtures
combination of two or more pure substances
Heterogeneous
substances are in different phases.
ex: Milk
Homogenous
all components in one phase (sometimes called a solution)
ex: koolaide
Physical properties
measured without changing the substance
ex: color, mass, density, melting or boiling point
Chemical Properties
describes how a substance reacts to form a new compound
ex: flammability
Intensive Properties
dont depend the amount of substance (think about independent)
ex: density, melting point, temp.
Extensive Properties
does depend on the amount of substance
ex: mass, volume, internal energy
Physical Change
substances change physical appearance. Without changing its identity (change in state: gas, liquid, solid)
ex: water molecules boiling
Chemical Changes
chemical reaction
ex: iron nail that rusts
Energy
is defined as the total kinetic energy plus potential energy
-the ability to do work
Work
is defined as the action of a force through a distance
equation: W=f*d
Heat
is the transfer of energy from one substance to another
Kinetic energy
the energy an object possess by virtue of its motion
equation: 1/2mv^2
Potential Energy
the energy an object possess by virtue of its position relative to other objects
ex: weight on ground (gravity acting on the weight)
Law of Conservation of Energy
Energy is neither created nor destroyed only changed from one form to another OR transferred from one object to another
Mass
is a measure of the amount of material in an object
Temperature
scientific studies use the Kelvin Scale and the Celcius scales
Kilo
1,000 (k)
Centi
.01 (c)
Milli
0.001 (m)
Micro
10^-6 (weird M sign)
Nano
10^-9 (n)
Derived Units
are formed from the seven base units
Volume
has units of length
Density
is used to characterize substances
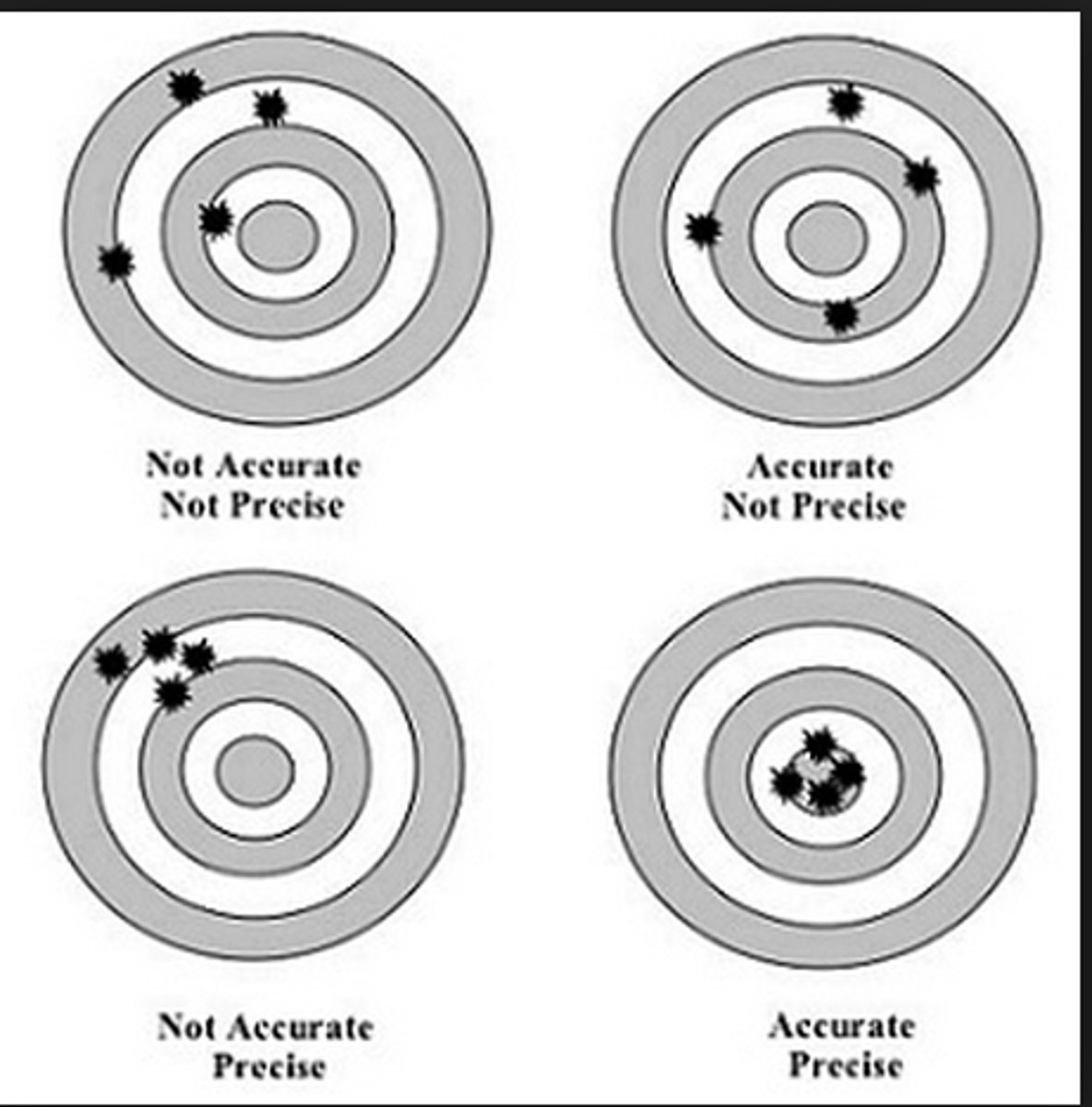
Precision
how well measured qualities agree with one another
Accuracy
how well measured qualities agree with the "true value"