Personality theories: Ellis (Helen Walters)
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
How are humans thought to think
like scientists, constantly evaluating the world around them
Who developed the Rational Emotive Behaviour Therapy (REBT)
Ellis, in 1955
What is Rational Emotive Behaviour Therapy (REBT)
an action-oriented therapeutic approach that encourages emotional growth by helping people replace their self-defeating (irrational) thoughts, feelings, and actions with new and more effective ones
What are the two main concepts in REBT
rational thought
irrational (self-defeating) thought
How does Ellis define rational thought
in the context that all people have fundamental goals, purposes, and values in life that underlie their attempts to first stay alive and then be happy
Acting in what way can help achieve the goals of rational thought
acting rationally (self-helpful)
however, when people act irrationally (self-defeating), it can sabotage these goals
Ellis argues that ‘emotions’ and feelings of ‘emotional disturbance’ are due to …
our own thoughts
he suggests that people disturb themselves, and it is their own unreasonable, or irrational, ideas that make them feel anxious, depressed, self-hating, angry, self-pitying about anything
our emotions are perhaps not caused by other people but by how we think
What approach do these ideas describe: emotions depend on interpretation, the same situation can cause different emotions, and emotions are shaped by thinking
they describe a cognitive approach (e.g. cognitive appraisal / CBT)
this view argues that emotions are influenced by how we interpret and think about events, not directly by the events or other people themselves
What is a logico-empirical approach
an approach to theory-building that emphasises logical consistency and empirical testing using observable data
What do the ABC of emotional disturbance stand for
A - activating experience
B - beliefs
C - consequences (emotional or behavioural)
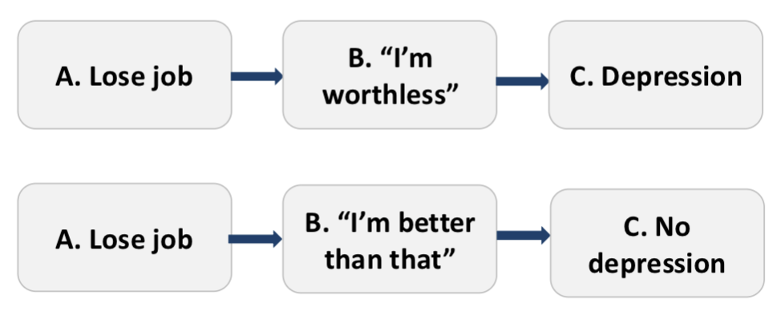
Give an example of an ABC model
A - e.g. losing job, family problems
B - e.g. thoughts, values, perspectives about what happened at A
C - e.g. depression, anxiety, anger
What type of thinking leads to self-defeating consequences
‘crooked thinking’
or
‘cognitive slippage’
What does ‘crooked thinking’ or ‘cognitive slippage’ create
shoulds
oughts
musts
commands and demands
What alternates our approach to a situation
something bad that happened in the past that later affects your life
learn from past experiences, don’t be overly attached to them
accept that the world is not fair, and it’s important to hold people accountable but some escape it sometimes
it is better to do rather than always need to do well, and accept fallibilities (mistakes) as humans
What are four other common irrational beliefs
need for approval
“to be happy, I must be loved by the people who are important to me”
demands about others
“most people who have been unfair to me are generally bad individuals”
awfulising
“it is terrible when things do not go the way that I would like”
emotions are externally caused
“I cannot help how I feel when everything is going wrong”
What is Ellis’s view on rational and irrational thinking in development
Ellis proposed that humans are born with the ability to think both rationally and irrationally
because caregivers also have irrational tendencies, children rarely experience a fully rational upbringing
What else is associated with irrational beliefs
high levels of anxiety
high levels of depression
social dysfunction
isolation and withdrawal
anger, guilt, and jealousy
relationship problems
problems of dealing with criticism
lack of control over situations
low self-esteem
Ellis saw the main aim of psychotherapy is to help individuals reduce the MUSTs. REBT is designed to help individuals acquire the following six personality traits:
self-interest
self-direction
tolerance
acceptance of uncertainty
flexibility
self-acceptance
Give an example of how an irrational belief might influence mood outcomes
“to be a worthwhile person, I must be thoroughly competent in everything I do”
make a mistake
depressive symptoms through feeling like a ‘worthless’ person
or
“well these things happen … practice makes perfect” (flexible)
What did David et al. (2018) find about the effectiveness of REBT
a systematic review and meta-analysis found that REBT showed a medium effect size in reducing irrational beliefs and improving emotional and behavioural outcomes (e.g. anxiety, depression, distress) compared to other interventions
a medium effect size means REBT had a moderate, practically meaningful impact
What does effect size mean
tells you how big or meaningful the treatment effect is, not just whether it exists
small effect = slight improvement
medium effect = clear, noticeable improvement
large effect = strong, substantial improvement
What did King et al. (2024) find about REBT
a systematic review of 162 studies found that REBT is associated with significant improvements in irrational beliefs and mental health outcomes
How can Ellis’s theory (REBT) be critically evaluated
description
Ellis provides very clear descriptions on systems to uncover the cognitive and belief structures of individuals
explanation
Ellis has a clear system for understanding and exploring the structure of an individual's cognitions, specifically referencing the ABC model
the approach provides insights into individual uniqueness but can be criticised for focusing heavily on the individual's thought processes
empirical validity
the most heavily researched theory in contemporary psychology
comprehensiveness
considers the effects of the individual's belief system, emotional state, and history of learning. It addresses both rational and irrational behaviour
parsimony
Ellis' theory has been described as simplistic due to its relatively few concepts
however, Ellis defended his approach by arguing that many groundbreaking ideas appear simple. While the theory seems straightforward, its application is more complex
testable concepts
easy to test and come up with hypotheses for testing in research and practice
heuristic value (how useful or insightful)
cognitive theories, like those of Ellis, are among the fastest-growing and most researched
applied value
Ellis' work has been applied in a wide range of fields including clinical psychology, business, education, and personal growth